Biocatalytic Potential of a Raoultella terrigena-Derived Lipolytic Enzyme for High-Performance Detergents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection, Processing, and Bacteria Isolation
2.2. Fresh Inoculum Preparation and Qualitative Activity Evaluation
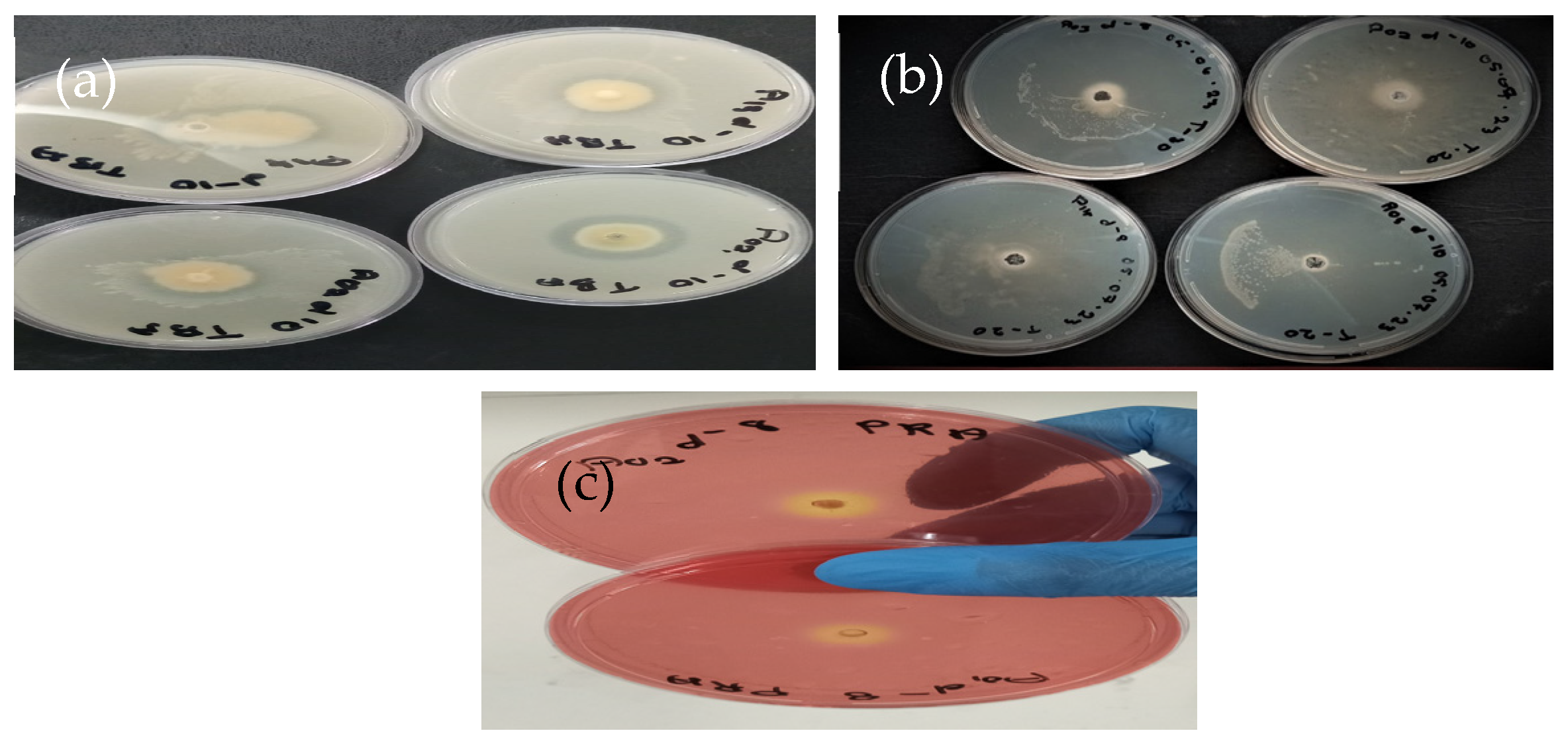
2.2.1. Screening for Lipolytic Potential Using Tributyrin Agar
2.2.2. Screening for Lipolytic Potential Using Tween-20 Agar
2.2.3. Screening for Lipolytic Potential Using Phenol Red Agar
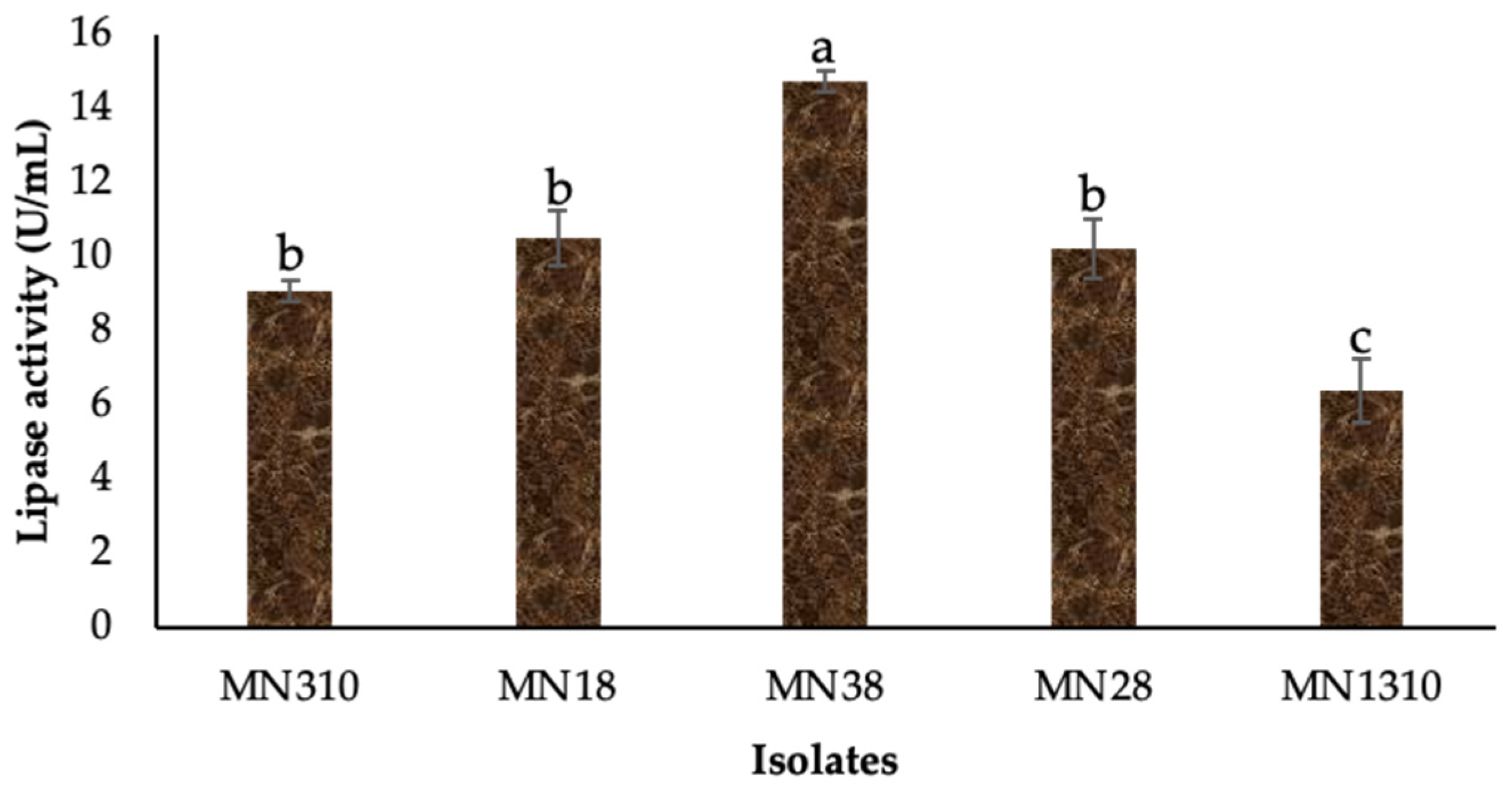
2.3. Quantitative Evaluation of Isolates for Lipolytic Potential
2.4. Lipolytic Activity Assay
2.5. Identification of Lipolytic Bacteria
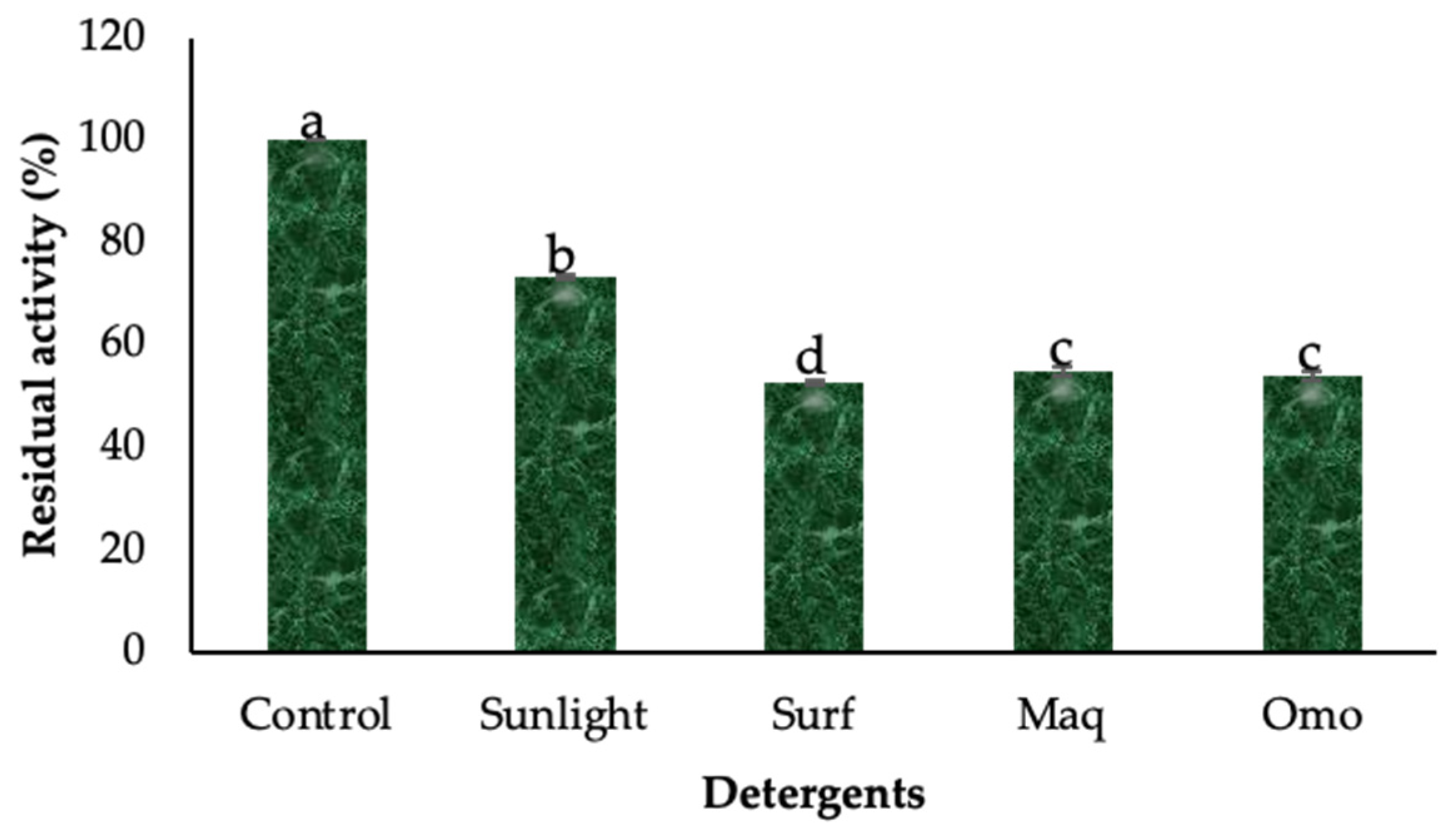
2.6. Evaluation of Enzyme Stability with Commercially Available Detergents
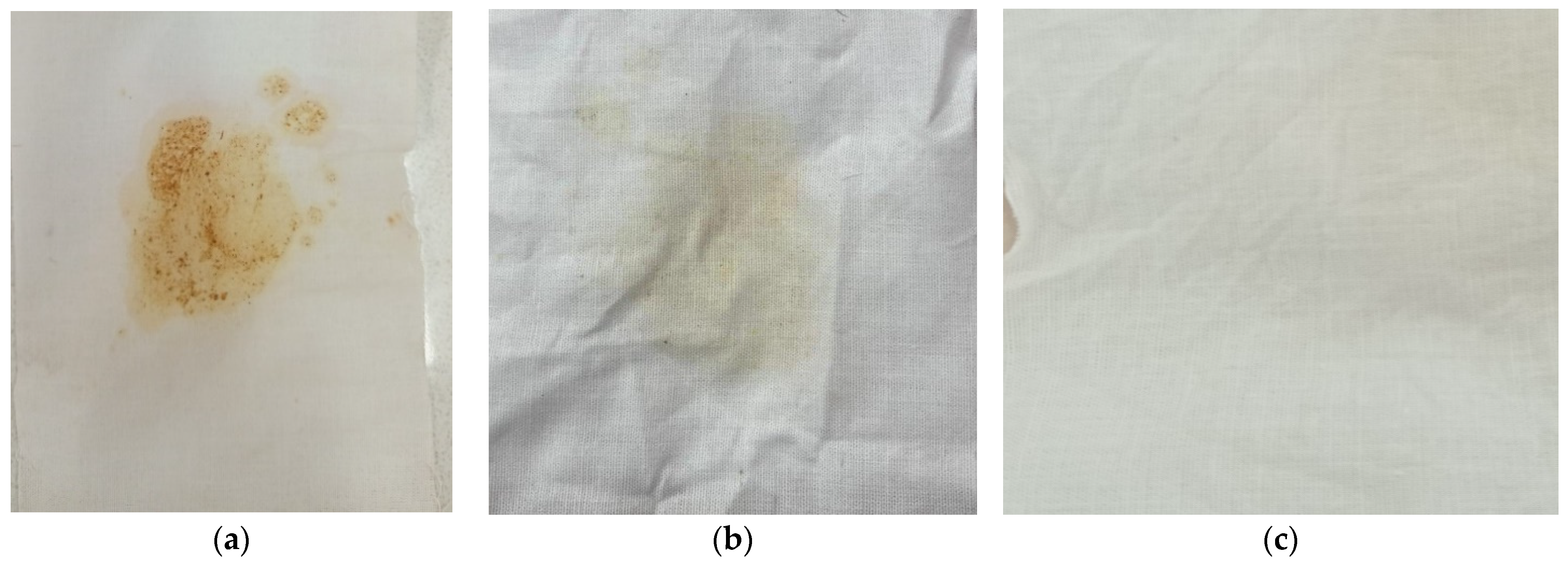
2.7. Lipolytic Enzyme Evaluation for Oil Stain Removal
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bacterial Isolation and Qualitative Evaluation of Lipolytic Activity
3.2. Quantitation of Lipase Production and Bacterial Identification
3.3. Stability Profile and Washing Performance of the Crude Lipase Against Laundry Detergents
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BSM | Basal salt media |
| FOG | Fat, oil, and grease |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| U | Unit |
References
- Qiu, M.; Dong, S.; Cui, Q.; Feng, Y.; Xuan, J. Recent progress in the mechanism and engineering of α/β hydrolases for chiral chemical production. Catalysts 2023, 13, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, T.; Sharma, T.; Sharma, S.; Kanwar, S.S. Role of Microbial Hydrolases in Bioremediation. In Microbes and Enzymes in Soil Health and Bioremediation; Kumar, A., Sharma, S., Eds.; Microorganisms for Sustainability; Springer: Singapore, 2019; Volume 16, pp. 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeeshma, E.; Habeeb, H.; Sinha, S.; Arora, P.; Chattaraj, S.; Mohapatra, P.K.D.; Panneerselvam, P.; Mitra, D. Enzymes-mediated solid waste management: A sustainable practice for recycling. Waste Manag. Bull. 2024, 1, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dhiman, S.; Krishan, B.; Samtiya, M.; Kumari, A.; Pathak, N.; Kumari, A.; Aluko, R.E.; Dhewa, T. Microbial enzymes and major applications in the food industry: A concise review. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2024, 6, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Rai, D.; Shivam, K.; Shahane, S.; Mishra, U. Lipases: Sources, production, purification, and applications. Recent Pat. Biotechnol. 2019, 13, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnoi, N.; Dixit, S.; Mishra, J. Microbial Lipases and Their Versatile Applications. In Microbial Enzymes: Roles and Applications in Industries; Arora, N., Mishra, J., Mishra, V., Eds.; Microorganisms for Sustainability; Springer: Singapore, 2020; Volume 11, pp. 207–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, M.; Fleuri, L.F.; Macedo, G.A. Seed lipases: Sources, applications and properties-a review. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 27, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, P.; Enespa; Singh, R.; Arora, P.K. Microbial lipases and their industrial applications: A comprehensive review. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Liu, K.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, W.; Wang, T. A valuable product of microbial cell factories: Microbial lipase. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 743377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanmani, P.; Aravind, J.; Kumaresan, K. An insight into microbial lipases and their environmental facet. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 1147–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, S.; Azeem, F.; Hussain, S.; Rasul, I.; Siddique, M.H.; Riaz, M.; Afzal, M.; Kouser, A.; Nadeem, H. Bacterial lipases: A review on purification and characterization. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2018, 132, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheibel, D.M.; Gitsov, I.P.I.; Gitsov, I. Enzymes in “Green” Synthetic Chemistry: Laccase and Lipase. Molecules 2024, 29, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savalia, H.J.; Dungrechiya, A. Identification and Optimization Study of Lipase Producing Bacteria Isolated from Municipal Waste and Bio-deteriorated Waste. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 16, 2592–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, K.E.; Ransac, S.; Dijkstra, B.W.; Colson, C.; van Heuvel, M.; Misset, O. Bacterial lipases. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1994, 15, 29–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oni, I.O.; Faeji, C.O.; Fasoro, A.A.; Kukoyi, O.; Akingbade, A.M. Optimization of amylase and lipase enzymes produced by Bacillus cereus and Bacillus subtilis isolated from waste dumpsites. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2022, 14, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, A.A.; Abo-Kamar, A.M.; Elkotb, E.S.; Al-Madboly, L.A. Microbial lipases: Advances in production, purification, biochemical characterization, and multifaceted applications in industry and medicine. Microb. Cell. Fact. 2025, 24, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Khan, S.A.; Hamayun, M.; Lee, I.J. The recent advances in the utility of microbial lipases: A review. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grbavčić, S.; Bezbradica, D.; Izrael-Živković, L.; Avramović, N.; Milosavić, N.; Karadžić, I.; Knežević-Jugović, Z. Production of lipase and protease from an indigenous Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain and their evaluation as detergent additives: Compatibility study with detergent ingredients and washing performance. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 11226–11233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, M.; Chauhan, R.S.; Garlapati, V.K. Evaluation of a new lipase from Staphylococcus sp. for detergent additive capability. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 374967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacha, A.B.; Al-Assaf, A.; Moubayed, N.M.; Abid, I. Evaluation of a novel thermo-alkaline Staphylococcus aureus lipase for application in detergent formulations. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedijani, P.; Khovia, N.; Rasmi, D.A.C.; Kusmiyati. Fungal Crude Lipase Enzyme Produced Using the SSF (Solid State Fermentation) Method Increases the Washing Test Performance. J. Biol. Trop. 2023, 23, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramnath, L.; Sithole, B.; Govinden, R. Identification of lipolytic enzymes isolated from bacteria indigenous to Eucalyptus wood species for application in the pulping industry. Biotechnol. Rep. 2017, 15, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, S.C.B.; Anbu, P.; Hilda, A. Extracellular enzymatic activity profiles in fungi isolated from oil-rich environments. Mycoscience 2005, 46, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Gupta, N.; Goswami, V.K.; Gupta, R. A simple activity staining protocol for lipases and esterases. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 70, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.P.; Jha, D.K. Isolation of a lipolytic and proteolytic Bacillus licheniformis from refinery oily sludge and optimization of culture conditions for production of the enzymes. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 48, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, A.; Shamaei, M.; Ziazi, L.M.; Pourabdollah, M.; Dorudinia, A.; Seyedmehdi, S.M.; Karimi, S. Qualification study of two genomic DNA extraction methods in different clinical samples. Tanaffos 2014, 13, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Santos, H.R.M.; Argolo, C.S.; Argôlo-Filho, R.C.; Loguercio, L.L. A 16S rDNA PCR-based theoretical to actual delta approach on culturable mock communities revealed severe losses of diversity information. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvinen, A.K.; Laakso, S.; Piiparinen, P.; Aittakorpi, A.; Lindfors, M.; Huopaniemi, L.; Piiparinen, H.; Mäki, M. Rapid identification of bacterial pathogens using a PCR-and microarray-based assay. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokashe, N.; Chaudhari, B.; Patil, U. Detergent-compatible robust alkaline protease from newly isolated halotolerant Salinicoccus sp. UN-12. J. Surfact. Deterg. 2017, 20, 1377–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, T.; Das, A.; Mandal, A.; Halder, S.K.; Jana, A.; Maity, C.; DasMohapatra, P.K.; Pati, B.R.; Mondal, K.C. An efficient cloth cleaning properties of a crude keratinase combined with detergent: Towards industrial viewpoint. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 66, 672–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadati, R.; Barghi, A.; Larki, R.A. Isolation and screening of lipolytic fungi from coastal waters of the Southern Caspian sea (North of Iran). Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2015, 8, e16426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salwoom, L.; Raja Abd Rahman, R.N.Z.; Salleh, A.B.; Mohd Shariff, F.; Convey, P.; Pearce, D.; Mohamad Ali, M.S. Isolation, characterisation, and lipase production of a cold-adapted bacterial strain Pseudomonas sp. LSK25 isolated from Signy Island, Antarctica. Molecules 2019, 24, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fojan, P.; Jonson, P.H.; Petersen, M.T.; Petersen, S.B. What distinguishes an esterase from a lipase: A novel structural approach. Biochimie 2000, 82, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, M.D.K.G.; Facundes, B.C.; Júnior, A.F.C.; da Silva, E.M. Assessment of lipolytic activity of isolated microorganisms from the savannah of the Tocantins. Acta Sci. Biol. Sci. 2015, 37, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Kumar, L.; Nagar, S.; Raina, C.; Parshad, R.; Gupta, V.K. Screening, isolation and production of lipase/esterase producing Bacillus sp. strain DVL2 and its potential evaluation in esterification and resolution reactions. Arch. Appl. Sci. Res. 2012, 4, 1763–1770. [Google Scholar]
- Ugras, S.; Uzmez, S. Characterization of a newly identified lipase from a lipase-producing bacterium. Front. Biol. 2016, 11, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunarathna, J.A.D.D.; Samaraweera, P. Investigation of lipase producing bacteria from oil contaminated soil and characterization of lipase. Sri Lankan J. Appl. Sci. 2024, 3, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, L.P.; Karbul, H.M.; Citartan, M.; Gopinath, S.C.; Lakshmipriya, T.; Tang, T.H. Lipase-secreting Bacillus species in an oil-contaminated habitat: Promising strains to alleviate oil pollution. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 820575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Yang, J.; Chen, H.Y.; Wang, W.F.; Lian, X.J.; Xie, X.J.; Wang, M.; Yu, K.F.; Zheng, H.B. Construction and application of highly efficient waste cooking oil degrading bacteria consortium in oily wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 125677–125688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, D.; Rajalakshmi, G.; Komathi, S. Optimization and production of lipase enzyme from bacterial strains isolated from petrol spilled soil. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2019, 31, 898–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, B.D.; Sarrouh, B.; Bicas, J.L.; Lofrano, R.C. Lipase production by microorganisms isolated from the Serra de Ouro Branco State Park. An. Acad. Bras. Ciênc. 2021, 93, e20190672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, P.D.; Silva, V.S.; Tenreiro, R. Integrated selection and identification of bacteria from polluted sites for biodegradation of lipids. Int. Microbiol. 2020, 23, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layly, I.R.; Meryandini, A.; Helianti, I.; Astuti, R.I. Identification of lipase producing bacteria from palm oil sewage sludge processing plant at Malimping, Banten, Indonesia. Biodiversitas 2021, 22, 4512–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutar, V.P.; Singh, V.K.; Sinha, R.P. Biodegradation of various edible oils and fat by Staphylococcus petrasii sub sp. jettensis VSJK R1 for application in bioremediation of lipid rich restaurant wastewater. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2025, 56, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauba, A.; Rahman, K.M. Evaluation of antibiotic resistance mechanisms in gram-negative bacteria. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdette, L.A.; Leach, S.A.; Wong, H.T.; Tullman-Ercek, D. Developing Gram-negative bacteria for the secretion of heterologous proteins. Microb. Cell Fact. 2018, 17, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, P.; Bhowmik, A.; Verma, S.; Srivastava, S.; Chakdar, H.; Saxena, A.K. Multi-substrate sequential optimization, characterization and immobilization of lipase produced by Pseudomonas plecoglossicida S7. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 4555–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdar, A.; Ismail, F.; Imran, M. Characterization of detergent-compatible lipases from Candida albicans and Acremonium sclerotigenum under solid-state fermentation. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 32740–32751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ren, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, T.; Xiao, J.; Chen, H. Enhancing Alkaline Protease stability through enzyme-catalyzed crosslinking and its application in detergents. Processes 2024, 12, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürkök, S. Microbial enzymes in detergents: A review. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2019, 10, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Nadaroglu, H.; Baran, A.; Bayrakceken, H. Spray-dried immobilized lipase from Staphylococcus aureus HA25 for application in detergent industry. J. Surfact. Deterg. 2024, 24, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrea, T.; Marcela, F.; Lucía, C.; Esther, F.; Elena, M.; Simona, M. Microencapsulation of lipase and savinase enzymes by spray drying using arabic gum as wall material. J. Encapsul. Adsorp. Sci. 2016, 6, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemachander, C.; Puvanakrishnan, R. Lipase from Ralstonia pickettii as an additive in laundry detergent formulations. Process Biochem. 2000, 35, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dab, A.; Hasnaoui, I.; Mechri, S.; Allala, F.; Bouacem, K.; Noiriel, A.; Bouanane-Darenfed, A.; Saalaoui, E.; Asehraou, A.; Wang, F.; et al. Biochemical characterization of an alkaline and detergent-stable Lipase from Fusarium annulatum Bugnicourt strain CBS associated with olive tree dieback. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0286091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouassida, M.; Fourati, N.; Ghazala, I.; Ellouze-Chaabouni, S.; Ghribi, D. Potential application of Bacillus subtilis SPB1 biosurfactants in laundry detergent formulations: Compatibility study with detergent ingredients and washing performance. Eng. Life Sci. 2018, 18, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| S/N | Isolate Code | Diameter (mm) * |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | MN38 | 11.0 ± 1.4 a |
| 2. | MN1310 | 8.5 ± 0.7 b |
| 3. | MN28 | 6.5 ± 0.71 c |
| 4. | MN18 | 7.0 ±1.4 bc |
| 5. | MN310 | 8.15 ± 0.21 bc |
| 6. | MN210 | 2.25 ± 0.35 d |
| 7. | MN118 | 0 |
| 8. | MN135 | 0 |
| 9. | MN35 | 0 |
| 10. | MN15 | 2.25 ± 0.35 d |
| 11. | MN148 | 2.35 ± 0.49 d |
| 12. | MN48 | 3.1 ± 0.14 d |
| S/N | Isolate Code | Reference Organism | Percentage Similarity (%) | Sequence Identity | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | MN38 | Raoultella terrigena PKG-3X-1D (KJ685494) | 98.92 | Raoultella terrigena veli18 | PQ278865 |
| 2. | MN28 | Viridibacillus arenosi YT114 (MW405667) Viridibacillus arvi (HG798348) | 98.21 | Viridibacillus sp. veli10 | PQ278866 |
| 3. | MN18 | Stenotrophomonas maltophilia SN_33 (MT448767) Stenotrophomonas geniculata NM208 (MT114514) | 99.40 | Stenotrophomonas sp. veli19 | PQ278867 |
| 4. | MN1310 | Stenotrophomonas maltophilia L15 (KF358258) | 100 | Stenotrophomonas maltophilia veli96 | PQ278868 |
| 5. | MN310 | Klebsiella oxytoca RCB646 (KT260858) Klebsiella pneumoniae E3-2 (KP058371) | 99.46 | Klebsiella sp. veli70 | PQ278869 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noxhaka, M.; Nnolim, N.E.; Mpaka, L.; Nwodo, U.U. Biocatalytic Potential of a Raoultella terrigena-Derived Lipolytic Enzyme for High-Performance Detergents. Fermentation 2025, 11, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040225
Noxhaka M, Nnolim NE, Mpaka L, Nwodo UU. Biocatalytic Potential of a Raoultella terrigena-Derived Lipolytic Enzyme for High-Performance Detergents. Fermentation. 2025; 11(4):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040225
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoxhaka, Mfezeko, Nonso E. Nnolim, Lindelwa Mpaka, and Uchechukwu U. Nwodo. 2025. "Biocatalytic Potential of a Raoultella terrigena-Derived Lipolytic Enzyme for High-Performance Detergents" Fermentation 11, no. 4: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040225
APA StyleNoxhaka, M., Nnolim, N. E., Mpaka, L., & Nwodo, U. U. (2025). Biocatalytic Potential of a Raoultella terrigena-Derived Lipolytic Enzyme for High-Performance Detergents. Fermentation, 11(4), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040225







