Circular RNAs Activity in the Leukemic Bone Marrow Microenvironment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Hematopoietic Stem Cells and Their Niche
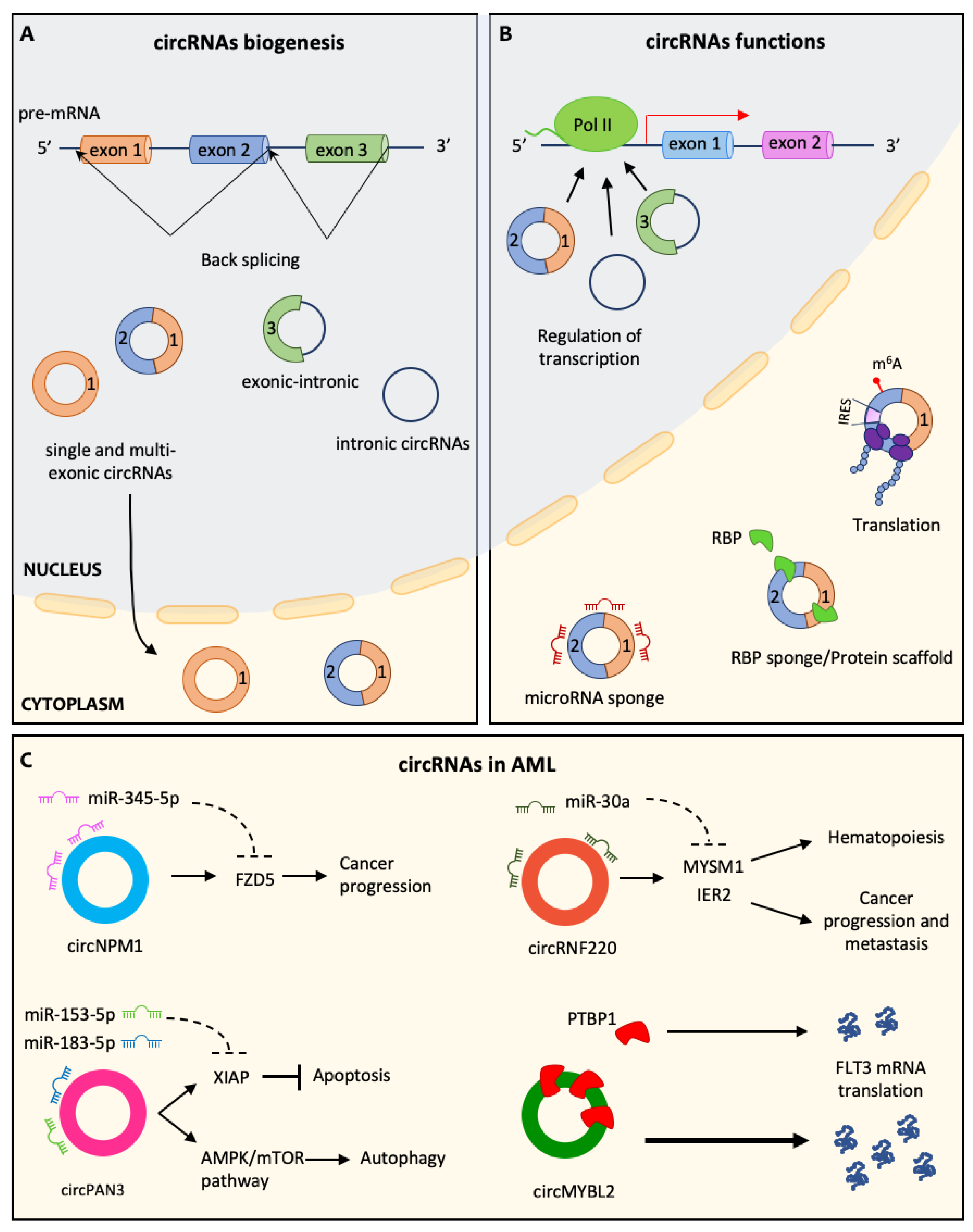
3. Circular RNAs and Their Role in Hematopoiesis
4. AML and the Leukemic BM Niche
5. circRNA in AML Pathogenesis
6. circRNA in Leukemic Bone Marrow Niche
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shallis, R.M.; Wang, R.; Davidoff, A.; Ma, X.; Zeidan, A.M. Epidemiology of Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Recent Progress and Enduring Challenges. Blood Rev. 2019, 36, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löwenberg, B.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; van Putten, W.; Schouten, H.C.; Graux, C.; Ferrant, A.; Sonneveld, P.; Maertens, J.; Jongen-Lavrencic, M.; von Lilienfeld-Toal, M.; et al. High-Dose Daunorubicin in Older Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1235–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelissen, J.J.; Blaise, D. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Patients with AML in First Complete Remission. Blood 2016, 127, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döhner, H.; Weisdorf, D.J.; Bloomfield, C.D. Acute Myeloid Leukemia1. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1136–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stanchina, M.; Soong, D.; Zheng-Lin, B.; Watts, J.M.; Taylor, J. Advances in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Recently Approved Therapies and Drugs in Development. Cancers 2020, 12, 3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masciarelli, S.; Capuano, E.; Ottone, T.; Divona, M.; de Panfilis, S.; Banella, C.; Noguera, N.I.; Picardi, A.; Fontemaggi, G.; Blandino, G.; et al. Retinoic Acid and Arsenic Trioxide Sensitize Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia Cells to ER Stress. Leukemia 2018, 32, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masciarelli, S.; Capuano, E.; Ottone, T.; Divona, M.; Lavorgna, S.; Liccardo, F.; Śniegocka, M.; Travaglini, S.; Noguera, N.I.; Picardi, A.; et al. Retinoic Acid Synergizes with the Unfolded Protein Response and Oxidative Stress to Induce Cell Death in FLT3-ITD1 AML. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 4155–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Short, N.J.; Konopleva, M.; Kadia, T.M.; Borthakur, G.; Ravandi, F.; DiNardo, C.D.; Daver, N. Advances in the Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia: New Drugs and New Challenges. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 506–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pagano, F.; de Marinis, E.; Grignani, F.; Nervi, C. Epigenetic Role of MiRNAs in Normal and Leukemic Hematopoiesis. Epigenomics 2013, 5, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatica, A.; Fazi, F. MicroRNA-Regulated Pathways in Hematological Malignancies: How to Avoid Cells Playing out of Tune. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 20930–20953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mangiavacchi, A.; Sorci, M.; Masciarelli, S.; Larivera, S.; Legnini, I.; Iosue, I.; Bozzoni, I.; Fazi, F.; Fatica, A. The MiR-223 Host Non-Coding Transcript Linc-223 Induces IRF4 Expression in Acute Myeloid Leukemia by Acting as a Competing Endogenous RNA. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 60155–60168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Agostino, S.; Riccioli, A.; de Cesaris, P.; Fontemaggi, G.; Blandino, G.; Filippini, A.; Fazi, F. Circular RNAs in Embryogenesis and Cell Differentiation With a Focus on Cancer Development. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Till, J.E.; McCulloch, E.A. A Direct Measurement of the Radiation Sensitivity of Normal Mouse Bone Marrow Cells. Radiat. Res. 1961, 14, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, S.J.; Uchida, N.; Weissman, I.L. The Biology of Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1995, 11, 35–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, M.; Kocherlakota, K.S.; Murphy, M.M.; Peyer, J.G.; Oguro, H.; Inra, C.N.; Christabel, J.; Zhao, Z.; Luby-Phelps, K.; Morrison, S.J. Deep imaging of bone marrow shows non-dividing stem cells are mainly perisinusoidal. Nature 2015, 526, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kokkaliaris, K.D.; Kunz, L.; Cabezas-Wallscheid, N.; Christodoulou, C.; Renders, S.; Camargo, F.; Trumpp, A.; Scadden, D.T.; Schroeder, T. Adult blood stem cell localization reflects the abundance of reported bone marrow niche cell types and their combinations. Blood 2020, 136, 2296–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, B.A.; Link, D.C. Regulation of hematopoietic stem cells by bone marrow stromal cells. Trends Immunol. 2013, 35, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baccin, C.; Al-Sabah, J.; Velten, L.; Helbling, P.M.; Grünschläger, F.; Hernández-Malmierca, P.; Nombela-Arrieta, C.; Steinmetz, L.M.; Trumpp, A.; Haas, S. Combined single-cell and spatial transcriptomics reveal the molecular, cellular and spatial bone marrow niche organization. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Ferrer, S.; Bonnet, D.; Steensma, D.P.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Ghobrial, I.M.; Gribben, J.G.; Andreeff, M.; Krause, D.S. Bone marrow niches in haematological malignancies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán-Díez, M.; Kousteni, S. The Osteoblastic Niche in Hematopoiesis and Hematological Myeloid Malignancies. Curr. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2017, 3, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.O.; Yu, H.; Yue, R.; Zhao, Z.; Rios, J.J.; Naveiras, O.; Morrison, S.J. Bone marrow adipocytes promote the regeneration of stem cells and haematopoiesis by secreting SCF. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winkler, I.G.; Sims, N.A.; Pettit, A.R.; Barbier, V.; Nowlan, B.; Helwani, F.; Poulton, I.J.; Van Rooijen, N.; Alexander, K.; Raggatt, L.J.; et al. Bone marrow macrophages maintain hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) niches and their depletion mobilizes HSCs. Blood 2010, 116, 4815–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Comazzetto, S.; Shen, B.; Morrison, S.J. Niches that regulate stem cells and hematopoiesis in adult bone marrow. Dev. Cell 2021, 56, 1848–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Frenette, P.S. Niches for Hematopoietic Stem Cells and Their Progeny. Immunity 2018, 48, 632–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goode, D.K.; Obier, N.; Vijayabaskar, M.S.; Lie, M.; Lilly, A.J.; Hannah, R.; Lichtinger, M.; Batta, K.; Florkowska, M.; Patel, R.; et al. Dynamic Gene Regulatory Networks Drive Hematopoietic Specification and Differentiation. Dev. Cell 2016, 36, 572–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, M.; Jeong, M.; Sun, D.; Park, H.J.; Rodriguez, B.A.T.; Xia, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Sheng, K.; Darlington, G.J.; et al. Long Non-Coding RNAs Control Hematopoietic Stem Cell Function. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 16, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bissels, U.; Bosio, A.; Wagner, W. MicroRNAs are shaping the hematopoietic landscape. Haematologica 2011, 97, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.O.; Wang, H.B.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Chen, L.L.; Yang, L. Complementary Sequence-Mediated Exon Circularization. Cell 2014, 159, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conn, S.J.; Pillman, K.A.; Toubia, J.; Conn, V.M.; Salmanidis, M.; Phillips, C.A.; Roslan, S.; Schreiber, A.W.; Gregory, P.A.; Goodall, G.J. The RNA Binding Protein Quaking Regulates Formation of circRNAs. Cell 2015, 160, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Meyer, M.; Pamudurti, N.R.; Ivanov, A.; Bartok, O.; Hanan, M.; Evantal, N.; Memczak, S.; Rajewsky, N.; Kadener, S. circRNA Biogenesis Competes with Pre-mRNA Splicing. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.-L. The expanding regulatory mechanisms and cellular functions of circular RNAs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, P.; Wang, S.; Ye, B.; Du, Y.; Li, C.; Xiong, Z.; Qu, Y.; Fan, Z. A Circular RNA Protects Dormant Hematopoietic Stem Cells from DNA Sensor cGAS-Mediated Exhaustion. Immunity 2018, 48, 688–701.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nicolet, B.P.; Engels, S.; Aglialoro, F.; Van Den Akker, E.; Von Lindern, M.; Wolkers, M.C. Circular RNA expression in human hematopoietic cells is widespread and cell-type specific. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 8168–8180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolet, B.P.; Jansen, S.B.G.; Heideveld, E.; Ouwehand, W.H.; Akker, E.; von Linderen, M.; Wolkers, M.C. Circular RNAs exhibit limited evidence for translation, or translation regulation of the mRNA counterpart in terminal hematopoiesis. RNA 2022, 28, 194–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corces-Zimmerman, M.R.; Majeti, R. Pre-leukemic evolution of hematopoietic stem cells: The importance of early mutations in leukemogenesis. Leukemia 2014, 28, 2276–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandolfi, A.; Barreyro, L.; Steidl, U. Concise Review: Preleukemic Stem Cells: Molecular Biology and Clinical Implications of the Precursors to Leukemia Stem Cells. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2013, 2, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velten, L.; Story, B.A.; Hernández-Malmierca, P.; Raffel, S.; Leonce, D.R.; Milbank, J.; Paulsen, M.; Demir, A.; Szu-Tu, C.; Frömel, R.; et al. Identification of leukemic and pre-leukemic stem cells by clonal tracking from single-cell transcriptomics. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.H.; Qu, C.K.; Pauly, M. Germline mutations in the bone marrow microenvironment and dysregulated hematopoiesis. Exp. Hematol. 2018, 66, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, S.; Shmelkov, S.V.; Lam, G.; Rafii, S. VEGF165 promotes survival of leukemic cells by Hsp90-mediated induction of Bcl-2 expression and apoptosis inhibition. Blood 2002, 99, 2532–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatfield, K.; Ryningen, A.; Corbascio, M.; Bruserud, Ø. Microvascular endothelial cells increase proliferation and inhibit apoptosis of native human acute myelogenous leukemia blasts. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 2313–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, D.; di Tullio, A.; Abarrategi, A.; Rouault-Pierre, K.; Foster, K.; Ariza-McNaughton, L.; Montaner, B.; Chakravarty, P.; Bhaw, L.; Diana, G.; et al. Increased Vascular Permeability in the Bone Marrow Microenvironment Contributes to Disease Progression and Drug Response in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 324–341.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanoun, M.; Zhang, D.; Toshihide, M.; Piho, S.; Pierce, H.; Kunisaki, Y.; Lacombe, J.; Armstrong, S.A.; Dührsen, U.; Frenette, P.S. Acute Myelogenous Leukemia-Induced Sympathetic Neuropathy Promotes Malignancy in an Altered Hematopoietic Stem Cell Niche. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 15, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tettamanti, S.; Pievani, A.; Biondi, A.; Dotti, G.; Serafini, M. Catch me if you can: How AML and its niche escape immunotherapy. Leukemia 2022, 36, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Matary, Y.S.; Botezatu, L.; Opalka, B.; Hönes, J.M.; Lams, R.F.; Thivakaran, A.; Schütte, J.; Köster, R.; Lennartz, K.; Schroeder, T.; et al. Acute myeloid leukemia cells polarize macrophages towards a leukemia supporting state in a Growth factor independence 1 dependent manner. Haematologica 2016, 101, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sriskanthadevan, S.; Jeyaraju, D.V.; Chung, T.E.; Prabha, S.; Xu, W.; Skrtic, M.; Jhas, B.; Hurren, R.; Gronda, M.; Wang, X.; et al. AML cells have low spare reserve capacity in their respiratory chain that renders them susceptible to oxidative metabolic stress. Blood 2015, 125, 2120–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabe, Y.; Konopleva, M. Break the lifeline of AML cells. Blood 2021, 137, 3465–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafat, M.S.; Oellerich, T.; Mohr, S.; Robinson, S.D.; Edwards, D.R.; Marlein, C.R.; Piddock, R.E.; Fenech, M.; Zaitseva, L.; Abdul-Aziz, A.; et al. Leukemic blasts program bone marrow adipocytes to generate a protumoral microenvironment. Blood 2017, 129, 1320–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moschoi, R.; Imbert, V.; Nebout, M.; Chiche, J.; Mary, D.; Prebet, T.; Saland, E.; Castellano, R.; Pouyet, L.; Collette, Y.; et al. Protective mitochondrial transfer from bone marrow stromal cells to acute myeloid leukemic cells during chemotherapy. Blood 2016, 128, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marlein, C.R.; Zaitseva, L.; Piddock, R.E.; Robinson, S.D.; Edwards, D.R.; Shafat, M.S.; Zhou, Z.; Lawes, M.; Bowles, K.M.; Rushworth, S. NADPH oxidase-2 derived superoxide drives mitochondrial transfer from bone marrow stromal cells to leukemic blasts. Blood 2017, 130, 1649–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, D.; García-Fernández, M.; Sánchez-Aguilera, A.; Stavropoulou, V.; Fielding, C.; Martín-Pérez, D.; López, J.A.; Costa, A.S.; Tronci, L.; Nikitopoulou, E.; et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Support Acute Myeloid Leukemia Bioenergetics and Enhance Antioxidant Defense and Escape from Chemotherapy. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 829–843.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Garcia, M.; Weng, L.; Jung, X.; Murakami, J.L.; Hu, X.; McDonald, T.; Lin, A.; Kumar, A.R.; DiGiusto, D.L.; et al. Acute myeloid leukemia transforms the bone marrow niche into a leukemia-permissive microenvironment through exosome secretion. Leukemia 2018, 32, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.; Garcia, M.; Murakami, J.L.; Chen, C.C. Exosome-mediated microenvironment dysregulation in leukemia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Féral, K.; Jaud, M.; Philippe, C.; Bella, D.B.; Pyronnet, S.; Rouault-Pierre, K.; Mazzolini, L.; Touriol, C. ER Stress and Unfolded Protein Response in Leukemia: Friend, Foe, or Both? Biomolecules 2021, 11, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doron, B.; Abdelhamed, S.; Butler, J.T.; Hashmi, S.K.; Horton, T.M.; Kurre, P. Transmissible ER stress reconfigures the AML bone marrow compartment. Leukemia 2019, 33, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Shi, Y.X.; Samudio, I.J.; Wang, R.Y.; Ling, X.; Frolova, O.; Levis, M.; Rubin, J.B.; Negrin, R.R.; Estey, E.H.; et al. Targeting the leukemia microenvironment by CXCR4 inhibition overcomes resistance to kinase inhibitors and chemotherapy in AML. Blood 2009, 113, 6215–6224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacamo, R.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ma, W.; Zhang, M.; Spaeth, E.L.; Wang, Y.; Battula, V.L.; Mak, P.Y.; Schallmoser, K.; et al. Reciprocal leukemia-stroma VCAM-1/VLA-4-dependent activation of NF-κB mediates chemoresistance. Blood 2014, 123, 2691–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shan, G. CircRNA in cancer: Fundamental mechanism and clinical potential. Cancer Lett. 2021, 505, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issah, M.A.; Wu, D.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, W.; Liu, Y.; Chen, R.; Lai, G.; Shen, J. Expression profiling of N6-methyladenosine modified circRNAs in acute myeloid leukemia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 601, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnerio, J.; Bezzi, M.; Jeong, J.C.; Paffenholz, S.V.; Berry, K.; Naldini, M.M.; Lo-Coco, F.; Tay, Y.; Beck, A.H.; Pandolfi, P.P. Oncogenic Role of Fusion-circRNAs Derived from Cancer-Associated Chromosomal Translocations. Cell 2016, 165, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Liu, T.; Liu, J.; Feng, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Bai, J.; Zhao, W.; Shen, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Circ-ANAPC7 is Upregulated in Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Appears to Target the MiR-181 Family. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 1998–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, S.; Blätte, T.J.; Grasedieck, S.; Cocciardi, S.; Rouhi, A.; Jongen-Lavrencic, M.; Paschka, P.; Krönke, J.; Gaidzik, V.I.; Döhner, H.; et al. Circular RNAs of the nucleophosmin (NPM1) gene in acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2017, 102, 2039–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, X.; Xue, J.; Fang, L.; Ban, C.; Song, B.; Wu, L. CircNPM1 strengthens Adriamycin resistance in acute myeloid leukemia by mediating the miR-345-5p/FZD5 pathway. Central Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 46, 162–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.-M.; Wen, X.; Han, X.-R.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.-J.; Shen, M.; Fan, S.-H.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Shan, Q.; Li, M.-Q.; et al. Role of Circular RNA DLEU2 in Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2018, 38, e00259-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, Y.; Dong, Y.; Lu, H.; Luo, X.; Fu, J.; Xiu, B.; Liang, A.; Zhang, W. Circular RNA profile of acute myeloid leukaemia indicates circular RNA annexin A2 as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for acute myeloid leukaemia. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 1683–1699. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.Y.; Yi, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Tang, X.; Lin, J.; Wang, P.; Deng, Z.Q. Circular RNA of vimentin expression as a valuable predictor for acute myeloid leukemia development and prognosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 3711–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Ma, Y.; Tan, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhao, M.; Chen, B.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Z.; Wang, K. Profiling and functional analysis of circular RNAs in acute promyelocytic leukemia and their dynamic regulation during all-trans retinoic acid treatment. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Chen, W.M.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.H.; Wei, T.N.; Chen, Z.Z.; Wu, W.B. CircPAN3 contributes to drug resistance in acute myeloid leukemia through regulation of autophagy. Leuk. Res. 2019, 85, 106198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Chen, W.M.; Wang, Z.H.; Wei, T.N.; Chen, Z.Z.; Wu, W.B. CircPAN3 mediates drug resistance in acute myeloid leukemia through the miR-153-5p/miR-183-5p–XIAP axis. Exp. Hematol. 2019, 70, 42–54.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhong, C.; Jiao, J.; Li, P.; Cui, B.; Ji, C.; Ma, D. Characterization of hsa_circ_0004277 as a New Biomarker for Acute Myeloid Leukemia via Circular RNA Profile and Bioinformatics Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Jin, Y.; Wang, W. Circular RNA circ_0004277 Inhibits Acute Myeloid Leukemia Progression Through MicroRNA-134-5p/Single stranded DNA binding protein 2. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 9662–9673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Li, N.; Zhou, K.; Liao, C. Homo sapiens circular RNA 0003602 (Hsa_circ_0003602) accelerates the tumorigenicity of acute myeloid leukemia by modulating miR-502-5p/IGF1R axis. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2022, 477, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.M.; Wang, W.T.; Zeng, Z.C.; Chen, T.Q.; Han, C.; Pan, Q.; Huang, W.; Fang, K.; Sun, L.Y.; Zhou, Y.F.; et al. circMYBL2, a circRNA from MYBL2, regulates FLT3 translation by recruiting PTBP1 to promote FLT3-ITD AML progression. Blood 2019, 134, 1533–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Ming, X.; Xu, J.; Xiao, Y. Circ_0009910 shuttled by exosomes regulates proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia cells by regulating miR-5195-3p/GRB10 axis. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, L.; Jian-Jun, C.; Chu-Shu, L.; Guang-Hua, L.; Ming, Z. Silencing of circ_0009910 inhibits acute myeloid leukemia cell growth through increasing miR-20a-5p. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2018, 75, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Lei, P.; Zhou, M. hsa_circ_0121582 inhibits leukemia growth by dampening Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 22, 2293–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, L.Y.; Tang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhai, L.-L.; Yi, Y.Y.; Yi, J.; Lin, J.; Qian, J.; Deng, Z.-Q. Circ-Foxo3 is positively associated with the Foxo3 gene and leads to better prognosis of acute myeloid leukemia patients. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Cai, M.; Luo, A.; He, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Xu, L.; Jiang, H. CircRNF220, not its linear cognate gene RNF220, regulates cell growth and is associated with relapse in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Bai, J.; Li, W. Circular RNA-100290 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells via sponging miR. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 507, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhu, K.; Zhang, G. The Regulation of circRNA RNF13/miRNA-1224-5p Axis Promotes the Malignant Evolution in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 5654380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Zhou, L.; Luo, J.; Yang, Q. Circ-PTK2 promotes the proliferation and suppressed the apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia cells through targeting miR-330-5p/FOXM1 axis. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2021, 86, 102506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Ming, X.; Wu, J. Hsa_circ_0002483 regulates miR-758-3p/MYC axis to promote acute myeloid leukemia progression. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Luan, Q.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, J.; Wu, F.; Yan, J. Circular RNA circ_0005774 contributes to proliferation and suppresses apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia cells via circ_0005774/miR-192–5p/ULK1 ceRNA pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 551, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Cheng, F. Circular RNA circCRKL inhibits the proliferation of acute myeloid leukemia cells via the miR-196a-5p/miR-196b-5p/p27 axis. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 7704–7713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Bi, K.; Feng, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, C. CircRNA circ_POLA2 is Upregulated in Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) and Promotes Cell Proliferation by Suppressing the Production of Mature miR-34a. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 3629–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Gu, Y.; Chen, S.; Tian, Y.; Yang, S. Hsa_circ_0079480 promotes tumor progression in acute myeloid leukemia via miR-654-3p/HDGF axis. Aging 2021, 13, 1120–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Kou, R.; Song, Y.; Li, G.; Jia, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y. Serum hsa_circ_0079480 is a novel prognostic marker for acute myeloid leukemia. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, D.; Volinia, S.; Nicolet, D.; Świerniak, M.; Petri, A.; Mrózek, K.; Bill, M.; Pepe, F.; Walker, C.J.; Walker, A.E.; et al. Clinical and functional significance of circular RNAs in cytogenetically normal AML. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, D.M.; Ma, J.; Fang, W.B. Identification of non-coding RNA regulatory networks in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia reveals circ-0004136 could promote cell proliferation by sponging miR-142. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 9251–9258. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Yin, J.; He, R.; Chao, R.; Zhu, S. Circ_KCNQ5 participates in the progression of childhood acute myeloid leukemia by enhancing the expression of RAB10 via binding to miR. Hematology 2022, 27, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Sun, L.; Guo, Z.; Li, H.; Kong, D.; Xu, B.; Lin, L.; Liu, T.; Guo, D.; Zhou, J.; et al. Circular RNA regulatory network reveals cell–cell crosstalk in acute myeloid leukemia extramedullary infiltration. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Bu, Z.; Shen, J.; Shang, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. A novel circular RNA (hsa_circ_0000370) increases cell viability and inhibits apoptosis of FLT3-ITD-positive acute myeloid leukemia cells by regulating miR-1299 and S100A7A. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 122, 109619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Yang, B.; Jin, J.; He, Y.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, W.; He, Z. Circular RNA circ_0040823 inhibits the proliferation of acute myeloid leukemia cells and induces apoptosis by regulating miR-516b/PTEN. J. Gene Med. 2022, 24, e3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, Y.; Bian, S.; Sun, L.; Guo, Z.; Kong, D.; Zhao, L.; Guo, D.; Li, Q.; Wu, M.; et al. A circular RNA derived from PLXNB2 as a valuable predictor of the prognosis of patients with acute myeloid leukaemia. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.Y.; Zhao, Q.; Ke, J.M.; Wu, D.H.; Zhu, X.; Lin, J.; Deng, Z.Q. Circ_0002232 Acts as a Potential Biomarker for AML and Reveals a Potential ceRNA Network of Circ_0002232/miR-92a-3p/PTEN. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 11871–11881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Z.; Ming, X.; Wu, J.; Xiao, Y. Downregulation of circ_0012152 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells through the miR-625-5p/SOX12 axis. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.; Shang, Z.; Ming, X.; Wu, J.; Xiao, Y. Circ-SFMBT2 Facilitates the Malignant Growth of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells by Modulating MiR-582-3p/ZBTB20 Pathway. Histol. Histopathol. 2022, 37, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chen, F. The role of circular RNA plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 as a biomarker for prognostication of acute myeloid leukemia. Hematology 2021, 26, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Zhong, C.; Li, W.; Wang, R.; Zhang, C.; Yang, X.; Ji, C.; Ma, D. hsa_circ_0001947 suppresses acute myeloid leukemia progression via targeting hsa-miR-329-5p/CREBRF axis. Epigenomics 2020, 12, 935–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pan, J.; Huang, S.; Li, F.; Huang, J.; Li, X.; Ling, Q.; Ye, W.; Wang, Y.; Yu, W.; et al. Development and validation of a novel circular RNA as an independent prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochtler, T.; Fröhling, S.; Krämer, A. Role of chromosomal aberrations in clonal diversity and progression of acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2015, 29, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunchala, P.; Kuravi, S.; Jensen, R.; McGuirk, J.; Balusu, R. When the good go bad: Mutant NPM1 in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Rev. 2018, 32, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagunas-Rangel, F.A.; Chávez-Valencia, V. FLT3–ITD and its current role in acute myeloid leukaemia. Med. Oncol. 2017, 34, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Ma, J.; Sun, T.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, G.; Wu, P.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L.; et al. Exosomal circRNAs: Biogenesis, effect and application in human diseases. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Fang, N.; Wang, T.; Xu, T.; Shu, Y. CircRNAs in cancer metabolism: A review. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, Y.; Lu, B. The crosstalk between circular RNAs and the tumor microenvironment in cancer metastasis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyiadzis, M.; Whiteside, T.L. Plasma-derived exosomes in acute myeloid leukemia for detection of minimal residual disease: Are we ready? Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2016, 16, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakst, R.L.; Tallman, M.S.; Douer, D.; Yahalom, J. How I treat extramedullary acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2011, 118, 3785–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glažar, P.; Papavasileiou, P.; Rajewsky, N. circBase: A database for circular RNAs. RNA 2014, 20, 1666–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buratin, A.; Gaffo, E.; Molin, A.D.; Bortoluzzi, S. CircIMPACT: An R Package to Explore Circular RNA Impact on Gene Expression and Pathways. Genes 2021, 12, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Molin, A.; Gaffo, E.; Difilippo, V.; Buratin, A.; Tretti Parenzan, C.; Bresolin, S.; Bortoluzzi, S. Correction to: CRAFT a bioinformatics software for custom prediction of circular RNA functions. Briefings Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbab601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yang, Q.; He, A.T.; Yang, B.B. Circular RNAs in cancer: Limitations in functional studies and diagnostic potential. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 75, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liang, D.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Amu, G.; Yang, J.; Yu, L.; Dmochowski, I.J.; Tang, X. Circular siRNAs for Reducing Off-Target Effects and Enhancing Long-Term Gene Silencing in Cells and Mice. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2018, 10, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palombarini, F.; Masciarelli, S.; Incocciati, A.; Liccardo, F.; Di Fabio, E.; Iazzetti, A.; Fabrizi, G.; Fazi, F.; Macone, A.; Bonamore, A.; et al. Self-Assembling Ferritin-Dendrimer Nanoparticles for Targeted Delivery of Nucleic Acids to Myeloid Leukemia Cells. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Name | Gene of Origin | Levels | Pathway Targeted/ Mode of Action | Impact | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| f-circPR | PML-RARA | de novo in AML | AKT signaling | Increased cell proliferation and chemotherapy resistance | [59] |
| f-circM9 | MLL-AF9 | de novo in AML | MAPK and AKT signalling | Increased cell proliferation and chemotherapy resistance | [59] |
| circ ANAPC7 hsa_circ_101141 | ANAPC7 | ↑ in AML | miR181 | Prognostic biomarker | [60] |
| circNPM1 hsa_circ_0075001 | NPM1 | ↑ in AML | mir181 and TLR signalling miR-345-5p/FZD5 | Hematopoietic differentiation Chemotherapy resistance | [61,62] |
| circDLEU hsa_circ_0000488 | DLEU | ↑ in AML | miR496/PRKACB | Increased cell proliferation and apoptosis inhibition | [63] |
| circANXA2 hsa_circ_0035559 | Annexin A2 | ↑ in AML | miR-23a-5p and miR-503-3p | Prognostic biomarker and chemotherapy resistance | [64] |
| circVIM | Vimentin | ↑ in AML | Unknown | Diagnostic and prognostic biomarker | [65] |
| circHIPK2 | HIPK2 | ↓ in AML (APL) | miR-124-3p/CEBPA | Prognostic biomarker and ATRA-induced differentiation | [66] |
| circPAN3 hsa_circ_0100181 | PAN3 | ↑ in AML ADM resistant | AMPK/mTOR miR-153-5p/XIAP | Chemotherapy resistance | [67,68] |
| hsa_circ_0004277 | WDR7 | ↓ in AML | miR-134-5p/SSBP2 | Diagnostic and prognostic biomarker | [69,70] |
| hsa_circ_0003602 | SMARCC1 | ↑ in AML | miR-502-5p/IGF1R | Increased cell proliferation and apoptosis inhibition | [71] |
| circMYBL2 hsa_circ_0006332 | MYBL2 | ↑ in AML FLT3-ITD+ | PTPB1/FLT3 translation | Increased cell proliferation and resistance to quizartinib | [72] |
| hsa_circ_0009910 | MFN2 | ↑ in AML and AML exosomes | miR-5195-3p/GRB10 miR-20a-5p | Increased cell proliferation and apoptosis inhibition | [73,74] |
| hsa_circ_0121582 | GSK3beta | ↓ in AML | miR-224/GSK3β/Wnt/βcatenin | Inhibited cell proliferation | [75] |
| circFOXO3 | FOXO3 | ↓ in AML | Apoptotic pathways | Increased apoptosis Diagnostic and prognostic biomarker | [76] |
| circRNF220 hsa_circ_0012152 | RNF220 | ↑ in AML relapse | miR30a/MYSM1-IER2 | Increased cell proliferation and apoptosis inhibition, biomarker to predict relapse | [77] |
| hsa_circ_100290 | SLC30A7 | ↑ in AML | miR-203/Rab10 | Increased cell proliferation and apoptosis inhibition | [78] |
| circRNF13 hsa_circ_0001346 | RNF13 | ↑ in AML | miR-1224-5p | Increased cell proliferation and apoptosis inhibition | [79] |
| hsa_circ_104700 | PTK2 | ↑ in AML | miR-330-5p/FOXM1 | Increased cell proliferation and apoptosis inhibition | [80] |
| hsa_circ_002483 | PTK2 | ↑ in AML | miR-758-3p/MYC | Increased cell proliferation and apoptosis inhibition | [81] |
| hsa_circ_0005774 | CDK1 | ↑ in AML | miR192-5p/ULK1 | Increased cell proliferation and apoptosis inhibition | [82] |
| circCRKL | CRKL | ↓ in AML | miR-196a-5p/p27 miR-196b-5p/p27 | Inhibited cell proliferation | [83] |
| circPOLA2 | POLA2 | ↑ in AML | miR-34a | Increased cell proliferation | [84] |
| hsa_circ_0079480 | ISPD | ↑ in AML | miR-654-3p/HDGF | Increased cell proliferation and apoptosis inhibition Prognostic biomarker | [85,86] |
| circKLHL8 | KLHL8 | Associated with outcome | miR-155/CDKN1-CDKN2-BCL6-TLR4-CEBPD-CEBPB | Prognostic biomarker | [87] |
| circFBXW7 | FBXW7 | ↓ in AML | Signal transduction Leukocyte differentiation | Tumor suppressor | [87] |
| circ_KCNQ5 hsa_circ_0004136 | KCNQ5 | ↑ in AML | miR-142 miR-622/RAB10 | Increased cell proliferation and apoptosis inhibition | [88,89] |
| hsa_circ_0004520 | VAV2 | ↑ in AML | PLXNB2, VEGFA | Angiogenesis Prognostic biomarker for EMI | [90] |
| hsa_circ_0000370 | FLI-1 | ↑ in AML FLT3-ITD+ | miR-1299/S100A7A | Prognostic biomarker | [91] |
| circ_0040823 | BANP | ↓ in AML | miR-516b/PTEN | Inhibited cell proliferation and increased apoptosis | [92] |
| circPLXNB2 | PLXNB2 | ↑ in AML | PLXNB2 | Increased cell proliferation and migration, apoptosis inhibition Prognostic biomarker for EMI | [93] |
| circ_0002232 | PTEN | ↓ in AML | miR-92a-3p/PTEN | Diagnostic and prognostic biomarker | [94] |
| circ_0012152 | RNF220 | ↑ in AML | miR-625-5p/SOX12 | Increased cell proliferation and apoptosis inhibition | [95] |
| circ_SFMBT2 hsa_circ_0017639 | SFMBT2 | ↑ in AML | miR-582-3p/ZBTB20 | Increased cell proliferation, migration and invasion | [96] |
| circ-PVT1 | PVT1 | ↑ in AML | c-Myc and BCL-2? | Prognostic biomarker | [97] |
| hsa_circ_0001947 | AFF2 | ↓ in AML | miR-329-5p/CREBRF | Inhibited cell proliferation Prognostic biomarker | [98] |
| hsa_circ_0075451 | GMDS | ↑ in AML | miR-330-5p/PRDM16 miR-326/PRDM16 | Prognostic biomarker | [99] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liccardo, F.; Iaiza, A.; Śniegocka, M.; Masciarelli, S.; Fazi, F. Circular RNAs Activity in the Leukemic Bone Marrow Microenvironment. Non-Coding RNA 2022, 8, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8040050
Liccardo F, Iaiza A, Śniegocka M, Masciarelli S, Fazi F. Circular RNAs Activity in the Leukemic Bone Marrow Microenvironment. Non-Coding RNA. 2022; 8(4):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8040050
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiccardo, Francesca, Alessia Iaiza, Martyna Śniegocka, Silvia Masciarelli, and Francesco Fazi. 2022. "Circular RNAs Activity in the Leukemic Bone Marrow Microenvironment" Non-Coding RNA 8, no. 4: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8040050
APA StyleLiccardo, F., Iaiza, A., Śniegocka, M., Masciarelli, S., & Fazi, F. (2022). Circular RNAs Activity in the Leukemic Bone Marrow Microenvironment. Non-Coding RNA, 8(4), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8040050






