Volume Kinetic Analysis in Living Humans: Background History and Answers to 15 Questions in Physiology and Medicine
Abstract
:1. Drug Kinetics Versus Volume Kinetics
2. History
3. Procedure
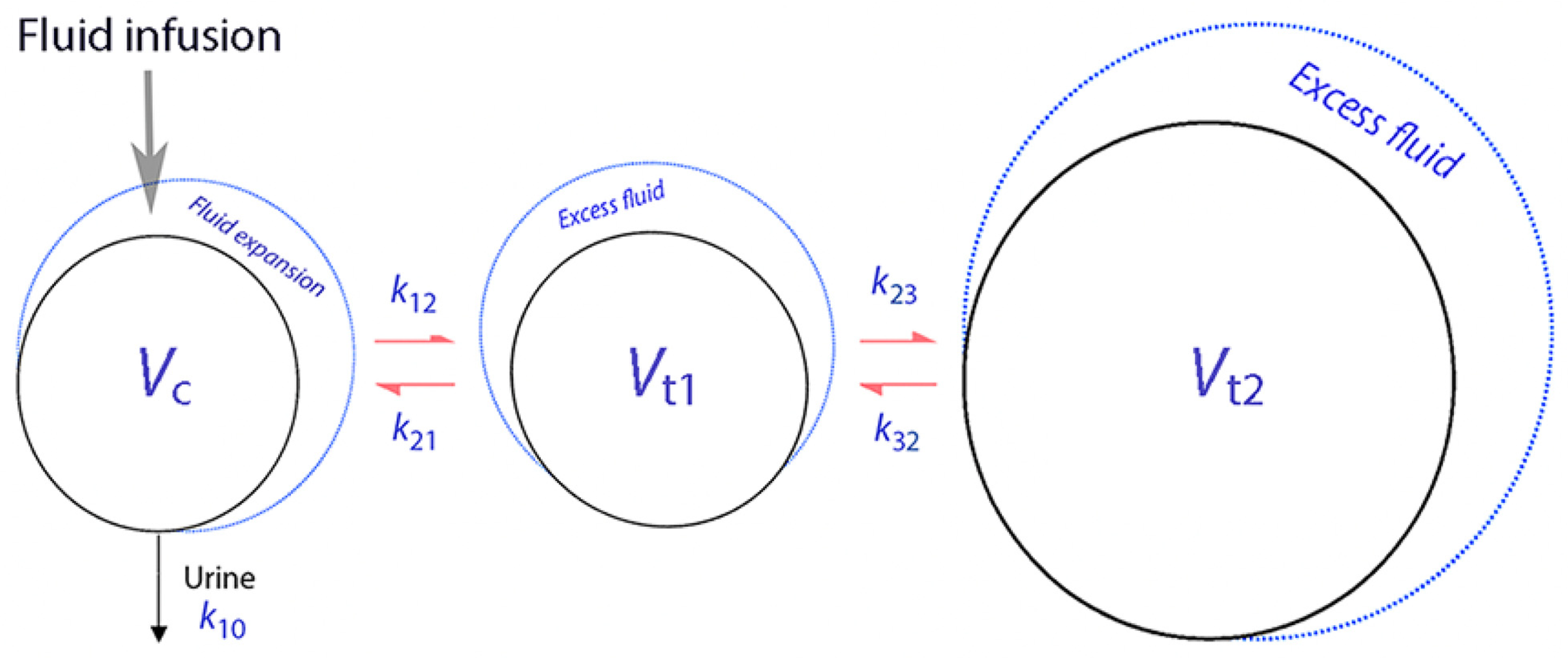
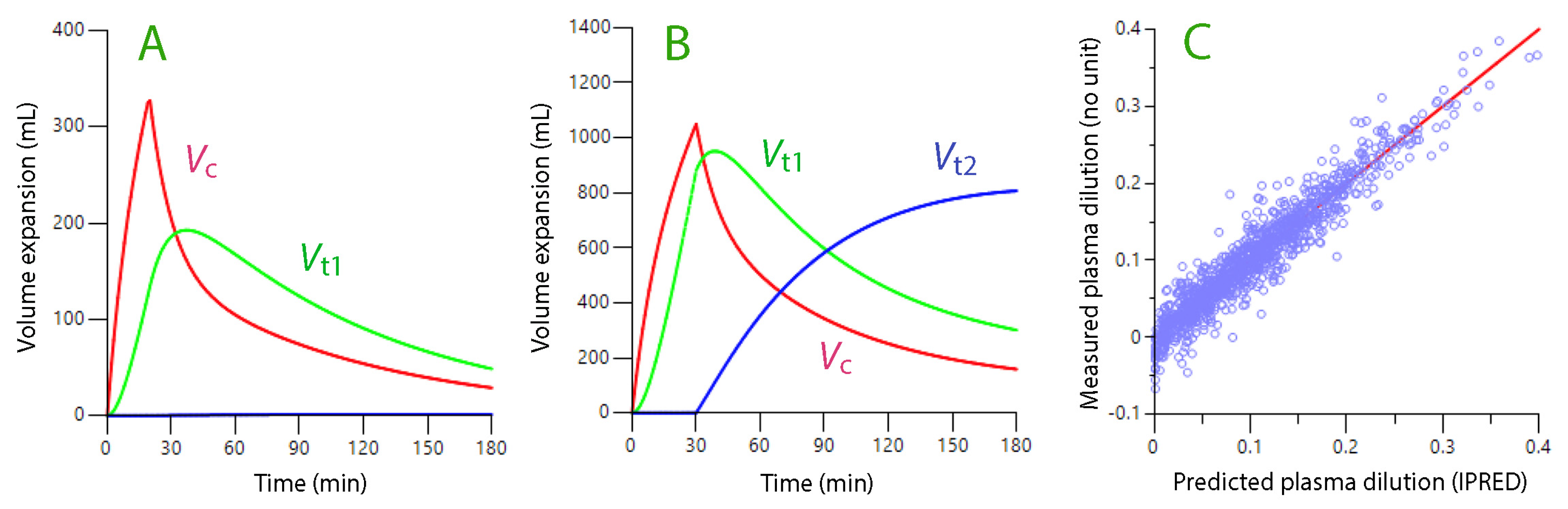
4. Crystalloid Fluid Model
5. Colloid Fluid Model
6. Fifteen Issues Studied by Volume Kinetics
6.1. Why Are Anesthetized Patients Oliguric?
6.2. Urine Creatinine and Urine Output
6.3. Oncotic Fluid Withdrawal by Albumin 20%
6.4. Capillary Filtration Is Increased During Anesthesia
6.5. Inhibitory Effect of General Anesthetics
6.6. Capillary Filtration in Spinal Anesthesia
6.7. Fluid Distribution in Pre-Eclampsia
6.8. Adrenergic Effect on the Kidneys
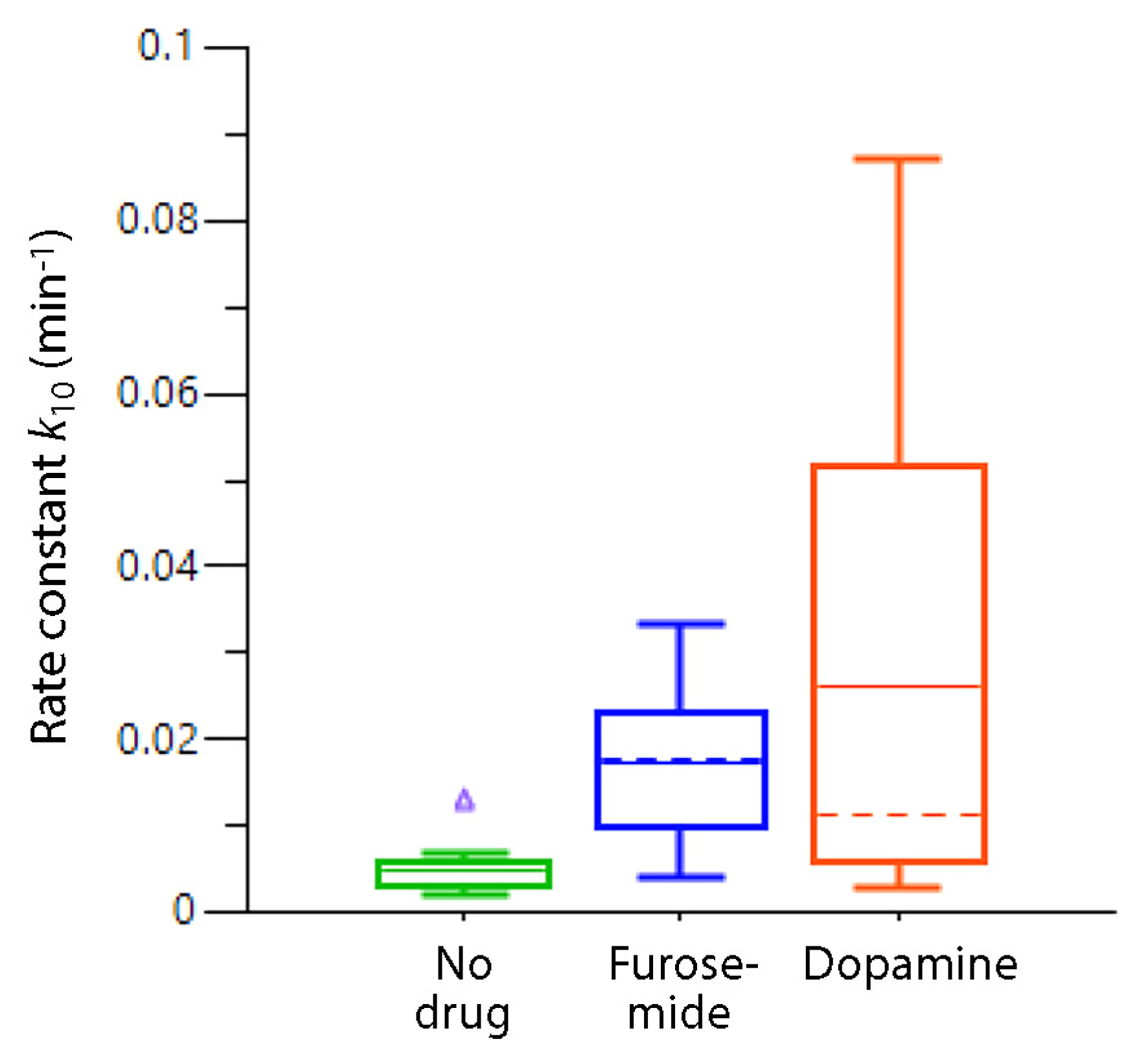
6.9. Dopamine as a Diuretic During Surgery
6.10. Dehydration and Blood Loss
6.11. Plasma Volume Oscillations
6.12. Redistribution of Fluid
6.13. Volume Kinetics and the Glycocalyx
6.14. Females Excrete Fluid Efficiently
6.15. How Much Water Is Present in the Glycocalyx?
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
9. Future Directions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Hb | hemoglobin |
| MAP | mean arterial pressure |
| Vc | central fluid space |
| Vt1 | fast-exchange interstitial fluid space |
| Vt2 | slow-exchange interstitial fluid space |
| k10 | rate constant for urine output |
References
- Owen, J.S.; Fiedler-Kelly, J. Introduction to Population Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Analysis with Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models; Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, R.G. Early detection of the TUR syndrome by marking the irrigating fluid with 1% ethanol. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 1989, 33, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.W.; Hahn, R.G.; Stalberg, H.P. Distribution of ethanol and water between plasma and whole-blood; inter- and intra-subject variations after administration of ethanol by intravenous infusion. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 1990, 50, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, R.G.; Drobin, D. Volume kinetics of Ringer’s acetate in human volunteers. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 1995, 39 (Suppl. S105), 155. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, R.G.; Drobin, D.; Ståhle, L. Volume kinetics of Ringer’s solution in female volunteers. Br. J. Anaesth. 1997, 78, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, R.G. Volume kinetics for infusion fluids (review). Anesthesiology 2010, 113, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.M.; Bang, J.Y.; Choi, B.; Cho, C.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, E.K.; Choi, B.M.; Noh, G.J. Population-based volume kinetics of crystalloids and colloids in healthy volunteers. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Choo, Y.J.; Lee, Y.H.; Rhim, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, B.M.; Oh, S.T.; Choi, K.T.; Noh, G.J. Population-based volume kinetics of Ringer’s lactate solution in patients undergoing open gastrectomy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, R.G. Evidence of serial connection between the plasma volume and two interstitial fluid compartments. Microvasc. Res. 2023, 151, 104599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, R.G. Sequential recruitment of body fluid spaces for increasing volumes of crystalloid fluid. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1439035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyton, A.C.; Scheel, K.; Murphree, D. Interstitial fluid pressure. 3. Its effect on resistance to tissue fluid mobility. Circ. Res. 1966, 19, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyton, A.C.; Granger, H.J.; Taylor, A.E. Interstitial fluid pressure. Physiol. Rev. 1971, 51, 527–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, R.G. Accelerated lymph flow from infusion of crystalloid fluid during general anesthesia. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024, 24, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haljamäe, H. Anatomy of the interstitial tissue. Lymphology 1978, 11, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aukland, K.; Reed, R.K. Interstitial-lymphatic mechanisms in the control of extracellular fluid volume. Physiol. Rev. 1993, 73, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cihoric, M.; Kehlet, H.; Højlund, J.; Lauritsen, M.L.; Kanstrup, K.; Foss, N.B. Perioperative changes in fluid distribution and haemodynamics in acute high-risk abdominal surgery. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, R.G. Colloid fluids. In Hemodynamic Monitoring and Fluid Therapy During Surgery; Joosten, A., Cannesson, M., Hahn, R.G., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2024; pp. 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Joosten, A.; Delaporte, A.; Ickx, B.; Touihri, K.; Stany, I.; Barvais, L.; Van Obbergh, L.; Loi, P.; Rinehart, J.; Cannesson, M.; et al. Crystalloid versus colloid for intraoperative goal-directed fluid therapy using a closed-loop system: A randomized, double-blinded, controlled trial in major abdominal surgery. Anesthesiology 2018, 128, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, R.G.; Bergek, C.; Gebäck, T.; Zdolsek, J. Interactions between the volume effects of hydroxyethyl starch 130/0.4 and Ringer’s acetate. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdolsek, M.; Sjöberg, F.; Hahn, R.G. Fast versus slow infusion of 20% albumin; a randomized controlled cross-over trial in volunteers. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2022, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, R.G.; Zdolsek, M.; Gunnström, M.; Hasselgren, E.; Zdolsek, J.H. Diuretic responses to Ringer’s solution and 20% albumin at different arterial pressures. Physiol Rep. 2024, 12, e70069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, C.; Schäfer, C.; von Bismarck, P.; Bolz, S.S.; Pohl, U. Elevation of plasma viscosity induces sustained NO-mediated dilation in the hamster cremaster microcirculation in vivo. Pflug. Arch. 1997, 434, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrales, P.; Tsai, A.G.; Martini, J.; Intaglietta, M. The role of plasma viscosity. In Hemodynamic Monitoring and Fluid Therapy During Surgery; Joosten, A., Cannesson, M., Hahn, R.G., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2024; pp. 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, R.G. Effects of diet, habitual water intake and increased hydration on body fluid volumes and urinary analysis of renal fluid retention in healthy volunteers. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hahn, R.G. Renal water conservation and the volume kinetics of fluid-induced diuresis; a retrospective analysis of two cohorts of elderly men. Clin. Exp. Pharm. Physiol. 2021, 48, 310–317. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, L.E.; Muñoz, C.X.; Armstrong, E.M. Distinguishing low and high water consumers—A paradigm of disease risk. Nutrients 2020, 12, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodcock, T.E.; Woodcock, T.M. Revised Starling equation and the glycocalyx model of transvascular fluid exchange: An improved paradigm for prescribing intravenous fluid therapy. Br. J. Anaesth. 2012, 108, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zdolsek, J.H.; Zdolsek, M.; Hahn, R.G. Recruitment of efferent lymph during infusion of 20% albumin. Microvasc. Res. 2023, 148, 104539. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, R.G.; Zdolsek, M.; Krizhanovskii, C.; Ntika, S.; Zdolsek, J. Elevated plasma concentrations of syndecan-1 do not correlate with the capillary leakage of 20% albumin. Anesth. Analg. 2021, 132, 856–865. [Google Scholar]
- Hasselgren, E.; Zdolsek, M.; Zdolsek, J.H.; Björne, H.; Krizhanovskii, C.; Ntika, S.; Hahn, R.G. Long intravascular persistence of 20% albumin in postoperative patients. Anesth. Analg. 2019, 129, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar]
- Gunnström, M.; Zdolsek, J.; Hahn, R.G. Plasma volume expansion and fluid kinetics of 20% albumin during general anesthesia and surgery lasting for more than 5 hours. Anesth. Analg. 2022, 134, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, R.G. Capillary filtration of plasma is accelerated during general anesthesia: A secondary volume kinetic analysis. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHale, N.G.; Thornbury, K.D. The effects of anesthetics on lymphatic contractility. Microvasc. Res. 1989, 37, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Hattori, J.I.; Yamakage, M.; Seki, S.; Okazaki, K.; Namiki, A. Inhibitory effects of the anesthetics propofol and sevoflurane on spontaneous lymphatic vessel activity. Anesthesiology 2004, 101, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, S.B.; Proulx, S.T.; He, Y.; Ries, M.; Detmar, M. Differential effects of anesthesia on the contractility of lymphatic vessels in vivo. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 2841–2852. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dull, R.O.; Hahn, R.G.; Dull, G.E. Anesthesia-induced lymphatic dysfunction (review). Anesthesiology 2024, 141, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dull, R.O.; Hahn, R.G. Hypovolemia with peripheral edema: What is wrong? Crit. Care 2023, 27, 206. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, R.G. Interstitial washdown during crystalloid loading in graded hypovolemia. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2023, 83, 105–116. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, R.G.; Drobin, D. Model-predicted capillary leakage in graded hypotension; extended analysis of experimental spinal anesthesia. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2021, 65, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, R.G. Maldistribution of fluid in preeclampsia; a retrospective kinetic analysis. Int. J. Obstet. Anesth. 2024, 57, 103963. [Google Scholar]
- Wiig, H.; Rubin, K.; Reed, R.K. New and active role of the interstitium in control of interstitial fluid pressure: Potential therapeutic consequences. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2003, 47, 111–121. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, R.K.; Rubin, K. Transcapillary exchange: Role and importance of the interstitial fluid pressure and the extracellular matrix. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 87, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vane, L.A.; Prough, D.S.; Kinsky, M.A.; Williams, C.A.; Grady, J.J.; Kramer, G.C. Effects of different catecholamines on dynamics and volume kinetics of crystalloid infusion. Anesthesiology 2004, 101, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, H.B.; Zheng, X.; Chen, H.J.; Shao, L.; Hahn, R.G. Low doses of esmolol and phenylephrine act as diuretics during intravenous anesthesia. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, R.G.; Drobin, D.; Li, Y.; Zdolsek, J. Kinetics of Ringer’s solution in extracellular dehydration and hemorrhage. Shock 2020, 53, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hahn, R.G. Plasma volume oscillations during fluid therapy in humans. J. Vasc. Res. 2024, 61, 16–25. [Google Scholar]
- Dull, R.O.; Hahn, R.G. The glycocalyx as a permeability barrier; basic science and clinical evidence. Crit. Care 2022, 26, 273. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hahn, R.G. The elimination half-life of crystalloid fluid is shorter in female than in male volunteers; a retrospective population kinetic analysis. Biol. Sex Differ. 2016, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehm, M.; Haller, M.; Orth, V.; Kreimeier, U.; Jacob, M.; Dressel, H.; Mayer, S.; Brechtelsbauer, H.; Finsterer, U. Changes in blood volume and hematocrit during acute perioperative volume loading with 5% albumin or 6% hetastarch solutions in patients before radical hysterectomy. Anesthesiology 2001, 95, 849–856. [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwdorp, M.; van Haeften, T.W.; Gouverneur, M.C.L.G.; Mooij, H.L.; van Lieshout, M.H.P.; Levi, M.; Meijers, J.C.M.; Holleman, F.; Hoekstra, J.B.L.; Vink, H.; et al. Loss of endothelial glycocalyx during acute hyperglycemia coincides with endothelial dysfunction and coagulation activation in vivo. Diabetes 2006, 55, 480–486. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, C.C.; Curry, F.E. Glycocalyx volume measurements: A critical review of tracer dilution methods for its measurement. Microcirculation 2009, 16, 213–219. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, R.G. Water content of the endothelial glycocalyx layer estimated by volume kinetic analysis. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2020, 8, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Brace, R.A.; Power, G.G. Effects of hypotonic, isotonic and hypertonic fluids on thoracic duct lymph flow. Am. J. Physiol. 1983, 45, R785–R791. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, R.G.; Olsson, J. Diuretic response to Ringer’s solution is normal shortly after awakening from general anaesthesia: A retrospective kinetic analysis. BJA Open 2022, 2, 100013. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jardot, F.; Hahn, R.G.; Engel, D.; Beilstein, C.; Wuethrich, P.Y. Blood volume and hemodynamics during treatment of major hemorrhage with Ringer solution, 5% albumin, and 20% albumin: A single-center randomized controlled trial. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Model | −2 log Likelihood | Akaike Criterion |
|---|---|---|
| Base model | −2940 | −2920 |
| + body weight (BW) | −2959 | −2937 |
| + drug | −2951 | −2927 |
| + MAP | −2989 | −2967 |
| + BW + MAP | −3009 | −2985 |
| + drug + MAP | −2994 | −2968 |
| + BW + MAP + drug | −3014 | −2986 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hahn, R.G. Volume Kinetic Analysis in Living Humans: Background History and Answers to 15 Questions in Physiology and Medicine. Fluids 2025, 10, 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids10040086
Hahn RG. Volume Kinetic Analysis in Living Humans: Background History and Answers to 15 Questions in Physiology and Medicine. Fluids. 2025; 10(4):86. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids10040086
Chicago/Turabian StyleHahn, Robert G. 2025. "Volume Kinetic Analysis in Living Humans: Background History and Answers to 15 Questions in Physiology and Medicine" Fluids 10, no. 4: 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids10040086
APA StyleHahn, R. G. (2025). Volume Kinetic Analysis in Living Humans: Background History and Answers to 15 Questions in Physiology and Medicine. Fluids, 10(4), 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids10040086







