Abstract
Hybrid RANS-LES methods are supposed to provide major contributions to future turbulent flow simulations, in particular for reliable flow predictions under conditions where validation data are unavailable. However, existing hybrid RANS-LES methods suffer from essential problems. A solution to these problems is presented as a generalization of previously introduced continuous eddy simulation (CES) methods. These methods, obtained by relatively minor extensions of standard two-equation turbulence models, represent minimal error simulation methods. An essential observation presented here is that minimal error methods for incompressible flows can be extended to stratified and compressible flows, which opens the way to addressing relevant atmospheric science problems (mesoscale to microscale coupling) and aerospace problems (supersonic or hypersonic flow predictions). It is also reported that minimal error methods can provide valuable contributions to the design of consistent turbulence models under conditions of significant modeling uncertainties.
1. Introduction
The introduction of two-equation turbulence models in the frame of Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes (RANS) equations is seen to be a very relevant milestone of the development of simulation methods for turbulent flows [1,2]. The specific advantage of such methods is their much improved ability to provide proper scale information (the characteristic length scale of turbulent motions) for turbulent flow simulations. However, it is well known that such methods seriously suffer from their inability to reflect the physics of flows that cannot be properly modeled, as is the case for separated turbulent flows. Reliable simulations of such flows (as illustrated, for example, in Section 3) require the inclusion of flow resolution.
The first method used to overcome this problem is the introduction of flow-resolving simulation methods, as given by large eddy simulation (LES). The LES concept is actually simple. A much smaller characteristic length scale of turbulent motions is applied than that used in RANS. (Usually, the filter width is used as the length scale.) The consequence is the need to use much finer computational grids than those applied in RANS. Thus, LES suffers from its huge computational requirements, especially in regard to simulations of wall-bounded turbulent flows at a high Reynolds number . The practical consequence is that LES is inapplicable to many high flows that need to be considered. A concrete illustration of the dimension of this problem is given in Section 3.1.
The second method applied to overcome the fundamental shortcomings of RANS methods is the hybridization of RANS and LES (i.e., the development of hybrid RANS-LES) [3,4,5]. We have traditionally applied methods such as wall-modeled LES (WMLES) [6,7,8] and detached eddy simulation (DES) [4,9,10,11], as well as a variety of other methods, including scale-adaptive simulation (SAS) methods [4,12,13], lattice Boltzmann (LB) methods [14], Reynolds stress-constrained LES (RSC-LES) [15], unified RANS-LES [16,17,18,19,20,21,22], partially averaged Navier–Stokes (PANS) [23], partially integrated transport modeling (PITM) methods [24,25], and continuous eddy simulation (CES) methods [5,26,27,28,29,30,31,32]. The problem is that such hybrid RANS-LES methods suffer from fundamental problems. In particular, under conditions where validation data are unavailable, the problem is that such methods cannot reliably deal with simulations of flows that require flow resolution (see the explanations in Section 2). Thus, such methods face the same problem as RANS equations.
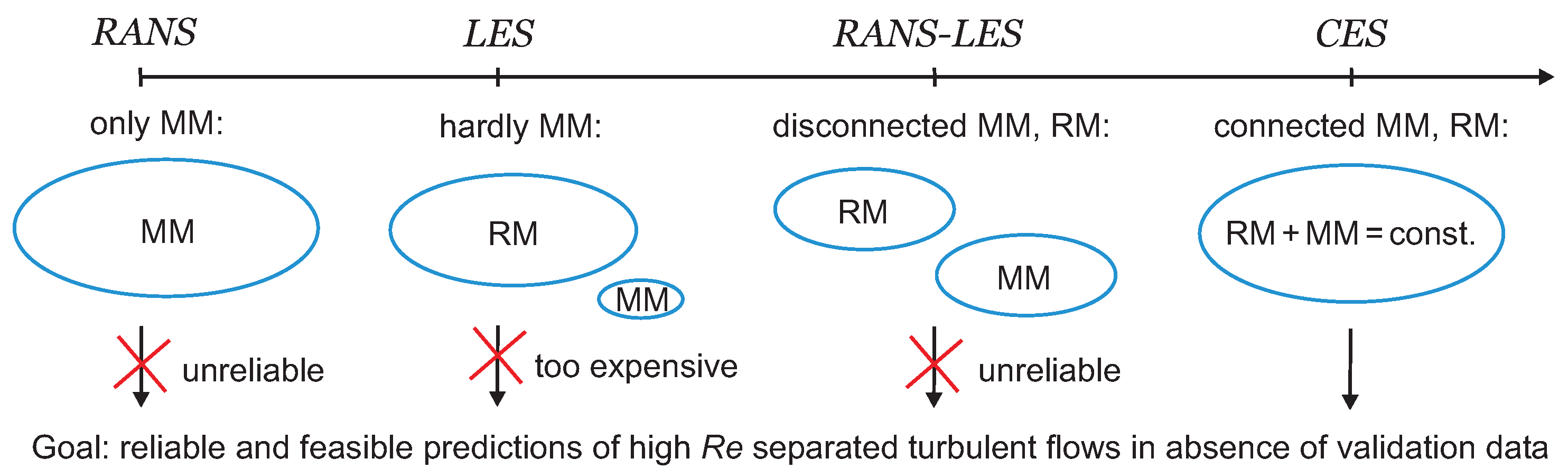
It has to be expected that this development will continue for a long time, as long as there is no clarification of what specifically causes the problems of existing RANS-LES methods, what the implied consequences are, and how it is possible to overcome these issues. The latter questions will be addressed here in Section 2, Section 3 and Section 4, respectively. Specific emphasis is placed on the explanation of the structure of novel minimal error hybrid simulation methods, which generalize CES methods (see the illustration in Figure 1). These methods may be seen as a relatively simple, mathematically exact modification of the originally introduced RANS two-equation turbulence models. A specific motivation is to significantly extend the corresponding methods developed thus far to the modeling of stratified and compressible flows. Section 5 describes applications of the novel methods presented thus far, and the conclusions are presented in Section 6.
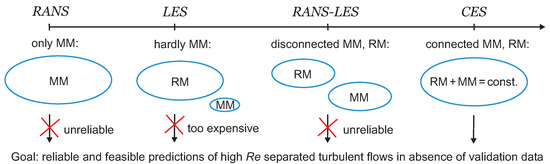
Figure 1.
Abilities of computational methods in regard to reliable and feasible predictions of high flows that require flow resolution. Here, hybrid RANS-LES refers to popular methods, MM (RM) refers to modeled (resolved) motion, and CES refers to continuous eddy simulation.
2. Basic Problems of Existing Hybrid RANS-LES Methods
The most relevant problem of hybrid RANS-LES is (particularly under conditions where validation data are unavailable) the lack of predictive power of flow simulations that require the inclusion of flow resolution. A physically correct simulation mechanism requires a swing between the amounts of resolved motion (fluctuations implied by the grid and ) and the modeled motion imposed by the model equations. The model’s contribution needs to decrease (increase) in response to a higher (lower) amount of resolved motion. However, in existing hybrid RANS-LES methods, the model does not receive (correct) information about the amount of resolved motion [32], which does not allow a (proper) model response. This implies the following: simulations for which validation data are hardly available (see the challenges described in Section 3) will involve a certain amount of resolved motion, which changes with the grid and . Then, if there is no guidance about an appropriate set-up of modeled motion, such simulations will produce random results in general. In particular, effects calculated on this basis cannot be considered to be reliable. By taking reference to Figure 1, an illustration of this problem is given in Figure 2.

Figure 2.
Problem illustration. MM (RM) refers to modeled (resolved) motion, and MM is MM implied by swing. (a) Desired: RANS-LES swing. (b) Reality: random model MM − MM, with unreliable predictions at high .
The second problem is closely related to . In many cases, we need reliable hybrid methods that are (1) applicable on coarse grids in almost RANS mode and (2) reliable hybrid methods that are applicable in almost resolving mode independent of the LES resolution requirements (which are hard to assess and control). The essential ingredients to properly deal with these requirements are (1) a stable dependence of the modeled length scale on the resolved length scale (the latter reflects fluctuations (i.e., this stable dependence of length scales ensures a stable involvement of fluctuations even under almost RANS conditions)) and (2) an appropriate representation of the characteristic LES length scale independent of the filter width . Existing hybrid RANS-LES methods do not involve these ingredients (i.e., they cannot reliably cover these two regimes).
The third problem of existing popular hybrid RANS-LES methods is the lack of guidance through exact theory, which has several consequences. Most hybrid RANS-LES methods were introduced on the basis of empirical reasoning, but some hybrid RANS-LES methods were introduced on the basis of sound theoretical concepts [5]. However, there is the question of which theoretical concept should be preferred. The lack of an answer to this question leads to a large variety of potential methods that can be used in applications. In addition, existing hybrid RANS-LES methods suffer from significant uncertainty in their predictions in the absence of validation data. For example, the WMLES, DES, and PANS results depend significantly on the model option settings [5]. Thus, it is usual practice to choose such settings to produce the best possible agreement with the available data. The search for the best model and best model set-up is demanding and time-consuming. Another problem is implied by the fact that hybrid RANS-LES methods include a RANS component, but such RANS equations can be significantly affected by modeling uncertainties, in particular for stratified and compressible flows.
3. Challenges
Concrete examples for the relevance of such RANS problems will be given next. In particular, Section 3.1 addresses the need to overcome the problem , whereas Section 3.2 and Section 3.3 illustrate the requirement to also overcome the problems and .
3.1. NASA’s CFD 2030 Vision
There are many computational challenges related to incompressible flow, such as NASA’s 2030 Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Vision Report challenge to accomplish LES of a powered aircraft configuration across the full flight envelope [33,34,35,36]. This case focuses on the ability of CFD to simulate the flow about a complete aircraft geometry at the critical corners of the flight envelope including low-speed approach and takeoff conditions, transonic buffet, and possibly undergoing dynamic maneuvers, where aerodynamic performance is highly dependent on the prediction of turbulent flow phenomena such as smooth body separation and shock–boundary layer interaction [34]. A specific overview of the essential further steps required to deal with the challenge was provided by Slotnick and Mavriplis [37].
A specific indication of this challenge arises from the computational cost analysis offered by Probst et al. [35] and the Federal Republic of Germany’s research centre for aeronautics and space (DLR), which considers the cost of resolving LES simulations of a full three-dimensional (3D) wing of an aircraft at flight . The conclusion of this conservative cost estimation was the following: Even with exclusive access to the largest existing cluster of Xeon-CPUs comparable to DLR’s “Tianhe-2A” with almost 5 million cores, such a simulation would take around 650 years when extrapolated linearly. The computational cost required for addressing this partial problem clearly demonstrates the relevance of properly functioning hybrid RANS-LES models. In particular, as pointed out by Slotnick et al., progress toward this goal can be measured through the demonstration of effective hybrid RANS-LES and WMLES simulations with increasing degrees of modeled versus resolved near-wall turbulence structures with increasing geometric complexity [34]. However, existing hybrid RANS-LES methods face significant problems in this regard (see Section 2).
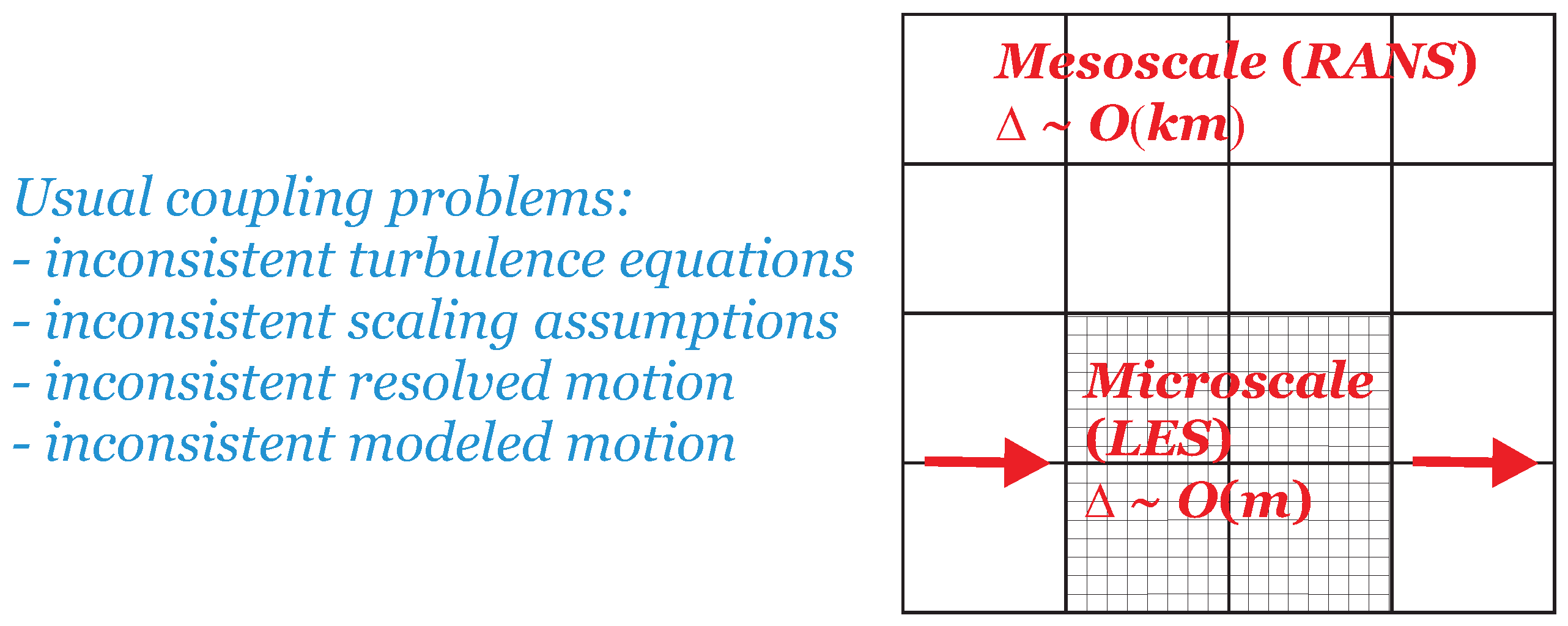
3.2. Atmospheric Mesoscale to Microscale Coupling
Another motivation for the development of exact hybrid RANS-LES models arises from the coupling of atmospheric mesoscale and microscale simulations (The term microscale simulation refers here to methods aiming at flow resolution, in contrast to flow modeling). The latter is an essential requirement to predict, for example, the performance of wind farms under the influence of large-scale weather processes. The usually related problems of such simulations are shown in Figure 3. A direct coupling of simulation methods as illustrated in Figure 3 is inappropriate, as the outer RANS simulation blocks the simulation of resolved motions in the inner domain, and (depending on the set-up) the abrupt decay of modeled motion in the transition region can provide inappropriate boundary conditions for the outer RANS simulation. Thus, it needs a transitional region between the two RANS and LES regions which applies relatively coarse grids. This implies a fundamental problem (referred to as the Terra Incognita problem by Wyngaard [38]): such simulations contradict basic RANS or LES principles, their value is at least questionable.
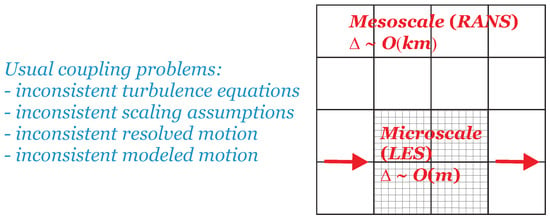
Figure 3.
Typical problems related to the coupling of mesoscale (RANS) and microscale (LES) methods, where refers to the characteristic grid size used in simulations.
There are obvious requirements for dealing with this problem. It needs hybrid RANS-LES equations that are able to cover both LES and RANS regimes (including the need that the length scale information used in the RANS is able to provide correct length scale information for LES independent of the LES filter width ). The most important requirement is the model’s ability to respond correctly to the amount of resolved motion by appropriate changes of the model’s contribution to the simulation. In other words, it needs minimal error hybrid RANS-LES models, which have this ability. Because of the coarse grids that usually need to be applied for atmospheric boundary layer (ABL) simulations, a specific aspect of the problem considered is the need for hybrid RANS-LES simulation methods that work stably in the almost RANS regime. As a matter of fact, it also needs a significant extension of previously developed methods: the inclusion of stratification effects, which is needed to simulate ABL processes. The latter is affected by modeling questions (see the discussion below Equation (22)). Thus, in addition to the need to deal with problem described Section 2, it also requires solutions to problems and in this case.
3.3. High Angle of Attack Supersonic and Hypersonic Flow Predictions
The challenges described in Section 3.1 are significantly enhanced if aircraft are considered which fly at very high (supersonic or hypersonic) speeds. Commercial transports rarely fly at an angle of attack larger than , but tactical aircraft and missiles can fly at much higher angles of attack [39]. Therefore, on top of the problems described in Section 3.1, additional challenges arise from the much bigger variety of flow separation induced by angle of attack variations and structural flow variations induced by compressibility [16]. Arguably, the biggest challenge of such flow simulations arises from the questionable basis given by model equations for compressible flows. There is, for example, an ongoing debate about the structure of the dissipation rate equation considered in conjunction with the modeled kinetic energy equation (see [40,41] and the discussion below Equation (26)). It is worth noting that such RANS model issues are transferred to LES models via the required k transport equation [42]. Correspondingly, existing hybrid RANS-LES methods that combine RANS and LES components suffer from the same problem.
First, the conclusion is the same as in regard to the problems described in Section 3.1: it needs hybrid RANS-LES models which properly function under significant variations of resolved motion. Second, another question concerns the theoretical basis of such simulations. The possibility to develop minimal error hybrid methods depends on the structure of the model equations considered. This leads to the question of whether the minimal error design approach can provide valuable guidelines for the establishment of compressible flow models. Given the lack of a theoretical basis to deal directly with this issue, it is difficult to see which other approaches can help to overcome this relevant problem. Third, the development of exact hybrid RANS-LES models is needed because of the following. Different from the need for such methods described in Section 3.2 (which requires well-functioning methods under almost RANS conditions), for highly compressible flows, we need methods that can be used as resolving methods independent of the LES resolution requirements. This ability is is the most reliable way to deal with several flow physics questions (e.g., about structural compressibility effects) that need clarification. Thus, in addition to the need to address the problem described in Section 2, we see here again the need for solutions to the problems and .
4. Minimal Error Methods
Mimimal error hybrid simulation methods will be presented in the following three subsections in regard to incompressible flows, stratified flows, and compressible flows. It is worth noting that the presentation of such methods for incompressible flows in Section 4.1 provides the technical basis for extensions to the stratified and compressible flows in Section 4.2 and Section 4.3, respectively.
4.1. Incompressible Flows
The design of minimal error methods will be described first for incompressible flows with respect to the widely used model (other turbulence models were considered elsewhere [32]). The suitability of this model is well known in the context of RANS equations. Evidence for the suitability of this model to also provide resolved motions on appropriate grids is given by corresponding PANS [23] and PITM [24,25] methods. The model considered is given by the incompressible continuity equation and the momentum equation
Here, denotes the filtered Lagrangian time derivative, and the sum convention is used throughout this paper. refers to the component of the spatially filtered velocity. We have here the filtered pressure , the constant mass density , the modeled energy k, the constant kinematic viscosity , and the rate-of-strain tensor . The modeled viscosity is given by . Here, is the modeled dissipation rate of the modeled energy k, is the dissipation time scale, and has a standard value . For k and , we consider the transport equations
The diffusion terms reads , , and is the production of k, where is the characteristic shear rate. is a constant with a standard value , and . In RANS, , where [2] implies .
One possibility to hybridize Equation (2) is to consider a variable (instead of a constant ) combined with an appropriate calculation of :
The diffusion terms are adjusted accordingly such that we have the expressions and . The setting of will be addressed below. The determination of will be described by applying variational analysis. We consider variations of model parameters () and related variations of model variables (such as k and ). The question is which model coefficient satisfies the variation equations implied by the turbulence model considered. The analysis follows the approach presented in [26]. The technical framework applied to derive these results was provided by an analysis of Friess et al. [11]. The significant difference with the latter findings is that Friess et al. focused on a different question: for given PANS/PITM-type relations between model coefficients and resolution indicators, they determined the equivalence criteria for hybrid methods based on other turbulence models. A relevant assumption made throughout this paper is that the energy partition ( and ; see below) does not change in space and time. This assumption is not a restriction but a desired stability requirement, as it ensures that physically equivalent flow regions are equally resolved without significant oscillations of or [26,27,28].
In an exact analysis option , we set in and and introduce a hybridization error as a residual of the equation:
where the k equation is used to replace in the previous expression. The subscript 1 refers to option . The normalized error reads as follows:
Justification for the normalization applied can be obtained by taking the variation of and combining the terms that involve . In the first order of variations (denoted by ), we have
Correspondingly, we find that the variation of the last two terms in Equation (5) disappears because of
Thus, the variation of Equation (5) provides
An extremal error is found by setting the first variation equal to zero:
This equation can be integrated from the RANS state to a state with a certain level of resolved motion . We obtain it in this way:
where refers to the modeled-to-total time scale ratio, which is calculated as (see the explanations in regard to option below). For all models considered in this paper, we find a zero second variation, and we need to ask whether provides a minimum or maximum error. The results were equal to the variational results obtained by considering ; that is, the analysis presented implies minimal error models.
A different analysis option is as follows. The analysis option is exact, but the disadvantage is the need to involve in the equations solved in the simulations. The latter is avoided in analysis option , where the substantial derivatives and are neglected in regard to the derivation of model coefficients. This approach appears to be well justified for most applications. It was found to work very well in previous applications to periodic hill flows [27]. Correspondingly, we consider (the subscript 2 refers to the analysis option ) in and in conjunction with the hybridization error:
where the k equation is used again to replace in the previous expression. The normalized error reads as follows:
where the modeled length scale is introduced in the first term on the right-hand side (RHS). Because of , we find in the option in the first order of variations the relations
which imply that the variation of the last two terms in Equation (12) disappears because of
Thus, the variation of Equation (12) provides
An extremal error is found by setting the first variation equal to zero:
This equation can be integrated from the RANS state to a state with a certain level of resolved motion: . We obtain in this way
where refers to the modeled-to-total length scale ratio. A relevant technical detail is the calculation of ( is calculated correspondingly). The turbulence length scale resolution ratio involves the modeled (L) and total contributions () [26]. The modeled contribution is calculated by , where the brackets refer to the averaging over time. The total length scale is calculated correspondingly by . Corresponding to , is the sum of the modeled and resolved contributions . Here, the resolved contributions are calculated by , .
The consideration of Equation (3) is one possibility to hybridize the equations considered. Another possibility is to consider
where the dissipation in the k equation is modified by introducing the unknown . By following the analysis of Equation (3), we consider the hybridization error in analysis option :
where the k equation is used to replace in the previous expression. The comparison with Equation (4) shows the equivalence of both approaches, provided that . The comparison of the corresponding in analysis option leads to the same conclusion.
4.2. Stratified Flows
In regard to stratified flows, we begin with describing the typical structure of an ABL microscale model [43]. We have the incompressible continuity equation , and the momentum and potential temperature equations read as follows:
Here, is the potential temperature. In addition, is the gravity vector, is the Coriolis vector, and is the Levi-Civita symbol. In the equation, we have the molecular and turbulent heat diffusivities and , where and are the Prandtl number and turbulent Prandtl number, respectively. The effect of radiation can be taken into account via the source term . Equations (20) and (21) are combined with the model [43]:
The diffusion terms read and , and is the production of k. In regard to Equation (2), has a standard value , , and in RANS equations. The effect of buoyancy is reflected by the buoyancy production , where is the gradient Richardson number [16,44,45,46]. The buoyancy coefficient is characterized by a large uncertainty: its values range from to [47,48], including [49]. For simplicity, we assume in the following, in line with the recommendation of Mellor and Yamada [49].
Corresponding mesoscale models actually represent equivalent or simplified versions of the microscale model given by Equations (20)–(22). A hierarchy of model versions can be considered [50,51,52,53,54]. Several options will be considered in the following with the understanding that the model version considered is applied to both the microscale and mesoscale.
The first option is referred to as CES-MIME. CES stands for continuous eddy simulation, and MIME stands for microscale-mesoscale model, meaning that the model can be continuously applied through microscales and mesoscales. This model is equivalent to Equations (20)–(22). Although the use of this model on the mesoscale is not the common choice, there exist several applications of corresponding models [55,56,57,58,59]. One possibility for hybridizing this model is to consider a variable (instead of a constant ) combined with an appropriate calculation of . Hence, in conjunction with , we consider
We introduce the hybridization error according to the analysis option in conjunction with replacing in and by :
where the abbreviation is used. It turns out that this equation is equal to Equation (4), which means that the implications presented above are recovered. The same conclusion is obtained in regard to the analysis according to option , where is not replaced by in the diffusion terms. Another possibility for hybridizing the CES-MIME model version is to hybridize the k equation via introducing . This means we consider
The same analysis as that presented in Section 4.1 leads to the conclusion that this approach represents an equivalent approach as long as the model coefficients are properly related by .
The second option is the CES-MIME-AE model. This model is a reduced version of CES-MIME, where in Equations (20)–(22) is provided by an algebraic expression (AE refers to an algebraic equation). This option is, for example, applied in conjunction with Mellor and Yamada’s level 2.5 closure model [49] (see also the last paragraph of Section 4.2), which is a standard model applied for mesoscale simulations [60]. A usually applied expression reads . Here, is a stability function, and l is a length scale that is algebraically provided [43]. A corresponding analysis of the CES-MIME-AE model version is presented in Appendix A.
A third option is the CES-MIME-HH set-up, which is a reduced version of either the CES-MIME or CES-MIME-AE model where horizontal transport processes are neglected [49,61,62] (HH refers to horizontal homogeneity of the ABL). With respect to this model option, the analysis in Section 4.2 shows that this option is independent of the hybridization, and the hybridization functions and are unaffected. Given that the neglect of horizontal transport is often considered to be appropriate in a mesoscale model, the consequence of this simplification will be a discontinuous transition between mesoscale and microscale models, (Usually, the neglect of horizontal transport processes will be at least questionable for microscale simulations.) but this assumption will not hamper the combined model’s ability to maintain a meaningful balance of resolved and modeled motions.
Another often-applied approximation is to replace the turbulent viscosity with algebraic expressions depending on the vertical coordinate and stability. In this case, there is no need for a k or an equation [43]. However, this modeling assumes that the turbulent viscosity is always fully modeled in terms of RANS-type variables (total variables). This concept does not provide a meaningful basis for hybridization. Thus, this option is not considered here.
In regard to the developments presented here, it is worth noting that the applicability of these methods is not limited to eddy viscosity models, applied for simplicity. The same approach can be applied, for example, in the frame of Reynolds stress models, as given by Mellor and Yamada’s closure model [49,60] (see the explanations given in Appendix B). A Reynolds stress model is a k equation extended by Reynolds stress anisotropy and combined with a scale model (usually for ), which provides scale information for the Reynolds stress model via or . If an transport equation is involved, then the hybridization can be driven through the equation as described above. If an algebraic expression is applied, then the hybridization can be driven by the k equation implied by the Reynolds stress model as described above. This case is usually considered in Mellor and Yamada’s closure model because the original Mellor and Yamada master length scale formulation provides inappropriate results [60].
4.3. Compressible Flows
Compressible flow modeling will be addressed by considering the spatially filtered mass density , and tilde variables will be used to reflect the mass density-weighted variables by following the notation used above. The continuity and momentum equations considered are then given by
Here, , and the modeled viscosity is given by . Many different methods have been applied to provide k and for compressible flows [16,40,41,63,64,65]. We follow the usual approach of involving explicit compressibility corrections (the dilatational dissipation and pressure dilation ) only in the k equation [63,64,65]:
The production is given here by . The usual models for and , which are not applied because there is no need to do so, are and [63], where , , and are the model parameters and the turbulence Mach number is defined by , where a refers to the speed of sound.
For simplicity, we only consider the option to hybridize the k equation via introducing in the following. This means we consider
where , the production to dissipation ratio due to dilatational compressibility effects, is introduced as an abbreviation. These equations are equivalent to Equation (18), where is replaced with . The same analysis presented above implies that , where refers to the total value of . In the two options and considered, we have and (see Equations (10) and (17)). Hence, the incompressible flow models presented above can be easily extended to the compressible flow.
5. Applications: Periodic Hill Flow Simulations
In regard to the problems , , and of the hybrid RANS-LES model described in Section 2, we observe the following. The analysis presented in Section 4 provides the desired guideline with respect to problem . For several turbulence model structures and hybridization types, the use of the minimal error technique provides exactly one optimal computational method. A question that is unaddressed in this way is about the computational performance differences of different model structures and hybridization options. The analysis presented in Section 4 also provides a solution to the problem . With respect to the almost RANS regime, the relationship , (for an example, see Equation (17)), implies a stable dependence of the modeled length scale calculated via the model on the resolved length scale involved in the definition of . In regard to the almost LES regime, the modeled length scale calculated via the model can serve as an LES length scale independent of the LES filter width (i.e., the usual LES resolution requirement that needs to be sufficiently small does not apply). However, an answer to the question of whether the methods presented in Section 4 can also overcome the problem , which requires a well functional “RANS-LES swing”, requires computational evidence.
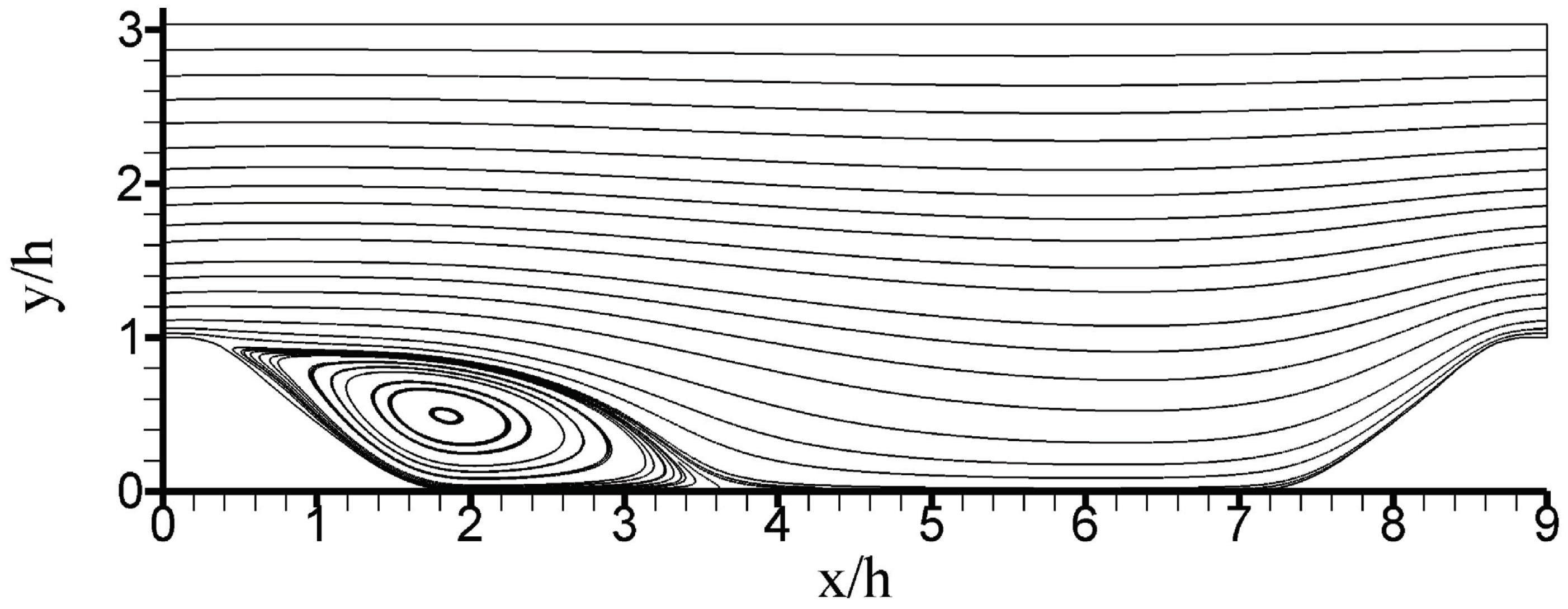
The latter question was addressed by the simulations of periodic hill flows reported in [27]. Figure 4 illustrates the flow configuration considered, a channel flow (flowing from the left to the right) with periodic restrictions (hills). This considered flow configuration is often used for the evaluation of turbulence models. It creates a variety of relevant flow features such as separation, recirculation, and natural reattachment. The hill crest is located at . The height h and bulk velocity are used as scaling variables, they define . The simulations were performed by using the OpenFOAM CFD Toolbox [66]. A CES model formulation corresponding to option was applied, including the comparison of different hybridization options. A range of and grids was considered. ranged from to . The data for model validation were only available for the case [67]. Several grids were used, with the finest (coarsest) grid applied having () grid points. The grids were referred to as and , respectively. An almost complete flow resolution was accomplished at using the finest grid, and an almost RANS simulation was accomplished at using the coarsest grid ().
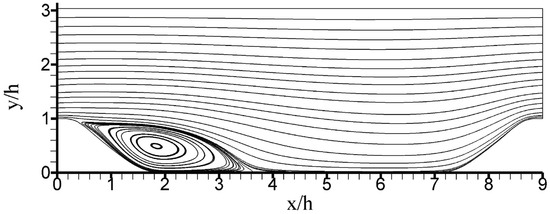
Figure 4.
Periodic hill flow velocity streamlines obtained by CES at on ( refers to grid points). Reprinted with permission from [27]. Copyright 2020 AIP Publishing.
The observations obtained by these simulations are the following:
- Problem : The most relevant fact is the conclusion that the “RANS-LES swing” was fully functional. There was a stable redistribution between the resolved and modeled motions, depending on the grid and variations. In particular, a spatially relatively uniform mode variation reflected by the resolution indicator was found.
- Problem : In regard to the almost RANS regime, a stable generation mechanism of turbulent velocity fluctuations was observed. In particular, fluctuations were not extinguished even for very high values and very coarse grids. In regard to the almost LES regime, it was found that the characteristic length scale provided by CES, which was independent of the LES filter width , properly worked. The LES simulations performed on this basis (with grid points) showed better performance than almost resolving LES using 20 million grid points.
- Problem : Another relevant observation is that different model hybridization options worked equally well; there were hardly differences regarding the simulation results obtained. This fact confirms the applicability of the CES approach to at least several turbulence model structures, as long as the “RANS-LES swing” is functional.
6. Summary
The current stagnation of the development of computational simulation methods for turbulent flows was addressed here by clarification of what specifically causes the problems of existing RANS-LES methods, what the implied consequences are, and how it is possible to overcome these issues (see Section 2, Section 3 and Section 4). The facts presented here can be summarized as follows:
- 1.
- The minimal error approach presented here (which generalizes CES methods) minimizes the hybridization error among many other hybrid RANS-LES methods. It provides a theoretical solution to the problems , , and . Applications demonstrated the excellent performance of such simulation methods (see Section 5). It is essential to note that these methods represent a relatively minor extension of standard two-equation turbulence models.
- 2.
- An essential observation presented here is that minimal error methods for incompressible flows [32] can be extended to stratified and compressible flows. This opens the way to addressing relevant atmospheric science problems (mesoscale to microscale coupling) and aerospace problems (supersonic and hypersonic flow predictions) (see the discussions in Section 3). It was argued that such simulations need, in particular, the ability to perform reliable predictions under almost RANS and almost LES conditions.
- 3.
- Hybrid RANS-LES models are based on RANS equations, and such RANS equations face relevant modeling questions, particularly for stratified and compressible flows. Minimal error methods are in line with standard modeling options, and they exclude many other options. Thus, minimal error methods can provide valuable contributions to the design of consistent turbulence models. In regard to compressible flows, models are excluded that include a variety of compressibility effects in the equation [40,41]. In regard to stratified flows, a welcome byproduct of considering the hybridization of the closure model of Mellor and Yamada [49] (see Appendix B) is the correct specification of the length scales involved, which is seen as a major issue of such simulations.
- 4.
- From a more general view point, the relevance of the minimal error methods presented is the following. We need reliable methods to simulate high flows. LES models and experiments are restricted by resolution requirements, and popular hybrid RANS-LES models are known to be unreliable. In this situation, minimal error methods can provide an error-free simulation contribution in response to the flow resolution (see the illustration in Figure 2). The latter is the essential requirement for providing reliable predictions under conditions where validation data are unavailable.
Funding
This work received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
I would like to acknowledge support from the National Science Foundation (AGS, Grant No. 2137351, with N. Anderson as Technical Officer) and support from the Hanse-Wissenschaftskolleg (Delmenhorst, Germany, with M. Kastner as Technical Officer). This work was supported by the Wyoming NASA Space Grant Consortium (NASA Grant No. 80NSSC20M0113) and the University of Wyoming School of Computing (Wyoming Innovation Partnership grant).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
Let us consider the CES-MIME-AE model, which makes use of an algebraic expression for instead of using the transport equation considered in the CES-MIME version. Because of the lack of an transport equation, the basis for this approach is given by the k equation
Here, appears as an unknown function considered for setting up the hybridization, and the abbreviation was used. Then, the latter equation can be written:
In an exact analysis option , we have , and is involved. The hybridization error divided by k reads as follows:
Here, is unaffected by variations. This is a requirement, the assumption of an algebraic model is equivalent to assuming that is given by its total value. Equation (7) applies, leading to the fact that the variation in the last two terms on the RHS disappears. The variation of Equation (A3) then implies
By setting the first variation equal to zero, we have
We can integrate from the RANS state to a state with a certain level of resolution to obtain
where refers to the total value of p (including contributions such as and ).
In the analysis option , we have , and is not involved. The hybridization error divided by reads as follows:
According to Equation (14), the variation of the last term on the RHS disappears, and we obtain the variational equation
We set the first variation equal to zero and obtain
Then, we integrate from the RANS state to a state with a certain level of resolution to obtain
Appendix B
We consider a usual, incompressible flow Lagrangian stochastic particle model for the position , velocity , and scalar (potential temperature) [16]. We have combined with
The terms and ensure consistency with the mean velocity and potential temperature equations, respectively [16]. With respect to the velocity field, we applied the usual Rotta assumption. In regard to the scalar field, we excluded a stochastic source term and specified the scalar mixing frequency with . This mixing frequency is not assumed to be proportional to ( refers to the scalar dissipation time scale and is related to the scalar dissipation rate by , where ). In addition, refers to the derivative of a Wiener process [16], and , , , and are the model parameters. The body forces involved are represented by . Here, is the coefficient of thermal expansion (the inverse reference temperature).
The particle model Equation (A11) implies the following exact Reynolds stress equations [16,28]:
We have here , where , , and refer to the corresponding triple correlations, and we introduce the abbreviations
The consistency of these equations with the definitions of the dissipation rates and in the transport equations for and requires two coefficient relations:
Equations (A12)–(A14) agree with the level 4 closure model of Mellor and Yamada [49], with the exception of Mellor and Yamada’s neglect of higher-order anisotropy effects, leading to an isotropic version of the term on the RHS of Equation (A12) (which then reads ) and the neglect of the last term in Equation (A13). A comparison of the coefficients applied here with coefficients , , , and applied by Mellor and Yamada reveals, in conjunction with , the relations
We find, in addition to the relationship , the following condition for , , and :
Here, and the mechanical-to-scalar time scale ratio are involved. (A constant was applied for stratified flow [68,69]) Equations (A12)–(A14) receive scale information via or L; that is, or L needs to be provided in a physically meaningful way under changing stratification.
References
- Pope, S.B. Turbulent Flows; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, D.C. Turbulence Modeling for CFD, 2nd ed.; DCW Industries: La Canada, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Fröhlich, J.; Terzi, D.V. Hybrid LES/RANS methods for the simulation of turbulent flows. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2008, 44, 349–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouat, B. The state of the art of hybrid RANS/LES modeling for the simulation of turbulent flows. Flow Turbul. Combust. 2017, 99, 279–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinz, S. A review of hybrid RANS-LES methods for turbulent flows: Concepts and applications. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2020, 114, 100597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piomelli, U. Large eddy simulations in 2030 and beyond. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2014, 372, 20130320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, J.; Kawai, S.; Bodart, J.; Bermejo-Moreno, I. Large eddy simulation with modeled wall-stress: Recent progress and future directions. Mech. Eng. Rev. 2016, 3, 15-00418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.T.; Park, G.I. Wall-modeled large-eddy simulation for complex turbulent flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2018, 50, 535–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalart, P.R.; Jou, W.H.; Strelets, M.; Allmaras, S.R. Comments on the feasibility of LES for wings, and on a hybrid RANS/LES approach. In Advances in DNS/LES; Liu, C., Liu, Z., Eds.; Greyden Press: Dayton, OH, USA, 1997; pp. 137–147. [Google Scholar]
- Spalart, P.R. Detached-eddy simulation. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2009, 41, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friess, C.; Manceau, R.; Gatski, T.B. Toward an equivalence criterion for hybrid RANS/LES methods. Comput. Fluids 2015, 122, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, F.R.; Egorov, Y. The scale-adaptive simulation method for unsteady turbulent flow prediction: Part 1: Theory and model description. Flow Turbul. Combust. 2010, 78, 113–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakirlić, S.; Maduta, R. Extending the bounds of "steady" RANS closures: Toward an instability-sensitive Reynolds stress model. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2015, 51, 175–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhong, C.; Pan, D.; Zhuo, C. A gas-kinetic scheme coupled with SST model for turbulent flows. Comput. Math. Appl. 2019, 78, 1227–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xia, Z.; Pei, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Shi, Y. Reynolds-stress-constrained large-eddy simulation of wall-bounded turbulent flows. J. Fluid Mech. 2012, 703, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, S. Statistical Mechanics of Turbulent Flows; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Heinz, S. Comment on “A dynamic nonlinear subgrid-scale stress model” [Phys. Fluid 17, 035109 (2005)]. Phys. Fluids 2005, 17, 099101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, S. Unified turbulence models for LES and RANS, FDF and PDF simulations. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 2007, 21, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalan, H.; Heinz, S.; Stöllinger, M. A unified RANS-LES model: Computational development, accuracy and cost. J. Comput. Phys. 2013, 249, 249–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtarpoor, R.; Heinz, S.; Stoellinger, M. Dynamic unified RANS-LES simulations of high Reynolds number separated flows. Phys. Fluids 2016, 28, 095101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtarpoor, R.; Heinz, S. Dynamic large eddy simulation: Stability via realizability. Phys. Fluids 2017, 29, 105104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöllinger, M.; Heinz, S.; Zemtsop, C.; Gopalan, H.; Mokhtarpoor, R. Stochastic-based RANS-LES simulations of swirling turbulent jet flows. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2017, 18, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girimaji, S. Partially-averaged Navier-Stokes method for turbulence: A Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes to direct numerical simulation bridging method. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 2006, 73, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouat, B.; Schiestel, R. A new partially integrated transport model for subgrid-scale stresses and dissipation rate for turbulent developing flows. Phys. Fluids 2005, 17, 065106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouat, B.; Schiestel, R. Analytical insights into the partially integrated transport modeling method for hybrid Reynolds averaged Navier-Stokes equations-large eddy simulations of turbulent flows. Phys. Fluids 2012, 24, 085106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, S. The large eddy simulation capability of Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes equations: Analytical results. Phys. Fluids 2019, 31, 021702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, S.; Mokhtarpoor, R.; Stoellinger, M.K. Theory-Based Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes Equations with Large Eddy Simulation Capability for Separated Turbulent Flow Simulations. Phys. Fluids 2020, 32, 065102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, S. The Continuous Eddy Simulation Capability of Velocity and Scalar Probability Density Function Equations for Turbulent Flows. Phys. Fluids 2021, 33, 025107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, S. Theory-Based Mesoscale to Microscale Coupling for Wind Energy Applications. Appl. Math. Model. 2021, 98, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, S.; Peinke, J.; Stoevesandt, B. Cutting-Edge Turbulence Simulation Methods for Wind Energy and Aerospace Problems. Fluids 2021, 6, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagbade, A.; Heinz, S. Application of Mode-Controlled Hybrid RANS-LES to the NASA Wall-Mounted Hump Flow. In Proceedings of the 2022 AIAA SciTech Forum, San Diego, CA, USA, 3–7 January 2022; AIAA Paper 22-0180. pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Heinz, S. Minimal error partially resolving simulation methods for turbulent flows: A dynamic machine learning approach. Phys. Fluids 2022, 34, 051705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotnick, J.; Khodadoust, A.; Alonso, J.; Darmofal, D.; Gropp, W.; Lurie, E.; Mavriplis, D. CFD Vision 2030 Study: A Path to Revolutionary Computational Aerosciences. NASA/CR-2014-218178. 2014. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/search.jsp?R=20140003093 (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- Slotnick, J.P.; Khodadoust, A.; Alonso, J.J.; Darmofal, D.L.; Gropp, W.D.; Lurie, E.A.; Mavriplis, D.J.; Venkatakrishnan, V. Enabling the environmentally clean air transportation of the future: A vision of computational fluid dynamics in 2030. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2014, 372, 20130317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probst, A.; Knopp, T.; Grabe, C.; Jägersküpper, J. HPC requirements of high-fidelity flow simulations for aerodynamic applications. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Parallel Processing, Warsaw, Poland, 24–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 375–387. [Google Scholar]
- Goc, K.A.; Lehmkuhl, O.; Park, G.I.; Bose, S.T.; Moin, P. Large eddy simulation of aircraft at affordable cost: A milestone in computational fluid dynamics. Flow 2021, 1, E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotnick, J.P.; Mavriplis, D. A Grand Challenge for the Advancement of Numerical Prediction of High Lift Aerodynamics. In Proceedings of the AIAA SciTech Forum, Virtual, 11–15 & 19–21 January 2021; AIAA Paper 22-0955. pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wyngaard, J.C. Toward numerical modeling in the “Terra Incognita”. J. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 61, 1816–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, R.M.; Forsythe, J.R.; Morton, S.A.; Squires, K.D. Computational challenges in high angle of attack flow prediction. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2003, 39, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassaing, P. The modeling of variable density turbulent flows. A review of first-order closure schemes. Flow Turb. Combust. 2001, 66, 293–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassaing, P.; Antonia, R.A.; Anselmet, F.; Joly, L.; Sarkar, S. Variable Density Fluid Turbulence; Springer Science & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 69. [Google Scholar]
- Park, N.; Mahesh, K. Numerical and modeling issues in LES of compressible turbulence on unstructured grids. In Proceedings of the 45th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV, USA, 8–11 January 2007; AIAA Paper 07-0722. pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Temel, O.; Porchetta, S.; Bricteux, L.; van Beeck, J. RANS closures for non-neutral microscale CFD simulations sustained with inflow conditions acquired from mesoscale simulations. Appl. Math. Model. 2018, 53, 635–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, S. Nonlinear Lagrangian equations for turbulent motion and buoyancy in inhomogeneous flows. Phys. Fluids 1997, 9, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Heinz, S. Connections between Lagrangian stochastic models and the closure theory of turbulence for stratified flows. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 1998, 19, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, S.; van Dop, H. Buoyant plume rise described by a Lagrangian turbulence model. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 2031–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumert, H.; Peters, H. Second-moment closures and length scales for weakly stratified turbulent shear flows. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2000, 105, 6453–6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogachev, A. A note on two-equation closure modelling of canopy flow. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2009, 130, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellor, G.L.; Yamada, T. Development of a turbulence closure model for geophysical fluid problems. Rev. Geophys. 1982, 20, 851–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Esparza, D.; Kosović, B.; Mirocha, J.; van Beeck, J. Bridging the transition from mesoscale to microscale turbulence in numerical weather prediction models. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2014, 153, 409–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz Rodrigo, J.; Chavez Arroyo, R.A.; Moriarty, P.; Churchfield, M.; Kosović, B.; Réthoré, P.E.; Hansen, K.S.; Hahmann, A.; Mirocha, J.D.; Rife, D. Mesoscale to microscale wind farm flow modeling and evaluation. Wires Energy Environ. 2017, 6, e214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veers, P.; Dykes, K.; Lantz, E.; Barth, S.; Bottasso, C.L.; Carlson, O.; Clifton, A.; Green, J.; Green, P.; Holttinen, H.; et al. Grand challenges in the science of wind energy. Science 2019, 366, eaau2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meneveau, C. Big wind power: Seven questions for turbulence research. J. Turbul. 2019, 20, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, S.E.; Berg, L.; Churchfield, M.; Kosović, B.; Mirocha, J.; Shaw, W. Mesoscale to Microscale Coupling for Wind Energy Applications: Addressing the Challenges. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1452, 012076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detering, H.W.; Etling, D. Application of the E-ε turbulence model to the atmospheric boundary layer. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1985, 33, 113–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duynkerke, P.; Driedonks, A. A model for the turbulent structure of the stratocumulus–topped atmospheric boundary layer. J. Atmos. Sci. 1987, 44, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duynkerke, P.G. Application of the E–ε turbulence closure model to the neutral and stable atmospheric boundary layer. J. Atmos. Sci. 1988, 45, 865–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Xue, M. Evaluation of an E–ε and three other boundary layer parameterization schemes in the WRF model over the Southeast Pacific and the Southern Great Plains. Mon. Weather Rev. 2020, 148, 1121–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.; Ng, E.Y.K.; Skote, M. CFD simulation of dense gas dispersion in neutral atmospheric boundary layer with OpenFOAM. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2020, 132, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliano, T.W.; Kosović, B.; Jiménez, P.A.; Eghdami, M.; Haupt, S.E.; Martilli, A. “Gray Zone” simulations using a three-dimensional planetary boundary layer parameterization in the Weather Research and Forecasting Model. Mon. Weather Rev. 2022, 150, 1585–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.Y.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, M.; Niino, H. Development of an improved turbulence closure model for the atmospheric boundary layer. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 2009, 87, 895–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S. The pressure–dilatation correlation in compressible flows. Phys. Fluids A 1992, 4, 2674–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzen, Y.; Hoffmann, K. Investigation of supersonic jet exhaust flow by one-and two-equation turbulence models. In Proceedings of the 36th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24–28 July 1998; AIAA Paper 98-0322. pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe, J.R.; Hoffmann, K.A.; Cummings, R.M.; Squires, K.D. Detached-eddy simulation with compressibility corrections applied to a supersonic axisymmetric base flow. J. Fluids Eng. 2002, 124, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Openfoam Documentation; Technical Report. 2009. Available online: https://openfoam.org/release/1-6/ (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Rapp, C.; Manhart, M. Flow over periodic hills—An experimental study. Exp. Fluids 2011, 51, 247–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warhaft, Z. Passive scalars in turbulent flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2000, 32, 203–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Durbin, P.A. A Lagrangian stochastic model for dispersion in stratified turbulence. Phys. Fluids 2005, 17, 025109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).