Long Noncoding RNA H19: A Novel Oncogene in Liver Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. LncRNAs and H19
2.1. LncRNAs
2.2. H19
3. LncRNA H19 in HCC
3.1. Genetic Polymorphisms
3.2. Epigenetic Modification
3.3. H19/miR-675 Axis
3.4. Sponge of miRNAs
3.5. Drug Resistance
3.6. Cancer Stem Cells
3.7. Other Mechanisms
4. LncRNA H19 in CCA
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asrani, S.K.; Devarbhavi, H.; Eaton, J.; Kamath, P.S. Burden of liver diseases in the world. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.D.; Hainaut, P.; Gores, G.J.; Amadou, A.; Plymoth, A.; Roberts, L.R. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Tang, S. WNT/beta-catenin signaling in the development of liver cancers. Biomed. Pharm. 2020, 132, 110851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perugorria, M.J.; Olaizola, P.; Labiano, I.; Esparza-Baquer, A.; Marzioni, M.; Marin, J.J.G.; Bujanda, L.; Banales, J.M. Wnt-beta-catenin signalling in liver development, health and disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGlynn, K.A.; Petrick, J.L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2021, 73, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udompap, P.; Kim, D.; Kim, W.R. Current and future burden of chronic nonmalignant liver disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 2031–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brannan, C.I.; Dees, E.C.; Ingram, R.S.; Tilghman, S.M. The product of the H19 gene may function as an RNA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1990, 10, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Beylerli, O.; Gareev, I.; Sufianov, A.; Ilyasova, T.; Guang, Y. Long noncoding RNAs as promising biomarkers in cancer. Noncoding RNA Res. 2022, 7, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipoor, B.; Parvar, S.N.; Sabati, Z.; Ghaedi, H.; Ghasemi, H. An updated review of the H19 lncRNA in human cancer: Molecular mechanism and diagnostic and therapeutic importance. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 6357–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.F.; Li, Y.C.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.B. The Effect of LncRNA H19/miR-194-5p Axis on the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Colorectal Adenocarcinoma. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 50, 196–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, H.; Matsuda, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Michishita, M.; Takahashi, K.; Sasaki, N.; Ishikawa, N.; Aida, J.; Takubo, K.; Arai, T.; et al. Reduced expression of the H19 long non-coding RNA inhibits pancreatic cancer metastasis. Lab. Investig. 2018, 98, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Luo, M.; Zhang, J.; Guo, B.; Singh, S.; Lin, X.; Xiong, H.; Ju, S.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; et al. The role of lncRNA H19 in tumorigenesis and drug resistance of human Cancers. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1005522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecerf, C.; Le Bourhis, X.; Adriaenssens, E. The long non-coding RNA H19: An active player with multiple facets to sustain the hallmarks of cancer. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 4673–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danko, C.G.; Hah, N.; Luo, X.; Martins, A.L.; Core, L.; Lis, J.T.; Siepel, A.; Kraus, W.L. Signaling pathways differentially affect RNA polymerase II initiation, pausing, and elongation rate in cells. Mol. Cell 2013, 50, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, X.-F.; Huang, S.-F.; Chen, L.-J.; Xu, L.; Ye, W.-C. Targeting epigenetics and lncRNAs in liver disease: From mechanisms to therapeutics. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 172, 105846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uszczynska-Ratajczak, B.; Lagarde, J.; Frankish, A.; Guigó, R.; Johnson, R. Towards a complete map of the human long non-coding RNA transcriptome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbastabar, M.; Sarfi, M.; Golestani, A.; Khalili, E. lncRNA involvement in hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis and prognosis. EXCLI J. 2018, 17, 900–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposti, D.D.; Hernandez-Vargas, H.; Voegele, C.; Fernandez-Jimenez, N.; Forey, N.; Bancel, B.; Le Calvez-Kelm, F.; McKay, J.; Merle, P.; Herceg, Z. Identification of novel long non-coding RNAs deregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma using RNA-sequencing. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 31862–31877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, F.J.; Zheng, J.J.; Dong, P.H.; Fan, X.M. Long non-coding RNAs and hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 3, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seidl, C.I.; Stricker, S.H.; Barlow, D.P. The imprinted Air ncRNA is an atypical RNAPII transcript that evades splicing and escapes nuclear export. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 3565–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabory, A.; Jammes, H.; Dandolo, L. The H19 locus: Role of an imprinted non-coding RNA in growth and development. Bioessays 2010, 32, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, R.; Yang, J.; Sun, L.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Z.; Puri, P.; Gurley, E.C.; Lai, G.; Tang, Y. The role of long noncoding RNA H19 in gender disparity of cholestatic liver injury in multidrug resistance 2 gene knockout mice. Hepatology 2017, 66, 869–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Tai, Y.-L.; Way, G.; Zeng, J.; Zhao, D.; Su, L.; Jiang, X.; Jackson, K.G.; Wang, X.; Gurley, E.C. RNA binding protein HuR protects against NAFLD by suppressing long noncoding RNA H19 expression. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachmilewitz, J.; Goshen, R.; Ariel, I.; Schneider, T.; de Groot, N.; Hochberg, A. Parental imprinting of the human H19 gene. FEBS Lett. 1992, 309, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monnier, P.; Martinet, C.; Pontis, J.; Stancheva, I.; Ait-Si-Ali, S.; Dandolo, L. H19 lncRNA controls gene expression of the Imprinted Gene Network by recruiting MBD1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20693–20698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thorvaldsen, J.L.; Duran, K.L.; Bartolomei, M.S. Deletion of the H19 differentially methylated domain results in loss of imprinted expression of H19 and Igf2. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 3693–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Hylemon, P.B.; Zhou, H. Long Noncoding RNA H19: A Key Player in Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2021, 74, 1652–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keniry, A.; Oxley, D.; Monnier, P.; Kyba, M.; Dandolo, L.; Smits, G.; Reik, W. The H19 lincRNA is a developmental reservoir of miR-675 that suppresses growth and Igf1r. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, J.; Ma, L.; Chen, X.L.; Huang, X.H.; Wang, Q. Downregulation of LncRNAH19 and MiR-675 promotes migration and invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through AKT/GSK-3beta/Cdc25A signaling pathway. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 2014, 34, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; He, M.; Chen, Q.; Liang, S. LncRNA H19 acts as miR-301a-3p sponge to alleviate lung injury in mice with sepsis by regulating Adcy1. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2022, 44, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Feng, Q.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, D.; Jin, J.; Zhang, S.; Bai, Y.; Xu, J. LncRNA H19 sponges miR-103-3p to promote the high phosphorus-induced osteoblast phenotypic transition of vascular smooth muscle cells by upregulating Runx2. Cell. Signal. 2022, 91, 110220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.-C.; Fu, W.-M.; Wong, C.-W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.-M.; Hu, G.-X.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, L.-J.; Wan, D.C.-C.; Zhang, J.-F. The lncRNA H19 promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition by functioning as miRNA sponges in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 22513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Han, S.; Kusumanchi, P.; Huda, N.; Jiang, Y.; Liangpunsakul, S. Long noncoding RNA H19—A new player in the pathogenesis of liver diseases. Transl. Res. 2021, 230, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovarelli, M.; Bucci, G.; Ramos, A.; Bordo, D.; Wilusz, C.J.; Chen, C.-Y.; Puppo, M.; Briata, P.; Gherzi, R. H19 long noncoding RNA controls the mRNA decay promoting function of KSRP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E5023–E5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sayiner, M.; Golabi, P.; Younossi, Z.M. Disease burden of hepatocellular carcinoma: A global perspective. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Shoorei, H.; Bahroudi, Z.; Abak, A.; Taheri, M. The role of H19 lncRNA in conferring chemoresistance in cancer cells. Biomed. Pharm. 2021, 138, 111447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietze, L.; Kessler, S.M. The Good, the Bad, the Question-H19 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Liao, Y.; Gong, D.; Zhao, X.; Ji, W. Effect of long non-coding RNA H19 on oxidative stress and chemotherapy resistance of CD133+ cancer stem cells via the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 502, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Wang, Q.; Hu, S.; Yang, X. Rs217727 polymorphism in H19 promotes cell apoptosis by regulating the expressions of H19 and the activation of its downstream signaling pathway. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 7279–7291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Li, Z.; Wu, D. The long non-coding RNA H19 induces hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by up-regulating autophagy in the hepatoma carcinoma cells. Biol. Res. 2019, 52, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Han, T.; Liu, K.; Lei, C.G.; Wang, Z.C.; Shi, G.J. LncRNA H19 promotes the development of hepatitis B related hepatocellular carcinoma through regulating microRNA-22 via EMT pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 5392–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, L.; Lu, B.; Zhao, M.; Li, L.; Sun, W.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, B. LncRNA H19/microRNA-675/PPARalpha axis regulates liver cell injury and energy metabolism remodelling induced by hepatitis B X protein via Akt/mTOR signalling. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 116, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.Q.; Li, L.; Lu, C.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, H. Involvement of H19/miR-326 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma development through modulating TWIST1. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 5153–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Han, C.; Ungerleider, N.; Chen, W.; Song, K.; Wang, Y.; Kwon, H.; Ma, W.; Wu, T. A Transforming Growth Factor-beta and H19 Signaling Axis in Tumor-Initiating Hepatocytes That Regulates Hepatic Carcinogenesis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1549–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Fan, R.G.; Qin, C.L.; Jia, J.; Wu, X.D.; Zha, W.Z. LncRNA-H19 activates CDC42/PAK1 pathway to promote cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting miR-15b in hepatocellular carcinoma. Genomics 2019, 111, 1862–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Xue, S.; Zhang, M.; Xu, H.; Hu, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Guo, M.; Cui, H. Aberrant NSUN2-mediated m(5)C modification of H19 lncRNA is associated with poor differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2020, 39, 6906–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xing, N.; Yang, T.; Liu, J.; Zhao, H.; He, J.; Ai, Y.; Yang, J. Exosomal lncRNA H19 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma treated with Propofol via miR-520a-3p/LIMK1 axis. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 7218–7230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Yan, L.; Mao, J.; Shen, J.; Chen, W.; Xue, F. Long non-coding RNA H19 is involved in sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by upregulating miR-675. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 44, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Guo, J.; Xiao, P.; Ning, J.; Zhang, R.; Liu, P.; Yu, W.; Xu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, J. Macrophages-induced long noncoding RNA H19 up-regulation triggers and activates the miR-193b/MAPK1 axis and promotes cell aggressiveness in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2020, 469, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shen, L.; Yuan, W.; Liu, Y.; Guo, R.; Luo, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Xie, Z.; Wu, G.; Wu, W.; et al. Loss of SRSF2 triggers hepatic progenitor cell activation and tumor development in mice. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Huang, S.; Liu, D.; Jiang, Z.; Jin, Q.; Li, C.; Da, L.; Yao, Q.; Wang, D. Galangin promotes cell apoptosis through suppression of H19 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 5546–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamaev, L.; Mizrahi, L.; Friehmann, T.; Rosenberg, N.; Pappo, O.; Olam, D.; Zeira, E.; Bahar Halpern, K.; Caruso, S.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; et al. The pro-oncogenic effect of the lncRNA H19 in the development of chronic inflammation-mediated hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2021, 40, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harari-Steinfeld, R.; Gefen, M.; Simerzin, A.; Zorde-Khvalevsky, E.; Rivkin, M.; Ella, E.; Friehmann, T.; Gerlic, M.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Caruso, S.; et al. The lncRNA H19-Derived MicroRNA-675 Promotes Liver Necroptosis by Targeting FADD. Cancers 2021, 13, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Chu, L.; Liang, J.; Tan, X.; Wang, Y.; Wen, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Liao, J.; et al. H19 Promotes HCC Bone Metastasis Through Reducing Osteoprotegerin Expression in a Protein Phosphatase 1 Catalytic Subunit Alpha/p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase-Dependent Manner and Sponging microRNA 200b-3p. Hepatology 2021, 74, 214–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, W.C.; Bao, G.J.; Yang, F.W.; Sun, L.; Han, R. Role of lncRNA NR2F1-AS1 and lncRNA H19 Genes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Their Effects on Biological Function of Huh-7. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, H.; Ni, Z.; Feng, H.; Xing, Y.; Wu, X.; Huang, D.; Chen, L.; Niu, Y.; Shi, G. Combination of curcumin with N-n-butyl haloperidol iodide inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma malignant proliferation by downregulating enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2)-lncRNA H19 to silence Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Phytomedicine 2021, 91, 153706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, F.F.; Zheng, Y.B.; Shi, C.J.; Zhang, F.W.; Zhang, J.F.; Fu, W.M. H19-Wnt/beta-catenin regulatory axis mediates the suppressive effects of apigenin on tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 893, 173810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habashy, D.A.; Hamad, M.H.M.; Ragheb, M.; Khalil, Z.A.; El Sobky, S.A.; Hosny, K.A.; Esmat, G.; El-Ekiaby, N.; Fawzy, I.O.; Abdelaziz, A.I. Regulation of IGF2BP1 by miR-186 and its impact on downstream lncRNAs H19, FOXD2-AS1, and SNHG3 in HCC. Life Sci. 2022, 310, 121075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahon, P.; Zucman-Rossi, J. Single nucleotide polymorphisms and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Esmaeili, M.; Taheri, M. H19 lncRNA: Roles in tumorigenesis. Biomed. Pharm. 2020, 123, 109774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.L.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Chen, H.H.; Ma, S.N.; Wu, R.; Cai, W.S. The association of polymorphisms in lncRNA-H19 with hepatocellular cancer risk and prognosis. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, E.R.; Chou, Y.E.; Liu, Y.F.; Hsueh, K.C.; Lee, H.L.; Yang, S.F.; Su, S.C. Association of lncRNA H19 Gene Polymorphisms with the Occurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Genes 2019, 10, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.; Xing, H.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, N.; Yang, M. LncRNA H19 modulated by miR-146b-3p/miR-1539-mediated allelic regulation in transarterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 3063–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.S.; Ban, H.S.; Hur, K.; Cho, H.S. The Epigenetic Regulation of HCC Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braghini, M.R.; Lo Re, O.; Romito, I.; Fernandez-Barrena, M.G.; Barbaro, B.; Pomella, S.; Rota, R.; Vinciguerra, M.; Avila, M.A.; Alisi, A. Epigenetic remodelling in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Su, Y.; Maimaitiyiming, Y.; Yang, S.; Shen, Z.; Lin, S.; Shen, S.; Zhan, G.; Wang, F.; et al. Distinct Roles of m(5)C RNA Methyltransferase NSUN2 in Major Gynecologic Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 786266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, W.; Kwok, T. Riboregulator H19 induction of MDR1-associated drug resistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncogene 2007, 26, 4877–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Fang, J.; Xu, A.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z. H19-derived miR-675 contributes to bladder cancer cell proliferation by regulating p53 activation. Tumour. Biol. 2016, 37, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, X.; Wu, C.; Deng, D.; Yao, Z. Roles of the H19/microRNA-675 axis in the proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Jia, S.; Wu, M.; An, J.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, W.; Lu, D. miR675 upregulates long noncoding RNA H19 through activating EGR1 in human liver cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 31958–31984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelsattar, S.; Sweed, D.; Kamel, H.F.M.; Kasemy, Z.A.; Gameel, A.M.; Elzohry, H.; Ameen, O.; Elgizawy, E.I.; Sallam, A.; Mosbeh, A.; et al. The Potential Utility of Circulating Oncofetal H19 Derived miR-675 Expression versus Tissue lncRNA-H19 Expression in Diagnosis and Prognosis of HCC in Egyptian Patients. Biomolecules 2022, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.-S.; Hur, K.; Cho, H.-S.; Ban, H.S. Epigenetic associations between lncRNA/circRNA and miRNA in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Jiang, J. The role of lncRNA-mediated ceRNA regulatory networks in pancreatic cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angrand, P.-O.; Vennin, C.; Le Bourhis, X.; Adriaenssens, E. The role of long non-coding RNAs in genome formatting and expression. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mak, L.-Y.; Wong, D.K.-H.; Pollicino, T.; Raimondo, G.; Hollinger, F.B.; Yuen, M.-F. Occult hepatitis B infection and hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology, virology, hepatocarcinogenesis and clinical significance. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 952–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Guo, J.; Li, W.; Lu, Y.; Fu, S.; Xie, X.; Xia, H.; Dong, X.; Chen, Y.; Quan, M. Hepatitis B virus X protein induces expression of alpha-fetoprotein and activates PI3K/mTOR signaling pathway in liver cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 12196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.M.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Mustapic, M.; Kapogiannis, D.; Gorospe, M. RNA in extracellular vesicles. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2017, 8, e1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabiati, M.; Salvadori, C.; Basta, G.; Del Turco, S.; Aretini, P.; Cecchettini, A.; Del Ry, S. miRNA and long non-coding RNA transcriptional expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cell line-secreted extracellular vesicles. Clin. Exp. Med. 2022, 22, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescitelli, R.; Lässer, C.; Szabo, T.G.; Kittel, A.; Eldh, M.; Dianzani, I.; Buzás, E.I.; Lötvall, J. Distinct RNA profiles in subpopulations of extracellular vesicles: Apoptotic bodies, microvesicles and exosomes. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 20677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Hu, J.-G.; Lin, X.-J.; Li, X.-G. Bone metastases from hepatocellular carcinoma: Clinical features and prognostic factors. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2017, 16, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, T.; Lee, S.S.; Kaseb, A.O. Systemic therapy of liver cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2021, 149, 257–294. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Yang, F. The role of long non-coding RNA H19 in breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, K.-F.; Liang, W.-C.; Feng, L.; Pang, J.-X.; Waye, M.M.-Y.; Zhang, J.-F.; Fu, W.-M. H19 mediates methotrexate resistance in colorectal cancer through activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 350, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.W.S.; Xiang, X.; Garg, M.; Le, M.T.; Wong, A.L.-A.; Wang, L.; Goh, B.-C. The double-edged sword of H19 lncRNA: Insights into cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2021, 500, 253–262. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Yuan, L.; Li, W.; Xu, K.; Yang, L. The LncRNA H19/miR-193a-3p axis modifies the radio-resistance and chemotherapeutic tolerance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting PSEN1. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 8325–8335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.C.; Yeh, C.T.; Lin, K.H. Cancer Stem Cell Functions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Comprehensive Therapeutic Strategies. Cells 2020, 9, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Guo, Y.; Hu, Y.; Bao, X.; Zhu, X.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Tong, Z.; Liu, L.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Immunotherapy for targeting cancer stem cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics 2021, 11, 3489–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, Á.; Gil-Gómez, A.; de la Cruz-Ojeda, P.; Muñoz-Hernández, R.; Sánchez-Torrijos, Y.; Gallego-Durán, R.; Millán, R.; Rico, M.C.; Montero-Vallejo, R.; Gato-Zambrano, S. Long non-coding RNA H19 as a biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 1410–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conigliaro, A.; Costa, V.; Lo Dico, A.; Saieva, L.; Buccheri, S.; Dieli, F.; Manno, M.; Raccosta, S.; Mancone, C.; Tripodi, M.; et al. CD90+ liver cancer cells modulate endothelial cell phenotype through the release of exosomes containing H19 lncRNA. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fazi, B.; Garbo, S.; Toschi, N.; Mangiola, A.; Lombari, M.; Sicari, D.; Battistelli, C.; Galardi, S.; Michienzi, A.; Trevisi, G. The lncRNA H19 positively affects the tumorigenic properties of glioblastoma cells and contributes to NKD1 repression through the recruitment of EZH2 on its promoter. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 15512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.-M.; Lin, Z.-Y.; Yang, Z.-H.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Wan, D.; Zhong, J.-L.; Zhuang, P.-L.; Huang, Z.-Q.; Zhou, B.; Chen, W.-L. IncRNA H19 promotes tongue squamous cell carcinoma progression through β-catenin/GSK3β/EMT signaling via association with EZH2. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 3474. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raveh, E.; Matouk, I.J.; Gilon, M.; Hochberg, A. The H19 Long non-coding RNA in cancer initiation, progression and metastasis—A proposed unifying theory. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rizvi, S.; Khan, S.A.; Hallemeier, C.L.; Kelley, R.K.; Gores, G.J. Cholangiocarcinoma—Evolving concepts and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wangyang, Z.; Daolin, J.; Yi, X.; Zhenglong, L.; Lining, H.; Yunfu, C.; Xingming, J. NcRNAs and Cholangiocarcinoma. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Huang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhong, X.; Tai, S.; Jiang, X.; Cui, Y. Functions and roles of long noncoding RNA in cholangiocarcinoma. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 17113–17126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merdrignac, A.; Papoutsoglou, P.; Coulouarn, C. Long Noncoding RNAs in Cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 2021, 73, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, R.; Huang, Z.; Gurley, E.C.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; He, H.; Yang, H.; Lai, G.; Zhang, L. Cholangiocyte-derived exosomal long noncoding RNA H19 promotes cholestatic liver injury in mouse and humans. Hepatology 2018, 68, 599–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Liu, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhao, D.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Gurley, E.C.; Chen, W.; Hylemon, P.B. Cholangiocyte-derived exosomal lncRNA H19 promotes macrophage activation and hepatic inflammation under cholestatic conditions. Cells 2020, 9, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.; Li, X.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, X.; Gurley, E.C.; Liang, G.; Chen, W.; Lai, G. Cholangiocyte-derived exosomal long noncoding RNA H19 promotes hepatic stellate cell activation and cholestatic liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1317–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Trottier, J.; Beaudoin, M.; Zhang, L.; Pope, C.; Peng, G.; Barbier, O.; Zhong, X. H19 promotes cholestatic liver fibrosis by preventing ZEB1-mediated inhibition of epithelial cell adhesion molecule. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1183–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Kai, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, Z.; Shao, J.; Tan, S.; Chen, A.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S. HIF-1α-upregulated lncRNA-H19 regulates lipid droplet metabolism through the AMPKα pathway in hepatic stellate cells. Life Sci. 2020, 255, 117818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-M.; Xia, S.-W.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Yang, X.; Kai, J.; Cheng, X.-D.; Shao, J.-J.; Tan, S.-Z.; Chen, A.-P. LncRNA-H19 induces hepatic stellate cell activation via upregulating alcohol dehydrogenase III-mediated retinoic acid signals. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 84, 106470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, R.; Li, X.; Gurley, E.C.; Hylemon, P.B.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Cai, W. Long noncoding RNA H19 contributes to cholangiocyte proliferation and cholestatic liver fibrosis in biliary atresia. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1658–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Huang, W.; Wu, J. H19 potentiates let-7 family expression through reducing PTBP1 binding to their precursors in cholestasis. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, G.; Huan, Y.; Li, L.; Gao, W. Comprehensive analysis of competing endogenous RNA networks associated with cholangiocarcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 4103–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.T.; Ye, H.; Wei, P.P.; Han, B.W.; He, B.; Chen, Z.H.; Chen, Y.Q. LncRNAs H19 and HULC, activated by oxidative stress, promote cell migration and invasion in cholangiocarcinoma through a ceRNA manner. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, X.; Cui, Y. Overexpression of long noncoding RNA H19 indicates a poor prognosis for cholangiocarcinoma and promotes cell migration and invasion by affecting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Biomed. Pharm. 2017, 92, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.; Zhao, L.; Kang, Q.; Li, J.; Chen, K.; Fu, H. Transcription factor HIF1alpha promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of cholangiocarcinoma via long noncoding RNA H19/microRNA-612/Bcl-2 axis. Transl. Res. 2020, 224, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Animal Models or Human Samples | In Vitro Models | Targets | Potential Mechanisms | Reference and Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCC patients and cancer-free controls (n = 42) | Huh 7 | oxidative stress MAPK/ERK | Downregulation of H19-induced oxidative stress and reversed chemotherapy resistance of CD133+ cancer stem cells by blocking the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway in HCC | [38], 2018 |
| HCC patients (n = 214) | HepG2 and huh-7 cell lines | miR-675/FADD/caspase-8/caspase-3 | H19 upregulated the expression of miR-675, reducing the expression of FADD, caspase-3, and caspase-8. | [39], 2018 |
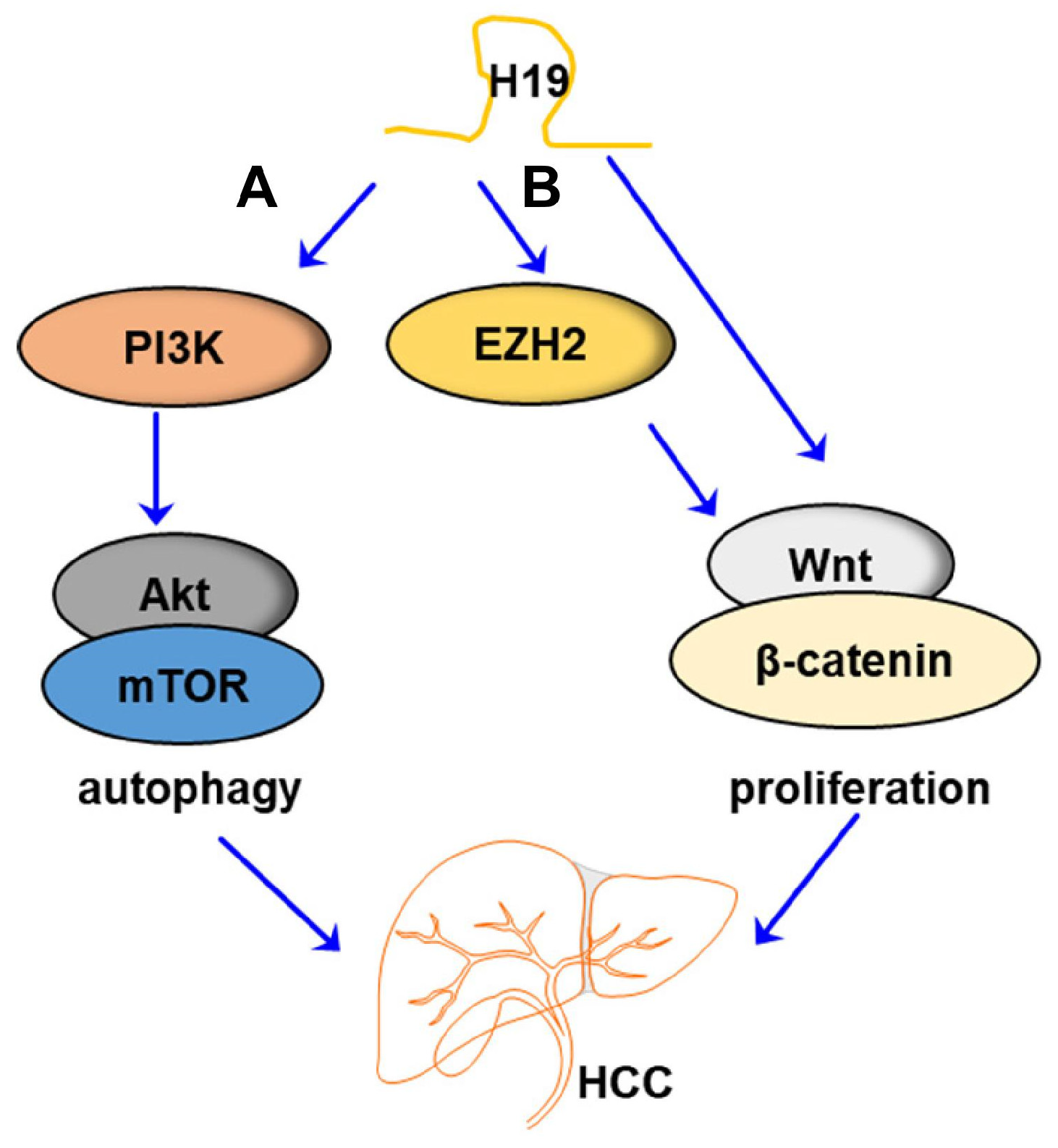
| _ | HepG2 and HCCLM3 cell lines | PI3K-Akt-mTOR/ autophagy | H19 induced the expression of PI3K, which further activated the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway, thus modulating autophagy in HCC | [40], 2019 |
| HBV-related HCC liver tissues and matched normal tissue (n = 20) | HepG2, HepG2.2.15, and LO2 cell lines | miRNA-22 | H19 promoted the development of hepatitis B-related HCC by regulating miRNA-22 via the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) pathway | [41], 2019 |
| HBV patient liver tissues and matched normal tissue (n = 20) | LO2 cell lines | miR-675/PPARα Akt/mTOR | H19/miR-675 suppressed the expression of PPARα, which further activated the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway, thus modulating energy metabolism and cell apoptosis | [42], 2019 |
| _ | Hep3B, HepG2, MHCC-97L, SK-hep1, Hun7, SMCC-7721 and LO2 cell lines | miR-326/TWIST1 | H19 sponged miR-326, thus increasing the expression of TWIST1, eventually promoting the development of HCC | [43], 2019 |
| C57/BL6J mice transplanted with TICs from DEN-treated Tgfbr2fl/fl mice by splenic injection followed by i.p. injection of CCl4 and tail vein injection of Ad-Cre. | TICs isolated from B6.129S6-Tgfbr2fl/fl mice injected with DEN | TGFβ/Tgfbr2-Sox2 | TGF-β signaling in TICs inhibited H19 expression via Sox2, which was crucial for the inhibition of HCC development | [44], 2019 |
| HCC patient liver tissues and the adjacent normal liver tissues (n = 46) | HepG2, SMMC-7721, Bel-7402, and Huh-7 cell lines | miR-15b/CDC42/PAK1 axis | H19 activated CDC42/PAK1 pathway to promote cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting miR-15b in hepatocellular carcinoma | [45], 2019 |
| HCC patient liver tissues and matched noncancerous liver tissues (n = 55) | HepG2 cell lines | NSUN2 G3BP1/Myc | NSUN2-mediated m5C-modified H19 promoted HCC by recruiting G3BP1 oncoprotein, which leads to MYC accumulation | [46], 2020 |
| BALB/c nude mice injected with Huh7 cells, then injected with exosomes derived from Huh7 cells treated with Propofol and Vector or Over H19. | Huh7, MHCC97-H, and HCCLM3 cell lines | miR-520a-3p/ LIMK1 axis | Exosomal H19 facilitated the malignant potential of Propofol-exposed HCC cells via miR-520a-3p/LIMK1 axis | [47], 2020 |
| HCC patient liver tissues (n = 242) with matched nontumor tissues (n = 298) | Huh7, Hep3B, SNU-449, and SNU-387 cell lines | miR-675 | Knockdown of H19 sensitized HCC cells to sorafenib by downregulating miR-675, thereby preventing EMT | [48], 2020 |
| HCC patient liver tissues (n = 64) and TCGA cohort (n = 393) | HepG2, Hep2B2, THP-1, SK-OV-3, and NCI-H520 cell lines | miRNA-193b MAPK1 axis | TAM-derived H19 promoted tumor cell migration and invasion and immune cell infiltration by hijacking miR-193b as a sponge and activating MAPK | [49], 2020 |
| Srsf2f/f mice and Srsf2f/f-Mx1cre mice | _ | Srsf2/IGF2 PI3K/Akt MAPK/ERK | Demethylation-induced high expression of IGF2/H19, followed by activation of PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK signaling, contributed to the tumorigenesis of Srsf2 HKO mice | [50], 2020 |
| Nude mice injected with pcDNA3.1-H19, and H19-KO cells or control | MHCC97H, MHCC97L, and HCC-LM3 cell lines | p53 | Knockdown of H19 induced the protein expression of p53, eventually promoting cell apoptosis | [51], 2020 |
| 16-month-old female and 17.7-month-old male C57/BL6 Mdr2−/− and Mdr2−/−/H19−/− DKO mice | Primary cells | liver injury/hepatocyte polyploidy | H19 was a pro-oncogenic during the development of chronic inflammation-mediated HCC by increasing liver injury and decreasing hepatocyte polyploidy | [52], 2020 |
| HCC patient samples and matched healthy controls (n = 60); BALB/C mice injected with miR-675 or siCtrl | Huh7, HepG2, Hep3B, and FLC4 cell lines | miR-675/FADD | miR-675 repressed FADD, leading to the development of necroptosis | [53], 2021 |
| HCC patient samples (n = 81) BALB/cA-nude mice injected with BM4-1/H19 and BM4-1/H19 | MDA-MB-231 and PC-3 cell lines | PPP1CA/p38MAPK and miR-200b-3p | H19 promoted HCC bone metastasis by upregulating zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1) via functioning as a sponge for miR-200b-3p | [54], 2021 |
| HCC patients and matched healthy controls (n = 42) | BEL-7402, Huh-7, and HL-7702 cell lines | miR-140-5p/EMT process and apoptosis. | H19 targeted miR-140-5p and effectively inhibited the EMT process of HCC cells and promoted apoptosis | [55], 2021 |
| _ | Hep3B and SMMC-7721 cell lines | EZH2/ Wnt/β-catenin | EZH2 interacted with H19 in HCC development in regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling | [56], 2021 |
| _ | LO2, SMMC-7721 and HepG2 cell lines | Wnt/β-catenin | H19 overexpression activated canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling | [57], 2021 |
| HCC patient tissues and matched healthy controls (n = 10) | Huh-7 cell lines | miR-186/IGF2BP1 | miR-186 decreased IGF2BP1, thus inhibiting H19, exerting tumor suppressor effects in HCC | [58], 2022 |
| Number of Cases | H19 Variant Associated with HCC Risk | Reference and Year |
|---|---|---|
| 472 HCC patients and 472 healthy controls | rs2839698 | [61], 2018 |
| 214 HCC patients | rs217727 | [39], 2018 |
| 359 HCC patients and 1190 healthy controls | rs2839698 rs3741219 rs2107425 rs3024270 | [62], 2019 |
| 273 human HCC patients treated with transarterial chemoembolization and 26 HCC patients receiving curative resection | rs3741219 | [63], 2021 |
| Animal Models or Human Samples | In Vitro Models | Targets | Potential Mechanisms | Reference and Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
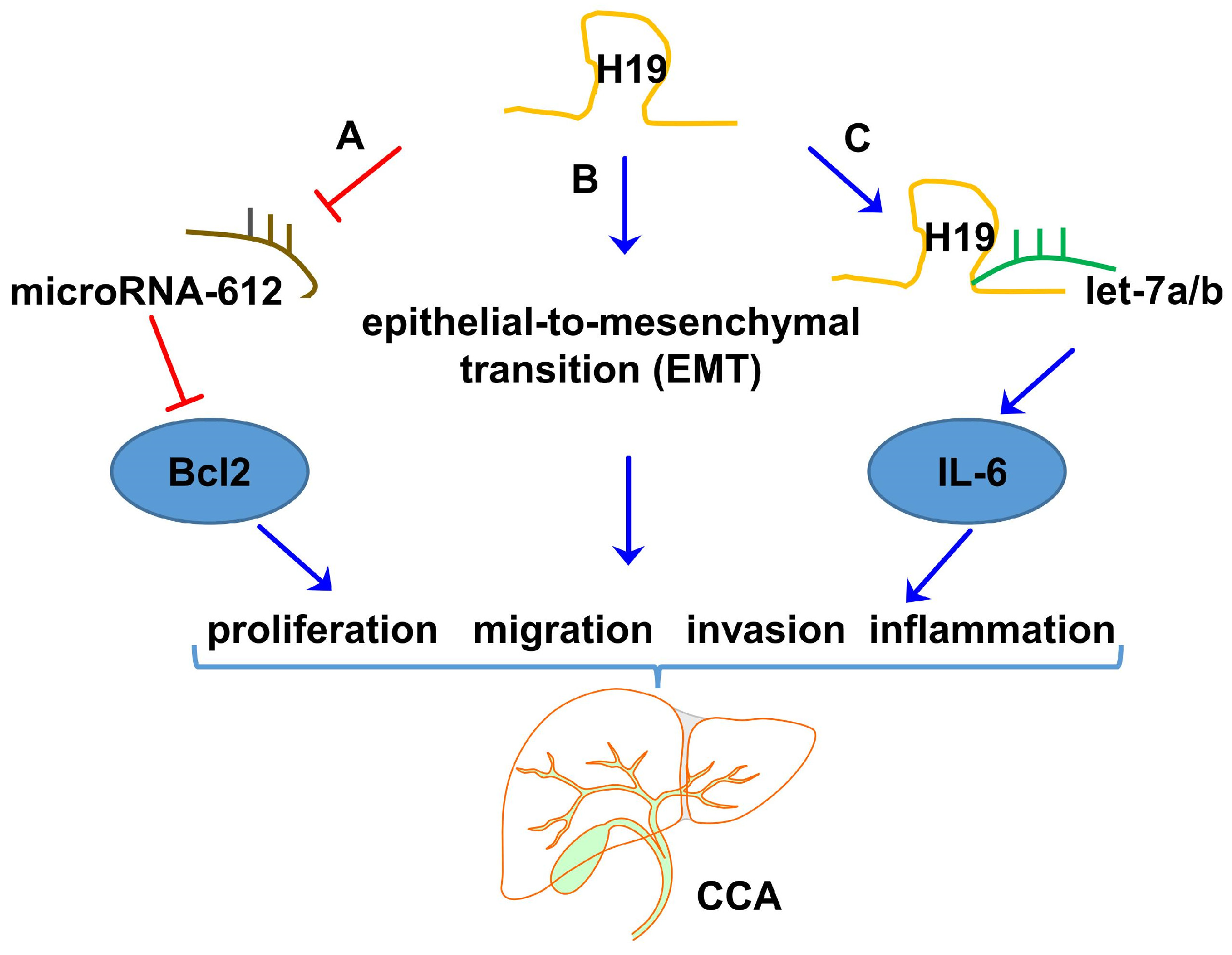
| year_ | QBC939, SK-cha-1, and RBE cell lines | let-7a/IL-6 | H19 functioned as competing endogenous RNAs by sponging let-7a/b, which activated pivotal inflammation cytokine IL-6. | [106], 2016 |
| Human CCA tissues and corresponding adjacent non-tumor tissues (n = 56) | QBC939 and RBE cell lines | EMT | H19 promoted cell migration and invasion by affecting EMT | [107], 2017 |
| Human CCA tissues and matched normal bile duct tissues (n = 43) | HUCCT1, QBC939, HCCC 9810, and RBE cell lines | HIF1α/miRNA-612/Bcl-2 axis | Transcription factor HIF1α promoted proliferation, migration, and invasion of cholangiocarcinoma via H19/miRNA-612/Bcl-2 axis | [108], 2020 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zeng, J.; Chen, W.; Fan, J.; Hylemon, P.B.; Zhou, H. Long Noncoding RNA H19: A Novel Oncogene in Liver Cancer. Non-Coding RNA 2023, 9, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9020019
Wang Y, Zeng J, Chen W, Fan J, Hylemon PB, Zhou H. Long Noncoding RNA H19: A Novel Oncogene in Liver Cancer. Non-Coding RNA. 2023; 9(2):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9020019
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yanyan, Jing Zeng, Weidong Chen, Jiangao Fan, Phillip B. Hylemon, and Huiping Zhou. 2023. "Long Noncoding RNA H19: A Novel Oncogene in Liver Cancer" Non-Coding RNA 9, no. 2: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9020019
APA StyleWang, Y., Zeng, J., Chen, W., Fan, J., Hylemon, P. B., & Zhou, H. (2023). Long Noncoding RNA H19: A Novel Oncogene in Liver Cancer. Non-Coding RNA, 9(2), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9020019








