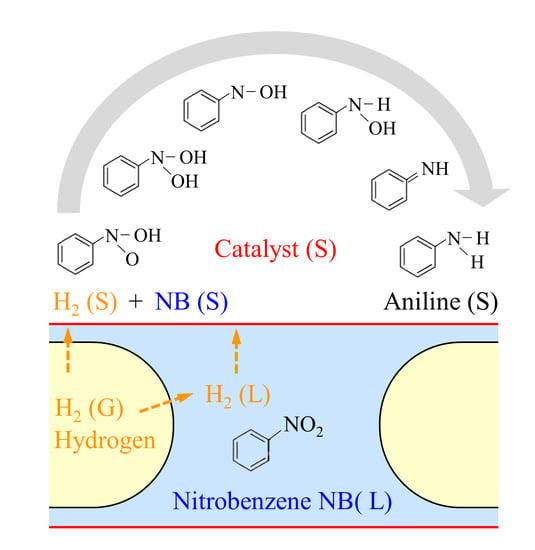
A Qualitative Numerical Study on Catalytic Hydrogenation of Nitrobenzene in Gas-Liquid Taylor Flow with Detailed Reaction Mechanism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Numerical Methodology
2.1. General Assumptions
2.2. Hydrodynamic Equations
2.3. Mass Transfer Equations
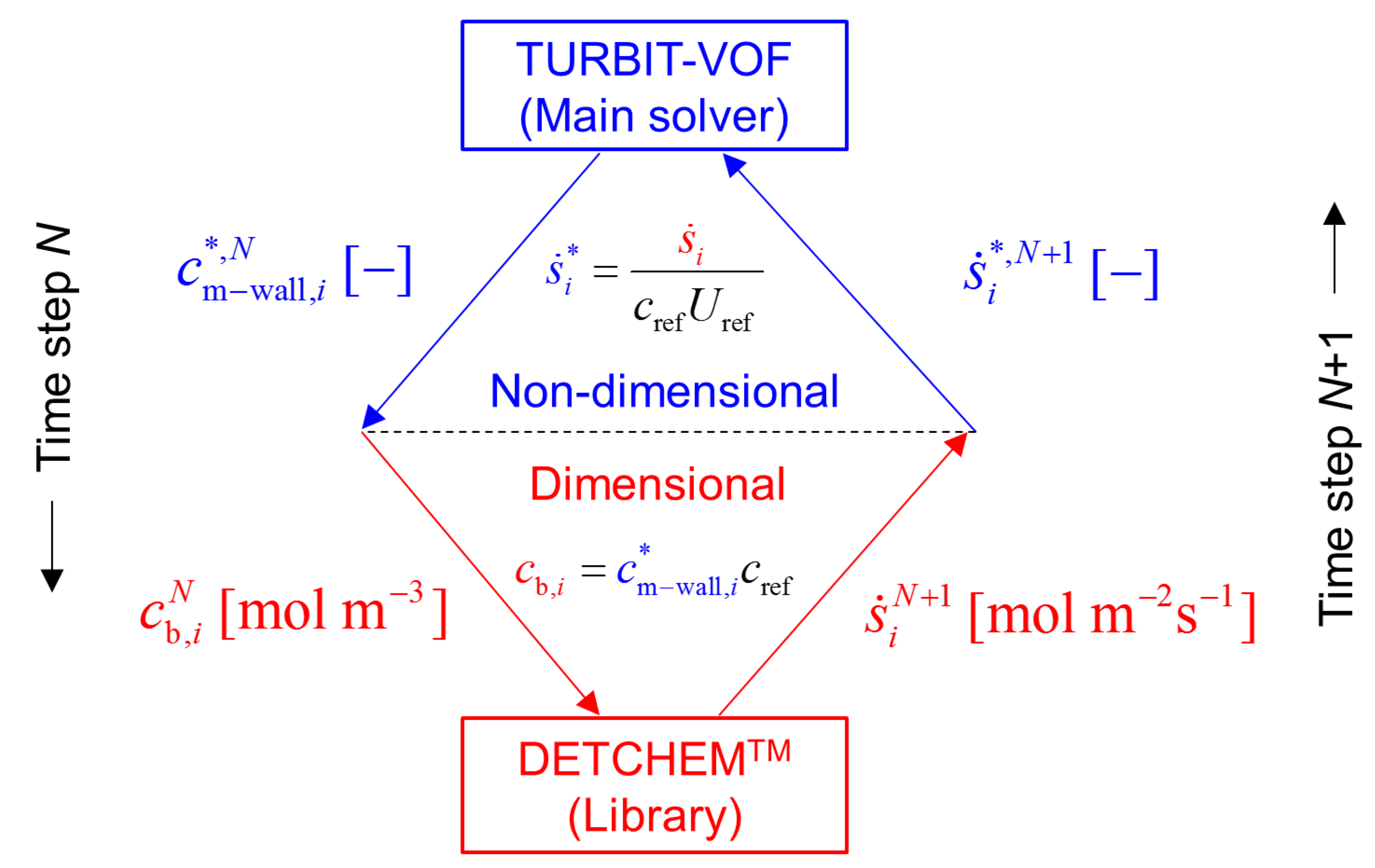
2.4. Coupling Mass Transfer Simulation and Surface Chemistry
3. Chemical Model
3.1. Reaction Mechanism
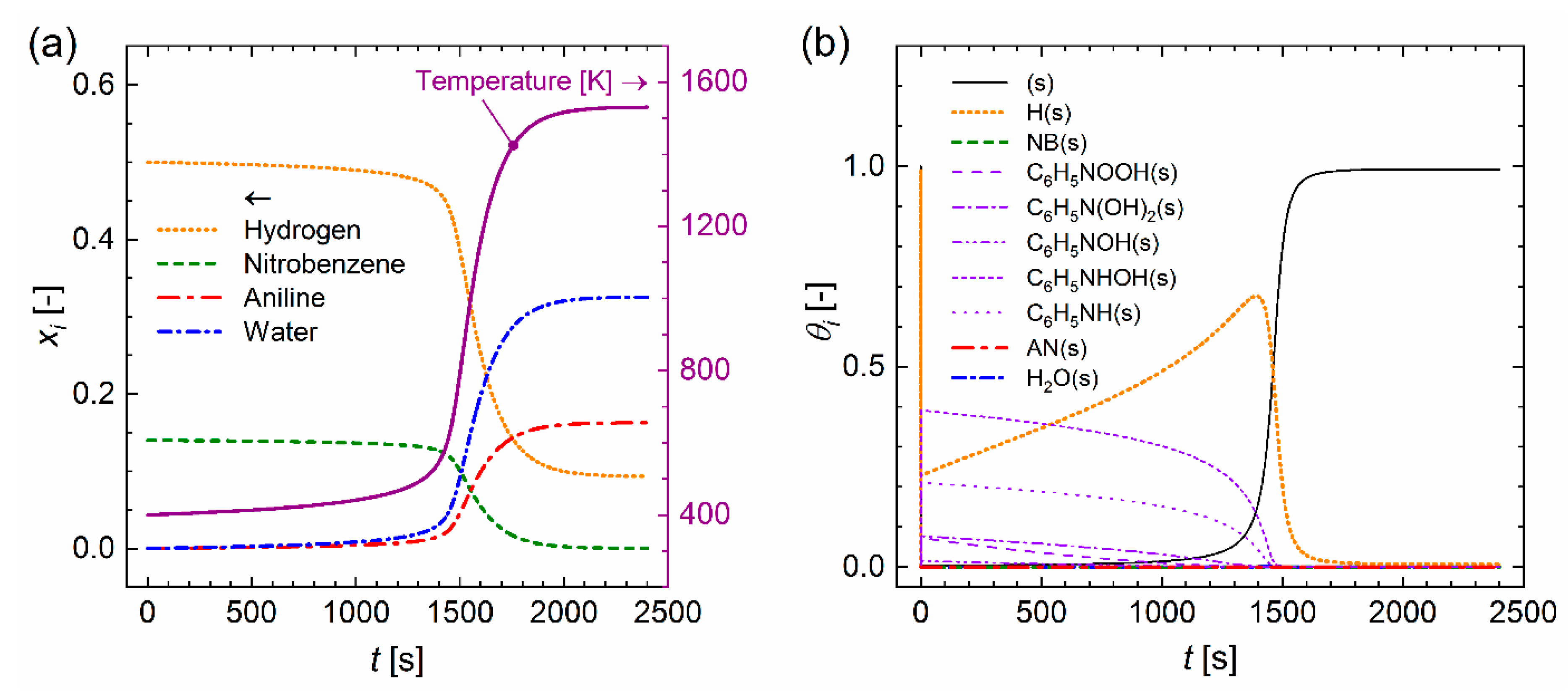
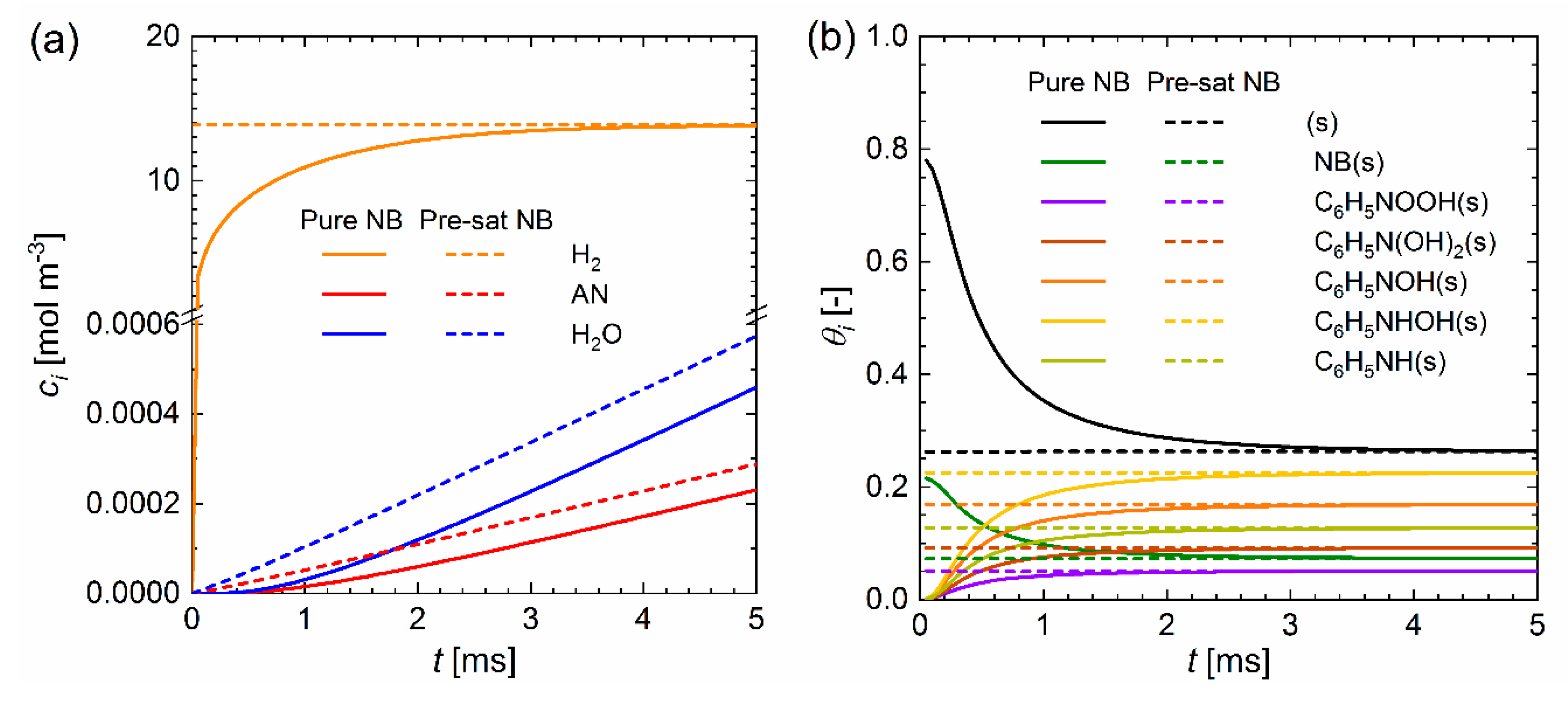
3.2. Continuously Stirred Tank Reactor
4. Hydrogenation of Nitrobenzene in Taylor Flow
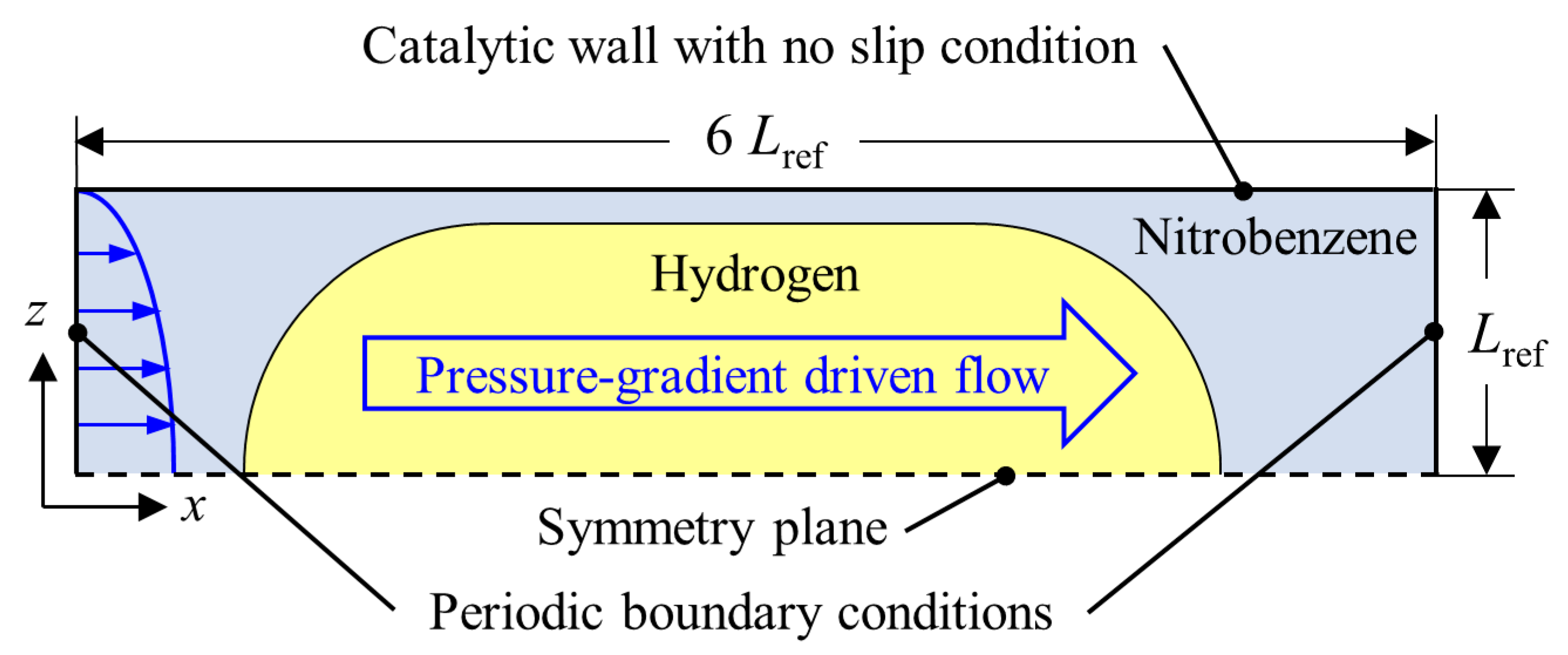
4.1. General Set-Up for Taylor Flow
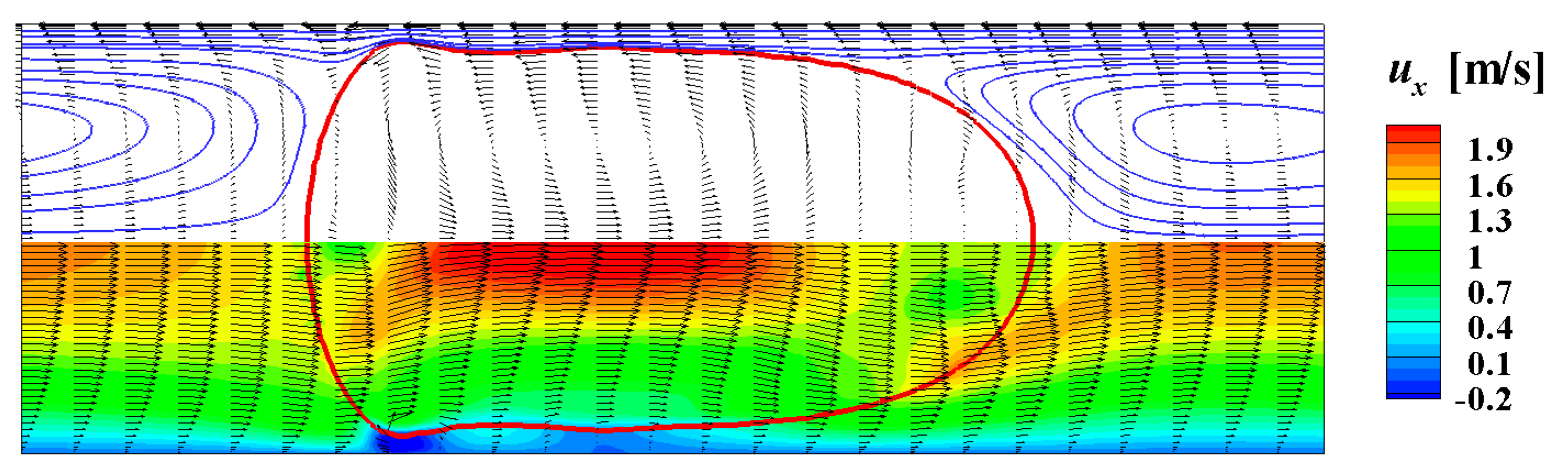
4.2. Hydrodynamic Simulation
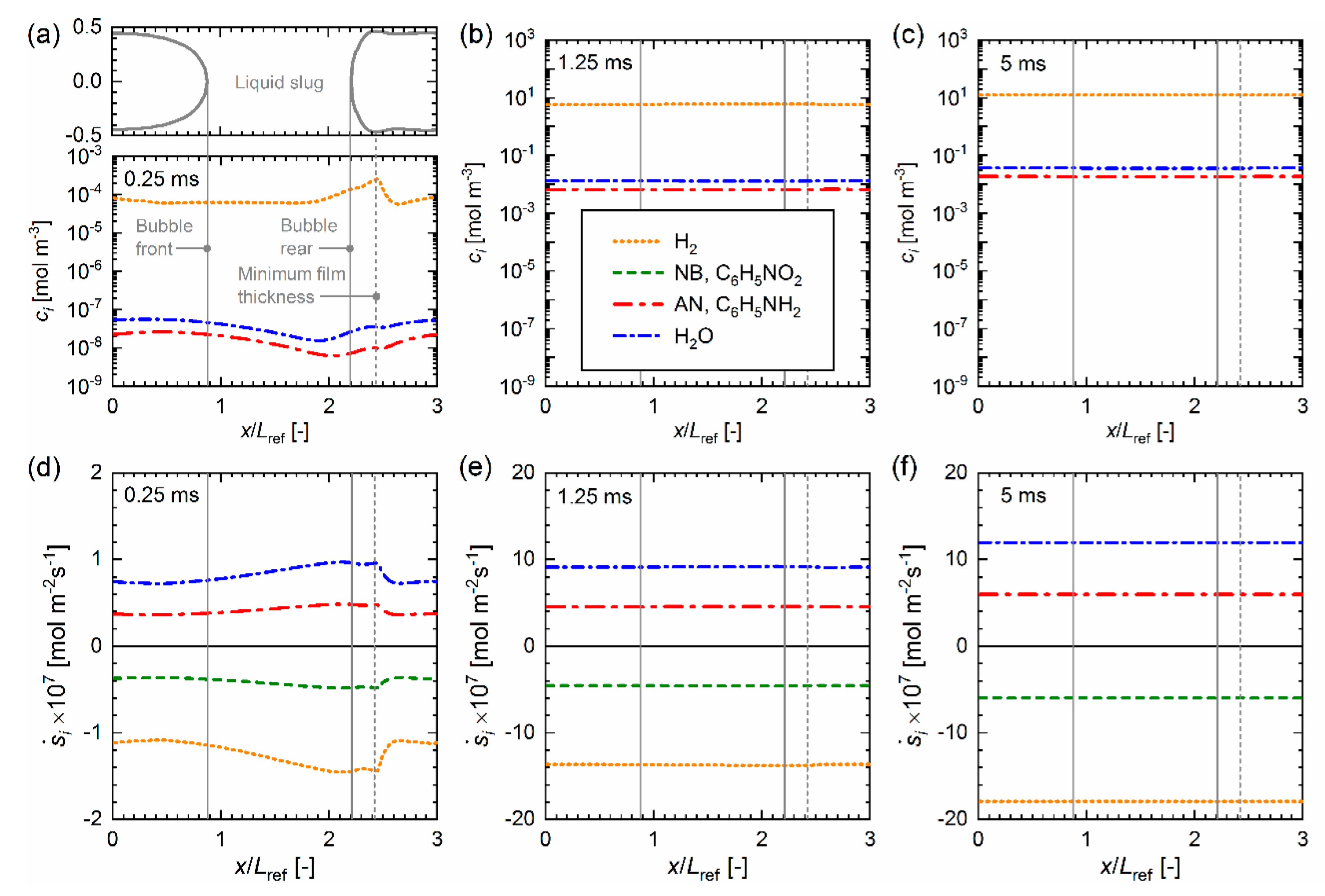
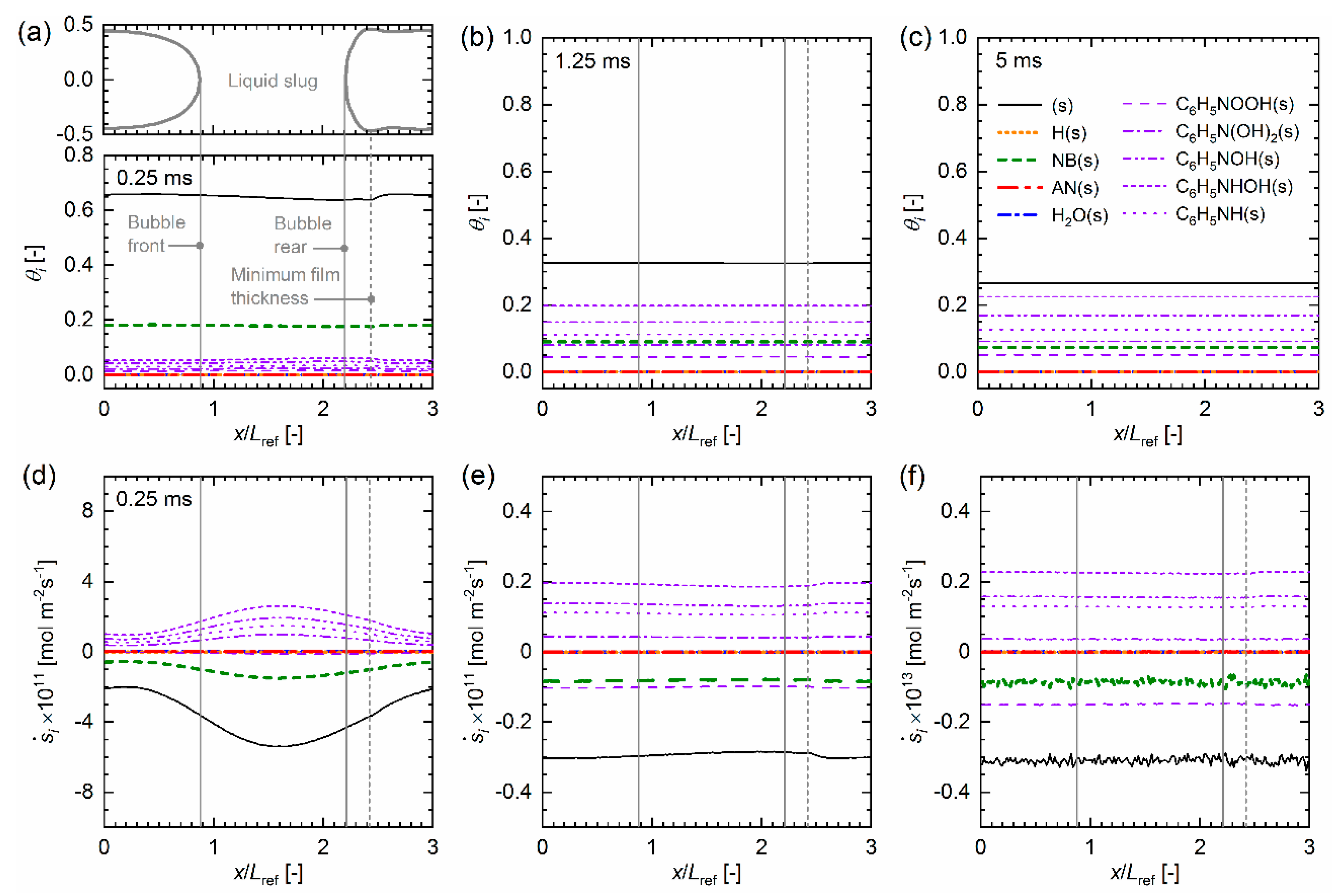
4.3. Mass Transfer Simulation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Pre-exponential factor | () | |
| Specific interfacial area | ||
| Capillary number, | - | |
| Molar bulk concentration of species | ||
| Non-dimensional bulk concentration | - | |
| Molar surface concentration of species | ||
| Diffusivity of species in solvent | ||
| Activation energy | ||
| Ratio of catalytic to geometric surface area | - | |
| Liquid volume fraction | - | |
| Henry number | - | |
| Molar flux, | ||
| Arrhenius-type rate factor | () | |
| Reference length, | m | |
| Molecular weight | ||
| Number of surface reactions | - | |
| Number of surface species | - | |
| Reduced pressure | - | |
| Pressure | Pa | |
| Gas constant | ||
| Reynolds number, | - | |
| Initial sticking coefficient | - | |
| Surface reaction rate | ||
| Temperature | K | |
| Time | s | |
| Reference velocity, | ||
| Velocity field, | ||
| Mole fraction | - | |
| Axial coordinate | ||
| Wall-normal coordinate | ||
| Greek symbols | ||
| Surface site density | ||
| Surface site fraction | - | |
| Interface curvature | - | |
| Dynamic viscosity | Pa s | |
| Stoichiometric coefficient | - | |
| Density | ||
| Surface tension coefficient | ||
| Subscripts | ||
| B | Bubble | |
| b | Bulk | |
| G | Gas phase | |
| Species index | ||
| Reaction index | ||
| int | Interface | |
| L | Liquid phase | |
| m | Two-phase mixture | |
| ref | Reference value | |
| s | Surface | |
| UC | Unit cell | |
| Superscripts | ||
| * | Dimensionless quantity | |
| Abbreviations | ||
| AN | Aniline, | |
| CSTR | Continuously stirred tank reactor | |
| NB | Nitrobenzene, |
References
- Shui, L.; Eijkel, J.C.T.; van den Berg, A. Multiphase flow in microfluidic systems—Control and applications of droplets and interfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 133, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. Deposition of a Viscous Fluid on the Wall of a Tube. J. Fluid Mech. 1961, 10, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, B.; Barrow, D.; Wirth, T. Enhancement of reaction rates by segmented fluid flow in capillary scale reactors. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2006, 348, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutzer, M.T.; Kapteijn, F.; Moulijn, J.A.; Heiszwolf, J.J. Multiphase monolith reactors: Chemical reaction engineering of segmented flow in microchannels. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 5895–5916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irandoust, S.; Andersson, B. Mass-Transfer and Liquid-Phase Reactions in a Segmented Two-Phase Flow Monolithic Catalyst Reactor. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1988, 43, 1983–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irandoust, S.; Ertle, S.; Andersson, B. Gas-Liquid Mass-Transfer in Taylor Flow through a Capillary. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1992, 70, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessimoz, A.L.; Cavin, L.; Renken, A.; Kiwi-Minsker, L. Liquid-liquid two-phase flow patterns and mass transfer characteristics in rectangular glass microreactors. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2008, 63, 4035–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roudet, M.; Loubiere, K.; Gourdon, C.; Cabassud, M. Hydrodynamic and mass transfer in inertial gas-liquid flow regimes through straight and meandering millimetric square channels. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 2974–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kastens, S.; Hosoda, S.; Schlüter, M.; Tomiyama, A. Mass Transfer from Single Taylor Bubbles in Minichannels. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2015, 38, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, S.; Murzin, D.Y.; Salmi, T. Review on hydrodynamics and mass transfer in minichannel wall reactors with gas-liquid Taylor flow. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 113, 304–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiev, R.; Svetlov, S.; Haase, S. Hydrodynamics and mass transfer of gas-liquid and liquid-liquid Taylor flow in microchannels. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2017, 40, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, P.; Gavriilidis, A. Hydrodynamics of Taylor flow in small channels: A review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C 2008, 222, 737–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, U.; Dittmeyer, R.; Patyk, A.; Wetzel, T.; Lange, R.; Freund, H.; Schwieger, W.; Grünewald, M.; Schlüter, M.; Petasch, U. The Helmholtz Energy Alliance “Energy Efficient Multiphase Chemical Processes”. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2013, 85, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, F. Über stufenweise Reduktion des Nitrobenzols mit begrenztem Kathodenpotential. Z. Für Elektrochem. 1898, 4, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.B.; O‘Driscoll, K.F.; Rempel, G.L. Kinetics of nitrobenzene hydrogenation using a gel entrapped palladium catalyst. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1978, 56, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushch, S.D.; Izakovich, E.N.; Khidekel, M.L.; Strelets, V.V. Mechanism of Catalytic-Hydrogenation of Nitrobenzene in an Aprotic Medium in the Presence of Quinones. Bull. Acad. Sci. Ussr Div. Chem. Sci. 1981, 30, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniak, J.; Klein, M. Reduction of Nitrobenzene to Aniline. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1984, 23, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, L.; Kumbilieva, K.; Kirkov, N. Kinetic-Model of Nitrobenzene Hydrogenation to Aniline over Industrial Copper Catalyst Considering the Effects of Mass-Transfer and Deactivation. Appl. Catal. 1990, 59, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelder, E.A.; Jackson, S.D.; Lok, C.M. The hydrogenation of nitrobenzene to aniline: A new mechanism. Chem. Commun. 2005, 522–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turek, F.; Geike, R.; Lange, R. Liquid-phase hydrogenation of nitrobenzene in a slurry reactor. Chem. Eng. Process. 1986, 20, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höller, V.; Wegricht, D.; Yuranov, I.; Kiwi-Minsker, L.; Renken, A. Three-phase nitrobenzene hydrogenation over supported glass fiber catalysts: Reaction kinetics study. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2000, 23, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, E.; Amon, B.; Redlingshofer, H.; Dieterich, E.; Emig, G. Deactivation kinetics in the hydrogenation of nitrobenzene to aniline on the basis of a coke formation kinetics—Investigations in an isothermal catalytic wall reactor. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2001, 56, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frikha, N.; Schaer, E.; Houzelot, J.L. Methodology of multiphase reaction kinetics and hydrodynamics identification: Application to catalyzed nitrobenzene hydrogenation. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 124, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, J.; Shi, W.; Xia, S.; Ni, Z.; Xiao, X. Insights into the hydrogenation mechanism of nitrobenzene to aniline on Pd3/Pt(111): A density functional theory study. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 34319–34326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahata, A.; Rai, R.K.; Choudhuri, I.; Singh, S.K.; Pathak, B. Direct vs. indirect pathway for nitrobenzene reduction reaction on a Ni catalyst surface: A density functional study. PCCP 2014, 16, 26365–26374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatziantoniou, V.; Andersson, B.; Schöön, N.-H. Mass-Transfer and Selectivity in Liquid-Phase Hydrogenation of Nitrocompounds in a Monolithic Catalyst Reactor with Segmented Gas-Liquid Flow. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev. 1986, 25, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, R.M.; Broekhuis, R.R.; Nordquist, A.F.; Roy, B.P.; Carney, S.R. Applying monolith reactors for hydrogenations in the production of specialty chemicals—Process and economic considerations. Catal. Today 2005, 105, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irandoust, S.; Andersson, B. Simulation of Flow and Mass-Transfer in Taylor Flow through a Capillary. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1989, 13, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Baten, J.M.; Krishna, R. CFD simulations of mass transfer from Taylor bubbles rising in circular capillaries. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2004, 59, 2535–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, S. Gas-Liquid Mass Transfer in Taylor Flow through Circular Capillaries. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 2323–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, N.; Gavriilidis, A.; Angeli, P. Mass transfer during Taylor flow in microchannels with and without chemical reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 160, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.L.D.; Julcour, C.; Billet, A.-M.; Larachi, F. Modelling and simulations of a monolith reactor for three-phase hydrogenation reactions—Rules and recommendations for mass transfer analysis. Catal. Today 2016, 273, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Y.; Cai, W. Instantaneous Mass Transfer under Gas-Liquid Taylor Flow in Circular Capillaries. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2014, 37, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wörner, M. Numerical modeling of multiphase flows in microfluidics and micro process engineering: A review of methods and applications. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2012, 12, 841–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, T.; Cui, Z.F. CFD modelling of slug flow in vertical tubes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, T.; Cui, Z.F. CFD modelling of slug flow inside square capillaries. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghidersa, B.E.; Wörner, M.; Cacuci, D.G. Exploring the flow of immiscible fluids in a square vertical mini-channel by direct numerical simulation. Chem. Eng. J. 2004, 101, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onea, A.; Wörner, M.; Cacuci, D.G. A qualitative computational study of mass transfer in upward bubble train flow through square and rectangular mini-channels. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 1416–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talimi, V.; Muzychka, Y.S.; Kocabiyik, S. Numerical simulation of the pressure drop and heat transfer of two phase slug flows in microtubes using moving frame of reference technique. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 6463–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Guo, Y.; Dai, C.; Zi, L.; Chen, B. Simulation of hydrodynamic and mass transfer performances in monolith channel. Catal. Today 2016, 276, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckmann, C.; Kurt, S.K.; Ehrhard, P.; Kockmann, N. Stofftransport in einer Flüssig/Flüssig-Pfropfenströmung im Mikrokapillarreaktor. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2017, 89, 1642–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Fletcher, D.F.; Haynes, B.S. Taylor Flow in Microchannels: A Review of Experimental and Computational Work. J. Comput. Multiph. Flows 2010, 2, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talimi, V.; Muzychka, Y.S.; Kocabiyik, S. A review on numerical studies of slug flow hydrodynamics and heat transfer in microtubes and microchannels. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2012, 39, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabisch, W. Dreidimensionale Numerische Simulation der Dynamik von Aufsteigenden Einzelblasen und Blasenschwärmen mit Einer Volume-of-Fluid-Methode; Wissenschaftliche Berichte, FZKA 6478; Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Deutschmann, O.; Tischer, S.; Kleditzsch, S.; Janardhanan, V.M.; Correa, C.; Chatterjee, D.; Mladenov, N.; Minh, H.D.; Karadeniz, H.; Hettel, M.; et al. DETCHEM Software Package, 2.8, 2019, Karlsruhe. Available online: http://www.detchem.com (accessed on 1 December 2020).
- Woo, M.; Tischer, S.; Deutschmann, O.; Wörner, M. A step toward the numerical simulation of catalytic hydrogenation of nitrobenzene in Taylor flow at practical conditions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2021, 230, 116132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kececi, S.; Wörner, M.; Onea, A.; Soyhan, H.S. Recirculation time and liquid slug mass transfer in co-current upward and downward Taylor flow. Catal. Today 2009, 147S, S125–S131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, D.M.N.; Prat, L. Numerical Study of the Coupling between Reaction and Mass Transfer for Liquid-Liquid Slug Flow in Square Microchannels. AIchE J. 2011, 57, 1719–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassanvand, A.; Hashemabadi, S.H. Direct numerical simulation of mass transfer from Taylor bubble flow through a circular capillary. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 5959–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Nieves-Remacha, M.J.; Jensen, K.F. Simulations and analysis of multiphase transport and reaction in segmented flow microreactors. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 169, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztaskin, M.C.; Wörner, M.; Soyhan, H.S. Numerical investigation of the stability of bubble train flow in a square minichannel. Phys. Fluids 2009, 21, 042108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petera, J.; Weatherley, L.R. Modelling of mass transfer from falling droplets. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2001, 56, 4929–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Mao, Z.-S. Numerical simulation of interphase mass transfer with the level set approach. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 2643–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, M.; Wörner, M.; Tischer, S.; Deutschmann, O. Validation of a numerical method for interface-resolving simulation of multicomponent gas-liquid mass transfer and evaluation of multicomponent diffusion models. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 54, 697–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stotz, H.; Maier, L.; Deutschmann, O. Methane Oxidation over Palladium: On the Mechanism in Fuel-Rich Mixtures at High Temperatures. Top. Catal. 2017, 60, 83–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumesic, J.A.; Rudd, D.F.; Aparicio, L.M.; Rekoske, J.E.; Trevino, A.A. The Microkinetics of Heterogeneous Catalysis; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Burcat, A.; Ruscic, B. Third Millenium Ideal Gas and Condensed Phase Thermochemical Database for Combustion (with Update from Active Thermochemical Tables); ANL-05/20 TAE 960; Argonne National Lab. (ANL): Argonne, IL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, M. Numerical Simulation of Gas-Liquid Taylor Flow with Catalyzed Heterogeneous Reaction; Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT): Karlsruhe, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Halpern, D.; Gaver, D.P. Boundary-Element Analysis of the Time-Dependent Motion of a Semi-infinite Bubble in a Channel. J. Comput. Phys. 1994, 115, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, C.R.; Chang, P. Correlation of Diffusion Coefficients in Dilute Solutions. AIchE J. 1955, 1, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
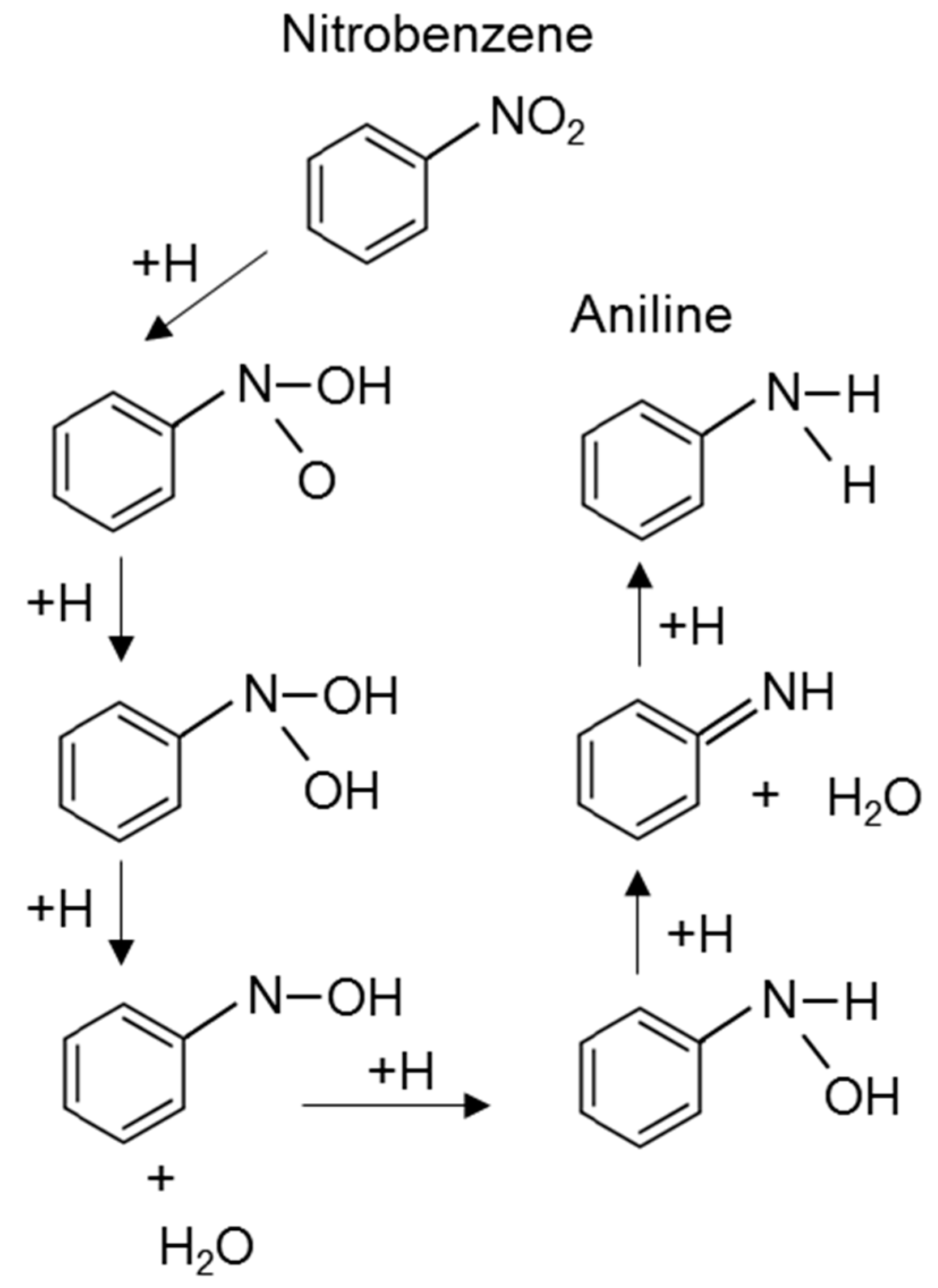


| No. | Reaction | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | → | ||
| R2 | → | 82.8 | |
| R3 | → | ||
| R4 | → | 88.8 | |
| R5 | → | ||
| R6 | → | 64.0 | |
| R7 | → | ||
| R8 | → | 41.8 | |
| R9 | → | 55.9 | |
| R10 | → | 20.2 | |
| R11 | → | 112.9–22 | |
| R12 | → | 135.1 | |
| R13 | → | 120.6–118 | |
| R14 | → | 250.9 | |
| R15 | → | 99.4–60 | |
| R16 | → | 159.2 | |
| R17 | → | 166.9–104 | |
| R18 | → | 272.1 | |
| R19 | → | 153.4–147 | |
| R20 | → | 200.7 |
| Test Conditions | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Reference length, | 50 | µm |
| Reference velocity, | 1 | |
| Density ratio (L/G) | 1 | - |
| Viscosity ratio (L/G) | 138.32 | - |
| Surface tension, | 0.0406 | |
| Unit cell pressure drop, | 250 | |
| Results | ||
| Bubble velocity, | 1.367 | |
| Capillary number, | 0.0425 | - |
| Reynolds number, | 127.6 | - |
| Liquid film thickness | 6.08 | µm |
| Bubble length | 166.4 | µm |
| Slug length | 133.6 | µm |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Woo, M.; Maier, L.; Tischer, S.; Deutschmann, O.; Wörner, M. A Qualitative Numerical Study on Catalytic Hydrogenation of Nitrobenzene in Gas-Liquid Taylor Flow with Detailed Reaction Mechanism. Fluids 2020, 5, 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids5040234
Woo M, Maier L, Tischer S, Deutschmann O, Wörner M. A Qualitative Numerical Study on Catalytic Hydrogenation of Nitrobenzene in Gas-Liquid Taylor Flow with Detailed Reaction Mechanism. Fluids. 2020; 5(4):234. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids5040234
Chicago/Turabian StyleWoo, Mino, Lubow Maier, Steffen Tischer, Olaf Deutschmann, and Martin Wörner. 2020. "A Qualitative Numerical Study on Catalytic Hydrogenation of Nitrobenzene in Gas-Liquid Taylor Flow with Detailed Reaction Mechanism" Fluids 5, no. 4: 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids5040234
APA StyleWoo, M., Maier, L., Tischer, S., Deutschmann, O., & Wörner, M. (2020). A Qualitative Numerical Study on Catalytic Hydrogenation of Nitrobenzene in Gas-Liquid Taylor Flow with Detailed Reaction Mechanism. Fluids, 5(4), 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids5040234