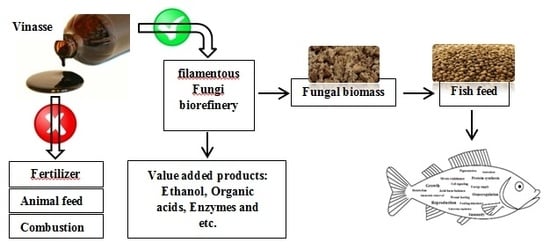
Evaluation of Filamentous Fungal Biomass Cultivated on Vinasse as an Alternative Nutrient Source of Fish Feed: Protein, Lipid, and Mineral Composition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Vinasse Characteristics
2.2. Fungi Species
2.3. Cultivation in Shake-Flasks
2.4. Analytical Procedures
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Filamentous Fungi Cultivation in Vinasse
3.1.1. The Effects of Vinasse Concentration on Fungal Cultivation
3.1.2. The Effect of pH on Fungal Cultivation in Vinasse
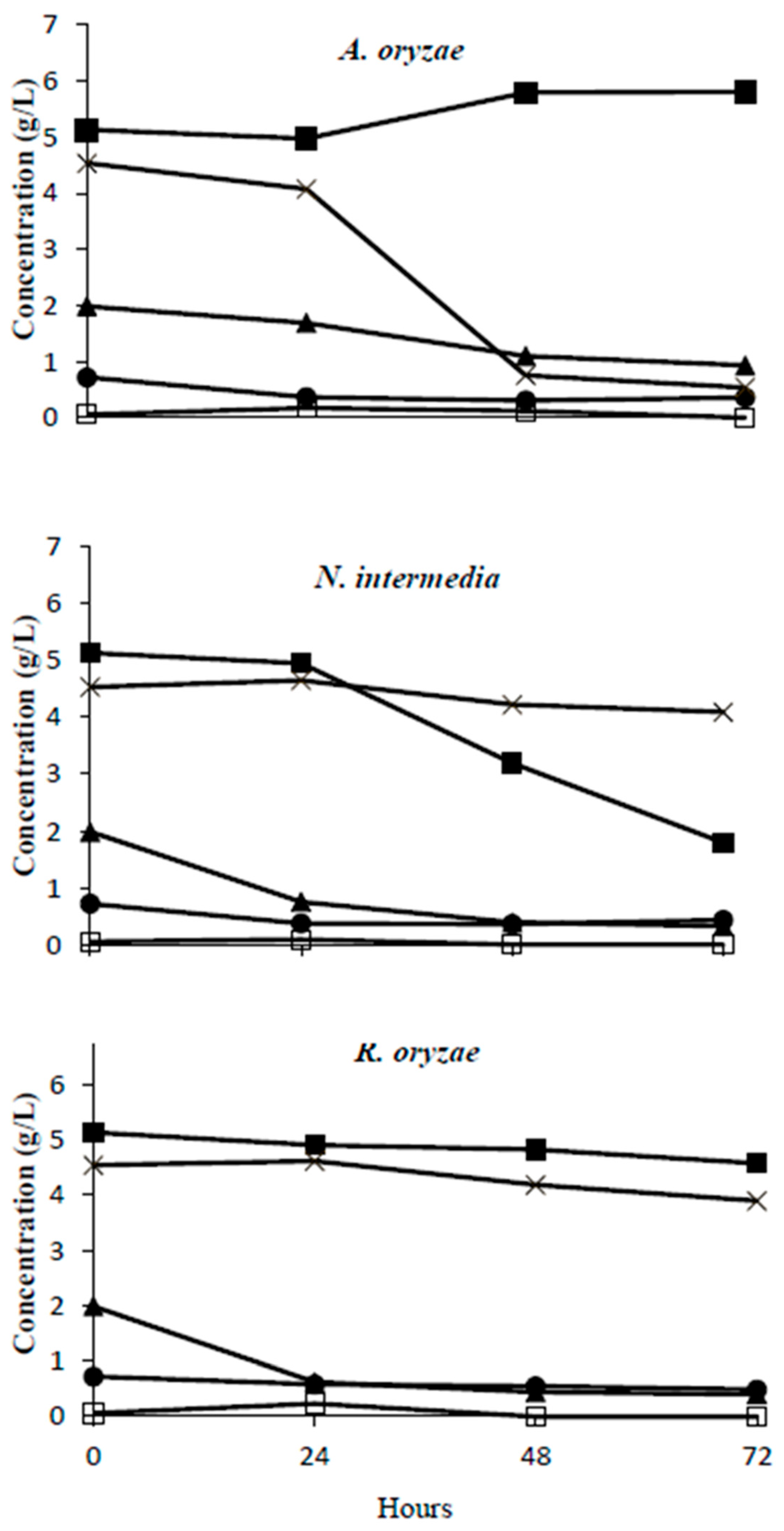
3.1.3. The Organic Removal and Metabolite Production of Fungi in Vinasse
3.2. Nutritional Characteristics of Fungal Biomass Cultivated on Vinasse
3.2.1. Protein and Amino Acid Composition of Fungal Biomass Cultivated on Vinasse
3.2.2. Lipid and Fatty acid Composition of the Fungal Biomass Cultivated in Vinasse
3.2.3. Minerals
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2018; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2018; p. 227. [Google Scholar]
- Moffitt, C.M.; Cajas-Cano, L. Blue Growth: The 2014 FAO State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture. Fisheries 2014, 39, 552–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monge-Ortiz, R.; Tomas-Vidal, A.; Gallardo-Alvarez, F.J.; Estruch, G.; Godoy-Olmos, S.; Jover-Cerda, M.; Martinez-Llorens, S. Partial and total replacement of fishmeal by a blend of animal and plant proteins in diets for Seriola dumerili: Effects on performance and nutrient efficiency. Aquac. Nutr. 2018, 24, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibbetts, S.M.; Mann, J.; Dumas, A. Apparent digestibility of nutrients, energy, essential amino acids and fatty acids of juvenile Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) diets containing whole-cell or cell-ruptured Chlorella vulgaris meals at five dietary inclusion levels. Aquaculture 2017, 481, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacon, A.G.J.; Metian, M. Global overview on the use of fish meal and fish oil in industrially compounded aquafeeds: Trends and future prospects. Aquaculture 2008, 285, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, D.T.; Pirozzi, I.; Glencross, B. Digestibility of canola meals in barramundi (Asian seabass; Lates calcarifer). Aquaculture 2015, 435, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.A.; Dumas, A.; Yossa, R.; Overturf, K.E.; Bureau, D.P. Effects of soybean meal and high-protein sunflower meal on growth performance, feed utilization, gut health and gene expression in Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus) at the grow-out stage. Aquac. Nutr. 2018, 24, 1540–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidakovic, A.; Langeland, M.; Sundh, H.; Sundell, K.; Olstorpe, M.; Vielma, J.; Kiessling, A.; Lundh, T. Evaluation of growth performance and intestinal barrier function in Arctic Charr (Salvelinus alpinus) fed yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae), fungi (Rhizopus oryzae) and blue mussel (Mytilus edulis). Aquac. Nutr. 2016, 22, 1348–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, S.J.; Morris, P.C. Influence of multiple amino acid supplementation on the performance of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), fed soya based diets. Aquac. Res. 1997, 28, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogdahl, A.; Bakke-McKellep, A.M.; Baeverfjord, G. Effects of graded levels of standard soybean meal on intestinal structure, mucosal enzyme activities, and pancreatic response in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquac. Nutr. 2003, 9, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allameh, S.K.; Soofiani, N.M.; Pourreza, J. Determination of digestible and metabolizable energy of fishmeal and soybean meal in rainbow trout with two different sizes (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Pak. J. Biol. Sci. PJBS 2007, 10, 3722–3725. [Google Scholar]
- Glencross, B.; Hawkins, W. A comparison of the digestibility of lupin (Lupinus sp.) kernel meals as dietary protein resources when fed to either, rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss or red seabream, Pagrus auratus. Aquac. Nutr. 2004, 10, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burel, C.; Boujard, T.; Tulli, F.; Kaushik, S.J. Digestibility of extruded peas, extruded lupin, and rapeseed meal in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and turbot (Psetta maxima). Aquaculture 2000, 188, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overland, M.; Sorensen, M.; Storebakken, T.; Penn, M.; Krogdahl, A.; Skrede, A. Pea protein concentrate substituting fish meal or soybean meal in diets for Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar)-Effect on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, carcass composition, gut health, and physical feed quality. Aquaculture 2009, 288, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Xue, M.; Wu, X.; Cai, X.; Cao, H.; Liang, Y. Partial or total replacement of fishmeal by solvent-extracted cottonseed meal in diets for juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquac. Nutr. 2006, 12, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Takeuchi, T.; Satoh, S.; Kiron, V. Digestible crude protein contents in various feedstuffs determined with four freshwater fish species. Fish. Sci. 1996, 62, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhangi, M.; Carter, C.G. Growth, physiological and immunological responses of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) to different dietary inclusion levels of dehulled lupin (Lupinus angustifolius). Aquac. Res. 2001, 32, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, G.; Makkar, H.P.S.; Becker, K. Antinutritional factors present in plant-derived alternate fish feed ingredients and their effects in fish. Aquaculture 2001, 199, 197–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, R.W.; Sealey, W.M.; Gatlin, D.M. Fisheries by-catch and by-product meals as protein sources for rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2005, 36, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Haroun, E.R.; Azevedo, P.A.; Bureau, D.P. High dietary incorporation levels of rendered animal protein ingredients on performance of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum, 1972). Aquaculture 2009, 290, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millamena, O.M. Replacement of fish meal by animal by-product meals in a practical diet for grow-out culture of grouper Epinephelus coioides. Aquaculture 2002, 204, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau, D.P.; Harris, A.M.; Bevan, D.J.; Simmons, L.A.; Azevedo, P.A.; Cho, C.Y. Feather meals and meat and bone meals from different origins as protein sources in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) diets. Aquaculture 2000, 181, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, S.; Soofiani, N.M.; Mahboubi, A.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Use of Organic Wastes and Industrial By-Products to Produce Filamentous Fungi with Potential as Aqua-Feed Ingredients. Sustain. Basel 2018, 10, 3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.A.; Mahboubi, A.; Lennartsson, P.R.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Waste biorefineries using filamentous ascomycetes fungi: Present status and future prospects. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 215, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akram, M.; Tan, C.K.; Garwood, R.; Thai, S.M. Vinasse—A potential biofuel—Cofiring with coal in a fluidised bed combustor. Fuel 2015, 158, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, J.D.; Benimeli, C.S.; Almeida, C.A.; Polti, M.A.; Colin, V.L. Integral use of sugarcane vinasse for biomass production of actinobacteria: Potential application in soil remediation. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, H.; Cereijo, C.R.; Teles, V.C.; Nascimento, R.C.; Fernandes, M.S.; Brunale, P.; Campanha, R.C.; Soares, I.P.; Silva, F.C.P.; Sabaini, P.S.; et al. Microalgae cultivation in sugarcane vinasse: Selection, growth and biochemical characterization. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 228, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.B.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Valorization of sugar-to-ethanol process waste vinasse: A novel biorefinery approach using edible ascomycetes filamentous fungi. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, P.M.; Pajot, H.F.; de Figueroa, L.I.C.; Gusils, C.H. Sustainable bioremediation of sugarcane vinasse using autochthonous macrofungi. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5177–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, J.D.; da Silva, A.L.L.; Costa, J.D.; Scheidt, G.N.; Novak, A.C.; Sydney, E.B.; Soccol, C.R. Development of a vinasse nutritive solution for hydroponics. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 114, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candido, C.; Lombardi, A.T. The physiology of Chlorella vulgaris grown in conventional and biodigested treated vinasses. Algal Res. 2018, 30, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, I.K.; Cekmecelioglu, D.; Yucel, A.M.; Oktem, H.A. Evaluation of heterotrophic and mixotrophic cultivation of novel Micractinium sp ME05 on vinasse and its scale up for biodiesel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 251, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, N.N.V.; Farenzena, M.; Trierweiler, J.O. Growth of Microalgae Scenedesmus sp in Ethanol Vinasse. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2014, 57, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitayavardhana, S.; Khanal, S.K. Innovative biorefinery concept for sugar-based ethanol industries: Production of protein-rich fungal biomass on vinasse as an aquaculture feed ingredient. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 9078–9085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitayavardhana, S.; Issarapayup, K.; Pavasant, P.; Khanal, S.K. Production of protein-rich fungal biomass in an airlift bioreactor using vinasse as substrate. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 133, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D.; Crocker, D. Determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass. In Laboratory Analytical Procedure (LAP); NREL: Golden, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bahlsberg-Pålsson, A.M. Förbehandling, uppslutning och extraktberedning av växt-och förnaprov. In I Handledning I Kemiska Metoder Vid Växtekologiska Arbeten; Meddelande från Växtekologiska avdelningen, Lunds Universitet: Lund, Sweden, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Langeland, M.; Vidakovic, A.; Vielma, J.; Lindberg, J.E.; Kiessling, A.; Lundh, T. Digestibility of microbial and mussel meal for Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus) and Eurasian perch (Perca fluviatilis). Aquac. Nutr. 2016, 22, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Stanley, G.H.S. A Simple Method for the Isolation and Purification of Total Lipides from Animal Tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar]
- Appelqvist, L.-Å. Rapid methods of lipid extraction and fatty acid methyl ester preparation for seed and leaf tissue with special remarks on preventing the accumulation of lipid contaminants. Ark. För Kemi 1968, 28, 551–570. [Google Scholar]
- Mahboubi Soufiani, A.; Ferreira, J.; Taherzadeh, M.; Lennartsson, P. Production of Fungal Biomass for Feed, Fatty Acids, and Glycerol by Aspergillus oryzae from Fat-Rich Dairy Substrates. Fermentation 2017, 3, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemian, A.; Asadollahzadeh, M.; Saraeian, A.; Resalati, H.; Taherzadeh, M. Effect of Acetic Acid on Growth and Ethanol Fermentation of Filamentous Fungi Rhizopus oryzae, Mucor indicus, Neurospora intermedia and Aspergilus oryzae. J. Exp. Anim. Sci. 2019, 7, 119–130. [Google Scholar]
- FazeliNejad, S.; Ferreira, J.A.; Brandberg, T.; Lennartsson, P.R.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Fungal biomass and ethanol from lignocelluloses using Rhizopus pellets under simultaneous saccharification, filtration, and fermentation (SSFF). Biofuel. Res. J. 2016, 3, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ytrestoyl, T.; Aas, T.S.; Asgard, T. Utilisation of feed resources in production of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) in Norway. Aquaculture 2015, 448, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRC. Nutrient Requirements of Fish and Shrimp; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; p. 392. ISBN 978-0-309-47322-4. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council. Nutrient Requirements of Swine: Eleventh Revised Edition; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; p. 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvant, D.; Perez, J.-M.; Tran, G. Tables of Composition and Nutritional Value of Feed Materials: Pigs, Poultry, Cattle, Sheep, Goats, Rabbits, Horses and Fish; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jobling, M. Feeding and digestive functions in fishes—Edited by J. E. P. Cyrino, D. Bureau and B. G. Kapoor. J. Fish Biol. 2009, 75, 756–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, F.; Tome, D.; Mirand, P.P. Converting nitrogen into Protein—Beyond 6.25 and Jones’ factors. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2008, 48, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stajich, J. Cellular and Molecular Biology of Filamentous Fungi; illBorkovich, K., Ebbole, D.J., Eds.; $209.95. xiii + 788 p.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; Volume 86, p. 59. ISBN 978-1-55581-473-1. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Che, J.F.; Tang, B.B.; Yu, S.L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.H. Dietary methionine requirement of juvenile Pseudobagrus ussuriensis. Aquac. Nutr. 2016, 22, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moughan, P.J.; Rutherfurd, S.M. A new method for determining digestible reactive lysine in foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 2202–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, M.J.; Cowey, C.B.; Adron, J.W. The Effect of Dietary Lysine Levels on Growth and Metabolism of Rainbow-Trout (Salmo-Gairdneri). Br. J. Nutr. 1984, 52, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, Y.N.; Austic, R.E.; Rumsey, G.L. Effect of Feeding Level and Dietary Electrolytes on the Arginine Requirement of Rainbow-Trout (Salmo-Gairdneri). Aquaculture 1988, 69, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, S.N.I.N.; Abdullah, M.F.; Zakaria, Z.; Yusof, S.J.H.M.; Abdullah, R. Formulation of Fish Feed with Optimum Protein-bound Lysine for African Catfish (Clarias Gariepinus) Fingerlings. Procedia Eng. 2016, 148, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelato, M.; Vidal, L.V.D.; Xavier, T.O.; de Moura, L.B.; de Almeida, F.L.A.; Pedrosa, V.B.; Furuya, V.R.B.; Furuya, W. Dietary lysine requirement to enhance muscle development and fillet yield of finishing Nile tilapia. Aquaculture 2016, 457, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.; Davis, D.A. Comparison of crystalline lysine and intact lysine used as a supplement in practical diets of channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) and Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2016, 464, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Mai, K.; Trushenski, J.; Wu, G. New developments in fish amino acid nutrition: Towards functional and environmentally oriented aquafeeds. Amino Acids 2009, 37, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, S.J.; Gomes, E.F. Effect of Frequency of Feeding on Nitrogen and Energy-Balance in Rainbow-Trout under Maintenance Conditions. Aquaculture 1988, 73, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.-C.; Zeng, W.-P.; Wang, H.-L.; Xie, F.-J.; Zheng, C.-Q. Dietary arginine requirement of juvenile yellow grouper Epinephelus awoara. Aquaculture 2012, 350, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yin, Y.L.; Li, D.; Kim, S.W.; Wu, G.Y. Amino acids and immune function. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 98, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buentello, J.A.; Reyes-Becerril, M.; Romero-Geraldo, M.D.; Ascencio-Valle, F.D. Effects of dietary arginine on hematological parameters and innate immune function of channel catfish. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2007, 19, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buentello, J.A.; Gatlin, D.M. Effects of elevated dietary arginine on resistance of channel catfish to exposure to Edwardsiella ictaluri. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2001, 13, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Yin, Y.L.; Chu, W.Y.; Li, Z.Q.; Deng, D.; Li, T.J.; Huang, R.L.; Zhang, J.S.; Tan, B.; Wang, W.; et al. Dietary arginine supplementation increases mTOR signaling activity in skeletal muscle of neonatal pigs. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, K.; Yakabe, Y.; Ishida, A.; Yamazaki, M.; Abe, H. Suppression of myofibrillar proteolysis in chick skeletal muscles by alpha-ketoisocaproate. Amino Acids 2007, 33, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.Y. Intestinal mucosal amino acid catabolism. J. Nutr. 1998, 128, 1249–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bystriansky, J.S.; Frick, N.T.; Ballantyne, J.S. Intermediary metabolism of Arctic char Salvelinus alpinus during short-term salinity exposure. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 1971–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.Z.; Yang, S.; Wu, G.Y. Free radicals, antioxidants, and nutrition. Nutrition 2002, 18, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamushaki, V.A.J.; Kasumyan, A.O.; Abedian, A.; Abtahi, B. Behavioural responses of the Persian sturgeon (Acipenser persicus) juveniles to free amino acid solutions. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 2007, 40, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, W.W.; Higgs, D.A.; Dosanjh, B.S.; Eales, J.G. Influence of dietary arginine and glycine content on thyroid function and growth of juvenile rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). Aquac. Nutr. 1996, 2, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brent, G.A. Mechanisms of thyroid hormone action. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 3035–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szebedinszky, C.; Gilmour, K.M. The buffering power of plasma in brown bullhead (Ameiurus nebulosus). Comp. Biochem. Phys. B 2002, 131, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, H.Y. Muscle buffering capacity of yellowtail fed diets supplemented with crystalline histidine. J. Fish Biol. 2002, 61, 1504–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargent, J.R.; Tocher, D.; Bell, J.G.B. Fish Nutrition; WHOLEY: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2002; pp. 181–257. [Google Scholar]
- Elagbar, Z.A.; Naik, R.R.; Shakya, A.K.; Bardaweel, S.K. Fatty Acids Analysis, Antioxidant and Biological Activity of Fixed Oil of Annona muricata L. Seeds. J. Chem. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skonberg, D.I.; Yogev, L.; Hardy, R.W.; Dong, F.M. Metabolic response to dietary phosphorus intake in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 1997, 157, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.A. Marine OMEGA-3 fatty acids in the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Fitoterapia 2017, 123, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innes, J.K.; Calder, P.C. Omega-6 fatty acids and inflammation. Prostaglandin Leukot. Essent. 2018, 132, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, I.; Steenfeldt, S.J.; Banta, G.; Hansen, B.W. The influence of dietary concentrations of arachidonic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid at various stages of larval ontogeny on eye migration, pigmentation and prostaglandin content of common sole larvae (Solea solea L.). Aquaculture 2008, 276, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senadheera, S.; Turchini, G.; Thanuthong, T.; Francis, D. Effects of dietary α-linolenic acid (18:3n−3)/linoleic acid (18:2n−6) ratio on growth performance, fillet fatty acid profile and finishing efficiency in Murray cod. Aquaculture 2010, 309, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halver, J.E.; Hardy, R.W. Fish Nutrition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization; World Health Organization. Vitamin and Mineral Requirements in Human Nutrition; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Takeda, E.; Yamamoto, H.; Yamanaka-Okumura, H.; Taketani, Y. Dietary phosphorus in bone health and quality of life. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, M.; Anderson, J.J.B.; Garner, S.C. Calcium and Phosphorus in Health and Disease; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Fairweather-Tait, S.J.; Cashman, K. Minerals and Trace Elements. World Rev. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 111, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.J.; MacGregor, G.A. Beneficial effects of potassium on human health. Physiol. Plant. 2008, 133, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Value | Concentration (ppm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 5.5 ± 0.09 | Minerals | |
| Total solids (%) | 65.27 ± 1.45 | Aluminum (Al) | 5.5 |
| Volatile solid (%) | 28.93 ± 0.37 | Arsenic (As) | 0 |
| Ash (%) | 25.16 ± 0.2 | Barium (Ba) | 0.1 |
| COD (g/L) | 835 ± 22 | Bor (B) ppm | 7 |
| SCOD (soluble COD) (g/L) | 740 ± 14 | Cadmium (Cd) | 0 |
| Soluble sugar (g/L) | Chromium (Cr) | 0 | |
| Arabinose | 1.39 ± 0.24 | Cobalt (Co) | 0 |
| Cellobiose | 19.27 ± 1.15 | Cupper (Cu) | 15 |
| Fructose | 11.03 ± 0.68 | Iron (Fe) | 350 |
| Galactose | 3.42 ± 0.17 | Lead (Pb) | 0 |
| Glucose | 14.4 ± 0.78 | Manganese | 35 |
| Mannose | 0.76 ± 0.04 | Molybdenum (Mo) | 0 |
| Sucrose | 4.71 ± 0.14 | Nickel (Ni) | 0.6 |
| Xylose | 0.88 ± 0.05 | Potassium (K) | 87,220 |
| Organic Acid, Metabolite (g/L) | Selenium (Se) | 2.5 | |
| Acetic acid | 39.7 ± 1.55 | Strontium (Sr) | 3.4 |
| Ethanol | 1.1 ± 0.11 | Zinc (Zn) | 50 |
| Glycerol | 90.7 ± 3.75 | Concentration (%) | |
| Lactic acid | 102.6 ± 7.09 | Calcium (Ca) | 1.2 |
| Magnesium (Mg) | 0.1 | ||
| Phosphorus (P) | 0.03 | ||
| Sodium (Na) | 1 |
| Culture Condition | A. Oryzae | N. Intermedia | R. Oryzae | M. Purpureus | F. Venenatum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (% v/v) | ||||||
| 5% | 103.0 ± 2.7 | 78.6 ± 1.0 | 27.9 ± 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| 10% | 91.1 ± 3.6 | 70.0 ± 2,4 | 23.6 ± 1,2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| 15% | 66.9 ± 1.5 | 56.2 ± 1.9 | 14.7 ± 1.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| 20% | 31.6 ± 2.4 | 9.3 ± 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| 50% | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| 5% Concentration | ||||||
| pH | ||||||
| 5.0 | 88.6 ± 4.2 | 79 ± 1.7 | 34.3 ± 2.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| 5.5 | 103.1 ± 5.3 | 85.1 ± 3.4 | 25 ± 1.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| 6.0 | 111.2 ± 4.2 | 77.2 ± 1.9 | 21.1 ± 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| 6.5 | 118.5 ± 3.9 | 75 ± 3.1 | 29.9 ± 1.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| AA (g/Kg DM) | AA (% of Total AA Content) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AO | NI | RO | FM | SBM | AO | NI | RO | FM | SBM | |
| DM (%) | 93.6 | 94.9 | 92.3 | 94.3 | 87.6 | |||||
| CP (%) | 44.7 | 57.6 | 50.9 | 62.6 | 43.3 | |||||
| CF (%) | 7.0 | 3.5 | 5.5 | 8.9 | 1.7 | |||||
| Indispensable Amino Acids | ||||||||||
| Arginine | 19.9 | 20.7 | 18.7 | 38.2 | 32.0 | 6.42 | 6.15 | 6.03 | 6.75 | 7.81 |
| Histidine | 7.51 | 8.65 | 7.66 | 15.9 | 11.5 | 2.42 | 2.57 | 2.47 | 2.81 | 2.81 |
| Isoleucine | 13.8 | 16.1 | 15.7 | 25.0 | 19.9 | 4.45 | 4.78 | 5.07 | 4.42 | 4.85 |
| Leucine | 24.6 | 27.1 | 24.5 | 44.5 | 31.9 | 7.94 | 8.05 | 7.9 | 7.86 | 7.78 |
| Lysine | 21.4 | 24.4 | 22.9 | 46.4 | 26.6 | 6.91 | 7.25 | 7.39 | 8.2 | 6.49 |
| Methionine | 5.66 | 6.05 | 5.98 | 16.3 | 6.2 | 1.83 | 1.8 | 1.93 | 2.88 | 1.51 |
| Phenylalanine | 14.2 | 15.8 | 14.6 | 24.3 | 21.7 | 4.58 | 4.69 | 4.71 | 4.29 | 5.29 |
| Threonine | 16.9 | 18.1 | 16.2 | 25.6 | 17.7 | 5.45 | 5.38 | 5.23 | 4.52 | 4.32 |
| Valine | 17.2 | 20.2 | 18.5 | 30.0 | 20.8 | 5.55 | 6.0 | 5.97 | 5.3 | 5.07 |
| Sum | 123.9 | 136.9 | 126.24 | 236.2 | 167.5 | 45.55 | 46.67 | 46.7 | 47.03 | 45.93 |
| Dispensable Amino Acids | ||||||||||
| Alanin | 23.7 | 27.8 | 23.7 | 39.7 | 19.0 | 7.65 | 8.26 | 7.65 | 7.02 | 4.64 |
| Aspargine | 32.3 | 36.6 | 32.3 | 57.7 | 49.0 | 10.42 | 10.87 | 10.42 | 10.2 | 11.95 |
| Cystein | 2.75 | 3.27 | 3.01 | 5.1 | 0.5 | 0.89 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.9 | 0.12 |
| Glutamine | 43.3 | 47.7 | 40.9 | 77.3 | 77.0 | 13.97 | 14.17 | 13.2 | 13.66 | 18.79 |
| Glycin | 17.2 | 18.9 | 16.5 | 48.0 | 18.1 | 5.55 | 5.61 | 5.32 | 8.48 | 4.42 |
| Hydroxyproline | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Ornithine | 0.97 | ND | 0.51 | ND | ND | 0.31 | ND | 0.16 | ND | ND |
| Proline | 18.5 | 14.1 | 20.2 | 28.3 | 21.6 | 5.97 | 4.19 | 6.52 | 5.0 | 5.27 |
| Serine | 17.2 | 17.6 | 15.6 | 24.5 | 21.8 | 5.55 | 5.23 | 5.03 | 4.33 | 5.32 |
| Tyrosine | 12.8 | 13.6 | 12.5 | 19.0 | 14.6 | 4.13 | 4.04 | 4.03 | 3.36 | 3.56 |
| Sum | 168.72 | 179.57 | 165.22 | 299.6 | 221.6 | 54.44 | 53.34 | 53.3 | 52.95 | 54.07 |
| Fatty Acids (% of Extracted Lipid Fraction) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. Oryzae | g/kg | N. Intermedia | g/kg | R. Oryzae | g/kg | FM (%) | FM (g/kg) | SBM (%) | SBM (g/kg) | |
| C14:0 (Myristic acid) | 0.47 | 0.33 | 0.73 | 0.26 | 0.86 | 0.47 | 6 | 4.10 | 0.1 | 0 |
| C14:1 (Myristolicacid) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| C16:0 (Palmitic acid) | 19.93 | 13.93 | 17.28 | 6.13 | 22.87 | 12.50 | 17.8 | 12.30 | 10.5 | 1.3 |
| C16:1 (Palmitoleic acid) | 3.17 | 2.21 | 3.84 | 1.36 | 5.78 | 3.16 | 7.2 | 5.00 | 0.2 | 0.00 |
| C18:0 (Stearic acid) | 7.73 | 5.40 | 4.97 | 1.76 | 6.26 | 3.42 | 3.6 | 2.50 | 3.8 | 0.5 |
| C18:1 (Oleic acid) | 33.93 | 23.72 | 39.70 | 14.09 | 27.97 | 15.29 | 12.3 | 8.50 | 21.7 | 2.8 |
| C18:1 (Vaccenic acid) | 0.48 | 0.33 | 1.97 | 0.70 | 1.42 | 0.78 | ||||
| C18:2 (Linolelaidic acid) | 32.36 | 22.62 | 29.40 | 10.43 | 34.31 | 18.76 | 2.1 | 1.40 | 53.1 | 6.8 |
| C18:3 (Linolenic acid) | 0.29 | 0.20 | 0.92 | 0.33 | 0.53 | 0.29 | 1.9 | 1.30 | 7.4 | 0.9 |
| C20:0 (Arachidic acid) | 0.31 | 0.22 | 0.26 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||
| C20:1 cis-11-ecosenoic acid | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 6.6 | 4.5 | ||
| C20:2 (cis-11,14-ecosadienoic acid) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||
| C20:3 (11,14,17-Eicosatrienoic acid) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||
| C20:4 (Arachidonic acid) | 0.55 | 0.38 | 0.36 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.4 | 1.7 | ||
| C20:5n-3 (Eicosapentaenoic acid) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 9.0 | 6.2 | ||
| C22:0 (Behenic acid) | 0.23 | 0.16 | 0.20 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||
| C22:1 (Erucic acid) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 7.7 | 5.3 | ||
| C24:0 (Lignoceric acid) | 0.55 | 0.39 | 0.37 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||
| C24:1 (Nervonic acid) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||
| C22:6n-3 (Docosahexaenoic acid) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 6.6 | 4.5 | ||
| Total | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | |||||||
| % SFA | 28.13 | 19.66 | 22.98 | 8.15 | 29.99 | 16.40 | ||||
| % MUFA | 37.57 | 26.26 | 45.51 | 16.15 | 35.17 | 19.23 | ||||
| % PUFA | 33.20 | 23.21 | 30.68 | 10.89 | 34.84 | 19.05 | ||||
| PUFA/SFA | 1.18 | 1.34 | 1.16 | |||||||
| Mineral (g/Kg) | A. oryzae | N. intermedia | R. oryzae | FM | SBM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca | 23.8 | 58.5 | 26.4 | 55.4 | 3.4 |
| K | 12.0 | 15.8 | 8.9 | 7.4 | 21.2 |
| P | 9.1 | 8.9 | 16.4 | 31.0 | 6.2 |
| Mg | 0.9 | 0.8 | 1.2 | 2.6 | 2.9 |
| Na | 1.1 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 11.2 | 0.0 |
| S | 4.7 | 4.8 | 3.9 | 7.4 | ND |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karimi, S.; Mahboobi Soofiani, N.; Lundh, T.; Mahboubi, A.; Kiessling, A.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Evaluation of Filamentous Fungal Biomass Cultivated on Vinasse as an Alternative Nutrient Source of Fish Feed: Protein, Lipid, and Mineral Composition. Fermentation 2019, 5, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation5040099
Karimi S, Mahboobi Soofiani N, Lundh T, Mahboubi A, Kiessling A, Taherzadeh MJ. Evaluation of Filamentous Fungal Biomass Cultivated on Vinasse as an Alternative Nutrient Source of Fish Feed: Protein, Lipid, and Mineral Composition. Fermentation. 2019; 5(4):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation5040099
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarimi, Sajjad, Nasrollah Mahboobi Soofiani, Torbjörn Lundh, Amir Mahboubi, Anders Kiessling, and Mohammad J. Taherzadeh. 2019. "Evaluation of Filamentous Fungal Biomass Cultivated on Vinasse as an Alternative Nutrient Source of Fish Feed: Protein, Lipid, and Mineral Composition" Fermentation 5, no. 4: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation5040099
APA StyleKarimi, S., Mahboobi Soofiani, N., Lundh, T., Mahboubi, A., Kiessling, A., & Taherzadeh, M. J. (2019). Evaluation of Filamentous Fungal Biomass Cultivated on Vinasse as an Alternative Nutrient Source of Fish Feed: Protein, Lipid, and Mineral Composition. Fermentation, 5(4), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation5040099