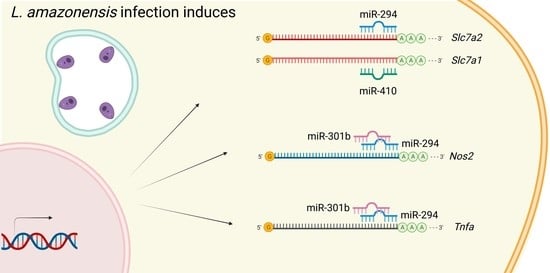
miR-294 and miR-410 Negatively Regulate Tnfa, Arginine Transporter Cat1/2, and Nos2 mRNAs in Murine Macrophages Infected with Leishmania amazonensis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
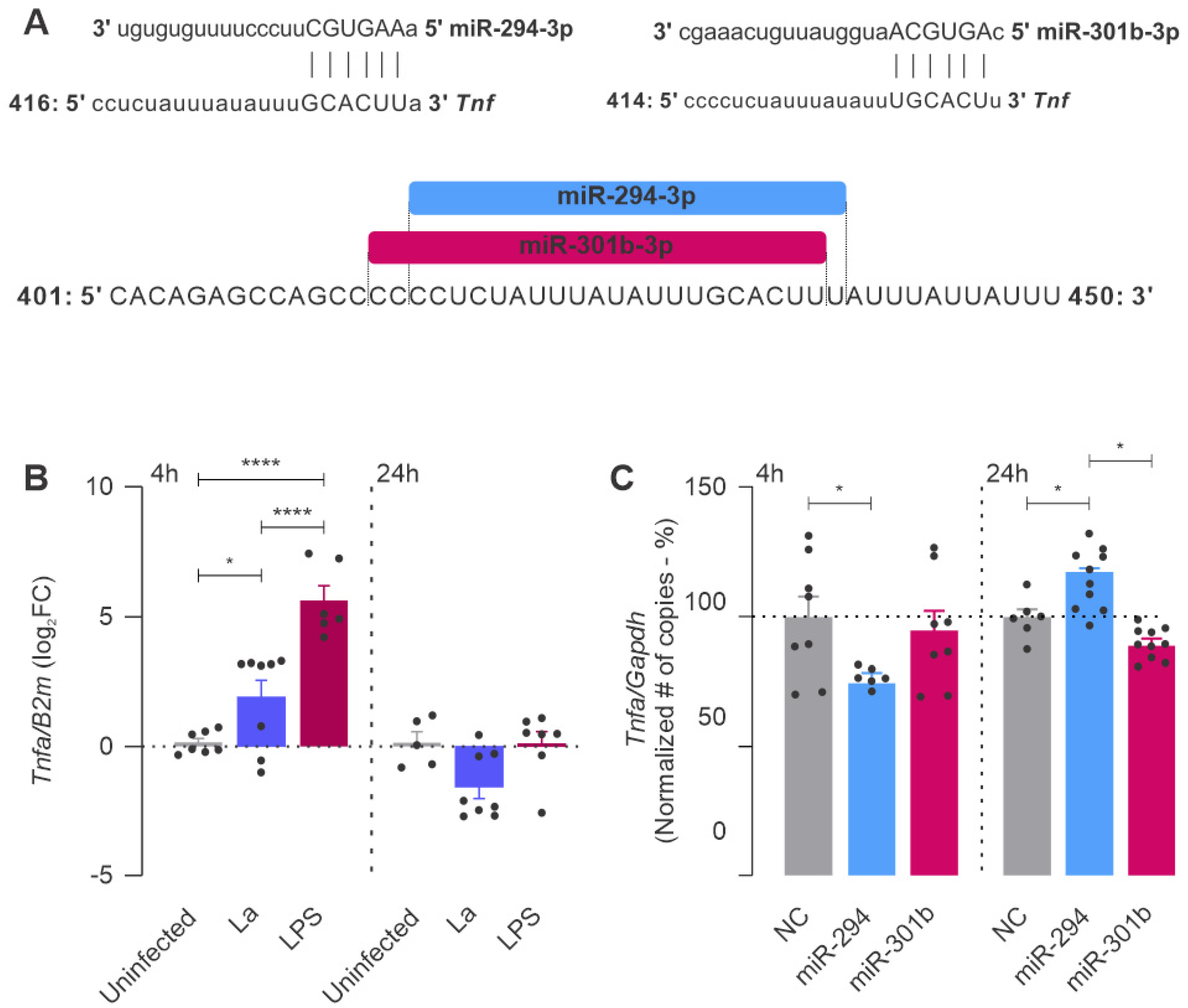
2.1. miR-294-3p, miR-301b-3p, and miR-410-3p Target the L-Arginine Metabolic Pathway
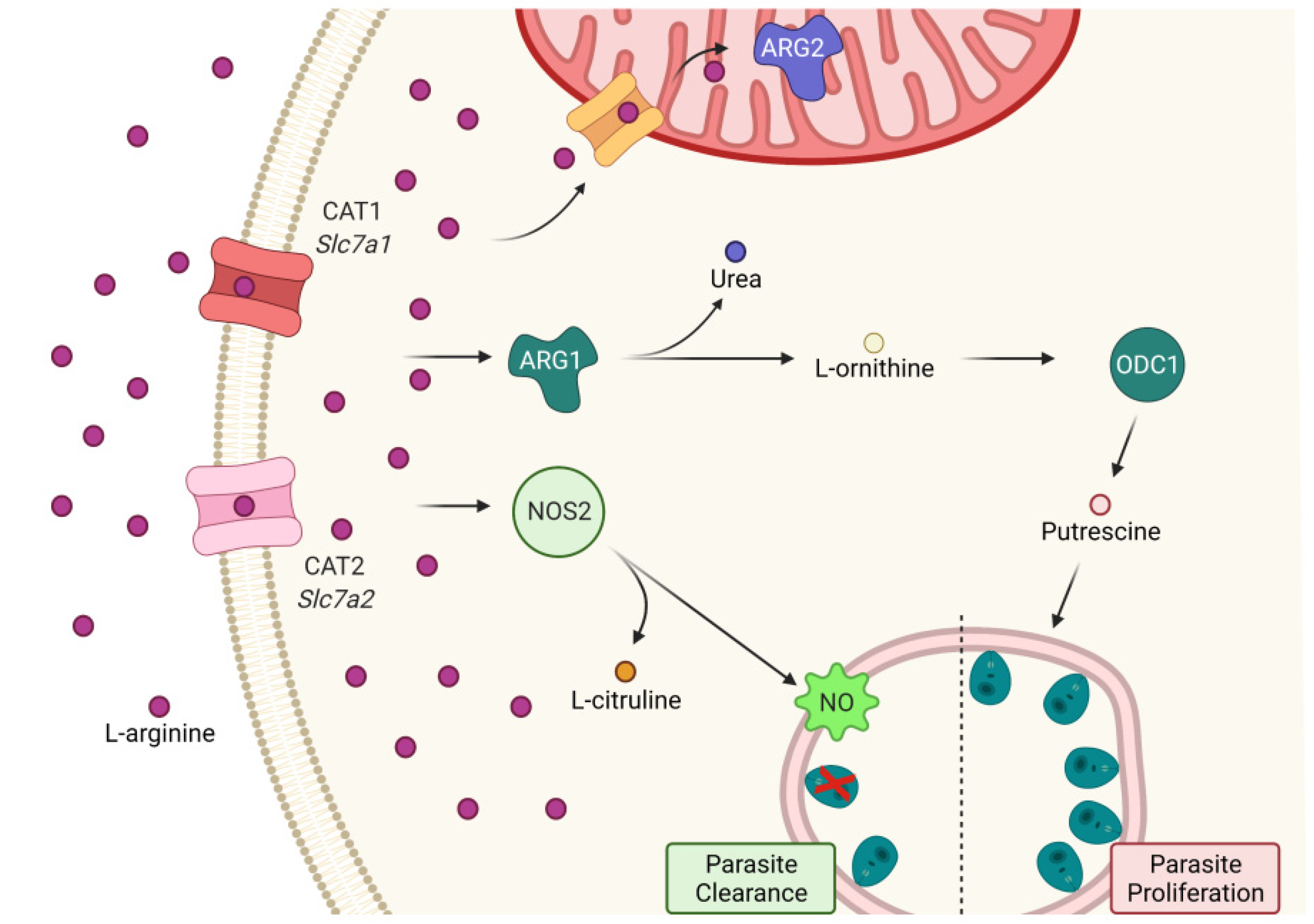
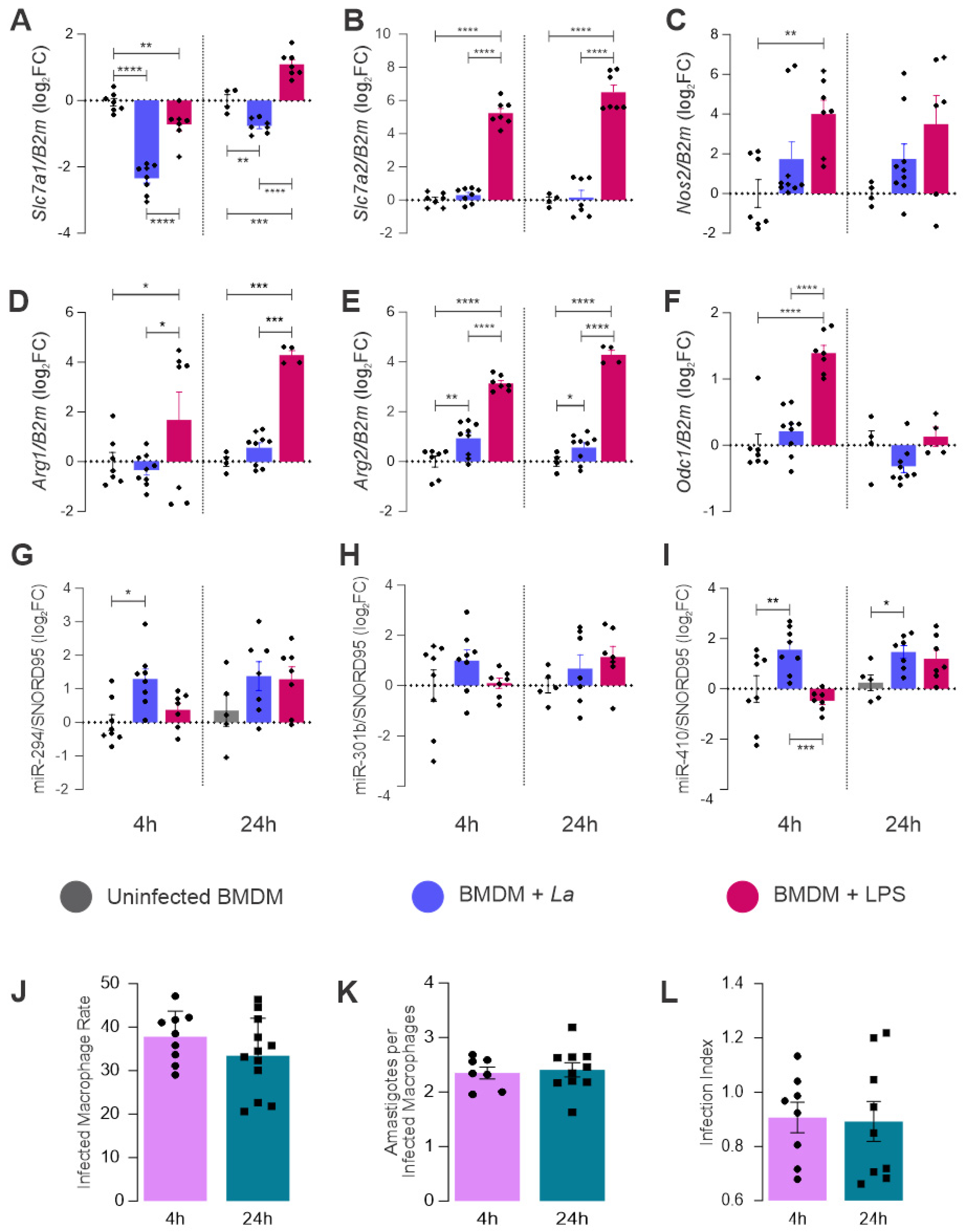
2.2. Expression of L-Arginine Metabolic Pathway and miR-294-3p, miR-301b-3p, and miR-410-3p
2.3. miRNAs Targeting mRNA from Arginine Metabolism Shift the Macrophage Response to Leishmania
2.4. miR-294 and miR-301b Can Also Interact with Other Inflammatory Factors during Macrophage Infection with L. amazonensis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. In Silico miRNA Binding Site Prediction
4.2. Parasite Culture
4.3. BMDM Harvesting and Culture
4.4. Macrophage Infection
4.5. Infection Assessment
4.6. RNA Extraction and cDNA Preparation
4.7. Transcript Quantification
4.8. miRNA Inhibition
4.9. Ethics Statement
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baltimore, D.; Boldin, M.; O’Connell, R.M.; Rao, D.; Taganov, K.D. MicroRNAs: New regulators of immune cell development and function. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, L.A.; Sheedy, F.J.; Mccoy, C.E. MicroRNAs: The fine-tuners of Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Imm. 2011, 268, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, R.; Mattei, V.; Al Hashmi, M.; Tomei, S. Updates on the Current Technologies for microRNA Profiling. MicroRNA 2019, 9, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.K.L. The Whereabouts of microRNA Actions: Cytoplasm and Beyond. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Acuña, S.M.; Floeter-Winter, L.M.; Muxel, S.M. MicroRNAs: Biological Regulators in Pathogen–Host Interactions. Cells 2020, 9, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Jiang, T.; Li, M.-Q.; Zheng, X.-L.; Zhao, G.-J. Transcriptional Regulation of Macrophages Polarization by MicroRNAs. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, F.O.; Helming, L.; Gordon, S. Alternative Activation of Macrophages: An Immunologic Functional Perspective. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 451–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akhoundi, M.; Kuhls, K.; Cannet, A.; Votypka, J.; Marty, P.; Delaunay, P.; Sereno, D. A Historical Overview of the Classification, Evolution, and Dispersion of Leishmania Parasites and Sandflies. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashford, R.W. The leishmaniases as emerging and reemerging zoonoses. Parasites Vectors 2000, 3, 1269–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burza, S.; Croft, S.L.; Boelaert, M. Leishmaniasis. Lancet 2018, 392, 951–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, C.; Shiloh, M. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen intermediates in the relationship between mammalian hosts and microbial pathogens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8841–8848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gregory, D.; Olivier, M. Subversion of host cell signalling by the protozoan parasite Leishmania. Parasitology 2005, 130, S27–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, M.; Fasel, N. How to master the host immune system? Leishmania parasites have the solutions! Int. Immunol. 2018, 30, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muxel, S.M.; Aoki, J.I.; Fernandes, J.C.R.; Laranjeira-silva, M.F.; Zampieri, R.A.; Acuña, S.M. Arginine and Polyamines Fate in Leishmania Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, S.C.; Tancer, M.J.; Polinsky, M.R.; Gibson, K.M.; Heby, O.; Ullman, B. Arginase Plays a Pivotal Role in Polyamine Precursor Metabolism in Leishmania. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 23668–23678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Silva, M.F.L.; Zampieri, R.A.; Muxel, S.M.; Beverley, S.M.; Floeter-Winter, L.M. Leishmania amazonensis arginase compartmentalization in the glycosome is important for parasite infectivity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wanasen, N.; Soong, L. L-arginine metabolism and its impact on host immunity against Leishmania infection. Immunol. Res. 2007, 41, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeramian, A.; Martin, L.; Arpa, L.; Bertran, J.; Soler, C.; McLeod, C.; Modolell, M.; Palacín, M.; Lloberas, J.; Celada, A. Macrophages require distinct arginine catabolism and transport systems for proliferation and for activation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006, 36, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sans-Fons, M.G.; Yeramian, A.; Pereira-Lopes, S.; Santamaría-Babi, L.F.; Modolell, M.; Lloberas, J.; Celada, A. Arginine Transport Is Impaired in C57Bl/6 Mouse Macrophages as a Result of a Deletion in the Promoter of Slc7a2 (CAT2), and Susceptibility to Leishmania Infection Is Reduced. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 207, 1684–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manzano-Román, R.; Siles-Lucas, M. MicroRNAs in parasitic diseases: Potential for diagnosis and targeting. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2012, 186, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynoso, R.; Laufer, N.; Hackl, M.; Skalicky, S.; Monteforte, R.; Turk, G.; Carobene, M.; Quarleri, J.; Cahn, P.; Werner, R.; et al. MicroRNAs differentially present in the plasma of HIV elite controllers reduce HIV infection in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, srep05915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petrini, E.; Caviglia, G.P.; Abate, M.L.; Fagoonee, S.; Smedile, A.; Pellicano, R. MicroRNAs in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma: Functions and potential clinical applications. Panminerva Med. 2015, 57, 500–509. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Yi, Z.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Xu, F. Circulating MicroRNAs in Patients with Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 4246–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Assis Souza, M.; Ramos-Sanchez, E.M.; Muxel, S.M.; Lagos, D.; Reis, L.C.; Pereira, V.R.A. miR-548d-3p Alters Parasite Growth and Inflammation in Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis Infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; She, Q.; Shen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, G. Potential Role of MicroRNA-375 as Biomarker in Human Cancers Detection: A Meta-Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filipów, S.; Łaczmański, Ł. Blood circulating miRNAs as cancer biomarkers for diagnosis and surgical treatment response. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muxel, S.M.; Laranjeira-Silva, M.F.; Zampieri, R.A.; Floeter-Winter, L.M. Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis induces macrophage miR-294 and miR-721 expression and modulates infection by targeting NOS2 and L-arginine metabolism. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep44141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muxel, S.M.; Acuña, S.M.; Aoki, J.I.; Zampieri, R.A.; Floeter-Winter, L.M. Toll-Like Receptor and miRNA-let-7e Expression Alter the Inflammatory Response in Leishmania amazonensis-Infected Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdan, C.; Röllinghoff, M. The immune response to Leishmania: Mechanisms of parasite control and evasion. Int. J. Parasitol. 1998, 28, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Stebut, E.; Ehrchen, J.M.; Belkaid, Y.; Kostka, S.L.; Mölle, K.; Knop, J. Interleukin 1α promotes TH1 differentiation and inhibits disease progression in Leishmania major-susceptible BALB/c mice. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, J.; Brombacher, F. T helper1/T helper2 cells and resistance/susceptibility to Leishmania infection: Is this paradigm still relevant? Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Felizardo, T.C.; Toma, L.S.; Borges, N.B.; Lima, G.M.C.A.; Abrahamsohn, I.A. Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis infection and dissemination in mice inoculated with stationary-phase or with purified metacyclic promastigotes. Parasitology 2007, 134, 1699–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasquez, L.G.; Galuppo, M.K.; De Rezende, E.; Brandão, W.N.; Peron, J.P.; Uliana, S.R.B. Distinct courses of infection with Leishmania (L.) amazonensis are observed in BALB/c, BALB/c nude and C57BL/6 mice. Parasitology 2016, 143, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, J.I.; Muxel, S.M.; Laranjeira-Silva, M.F.; Zampieri, R.A.; Müller, K.E.; Nerland, A.H.; Floeter-Winter, L.M. Dual transcriptome analysis reveals differential gene expression modulation influenced by Leishmania arginase and host genetic background. Microb. Genom. 2020, 6, e000427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vejnar, C.; Zdobnov, E.M. miRmap: Comprehensive prediction of microRNA target repression strength. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 11673–11683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerfali, F.Z.; Laouini, D.; Guizani-Tabbane, L.; Ottones, F.; Ben-Aissa, K.; Benkahla, A.; Manchon, L.; Piquemal, D.; Smandi, S.; Mghirbi, O.; et al. Simultaneous gene expression profiling in human macrophages infected with Leishmania major parasites using SAGE. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, J.; Bose, M.; Roy, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.N. Leishmania donovani Targets Dicer1 to Downregulate miR-122, Lower Serum Cholesterol, and Facilitate Murine Liver Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 13, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernandes, J.C.R.; Aoki, J.; Acuña, S.M.; Zampieri, R.A.; Markus, R.P.; Floeter-Winter, L.M.; Muxel, S.M. Melatonin and Leishmania amazonensis Infection Altered miR-294, miR-30e, and miR-302d Impacting on Tnf, Mcp-1, and Nos2 Expression. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, J.; Mkannez, G.; Guerfali, F.; Gustin, C.; Attia, H.; Sghaier, R.M.; Dellagi, K.; Laouini, D.; Renard, P. Sysco-Consortium MicroRNA Expression Profile in Human Macrophages in Response to Leishmania major Infection. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degrossoli, A.; Bosetto, M.C.; Lima, C.B.C.; Giorgio, S. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α in mononuclear phagocytes infected with Leishmania amazonensis. Immunol. Lett. 2007, 114, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kumar, A.; Das, S.; Kumar, A.; Abhishek, K.; Verma, S. Leishmania donovani activates hypoxia inducible factor-1α and miR-210 for survival in macrophages by downregulation of NF-κB mediated pro-inflammatory immune respons. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Ali, N. Super enhancer-mediated transcription of miR146a-5p drives M2 polarization during Leishmania donovani infection. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houbaviy, H.B.; Murray, M.F. Embryonic Stem Cell-Specific MicroRNAs the regulation of development. Dev. Cell. 2003, 5, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Lu, Q. MicroRNA epigenetic alterations: Predicting biomarkers and therapeutic targets in human diseases. Clin. Genet. 2008, 74, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, J. MicroRNAs of the miR379-410 cluster: New players in embryonic neurogenesis and regulators of neuronal function. Neurogenesis 2015, 2, e1004970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wanasen, N.; MacLeod, C.L.; Ellies, L.G.; Soong, L. L-Arginine and Cationic Amino Acid Transporter 2B Regulate Growth and Survival of Leishmania amazonensis Amastigotes in Macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 2802–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darlyuk, I.; Goldman, A.; Roberts, S.C.; Ullman, B.; Rentsch, D.; Zilberstein, D. Arginine Homeostasis and Transport in the Human Pathogen Leishmania donovani. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 19800–19807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagarkoti, S.; Sadaf, S.; Awasthi, D.; Chandra, T.; Jagavelu, K.; Kumar, S.; Dikshit, M. L-Arginine and tetrahydrobiopterin supported nitric oxide production is crucial for the microbicidal activity of neutrophils. Free. Radic. Res. 2019, 53, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junior, D.S.L.; Costa, D.; Carregaro, V.; Cunha, L.D.; Silva, A.L.N.; Mineo, T.W.P.M.; Gutierrez, F.R.; Bellio, M.; Bortoluci, K.; A Flavell, R.; et al. Inflammasome-derived IL-1β production induces nitric oxide–mediated resistance to Leishmania. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamani-Huanca, M.; Muxel, S.M.; Acuña, S.M.; Floeter-Winter, L.M.; Barbas, C.; López-Gonzálvez, Á. Metabolomic reprogramming of c57bl/6-macrophages during early infection with L. amazonensis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunand-Sauthier, I.; Irla, M.; Carnesecchi, S.; Seguín-Estévez, Q.; Vejnar, C.E.; Zdobnov, E.M.; Santiago-Raber, M.-L.; Reith, W. Repression of Arginase-2 Expression in Dendritic Cells by MicroRNA-155 Is Critical for Promoting T Cell Proliferation. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 1690–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dowling, J.K.; Afzal, R.; Gearing, L.J.; Cervantes-Silva, M.P.; Annett, S.; Davis, G.M.; De Santi, C.; Assmann, N.; Dettmer, K.; Gough, D.J.; et al. Mitochondrial arginase-2 is essential for IL-10 metabolic reprogramming of inflammatory macrophages. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dichtl, S.; Lindenthal, L.; Zeitler, L.; Behnke, K.; Schlösser, D.; Strobl, B.; Scheller, J.; El Kasmi, K.C.; Murray, P.J. Lactate and IL6 define separable paths of inflammatory metabolic adaptation. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Xu, M.; Tian, X.; Cai, S.; Zeng, S. Research advances in the detection of miRNA. J. Pharm. Anal. 2019, 9, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishikawa, T.; Otsuka, M.; Tan, P.S.; Ohno, M.; Sun, X.; Yoshikawa, T.; Shibata, C.; Takata, A.; Kojima, K.; Takehana, K.; et al. Decreased miR122 in hepatocellular carcinoma leads to chemoresistance with increased arginine. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 8339–8352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, D.; Mo, G.; Zhang, L. Effects of microRNA-294 on inflammatory factor of sepsis by targeting triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue 2014, 26, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funamizu, N.; Lacy, C.R.; Parpart, S.T.; Takai, A.; Hiyoshi, Y.; Yanaga, K. MicroRNA-301b promotes cell invasiveness through targeting TP63 in pancreatic carcinoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gregorova, J.; Vychytilova-Faltejskova, P.; Sevcikova, S. Epigenetic Regulation of MicroRNA Clusters and Families during Tumor Development. Cancers 2021, 13, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Shang, F. MicroRNA-410-3p Binds to TLR2 and Alleviates Myocardial Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Chemokine Production in LPS-Induced Sepsis. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2020, 22, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Dai, H.; Wang, L.; Lin, S.; Tao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, R.; Fang, F.; Wu, Y. MicroRNA-410-3p modulates chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation by targeting high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) in an osteoarthritis mouse model. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, R.; Bernhart, S.H.; zu Siederdissen, C.H.; Tafer, H.; Flamm, C.; Stadler, P.F. ViennaRNA Package 2.0 Ronny. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 2011, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muxel, S.M.; Laranjeira-Silva, M.F.; Zampieri, R.A.; Aoki, J.I.; Acuña, S.M.; Floeter-Winter, L.M. Functional validation of miRNA-mRNA interactions in macrophages by inhibition/competition assays based in transient transfection. Protoc. Exch. 2017, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Target Gene | Primer (5′-3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| Nitric Oxide Synthase (Nos2) | Forward | 5′-agagccacagtcctctttgc-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-gctcctcttccaaggtgctt-3′ | |
| Arginase 1 (Arg1) | Forward | 5′-agcactgaggaaagctggtc-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-cagaccgtgggttcttcaca-3′ | |
| Arginase 2 (Arg2) | Forward | 5′-tctcctccacgggcaaattc-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-cactcctagcttcttctgccc-3′ | |
| Cationic amino acid transporter 1 (Cat1/Slc7A1) | Forward | 5′-cgtaatcgccactgtgacct-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-ggctggtaccgtaagaccaa-3′ | |
| Cationic amino acid transporter 2 (Cat2/Slc7A2) | Forward | 5′-tccaaaacgaagacaccagt-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-gccatgagggtgccaataga-3′ | |
| Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha (Tnfa) | Forward | 5′-ccaccacgctcttctgtcta-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-agggtctgggccatagaact-3′ | |
| Ornithine decarboxilase (Odc1) | Forward | 5′-ctgccagtaacggagtccag-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-tcagtggcaatccgtagaacc-3′ | |
| β-2-microglobulin (B2m) | Forward | 5′-cactgaattcacccccactga-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-acagatggagcgtccagaaag-3′ | |
| Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (Gapdh) | Forward | 5′-ggcaaattcaacggcacagt-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-ccttttggctccacccttca-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Acuña, S.M.; Zanatta, J.M.; de Almeida Bento, C.; Floeter-Winter, L.M.; Muxel, S.M. miR-294 and miR-410 Negatively Regulate Tnfa, Arginine Transporter Cat1/2, and Nos2 mRNAs in Murine Macrophages Infected with Leishmania amazonensis. Non-Coding RNA 2022, 8, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8010017
Acuña SM, Zanatta JM, de Almeida Bento C, Floeter-Winter LM, Muxel SM. miR-294 and miR-410 Negatively Regulate Tnfa, Arginine Transporter Cat1/2, and Nos2 mRNAs in Murine Macrophages Infected with Leishmania amazonensis. Non-Coding RNA. 2022; 8(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleAcuña, Stephanie Maia, Jonathan Miguel Zanatta, Camilla de Almeida Bento, Lucile Maria Floeter-Winter, and Sandra Marcia Muxel. 2022. "miR-294 and miR-410 Negatively Regulate Tnfa, Arginine Transporter Cat1/2, and Nos2 mRNAs in Murine Macrophages Infected with Leishmania amazonensis" Non-Coding RNA 8, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8010017
APA StyleAcuña, S. M., Zanatta, J. M., de Almeida Bento, C., Floeter-Winter, L. M., & Muxel, S. M. (2022). miR-294 and miR-410 Negatively Regulate Tnfa, Arginine Transporter Cat1/2, and Nos2 mRNAs in Murine Macrophages Infected with Leishmania amazonensis. Non-Coding RNA, 8(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8010017