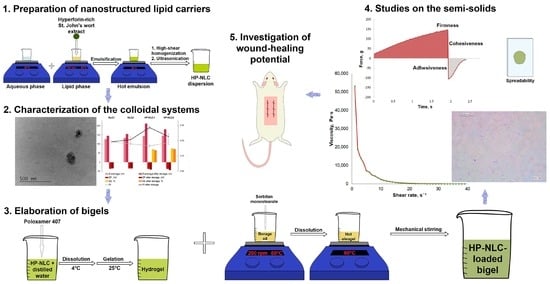
Bigel Formulations of Nanoencapsulated St. John’s Wort Extract—An Approach for Enhanced Wound Healing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
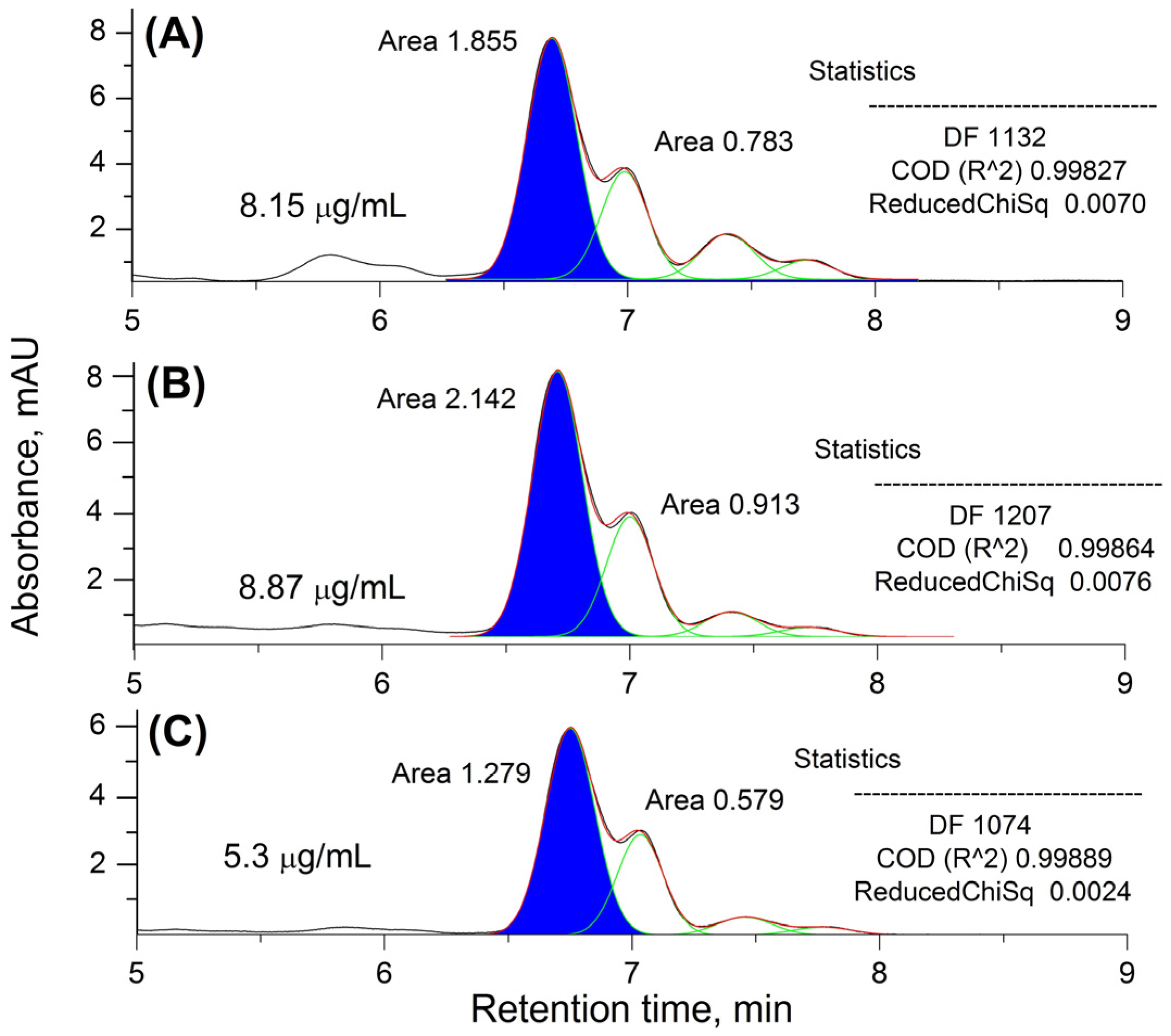
2.1. HPLC-UV Analysis and HP Quantification
2.2. Characterization of the Nanocarriers
2.2.1. Particle Size, Polydispersity Index, Zeta Potential, and Entrapment Efficiency
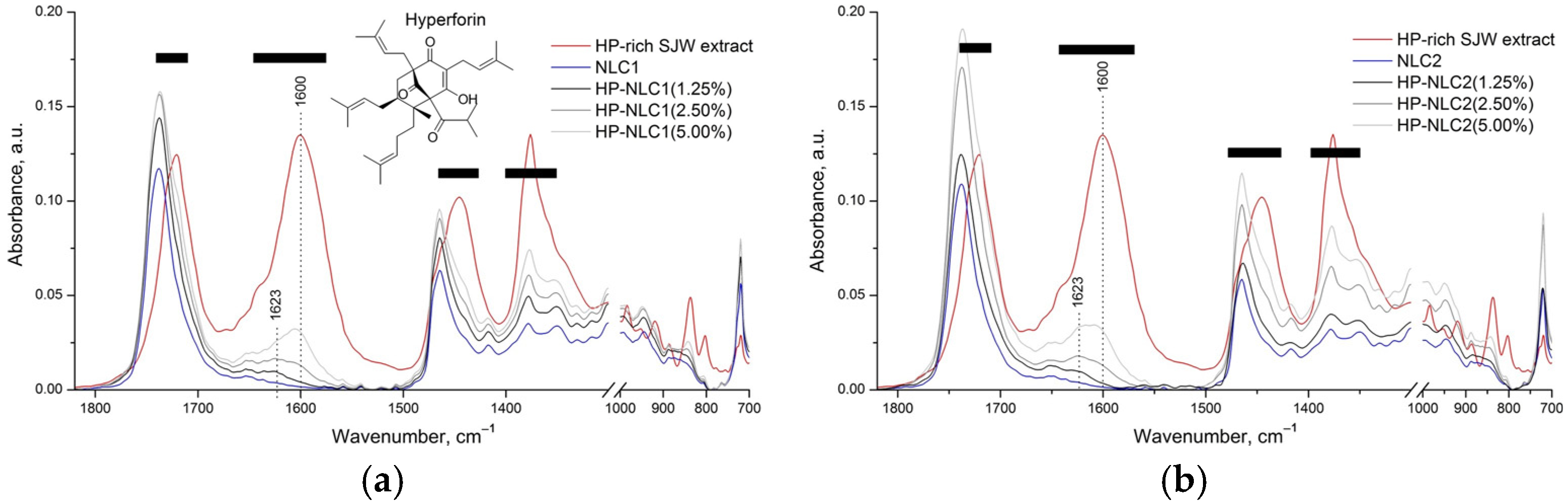
2.2.2. Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
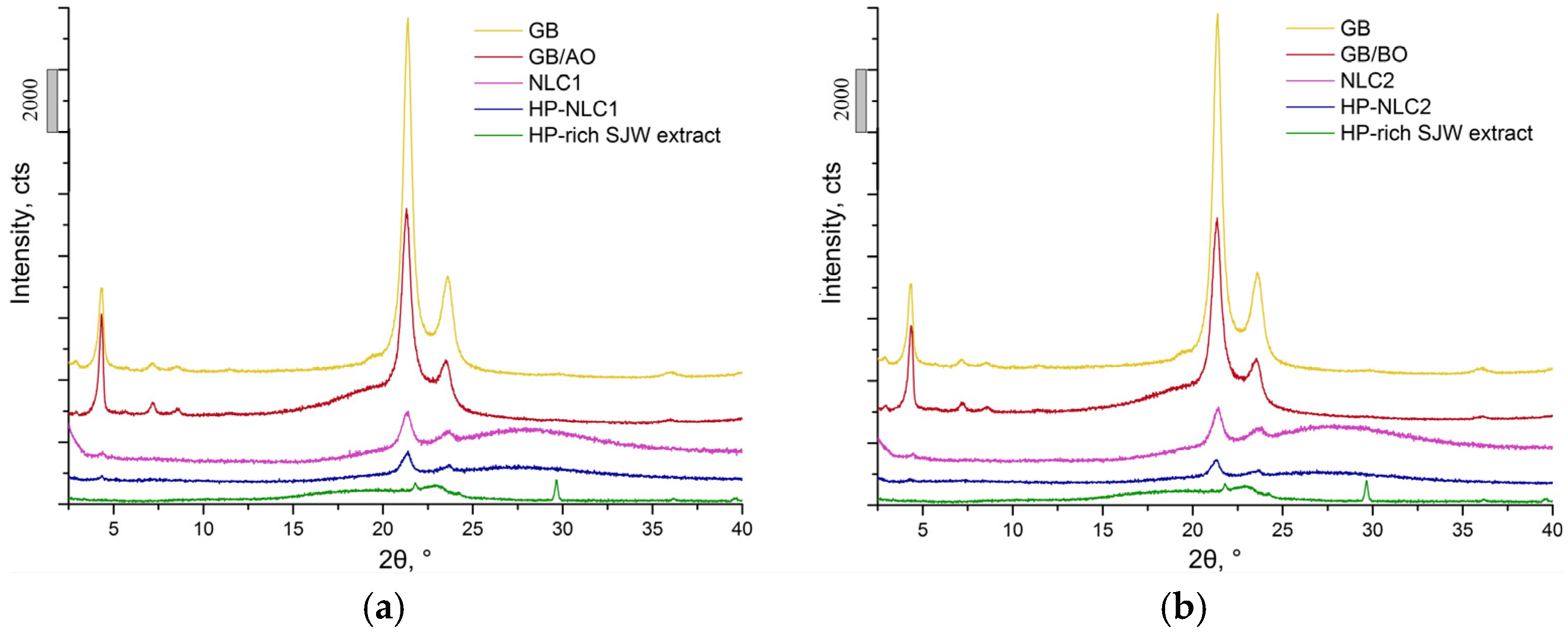
2.2.3. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
2.2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy Investigations
2.3. Characterization of the Bigels
2.3.1. Physical Appearance
2.3.2. Optical Microscopy
2.3.3. pH Analysis
2.3.4. Centrifugation Test
2.3.5. Spreadability
2.3.6. Textural Analysis
2.3.7. Rheological Studies
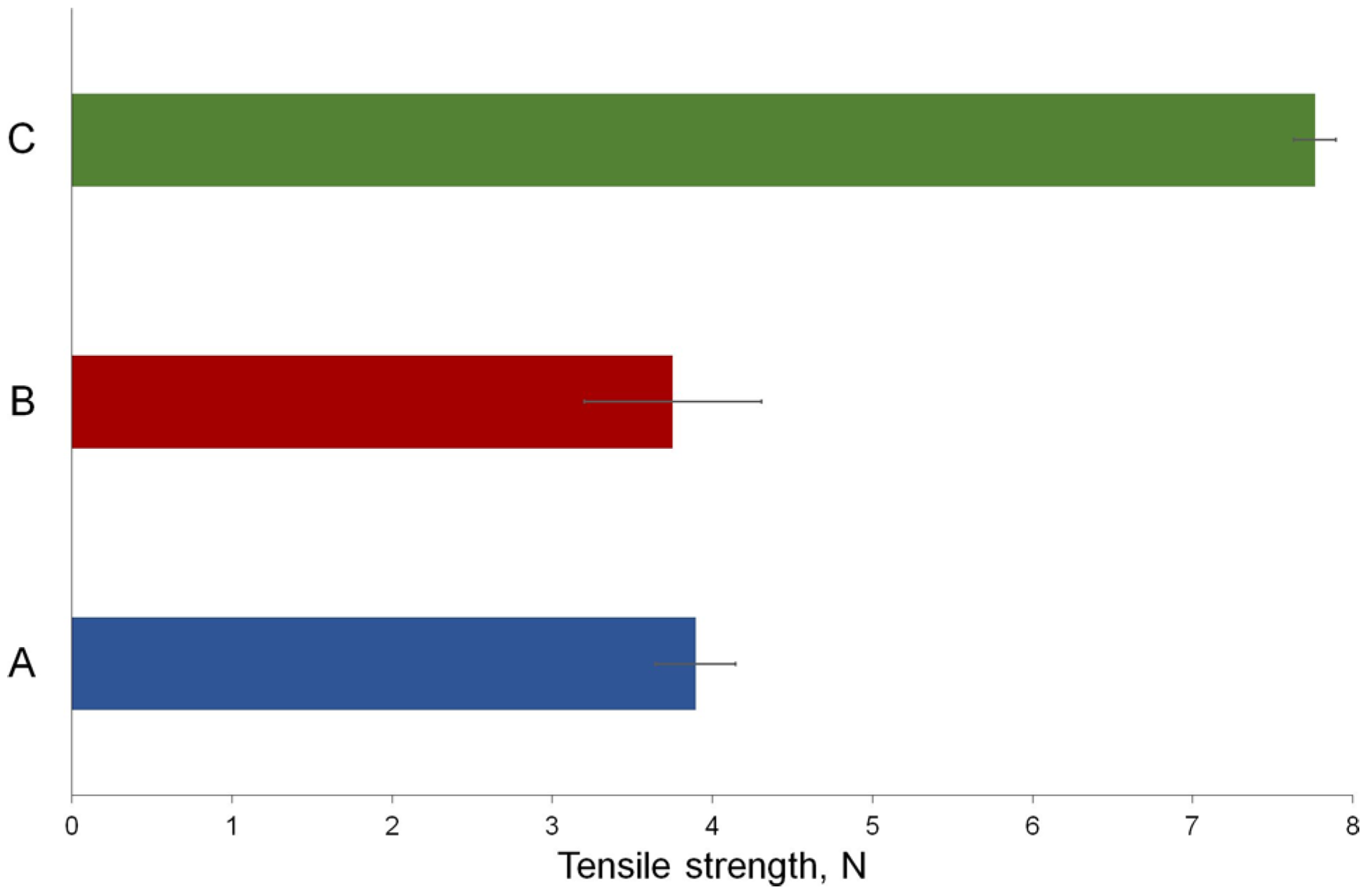
2.4. In Vivo Wound-Healing Effect
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Preparation of the Hypericum perforatum L. Extracts
4.2.2. HPLC Determination of HP
Chromatographic Method
Standard and Test Solutions Preparation
4.2.3. Preparation of NLC Dispersions
4.2.4. Characterization of the Carriers
Particle Size, Polydispersity Index, and Zeta Potential
Entrapment Efficiency Determination
ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy
X-ray Diffraction Analysis
Transmission Electron Microscopy Characterization
4.2.5. Preparation of Bigels
4.2.6. Studies on the Semisolids
Physical Appearance
Optical Microscopy
pH Determination
Centrifugation Test
Spreadability
Texture Analysis
Rheological Studies
4.2.7. Evaluation of Wound-Healing Potential
Experimental Animals
In Vivo Study
4.2.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oreopoulou, A.; Choulitoudi, E.; Tsimogiannis, D.; Oreopoulou, V. Six Common Herbs with Distinctive Bioactive, Antioxidant Components. A Review of Their Separation Techniques. Molecules 2021, 26, 2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubais-aljelehawy, Q.H.; Mohammadi, S.; Mohamadian, E.; Allah, O.R.M.; Mirzaei, A.; Ghahremanlou, M. Antimicrobial, anticancer, antidiabetic, antineurodegenerative, and antirheumatic activities of thymol: Clarification of mechanisms. Micro Nano Bio Asp. 2023, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Aljelehawy, Q.; Maroudi, Y.; Javid, H.; Mohammadi, M.R.; Allah, O.R.M.; Taheri, S.V.; Mohammadzade, H. Anticancer, antineurodegenerative, antimicrobial, and antidiabetic activities of carvacrol: Recent advances and limitations for effective formulations. Nano Micro Biosyst. 2023, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Agapouda, A.; Booker, A.; Kiss, T.; Hohmann, J.; Heinrich, M.; Csupor, D. Quality control of Hypericum perforatum L. analytical challenges and recent progress. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traeger, A.; Voelker, S.; Shkodra-Pula, B.; Kretzer, C.; Schubert, S.; Gottschaldt, M.; Schubert, U.S.; Werz, O. Improved Bioactivity of the Natural Product 5-Lipoxygenase Inhibitor Hyperforin by Encapsulation into Polymeric Nanoparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Radtke, M.; Wissing, S.A. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) in cosmetic and dermatological preparations. Adv. Drug. Del. Rev. 2002, 54, S131–S155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, R.; Gasco, M.R.; Chetoni, P.; Burgalassi, S.; Saettone, M.F. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) as ocular delivery system for tobramycin. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 238, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Radtke, M.; Wissing, S.A. Nanostructured lipid matrices for improved microencapsulation of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 242, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, N.K.; Tandel, N.; Bhadada, S.K.; Tyagi, R.K. Nanostructured Lipid Carrier-Mediated Transdermal Delivery of Aceclofenac Hydrogel Present an Effective Therapeutic Approach for Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 713616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhise, K.; Kashaw, S.K.; Sau, S.; Iyer, A.K. Nanostructured lipid carriers employing polyphenols as promising anticancer agents: Quality by design (QbD) approach. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 526, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh Hallan, S.; Sguizzato, M.; Pavoni, G.; Baldisserotto, A.; Drechsler, M.; Mariani, P.; Esposito, E.; Cortesi, R. Ellagic Acid Containing Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Topical Application: A Preliminary Study. Molecules 2020, 25, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daré, R.G.; Costa, A.; Nakamura, C.V.; Truiti, M.C.T.; Ximenes, V.F.; Lautenschlager, S.O.S.; Sarmento, B. Evaluation of lipid nanoparticles for topical delivery of protocatechuic acid and ethyl protocatechuate as a new photoprotection strategy. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 582, 119336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokce, E.H.; Korkmaz, E.; Dellera, E.; Sandri, G.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Ozer, O. Resveratrol-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles versus nanostructured lipid carriers: Evaluation of antioxidant potential for dermal applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 1841–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Su, G.; Li, Z. Gel-Based Luminescent Conductive Materials and Their Applications in Biosensors and Bioelectronics. Materials 2021, 14, 6759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.M. Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and applications: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, C.L.; Kirilov, P.; Roullin, V.G. Organogels, promising drug delivery systems: An update of state-of-the-art and recent applications. J. Control. Release 2018, 271, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.J.; Silva, P.; Maciel, F.; Pastrana, L.M.; Cunha, R.L.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Vicente, A.A. Hybrid gels: Influence of oleogel/hydrogel ratio on rheological and textural properties. Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Illana, A.; Notario-Pérez, F.; Cazorla-Luna, R.; Ruiz-Caro, R.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Tamayo, A.; Veiga, M.D. Bigels as drug delivery systems: From their components to their applications. Drug. Discov. Today 2022, 27, 1008–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Gao, J.; Han, L.; Han, K.; Wei, W.; Wu, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, M. Development and characterization of novel bigels based on monoglyceride-beeswax oleogel and high acyl gellan gum hydrogel for lycopene delivery. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andonova, V.; Peneva, P.; Georgiev, G.S.; Toncheva, V.T.; Apostolova, E.; Peychev, Z.; Dimitrova, S.; Katsarova, M.; Petrova, N.; Kassarova, M. Ketoprofen-loaded polymer carriers in bigel formulation: An approach to enhancing drug photostability in topical application forms. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 6221–6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburahma, M.H.; Badr-Eldin, S.M. Compritol 888 ATO: A multifunctional lipid excipient in drug delivery systems and nanopharmaceuticals. Expert. Opin. Drug. Deliv. 2014, 11, 1865–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farid, R.M.; El-Salamouni, N.S.; El-Kamel, A.H.; El-Gamal, S.S. Lipid-based nanocarriers for ocular drug delivery. In Nanostructures for Drug Delivery, 1st ed.; Andronescu, E., Grumezescu, A.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 495–522. [Google Scholar]
- Dobreva, M.; Stefanov, S.; Andonova, V. Natural Lipids as Structural Components of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Topical Delivery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 4524–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arif, S.T.; Zaman, S.u.; Khan, M.A.; Tabish, T.A.; Sohail, M.F.; Arshad, R.; Kim, J.-K.; Zeb, A. Augmented Oral Bioavailability and Prokinetic Activity of Levosulpiride Delivered in Nanostructured Lipid Carriers. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winarti, L.; Suwaldi, S.; Martien, R.; Hakim, L. Formulation of Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System of Bovine Serum Albumin Using HLB (Hydrophilic-Lypophilic Balance) Approach. Indones. J. Pharm. 2016, 27, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, L.V., Jr. The Art, Science, and Technology of Pharmaceutical Compounding, 5th ed.; American Pharmacists Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; Chapter 19 Emulsions; pp. 293–305. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, E.M. Specialty Oils: Functional and Nutraceutical Properties. In Functional Dietary Lipids: Food Formulation, Consumer Issues and Innovation for Health, 1st ed.; Sanders, T.A.B., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 69–101. [Google Scholar]
- Asadi-Samani, M.; Bahmani, M.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M. The chemical composition, botanical characteristic and biological activities of Borago officinalis: A review. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2014, 7, S22–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.-K.; Zhong, L.; Santiago, J.L. Anti-Inflammatory and Skin Barrier Repair Effects of Topical Application of Some Plant Oils. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas-Cardoso, L.; Mantell, C.; Obregón, S.; Cejudo-Bastante, C.; Alonso-Moraga, Á.; de la Ossa, E.J.M.; de Haro-Bailón, A. Health-Promoting Properties of Borage Seed Oil Fractionated by Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extraction. Foods 2021, 10, 2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szafraniec, J.; Antosik, A.; Knapik-Kowalczuk, J.; Chmiel, K.; Kurek, M.; Gawlak, K.; Odrobińska, J.; Paluch, M.; Jachowicz, R. The Self-Assembly Phenomenon of Poloxamers and Its Effect on the Dissolution of a Poorly Soluble Drug from Solid Dispersions Obtained by Solvent Methods. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodratti, A.M.; Alexandridis, P. Formulation of Poloxamers for Drug Delivery. J. Funct. Biomater. 2018, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanov, S.; Stoeva, S.; Georgieva, S.; Hristova, M.; Nikolova, K.; Dobreva, M.; Andonova, V. In vivo comparative assessment of incised wound healing in rats after application of hydrogel/organogel formulation containing St. John’s wort methanol extract. Bulg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 54, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Banu, K.S.; Cathrine, L. General Techniques Involved in Phytochemical Analysis. Int. J. Adv. Res. Chem. Sci. 2015, 2, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, M.; Jose, A.; Tomer, V.; Oz, E.; Proestos, C.; Zeng, M.; Elobeid, T.; Oz, F. Major Phytochemicals: Recent Advances in Health Benefits and Extraction Method. Molecules 2023, 28, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisenbacher, P.; Kovar, K.-A. Analysis and Stability of Hyperici Oleum. Planta Med. 1992, 58, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, S.; Costa, C.P.; Loureiro, J.A.; Alves, J.; Peixoto, A.F.; Forbes, B.; Sousa Lobo, J.M.; Silva, A.C. Double Optimization of Rivastigmine-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC) for Nose-to-Brain Delivery Using the Quality by Design (QbD) Approach: Formulation Variables and Instrumental Parameters. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caverzan, J.; de Jesus, M.B.; Durán, N. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Loaded with 17-α-Estradiol Accumulate into Hair Follicles. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2020, 31, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, M.; Abdin, S.M.; Kamal, L.; Orive, G. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Delivery of Chemotherapeutics: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, S.M.; Noronha, C.M.; Floriani, C.L.; Lino, R.C.; Rocha, G.; Bellettini, I.C.; Ogliari, P.J.; Barreto, P.L.M. Optimization of α-tocopherol loaded solid lipid nanoparticles by central composite design. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 49, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, K.K.; Parmar, B.; Mandal, S.A.; Petkar, K.C.; Patel, L.D. Valsartan Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: Development, Characterization, and In vitro and Ex vivo Evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 4, 1483–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadizadeh, M.; Bostan, A.; Kadkhodaee, R. Preparation and Characterization of α-Tocopherol-Loaded Nano-Lipid Carriers: Effect of Lipid Type and Carrier Oil Content. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2021, 40, 715–724. [Google Scholar]
- Eleraky, N.E.; Omar, M.M.; Mahmoud, H.A.; Abou-Taleb, H.A. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers to Mediate Brain Delivery of Temazepam: Design and In Vivo Study. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruchenthooran, V.; Świtalska, M.; Bonilla, L.; Espina, M.; García, M.L.; Wietrzyk, J.; Sánchez-López, E.; Gliszczyńska, A. Novel Strategies against Cancer: Dexibuprofen-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Z.; Yu, M.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, M.; Liu, P.; Opoku-Damoah, Y.; Webster, T.J.; Zhou, J. Preparation and characterization of nimodipine-loaded nanostructured lipid systems for enhanced solubility and bioavailability. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilić, T.; Pantelić, I.; Savić, S. The Implications of Regulatory Framework for Topical Semisolid Drug Products: From Critical Quality and Performance Attributes towards Establishing Bioequivalence. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardi-Ricart, A.; Linares, M.J.; Villca-Pozo, F.; Pérez-Lozano, P.; Suñé-Negre, J.M.; Bachs-deMiquel, L.; Roig-Carreras, M.; Suñé-Pou, M.; Nofrerias-Roig, I.; García-Montoya, E. A new design for the review and appraisal of semi-solid dosage forms: Semi-solid Control Diagram (SSCD). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashkurina, E.O.; Anurova, M.O.; Zavalniy, M.S.; Demina, N.B.; Bardakov, A.I.; Krasnyuk, I.I. Dermatologic gels spreadability measuring methods comparative study. Int. J. App. Pharm. 2022, 14, 164–168. [Google Scholar]
- Lardy, F.; Vennat, B.; Pouget, M.P.; Pourrat, A. Functionalization of hydrocolloids: Principal component analysis applied to the study of correlations between parameters describing the consistency of hydrogels. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2000, 26, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, H.; Lobão, P.; Frigerio, C.; Fonseca, J.; Silva, R.; Sousa Lobo, J.M.; Amaral, M.H. Preparation, characterization and biocompatibility studies of thermoresponsive eyedrops based on the combination of nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) and the polymer Pluronic F-127 for controlled delivery of ibuprofen. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2017, 22, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurler, J.; Engesland, A.; Poorahmary Kermany, B.; Škalko-Basnet, N. Improved texture analysis for hydrogel characterization: Gel cohesiveness, adhesiveness, and hardness. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 125, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróblewska, M.; Szymańska, E.; Szekalska, M.; Winnicka, K. Different Types of Gel Carriers as Metronidazole Delivery Systems to the Oral Mucosa. Polymers 2020, 12, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baixauli, R.; Bolivar-Prados, M.; Ismael-Mohammed, K.; Clavé, P.; Tárrega, A.; Laguna, L. Characterization of Dysphagia Thickeners Using Texture Analysis—What Information Can Be Useful? Gels 2022, 8, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Rahman, M.N.; Abdul Qader, O.A.J.; Sukmasari, S.; Ismail, A.F.; Doolaanea, A.A. Rheological Characterization of Different Gelling Polymers for Dental Gel Formulation. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2017, 9, 2633–2640. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, M.K.; Hussain, M.K. Badam (Prunus amygdalus Bail.): A Fruit with Medicinal Properties. Int. J. Herb. Med. 2017, 5, 114–117. [Google Scholar]
- Maver, T.; Kurečič, M.; Smrke, D.M.; Kleinschek, K.S.; Maver, U. Plant-Derived Medicines with Potential Use in Wound Treatment. In Herbal Medicine; Builders, P., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 121–150. [Google Scholar]
- Waghmode, A.B. An overview on: Botany, extraction, phytochemistry and medicinal uses of Vitex negundo Linn. J. Pharm. Innov. 2020, 9, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, M.; Chen, Q.; Chen, W.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.; Wu, A.; Lai, J.; Chen, J.; Mei, Q.; et al. A comprehensive review of Rubia cordifolia L.: Traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacological activities, and clinical applications. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 965390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellare, A.; Epperly, M.W.; Greenberger, J.S.; Fisher, R.; Glowacki, J. Development of tensile strength methodology for murine skin wound healing. MethodsX 2018, 5, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICH Guideline Q2(R2) on Validation of Analytical Procedures. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/ich-guideline-q2r2-validation-analytical-procedures-step-2b_en.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Cervera-Khelifi, C.; Saada, M.; Hayouni, E.A.; Tourette, A.; Bouajila, J.; Ksouri, R. Development and Characterization of Novel Bigel-Based 1,4-Naphthoquinones for Topical Application with Antioxidant Potential. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 45, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leusheva, E.; Brovkina, N.; Morenov, V. Investigation of Non-Linear Rheological Characteristics of Barite-Free Drilling Fluids. Fluids 2021, 6, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the Protection of Animals Used for Scientific Purposes. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2010:276:0033:0079:En:PDF (accessed on 7 February 2023).
- The Basel Declaration. Available online: http://www.basel-declaration.org/basel-declaration/ (accessed on 7 February 2023).
- ICLAS Ethics and Animal Welfare Committee. ICLAS Ethical Guideline for Researchers. Available online: http://iclas.org/committees/ethics-andanimal-welfare-committee (accessed on 7 February 2023).
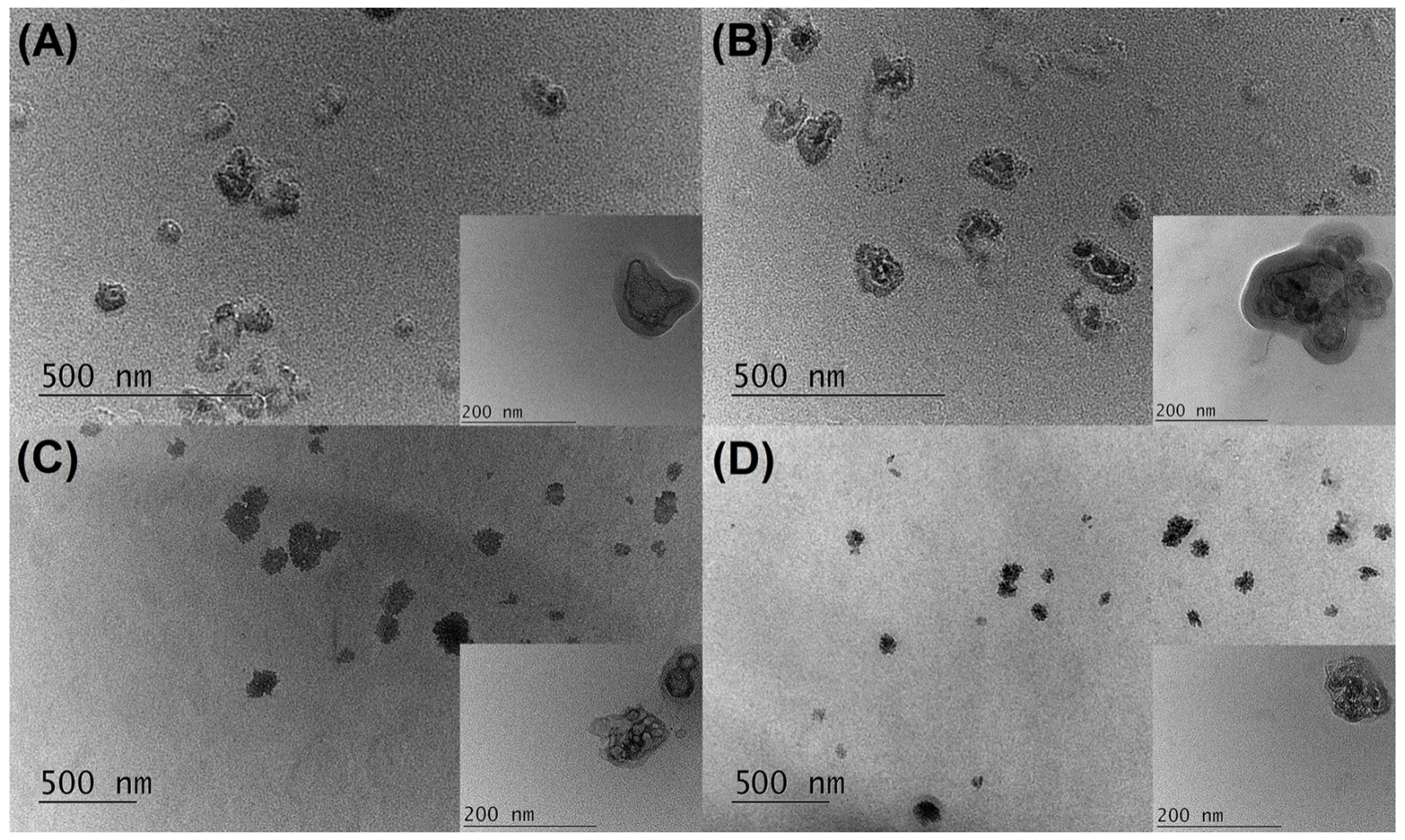
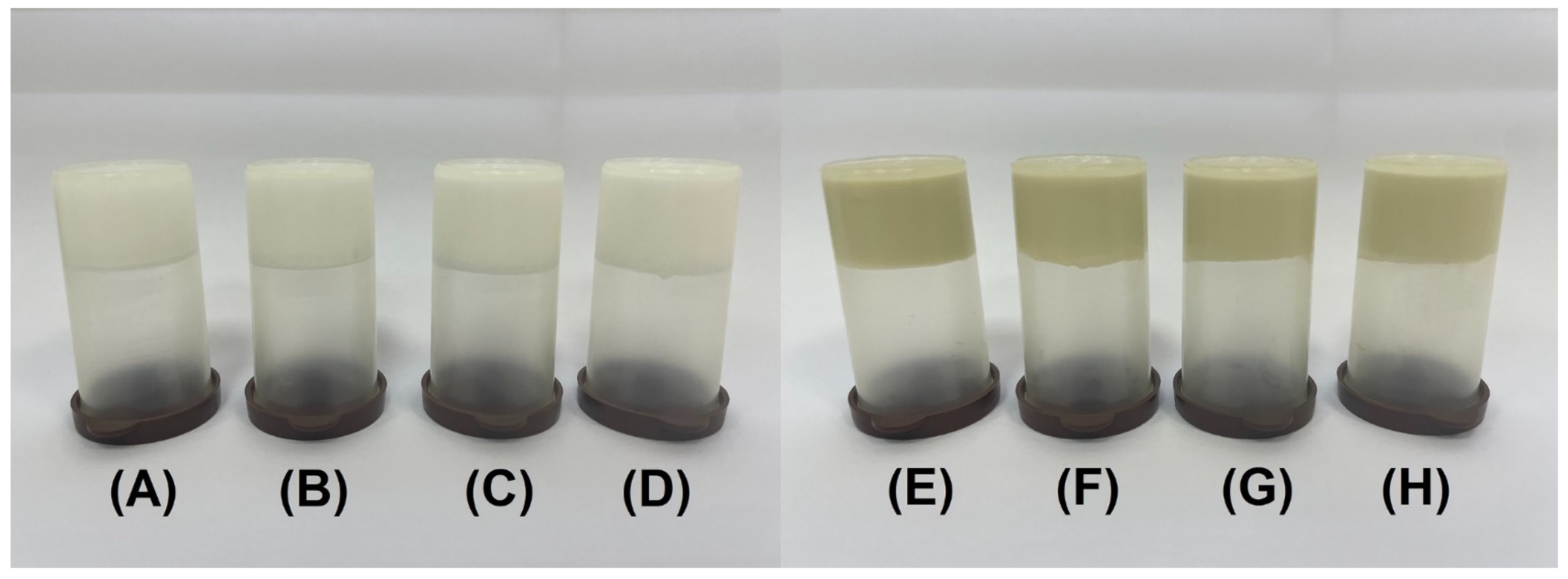

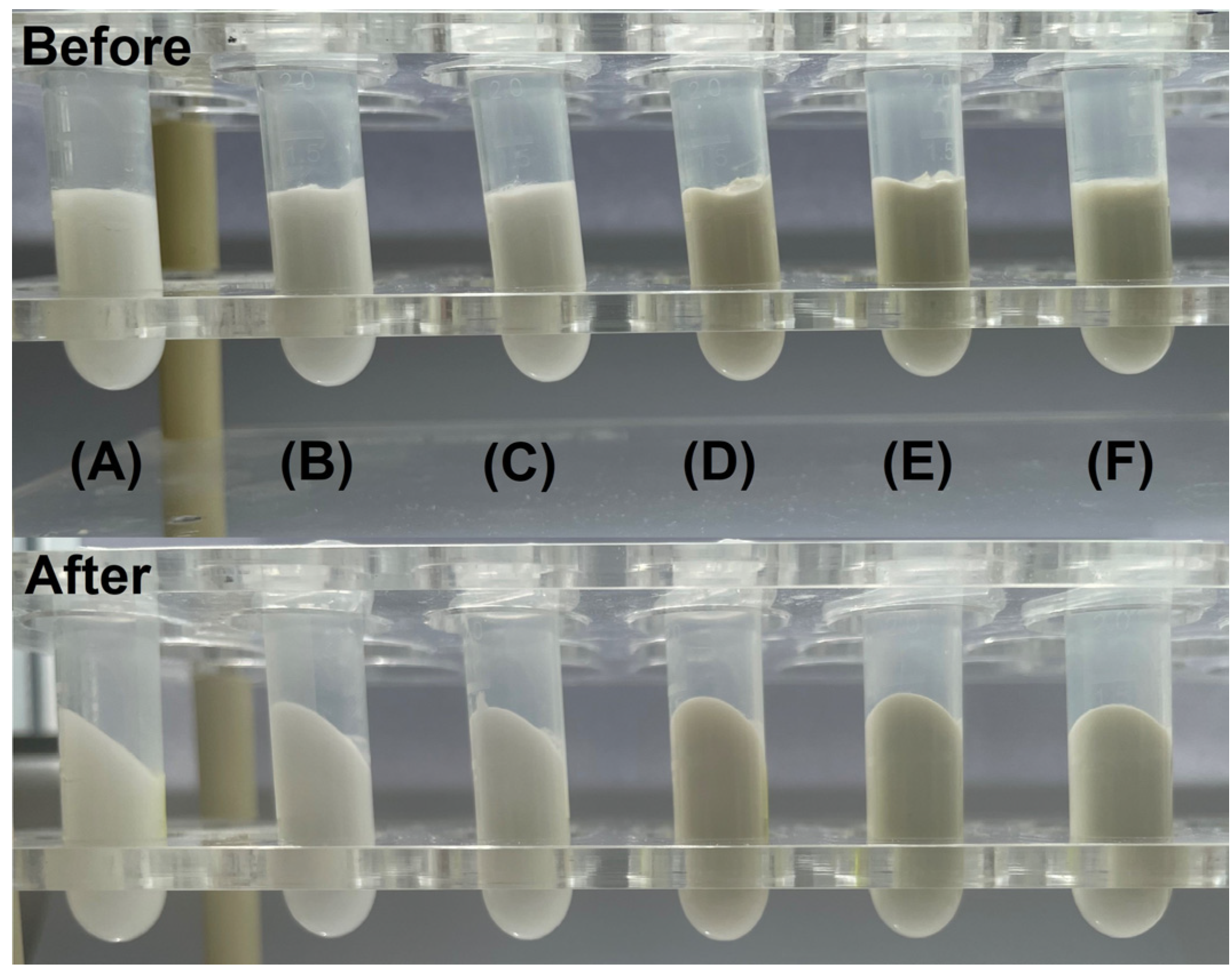

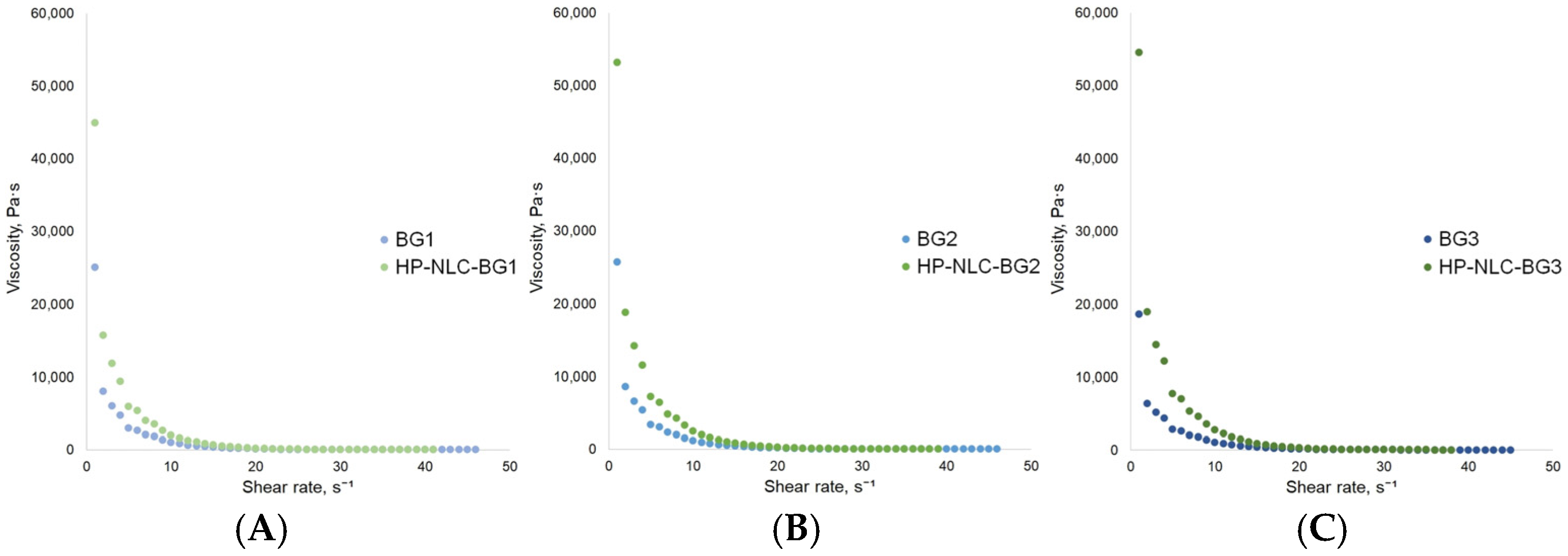
| Formulation | Days | Z-Average, nm | PI | ZP, mV | EE, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NLC1 | 0 | 125.27 ± 1.36 | 0.29 ± 0.01 | −35.33 ± 1.13 | NA |
| 30 | 144.93 ± 2.04 | 0.29 ± 0.01 | −33.51 ± 1.07 | NA | |
| NLC2 | 0 | 133.07 ± 2.30 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | −33.91 ± 1.01 | NA |
| 30 | 154.94 ± 2.10 | 0.31 ± 0.03 | −33.98 ± 1.19 | NA | |
| HP-NLC1 | 0 | 142.97 ± 2.00 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | −36.53 ± 3.02 | 70.44 ± 0.21 |
| 30 | 212.17 ± 2.76 | 0.43 ± 0.02 | −39.55 ± 3.25 | 65.61 ± 0.20 | |
| HP-NLC2 | 0 | 146.00 ± 3.25 | 0.28 ± 0.02 | −36.22 ± 1.68 | 74.49 ± 0.23 |
| 30 | 181.13 ± 3.65 | 0.34 ± 0.03 | −42.22 ± 1.36 | 72.10 ± 0.25 |
| BG1 | BG2 | BG3 | HP-NLC-BG1 | HP-NLC-BG2 | HP-NLC-BG3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH value | 6.79 ± 0.07 a | 6.81 ± 0.05 a | 6.82 ± 0.01 a | 6.05 ± 0.01 b | 6.04 ± 0.01 b | 6.05 ± 0.03 b |
| Formulation | Spreadability, mm | Firmness, g | Cohesiveness, g·s | Adhesiveness, g·s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BG1 | 31.50 ± 0.89 a | 71.07 ± 0.09 e | 86.27 ± 1.25 d | −14.17 ± 0.63 a |
| BG2 | 30.17 ± 0.42 a,b | 74.67 ± 0.94 e | 90.37 ± 1.20 d | −16.03 ± 0.31 a |
| BG3 | 29.00 ± 0.41 b,c | 81.00 ± 2.94 d | 93.7 ± 3.77 d | −15.13 ± 1.03 a |
| HP-NLC-BG1 | 28.17 ± 0.12 c,d | 112.33 ± 4.71 c | 138.8 ± 9.01 c | −19.37 ± 0.90 b |
| HP-NLC-BG2 | 26.83 ± 0.96 d | 137.33 ± 3.77 b | 167.6 ± 8.71 b | −25.10 ± 0.37 c |
| HP-NLC-BG3 | 24.75 ± 1.08 e | 148.03 ± 0.08 a | 182.63 ± 0.70 a | −25.17 ± 1.35 c |
| Type of Model | BG1 | BG2 | BG3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bingham plastic model (BPM) | ηp = 0.57 ± 0.04 Pa·s τ0 = 354.89 ± 9.1 Pa R2 = 0.84 | ηp = 0.30 ± 0.09 Pa·s τ0 = 440.44 ± 22.92 Pa R2 = 0.17 | ηp = 0.77 ± 0.06 Pa·s τ0 = 365.43 ± 12.28 Pa R2 = 0.78 |
| Power law model (PLM) | K = 322.63 ± 0.1 Pa·s n n = 0.11 ± 0.01 R2 = 0.88 | K = 394.62 ± 17.45 Pa·s n n = 0.08 ± 0.01 R2 = 0.72 | K = 328.76 ± 6.02 Pa·s n n = 0.12 ± 0.01 R2 = 0.96 |
| Herschel–Bulkley model (HBM) | τ0 = 283.59 ± 4.41 Pa K = 37.12 ± 3.25 Pa·s n n = 0.38 ± 0.01 R2 = 0.99 | τ0 = 0 ± 0.01 Pa K = 394.72 ± 48.4 Pa·s n n = 0.08 ± 0.01 R2 = 0.60 | τ0 = 236.02 ± 8.64 Pa K = 88.59 ± 7.99 Pa·s n n = 0.28 ± 0.01 R2 = 0.99 |
| Type of Model | HP-NLC-BG1 | HP-NLC-BG2 | HP-NLC-BG3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| BPM | ηp = 2.22 ± 0.01 Pa·s τ0 = 627.68 ± 8.32 Pa R2 = 0.93 | ηp = 2.61 ± 0.17 Pa·s τ0 = 758.79 ± 9.49 Pa R2 = 0.86 | ηp = 3.05 ± 0.15 Pa·s τ0 = 778.84 ± 6.57 Pa R2 = 0.92 |
| PLM | K = 627.79 ± 14.58 Pa·s n n = 0.11 ± 0.01 R2 = 0.88 | K = 768.86 ± 8.86 Pa·s n n = 0.06 ± 0.01 R2 = 0.87 | K = 768.89 ± 8.86 Pa·s n n = 0.06 ± 0.01 R2 = 0.87 |
| HBM | τ0 = 578.53 ± 2.53 Pa K = 27.09 ± 1.52 Pa·s n n = 0.55 ± 0.01 R2 = 0.99 | τ0 = 682.31 ± 5.41 Pa K = 59.90 ± 4.94 Pa·s n n = 0.40 ± 0.02 R2 = 0.99 | τ0 = 762.52 ± 8.15 Pa K = 11.35 ± 3.77 Pa·s n n = 0.73 ± 0.07 R2 = 0.94 |
| Source of Variation | SS | df | MS | F | p-Value | F crit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Between groups A and B | 0.060 | 1 | 0.060 | 0.326 | 0.581 | 4.965 |
| Within groups A and B | 1.849 | 10 | 0.185 | |||
| Total | 1.909 | 11 | ||||
| Between groups B and C | 48.256 | 1 | 48.256 | 297.428 | 9.086 × 10−9 | 4.965 |
| Within groups B and C | 1.622 | 10 | 0.162 | |||
| Total | 49.879 | 11 | ||||
| Between groups A and C | 44.907 | 1 | 44.907 | 1121.930 | 1.329 × 10−11 | 4.965 |
| Within groups A and C | 0.400 | 10 | 0.040 | |||
| Total | 45.308 | 11 |
| Formulation | GB (%w/w) | Liquid Lipid (%w/w) | SMO (%w/w) | PSMO (%w/w) | DDW (%w/w) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AO | BO | |||||
| NLC1 | 7 | 3 | − | 2 | 3 | 85 |
| NLC2 | − | 3 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sotirova, Y.; Gugleva, V.; Stoeva, S.; Kolev, I.; Nikolova, R.; Marudova, M.; Nikolova, K.; Kiselova-Kaneva, Y.; Hristova, M.; Andonova, V. Bigel Formulations of Nanoencapsulated St. John’s Wort Extract—An Approach for Enhanced Wound Healing. Gels 2023, 9, 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9050360
Sotirova Y, Gugleva V, Stoeva S, Kolev I, Nikolova R, Marudova M, Nikolova K, Kiselova-Kaneva Y, Hristova M, Andonova V. Bigel Formulations of Nanoencapsulated St. John’s Wort Extract—An Approach for Enhanced Wound Healing. Gels. 2023; 9(5):360. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9050360
Chicago/Turabian StyleSotirova, Yoana, Viliana Gugleva, Stanila Stoeva, Iliyan Kolev, Rositsa Nikolova, Maria Marudova, Krastena Nikolova, Yoana Kiselova-Kaneva, Minka Hristova, and Velichka Andonova. 2023. "Bigel Formulations of Nanoencapsulated St. John’s Wort Extract—An Approach for Enhanced Wound Healing" Gels 9, no. 5: 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9050360
APA StyleSotirova, Y., Gugleva, V., Stoeva, S., Kolev, I., Nikolova, R., Marudova, M., Nikolova, K., Kiselova-Kaneva, Y., Hristova, M., & Andonova, V. (2023). Bigel Formulations of Nanoencapsulated St. John’s Wort Extract—An Approach for Enhanced Wound Healing. Gels, 9(5), 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9050360