Abstract
Background: Transposable elements (TEs) are major components of eukaryotic genomes. The extensive body of evidence suggests that although they were once considered “genomic parasites”, transposons and their transcripts perform specific functions, such as regulation of early embryo development. Understanding the role of TEs in such parasites as trematodes is becoming critically important. Fasciola hepatica, a parasite affecting humans and livestock, undergoes a complex life cycle in diverse environments and hosts, and knowledge about its life cycle regulation is scarce so far. Methods: We summarized the data regarding the repetitive elements in F. hepatica and conducted bulk RNA-seq analysis across its life cycle stages. TE expression profiles were analyzed, focusing on differential expression and potential homology with previously described long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs). Results: Differential expression analysis revealed stage-specific TE transcription patterns, notably peaking during egg and metacercariae stages. Some TEs showed homology with known lncRNAs and contained putative transcription factor binding sites. Interestingly, TE transcription levels were highest in eggs and metacercariae compared to adults, suggesting regulatory roles in trematode life cycle transitions. Conclusions: These findings suggest that TEs may play roles in regulating trematode life cycle transitions. Moreover, TE homology with lncRNAs underscores their significance in gene regulation.
1. Introduction
Trematodes, a highly successful group of parasitic flatworms, infect both humans and domestic animals. According to the World Health Organization, millions of people are infected with trematode parasites, with nearly half of the global population at risk of infection [1] (https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/foodborne-trematode-infections, last accessed 15 April 2024). Trematode infestations can lead to various diseases, including urinary bladder cancer (caused by Schistosoma mansoni and S. haematobium infections [2,3,4]), cholangiocarcinoma (associated with Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrini infections [5,6]), and hepatitis (associated with Fasciola spp. infections [7]). Better understanding of the trematode life cycle would allow to effectively disrupt trematode development strategy, thus limiting infestations in definitive hosts.
Trematode life cycles encompass multiple generations occurring in diverse hosts and environments, regulated by intricate mechanisms. However, studies on trematode life cycle regulation remain scarce. Despite the comprehensive characterization of gene expression patterns in individual stages [8,9,10,11,12], the genomes of Schistosoma mansoni, S. japonicum, and Fasciola hepatica have been shown to encode long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs)—transcripts exceeding 200 nucleotides in length with no discernible protein-coding potential. Recent research has revealed differential expression of lncRNAs in F. hepatica and Schistosoma spp. [13,14,15], but the exact regulatory roles of these lncRNAs remain undetermined.
LncRNAs can originate from transposable elements or TEs [16,17], which are mobile genetic elements capable of relocating within the genome. TEs come in two main types: retrotransposons and DNA transposons [18,19,20,21]. Retrotransposons propagate throughout the genome using a “copy-paste” mechanism, facilitated by reverse transcription, whereas DNA transposons lack reverse transcription and move via a “cut-and-paste” mechanism. Retroelements, in turn, are divided into retrotransposons that have Long Terminal Repeats (LTRs) and those without LTRs (non-LTR retrotransposons). Non-LTR retrotransposons include LINEs (Long Interspersed Nuclear Elements) and SINEs (Short Interspersed Nuclear Elements), while LTR retrotransposons also include endogenous retroviruses. Due to imperfect transposition mechanisms and accumulated mutations, transposons can degenerate to shortened, mostly inactive sequences [18,19,20,21]. Transposons also vary greatly in size, from thousands of base pairs (retroviruses, Helitrons) to a few hundred base pairs (MITEs, Alu). Although rare [22], TE jumping events can nevertheless impact genome regulation in various ways, such as gene structure disruption, transcription modulation through the TEs’ own regulatory sequences, or by attracting small non-coding RNAs and other regulatory molecules, which facilitates ectopic recombination and affects genome size [23,24,25,26].
F. hepatica (Trematoda, Fasciolidae) is a cosmopolitan parasitic flatworm that causes fasciolosis in ruminants and less commonly in humans. The life cycle of F. hepatica is realized as follows: adult flukes lay eggs in the bile ducts, which are eventually excreted into the intestines and released into the environment. Here, ciliated embryos known as miracidia hatch from the eggs. The miracidia actively seek out and penetrate mollusks, typically snails of the Lymnaeidae family, serving as intermediate hosts for further development. Once inside the snail, the parasite undergoes asexual reproduction, progressing through rediae and cercariae stages, leading to clonal expansion. Mature cercariae exit the mollusk and rapidly encyst on plant substrates, forming metacercariae, which can remain infective for months. Infection occurs through ingestion of contaminated vegetation, meat, or water. Upon ingestion, the parasites emerge from their cysts in the intestine as newly excysted or newly emerged juveniles (NEJs), perforate the intestine, and migrate to the liver capsule and parenchyma via the peritoneal cavity [27,28].
F. hepatica has one of the largest genomes among trematodes. Its genome was sequenced several years ago [27,29], and TEs are estimated to comprise 40% [27] to 50% [29]. Recently, both short and long non-coding RNAs of this fluke have been described [15,30,31], yet the expression of mobile elements remains unexplored.
This research aims to investigate TE expression and identify critical points in the F. hepatica life cycle where transcription of mobile elements is likely most significant. In addition, our findings will provide insights into the influence of TEs on transcriptional regulation and the evolution of the trematode genome.
2. Results
2.1. Repeat Content in the F. hepatica Genome
We analyzed three of the five available F. hepatica genome assemblies in the NCBI database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/, last accessed 15 April 2024), including the latest assembly generated from PacBio long reads. During the search, the RepeatModeler2, a tool for repetitive element recognition, assigns a number to each of the repeats found in every round of the search and classifies them, for instance, as rnd-1_family-34#LINE/Penelope. Repeats that RepeatModeler2 was unable to assign to any known family are grouped together, and in the text, they will be designated as Unknown elements.
Each analyzed assembly revealed that repeats constitute 63–66% of the genome, with approximately one-third remaining unidentified (Supplementary File S1, Table S5).
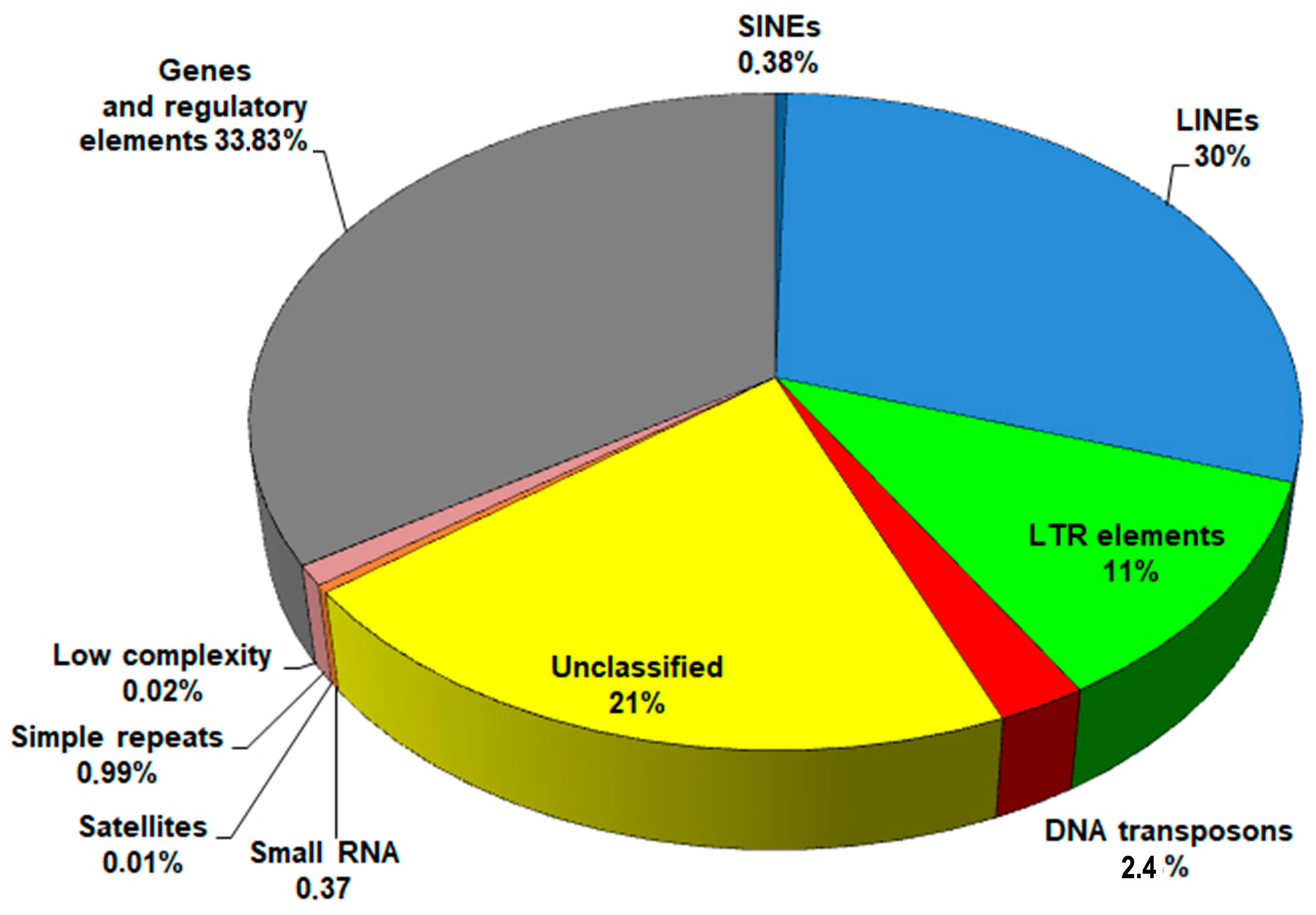
Average proportions of genomic sequences are shown in Figure 1. Despite slight variations in repeat content among the genomes, attributed to differences in sequencing technologies and assembly methods, LINEs consistently showed the most abundant presence, accounting for up to 29–30% of the genome.
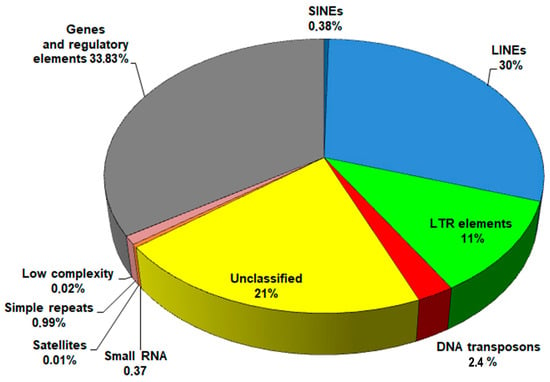
Figure 1.
The pie chart showing the mean composition of the F. hepatica genome.
2.2. Transcription of Repetitive Elements and Candidate TEs with Stage-Specific Expression
Repeat masking of the F. hepatica transcriptome assembly revealed the utmost abundance of LINEs, comprising 12.04% of assembled transcripts, with Penelope elements included. SINEs occupy 0.76%, DNA transposons account for 0.98%, and unclassified elements make up 6.76%. Thus, 20.54% of the assembled transcripts contain TE sequences. The investigation of solely protein-coding transcripts available at Wormbase (https://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/databases/wormbase/parasite/releases/WBPS19/species/fasciola_hepatica/PRJEB58756/fasciola_hepatica.PRJEB58756.WBPS19.CDS_transcripts.fa.gz, last accessed 15 June 2024) showed that TEs were present in 6.51% of these transcripts, with overwhelming prevalence of LINEs and Unknown elements, presumably due to intronic TEs.
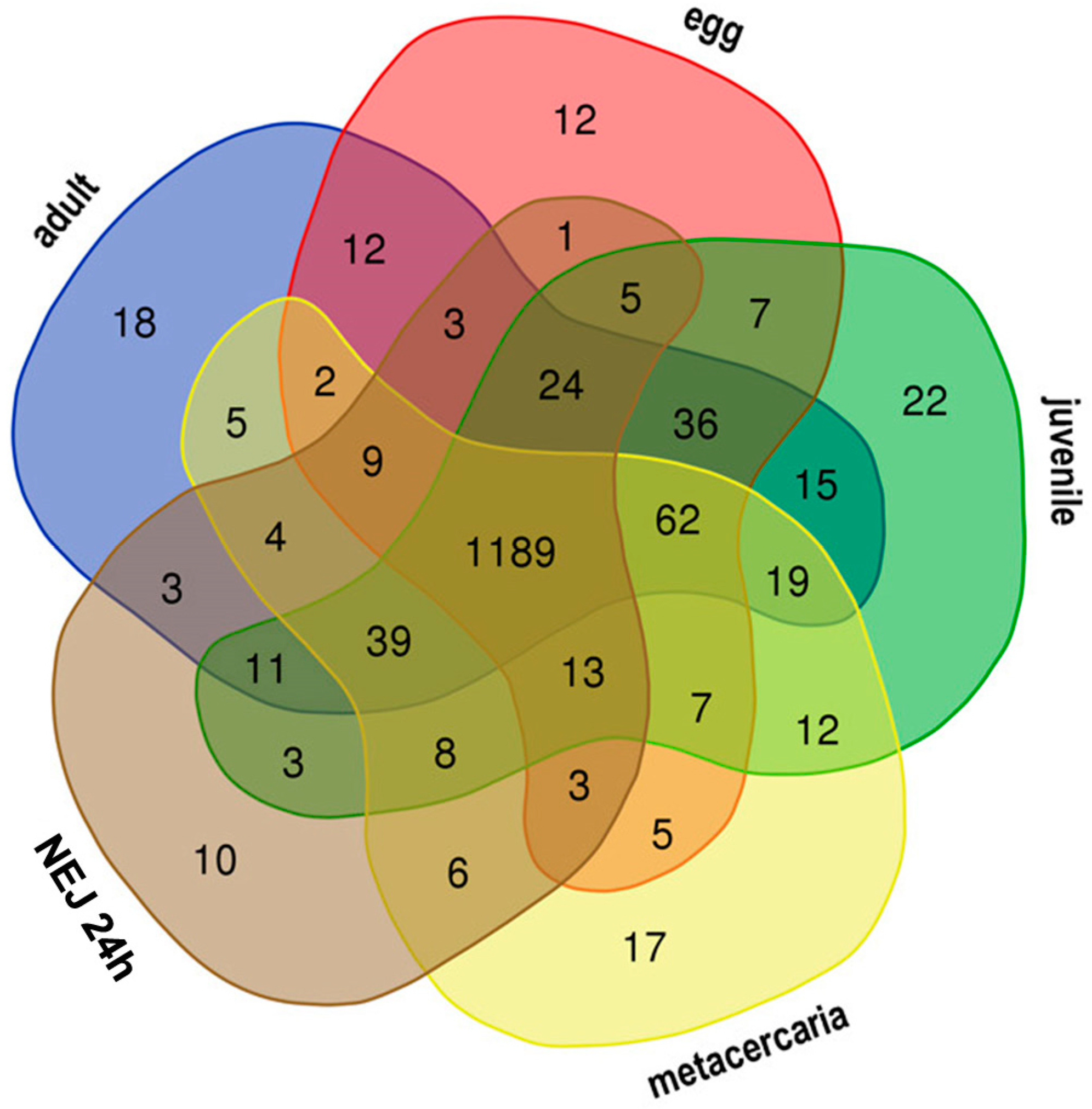
A primary qualitative analysis was performed to investigate the composition of expressed TEs at different stages of the F. hepatica life. Kallisto was used to identify TPM (transcripts per million) values for TEs, followed by the comparative analysis of TEs with expression levels over 1 TPM. Figure 2 shows the Venn diagram of transposon expression throughout five stages. Based on the comparative analysis results, Table 1 and Table 2 provide a detailed characterization of stage-specific TE expression profiles. Supplementary Materials (Table S1) include additional information on shared TEs at particular life cycle stages.
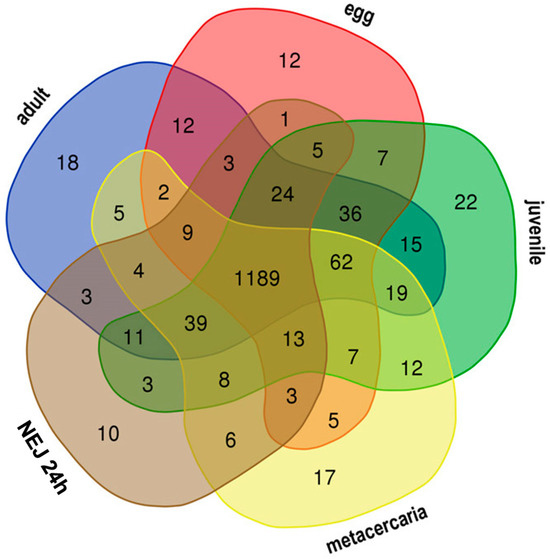
Figure 2.
Venn diagram showing candidate TEs with stage-specific expression in F. hepatica life cycle. The figures at the intersection of the diagram correspond to the number of commonly transcribed TEs, while the figures outside the intersections show the numbers of stage-specific TEs.

Table 1.
List of specific TEs expressed throughout 5 stages of the F. hepatica life cycle.

Table 2.
List of TEs selectively expressed in 7 stages of the F. hepatica life cycle.
The 21-day juvenile stage exhibits the highest number of specific TE transcripts across various comparison combinations, yielding 22 (Figure 2, Table 1 and Table S1) and 19 repeats (Table 2 and Table S1). When compared to the adult stage, metacercariae, eggs, and young juveniles, the majority of specific TEs for the 21-day juvenile stage are represented by Unknown elements, with only five transposons identified as retroelements.
When compared to larvae of other instars (see Table S6 in the Supplementary File S1 and Table S1), the 21-day juvenile is characterized by a greater number of specific TEs and expresses DNA transposons of the CMC-EnSpm and Pogo families. Among the DNA transposons, only the 2355#DNA/TcMar-Tigger is selectively transcribed in the metacercariae, while the remaining stages mainly express Unknown elements and retrotransposons from the CR1, Gypsy, and Pao families. Newly emerged (or excysted) juveniles (NEJs) of 1, 3, and 24 h age exhibit the lowest number of specifically transcribed transposable elements (TEs).
2.3. Differential Expression Analysis of Transposable Elements
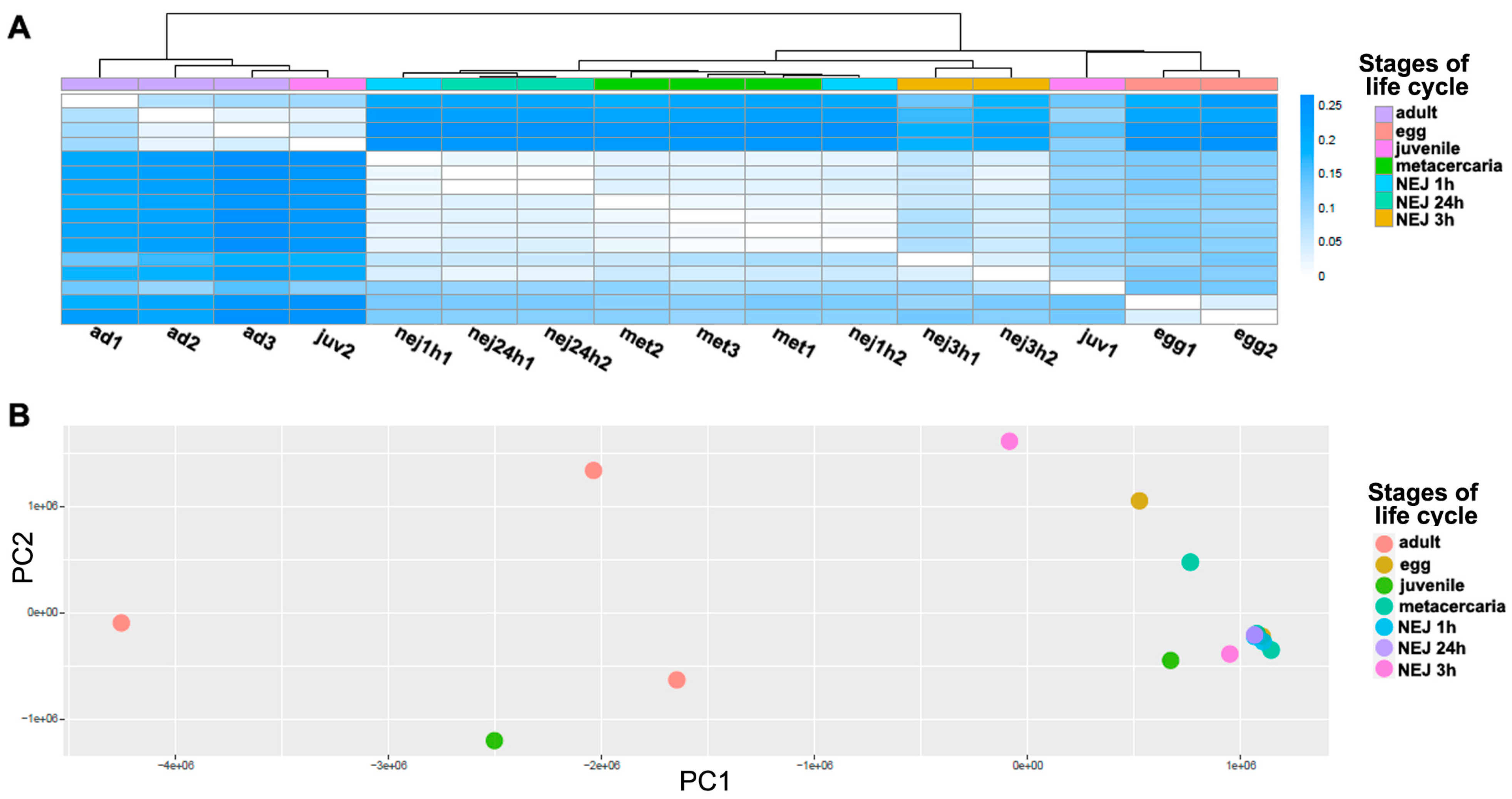
A differential expression analysis was carried out to identify the common features in the TE transcriptional profile of F. hepatica stages of the life cycle. The heatmap (Figure 3A) and principal component analysis (PCA, Figure 3B) were used to analyze similarities in the overall TE expression. The PCA revealed clustering of sample replicates and relative variance between samples in principal components 1 and 2 (PC1 and PC2, Figure 3B). Both PCA and Jensen–Shannon distances indicate that there is no clear clustering between stages based on the total transposon transcription. To identify differentially expressed TEs, the following two approaches were implemented: (1) the multiple comparison across all stages using a likelihood ratio test (LRT), and (2) pairwise comparisons of adults with the other stages using the Wald test. As expected, the analysis failed to identify TEs that were exclusively expressed at one stage as differentially expressed (see Table 1 and Table 2).
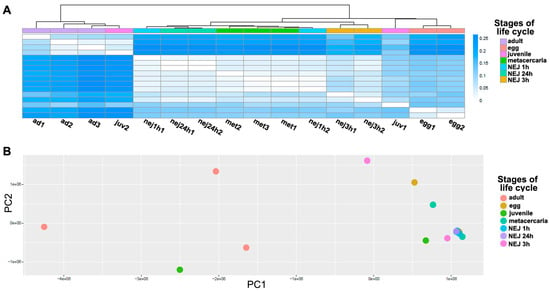
Figure 3.
The analysis of TE expression profiles between transcriptomes throughout F. hepatica life cycle stages. (A) The heatmap shows Jensen–Shannon divergence based on TE expression profiles for each sample; the darker the color, the greater the divergence. (B) The principal component analysis (PCA). Based on the TE expression profiles, the dot plot shows the distribution of samples between principal components 1 (X-axis) and 2 (Y-axis). Ad—adult; egg—egg; juv—21-day juvenile; met—metacercaria; NEJ1 h, 3 h, 24 h—newly emerged juveniles after 1, 3, and 24 h of excystment.
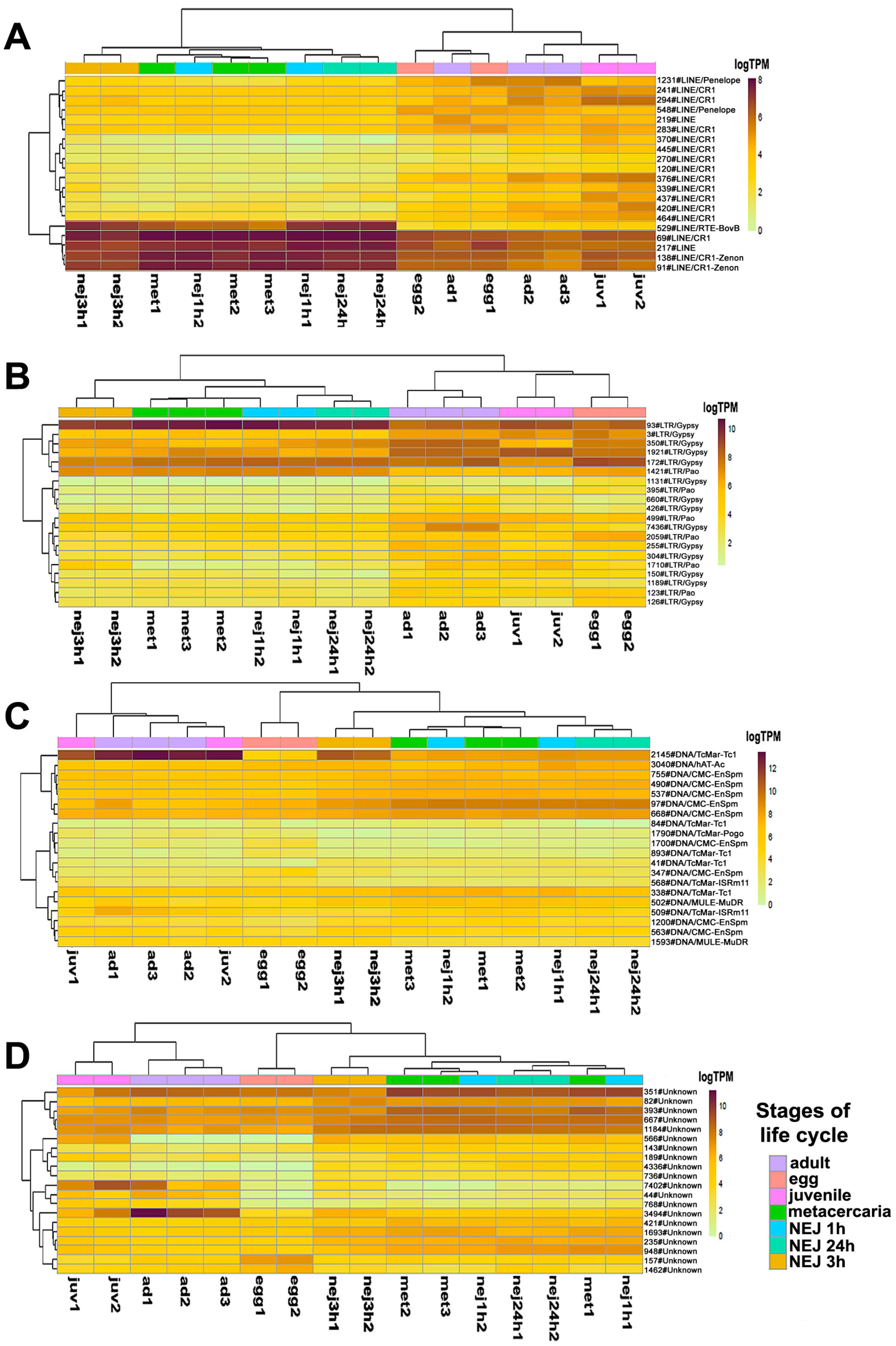
The likelihood ratio test (LRT) allowing multiple comparisons across all samples revealed 676 differentially expressed repeats (Table S2, tab sleuth_significant), comprising 320 Unknown elements, 181 LINEs, 2 SINEs, 128 LTR retroelements, 40 DNA transposons, 2 satellites and simple repeats, and 3 tRNA pseudogenes. Figure 4 shows the top 20 differentially expressed transposable elements (TEs), sorted in ascending order of p- and q-values of the LRT.
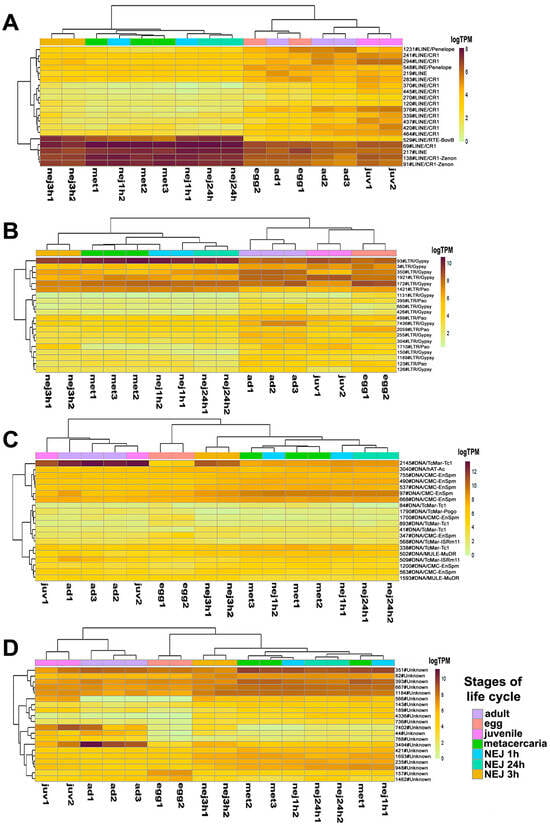
Figure 4.
The heatmap of the top 20 differentially expressed transposable elements sorted by p-values: (A)—LINE, (B)—LTR retroelements, (C)—DNA transposons, (D)—Unknown TE. Colored squares on the top indicate stages of the life cycle. Ad—adult, egg—egg, juv—21-day juvenile, met—metacercaria, NEJ1h, 3h, 24h—newly emerged juveniles after 1, 3, and 24 h after excystment.
Expression profile analysis of separate TE groups, particularly LTR and Unknown, revealed stage-specific clustering of samples. Several LINEs, including 529#LINE/RTE-BovB, 69#LINE/CR1, 217#LINE, 138#LINE/CR1-Zenon, and 91#LINE/CR1-Zenon, as well as the LTR element 93#LTR/Gypsy, exhibited high expression levels in metacercariae and NEJs (Figure 4). Many transposons showed significant changes in expression levels throughout the metacercaria stage, which coincided with the process of cercariae transformation.
BLAST with a 70% identity threshold was utilized to compare the differentially expressed TEs with the lncRNAs of F. hepatica published by McVeigh et al., 2023 [15]. As a result, 2784 lncRNAs matched 564 elements from the F. hepatica repeat database, i.e., one transposon is associated with several lncRNAs. Among these TEs, 370 were Unknown, 115 were LINEs, 3 were SINEs,
44 were LTRs, and 32 were DNA-transposons (see Table S2, tab lnc_rna_blast). Our analysis revealed 333 with differential expression among these 564 repeats.
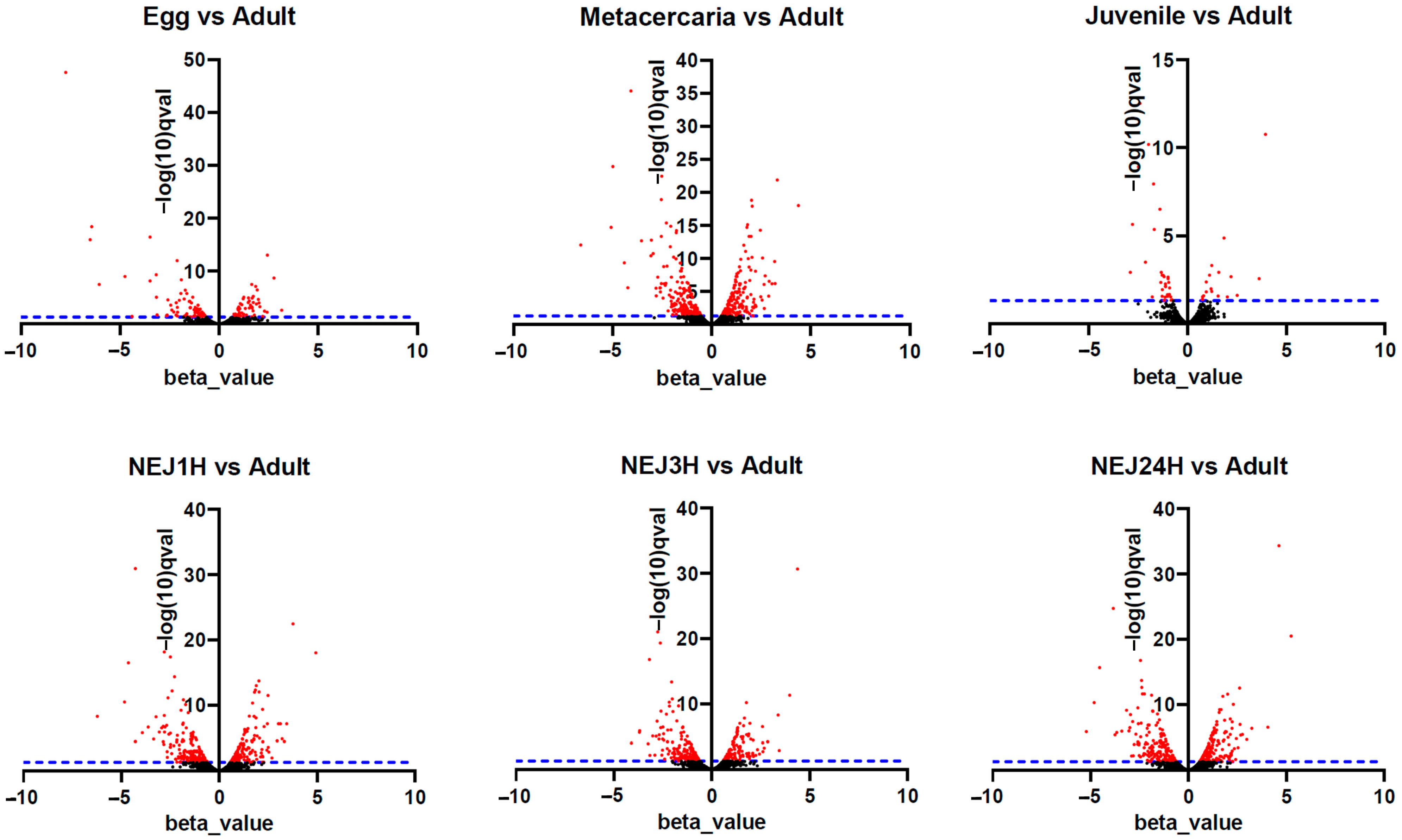
To identify up- or downregulated TEs, we used the Wald test to compare each stage with the marita (adult). Figure 5 represents changes in expression between stages of the life cycle, where each point on the graph indicates a different TE. Such a visualization allows us to observe statistically significant changes in TE expression between life cycle stages.
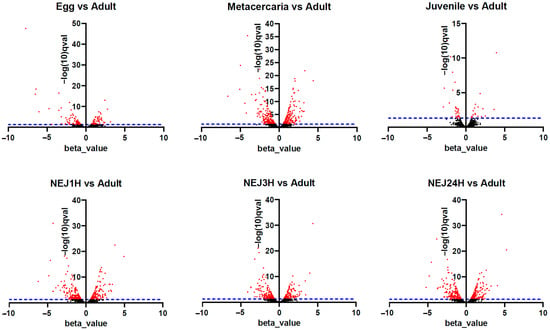
Figure 5.
Volcano plots for TE differential expression—adult stage vs. the other stages of the life cycle. The X-axis is a beta value, an analog of fold change, and Y-axis is −log(10)q-val, where qval—q-value, a false discovery rate-adjusted p-value in Wald test. The blue dotted line corresponds to q-value < 0.05. Each point in the chart represents a different TE. Black dots indicate false positives, while red dots indicate significant changes in expression. The positive beta value indicates upregulation, and negative is downregulation.
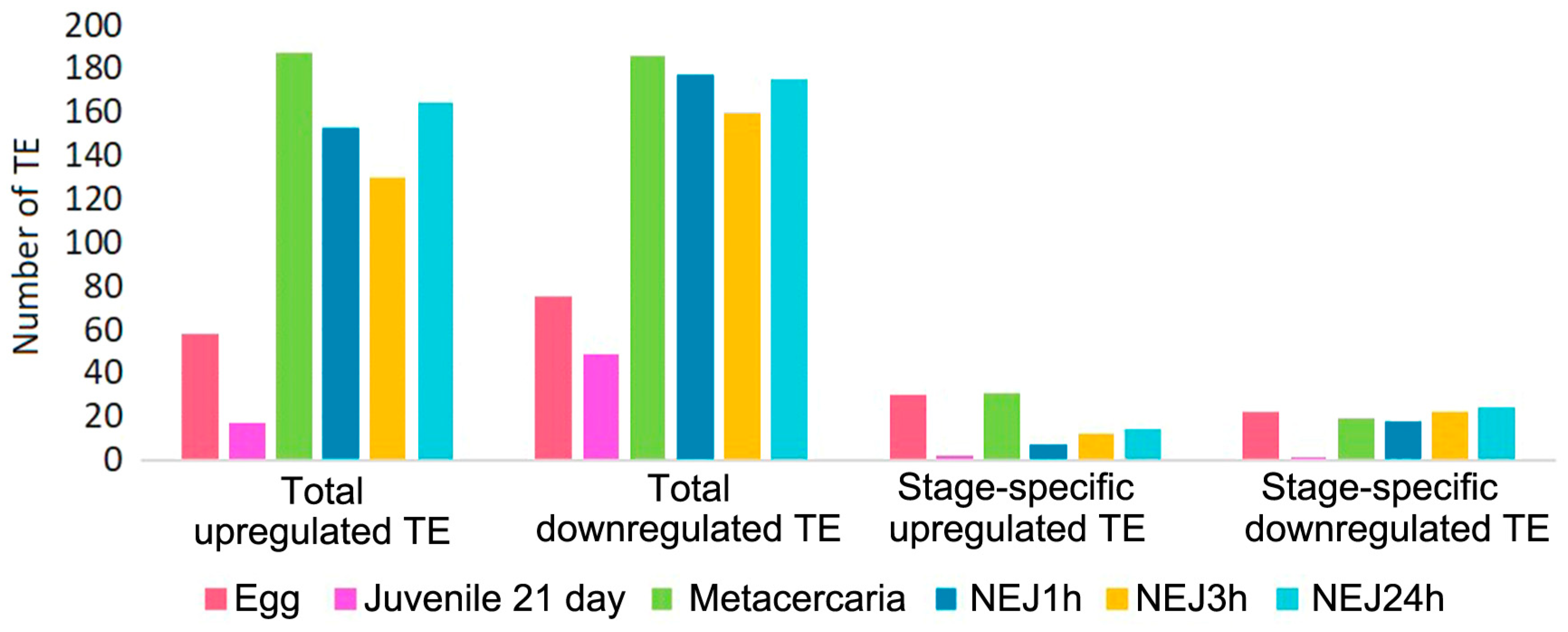
Upon initial inspection, metacercariae and NEJs appear to display the greatest number of repeats with significantly differential expression (Figure 5 and Figure 6, Table S3). However, the objective was to identify potential stage-specific repeats with differential expression, i.e., the expression which is highly divergent from the adult and restricted to one particular stage. To this end, sets of differentially expressed TE families (according to the Wald test) were intersected. Venn diagrams were utilized to identify transposons expressed exclusively at one particular stage. The number of TEs is summarized in Figure 6, and the full list of transposons with the stage-specific expression is provided in Table S3 (stage_specific_wald_test tab). Additionally, we tagged TEs with a high identity to lncRNAs, as discovered earlier [15] (see Table S3, stage_specific_wald_test tab, blue cells). As the newly excysted juvenile develops and matures, there are fewer differences in TE expression from the adult stage.
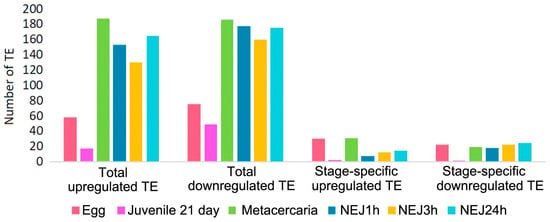
Figure 6.
Number of upregulated and downregulated TEs at each stage in comparison to the F. hepatica adults. NEJ1h, 3h, 24h—newly emerged juveniles 1, 3 and 24 h after excystment.
Stage-specific transcription of DNA transposons (Tc1-Mariner, Cmc-EnSpm, Helitron, Pogo) was detected in the egg, metacercariae, and NEJ3h (Table S3). Every analyzed stage was found to express a few specific families of LINE, LTR, and Unknown TE. Owing to the unknown function of TEs in trematodes, defining precise criteria for expression change is challenging; even a small amount of transcript may possess a significant importance for the cell.
However, let us consider a b value (analogous to fold change value) for upregulated stage-specific TEs greater than 1.7, considering that in general, their b values rarely exceed 2 (Table S3). In the egg, ten such elements were identified: 4345#LTR/Gypsy, 420#LINE/Penelope, 1822#LINE/Penelope, 893#DNA/TcMar-Tc1, 956#LINE/L2, and Unknown elements 197#, 610#, 497#, 1252#, and 963#. Metacercariae exhibited five such repeats, respectively (142#DNA/TcMar-Tc1 and Unknown elements 84#, 192#, 408#, 208#), NEJ24h had four Unknown elements (1466#, 3410#, 4521#), while NEJ1h had one (2217#Unknown) and NEJ3h had one (369#DNA/TcMar-Tc1). These TE transcripts could probably be indirectly associated with a possible significant regulatory impact of TEs on the biological processes occurring during specific periods of the parasite life cycle. Thus, the egg and metacercaria stages displayed the highest rates of stage-specific TE expression, along with the highest number of upregulated TEs, corresponding to significant changes to the parasite organism during these stages. In addition, both stages showed the highest number of lncRNA-relative TEs. The egg is characterized by the embryonic development of the miracidium, while the metacercaria undergoes transformation into a young excysted juvenile, which will further migrate from the intestine to the liver, its final localization in the host organism.
It was observed that one of the unclassified TEs, 4336#Unknown (relative to lncRNA), exhibited significantly higher expression levels in metacercariae and NEJ compared to the adult stage (b values > 4). However, in 21-day-old juveniles, the expression level of this transcript did not differ from the adult, though it was downregulated in the egg. Similarly, 529#LINE/RTE-BovB (relative to lncRNA) was upregulated in metacercariae and subsequent stages but not in the egg and 21-day juveniles. Some other transcripts displayed a similar pattern (see Table S3). On the other hand, when compared to the adult stage, some TEs, such as 2145#DNA/TcMar-Tc1 (relative to lncRNA), were significantly downregulated across all investigated stages, except for the 21-day juvenile, and therefore could be potential adult-stage markers.
To determine whether the stage-specific upregulated transcripts of TEs (Table S3) can presumably act as cis-regulatory elements, we had to identify the binding sites of transcription factors (TFs). We analyzed the nucleotide sequences of selected TEs using the MEME program [32], implemented in Galaxy (https://usegalaxy.eu/, last accessed 10 June 24). The results are presented in Figure 7 and Figure 8.

Figure 7.
Transcription factor binding site predictions in stage-specific upregulated TE transcripts in egg, metacercaria, and 21-day juvenile. The figure is the layout showing the localization of the identified TF binding sites (colored rectangles) on the forward and reverse TE chain (labelled to the left of the schemes) with the combined match p-value. The block height corresponds to the site significance, i.e., taller blocks are more significant. The consensus sequences of the TF binding sites are indicated in boxes under the schemes. Blue asterisks indicate the similar lncRNA TEs.
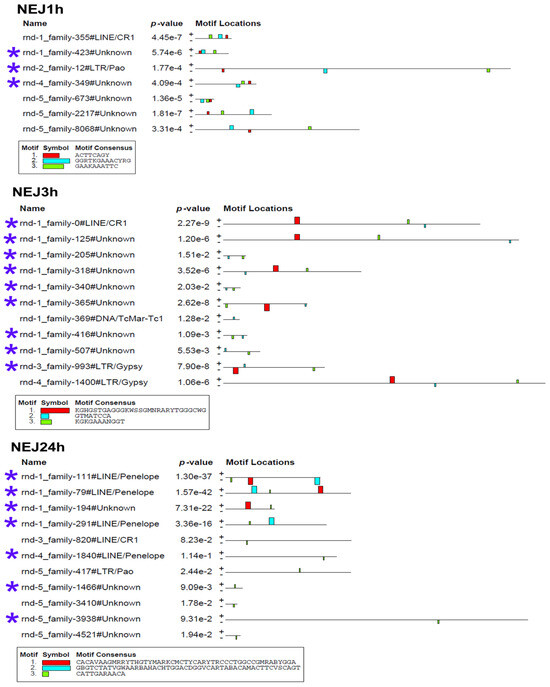

Figure 8.
Transcription factor binding site predictions in stage-specific upregulated TE transcripts in newly emerged juveniles of 1, 3, and 24 h age. The figure is the layout showing the localization of the identified TF binding sites (colored rectangles) on the forward and reverse TE chain (labelled to the left of the schemes) with the combined match p-value. The block height corresponds to the site significance, i.e., taller blocks are more significant. The consensus sequences of the TF binding sites are indicated in boxes under the schemes. Blue asterisks indicate the similar lncRNA TEs.
The MEME Suite sequential analysis of TF binding sites [32] revealed potential TF binding site (TFBS) sequences in a significant portion of upregulated TEs. Subsequent searches for known TF motifs with TomTom tool [33] confirmed the presence of several TFBS. For instance, TEs upregulated in eggs were enriched with HLH-2, Rsc30, and REF-1 sites—the transcription factors that are active during early larval development and promote hypodermal cell fusion patterning.
Additionally, juvenile TEs were found to contain sequences similar to those recognized by Zfp410 zinc-finger proteins and multifunctional Sox TF family members. In newly excysted juveniles, upregulated TEs also exhibited TFBS similar to those of Rara_DBD_3 (hormone receptor domain), retinoic acid receptors RARG and RARB, FOXG1 (fork-head DNA-binding domain), Nkx-2.9, SFFV, and the Sox TF family.
The metacercaria stage exhibited the majority of the identified TF binding sites, including those for the Sox family, Ndt80 (meiosis-specific transcription factor), HLH-2, Gm5454 (predicted protein), Etv4 (E1A enhancer binding protein), Gabpa (GA repeat binding protein), and Elk3 (member of the ETS oncogene family).
3. Discussion
Eukaryotic genomes contain a substantial portion of repetitive sequences, primarily composed of mobile elements. Transposons can integrate into gene regulatory regions and play a role in transcription regulation. Additionally, they serve as a source for non-coding RNAs, encompassing both short (e.g., microRNAs) and long (e.g., lncRNAs) variants [16]. Previously considered as “junk DNA”, transposons are now acknowledged as significant contributors to the structure and operation of the eukaryotic genome. This assertion finds support in various instances of transposon exaptation [23,34,35,36].
The study of the role of transposons and non-coding RNAs in the genomes of parasitic flatworms, specifically trematodes, holds significant interest. Trematodes undergo a complex life cycle, with multiple developmental stages spanning across diverse animal hosts and environments. Yet the molecular mechanisms governing stage transitions remain elusive. In recent years, research on non-coding RNAs in trematodes has garnered attention [13,15,37,38,39,40]. However, studies elucidating the role of transposons in trematodes remain relatively scarce [41,42,43,44,45,46,47]. This underscores a notable gap in our understanding, considering the pivotal role transposons play in eukaryotic genomes and their potential significance in parasite life cycles.
This work summarizes the data on repeats in the F. hepatica genome and is a pioneering attempt to trace the transposon transcription at different stages. In different studies, the F. hepatica genome, one of the largest among trematodes, exhibits varying repeat compositions, ranging from ~40% in Liverpool isolates [27] to ~50% in Oregon isolates [29,48,49]. A comprehensive analysis was conducted [49] revealing an expansion of DNA transposons (3- or 4-fold) and LTR retroelements (almost 7-fold more copies per genome) in F. hepatica and F. gigantica genomes compared to closely related Fasciolopsis buski species; Fasciola spp. diverged ~90 million years ago. Moreover, F. hepatica and F. gigantica genomes contain more intronic TEs. Despite these variations, the overall proportions of TEs remain similar across trematodes [45,50,51,52,53,54], with LINE elements prevailing in the genome (occupying between 10% and 30%) and LTR retrotransposons ranging from 4% in schistosomes to 15% in Fasciola spp. [48]. We suggest that a database of repeats, generated in this study with the most recent genome assembly of F. hepatica, has higher reliaility, considering that PacBio technology is believed to yield a better assembly of repeats compared to genome sequencing by Illumina [55]. Our analysis revealed that the mean proportion of repeats in the genome is more than 60%, with slight differences among TE groups in assemblies. Unknown elements constitute a significant portion, which causes challenges for annotation by making the program unable to assign them to known groups. Annotation of Unknown elements is a labor-intensive task and merits a separate study, given the numerous nuances involved [56,57,58]. Considering the differences in sequencing methodologies and assembly techniques, slight variations in TE composition may be attributed to assembly artifacts or intraspecific polymorphism.
A primary analysis showed that transcription of both DNA transposons and retroelements takes place at all stages, revealing sets of elements that appear to be specific to certain stages and not expressed in others. However, these TEs were not included in the list of differentially expressed repeats due to failure to pass the internal filter of the sleuth R package. In these cases, experimental validation (PCR-based) seems to be the only feasible option.
In the overall evaluation of TE expression profiles, samples were not segregated according to stages, likely due to their inherent characteristics, such as potential delays in larval development or sequencing artifacts. Notably, when looking at the expression of LTRs or Unknown elements only, sample clustering is aligned with stages, while no such pattern is observed for LINEs. Nevertheless, it has been shown that in a number of Fasciola gigantica genes, intronic LINEs insertions presumably contributed to the modulation of gene networks associated with the regulation of membrane transport, protein synthesis, and histone modification [49].
Futhermore, the expression of LTR retrotransposons, especially endogenous retroviruses (ERVs), is crucial for cellular processes. For instance, HERVH has been implicated in maintaining stemness in human cells [59,60] and in mice. A gradient change in transposon expression, including LTRs and LINEs, occurs during embryogenesis [61]. In contrast, other species, such as zebrafish [62] or Xenopus tropicalis [63], overwhelmingly express DNA transposons at these developmental stages. TE expression during embryogenesis has also been observed in other model organisms [64,65,66,67,68].
In the trematode life cycle, embryogenesis runs at a few stages: in the egg and in the rediae during parthenogenetic reproduction. Unfortunately, we do not know exactly what part of TE transcripts in the egg was accumulated during oogenesis and what part was newly synthesized during embryo development, since the original study [27] did not specify the timespan of RNA being isolated from eggs. RNA-seq data for parthenogenetic stages of F. hepatica are unavailable, making it impossible to determine TE expression levels during this stage. Likewise, significant changes occur during the metacercaria stage, where many processes are activated, including high expression levels of genes related to metabolic activity, cell signaling, DNA replication, and transcription [69,70,71,72]. Moreover, metacercariae express a set of microRNAs and lncRNAs [15,31,73]. Our data indicate that the egg and metacercariae have the highest number of specific upregulated TEs, and the putative role of these transcripts is yet to be determined.
In addition to the previously discussed TEs, lncRNAs play an important role in early development [74,75,76]. LncRNAs are known to participate in various regulatory processes, including chromatin remodeling, transcription regulation, and post-transcriptional modification [77]. Despite their low sequence homology, lncRNAs contain domains that are highly similar to TEs. These domains are assumed to be functionally significant for lncRNAs by triggering the recruitment of TFs, microRNAs, or proteins associated with chromatin modifications [78,79,80]. In our study, we identified TF binding sites within upregulated TEs, including those associated with lncRNAs. However, it is noteworthy that the presence of predicted transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs) alone does not conclusively assign a regulatory function to the TE sequences. Predicted TFBSs are often degenerate and may not fully match the canonical binding motifs. Therefore, further experimental validation of actual transcription factor binding to these sequences is required. For trematodes, this area is still in its early stages of research. For instance, in S. mansoni, Sox transcription factors were described only recently [81]. Nevertheless, in other organisms, such as humans and mice, it has been shown that approximately 40% of TF binding sites originate from TEs, including critical TFs like STAT1, TP53, OCT4, NANOG, and CTCF [82]. Furthermore, the interaction of transcription factors (TFs) with transposable element transcripts in various regulatory networks has been demonstrated. ZFP352 (Klf family), which binds to the SINE_B1 element in mouse embryos, facilitates the transition from the two-cell stage to further development [83]. TF Foxa1 (Forkhead family) binds to hypomethylated regions of SINE/MER1 and activates transcription of the α-fetoprotein gene (Afp) in human embryonic stem cells [84]. Human HERVs interact with numerous TFs during early human embryogenesis [85], including the Sox TF family, whose potential binding sites were identified in stage-specific upregulated TEs (Figure 7 and Figure 8).
Furthermore, stage-specific expression of TEs and their association with lncRNAs may shed light on complicated regulatory interactions, contributing to the fine-tuning of gene expression during key transitions in the trematode life cycle.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Genomic Data and Repetitive Element Discovery
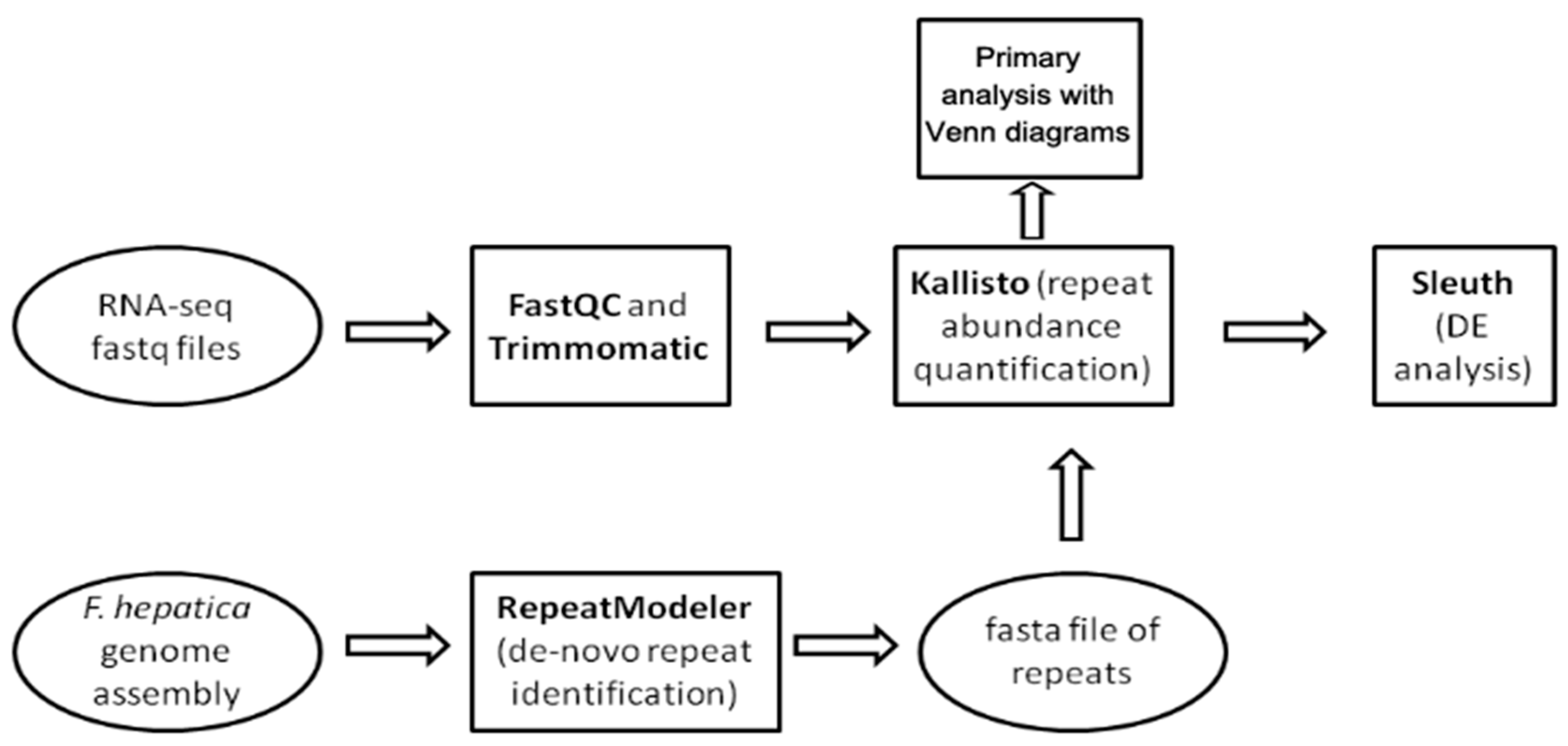
The workflow showing the steps of the study is provided in Figure 9. We used three public F. hepatica genome assemblies: GCA_900302435.1 (Bioproject PRJEB25283), GCA_002763495.2 (Bioproject PRJNA179522), and GCA_948099385.1 (Bioproject PRJEB58756). The latter was assembled in 2023 using PacBio long reads.
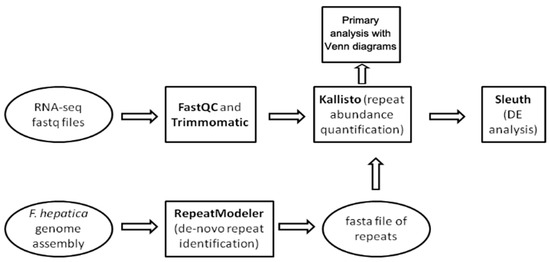
Figure 9.
Pipeline for differential expression (DE) analysis of mobile elements within various Fasciola hepatica life cycle stages.
The de novo search for repetitive elements was performed with RepeatModeler v. 2.0.5. software [86] hosted on the Galaxy server (https://usegalaxy.eu/, last accessed 13 February 24) and GCA_948099385.1 genome assembly. RepeatModeller2 uses clustering algorithms to group similar sequences together and to identify repetitive elements de novo. Then, these clusters are used to perform multiple sequence alignments and refine the identification of repeats. For each cluster, a consensus sequence is generated, representing the common features of the sequences within the cluster, thus providing a representative model of the repetitive element. Next, repetitive elements are classified into known repeat families and the final output of a refined repeat library is generated [86]. The generated library is utilized for RepeatMasker (https://www.repeatmasker.org/, last accessed 13 April 2024) to compare the repeat content of three F. hepatica genome assemblies. The results are summarized in Supplementary File S1 (Table S5). In addition, we used a generated library of repeats to investigate repeat content in the transcriptome assembly (https://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/databases/wormbase/parasite/releases/WBPS18/species/fasciola_hepatica/PRJEB25283/fasciola_hepatica.PRJEB25283.WBPS18.mRNA_transcripts.fa.gz, last accessed 28 February 2024) and protein coding transcripts (https://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/databases/wormbase/parasite/releases/WBPS19/species/fasciola_hepatica/PRJEB58756/fasciola_hepatica.PRJEB58756.WBPS19.CDS_transcripts.fa.gz last accessed 10 June 2024) available at Wormbase Parasite. The repeat database and processing scripts are available on the GitHub page of our project (https://github.com/LisaSkalon/Mobile_elements_of_F.hepatica, last accessed 10 June 2024).
4.2. RNA-Seq Data Preprocessing
The study relied on publicly avaliable RNA-seq datasets for several life cycle stages of F. hepatica [27], with a minimum of 2 biological replicates for each stage. Raw fastq read files were downloaded from the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (Accession numbers ERR576952-ERR576969, ERR577157-ERR577160). The samples encompassed distinct developmental stages of the liver fluke, adult parasites (ad, n = 3), eggs (n = 2), metacercariae (met, n = 3), NEJ, i.e., young larvae excysted from metacercariae (1 h post-excystment: nej1h, n = 2; 3 h post-excystment: nej3h, n = 2; 24 h post-excystment: nej24h, n = 2), and 21-day liver-stage juveniles (juv; n = 2). NEJs, offspring of metacercariae, develop into juveniles and eventually mature into adults that produce eggs. A sequencing depth for each sample varies from 7058 Mb (egg1) to 15,924 Mb (NEJ24h2). A detailed list of the downloaded samples and their specifications is provided in Table S4.
The downloaded RNA-seq reads (Table S4) underwent quality control analysis using FastQC v0.12.1 [87] (Figure 9). Runs from identical samples sequenced under the same technical conditions and sharing identical BioSample names were merged using the cat Unix utility. Subsequently, reads were filtered using Trimmomatic v0.39 [88] to remove residual Illumina TruSeq adapters and eliminate low-quality bases (Phred quality score < 25).
4.3. Differential Expression Analysis of Transposable Elements
The expression of repetitive elements was assessed using the Kallisto v. 0.48.0 pseudoalignment-based quantification tool [89]. The output file from RepeatModeler2, containing consensus repeat sequences, served as the reference and was indexed by Kallisto. The repeat abundance for each developmental stage was quantified as transcripts per million (TPM) by aligning the set of targeted k-mers to the k-mers of the clean RNA-seq reads (with 1000 bootstrap samples).
Differential expression analysis was conducted on the Kallisto output using the sleuth R package v. 0.29.0 [90] (Figure 9). Based on the obtained data, a sample heatmap clustered by Jensen–Shannon divergence and a PCA plot were generated (Figure 3). Using the likelihood ratio test (LRT), 676 out of 1824 transposable elements with a p-value < 0.05 were identified as differentially expressed (Table S2, tab sleuth_significant list) following multiple comparison across all stages. Additionally, a Wald test was performed to detect false positive results for pairwise stage comparisons and reveal the fold change of TE expression.
To identify TEs expressed at specific life cycle stages, we compared lists of all the expressed TEs (with a TPM > 1 cutoff) by feeding Kallisto raw counts into Open Office Calc v. 4.1.15. Subsequently, the results were visualized using the web-based tool Venn (https://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/Venn/, last accessed 28 February 2024). Additionally, this tool was utilized to analyze data obtained from pairwise comparisons of stages, where the Wald test was applied. The results are presented as volcanoplots using Graphpad prism (https://www.graphpad.com/, accessed 10 June 2024) in Figure 5. We compared lists of transposons exhibiting statistically significant differences in expression, as well as separately analyzed upregulated TEs. Raw results of all described comparisons are available in Table S3. To identify TE-associated lncRNAs, a local BLAST search using Galaxy platform (https://usegalaxy.eu/last accessed 10 April 2024) was performed against the F. hepatica repeat database with a 70% sequence similarity parameter. The results are shown in Table S2.
4.4. Identification of Transcription Factor Binding Sites in Stage-Specific Upregulated TEs
Transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs) were identified in stage-specific TEs using MEME version 5.4.1 [32], implemented in the Galaxy server (https://usegalaxy.eu/, last accessed 15 June 2024). The motif search was conducted on both the forward and reverse strands, with motif widths ranging from 8 to 50 base pairs. Simple Dirichlet priors were constructed from the primary sequences, and the Zero or One Occurrence Per Sequence (ZOOPS) model was employed to identify motifs. The identified motifs were searched against the UniPROBE PBM database [91] using the Tomtom tool with E-value < 10−3 threshold (available at https://meme-suite.org/meme/tools/tomtom, last accessed 15 June 2024) to identify probable associated TFs.
5. Conclusions
Our findings regarding the expression of TEs at different life cycle stages of the F. hepatica trematode suggest that these transcripts play a significant role in molecular regulation. The outlined stage-specific TE expression profiles shed light on the potential TE involvement in the mechanisms regulating parasite development and adaptation to various hosts and environmental conditions. The research provides extra evidence in favor of the correlation between transposons and lncRNAs, opening new avenues to explore gene expression regulation in parasites.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ncrna10040039/s1, Supplementary File S1: Table S5: F. hepatica genome content comparison, and Table S6: Juveline TE expression; Table S1: Raw results of expressed repeat comparisons, Table S2: Differential expression analysis and lncRNA BLAST search; Table S3: Wald test results; Table S4: list of samples.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.I.S. and O.I.P.; methodology, E.K.S., A.I.S. and N.V.P.; software, E.K.S. and N.V.P.; formal analysis, E.K.S., A.I.S. and A.R.S.; investigation, E.K.S., A.I.S. and N.V.P.; resources, O.I.P.; writing—original draft preparation, A.I.S. and N.V.P.; writing—review and editing, E.K.S., N.V.P. and O.I.P.; visualization, A.R.S., A.I.S. and E.K.S.; supervision, O.I.P.; project administration, A.I.S.; funding acquisition, A.I.S. and O.I.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Russian Science Foundation: №23-74-01060.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All the data are presented in Supplementary Files and hosted on Github (https://github.com/LisaSkalon/Mobile_elements_of_F.hepatica, last accessed 10 June 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Tidman, R.; Kanankege, K.S.T.; Bangert, M.; Abela-Ridder, B. Global prevalence of 4 neglected foodborne trematodes targeted for control by WHO: A scoping review to highlight the gaps. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindley, P.J.; da Costa, J.M.C.; Sripa, B. Why does infection with some helminths cause cancer? Trends Cancer 2015, 1, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efared, B.; Bako, A.B.A.; Idrissa, B.; Alhousseini, D.; Boureima, H.S.; Sodé, H.C.; Nouhou, H. Urinary bladder Schistosoma haematobium-related squamous cell carcinoma: A report of two fatal cases and literature review. Trop. Dis. Travel Med. Vaccines 2022, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bülow, V.; Lichtenberger, J.; Grevelding, C.G.; Falcone, F.H.; Roeb, E.; Roderfeld, M. Does Schistosoma Mansoni Facilitate Carcinogenesis? Cells 2021, 10, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripa, B.; Brindley, P.J.; Mulvenna, J.; Laha, T.; Smout, M.J.; Mairiang, E.; Bethony, J.M.; Loukas, A. The tumorigenic liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini—Multiple pathways to cancer. Trends Parasitol. 2012, 28, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-S.; Pak, J.H.; Kim, J.-B.; Bahk, Y.Y. Clonorchis sinensis, an oriental liver fluke, as a human biological agent of cholangiocarcinoma: A brief review. BMB Rep. 2016, 49, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, D.Y.; Kerimoglu, U.; Oto, A.; Erguven, S.; Arslan, S.; Unal, S.; Batman, F.; Bayraktar, Y. Infection with Fasciola hepatica. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2005, 11, 859–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterenko, M.A.; Starunov, V.V.; Shchenkov, S.V.; Maslova, A.R.; Denisova, S.A.; Granovich, A.I.; Dobrovolskij, A.A.; Khalturin, K.V. Molecular signatures of the rediae, cercariae and adult stages in the complex life cycles of parasitic flatworms (Digenea: Psilostomatidae). Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindley, P.J. The molecular biology of schistosomes. Trends Parasitol. 2005, 21, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobert, G.N.; Moertel, L.; Brindley, P.J.; McManus, D.P. Developmental gene expression profiles of the human pathogen Schistosoma japonicum. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X.; Cong, W.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Liu, G.H.; Ma, J.G.; Huang, W.Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhu, X.Q. De novo transcriptome sequencing and analysis of the juvenile and adult stages of Fasciola gigantica. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 51, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancela, M.; Ruétalo, N.; Dell’Oca, N.; da Silva, E.; Smircich, P.; Rinaldi, G.; Roche, L.; Carmona, C.; Alvarez-Valín, F.; Zaha, A.; et al. Survey of transcripts expressed by the invasive juvenile stage of the liver fluke Fasciola hepatica. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, E.J.R.; Dasilva, L.F.; Pires, D.S.; Lavezzo, G.M.; Pereira, A.S.A.; Amaral, M.S.; Verjovski-Almeida, S. The Schistosoma mansoni genome encodes thousands of long non-coding RNAs predicted to be functional at different parasite life-cycle stages. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, E.J.R.; Mesel, V.C.; DaSilva, L.F.; Pires, D.S.; Lavezzo, G.M.; Pereira, A.S.A.; Amaral, M.S.; Verjovski-Almeida, S. Atlas of Schistosoma mansoni long non-coding RNAs and their expression correlation to protein-coding genes. Database 2018, 2018, bay068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McVeigh, P.; McCammick, E.; Robb, E.; Brophy, P.; Morphew, R.M.; Marks, N.J.; Maule, A.G. Discovery of long non-coding RNAs in the liver fluke, Fasciola hepatica. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapusta, A.; Kronenberg, Z.; Lynch, V.J.; Zhuo, X.; Ramsay, L.A.; Bourque, G.; Yandell, M.; Feschotte, C. Transposable Elements Are Major Contributors to the Origin, Diversification, and Regulation of Vertebrate Long Noncoding RNAs. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fort, V.; Khelifi, G.; Hussein, S.M.I. Long non-coding RNAs and transposable elements: A functional relationship. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Res. 2021, 1868, 118837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourque, G.; Burns, K.H.; Gehring, M.; Gorbunova, V.; Seluanov, A.; Hammell, M.; Imbeault, M.; Izsvák, Z.; Levin, H.L.; Macfarlan, T.S.; et al. Ten things you should know about transposable elements. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, I.A.; Naville, M.; Chalopin, D.; Levin, P.; Berger, C.S.; Galiana, D.; Volff, J.N. Evolutionary impact of transposable elements on genomic diversity and lineage-specific innovation in vertebrates. Chromosom. Res. 2015, 23, 505–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalopin, D.; Naville, M.; Plard, F.; Galiana, D.; Volff, J.N. Comparative analysis of transposable elements highlights mobilome diversity and evolution in vertebrates. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicker, T.; Sabot, F.; Hua-Van, A.; Bennetzen, J.L.; Capy, P.; Chalhoub, B.; Flavell, A.; Leroy, P.; Morgante, M.; Panaud, O.; et al. A unified classification system for eukaryotic transposable elements. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.R.L.; Burns, K.H.; Boeke, J.D. Active transposition in genomes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2012, 46, 651–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuong, E.B.; Elde, N.C.; Feschotte, C. Regulatory activities of transposable elements: From conflicts to benefits. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 18, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazazian, H.H. Mobile elements: Drivers of genome evolution. Science 2004, 303, 1626–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deininger, P.L.; Moran, J.V.; Batzer, M.A.; Kazazian, H.H. Mobile elements and mammalian genome evolution. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2003, 13, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chénais, B.; Caruso, A.; Hiard, S.; Casse, N. The impact of transposable elements on eukaryotic genomes: From genome size increase to genetic adaptation to stressful environments. Gene 2012, 509, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwiklinski, K.; Dalton, J.P.; Dufresne, P.J.; La Course, J.; Williams, D.J.; Hodgkinson, J.; Paterson, S. The Fasciola hepatica genome: Gene duplication and polymorphism reveals adaptation to the host environment and the capacity for rapid evolution. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Valero, M.A.; Bargues, M.D. Fascioliasis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1154, 71–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNulty, S.N.; Tort, J.F.; Rinaldi, G.; Fischer, K.; Rosa, B.A.; Smircich, P.; Fontenla, S.; Choi, Y.J.; Tyagi, R.; Hallsworth-Pepin, K.; et al. Genomes of Fasciola hepatica from the Americas Reveal Colonization with Neorickettsia Endobacteria Related to the Agents of Potomac Horse and Human Sennetsu Fevers. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontenla, S.; Langleib, M.; de la Torre-Escudero, E.; Domínguez, M.F.; Robinson, M.W.; Tort, J. Role of Fasciola hepatica Small RNAs in the Interaction with the Mammalian Host. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 11, 812141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herron, C.M.; O’Connor, A.; Robb, E.; McCammick, E.; Hill, C.; Marks, N.J.; Robinson, M.W.; Maule, A.G.; McVeigh, P. Developmental Regulation and Functional Prediction of microRNAs in an Expanded Fasciola hepatica miRNome. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 811123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME Suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Stamatoyannopoulos, J.A.; Bailey, T.L.; Noble, W.S. Quantifying similarity between motifs. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goubert, C.; Zevallos, N.A.; Feschotte, C. Contribution of unfixed transposable element insertions to human regulatory variation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 375, 20190331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, N.K.H.; Li, L.; Taher, L. Independent Transposon Exaptation Is a Widespread Mechanism of Redundant Enhancer Evolution in the Mammalian Genome. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolau, M.; Picault, N.; Moissiard, G. The Evolutionary Volte-Face of Transposable Elements: From Harmful Jumping Genes to Major Drivers of Genetic Innovation. Cells 2021, 10, 2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, G.O.; Coelho, H.S.; Pereira, A.S.A.; Miyasato, P.A.; Santos, D.W.; Maciel, L.F.; Olberg, G.G.G.; Tahira, A.C.; Nakano, E.; Oliveira, M.L.S.; et al. Long non-coding RNAs are essential for Schistosoma mansoni pairing-dependent adult worm homeostasis and fertility. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.; Chen, D.; He, J.J.; Zheng, W.B.; Tian, A.L.; Zhao, G.H.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Zhu, X.Q. Fasciola gigantica–Derived Excretory-Secretory Products Alter the Expression of mRNAs, miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs Involved in the Immune Response and Metabolism in Goat Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 653755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontenla, S.; Rinaldi, G.; Smircich, P.; Tort, J.F. Conservation and diversification of small RNA pathways within flatworms. BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardim Poli, P.; Fischer-Carvalho, A.; Tahira, A.C.; Chan, J.D.; Verjovski-Almeida, S.; Sena Amaral, M. Long Non-Coding RNA Levels Are Modulated in Schistosoma mansoni Following In Vivo Praziquantel Exposure. Non-Coding RNA 2024, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laha, T.; Loukas, A.; Smyth, D.J.; Copeland, C.S.; Brindley, P.J. The fugitive LTR retrotransposon from the genome of the human blood fluke, Schistosoma mansoni. Int. J. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, C.S.; Brindley, P.J.; Heyers, O.; Michael, S.F.; Johnston, D.A.; Williams, D.L.; Ivens, A.C.; Kalinna, B.H. Boudicca, a retrovirus-like long terminal repeat retrotransposon from the genome of the human blood fluke Schistosoma mansoni. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 6153–6166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindley, P.J.; Copeland, C.S.; Kalinna, B.H. Schistosome Retrotransposons BT—In Schistosomiasis. In World Class Parasites; Secor, W.E., Colley, D.G., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2005; pp. 13–26. ISBN 978-0-387-23362-8. [Google Scholar]
- Galaktionov, N.K.; Solovyeva, A.I.; Fedorov, A.V.; Podgornaya, O.I. Trematode Himasthla elongata mariner element (Hemar): Structure and applications. J. Exp. Zool. Part B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2014, 322, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyeva, A.; Levakin, I.; Zorin, E.; Adonin, L.; Khotimchenko, Y.; Podgornaya, O. Transposons-based clonal diversity in trematode involves parts of cr1 (Line) in eu-and heterochromatin. Genes 2021, 12, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsunenko, A.; Chrisanfova, G.; Arifov, A.; Ryskov, A.; Semyenova, S. Characterization of randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) fragments revealing clonal variability in cercariae of avian schistosome Trichobilharzia szidati (Trematoda: Schistosomatidae). Open J. Genet. 2013, 2013, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMarco, R.; Kowaltowski, A.T.; Machado, A.A.; Soares, M.B.; Gargioni, C.; Kawano, T.; Rodrigues, V.; Madeira, A.M.B.N.; Wilson, R.A.; Menck, C.F.M.; et al. Erratum: Saci-1, -2, and -3 and Perere, Four Novel Retrotransposons with High Transcriptional Activities from the Human Parasite Schistosoma mansoni. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 2967–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Fontenla, S.; Fischer, P.U.; Le, T.H.; Costábile, A.; Blair, D.; Brindley, P.J.; Tort, J.F.; Cabada, M.M.; Mitreva, M. Adaptive Radiation of the Flukes of the Family Fasciolidae Inferred from Genome-Wide Comparisons of Key Species. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Cui, K.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Huang, W.; Zhu, X.Q.; Ruan, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Q. High-quality reference genome of Fasciola gigantica: Insights into the genomic signatures of transposon-mediated evolution and specific parasitic adaption in tropical regions. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindley, P.J. Mobile Genetic Elements in Metazoan Parasites; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; ISBN 9781587060939. [Google Scholar]
- Ershov, N.I.; Mordvinov, V.A.; Prokhortchouk, E.B.; Pakharukova, M.Y.; Gunbin, K.V.; Ustyantsev, K.; Genaev, M.A.; Blinov, A.G.; Mazur, A.; Boulygina, E.; et al. New insights from Opisthorchis felineus genome: Update on genomics of the epidemiologically important liver flukes. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berriman, M.; Haas, B.J.; LoVerde, P.T.; Wilson, R.A.; Dillon, G.P.; Cerqueira, G.C.; Mashiyama, S.T.; Al-Lazikani, B.; Andrade, L.F.; Ashton, P.D.; et al. The genome of the blood fluke Schistosoma mansoni. Nature 2009, 460, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Huang, Y.; Sun, J.; Men, J.; Liu, H.; Luo, F.; Guo, L.; Lv, X.; Deng, C.; et al. The draft genome of the carcinogenic human liver fluke Clonorchis sinensis. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zheng, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, K.; Guo, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Huang, W.; Jin, K.; et al. The Schistosoma japonicum genome reveals features of host-parasite interplay. Nature 2009, 460, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, A.; Au, K.F. PacBio Sequencing and its Applications. Genomics. Proteom. Bioinform. 2015, 13, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurka, J. Repbase update: A database and an electronic journal of repetitive elements. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Kojima, K.K.; Kohany, O. Repbase Update, a database of repetitive elements in eukaryotic genomes. Mob. DNA 2015, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loreto, E.L.S.; de Melo, E.S.; Wallau, G.L.; Gomes, T.M.F.F. The good, the bad and the ugly of transposable elements annotation tools. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, e20230138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsay, L.A.; Marchetto, M.C.; Caron, M.; Chen, S.H.; Busche, S.; Kwan, T.; Pastinen, T.; Gage, F.H.; Bourque, G. Conserved expression of transposon-derived non-coding transcripts in primate stem cells. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macia, A.; Blanco-Jimenez, E.; García-Pérez, J.L. Retrotransposons in pluripotent cells: Impact and new roles in cellular plasticity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gene Regul. Mech. 2015, 1849, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadloun, A.; Le Gras, S.; Jost, B.; Ziegler-Birling, C.; Takahashi, H.; Gorab, E.; Carninci, P.; Torres-Padilla, M.E. Chromatin signatures and retrotransposon profiling in mouse embryos reveal regulation of LINE-1 by RNA. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.C.; Rovira, Q.; Wells, J.; Feschotte, C.; Vaquerizas, J.M. Zebrafish transposable elements show extensive diversification in age, genomic distribution, and developmental expression. Genome Res. 2022, 32, 1408–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faunes, F.; Lee-Liu, D.; Larrain, J. Expression of DNA transposable elements during nervous system development: A discussion about its possible functions. Mob. Genet. Elem. 2011, 1, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ansaloni, F.; Scarpato, M.; Di Schiavi, E.; Gustincich, S.; Sanges, R. Exploratory analysis of transposable elements expression in the C. elegans early embryo. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Padilla, M.E. On transposons and totipotency. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 375, 20190339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdes, P.; Richardson, S.R.; Mager, D.L.; Faulkner, G.J. Transposable elements in the mammalian embryo: Pioneers surviving through stealth and service. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiRusso, J.A.; Clark, A.T. Transposable elements in early human embryo development and embryo models. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2023, 81, 102086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panyushev, N.; Okorokova, L.; Danilov, L.; Adonin, L. Pattern of repetitive element transcription segregate cell lineages during the embryogenesis of sea urchin strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesterenko, M.; Shchenkov, S.; Denisova, S.; Starunov, V. The digenean complex life cycle: Phylostratigraphy analysis of the molecular signatures. Biol. Commun. 2022, 67, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X.; Cwiklinski, K.; Hu, R.S.; Zheng, W.B.; Sheng, Z.A.; Zhang, F.K.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Dalton, J.P.; Zhu, X.Q. Complex and dynamic transcriptional changes allow the helminth Fasciola gigantica to adjust to its intermediate snail and definitive mammalian hosts. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomaznoy, M.Y.; Logacheva, M.D.; Young, N.D.; Penin, A.A.; Ershov, N.I.; Katokhin, A.V.; Mordvinov, V.A. Whole transcriptome profiling of adult and infective stages of the trematode Opisthorchis felineus. Parasitol. Int. 2016, 65, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, P.Y.; Kim, T.I.; Whang, S.M.; Hong, S.J. Gene expression profile of Clonorchis sinensis metacercariae. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 102, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Khalil, A.M.; Jolly, E.R. LncRNAs in molluscan and mammalian stages of parasitic schistosomes are developmentally-regulated and coordinately expressed with protein-coding genes. RNA Biol. 2020, 17, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Fang, F. Long Noncoding RNA Mediated Regulation in Human Embryogenesis, Pluripotency, and Reproduction. Stem Cells Int. 2022, 2022, 8051717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Mu, H.; Wen, B.; Zhang, W.; Wei, Q.; Gao, G.; Han, J.; Cao, S. Long non-coding RNAs involved in the regulatory network during porcine pre-implantation embryonic development and iPSC induction. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akay, A.; Jordan, D.; Navarro, I.C.; Wrzesinski, T.; Ponting, C.P.; Miska, E.A.; Haerty, W. Identification of functional long non-coding RNAs in C. elegans. BMC Biol. 2019, 17, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, A.B.; Tsitsipatis, D.; Gorospe, M. Integrated lncRNA function upon genomic and epigenomic regulation. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 2252–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaram, V.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, Z.; Li, D.; Xing, X.; Edge, P.; Snyder, M.P.; Wang, T. Widespread contribution of transposable elements to the innovation of gene regulatory networks. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 1963–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapusta, A.; Feschotte, C. Volatile evolution of long noncoding RNA repertoires: Mechanisms and biological implications. Trends Genet. 2014, 30, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecco, G.; Cassano, M.; Kauzlaric, A.; Duc, J.; Coluccio, A.; Offner, S.; Imbeault, M.; Rowe, H.M.; Turelli, P.; Trono, D. Transposable Elements and Their KRAB-ZFP Controllers Regulate Gene Expression in Adult Tissues. Dev. Cell 2016, 36, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.; Ishida, K.; Hagerty, J.R.; Karahodza, A.; Dennis, J.N.; Jolly, E.R. Characterization of Schistosome Sox Genes and Identification of a Flatworm Class of Sox Regulators. Pathogens 2023, 12, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, V.; Wysocka, J. Transposable elements as a potent source of diverse cis-regulatory sequences in mammalian genomes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 375, 20190347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, D.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Xue, Z.; Zhan, G.; et al. Selective binding of retrotransposons by ZFP352 facilitates the timely dissolution of totipotency network. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taube, J.H.; Allton, K.; Duncan, S.A.; Shen, L.; Barton, M.C. Foxa1 functions as a pioneer transcription factor at transposable elements to activate Afp during differentiation of embryonic stem cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 16135–16144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, J.; Sugimoto, R.; Nakaoka, H.; Yamada, S.; Kimura, T.; Hayano, T.; Inoue, I. Systematic identification and characterization of regulatory elements derived from human endogenous retroviruses. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, J.M.; Hubley, R.; Goubert, C.; Rosen, J.; Clark, A.G.; Feschotte, C.; Smit, A.F. RepeatModeler2 for automated genomic discovery of transposable element families. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9451–9457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. Babraham Bioinforma. 2010. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/ (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, N.L.; Pimentel, H.; Melsted, P.; Pachter, L. Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, H.; Bray, N.L.; Puente, S.; Melsted, P.; Pachter, L. Differential analysis of RNA-seq incorporating quantification uncertainty. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 687–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Stormo, G.D. Quantitative analysis demonstrates most transcription factors require only simple models of specificity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).