Abstract
Anaerobic digestion of waste-activated sludge (WAS) towards biogas recovery is constrained by the limited hydrolysis and inhibited acetogenesis steps that hinder subsequent energy recovery. This study employed Fe(VI)/S(IV) oxidation to enhance the WAS solubilization and coupled it with the syntrophic interaction of hydrogen-producing acetogen (HPA) and sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) to stimulate the successive procedure towards methane production. Results showed that the dosage ratio of HPA-SRB to WAS (H-S-W) with 1:1:50 outperformed with the highest methane production potential (11.63 ± 1.87 mL CH4/(g VSS·d). Meanwhile, the efficient and sequential process from acetogenesis to methanogenesis stimulated by HPA-SRB was evidenced by a significant decrease of 30.2% in the acetate concentration. The microbial community structure further manifested the crucial role of HPA-SRB with increased abundance of Desulfobulbus (2.07%), Syntrophomonas (1.24%) and Smithella (1.63%), which stimulated acetophilic methanogen boost with Methanobacterium dominating with 77.51% in H-S-W100. Furthermore, the positive syntrophic relationships among HPA-SRB and acetophilic methanogens towards methane production were confirmed via molecular ecological network and canonical correspondence analysis. This study highlighted the syntrophic cooperation of the mixed consortia of HPA and SRB on methane production based on Fe(VI)/S(IV) pretreatment and provided the theoretical and technical basis for the potential implementation of novel methanogenesis technology for WAS treatment.
1. Introduction
Due to the progressive development of urbanization and the population, tremendous waste-activated sludge (WAS) has been produced with a significantly increasing rate as a predominant by-product of the biological treatment process in wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs), which poses challenges in both high disposal cost and potential environmental risks [1,2]. Fortunately, the various organic compounds embedded in WAS, including proteins, carbohydrates and lipids, could be recovered as valuable resources [3,4]. Anaerobic digestion (AD) has been widely recognized as a cost-effective and environmentally friendly technology which could convert the organics to biogas [5]. However, methane production through AD from WAS was typically constrained by several factors. As acknowledged, four steps were involved in AD, i.e., hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis and methanogenesis. Organics’ release was often restricted by the semirigid cell structure and entrapment of extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) around the cells, which could have been alleviated by sludge pretreatment as revealed in the literature [6]. Hence, with accelerated hydrolysis, organics were metabolized by anaerobic fermentation bacteria to produce C3-C5 short chain fatty acids (SCFAs), like propionate (HPr), butyrate (HBu) and valeric acid (HVa) in the acidogenesis stage. Subsequently, SCFAs would be converted to acetic acids (HAc) and hydrogen by hydrogen-producing acetogen (HPA), namely, the acetogenesis stage [7]. However, with the procedure of acidogenesis and acetogenesis, HAc conversion from SCFAs was hindered by the rising hydrogen partial pressure due to its toxic inhibition to HPA [8]. In addition, the positive Gibbs free energy (HBu + 2H2O = 2Hac + 2H2 + 2H+, ΔG0′ = +48.3 kJ/reaction, for instance) meant that SCFAs to HAc was a non-spontaneous reaction [9,10]. In other words, acetogenesis was constrained from a thermodynamics perspective, which might lead to inhibition to microbes due to SCFA accumulation, especially to the impressionable methanogens (6.7~9.0 mol/m3). Hence, methanogenesis was blocked due to insufficiency of crucial upstream fermentation. In addition, it was revealed that the combination with Fe(VI)/S(IV) oxidation and SRB products (HAc) supports methane production.
Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) are being considered a promising option for the pretreatment of WAS. Among them, sulfate radicals have attracted significant attention recently due to the various pathways through which they can be generated [11]. It has been indicated that Fe(VI) exhibits rapid oxidation of S(IV) at second-order rate constants ranging from 103 to 102 M−1 s−1 in the pH range of 9.0 to 10.5 [12], and various free radicals are generated, including ∙OH, SO4− and SO5−. Zhou et al. reported that the coupled Fe(VI)/S(IV) oxidation could generate multiple radicals including ∙OH, SO4− and ∙O2−, boosting SCFA production of 2521 ± 109 mg COD/L with 50.6 ± 0.3% HAc from WAS consortia, beneficial for acetate conversion by an increase rate of 10.3%. It has recorded that the introduction of hydrogen-consuming bacteria in an anaerobic system was efficient in promoting SCFA conversion towards HAc by reducing hydrogen partial pressure [13,14]. Moreover, with the anticipation of hydrogen-consuming bacteria, sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB), HAc conversion from SCFAs was feasible with reduced Gibbs free energy. For example, with syntrophic cooperation of HBu-degrading bacteria and SRB, HAc production from HBu was spontaneous (2HBu + SO42− = 4Hac + H+ + HS−, ΔG0′ = −55.7 kJ/reaction).
It has found that SRB, under suitable anaerobic conditions, might promote methane production by boosting the metabolism of acetophilic methanogens. For example, Bryant studied the symbiotic system between SRB and methanogen with lactic acid/ethanol as the carbon source and found that SRB significantly promoted methane production efficiency in sulfate-deficient environments [9]. It was also found that SRB significantly promoted HAc generation and conversion towards methane in the anaerobic treatment of starch wastewater in a methane reactor [9]. Visser verified the feasibility of the syntrophism association of HPA and hydrogen-consuming bacteria by revealing the syntrophism process among Desulfobulbus (SRB), Syntrophobacter wolinii (HPA) and Methanobacterium formicicum [15]. The research more or less involved the possible syntrophic cooperation HPA and SRB. But the effect of the syntrophic interaction of HPA and SRB and its interaction with acetophilic methanogens metabolism on methane production was relatively untapped.
This work explored the stimulation effect of methane production via successive and syntrophic interaction of SRB-HPA and acetophilic methanogens based on Fe(VI)/S(IV) pretreatment during anaerobic digestion of WAS. Due to the possible block effect on methane production from SCFA accumulation in the one-stage anaerobic digestion system, a two-stage anaerobic digestion process was performed with pre-fermentation by a continuous stirred tank reactor (CSRT for 4 d) followed by a biochemical methane potential (BMP) system. The effect of dosage ratio of HPA-SRB to WAS on the SCFAs and methane production process was investigated with the HAc accumulation and consumption process elaborated. Then, the shift in microbial community structure was analyzed and was constructed to reveal the ecological relationships between the functional SRB, HPA and acetophilic methanogens, and their interactions with environmental factors were explored by microbial ecological network (MEN) construction and canonical correspondence analysis (CCA). Furthermore, the underlying mechanism and potential application significance was touched upon, based on the experimental results and previous studies. This research is anticipated to provide a theoretical and technical basis for enhancing energy recovery from WAS.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characteristics of WAS
The sludge was obtained from the sludge thickening tank of the Zhengyang Wastewater Treatment Plant located in Jinzhong City, Shanxi Province, China. After filtering through a 200-mesh sieve, the supernatant was decanted after settling with sludge obtained for experiments. The characteristics of the sludge were as follows: total suspended solid (TSS) 14.9 ± 0.4 g/L, volatile suspended solid (VSS) 11.1 ± 0.4 g/L, total chemical oxygen demand (TCOD) 18,900 ± 24 mg/L, soluble chemical oxygen demand (SCOD) 309.7 ± 7.4 mg/L, soluble proteins 247.9 ± 1.8 mg COD/L, soluble carbohydrates 9.3 ± 0.1 mg COD/L, NH4+ 25.2 ± 0.8 mg/L, PO43− 10.2 ± 1.1 mg/L, sulfate 2.3 mg/L, sulfite 1.8 mg/L, pH value 7.0 ± 0.1.
2.2. Enrichment of io-SRB and HPA Consortia
HPA was enriched from an anaerobic baffled reactor with a selective medium. Ten mL seed sludge, 100 mL culture solution enriched with HPr and HBu (10 g/L) and 1% of trace element were dozed in a 300 mL anaerobic fermenter. After being purged by nitrogen, the fermenters were cultured in an air-bath shaker (130 rpm) at 35 ± 0.1 °C for 10 transfers with the cultured suspensions transformed to the same selective medium every 3 days. The utilization of SCFAs by HPA in domestication was determined with high conversion efficiency of HPr and HBu (Figure S1). The inoculum SRB had been enriched from activated sludge and garden soil and cultured with HPr and HBu as a carbon source and (NH4)2SO4 as SO42− as an e-acceptor in a selective medium. The cultured SRB was beneficial in C3–C5 conversion towards HAc as revealed in previous research [16].
2.3. Experimental Design for Enhanced Methane Production by HPA-SRB-Stimulation
The experiments were conducted in anaerobic fermenters with a working volume of 300 mL. WAS was pretreated with coupled Fe (VI)/S(IV)oxidation by an optimal potassium ferrate (PF) to Na2SO3 ratio of 1:1 as conducted in a previous study [17]. HPA was A series of HPA-SRB to WAS dosage ratio (VSSHPA:VSSSRB:VSSWAS, hereinafter written as H-S-W), was set to investigate its effect on methane production, including 1:1:50, 1:1:100, 1:1:200 and 1:1:400 (recorded as H-S-W50, H-S-W100, H-S-W200 and H-S-W400). Fe(VI)/S(IV)-treated WAS with no HPA-SRB addition was set as Control. After purging by nitrogen to maintain an anaerobic environment, the fermenters were capped, sealed and placed in an air-bath shaker (110 rpm) at 35 ± 0.1 °C for 4 d for SCFA production. Then, methane production was conducted using BMP by a methane potential testing system (AMPTSII) for another 21 d. All the fermentation experiments were carried out in triplicate. The contents of soluble carbohydrates, soluble proteins, SCOD and SCFAs were determined every 3 d, and methane was determined every 1 d.
2.4. MiSeq Sequencing of Key Microflora
The microbial community diversity was evaluated using Illumina MiSeq sequencing. Sludge samples were centrifuged to remove the supernatant at 8000× g; DNA was extracted from WAS samples via an EZNA® Soil DNA kit, and 16S rRNA genes used for polymerase chain reaction (PCR) were fused to the V3−V4 universal primers (344F and 915R). Then, the recovered products were sequenced using Illumina MiSeq sequencing after purification and quantification. The raw sequences were registered in the NCBI Short Read Archive database with accession No. SUB5344530. Canonical correlation analysis (CCA) performed with Canoco 4.5 software and Pearson correlation matrix based on R-project were used to calculate and visualize the correlations between characteristic genera and the environmental. MENs were constructed to assess the interspecific interaction among acid-forming bacteria [18,19], SRB and HPA in the fermentation broth of WAS with selected operational taxonomic unit (OTU) functional genes by Cytoscape 3.8.1.
2.5. Analytical Methods
VSS and TSS were determined by gravimetric analysis. SCOD and TCOD were determined by the potassium dichromate method. Soluble proteins (Spr) were determined by the modified BCA method, and soluble polysaccharides (Spo) were determined by the phenol-sulfuric-acid method. SCFAs were determined by Agilent 6890 gas chromatograph with hydrogen flame ionization detector (FID). For comparative analysis, the above-measured concentrations (mg/L) were converted to COD concentration (mg COD/L) with the following conversion factors: 1.06 g COD/g (carbohydrate), 1.50 g COD/g (protein), 1.07 g COD/g (HAc), 1.51 g COD/g (HPr), 1.82 g COD/g (HBu) and 2.04 g COD/g (HVa). Changes in size distribution after pretreatment were measured by a laser particle size distribution instrument (QL-1076, Xiamen, China).
The modified Gompertz model is used to predict the methane production performance of a two-phase anaerobic system, with Equation (1) [20].
where P is cumulative specific methane production, mL CH4/g VSS; Pm is maximum specific methane production potential, mL CH4/g VSS; Rm is maximum methane production rate, mL CH4/(g VSS·d); λ is delay period, d; t is incubation time, d.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Overall Performance of Methane Production by HPA-SRB-Mediation
Figure 1 demonstrates the success of enhanced methane production by HPA-SRB-mediation. Fe(VI)/S(IV) pretreatment caused violent decomposition to the sludge matrix with particle size (D50) decreasing by 3.0–5.4% compared with Control (Figure S2, Table S1). It has been demonstrated that SO4− and∙OH played an important role in EPS disintegration in the coupled Fe(VI)/S(IV) system. As a result, soluble proteins and soluble polysaccharides were dramatically released. As depicted in Figure 1A, Fe(VI)/S(IV) pretreatment accelerated the release of soluble organics from both intracellular and extracellular substrates with Spr and Spo in Control increasing from the initial concentrations of 202 ± 3.2 mg COD/L and 500.2 ± 11.5 mg COD/L to 528.12 ± 8.2 mg COD/L and 1214.8 ± 9.1 mg COD/L, increased by 143% and 161%, respectively. This was also confirmed by the sharp increase in SCOD concentration (Figure S3). The content of SCOD peaked at 5973 ± 3.3 mg/L in Control, which was 1.1–1.3 times higher than other groups. This trend tied well with previous studies wherein chemical disruption promoted the release of soluble organics [17]. Note that SCOD in groups with HPA-SRB addition was lower than that in Control, revealing the possible consumption of SCOD (4.0~23.1%) for acid production with HPA-SRB addition. It is worth noting that a stepwise decrease was also observed in changes in Spr and Spo from 1 d onward till 13 d, suggesting the consumption of soluble organics by fermentative bacteria to produce acids. In addition, more Spr and Spo were consumed with the increase in the dosage of HPA-SRB. As calculated, 47.8% of Spo was consumed in H-S-W50, 6.4% higher than that in Control. The changes in soluble organics indicated the promotion in hydrolysis by coupled Fe(VI)/S(IV) and HPA-SRB addition, which may facilitate the subsequent acidogenic stage. Due to the abundant substrates provided by hydrolysis acceleration, the concentration of SCFAs increased rapidly and peaked at 4 d (Figure 1B). As revealed, H-S-W50 obtained the highest SCFA concentration among the test groups with the initial 229.2 ± 3.3 mg COD/L gradually increasing to the peak value of 3989 ± 51.2 mg COD/L (corresponding to 359.4 mg COD/g VSS), which is 1.4-times higher than that in the Control. This was slightly higher than the SCFA yields in the Fe (VI) pretreatment group (343 mg COD/g VSS) [21] and 6.9% higher than the results from Wang when PF dosage was as high as 0.4 g/g VSS (334.7 mg COD/g VSS) [22]. The promoted SCFA production might be attributed to the driving force to pull more C3-C5 SCFAs smoothly converted to HAc by more HPA-SRB addition, which partially facilitated SCFA yields by reducing more products. As revealed, H-S-W400 with less HPA-SRB dosage produced less SCFA yields, 41.9% lower than that in H-S-W50. The alleviation of hydrolysis limitation by Fe (VI)/S(IV) pretreatment and acceleration in SCFAs production by SRB addition has also been confirmed by the previous research [17].
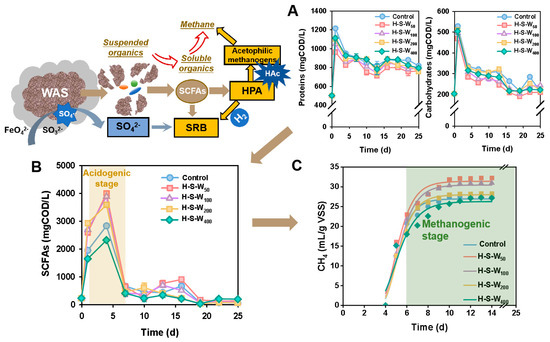
Figure 1.
Concentrations of proteins and carbohydrates (A), SCFAs (B), CH4 (C) in each system under different dosage ratios of HPA and SRB.
Subsequently, with the blessing of HPA to accelerate HAc production from C3–C5 SCFA conversion and SRB to consume extra hydrogen and alleviate thermodynamic restriction of HPA, acetophilic methanogens were stimulated to produce methane. BMP testing was conducted to monitor methane production performance (Figure 1C). As demonstrated, the cumulative methane exhibited a sharp increase from 4th day onwards till 10 d and then stabilized. In general, the cumulative methane decreased with the dosage amount of HPA and SRB. The H-S-W50 group achieved the maximum methane production with 31.40 ± 0.78 mL CH4/g VSS, 1.2- and 1.04-times higher than that of the Control (26.9 ± 0.46 mL CH4/g VSS) and H-S-W100 group (30.45 ± 0.55 mL CH4/g VSS), respectively. Wang obtained an uppermost methane yield of 85.32 mL/g VSS when PF dosage was 0.04 g/g VSS, but this was completely inhibited with PF dosage of 0.4 g/g VSS [22]. It is obvious that the appropriate dosage of the coupled Fe(VI)/S(IV) could ensure the procedure of methane production. In addition, the methanogen boost was due to abundance of substrates from the efficient promotion of previous hydrolysis, acidogenesis and acetogenesis via PF pretreatment and SRB-HPA mediation [17]. The promotion effect was partially confirmed by the Gompertz correction mode curving with high consistency (R2 above 0.97). As depicted in Table 1, the H-S-W50 group obtained the highest methane production rate with 11.63 ± 1.87 mL CH4/(g VSS·d), 11.7% higher than that in Control. The 4% reduction of H-S-W50 compared with H-S-W400 in the delay period (3.85 ± 0.23 vs. 4.01 ± 0.38) also confirmed the positive stimulating role of SRB-HPA with a suitable dosage ratio [23]. Since a subtle marginal of 4 ± 0.1% was shown between H-S-W100 and H-S-W50 in methane production, H-S-W100 was chosen as the optimal dosage from economic and environmental prospection.

Table 1.
Dynamic parameters of Gompertz modified model for methane phase.
3.2. Acetic Acid Conversion towards Methane via HPA-SRB Cooperation
The procedure of acetogenesis, another crucial link towards methane generation, is displayed by HAc accumulation and consumption in Figure 2. Figure 2A depicts the trend of acetic acid production under various dosages of HPA and SRB. As demonstrated, the concentration of HAc stepwise increased with the increase in HPA-SRB dosage. Similar to the trend of SCFA production (Figure 1B), HAc continued to increase and climbed at 1307 ± 0.9 mg COD/L in the H-S-W50 group, with 29.8% of the SCFAs, suggesting the contribution of HPA in efficiently converting SCFAs to HAc. This was consistent with the preliminary experiment results in HPA enrichment that the tamed HPA could convert HPr and HBu to HAc with 36 ± 0.2% and 41 ± 0.3%, respectively (Figure S1). SRB also made a positive contribution in decreasing the higher hydrogen pression to lower than 10−4~10−5 atm, which stimulated HPA to use SCFAs. The dramatic decrease in HAc concentration from 4 d onwards till 12 d further confirmed the contribution of HPA-SRB in HAc conversion, as revealed by the larger slope in H-S-W50 than the other groups. A further comparison of spectrum changes in the maximum SCFAs at different stages revealed the consumption of SCFAs (Figure 2B). As revealed, HAc accounted for 32.5% of the SCFAs concentrations at 4 d, 11.3% higher than that in the Control, which echoed the efficiency in hydrolysis and acidogenesis as discussed in Section 3.1. With the successive transition from acidogenesis to acetogenesis, 21.5% more HAc was produced from conversion of C3–C5 SCFAs, which echoed the lowered proportion of HPr and HBu at 13 d, decreased by 10.1% and 0.6%, respectively. This indicated success in the acetogenesis procedure by HPA-SRB mediation to stimulate HAc production.
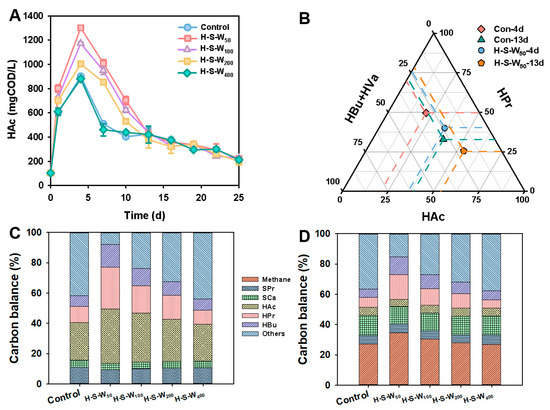
Figure 2.
Performance of acetic acid conversion towards methane: changes in HAc production under different systems (A); spectrum changes in the maximum SCFAs (B); carbon balance analysis with fermentation time of 4 d (C) and 16 d (D).
To further figure out the organics conversion of WAS by HPA-SRB cooperation, the carbon balance at the initial hydrolysis and acidogenesis stage (4 d, Figure 2C) as well as the later acetogenesis and methanogenesis stage (16 d, Figure 2D) were compared. As revealed, SCFAs including HBu and HPr decreased significantly from 4 d to 16 d, indicating the procedure of the bioconversion towards HAc. As shown, 5.8% of the sum proportion of HBu + HPr was reduced in Control. With the increase in HPA-SRB dosage, more SCFAs were converted to HAc, as revealed by the reduced 14.4% in H-S-W50, 5.2% and 6.6% higher than that in H-S-W50 and H-S-W50, respectively. This indicated that the syntrophic interaction between SRB and HPA was beneficial to converting C3-C5 SCFAs towards HAc via alleviating the toxic inhibition from high PH2 and relieving the thermodynamic limitations, with the residual SO42− (from Fe (VI)/S(IV) pretreatment) as an e-acceptor as well, as revealed by the previous research [17]. Note that methane production was observed and accounted for a large proportion at 16 d, suggesting the smooth procedure of methanogenesis by HPA-SRB stimulation. H-S-W50 obtained the largest methane production with 34.5%, 7.6% higher than that in the Control. The high methane yield in H-S-W50 was an echo of the increased SCFA production but decreased HAc, revealing the contribution of the acetoclastic pathway to methane production. Meanwhile, the dramatic decrease in HAc and climbing proportion of CH4 confirmed the successful construction of a syntrophism pattern among HPA-SRB and acetophilic methanogens.
3.3. Microbial Community Distribution and MEN Network Analysis between Key Microbiomes
In order to acknowledge the underlying microbial metabolic mechanism, the microbial community structure was analyzed via MiSeq sequencing. It revealed that Proteobacteria, Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes were the dominant phyla, accounting for 74.5%, 65.2%, 58.7% and 68.0% of the total sequences, respectively (Figure S4A). These phyla were capable of degrading complex organic compounds to produce SCFAs, including HAc, which served as substrates for methanogens [24]. Accordingly, Gammaproteobacteria, Deltaproteobacteria, Clostridia and Bacteroidia dominated at the class level (Figure S4B). Clostridia, hydrolytic and fermentative bacteria, possessed the ability to utilize cellulases in the production of SCFAs; the relative abundance peaked in the H-S-W50-25d group (25.36%). Following the adding of HPA-SRB, Clostridia exhibited a minor increase, suggesting that this anaerobic system is more favorable for SCFA production. The community distribution at the genus level is shown in Figure 3A. Hyphomicrobium and Candidatus_Microthrix are usually hydrolyzing fermentating bacteria [25], which were enriched to 0.29% and 0.46% in the H-S-W100 group and 0.16% and 0.25% in the Control group on day 4, respectively. Christensenellaceae R-7 group, with the ability to hydrolyze proteins and carbohydrates into SCFAs [26,27], boosted from 1.5% (Control-4d) to 2.6% (H-S-W100-4d) with an SRB and HPA trigger. Pseudomonas, which metabolized glucose into SCFAs and hydrogen during anaerobic fermentation, showed the same trend. The high abundance of anaerobic fermentation bacteria provided abundant material basis for the subsequent process. Notably, the increase in SRB was observed, with Desulfobulbus dominated in H-S-W100-25d with 2.07%, 16.4% higher than that in Control-25d. Desulfovibrio also increased by 67.2%, from 0.65% (Control-25d) to 1.10% (H-S-W100-25d). The increase in HPA echoed the efficient HAc accumulation in Section 3.2. For example, Syntrophobacter increased from 0.43% (4 d) to 0.87% (25 d) in H-S-W100, 74.21% higher than that in Control (25 d). The high proportion of other HPA, including Syntrophomonas (from 0.76% to 1.24%) and Smithella (from 1.19% to 1.63%), suggested that the limitations imposed by hydrogen partial pressure as well as thermodynamics have been successfully surmounted.
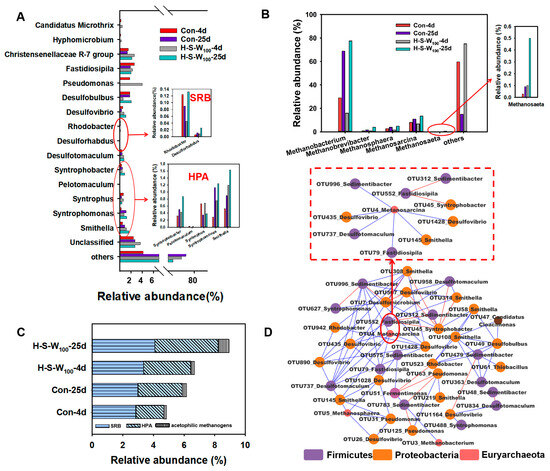
Figure 3.
Microbial community structure and interactions among functional microbiome: taxonomic classification of pyrosequence (A) and archaea (B) at genus level; summary of relative abundances of SRB, HPA, and acetophilic methanogens (C); molecular ecological sub-network of OTUs (D).
As a result, methanogen was boosted (Figure 3B) with Methanobacterium, a typical methane-producing genus, climbing from 15.83% to 77.51% in H-S-W100, 8.69% higher than that in Control. The facultative methanogens Methanosarcina, related not only to the acetoclastic pathway but also the hydrogenotrophic and methylotrophic pathway [28], increased by 6.64% with SRB-HPA addition, as did Methanosaeta with the acetoclastic pathway, from 0.2% to 0.5%, suggesting efficient HAc consumption due to a subtle successive procedure from hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis to methanogenesis [29]. Figure 3C further summarizes the shifts of SRB, HPA and acetophilic methanogens. As seen, a higher proportion of SRB and HPA with 4.10% and 4.14%, respectively, induced acetophilic methanogen boosting from 0.24% to 0.69%, 2.59-times higher than that in Control (0.27%).
MENs of all OTUs and functional genes are constructed based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing identification to better analyze the underlying mechanisms between anaerobic fermentation bacteria, SRB, HPA and acetophilic methanogens and explore their ecological relationships (cooperation or competition) towards methane production (Figure 3D). Table S2 presents the topological properties of this network, and the average connectivity, average path distance and modularity of the topological properties were 3.884, 4.810 and 0.317, respectively. Pseudomonas (OTU63) and Pseudomonas (OTU125) were negatively correlated with Sedimentibacter (OTU783). Pseudomonas are known to produce SCFAs metabolized from glucose, and Sedimentibacter can produce HAc from other organics. This result indicated that these microbes (SCFA-producing bacteria and HPA) had competing relationships. It could also be observed that the obvious positive correlation (blue lines) was among SRB, HPA and acetophilic methanogens. Metanosarcina, as a typical acetophilic methanogen [27], was positively related to the fermenter Fastidiosipila (OTU79) [30], three typical SRBs including Desulfovibrio (OTU435), Desulfotomaculum (OTU737) and Desulfovibrio (OTU1428) and two HPAs Smithella (OTU145) and Sedimentibacter (OTU996). This was due to their synergistic reaction in which acetophilic methanogens had the ability to use HAc promoted by SRB-HPA to produce methane. In this sense, the possible syntrophism pattern among HPA-SRB and acetophilic methanogens was verified. These results signified potential cooperative relationships among these functional microbiomes, which synergistically promoted the methane of WAS. Notably, the competition was observed from the negative correlation (red lines) among the acid-producing Fastidiosipila (OTU552) and Syntrophobacter (OTU45) and Sedimentibacter (OTU312); this might be due to the decrease in substrate utilization of Fastidiosipila during the later fermentation. This was also the reason for the decrease in Synergistetes mentioned above.
3.4. Interactions between Environmental Factors and the Key Microbiome
CCA is employed as a method to enhance comprehension of the relationship between environmental factors and functional genera (Figure 4A). Except for methane and pH value, nearly all performance parameters exhibited a negative correlation with the first typical axis CCA1 (explaining 89.7% of the variance of generic distribution) and were positively correlated with the second typical axis CCA2 (explaining 7.5% of the variance). The acute angle formed by HAc and methane indicated a negative correlation among them, implying the utilization of HAc in methane production. This association was further supported by the strong negative correlation observed between protein, carbohydrate and methane. The narrow angle between SCFAs and methane and that coinciding between SCFAs and HAc indicated that HAc is the main impact for production methane in SCFAs, and the syntrophism pattern of HPA and SRB promoted the production of HAc towards methane. Desulforhabdus, Syntrophomonas, Smithella and Methanobacterium were positively correlated with environmental factors of methane. Among them, Methanobacterium was significantly positively correlated with methane.
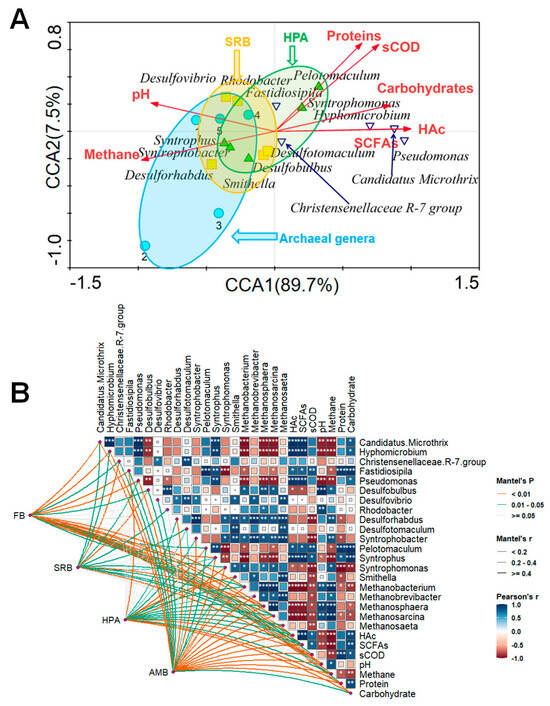
Figure 4.
CCA (A) and the Pearson correlation matrix (B) between the environmental factors and characteristic genera. The color gradient represents the Spearman correlation coefficient, while *, **, and *** indicate significant correlations at p < 0.05, p < 0.01 and p < 0.001, respectively. The edge width corresponds to Mantel’s r statistic for the corresponding distance correlations, and the edge color denotes statistical significance.
The Pearson correlation matrix elucidates the relationship between environmental factors and microorganisms during the fermentation process (Figure 4B). Among them, there was a positive correlation between the most characteristic genera, Pseudomonas and Metanosarcina, for instance, indicating that cooperation between HPA and acetophilic methanogens contributes significantly to methane production. Proteins and carbohydrates were negatively correlated with SRB and HPA (p < 0.05), revealing the fact that more soluble organics consumption means more substrates for HPA to grow and boost to produce HAc. This was also the reason for the difference in methane performance between Control and H-S-W groups. It was obvious that acetophilic methanogens had a significant negative correlation with HAc (p < 0.001), indicating that HAc was effectively converted by acetophilic methanogens. SRB, HPA and acetophilic methanogens had a mutually beneficial symbiotic relationship, indicating that they can form a synergistic system during anaerobic fermentation. HPA and SRB could accelerate the accumulation of HAc, providing substrates for acetophilic methanogens and, then, promoting the accumulation of methane.
3.5. Underlying Mechanism and Implication Benefits
The underlying mechanism to enhance methane production using sulfate radical AOPs to pretreat WAS with the syntrophism pattern formed by HPA, SRB and acetophilic methanogens is illustrated in Figure 5. Coupled Fe(VI)/S(IV) oxidation generated multiple radicals, which caused apparent cell rupture and enhanced the solubilization of WAS. The released proteins, carbohydrates and lipids were further biodegraded into amino acids, monosaccharides and fatty acids during hydrolysis, providing abundant substrates for the subsequent acidification to produce C3–C5 SCFAs. Previous research has confirmed that coupling SO4− oxidation with SRB mediation improved SCFA accumulation and HAc conversion [17]. The addition of the cultured HPA further boosted the HAc production, providing an abundant and suitable substrate for acetophilic methanogen metabolism, due to the reduced hydrogen partial pressure and the released thermodynamic limitations by SRB mediation. Syntrophus and Smithella were the main HPAs detected in this system (Section 3.3) to convert SCFAs into HAc accompanied by H2 production (ΔG0′ = +76.1 kJ/reaction) [31]. The dominated SRBs like Desulfobulbus and Desulfotomaculum also confirmed the fact that SRB played a crucial role in consuming extra H2 and the residual SO42− from the Fe(VI)/S(IV) pretreatment, lifting the thermodynamic limitations of HPA and further “driving” HAc production. As a result, acetophilic methanogens were stimulated and (Methanosarcina and Methanosaeta) boosted to produce methane in the suitable habitat with rich HAc (ΔG0′ = −65.0 kJ/reaction) [30]. The positive relation among anaerobic fermentation bacteria Fastidiosipila (OTU79), the typical SRB (Desulfovibrio (OTU435), Desulfotomaculum (OTU737) and Desulfovibrio (OTU1428)), HPA (Smithella (OTU145) and Sedimentibacter (OTU996)) and acetophilic methanogens (Metanosarcina) by MENs’ analysis further confirmed the possible syntrophism pattern among HPA-SRB and acetophilic methanogens. Consequently, with reduced Gibbs free energy, a subtle synergetic interaction system among SRB, HPA and acetophilic methanogens was constructed to accelerate the carbon metabolism cycle of the anaerobic biological chain (Organic matter-SCFAs-HAc-CH4) in sludge digestion.
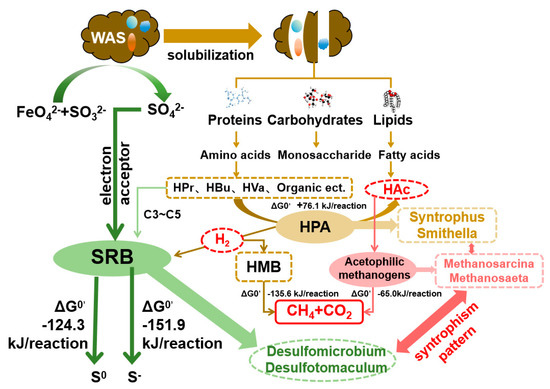
Figure 5.
Underlying mechanism of enhanced methane recovery from WAS by coupling SO4− oxidation with the syntrophism pattern of HPA-SRB and acetophilic methanogens.
In general, this ingenious design using advanced chemical oxidation pretreatment coupled with microbial cooperative regulation provides new insights for resources and energy recovery from WAS. From the perspective of engineering application, once the proposed technology had been scaled up, the potential economic and environmental benefits was invisible. A preliminary evaluation was made (Table S3 [32]) based on the study results when scaling up to WWTPs with a daily capacity of 100,000 m3/d. As evaluated, the daily SCFAs yields in this study were equivalent to 2.60 tons methanol and 5.01 tons sodium acetate, suggesting a large cost (6068.9~11,771.2 CNY/d) reduction in purchasing external carbon sources. By HPA-SRB addition, 1.04~2 tons more chemicals could be saved with further cost reduction by 28.5%. Although the energy input was higher than the energy output generated from the produced methane, equivalent electric energy of about 2637.90 kWh/d could be generated (2110.3 CNY/d) this could partially make up the power consumption in WWTPs. Meanwhile, carbon emissions due to SCFAs and equivalent chemical production, as well as energy recovery, could be avoided. For example, according to the data, with −0.89 tCO2/t commercial methanol, with natural gas as a raw material, 3.25 tons CO2/d emission could be reduced, which could push for carbon neutrality in the sewage treatment industry.
4. Conclusions
The aim of the present research was to examine the effect of the syntrophic interaction of HPA and SRB and their interaction with acetophilic methanogen metabolism on methane production from Fe (VI)/S(IV) pretreated WAS. The findings clearly indicated that by subtly aiming to regulate the interspecies hydrogen transfer among HPA-SRB and acetophilic methanogens, accelerated SCFA production (398.0 mg COD/g VSS) with 21.5% more HAc accumulation in H-S-W50 was obtained, benefiting from the breaking and alleviation of hydrolysis limitation, hydrogen accumulation and thermodynamic restricts. This consequently stimulated methane production potential to 31.40 mL CH4/g VSS. Visible alternation and evolution and their positive interaction were confirmed by changes in the microbial community structure and the microbial ecological networks (MENs) analysis among HPA (Sedimentibacter, Syntrophomonas and Smithella), SRB (Desulfobulbus, Rhodobacter and Desulfotomaculum) and acetophilic methanogens. It was the syntrophic interaction between HPA and SRB that stimulated the successive procedure towards methane production and pulled the carbon metabolism cycle of the anaerobic biological chain (Organic matter-SCFAs-HAc-CH4) in WAS digestion. This study shed new insights into the synergetic cooperation process of microbial metabolism for resource conversion and energy recovery from waste sludge.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fermentation10050243/s1, Table S1: Effects on particle size of WAS; Table S2: Major topological properties of the empirical network and its associated random network during WAS anaerobic fermentation; Table S3: Economic analysis of SCFAs and CH4 recovery; Figure S1: Utilization of SCFAs (A) and removal rate (B) by HPA in domestication; Figure S2: Effect on particle size distribution of sludge; Figure S3: Changes of SCOD in anaerobic digestion of excess sludge under different control systems; Figure S4: Taxonomic classification of pyrosequences at the phylum (A) and class (B) levels.
Author Contributions
H.W.: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing—original draft. Y.D.: Methodology, Writing—review and editing. A.Z.: Conceptualization. Writing—review and editing. Z.L.: Visualization. Z.H.: Writing—review and editing. W.L.: Supervision, Writing—review and editing. X.Y.: Resources, Project administration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, No. 52070139, 52270134), the Scientific and Technological Cooperation Project of Shanxi Province (No. 202204041101012), the Natural Science Foundation for Young Scientists of Shanxi Province (No. 202103021222009).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Yang, G.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H. Current state of sludge production, management, treatment and disposal in China. Water Res. 2015, 78, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S.; Dong, B.; Dai, X. Effect of nitrite addition on the two-phase anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge: Optimization of the acidogenic phase and influence mechanisms. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yuan, H.; Zhou, Q.; Gu, G. Hydrolysis and acidification of waste activated sludge at different pHs. Water Res. 2007, 41, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, L.; Feng, Q.; Fang, F.; Xue, Z.; Li, C.; Cao, J. Improving anaerobic fermentation of waste activated sludge using iron activated persulfate treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 268, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.; Liu, Z.; Fan, Y.; He, Z.W.; Liu, W.; Yue, X.; Zhou, A. Improving methane production from waste activated sludge assisted by Fe(II)-activated peroxydisulfate pretreatment via anaerobic dgestion: Role of interspecific syntrophism mediated by sulfate-reducing bacteria. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 3012–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Tian, L.; Wei, W.; Zhu, T.; Liu, Y. Insight into the enhancing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) production from waste activated sludge via polyoxometalates pretreatment: Mechanisms and implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 800, 149392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masse, D.I.; Droste, R.L. Comprehensive model of anaerobic digestion of swine manure slurry in a sequencing batch reactor. Water Res. 2000, 34, 3087–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Lee, K.-M.; Kim, H.-E.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, C.; Lee, C. Disintegration of waste activated sludge by thermally-activated persulfates for enhanced dewaterability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7106–7115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyzer, G.; Stams, A.J.M. The ecology and biotechnology of sulphate-reducing bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coma, M.; Vilchez-Vargas, R.; Roume, H.; Jauregui, R.; Pieper, D.H.; Rabaey, K. Product diversity linked to substrate usage in chain elongation by mixed-culture fermentation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 6467–6476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklos, D.B.; Remy, C.; Jekel, M.; Linden, K.G.; Drewes, J.E.; Huebner, U. Evaluation of advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment—A critical review. Water Res. 2018, 139, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Pang, S.; Jiang, J.; Ma, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, C.; Liu, Q.; Yuan, Y. The combination of ferrate (VI) and sulfite as a novel advanced oxidation process for enhanced degradation of organic contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 333, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Wei, Y.; Fan, Y.; Shyryn, A.; Wang, S.; Liu, W.; Yuan, J.; Yue, X. Sulfate reduction-mediated syntrophic microbiomes accelerated waste-activated sludge fermentation on the basis of SO4·− oxidation and eliminated superfluous sulfate. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 9325–9334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schink, B. Energetics of syntrophic cooperation in methanogenic degradation. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1997, 61, 262–280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Visser, A.; Beeksma, I.; Zee, F.; Lettinga, A.J.M.S. Anaerobic degradation of volatile fatty acids at different sulphate concentrations. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 1993, 40, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhou, A.; Fan, Y.; Duan, Y.; Liu, Z.; He, Z.; Liu, W.; Yue, X. Using heat-activated persulfate to accelerate short-chain fatty acids production from waste activated sludge fermentation triggered by sulfate-reducing microbial consortium. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 861, 160795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, A.; Liu, H.; Varrone, C.; Shyryn, A.; Defemur, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, W.; Yue, X. New insight into waste activated sludge acetogenesis triggered by coupling sulfite/ferrate oxidation with sulfate reduction-mediated syntrophic consortia. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.-Q.; Li, Z.-L.; Liang, B.; Zhai, H.-L.; Cai, W.-W.; Nan, J.; Wang, A.-J. Accelerated microbial reductive dechlorination of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol by weak electrical stimulation. Water Res. 2019, 162, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Yang, Y.; He, Z.; Luo, F.; Zhou, J. Molecular ecological network analyses. BMC Bioinf. 2012, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardilho, S.; Pires, J.C.; Boaventura, R.; Almeida, M.; Dias, J.M. Biogas production from residual marine macroalgae biomass: Kinetic modelling approach. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 359, 127473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wu, L.; Feng, Q.; Fang, F.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Su, Y. Synergistic effects of iron and persulfate on the efficient production of volatile fatty acids from waste activated sludge: Understanding the roles of bioavailable substrates, microbial community & activities, and environmental factors. Biochem. Eng. J. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 141, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Fan, X.; Sangeetha, T.; Pan, K.; Bi, X.; Liu, W.; Lin, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, A.; et al. The dual role of potassium ferrate in promoting primary sludge hydrolysis and acidogenesis in anaerobic fermentation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 477, 147023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerrou, O.; Lahboubi, N.; Bakraoui, M.; Karouach, F.; El Gnaoui, Y.; Schuech, A.; Stinner, W.; El Bari, H. Methane production from anaerobic digestion of date palm leaflet waste in Morocco. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2021, 23, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.C.; Morrison, M.; Yu, Z. A meta-analysis of the microbial diversity observed in anaerobic digesters. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 3730–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Tian, L.; Zheng, K.; Zhu, T.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y. Heat-assisted potassium ferrate pretreatment enhancing short-chain fatty acids production from waste activated sludge: Performance and mechanisms. J. Clean. 2022, 380, 134989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Haruta, S.; Cui, Z.J.; Ishii, M.; Yokota, A.; Igarashi, Y. Clostridium Straminisolvens sp. nov. a moderately thermophilic, aerotolerant and cellulolytic bacterium isolated from a cellulose-degrading bacterial community. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54 Pt 6, 2043–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, X. Obstacles faced by methanogenic archaea originating from substrate-driven toxicants in anaerobic digestion. J. Hazard. 2020, 403, 123938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotaru, A.-E.; Shrestha, P.M.; Liu, F.; Shrestha, M.; Shrestha, D.; Embree, M.; Zengler, K.; Wardman, C.; Nevin, K.P.; Lovley, D.R. A new model for electron flow during anaerobic digestion: Direct interspecies electron transfer to Methanosaeta for the reduction of carbon dioxide to methane. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falsen, E.; Collins, M.D.; Welinder-Olsson, C.; Song, Y.; Finegold, S.M.; Lawson, P.A. Fastidiosipila sanguinis gen. nov. sp nov. a new Gram-positive, coccus-shaped organism from human blood. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kniemeyer, O.; Musat, F.; Sievert, S.M.; Knittel, K.; Wilkes, H.; Blumenberg, M.; Michaelis, W.; Classen, A.; Bolm, C.; Joye, S.B.; et al. Anaerobic oxidation of short-chain hydrocarbons by marine sulphate-reducing bacteria. Nature 2007, 449, 898–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Dolfing, J.; Jin, G.; Fang, X.; Han, W.; Liu, L.; Tang, Y.; Cheng, L. Thermodynamic restrictions determine ammonia tolerance of methanogenic pathways in Methanosarcina barkeri. Water Res. 2023, 232, 119664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L. Investigation on the sludge yield of municipal wastewater treatment plants in key watershed of China. China Water Wastewater 2018, 34, 23–27. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).