Flexible Carbon Aerogels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Classification of Aerogels
2.2. Properties of Flexible Resorcinol-Formaldehyde and Carbon Aerogels
2.3. Microstructure of Resorcinol-Formaldehyde and Corresponding Carbon Aerogels
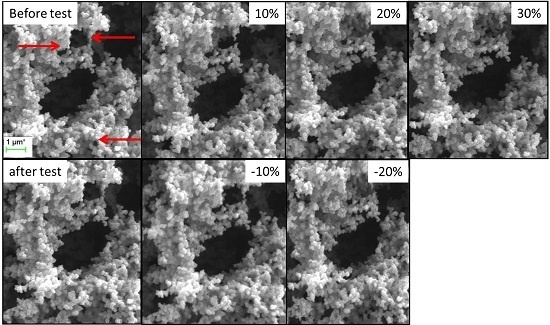
2.4. SEM with In-Situ Compression Test of Low-Flexible and Super-Flexible Carbon Aerogels
2.4.1. Low-Flexible Carbon Aerogel
2.4.2. Super-Flexible Carbon Aerogel
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Methods
3.2. Synthesis of Aerogels
3.3. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RF | Resorcinol-Formaldehyde |
| W | Water |
| C | Carbon |
| sf | super-flexible |
| lf | low-flexible |
References
- Pekala, R.W. Organic Carbon Aerogels from the Sol-Gel Polymerization of Phenolic-Furfural Mixtures. U.S. Patent 5744510A, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Biener, J.; Stadermann, M.; Suss, M.; Worsley, M.A.; Biener, M.M.; Rose, K.A.; Baumann, T.F. Advanced carbon aerogels for energy applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Huang, C.G.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Li, Z. Investigation of the microwave absorbing properties of carbon aerogels. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2002, 90, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrubesh, L.W. Aerogel applications. J. Noncryst. Solids 1998, 225, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekala, R.W.; Farmer, J.C.; Alviso, C.T.; Tran, T.D.; Mayer, S.T.; Miller, J.M.; Dunn, B. Carbon aerogels for electrochemical applications. J. Noncryst. Solids 1998, 225, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliger, R.; Fischer, U.; Herta, C.; Fricke, J. High surface area carbon aerogels for supercapacitors. J. Noncryst. Solids 1998, 225, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.-W.; Hyun, S.-H. Capacitance control of carbon aerogel electrodes. J. Noncryst. Solids 2004, 347, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekala, R.W.; Alviso, C.T. Carbon Aerogels and Xerogels; MRS Online Proceedings Library: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1992; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Reichenauer, G.; Fricke, J. Carbon aerogels derived from cresol–resorcinol–formaldehyde for supercapacitors. Carbon 2002, 40, 2955–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Endo, M.; Kaneko, K. A review of synthesis and nanopore structures of organic polymer aerogels and carbon aerogels. Recent Pat. Chem. Eng. 2008, 1, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekala, R.W. Organic aerogels from the polycondensation of resorcinol with formaldehyde. J. Mater. Sci. 1989, 24, 3221–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, O.; Ehrburger-Dolle, F.; Rieker, T.P.; Pajonk, G.M.; Pinto, N.; Venkateswara Rao, A. Small-angle X-ray scattering of a new series of organic aerogels. J. Noncryst. Solids 2001, 285, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzbacher, C.I.; Meier, S.R.; Pierce, J.R.; Korwin, M.L. Carbon aerogels as broadband non-reflective materials. J. Noncryst. Solids 2001, 285, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Ritter, J. Effect of synthesis pH on the structure of carbon xerogels. Carbon 1997, 35, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliger, R.; Bock, V.; Petricevic, R.; Tillotson, T.; Geis, S.; Fricke, J. Carbon aerogels from dilute catalysis of resorcinol with formaldehyde. J. Noncryst. Solids 1997, 221, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikawa, T.; Hayashi, J.I.; Muroyama, K. Controllability of pore characteristics of resorcinol–formaldehyde carbon aerogel. Carbon 2004, 42, 1625–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuß, M.; Ratke, L. Subcritically dried RF-aerogels catalysed by hydrochloric acid. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2008, 47, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Nishimura, T.; Suzuki, T.; Tamon, H. Control of mesoporosity of carbon gels prepared by sol-gel polycondensation and freeze drying. J. Noncryst. Solids 2001, 288, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czakkel, O.; Marthi, K.; Geissler, E.; László, K. Influence of drying on the morphology of resorcinol–formaldehyde-based carbon gels. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 86, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Shen, J.; Deng, Z.; Lai, Z.; Zhou, B.; Attia, S.; Chen, L. The investigation of the adsorption character of carbon aerogels. Nanostruct. Mater. 1999, 11, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanzawa, Y.; Hatori, H.; Yoshizawa, N.; Yamada, Y. Structural changes in carbon aerogels with high temperature treatment. Carbon 2002, 40, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanto, E.J.; Al-Muhtaseb, S.A.; Ritter, J.A. Sol-gel-derived carbon aerogels and xerogels: Design of experiments approach to materials synthesis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 41, 3151–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekala, R.W.; Alviso, C.T.; LeMay, J.D. Organic aerogels: Microstructural dependence of mechanical properties in compression. J. Noncryst. Solids 1990, 125, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwan, M.; Ratke, L. Flexibilisation of resorcinol-formaldehyde aerogels. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 13462–13468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwan, M.; Tannert, R.; Ratke, L. New soft and spongy resorcinol–formaldehyde aerogels. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2016, 107, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Li, F.; Cheng, H.-M. Progress in flexible lithium batteries and future prospects. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 1307–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wallace, G.G. Flexible electrodes and electrolytes for energy storage. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 175, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Xu, Z.; Gao, C. Multifunctional, ultra-flyweight, synergistically assembled carbon aerogels. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2554–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonijoly, M.; Oberlin, M.; Oberlin, A. A possible mechanism for natural graphite formation. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1982, 1, 283–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Ritter, J.A. Carbonization and activation of sol–gel derived carbon xerogels. Carbon 2000, 38, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrubesh, L.W.; Pekala, R.W. Thermal properties of organic and inorganic aerogels. J. Mater. Res. 1994, 9, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, H. Vakuumisolationspaneele-Gas- und Feuchteeintrag Sowie Feuchte- und Wärmetransport. Ph.D. Thesis, Bayerische Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Raed, K. Investigation of Knudsen and Gas-Atmosphere Effects on Effective Thermal Conductivity of Porous Media. Ph.D. Thesis, TU Bergakademie Freiberg, Freiberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Reichenauer, G. Structural characterization of aerogels. In Aerogels Handbook; Aegerter, M.A., Leventis, N., Koebel, M.M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 449–498. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Caps, R.; Fricke, J.; Alviso, C.T.; Pekala, R.W. Correlation between structure and thermal conductivity of organic aerogels. J. Noncryst. Solids 1995, 188, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Nilsson, O.; Fricke, J.; Pekala, R.W. Thermal and electrical conductivity of monolithic carbon aerogels. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 73, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.-J.L. Initial stage sintering. In Sintering; Kang, S.-J.L., Ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 39–55. [Google Scholar]
- Gruber, E.E.; Mullins, W.W. Extended analysis of surface scratch smoothing. Acta Metall. 1966, 14, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trick, K.A.; Saliba, T.E. Mechanisms of the pyrolysis of phenolic resin in a carbon/phenolic composite. Carbon 1995, 33, 1509–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulik, S.; Sotiriou-Leventis, C.; Churu, G.; Lu, H.; Leventis, N. Cross-linking 3D assemblies of nanoparticles into mechanically strong aerogels by surface-initiated free-radical polymerization. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 5035–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, S.; Yan, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, F. Compressive behaviors and morphological changes of resorcinol—Formaldehyde aerogel at high strain rates. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 133, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S.W. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (provisional). Pure Appl. Chem. 1982, 54, 2201–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Standards Authority of Ireland (NSAI). ISO 844: 2014(e) Rigid Cellular Plastics-Determination of Compression Properties; NSAI: Dublin, Ireland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- DIN EN ISO 643:2013-05. Stahl—Mikrophotographische Bestimmung der Erkennbaren Korngröße (ISO 643:2012), German version ENISO643:2012.
- De Boor, J.; Stiewe, C.; Ziolkowski, P.; Dasgupta, T.; Karpinski, G.; Lenz, E.; Edler, F.; Mueller, E. High-temperature measurement of seebeck coefficient and electrical conductivity. J. Electron. Mater. 2013, 42, 1711–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Sample | Bulk Density | Skeletal Density a | Porosity b | Electrical Conductivity c | SBET | Thermal Conductivity d | Compressive Modulus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g·cm−3) | (g·cm−3) | (%) | (S·cm−1) | (m2·g−1) | (W·m−1·K−1) | (MPa) | |
| lf-RF | 0.093 | 1.51 ± 0.007 | 94 | - | 5 | 0.044 ± 0.0002 | 0.07 |
| lf-C | 0.089 | 1.99 ± 0.010 | 95 | 0.21 ± 0.015 | 604 | 0.050 ± 0.0007 | 0.16 |
| sf-RF | 0.074 | 1.46 ± 0.007 | 95 | - | 28 | 0.041 ± 0.0009 | 0.02 |
| sf-C | 0.057 | 2.12 ± 0.033 | 97 | 0.11 ± 0.015 | 659 | 0.069 ± 0.0017 | 0.06 |
| Sample | Particle Size Determined from SEM Image, µm | Particle Size Calculated from TGA, µm |
|---|---|---|
| lf-C | 0.36 | 0.30 |
| sf-C | 0.09 | 0.07 |
| Type of Aerogel | R:Cat Molar Ratio | R:W Molar Ratio | R:F Molar Ratio | Stirring Time (Min) | Drying Conditions | Pyrolysis Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lf-RF | 50 | 0.008 | 0.5 | 30 | Ambient pressure, 80 °C, 1 day | - |
| lf-C | 50 | 0.008 | 0.5 | 30 | Ambient pressure, 80 °C, 1 day | 1000 °C, one hour, with Ar |
| sf-RF | 50 | 0.008 | 0.5 | 60 | With super-critical CO2 | - |
| sf-C | 50 | 0.008 | 0.5 | 60 | With super-critical CO2 | 1000 °C, one hour, with Ar |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schwan, M.; Ratke, L. Flexible Carbon Aerogels. C 2016, 2, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/c2030022
Schwan M, Ratke L. Flexible Carbon Aerogels. C. 2016; 2(3):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/c2030022
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchwan, Marina, and Lorenz Ratke. 2016. "Flexible Carbon Aerogels" C 2, no. 3: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/c2030022
APA StyleSchwan, M., & Ratke, L. (2016). Flexible Carbon Aerogels. C, 2(3), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/c2030022