The Stool Microbiome in African Ruminants: A Comparative Metataxonomic Study Suggests Potential for Biogas Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Description and Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.3. Sequencing Data Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
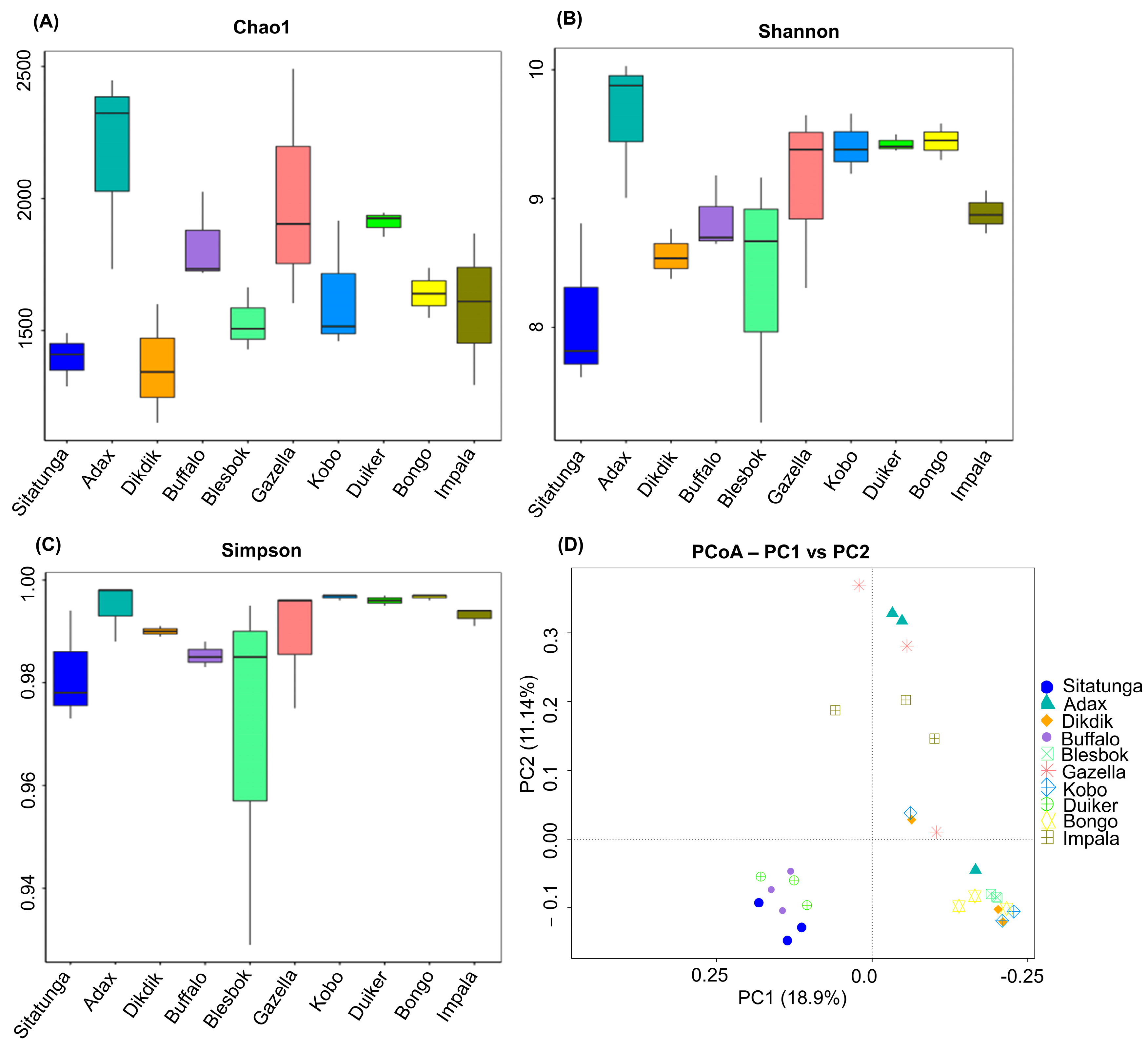
3.1. Microbial Community Diversity
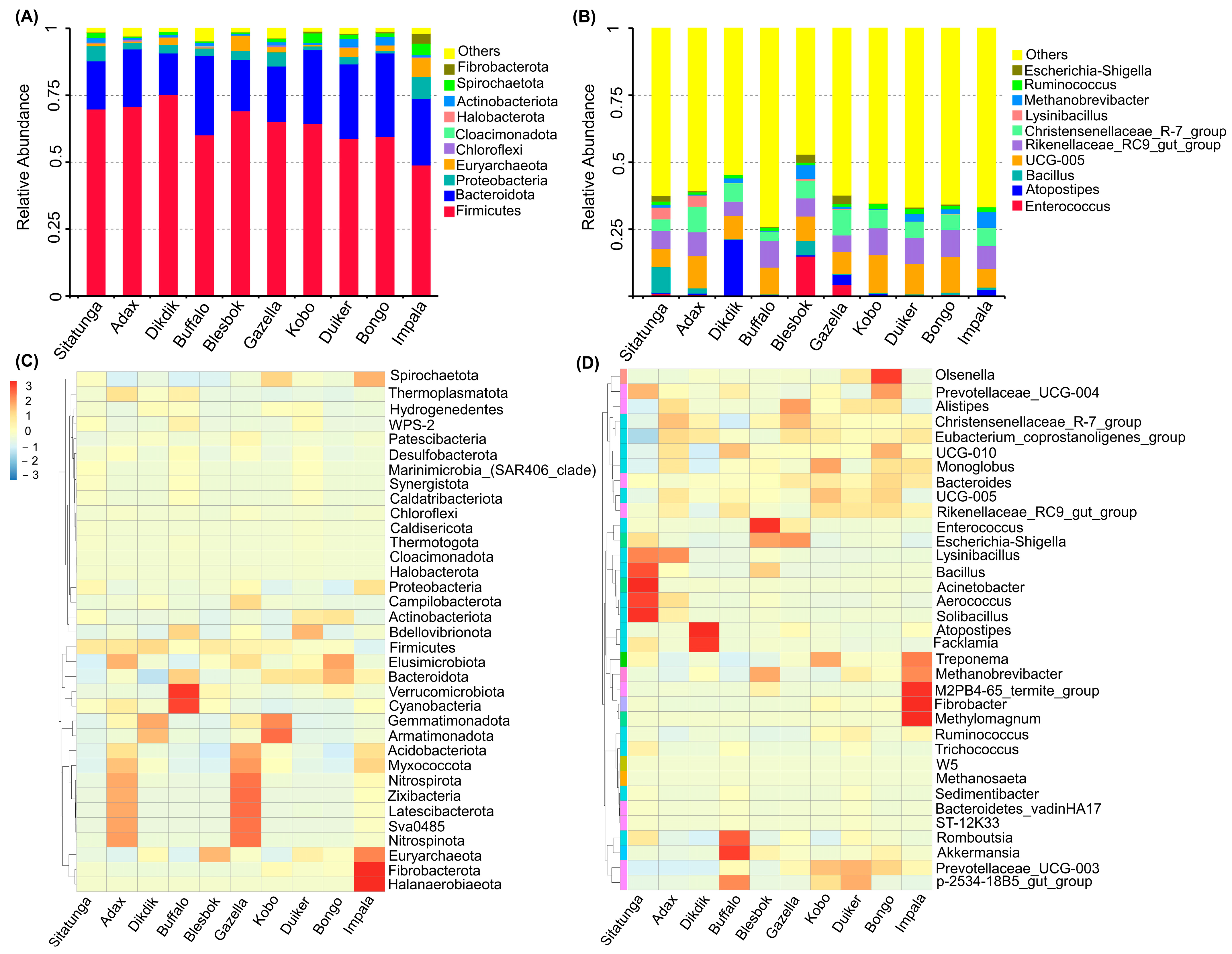
3.2. Bacteria Community Structure
3.3. Archaeal Community
3.4. Microbiome Profile and Bioaugmentation Potential
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ESDN: Reports. Available online: https://www.esdn.eu/publications/esdn-reports (accessed on 14 November 2023).
- Wang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, G.; Zhan, X. A Critical Review on Dry Anaerobic Digestion of Organic Waste: Characteristics, Operational Conditions, and Improvement Strategies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 176, 113208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malet, N.; Pellerin, S.; Girault, R.; Nesme, T. Does Anaerobic Digestion Really Help to Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions? A Nuanced Case Study Based on 30 Cogeneration Plants in France. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 384, 135578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theuerl, S.; Klang, J.; Prochnow, A. Process Disturbances in Agricultural Biogas Production—Causes, Mechanisms and Effects on the Biogas Microbiome: A Review. Energies 2019, 12, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, A.; Steinmetz, R.L.R.; do Amaral, A.C. Fundamentals of Anaerobic Digestion, Biogas Purification, Use and Treatment of Digestate; Embrapa: Brasília, Brazil, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, M.; Joshi, C.; Paritosh, K.; Thakur, J.; Pareek, N.; Masakapalli, S.K.; Vivekanand, V. Reprint of Organic Waste Conversion through Anaerobic Digestion: A Critical Insight into the Metabolic Pathways and Microbial Interactions. Metab. Eng. 2022, 71, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banu, R.; Kannah, R.Y. Anaerobic Digestion; BoD—Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2019; ISBN 978-1-83881-849-4. [Google Scholar]
- Sawatdeenarunat, C.; Surendra, K.C.; Takara, D.; Oechsner, H.; Khanal, S.K. Anaerobic Digestion of Lignocellulosic Biomass: Challenges and Opportunities. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 178, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.L.; Saha, B.C.; Slininger, P.J. Lignocellulosic Biomass Conversion to Ethanol by Saccharomyces. In Bioenergy; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 17–36. ISBN 978-1-68367-145-9. [Google Scholar]
- Paudel, S.R.; Banjara, S.P.; Choi, O.K.; Park, K.Y.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, J.W. Pretreatment of Agricultural Biomass for Anaerobic Digestion: Current State and Challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 1194–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agregán, R.; Güzel, N.; Guzel, M.; Punia Bangar, S.; Zengin, G.; Kumar, M.; Lorenzo, J.M. The Effects of Processing Technologies on Nutritional and Anti-Nutritional Properties of Pseudocereals and Minor Cereal. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2022, 16, 961–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsong, H.; Lianhua, L.; Ying, L.; Changrui, W.; Yongming, S. Bioaugmentation with Methanogenic Culture to Improve Methane Production from Chicken Manure in Batch Anaerobic Digestion. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabee, A.E.; Forster, R.; Sabra, E.A. Lignocelluloytic Activities and Composition of Bacterial Community in the Camel Rumen. AIMS Microbiol. 2021, 7, 354–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraja, T.G. Microbiology of the Rumen. In Rumenology; Millen, D.D., De Beni Arrigoni, M., Lauritano Pacheco, R.D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 39–61. ISBN 978-3-319-30533-2. [Google Scholar]
- Zened, A.; Combes, S.; Cauquil, L.; Mariette, J.; Klopp, C.; Bouchez, O.; Troegeler-Meynadier, A.; Enjalbert, F. Microbial Ecology of the Rumen Evaluated by 454 GS FLX Pyrosequencing Is Affected by Starch and Oil Supplementation of Diets. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 83, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbayram, E.G.; Ince, O.; Ince, B.; Harms, H.; Kleinsteuber, S. Comparison of Rumen and Manure Microbiomes and Implications for the Inoculation of Anaerobic Digesters. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutungwazi, A.; Ijoma, G.N.; Ogola, H.J.O.; Matambo, T.S. Physico-Chemical and Metagenomic Profile Analyses of Animal Manures Routinely Used as Inocula in Anaerobic Digestion for Biogas Production. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Alberdi, A.; Deng, J.; Zhong, Z.; Si, H.; Zheng, C.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. Comparative Microbiome Analysis Reveals the Ecological Relationships Between Rumen Methanogens, Acetogens, and Their Hosts. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1311. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Mal, G.; Gautam, S.K.; Mukesh, M. Microbial Resources from Wild and Captive Animals. In Advances in Animal Biotechnology; Singh, B., Mal, G., Gautam, S.K., Mukesh, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 39–49. ISBN 978-3-030-21309-1. [Google Scholar]
- Nordlund, K. Factors That Contribute to Subacute Ruminal Acidosis. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual Conference American Association of Bovine Practitioners, Columbus, OH, USA, 15–17 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Alshehri, K.; Li, Y.; Qian, H.; Sapsford, D.; Cleall, P.; Harbottle, M. Advances in Biological Techniques for Sustainable Lignocellulosic Waste Utilization in Biogas Production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 170, 112995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbayram, E.G.; Kleinsteuber, S.; Nikolausz, M.; Ince, B.; Ince, O. Enrichment of Lignocellulose-Degrading Microbial Communities from Natural and Engineered Methanogenic Environments. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Xu, J.; Wang, B.; Feng, J.; Jeney, Z.; Sun, X.; Xu, P. Phylogeny and Evolution of Multiple Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) Populations Clarified by Phylogenetic Analysis Based on Complete Mitochondrial Genomes. Mar. Biotechnol. 2015, 17, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satari, L.; Guillén, A.; Vidal-Verdú, À.; Porcar, M. The Wasted Chewing Gum Bacteriome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, O.; Harper, D.; Ryan, P. PAST: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Pitta, D.W.; Kumar, S.; Veiccharelli, B.; Parmar, N.; Reddy, B.; Joshi, C.G. Bacterial Diversity Associated with Feeding Dry Forage at Different Dietary Concentrations in the Rumen Contents of Mehshana Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) Using 16S Pyrotags. Anaerobe 2014, 25, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, W.; Mao, S. Comparative Studies of the Composition of Bacterial Microbiota Associated with the Ruminal Content, Ruminal Epithelium and in the Faeces of Lactating Dairy Cows. Microb. Biotechnol. 2016, 9, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Menezes, A.B.; Lewis, E.; O’Donovan, M.; O’Neill, B.F.; Clipson, N.; Doyle, E.M. Microbiome Analysis of Dairy Cows Fed Pasture or Total Mixed Ration Diets. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 78, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanks, O.C.; Kelty, C.A.; Archibeque, S.; Jenkins, M.; Newton, R.J.; McLellan, S.L.; Huse, S.M.; Sogin, M.L. Community Structures of Fecal Bacteria in Cattle from Different Animal Feeding Operations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2992–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Zhang, R.; Wang, D.; Zhu, W. The Diversity of the Fecal Bacterial Community and Its Relationship with the Concentration of Volatile Fatty Acids in the Feces during Subacute Rumen Acidosis in Dairy Cows. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Cao, W.; Liu, R. Kinetics of Methane Production from Swine Manure and Buffalo Manure. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 177, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, M.M.; Harris, H.M.B.; Ross, R.P.; O’Toole, P.W. Core Fecal Microbiota of Domesticated Herbivorous Ruminant, Hindgut Fermenters, and Monogastric Animals. MicrobiologyOpen 2017, 6, e00509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, F.; Wang, T.; Gao, N.L.; Liu, Z.; Cui, K.; Duan, Y.; Wu, S.; Luo, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, C.; et al. The Microbiome of the Buffalo Digestive Tract. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Morrison, M.; Yu, Z. Phylogenetic Diversity of Bacterial Communities in Bovine Rumen as Affected by Diets and Microenvironments. Folia Microbiol. 2011, 56, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, J.R.; Callaway, T.R.; Lourenco, J.M.; Ryman, V.E. Characterization of Rumen, Fecal, and Milk Microbiota in Lactating Dairy Cows. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 984119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Shi, B.; Zuo, Z.; Qi, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, X.; Lan, L.; Shi, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; et al. Effects of Two Different Straw Pellets on Yak Growth Performance and Ruminal Microbiota during Cold Season. Animals 2023, 13, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Wei, M.; Sun, F.; Bao, H.; Bao, M.; Ju, J.; Du, L. Effect of Lactic Acid Bacteria Preparations on Calf Fecal Flora. Rev. Bras. Zootec. 2023, 52, e20210199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Pei, C.; Degen, A.; Hao, L.; Cao, X.; Liu, H.; Zhou, J.; Long, R. A Comparison between Yaks and Qaidam Cattle in Vitro Rumen Fermentation, Methane Emission, and Bacterial Community Composition with Poor Quality Substrate. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2022, 291, 115395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zubair, M.; Chen, L.; Chang, J.; Fang, W.; Nabi, M.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; et al. Rumen Microbe Fermentation of Corn Stalk to Produce Volatile Fatty Acids in a Semi-Continuous Reactor. Fuel 2023, 350, 128905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransom-Jones, E.; Jones, D.L.; McCarthy, A.J.; McDonald, J.E. The Fibrobacteres: An Important Phylum of Cellulose-Degrading Bacteria. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 63, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suen, G.; Weimer, P.J.; Stevenson, D.M.; Aylward, F.O.; Boyum, J.; Deneke, J.; Drinkwater, C.; Ivanova, N.N.; Mikhailova, N.; Chertkov, O.; et al. The Complete Genome Sequence of Fibrobacter Succinogenes S85 Reveals a Cellulolytic and Metabolic Specialist. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Baldwin, R.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Connor, E.; Li, R. The Bacterial Community Composition of the Bovine Rumen Detected Using Pyrosequencing of 16S RRNA Genes. Metagenomics 2012, 1, 5571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutungwazi, A.; Ijoma, G.N.; Matambo, T.S. The Significance of Microbial Community Functions and Symbiosis in Enhancing Methane Production during Anaerobic Digestion: A Review. Symbiosis 2021, 83, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, F. Improving the Anaerobic Digestion of Switchgrass via Cofermentation of Rumen Microorganisms (Rumen Bacteria, Protozoa, and Fungi) and a Biogas Slurry. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.; Khan, A.; Badshah, M.; Degen, A.; Yang, G.; Liu, H.; Zhou, J.; Long, R. Yak Rumen Fluid Inoculum Increases Biogas Production from Sheep Manure Substrate. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 362, 127801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, C.; Crispie, F.; Lewis, E.; Reid, M.; O’Toole, P.W.; Cotter, P.D. The Rumen Microbiome: A Crucial Consideration when Optimising Milk and Meat Production and Nitrogen Utilisation Efficiency. Gut Microbes 2018, 10, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, E.E.; Smith, R.P.; St-Pierre, B.; Wright, A.-D.G. Differences in the Rumen Methanogen Populations of Lactating Jersey and Holstein Dairy Cows under the Same Diet Regimen. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamuad, L.L.; Kim, S.H.; Biswas, A.A.; Yu, Z.; Cho, K.-K.; Kim, S.-B.; Lee, K.; Lee, S.S. Rumen Fermentation and Microbial Community Composition Influenced by Live Enterococcus faecium Supplementation. AMB Express 2019, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLoughlin, S.; Spillane, C.; Claffey, N.; Smith, P.E.; O’Rourke, T.; Diskin, M.G.; Waters, S.M. Rumen Microbiome Composition Is Altered in Sheep Divergent in Feed Efficiency. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manafiazar, G.; Fitzsimmons, C.; Zhou, M.; Basarab, J.A.; Baron, V.S.; McKeown, L.; Guan, L.L. Association between Fecal Methanogen Species with Methane Production and Grazed Forage Intake of Beef Heifers Classified for Residual Feed Intake under Drylot Conditions. Animal 2021, 15, 100304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayané, A.; Guiot, S. Animal Digestive Strategies versus Anaerobic Digestion Bioprocesses for Biogas Production from Lignocellulosic Biomass. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groleau, D.; Forsberg, C.W. Cellulolytic Activity of the Rumen Bacterium Bacteroides succinogenes. Can. J. Microbiol. 1981, 27, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saluzzi, L.; Smith, A.; Stewart, C.S. Analysis of Bacterial Phospholipid Markers and Plant Monosaccharides during Forage Degradation by Ruminococcus flavefaciens and Fibrobacter succinogenes in Co-Culture. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1993, 139, 2865–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, P.H.; Kirs, M. Structure of the Archaeal Community of the Rumen. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 3619–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaster, A.-K.; Moll, J.; Parey, K.; Thauer, R.K. Coupling of Ferredoxin and Heterodisulfide Reduction via Electron Bifurcation in Hydrogenotrophic Methanogenic Archaea. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2981–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, T.L.; Wolin, M.J.; Kusel, E.A. Isolation and Characterization of Methanogens from Animal Feces. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1986, 8, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Miller, T.L. Phylogenetic Analysis of Methanobrevibacter Isolated from Feces of Humans and Other Animals. Arch. Microbiol. 1998, 169, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricke, W.F.; Seedorf, H.; Henne, A.; Krüer, M.; Liesegang, H.; Hedderich, R.; Gottschalk, G.; Thauer, R.K. The Genome Sequence of Methanosphaera Stadtmanae Reveals Why This Human Intestinal Archaeon Is Restricted to Methanol and H2 for Methane Formation and ATP Synthesis. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 642–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Singh, A.P.; Nilsson, T. Bacteria as Important Degraders in Waterlogged Archaeological Woods. Holzforschung 1996, 50, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Chen, Y.; Sun, S.; Hu, Y. Interaction among Multiple Microorganisms and Effects of Nitrogen and Carbon Supplementations on Lignin Degradation. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 155, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitta, D.W.; Pinchak, W.E.; Dowd, S.E.; Osterstock, J.; Gontcharova, V.; Youn, E.; Dorton, K.; Yoon, I.; Min, B.R.; Fulford, J.D.; et al. Rumen Bacterial Diversity Dynamics Associated with Changing from Bermudagrass Hay to Grazed Winter Wheat Diets. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 59, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Li, L.; Zhao, H.; Tu, Y.; Liu, M.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, Y. Characterization of the Dynamic Changes of Ruminal Microbiota Colonizing Citrus Pomace Waste during Rumen Incubation for Volatile Fatty Acid Production. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 11, e03517-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhu, W.; Jiang, L.; Mao, S. Comparative Metabolome Analysis of Ruminal Changes in Holstein Dairy Cows Fed Low- or High-Concentrate Diets. Metabolomics 2017, 13, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accetto, T.; Avguštin, G. The Diverse and Extensive Plant Polysaccharide Degradative Apparatuses of the Rumen and Hindgut Prevotella Species: A Factor in Their Ubiquity? Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 42, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grondin, J.M.; Tamura, K.; Déjean, G.; Abbott, D.W.; Brumer, H. Polysaccharide Utilization Loci: Fueling Microbial Communities. J. Bacteriol. 2017, 199, e00860-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naas, A.E.; Mackenzie, A.K.; Mravec, J.; Schückel, J.; Willats, W.G.T.; Eijsink, V.G.H.; Pope, P.B. Do Rumen Bacteroidetes Utilize an Alternative Mechanism for Cellulose Degradation? mBio 2014, 5, e01401-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, Q.N.M.; Mimoto, H.; Koyama, M.; Nakasaki, K. Lactic Acid Bacteria Modulate Organic Acid Production during Early Stages of Food Waste Composting. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wang, H.; Ding, J.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, Y.; Fan, S.; Zhang, A.; Shen, Y. Comparative Study on Aerobic Compost Performance, Microbial Communities and Metabolic Functions between Human Feces and Cattle Manure Composting. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 31, 103230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Zhang, Q.; De Jaegher, B.; Liu, J.; Sui, Q.; Zheng, X.; Wei, Y. Effect of Proton Pump Inhibitor on Microbial Community, Function, and Kinetics in Anaerobic Digestion with Ammonia Stress. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 319, 124118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Chen, Y.; Feng, L.; Zhou, Q. Metagenomic Analysis Reveals Nonylphenol-Shaped Acidification and Methanogenesis during Sludge Anaerobic Digestion. Water Res. 2021, 196, 117004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
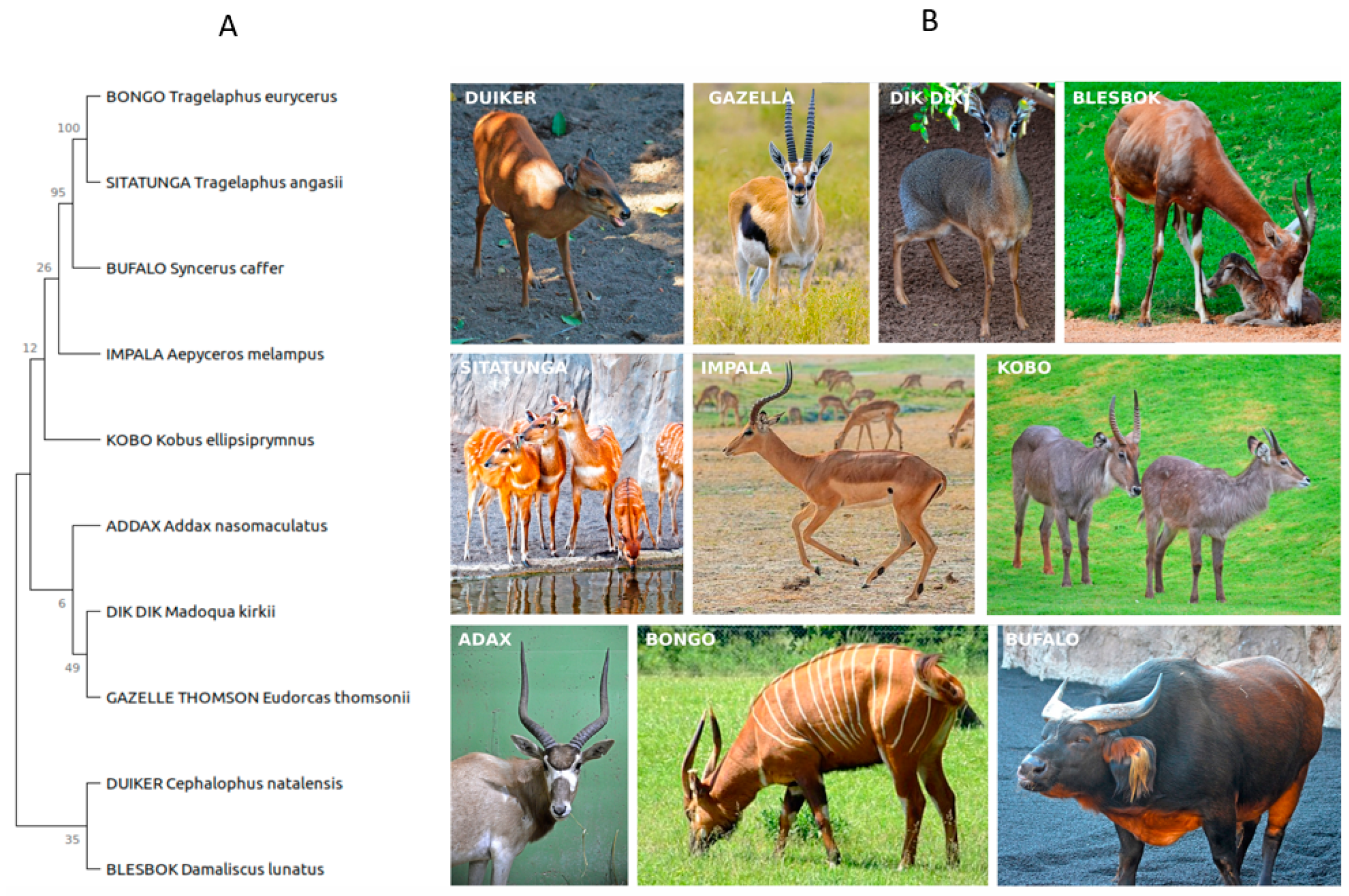


| No | Animal Type | Breakfast | Dinner |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sitatunga | Alfalfa; Feed * Vegetables | Alfalfa; Total pet food ** |
| 2 | Adax | Hay; Alfalfa | Hay; Alfalfa; Total pet food |
| 3 | Dikdik | Alfalfa; Feed | Alfalfa; Total pet food; Spinach |
| 4 | Buffalo | Hay | Hay; Alfalfa; Total pet food; Vegetables |
| 5 | Blesbok | Hay; Alfalfa; Feed | Hay; Alfalfa Total pet food |
| 6 | Gazella | Alfalfa; Feed | Hay; Alfalfa; Total pet food |
| 7 | Kobo | Hay; Alfalfa; Feed | Hay; Alfalfa; Total pet food |
| 8 | Duiker | Alfalfa; Feed | Hay; Alfalfa; Total pet food; Banana peel; Leafy vegetables |
| 9 | Bongo | Banana peel; Vegetables | Alfalfa; Total pet food; Vegetables |
| 10 | Impala | Hay; Alfalfa; Feed; Vegetables | Hay; Alfalfa; Total pet food |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vogel, F.W.; Carlotto, N.; Wang, Z.; Garrido, L.; Chatzi, V.; Herrero, R.G.; Benavent-Albarracín, L.; Gimenez, J.M.; Carbonell, L.; Porcar, M. The Stool Microbiome in African Ruminants: A Comparative Metataxonomic Study Suggests Potential for Biogas Production. Fermentation 2024, 10, 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10030119
Vogel FW, Carlotto N, Wang Z, Garrido L, Chatzi V, Herrero RG, Benavent-Albarracín L, Gimenez JM, Carbonell L, Porcar M. The Stool Microbiome in African Ruminants: A Comparative Metataxonomic Study Suggests Potential for Biogas Production. Fermentation. 2024; 10(3):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10030119
Chicago/Turabian StyleVogel, Felipe Werle, Nicolas Carlotto, Zhongzhong Wang, Lydia Garrido, Vasiliki Chatzi, Raquel Gonzalez Herrero, Luis Benavent-Albarracín, Javier Martinez Gimenez, Loles Carbonell, and Manuel Porcar. 2024. "The Stool Microbiome in African Ruminants: A Comparative Metataxonomic Study Suggests Potential for Biogas Production" Fermentation 10, no. 3: 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10030119
APA StyleVogel, F. W., Carlotto, N., Wang, Z., Garrido, L., Chatzi, V., Herrero, R. G., Benavent-Albarracín, L., Gimenez, J. M., Carbonell, L., & Porcar, M. (2024). The Stool Microbiome in African Ruminants: A Comparative Metataxonomic Study Suggests Potential for Biogas Production. Fermentation, 10(3), 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10030119






