Multifunctional Extracellular Matrix Hydrogel with Self-Healing Properties and Promoting Angiogenesis as an Immunoregulation Platform for Diabetic Wound Healing
Abstract
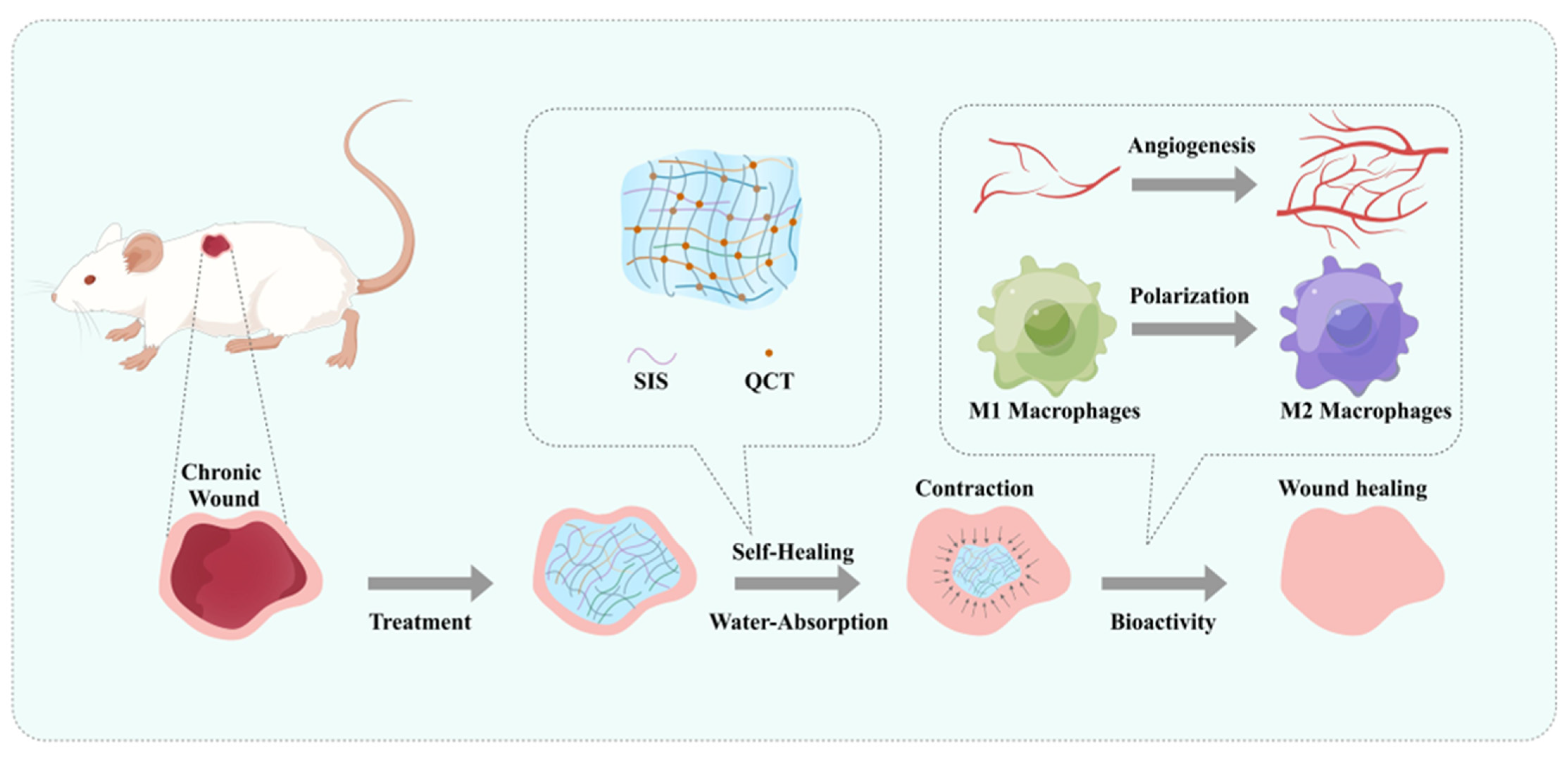
:1. Introduction
2. Results
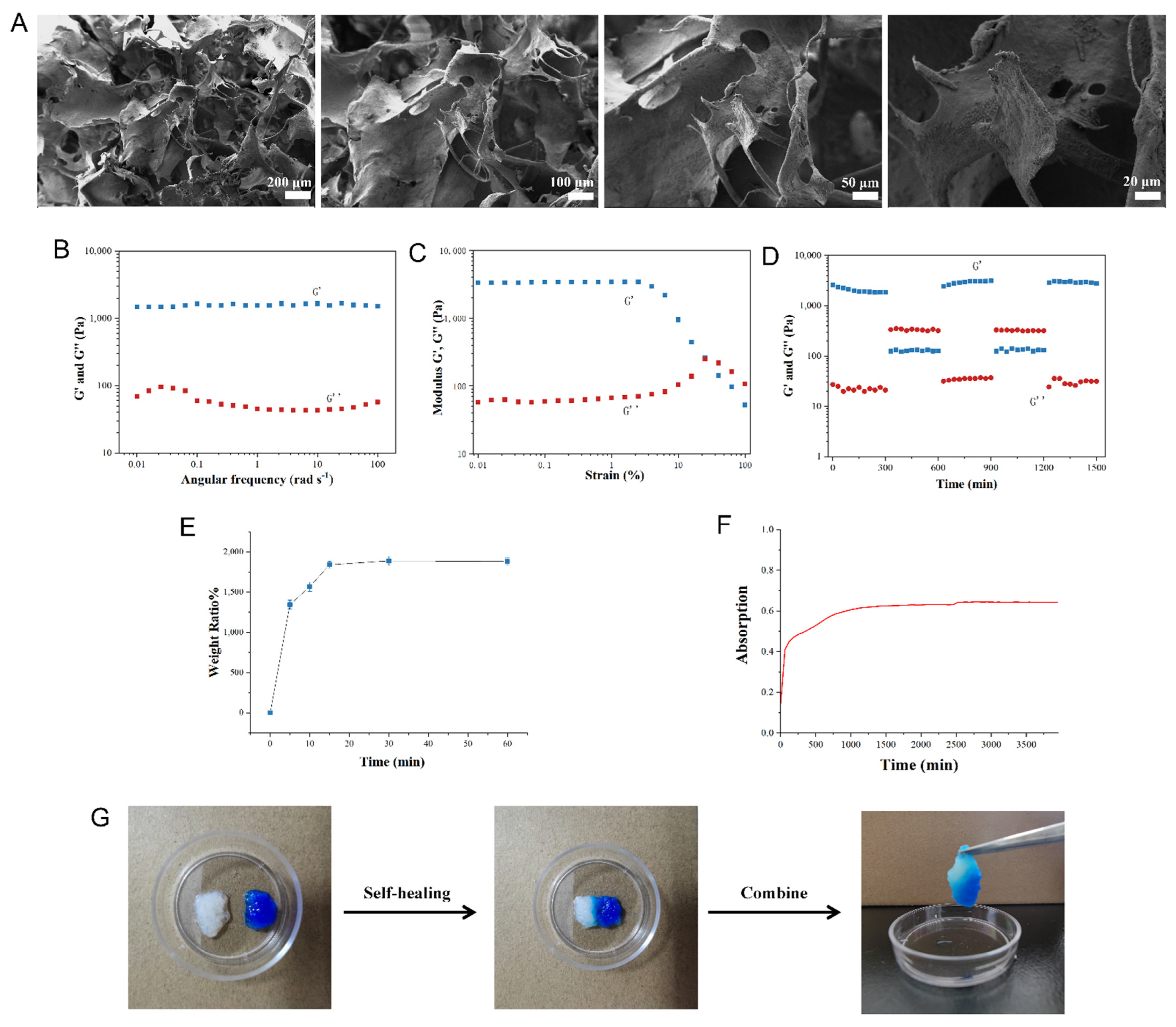
2.1. QCT@SIS Hydrogel Characterization
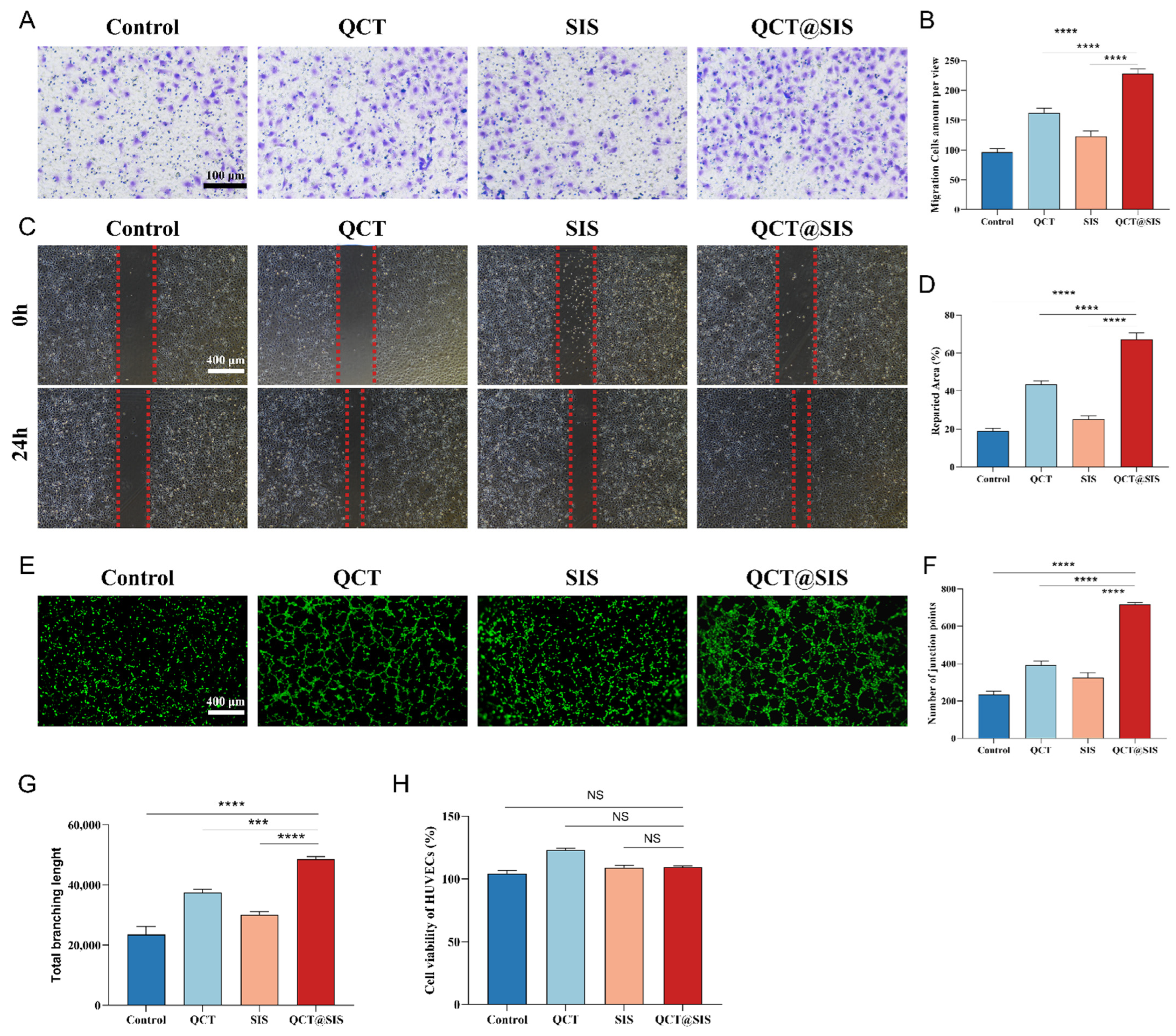
2.2. Biocompatibility Test, Cell Migration, and In Vitro Angiogenesis
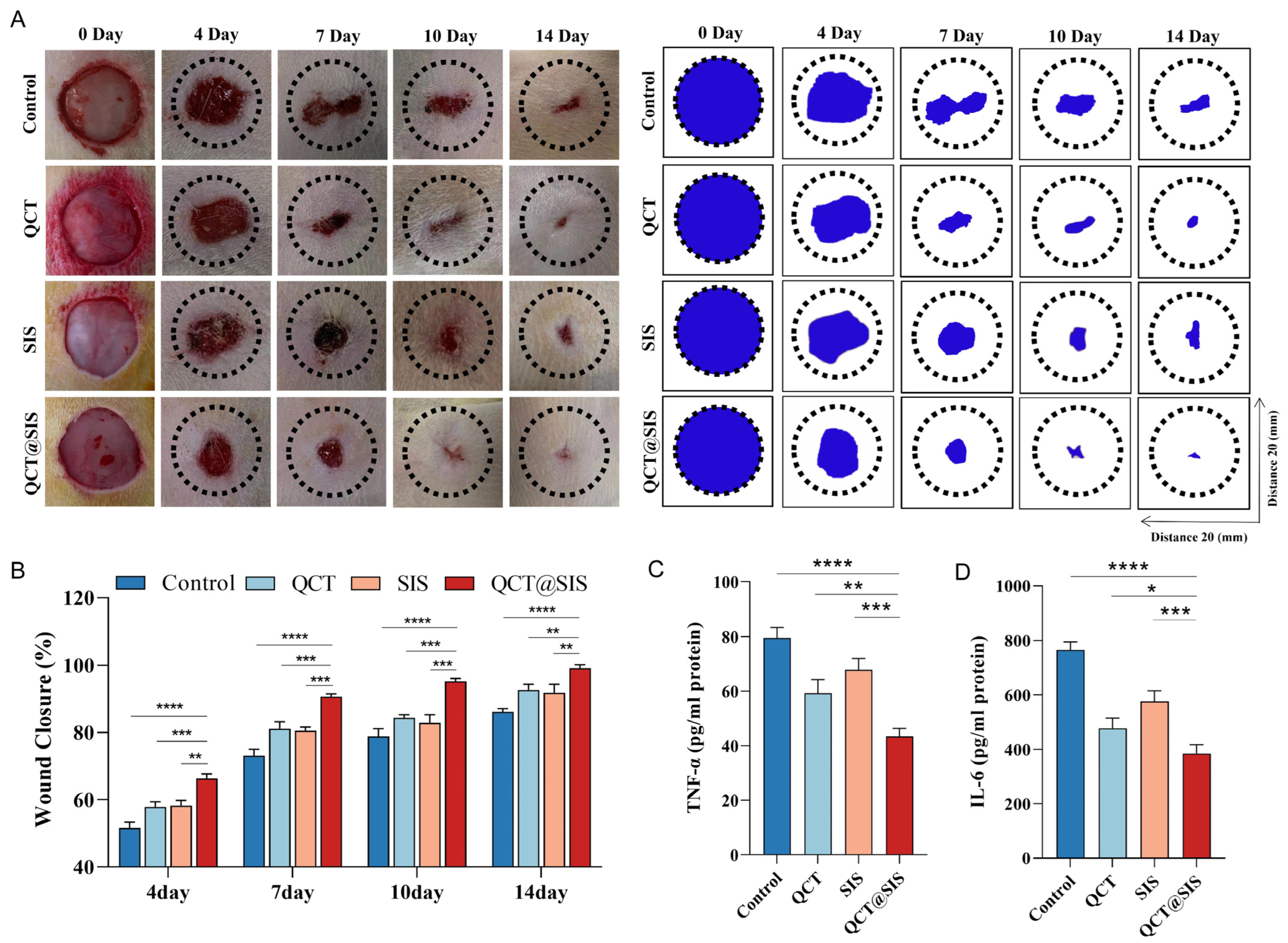
2.3. In Vivo Diabetic Wound Repair Tests
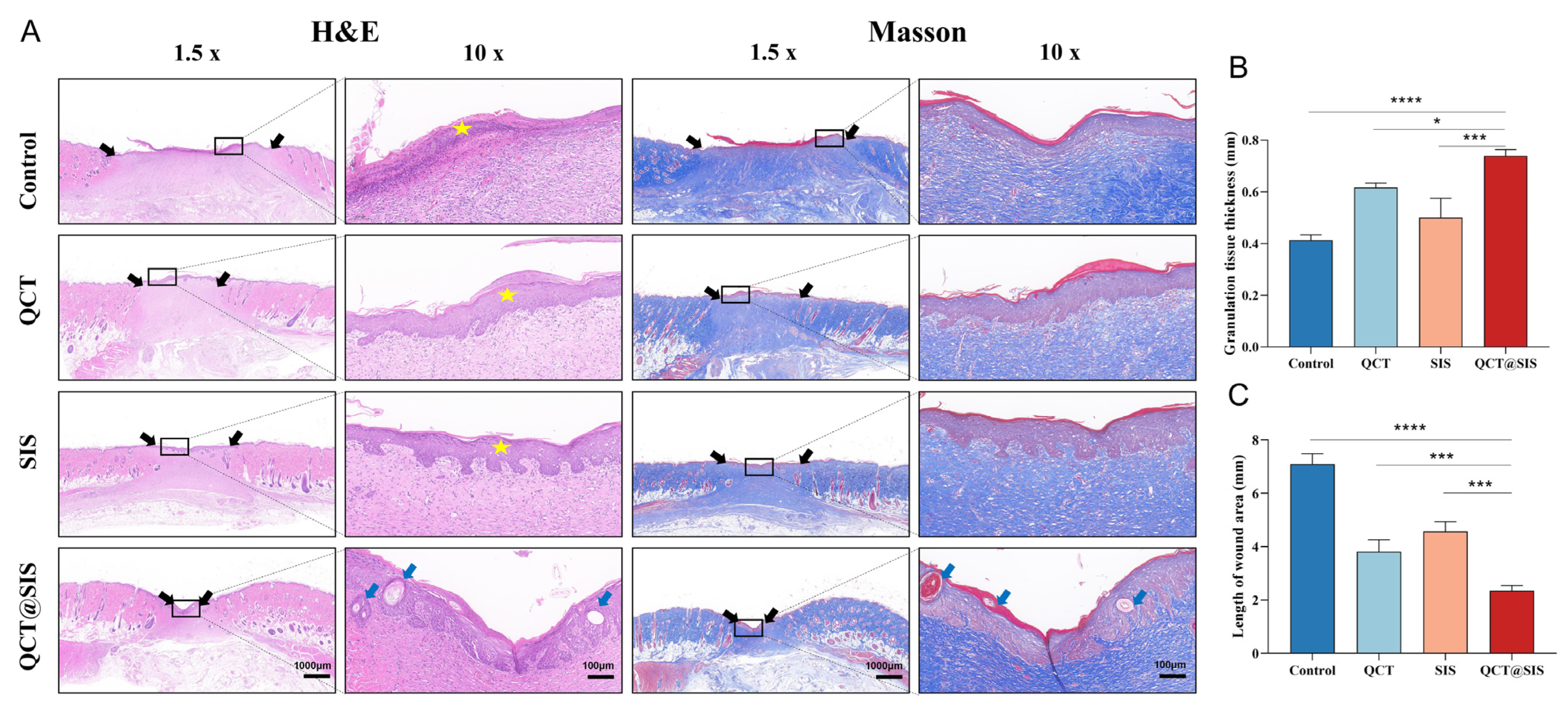
2.4. Histomorphological Evaluation
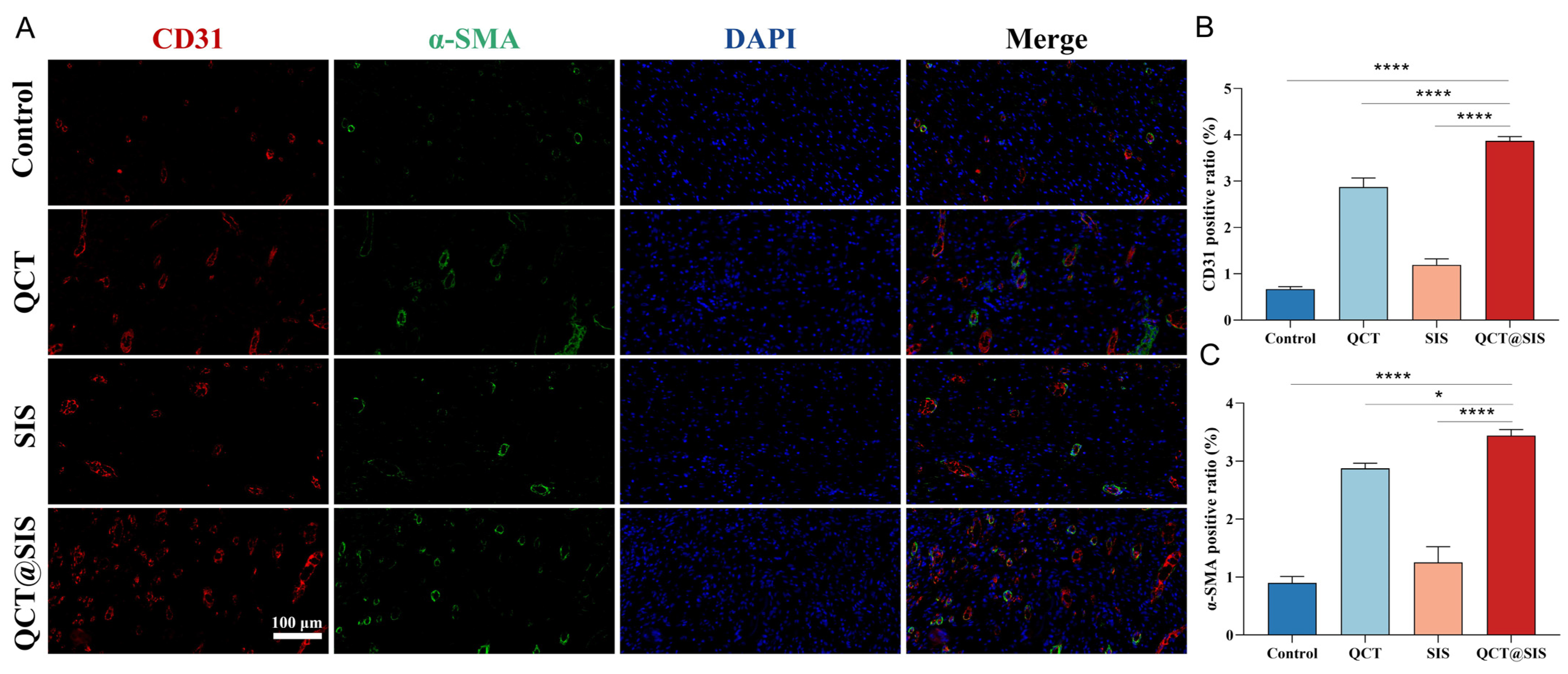
2.5. In Vivo Neovascularization Assessment
2.6. Macrophage Polarization Assessment In Vivo
2.7. In Vivo Biosecurity Assessment
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. SIS Membrane Fabrication
5.2. SIS Hydrogel Fabrication
5.3. Cell Culture
5.4. Preparation and Characterization of the QCT@SIS Hydrogel
5.5. Cytocompatibility Test for QCT@SIS Hydrogel
5.6. Migration, Proliferation, and Tube Formation Assays
5.7. Animal Model for Diabetic Wound
5.8. ELISA to Detect Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines
5.9. Histopathology Analysis
5.10. Biocompatibility of Hydrogels In Vivo
5.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crews, R.T.; Shen, B.J.; Campbell, L.; Lamont, P.J.; Boulton, A.J.; Peyrot, M.; Kirsner, R.S.; Vileikyte, L. Role and Determinants of Adherence to Off-loading in Diabetic Foot Ulcer Healing: A Prospective Investigation. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1371–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, P.; Nunan, R. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of repair in acute and chronic wound healing. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 173, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louiselle, A.E.; Niemiec, S.M.; Zgheib, C.; Liechty, K.W. Macrophage polarization and diabetic wound healing. Transl. Res. 2021, 236, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifiaghdam, M.; Shaabani, E.; Faridi-Majidi, R.; De Smedt, S.C.; Braeckmans, K.; Fraire, J.C. Macrophages as a therapeutic target to promote diabetic wound healing. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 2891–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Hou, Q.; Zhong, L.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, X. Macrophage Related Chronic Inflammation in Non-Healing Wounds. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 681710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audu, C.O.; Melvin, W.J.; Joshi, A.D.; Wolf, S.J.; Moon, J.Y.; Davis, F.M.; Barrett, E.C.; Mangum, K.D.; Deng, H.; Xing, X.; et al. Macrophage-specific inhibition of the histone demethylase JMJD3 decreases STING and pathologic inflammation in diabetic wound repair. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.; Pallua, N.; Bernhagen, J.; Bucala, R. The macrophage migration inhibitory factor protein superfamily in obesity and wound repair. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, e161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawaya, A.P.; Stone, R.C.; Brooks, S.R.; Pastar, I.; Jozic, I.; Hasneen, K.; O’Neill, K.; Mehdizadeh, S.; Head, C.R.; Strbo, N.; et al. Deregulated immune cell recruitment orchestrated by FOXM1 impairs human diabetic wound healing. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutts, P.M.; Ryan, J.; Sibbald, R.G. Case series of lower-extremity chronic wounds managed with an antibacterial foam dressing bound with gentian violet and methylene blue. Adv. Ski. Wound Care 2014, 27, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soubhagya, A.S.; Moorthi, A.; Prabaharan, M. Preparation and characterization of chitosan/pectin/ZnO porous films for wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 157, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, S.K.; Kumar, S.; Raut, J.; Singh, M.; Kaur, S.; Sharma, G.; Roldan, T.L.; Trehan, S.; Holloway, J.; Wahler, G.; et al. Systematic Development and Characterization of Novel, High Drug-Loaded, Photostable, Curcumin Solid Lipid Nanoparticle Hydrogel for Wound Healing. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, H.; Guo, B.; Dong, R.; Qiu, Y.; Ma, P.X. Antibacterial anti-oxidant electroactive injectable hydrogel as self-healing wound dressing with hemostasis and adhesiveness for cutaneous wound healing. Biomaterials 2017, 122, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiekh, P.A.; Singh, A.; Kumar, A. Exosome laden oxygen releasing antioxidant and antibacterial cryogel wound dressing OxOBand alleviate diabetic and infectious wound healing. Biomaterials 2020, 249, 120020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ding, Z.; Zheng, X.; Lu, G.; Lu, Q.; Kaplan, D.L. Injectable silk nanofiber hydrogels as stem cell carriers to accelerate wound healing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 7771–7781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, X. Promote anti-inflammatory and angiogenesis using a hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel with miRNA-laden nanoparticles for chronic diabetic wound treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 166, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Lu, H.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, W.; Deng, L.; Cao, W.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Ding, J.; et al. Promoting the healing of infected diabetic wound by an anti-bacterial and nano-enzyme-containing hydrogel with inflammation-suppressing, ROS-scavenging, oxygen and nitric oxide-generating properties. Biomaterials 2022, 286, 121597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Kang, X.; Jin, L.; Bai, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z. Stimulation of wound healing using bioinspired hydrogels with basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF). Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 3897–3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Pan, Z.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Wang, M.H.; Dong, L.; Gao, H.L.; Liu, C.Y.; Zhou, P.; Chen, L.; Shi, C.J.; et al. Anti-Swelling, Robust, and Adhesive Extracellular Matrix-Mimicking Hydrogel Used as Intraoral Dressing. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2200115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahbub, M.S.I.; Bae, S.H.; Gwon, J.G.; Lee, B.T. Decellularized liver extracellular matrix and thrombin loaded biodegradable TOCN/Chitosan nanocomposite for hemostasis and wound healing in rat liver hemorrhage model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 225, 1529–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Bashir, S.M.; Purohit, S.D.; Bhaskar, R.; Rather, M.A.; Ali, S.I.; Yadav, I.; Makhdoomi, D.M.; Din Dar, M.U.; Gani, M.A.; et al. Nanoceria laden decellularized extracellular matrix-based curcumin releasing nanoemulgel system for full-thickness wound healing. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 137, 212806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Liu, M.; Yao, S.; Ji, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Tang, K.; Chen, K.; Yang, H.; Guo, X. Biomimetic Composite Scaffold Containing Small Intestinal Submucosa and Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Exhibits High Osteogenic and Angiogenic Capacity. Tissue Eng. Part A 2018, 24, 1044–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Zhou, J.; Sun, T.; Tang, K.; Xiong, Z.; Ren, Z.; Yao, S.; Chen, K.; Yang, F.; Zhu, F.; et al. Diverse preparation methods for small intestinal submucosa (SIS): Decellularization, components, and structure. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2019, 107, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Bao, L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, X.; Mo, X.; Tang, R. The evaluation of functional small intestinal submucosa for abdominal wall defect repair in a rat model: Potent effect of sequential release of VEGF and TGF-β1 on host integration. Biomaterials 2021, 276, 120999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, S.; Wei, P.; Zhao, Y.; Mu, Y.; Wu, J.; Jing, W.; Zhao, B.; Deng, J.; Liu, Z. Small Intestinal Submucosa Membrane Modified by Fusion Peptide-Mediated Extracellular Vesicles to Promote Tissue Regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, e2101298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giobbe, G.G.; Crowley, C.; Luni, C.; Campinoti, S.; Khedr, M.; Kretzschmar, K.; De Santis, M.M.; Zambaiti, E.; Michielin, F.; Meran, L.; et al. Extracellular matrix hydrogel derived from decellularized tissues enables endodermal organoid culture. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palminteri, E.; Berdondini, E.; Colombo, F.; Austoni, E. Small intestinal submucosa (SIS) graft urethroplasty: Short-term results. Eur. Urol. 2007, 51, 1695–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, M.; Gu, Q.; Zhao, J. Small intestinal submucosa: A potential osteoconductive and osteoinductive biomaterial for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Cheng, L.; Yang, Y.; Pang, M.; Dong, Y.; Zhu, X.; Chen, C.; Yao, Z.; Wu, G.; Cheng, B.; et al. Co-administration of platelet-rich plasma and small intestinal submucosa is more beneficial than their individual use in promoting acute skin wound healing. Burn. Trauma 2021, 9, tkab033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xia, B.; Lu, X.B.; Zhang, Z.J.; Li, Z.; Li, W.L.; Xiong, A.B.; Deng, L.; Tan, M.Y.; Huang, Y.C. Grafting of mesenchymal stem cell-seeded small intestinal submucosa to repair the deep partial-thickness burns. Connect. Tissue Res. 2016, 57, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, S.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Shanti, R.M.; Le, A.D. SIS-ECM Laden with GMSC-Derived Exosomes Promote Taste Bud Regeneration. J. Dent. Res. 2019, 98, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, T.; Long, M.; Li, P. Quercetin: Its Main Pharmacological Activity and Potential Application in Clinical Medicine. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 8825387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.D.; Zhang, W.; Gao, Y.L.; Sun, Y.Z.; Wang, H.X.; Qi, R.Q.; Chen, H.D.; Gao, X.H. Anti-inflammatory effects of quercetin in a mouse model of MC903-induced atopic dermatitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 74, 105676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Gui, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Xia, L.; Lin, K.; Xu, Y. Quercetin alleviates rat osteoarthritis by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis of chondrocytes, modulating synovial macrophages polarization to M2 macrophages. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 145, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Wu, L.; Liu, L.; Ruan, Q.; Zhang, X.; Hong, W.; Wu, S.; Jin, G.; Bai, Y. Quercetin ameliorates kidney injury and fibrosis by modulating M1/M2 macrophage polarization. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 154, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Wan, Y.; Qi, M.; Chen, Q.; Sun, Y.; Sun, X.; Fang, J.; Fu, L.; Xu, L.; et al. Quercetin-Loaded Ceria Nanocomposite Potentiate Dual-Directional Immunoregulation via Macrophage Polarization against Periodontal Inflammation. Small 2021, 17, e2101505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKay, T.B.; Karamichos, D. Quercetin and the ocular surface: What we know and where we are going. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Farias, M.; Carrasco-Pozo, C. The Anti-Cancer Effect of Quercetin: Molecular Implications in Cancer Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X. Quercetin ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting SphK1/S1P signaling. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jin, Q.; Yao, Q.; Xu, B.; Li, L.; Zhang, S.; Tu, C. The Flavonoid Quercetin Ameliorates Liver Inflammation and Fibrosis by Regulating Hepatic Macrophages Activation and Polarization in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Huang, J.; Lin, M.; Xie, T.; You, T. Quercetin Promotes Diabetic Wound Healing via Switching Macrophages from M1 to M2 Polarization. J. Surg. Res. 2020, 246, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veith, A.P.; Henderson, K.; Spencer, A.; Sligar, A.D.; Baker, A.B. Therapeutic strategies for enhancing angiogenesis in wound healing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 146, 97–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, S.Q.; Huang, Y.Q.; Jing, W.; Wei, P.F.; Yu, X.Q.; Zhao, B. Mechanically active small intestinal submucosa hydrogel for accelerating chronic wound healing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 6279–6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kant, V.; Jangir, B.L.; Sharma, M.; Kumar, V.; Joshi, V.G. Topical application of quercetin improves wound repair and regeneration in diabetic rats. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2021, 43, 536–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Hu, H.; Wu, J.; Li, X.; Ma, X.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wu, C.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Y.; et al. Functional extracellular matrix hydrogel modified with MSC-derived small extracellular vesicles for chronic wound healing. Cell Prolif. 2022, 55, e13196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, M.; Kosaric, N.; Bonham, C.A.; Gurtner, G.C. Wound Healing: A Cellular Perspective. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 665–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Kong, L.; He, Y.; Chan, H.F.; Li, H. Modulation of macrophages by bioactive glass/sodium alginate hydrogel is crucial in skin regeneration enhancement. Biomaterials 2020, 256, 120216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Xu, P.; Yao, Z.; Cui, X.; Lei, X.; Li, L.; Dong, Y.; Zhu, W.; Guo, R.; Cheng, B. A composite hydrogel with co-delivery of antimicrobial peptides and platelet-rich plasma to enhance healing of infected wounds in diabetes. Acta Biomater. 2021, 124, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Wang, H.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tao, L.; Wei, Y.; Fan, Y.; Guo, X.; Liu, H. Improving Chronic Diabetic Wound Healing through an Injectable and Self-Healing Hydrogel with Platelet-Rich Plasma Release. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 55659–55674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qu, M.; Wang, C.; Xue, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, Q.; Sun, W.; Zhou, X.; Xu, G.; Jiang, X. A Dual-Cross-Linked Hydrogel Patch for Promoting Diabetic Wound Healing. Small 2022, 18, e2106172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.F.; Chen, G.W.; Chen, Y.C.; Shen, C.K.; Lu, D.Y.; Yang, L.Y.; Chen, J.H.; Yeh, W.L. Regulatory Effects of Quercetin on M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization and Oxidative/Antioxidative Balance. Nutrients 2021, 14, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cristo, F.; Valentino, A.; De Luca, I.; Peluso, G.; Bonadies, I.; Di Salle, A.; Calarco, A. Polylactic Acid/Poly(vinylpyrrolidone) Co-Electrospun Fibrous Membrane as a Tunable Quercetin Delivery Platform for Diabetic Wounds. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Shi, N.; Yao, Z.; Liu, H.; Guo, W. Gallium-modified gelatin nanoparticles loaded with quercetin promote skin wound healing via the regulation of bacterial proliferation and macrophage polarization. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1124944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; He, J.; Guo, B. Functional Hydrogels as Wound Dressing to Enhance Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 12687–12722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wu, N. Mechanism and application of exosomes in the wound healing process in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 187, 109882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, J.S.; Madden, L.; Chew, S.Y.; Becker, D.L. Drug therapies and delivery mechanisms to treat perturbed skin wound healing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 149–150, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Dong, L.; Zhao, B.; Lu, Y.; Huang, S.; Yuan, Z.; Luo, G.; Xu, Y.; Qian, W. Anti-inflammatory hydrogel dressings and skin wound healing. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.; Han, K.; Dong, K.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Long, Q.; Lu, T. Potential Applications of Nanomaterials and Technology for Diabetic Wound Healing. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 9717–9743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, D.; Edmonds, M. Managing Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Pharmacotherapy for Wound Healing. Drugs 2021, 81, 29–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Huang, Y.; Li, K.; Fan, Y.; Xie, H.; Li, X. Small intestinal submucosa: Superiority, limitations and solutions, and its potential to address bottlenecks in tissue repair. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 5038–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, M.; Tanaka, R. Porcine Small Intestinal Submucosa Alters the Biochemical Properties of Wound Healing: A Narrative Review. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodde, J.P.; Hiles, M.C.; Metzger, D.W. Characterization of the local wound environment following treatment of chronic leg ulcers with SIS wound matrix. J. Tissue Viability 2020, 29, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Chai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, H. Nano-silver modified porcine small intestinal submucosa for the treatment of infected partial-thickness burn wounds. Burns 2019, 45, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.; Purohit, S.D.; Bhaskar, R.; Yadav, I.; Bhushan, S.; Gupta, M.K.; Mishra, N.C. Curcumin in decellularized goat small intestine submucosa for wound healing and skin tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2022, 110, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bercea, M. Bioinspired Hydrogels as Platforms for Life-Science Applications: Challenges and Opportunities. Polymers 2022, 14, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, G.; Sun, C.; Peng, F.; Yu, L.; Chen, Y.; Tan, Y.; Cao, X.; Tang, Y.; Xie, X.; et al. Chemistry, pharmacokinetics, pharmacological activities, and toxicity of Quercitrin. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 1545–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatahet, T.; Morille, M.; Hommoss, A.; Devoisselle, J.M.; Müller, R.H.; Bégu, S. Quercetin topical application, from conventional dosage forms to nanodosage forms. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 108, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Cai, L.; Ruan, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Wu, Y.; Feng, S.; Chen, J. Electrospun chitosan oligosaccharide/polycaprolactone nanofibers loaded with wound-healing compounds of Rutin and Quercetin as antibacterial dressings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wangsawangrung, N.; Choipang, C.; Chaiarwut, S.; Ekabutr, P.; Suwantong, O.; Chuysinuan, P.; Techasakul, S.; Supaphol, P. Quercetin/Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex-Loaded Hydrogels for Accelerated Wound Healing. Gels 2022, 8, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangde, R.; Srivastava, S.; Singh, M.R.; Singh, D. In vitro and In vivo characterization of quercetin loaded multiphase hydrogel for wound healing application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, S.; Nair, A.B.; Shah, J.; Sreeharsha, N.; Gupta, S.; Shinu, P. Emerging Role of Hydrogels in Drug Delivery Systems, Tissue Engineering and Wound Management. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, I.P.; Spada, F. Hydrogels for Atopic Dermatitis and Wound Management: A Superior Drug Delivery Vehicle. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okonkwo, U.A.; DiPietro, L.A. Diabetes and Wound Angiogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrante, C.J.; Leibovich, S.J. Regulation of Macrophage Polarization and Wound Healing. Adv. Wound Care 2012, 1, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, C.; Graves, D.T. Abnormal cell responses and role of TNF-α in impaired diabetic wound healing. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 754802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhou, J.; Yu, K.; Yang, S.; Sun, T.; Ji, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Guo, X. Surface modified small intestinal submucosa membrane manipulates sequential immunomodulation coupled with enhanced angio- and osteogenesis towards ameliorative guided bone regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 119, 111641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kim, M.S. An injectable hydrogel derived from small intestine submucosa as a stem cell carrier. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2016, 104, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Shim, S.; Jang, H.; Myung, H.; Lee, J.; Bae, C.H.; Myung, J.K.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, S.B.; Jang, W.S.; et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stromal cells and small intestinal submucosa hydrogel composite promotes combined radiation-wound healing of mice. Cytotherapy 2017, 19, 1048–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Li, H.; He, Y. Injectable Quercetin-Loaded Hydrogel with Cartilage-Protection and Immunomodulatory Properties for Articular Cartilage Repair. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, G.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; He, X. Quercetin inhibits TNF-α induced HUVECs apoptosis and inflammation via downregulating NF-kB and AP-1 signaling pathway in vitro. Medicine 2020, 99, e22241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liu, K.; Guo, S.; Chang, R.; Zhang, C.; Guan, F.; Yao, M. Multifunctional hydrogel with reactive oxygen species scavenging and photothermal antibacterial activity accelerates infected diabetic wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2023, 155, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Z.; Xiong, H.; Lou, T.; Liu, W.; Xu, Y.; Yu, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Yang, L.; Zhou, C.; et al. Multifunctional Extracellular Matrix Hydrogel with Self-Healing Properties and Promoting Angiogenesis as an Immunoregulation Platform for Diabetic Wound Healing. Gels 2023, 9, 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9050381
Sun Z, Xiong H, Lou T, Liu W, Xu Y, Yu S, Wang H, Liu W, Yang L, Zhou C, et al. Multifunctional Extracellular Matrix Hydrogel with Self-Healing Properties and Promoting Angiogenesis as an Immunoregulation Platform for Diabetic Wound Healing. Gels. 2023; 9(5):381. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9050381
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Zhenghua, Hao Xiong, Tengfei Lou, Weixuan Liu, Yi Xu, Shiyang Yu, Hui Wang, Wanjun Liu, Liang Yang, Chao Zhou, and et al. 2023. "Multifunctional Extracellular Matrix Hydrogel with Self-Healing Properties and Promoting Angiogenesis as an Immunoregulation Platform for Diabetic Wound Healing" Gels 9, no. 5: 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9050381
APA StyleSun, Z., Xiong, H., Lou, T., Liu, W., Xu, Y., Yu, S., Wang, H., Liu, W., Yang, L., Zhou, C., & Fan, C. (2023). Multifunctional Extracellular Matrix Hydrogel with Self-Healing Properties and Promoting Angiogenesis as an Immunoregulation Platform for Diabetic Wound Healing. Gels, 9(5), 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9050381




