Succession of Microbial Communities of Corn Silage Inoculated with Heterofermentative Lactic Acid Bacteria from Ensiling to Aerobic Exposure
Abstract
:Highlights
- Microbial communities of corn silage were studied by SMRT.
- Heterofermentative LAB altered the microbial communities in different ways.
- Acetobacter fabarum was reported for the first time in silage.
- The presence of Acetobacter fabarum was related to aerobic exposure.
- Heterofermentative LAB improved the aerobic stability of corn silage.
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Silage Development and Aerobic Stability Test
2.2. Fermentation Profiles and Microbial Counts
2.3. Chemical Composition and DM Loss
2.4. Bacterial Analysis
2.4.1. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.4.2. Sequence Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Chemical and Microbial Composition of Corn before Ensiling
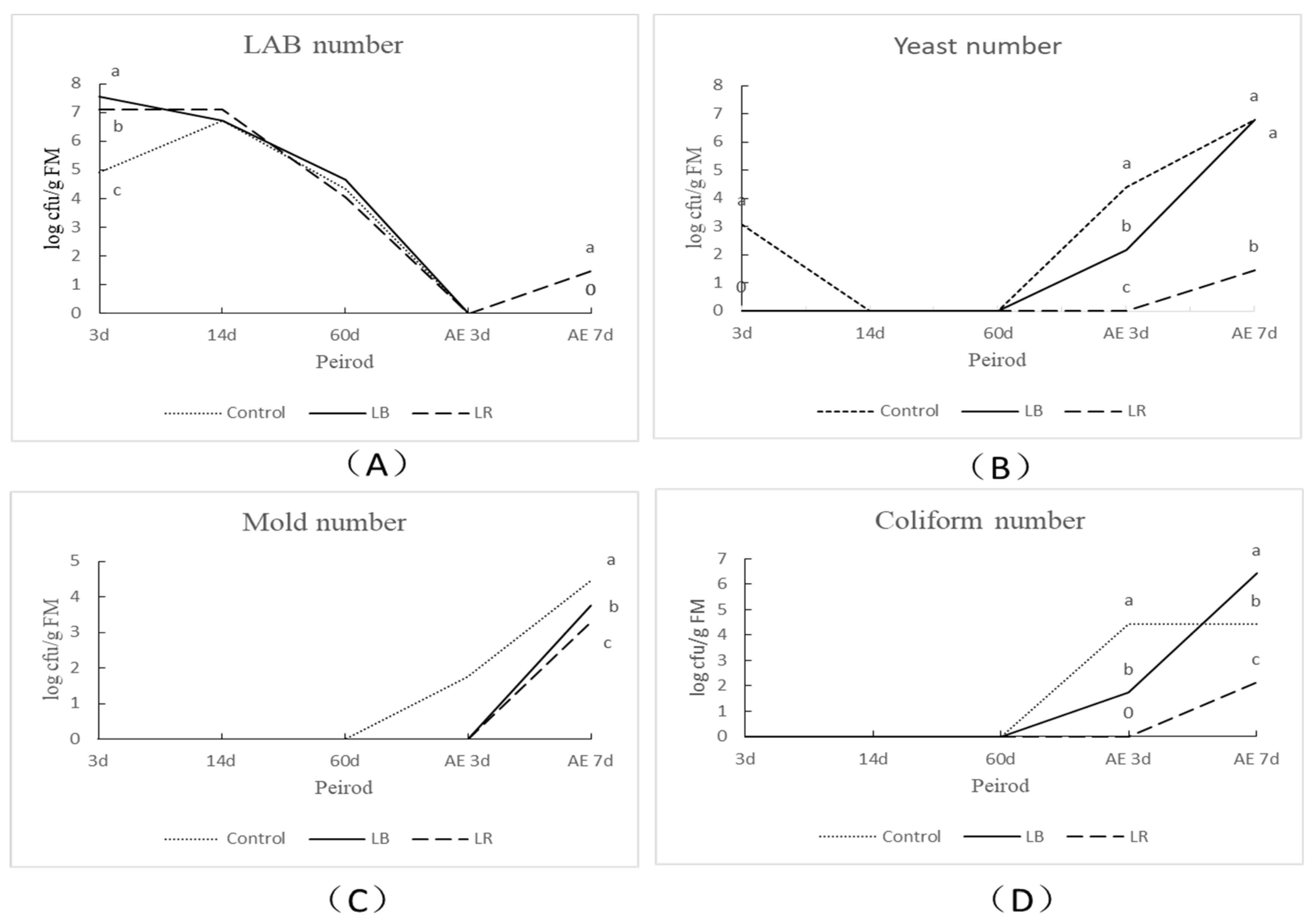
3.2. Fermentation Profiles and Microbial Counts of Corn Silage
3.3. Chemical Composition and Aerobic Stability of Corn Silage
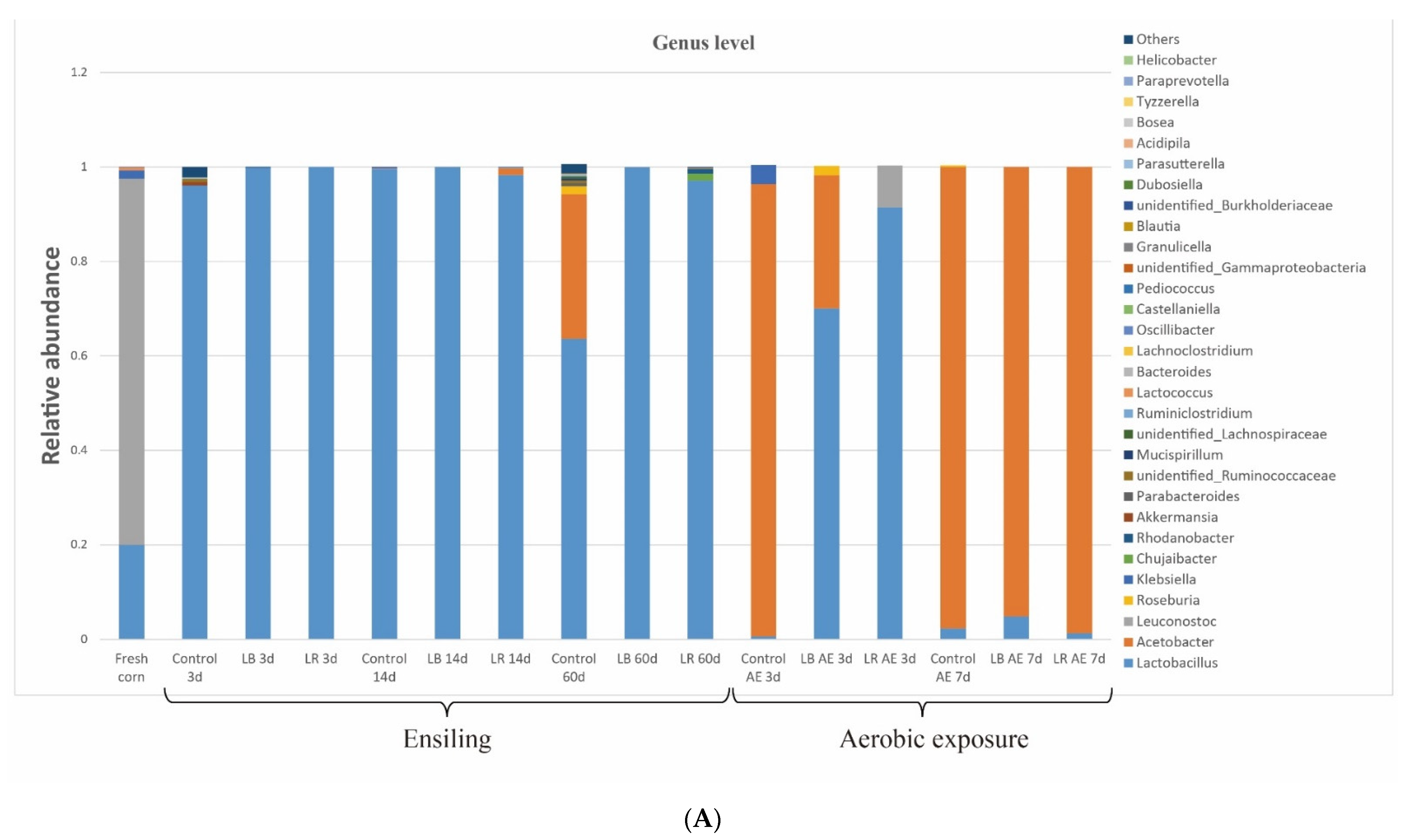
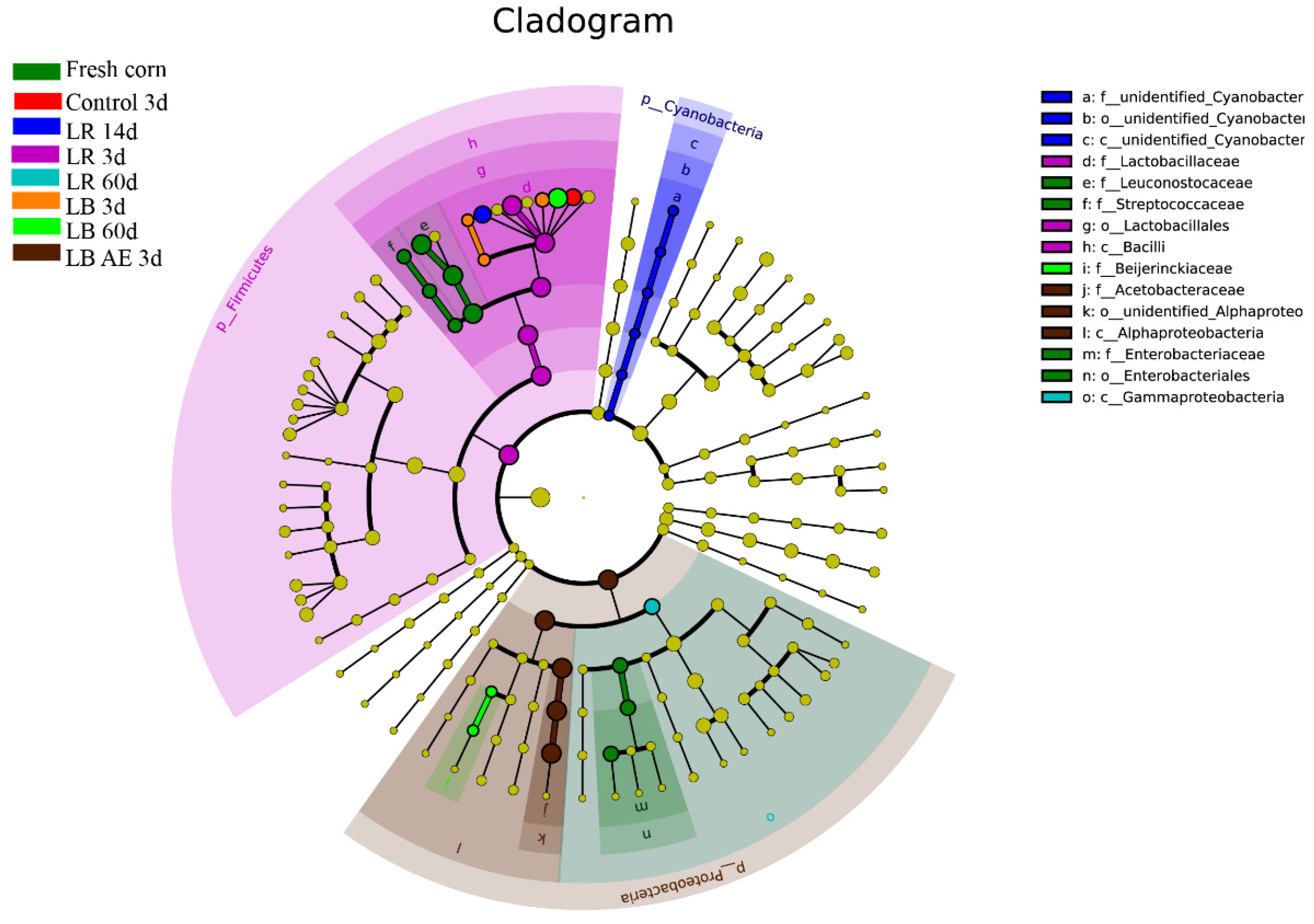
3.4. Changes in Bacterial Community from Ensiling to Aerobic Exposure
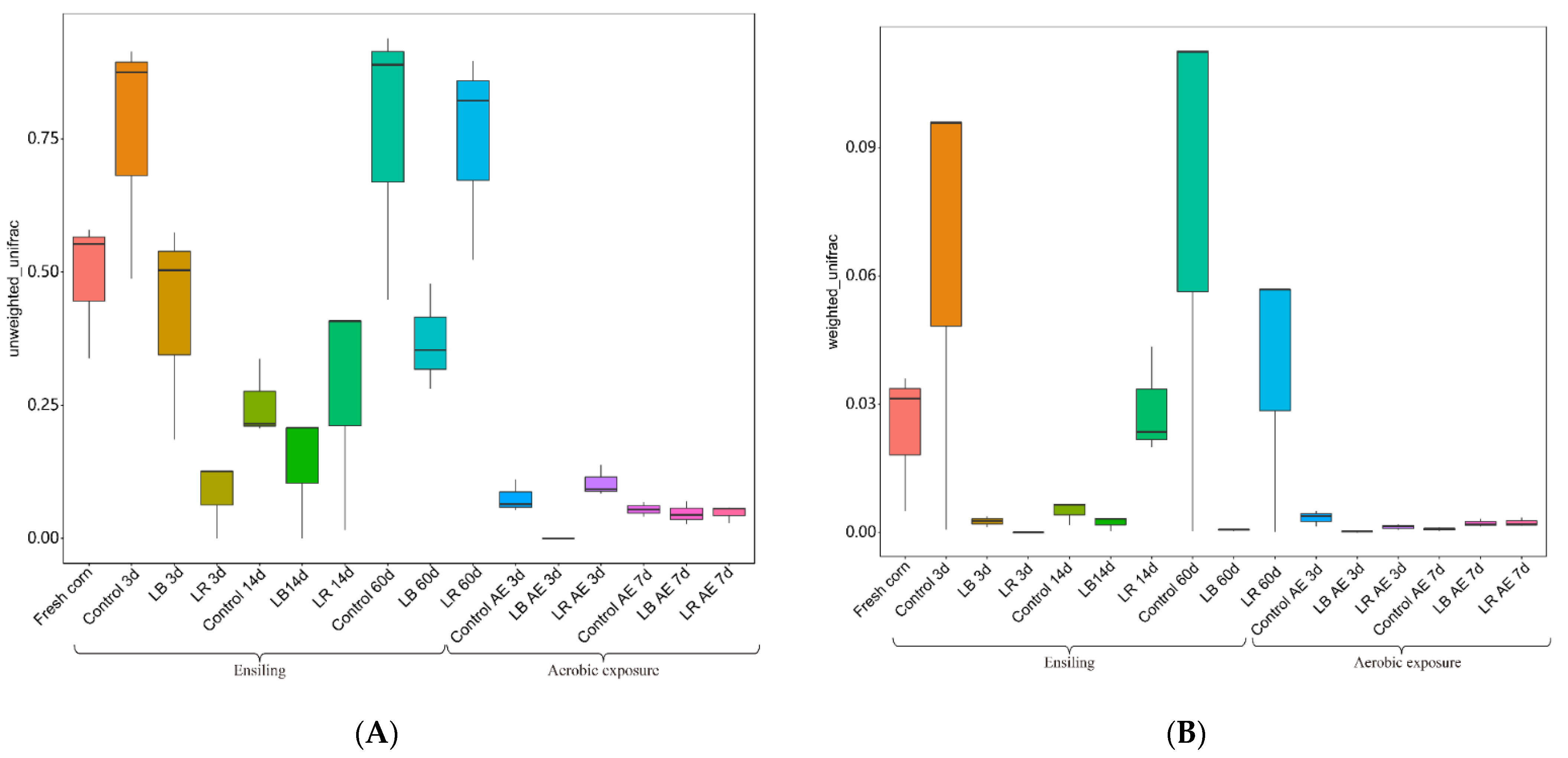
3.5. Diversity of Bacteria Ansilysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrae, J.G.; Hunt, C.; Pritchard, G.; Kennington, L.; Harrison, J.; Kezar, W.; Mahanna, W. Effect of hybrid, maturity, and mechanical processing of corn silage on intake and digestibility by beef cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 2001, 79, 2268–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ávila, C.L.S.; Carvalho, B.F.; Pinto, J.C.; Duarte, W.F.; Schwan, R.F. The use of Lactobacillus species as starter cultures for enhancing the quality of sugar cane silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 940–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, T.F.; Daniel, J.L.P.; Adesogan, A.T.; Mcallister, T.A.; Drouin, P.; Nussio, L.G.; Huhtanen, P.; Tremblay, G.F.; Bélanger, G.; Cai, Y. Silage review: Unique challenges of silages made in hot and cold regions. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4001–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y. Identification and characterization of Enterococcus species isolated from forage crops and their influence on silage fermentation. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 2466–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cleenwerck, I.; Gonzalez, Á.; Camu, N.; Engelbeen, K.; De Vos, P.; De Vuyst, L. Acetobacter fabarum sp. nov., an acetic acid bacterium from a Ghanaian cocoa bean heap fermentation. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 2180–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cole, J.R.; Chai, B.; Farris, R.J.; Wang, Q.; Kulam-Syed-Mohideen, A.S.; McGarrell, D.M.; Bandela, A.M.; Cardenas, E.; Garrity, G.; Tiedje, J.M. The ribosomal database project (RDP-II): Introducing myRDP space and quality controlled public data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D169–D172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Contreras-Govea, F.; Muck, R. Microbial inoculants for silage. Focus Forage 2006, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Danner, H.; Holzer, M.; Mayrhuber, E.; Braun, R. Acetic Acid Increases Stability of Silage under Aerobic Conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dogi, C.A.; Pellegrino, M.; Poloni, V.; Poloni, L.; Pereyra, C.M.; Sanabria, A.; Pianzzola, M.J.; Dalcero, A.; Cavaglieri, L. Efficacy of corn silage inoculants on the fermentation quality under farm conditions and their influence on Aspergillus parasitucus, A. flavus and A. fumigatusdetermined by q-PCR. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2015, 32, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driehuis, F.; Elferink, S.J.W.H.O.; Van Wikselaar, P.G. Fermentation characteristics and aerobic stability of grass silage inoculated with Lactobacillus buchneri, with or without homofermentative lactic acid bacteria. Grass Forage Sci. 2001, 56, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouin, P.; Tremblay, J.; Chaucheyras-Durand, F. Dynamic succession of microbiota during ensiling of whole plant corn following inoculation with Lactobacillus buchneri and Lactobacillus hilgardii alone or in combination. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duniere, L.; Xu, S.; Long, J.; Elekwachi, C.; Wang, Y.; Turkington, K.; Forster, R.; McAllister, T.A. Bacterial and fungal core microbiomes associated with small grain silages during ensiling and aerobic spoilage. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferraretto, L.; Shaver, R. Meta-analysis: Effect of corn silage harvest practices on intake, digestion, and milk production by dairy cows. Prof. Anim. Sci. 2012, 28, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraretto, L.F.; Shaver, R.D.; Luck, B.D. Silage review: Recent advances and future technologies for whole-plant and fractionated corn silage harvesting. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3937–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filya, I. The effect of Lactobacillus buchneri and Lactobacillus plantarum on the fermentation, aerobic stability, and ruminal degradability of low dry matter corn and sorghum silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 3575–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, H.; Ke, W.; Yan, Y.; Shuai, Y.; Li, X.; Ran, Q.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, X. Screening of natural lactic acid bacteria with potential effect on silage fermentation, aerobic stability and aflatoxin B1 in hot and humid area. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Shuai, Y.; Ran, Q.; Yan, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, X. The microbiome and metabolome of Napier grass silages prepared with screened lactic acid bacteria during ensiling and aerobic exposure. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2020, 269, 114673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Shuai, Y.; Yan, Y.; Ran, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, X. Microbial community and fermentation dynamics of corn silage prepared with heat-resistant lactic acid bacteria in a hot environment. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Yan, Y.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Shuai, Y.; Feng, G.; Ran, Q.; Cai, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Microbial communities and natural fermentation of corn silages prepared with farm bunker-silo in Southwest China. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulfam, A.; Guo, G.; Tajebe, S.; Chen, L.; Liu, Q.; Yuan, X.; Bai, Y.; Saho, T. Characteristics of lactic acid bacteria isolates and their effect on the fermentation quality of Napier grass silage at three high temperatures. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 1931–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.S.; Ke, W.C.; Ding, W.R.; Ding, L.M.; Xu, D.M.; Wang, W.W.; Zhang, P.; Yang, F.Y. Profiling of metabolome and bacterial community dynamics in ensiled Medicago sativa inoculated without or with Lactobacillus plantarum or Lactobacillus buchneri. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haas, B.; Gevers, D.; Earl, A.; Feldgarden, M.; Ward, D.; Giannoukos, G.; Ciulla, D.; Tabbaa, D.; Highlander, S.; Sodergren, E.; et al. Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in Sanger and 454-pyrosequenced PCR amplicons. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, L.; Harrison, J.H.; Hunt, C.; Shinners, K.; Doggett, C.G.; Sapienza, D. Nutritive value of corn silage as affected by maturity and mechanical processing: A contemporary review. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 2813–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.M.; Harrison, J.H.; Davidson, D.; Robutti, J.L.; Swift, M.; Mahanna, W.C.; Shinners, K. Corn silage management I: Effects of hybrid, maturity, and mechanical processing on chemical and physical characteristics. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 833–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khota, W.; Pholsen, S.; Higgs, D.; Cai, Y. Natural lactic acid bacteria population of tropical grasses and their fermentation factor analysis of silage prepared with cellulase and inoculant. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 9768–9781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kleinschmit, D.H.; Kung, L., Jr. A meta-analysis of the effects of Lactobacillus buchneri on the fermentation and aerobic stability of corn and grass and small-grain silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 4005–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinschmit, D.H.; Schmidt, R.J.; Kung, L., Jr. The effects of various antifungal additives on the fermentation and aerobic stability of corn silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 2130–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kraut-Cohen, J.; Tripathi, V.; Chen, Y.; Gatica, J.; Volchinski, V.; Sela, S.; Weinberg, Z.; Cytryn, E. Temporal and spatial assessment of microbial communities in commercial silages from bunker silos. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 6827–6835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kung, L., Jr.; Shaver, R.; Grant, R.; Schmidt, R. Silage review: Interpretation of chemical, microbial, and organoleptic components of silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4020–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Nishino, N. Bacterial and fungal communities of wilted Italian ryegrass silage inoculated with and without Lactobacillus rhamnosus or Lactobacillus buchneri. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 52, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Nishino, N. Effects of inoculation of Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus buchneri on fermentation, aerobic stability and microbial communities in whole crop corn silage. Grassl. Sci. 2011, 57, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Nishino, N. Monitoring the bacterial community of maize silage stored in a bunker silo inoculated with Enterococcus faecium, Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus buchneri. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 110, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Bolsen, K.; Brent, B.; Fung, D. Epiphytic lactic acid bacteria succession during the pre-ensiling and ensiling periods of alfalfa and maize. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1992, 73, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, F.; Zhang, J.; Shao, T. Characteristics of Lactobacillus parafarraginis ZH1 and its role in improving the aerobic stability of silages. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. UniFrac: A new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McAllister, T.; Dunière, L.; Drouin, P.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Munns, K.; Zaheer, R. Silage review: Using molecular approaches to define the microbial ecology of silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4060–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mcdonald, P.; Henderson, A.R.; Heron, S.J.E. The Biochemistry of Silage; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Mosher, J.J.; Bowman, B.; Bernberg, E.L.; Shevchenko, O.; Kan, J.; Korlach, J.; Kaplan, L.A. Improved performance of the PacBio SMRT technology for 16S rDNA sequencing. J. Microbiol. Methods 2014, 104, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck, R. Recent advances in silage microbiology. Agric. Food Sci. 2013, 22, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muck, R.E.; Nadeau, E.M.G.; McAllister, T.A.; Contreras-Govea, F.E.; Santos, M.C.; Kung, L. Silage review: Recent advances and future uses of silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3980–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunade, I.M.; Jiang, Y.; Pech, A.C.; Kim, D.H.; Oliveira, A.S.; Vyas, D.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Jeong, K.C.; Adesogan, A.T. Bacterial diversity and composition of alfalfa silage as analyzed by Illumina MiSeq sequencing: Effects of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 101, 2048–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.S.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Ogunade, I.M.; Cervantes, A.A.P.; Arriola, K.G.; Jiang, Y.; Kim, D.; Li, X.; Gonçalves, M.C.M.; Vyas, D. Meta-analysis of effects of inoculation with homofermentative and facultative heterofermentative lactic acid bacteria on silage fermentation, aerobic stability, and the performance of dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 4587–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oude Elferinck, S.J.; Driehuis, F.; Becker, P.M.; Gottschal, J.C.; Faber, F.; Spoelstra, S.F. The presence of Acetobacter sp. in ensiled forage crops and ensiled industrial byproducts. Mededelingen 2001, 66, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pahlow, G.; Muck, R.E.; Driehuis, F.; Elferink, S.O.; Spoelstra, S.F. Microbiology of Ensiling; OAI: Madison, WI, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree: Computing large minimum evolution trees with profiles instead of a distance matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjit, N.K.; Kung, L., Jr. The effect of Lactobacillus buchneri, Lactobacillus plantarum, or a chemical preservative on the fermentation and aerobic stability of corn silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, L.J.; Kung, L., Jr. Effects of combining Lactobacillus buchneri 40788 with various lactic acid bacteria on the fermentation and aerobic stability of corn silage. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2010, 159, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoelstra, S.F.; Courtin, M.G.; Beers, J.A.C. Acetic acid bacteria can initiate aerobic deterioration of whole crop maize silage. J. Agric. Sci. 1988, 111, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storm, I.M.L.D.; Kristensen, N.B.; Raun, B.M.L.; Smedsgaard, J.; Thrane, U. Dynamics in the microbiology of maize silage during whole-season storage. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabacco, E.; Piano, S.; Revello-Chion, A.; Borreani, G. Effect of Lactobacillus buchneri LN4637 and Lactobacillus buchneri LN40177 on the aerobic stability, fermentation products, and microbial populations of corn silage under farm conditions. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 5589–5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for Dietary Fiber, Neutral Detergent Fiber, and Nonstarch Polysaccharides in Relation to Animal Nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, A.F.; Meléndez, A.P.; Carulla, J.E.; Pabón, M.L.; Cárdenas, E.A. Study of microbiological and nutritional quality of corn silage in two Colombian ecosystems. Rev. Colomb. Cienc. Pecu. 2010, 23, 65–77. [Google Scholar]
- Weatherburn, M. Phenol-hypochlorite reaction for determination of ammonia. Anal. Chem. 1967, 39, 971–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Li, X.; Guan, H.; Huang, L.; Ma, X.; Peng, Y.; Li, Z.; Nie, G.; Zhou, J.; Yang, W.; et al. Microbial community and fermentation characteristic of Italian ryegrass silage prepared with corn stover and lactic acid bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 279, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Corn | |
|---|---|
| Dry matter (DM; % FM) | 28.38 |
| pH | 5.78 |
| Crude protein (% DM) | 5.93 |
| Neutral detergent fiber (% DM) | 45.15 |
| Acid detergent fiber (% DM) | 22.23 |
| Water-soluble carbohydrates (% DM) | 17.77 |
| Lactic acid bacteria (log cfu/g FM) | 4.37 |
| Enterobacteria (log cfu/g FM) | 7.34 |
| Yeasts (log cfu/g FM) | 5.13 |
| Molds (log cfu/g FM) | 1.27 |
| Period | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Items | Samples | 3 d | 14 d | 60 d | AE 3 d | AE 7 d | SEM | Treatment | Period | Interaction |
| Control | 3.91c | 3.92c | 3.84d | 5.58bA | 6.02aB | 0.04 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| pH | LB | 3.88c | 3.92c | 3.85c | 4.51bC | 6.54aA | ||||
| LR | 3.87c | 3.90c | 3.85c | 4.76bB | 5.04aC | |||||
| Control | 2.38cA | 3.20c | 4.25c | 10.69bA | 13.60aA | 0.109 | <0.01 | <0.01 | ||
| NH3-N (% TN) | LB | 1.50cB | 2.96b | 3.32b | 5.22aB | 8.97aB | ||||
| LR | 1.38dB | 2.15cd | 4.06b | 2.81cC | 6.81aB | |||||
| Control | 5.68aA | 4.28b | 4.06b | 0c | 0c | 0.141 | <0.01 | 0.774 | <0.05 | |
| LA (% DM) | LB | 4.42aB | 4.93a | 4.67a | 0c | 0.82c | ||||
| LR | 3.87aB | 4.95a | 4.42a | 0b | 2.65ab | |||||
| Control | 0bB | 0bC | 0.78aB | 0bB | 0bB | 0.085 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| AA (% DM) | LB | 2.42aA | 3.32aB | 2.51aA | 2.81aA | 0bB | ||||
| LR | 2.49abA | 4.28aA | 3.29aA | 2.83abA | 1.01bA | |||||
| Control | 0c | 0c | 0c | 1.11a | 0.76b | 0.023 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| PA (% DM) | LB | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| LR | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| Control | 0b | 0b | 0.79b | 3.36a | 3.23a | 0.125 | <0.01 | <0.05 | <0.05 | |
| BA (% DM) | LB | 0b | 0b | 0b | 0b | 3.18a | ||||
| LR | 0b | 0b | 0b | 0.27b | 2.57a | |||||
| DM % | DM Loss % | CP (% DM) | WSC (% DM) | NDF (% DM) | ADF (%DM) | Aerobic Stability (h) | DM Loss % AE 3 d | DM Loss % AE 7 d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 26.41 | 3.96 | 6.91 | 1.54 | 54 | 30 | 44B | 6.64A | 27.46A |
| LB | 26.22 | 3.75 | 6.35 | 1.86 | 55 | 30 | 82A | 3.07B | 26.53A |
| LR | 26.51 | 3.26 | 6.43 | 1.48 | 55 | 33 | 78A | 3.76B | 23.55B |
| SEM | 0.107 | 0.037 | 0.029 | 0.036 | 0.702 | 0.619 | 1.439 | 0.098 | 0.343 |
| p-value | 0.948 | 0.998 | 0.160 | 0.170 | 0.137 | 0.332 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| Group | Observed Species | Shannon | Simpson | Chao1 | Goods Coverage | PD Whole Tree |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh corn | 9 c | 0.197 cd | 0.052 de | 11.694 f | 0.999 | 1.05 cd |
| Control 3 d | 21 b | 0.747 a | 0.202 a | 23.117 b | 0.999 | 2.363 a |
| LB 3 d | 10 c | 0.17 cd | 0.035 de | 15.167 d | 0.999 | 1.081 cd |
| LR 3 d | 2 g | 0.005 d | 0.001 e | 2 l | 1 | 0.478 h |
| Control 14 d | 10 c | 0.212 cd | 0.053 de | 17.5 c | 0.999 | 1.216 c |
| LB 14 d | 5 cde | 0.146 cd | 0.041 de | 7 hij | 1 | 0.605 gh |
| LR 14 d | 10 c | 0.562 ab | 0.197 ab | 13.833 e | 0.999 | 1.527 b |
| Control 60 d | 28 a | 0.545 ab | 0.115 cd | 29.083 a | 0.999 | 2.647 a |
| LB 60 d | 4 efg | 0.076 cd | 0.017 e | 4.5 k | 1 | 0.961 cde |
| LR 60 d | 11 c | 0.218 cd | 0.055 de | 13.952 e | 0.999 | 1.745 b |
| Control AE 3 d | 5 cde | 0.096 d | 0.02 de | 5.833 jk | 1 | 0.827 def |
| LB AE 3 d | 3 fg | 0.046 d | 0.009 e | 3 l | 1 | 0.752 fg |
| LR AE 3 d | 3 fg | 0.165 cd | 0.036 de | 8.333 gh | 1 | 0.857 def |
| Control AE 7 d | 7 d | 0.228 cd | 0.055 de | 7.667 ghi | 1 | 0.864 def |
| LB AE 7 d | 6 e | 0.34 bc | 0.102 bc | 6.333 ij | 1 | 0.85 ef |
| LR AE 7 d | 6 e | 0.156 cd | 0.034 de | 9 g | 1 | 0.85 def |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, H.; Ran, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, X. Succession of Microbial Communities of Corn Silage Inoculated with Heterofermentative Lactic Acid Bacteria from Ensiling to Aerobic Exposure. Fermentation 2021, 7, 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7040258
Guan H, Ran Q, Li H, Zhang X. Succession of Microbial Communities of Corn Silage Inoculated with Heterofermentative Lactic Acid Bacteria from Ensiling to Aerobic Exposure. Fermentation. 2021; 7(4):258. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7040258
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Hao, Qifan Ran, Haiping Li, and Xinquan Zhang. 2021. "Succession of Microbial Communities of Corn Silage Inoculated with Heterofermentative Lactic Acid Bacteria from Ensiling to Aerobic Exposure" Fermentation 7, no. 4: 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7040258
APA StyleGuan, H., Ran, Q., Li, H., & Zhang, X. (2021). Succession of Microbial Communities of Corn Silage Inoculated with Heterofermentative Lactic Acid Bacteria from Ensiling to Aerobic Exposure. Fermentation, 7(4), 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7040258







