Abstract
Bacillus thuringiensis is the leading microbial-based biopesticide, thanks to its parasporal crystal proteins or δ-endotoxins, which are toxic to insect larvae upon ingestion. Once in the insect larvae midgut, the crystal is solubilized by the alkaline pH and the δ-endotoxins activated by proteolytic cleavage. Thanks to its high efficiency as a biopesticide, several efforts have been made to enhance its growth and δ-endotoxins production, in various types of culture media. In this study, a culture medium based on wheat bran (WB), the by-product of cereal grain milling, was used to grow Bacillus thuringiensis and produce δ-endotoxins. Using the response surface methodology (RSM), the effects of three variables were evaluated: WB particles granulometry, their concentration, and their agitation in a 48-h shake-flask culture at 30 °C. Three response parameters were targeted: δ-endotoxins production, final culture pH, and dry-matter consumption. According to the RSM results, the optimum would be at 3.7 g WB/50 mL, with a granulometry above 680 μm and agitation between 170 and 270 rpm. This study is key to developing natural and cheap culture media that can be used at an industrial level for Bacillus thuringiensis-based biopesticides.
1. Introduction
In the last century, the primary way of pest management has been based on the intensive use of synthetic chemical pesticides. While pesticide use has boosted agricultural production, it remains harmful not only to the environment, but also to the downstream consumer [1]. Pesticides infiltrate into streams and groundwater, polluting several areas and bed sediments, as well as aquatic and other wildlife [2,3]. In addition, pesticide exposure has been shown to induce neuro- or immunotoxicity in humans [4,5]. Many countries have implemented legislation to reduce the deleterious effect of pesticides [6], yet the best solution remains the gradual replacement of chemical synthetic pesticides by environmentally friendly biopesticides, of animal, plant, or microbial origin. Keeping in mind the need of consumers to have safe agricultural foodstuffs, as well as the scalability of their production, the biopesticides market has in fact witnessed stellar growth in the last years and is projected to register a compound annual growth rate of 14.7% by the year 2026, according to a recent report analyzing the global biopesticides market [7]. The most commercialized biopesticides are of microbial origin, with almost 90% being based on Bacillus thuringiensis (B. thuringiensis), a member of the B. cereus sensu lato group and a soil dwelling bacterium with entomopathogenic properties [8,9,10]. Bacillus thuringiensis produces a crystal inclusion during the sporulation phase, which is secreted into the environment alongside the spore at the end of sporulation [11]. The crystal is composed of δ-endotoxins (or Cry toxins), at times associated with cytolytic (Cyt) toxins. Following its ingestion by insect larvae, the crystal is solubilized by the alkaline pH of the midgut. Afterwards, δ-endotoxins will be activated by proteases, and will bind to specific receptors, oligomerize, and then be inserted into the epithelial cell membrane. This will be followed by the formation of pores that cause cell lysis and subsequent cell death [12]. Depending on the composition of the parasporal crystal, B. thuringiensis strains are active against a wide range of insect larvae, including Diptera [13,14], Lepidoptera [15], Coleoptera, as well as nematode larvae [12]. B. thuringiensis serovar (sv.) kurstaki is the reference serovar for anti-lepidopteran activity, thanks to a combination of toxins belonging to the Cry1 and Cry2 families, forming bipyramidal and cubic crystals, respectively [15,16,17,18,19].
Due to increasing demand, B. thuringiensis growth and crystal production is at the heart of many studies aiming to optimize the parameters that may affect production, while simultaneously trying to reduce its cost. B. thuringiensis growth and crystal production require primarily carbon, energy, and nitrogen sources, as well as ions such as Mg2+ and Mn2+ and good aeration [20,21,22,23]. Synthetic media with all these elements are commonly used in laboratory settings but have proven to be quite expensive on an industrial scale, hence the attempts to replace it by cost-effective agro-industrial by-products such as molasses, grains, starch, or beer wastewater [24]. A study by Devi et al. (2005) showed that wheat bran (WB), also known as a cereal milling by-product (CMB), is a good medium for production of B. thuringiensis crystals [20]. Wheat bran is the hard outer layer of the wheat kernel that gets separated from the endosperm and germ during milling and grinding of the wheat grain; hence, it is a by-product of this process [24]. This layer is rich in various nutrients and fiber since it is primarily composed of polysaccharides, both reserve and structural, with starch being a major reserve carbohydrate in WB. Other components include proteins, lignin, water, minerals, and fat [25]. In the study by Devi et al., the WB medium was enriched with carbon and nitrogen sources to allow initial bacterial growth [20]. However, a more recent study by our team proved that WB-based media is much more economical and more efficient than fully synthetic or semi-synthetic production media, in both shake-flask cultures and submerged fermentation [25]. In fact, in a 48-h shake-flask culture at 30 °C at 340 rpm, a 3% w/v WB-based media allowed for a toxin protein concentration of 1.25 ± 0.03 mg/mL, compared to 1 ± 0.04 mg/mL in Anderson medium [26]. In addition to a WB medium being efficient, it is also quite cost effective, costing only USD 0.006 per liter versus USD 1.8 and 3.9 for the Anderson or the standard semi-synthetic media, respectively [25]. This further prompted the need to optimize production in WB media and reduce the cost of biopesticides, making their use more accessible to farmers. Moreover, the use of WB would be valorizing this by-product and reducing the waste generated by the cereal grain-milling process.
However, an important aspect still needs to be addressed before moving on to producing B. thuringiensis in WB-based media at an industrial level. The larger granules could set back the downstream processing, i.e., formulation and pulverization of the finalized biopesticide product. The size of the granules could also impact the bacterial growth, since the access of microorganisms to nutrients depends on the specific surface (SS) of the WB granules. Large size particles will have a relatively small SS whereas very small size particles, which should have a very high SS, bare the risk of coagulating and forming large-size agglomerates, thus inducing a very low SS.
In this study, we aimed to clarify the effect of WB particle granulometry on B. thuringiensis growth and δ-endotoxin production. A response surface methodology (RSM) was employed in order to establish the optimal culture conditions for bacterial growth and, most importantly, δ-endotoxin production in the affordable WB-based natural medium. Three factors were taken into consideration: granulometry, agitation, and WB concentration. The RSM study targeted three response parameters—the key indicators of optimization—after a 48-h culture: the concentration of produced δ-endotoxins, the consumption of dry matter (DMC), and the final culture pH.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
B. thuringiensis sv. kurstaki strain Lip [15,27] was used in the current study. This strain was isolated from Lebanese soil and characterized for its anti-lepidopteran activity. The latter is due to the δ-endotoxins from the Cry1 and Cry2 families composing its crystal, whose morphology was analyzed in a previous study. Two crystal shapes are in fact produced by Lip, which has a bipyramidal shape, consistent with the presence of Cry1, and a cubic one, consistent with the presence of Cry2 [28]. Its ability to grow in a WB-based medium was also first assessed in a preliminary study [25].
2.2. Production Culture Media
Wheat bran (WB) particles were first sifted and separated into 4 granule classes (ELE international Sieve shaker; # 80-0352): Class 1 consists of granules bigger than 850 µm; Class 2 has a granule size between 500 and 850 µm; Class 3 has a granule size between 250 and 500 µm; and Class 4 consists of granules smaller than 250 µm.
2.3. Culture Conditions
B. thuringiensis sv. kurstaki Lip was kept in 30% glycerol stock solutions at −80 °C. The strain was defrosted on LB (lysogenic broth) agar medium at 30 °C, from which a colony was isolated and cultured in 6 mL LB medium for 24 h at 30 °C with a shaking speed of 250 rpm. Culturing in the WB medium followed, with an initial optical density (OD) of 0.15 in a 50 mL medium volume in a 500 mL flask for 48 h at 30 °C.
2.4. Analytical Methods/Analyzed Parameters
2.4.1. δ-Endotoxins Concentration
A total of 1 mL of the culture was first centrifuged, and then washed twice with 1 mL NaCl 1 M/Triton X-100 M-0.01%. Afterwards, the pellet was washed four times with cold sterile water. Finally, the spore-crystal mixtures were solubilized in 50 mM sodium hydroxide NaOH buffer at 30 °C for 2 h 30 min with shaking. Solubilized proteins were then quantified with Bradford reagent (Bio-Rad Protein assay, Cat. 500-0006; [29]).
2.4.2. pH
pH levels are an important factor in biopesticide production. Hence, the pH of the various cultures was measured using a calibrated pH meter after a 48-h culture at 30 °C.
2.4.3. Dry-Matter Consumption (DMC) Quantification
The remaining 48 mL of the various cultures were vacuum filtered on pre-weighed and dried Whatman paper (cut-off at 13 µm). These papers were then dried at 105 °C for 24 h and their mass was measured on an analytical balance. This allowed the calculation of the percentage of WB that was consumed by comparing to a flask containing only WB.
2.5. Response Surface Methodology (RSM)
RSM is an experimental optimization procedure based on physical experiments. It is an assemblage of statistical and mathematical methods used for product development, product improvement, and product-optimizing processes [30]. WB granule size and concentration as well as flask shaking speed (agitation) were varied to set up the various experimental conditions (Table 1).

Table 1.
Parameters varied during Lip culture in WB media.
The study domain is between the −1 and +1 ends. −α and +α indicate the star points situated outside of the study domain, at a distance of 1.6818 from the center 0. These star points aim to improve the variation in the response in function of the analyzed parameters. In this study, a rotatable central composite design (23 + star) was adopted with 20 runs with 8 factorial design points: the combination between levels −1 and +1 (runs number 1 to 8 in Table 2); 6-star points: combination of level 0, −α and +α (runs 9 to 14 in Table 2); and 6 repetitions at the central level: combination of level 0 for all parameters (runs 15 to 20 in Table 2). The experimental matrix is shown in Table 2. Experimental design and statistical treatment of the results were performed using STATGRAPHICS centurion version 19 (StatPoint Technologies, Inc.—Warrenton, Virginia, United States of America; https://www.statgraphics.com/; last accessed 30 March 2022). STATGRAPHICS was used to create the experimental design as well as process and treat the data. Statistical analysis was also performed, including analysis of variance (ANOVA), empirical modeling, regression analysis, and optimization. The statistical significance of each parameter at the 95% confidence level was estimated by the ANOVA test and was highlighted by the Pareto charts of the standardized effects. Considering three parameters and three responses, experimental data were fitted to obtain the following second-degree regression equations: for δ-endotoxins concentration, culture pH, and DMC, respectively:
E = 0.1233 − 0.0023 (G) + 0.0099 (Ag) − 0.032 (C) + 0.00087 (G)·(C) − 0.00002 (Ag)2;
pH = 6.1 + 0.00023 (G) + 0.012 (Ag) − 0.71 (C) + 0.0011 (G)·(C) − 0.000027 (Ag)2;
DMC = −0.0476 + 0.108 (G) + 0.23 (Ag) + 6.45 (C) − 0.00006 (G) 2 − 0.00025 (G)·(Ag) − 0.042(Ag)·(C).

Table 2.
RSM experimental matrix and results of the response parameters of the B. thuringiensis sv. kurstaki Lip culture in WB media under various conditions.
The response surfaces were generated and were plotted between two significant variables while the third was fixed at the central level. Iso-response curves, or the contours for the estimated response, which are a simple projection of the response surfaces on a two-dimensional base, helped in predicting the responses within the selected range of variables.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. RSM Results in WB Media
In order to optimize the culture conditions for δ-endotoxin production in a wheat bran-based medium, a response surface methodology (RSM) was used with three response parameters: (i) the concentration of δ-endotoxin proteins; (ii) the pH of the media post-culture; and (iii) the percentage of dry-matter consumption (DMC). These response parameters for 20 runs with variation in agitation, granulometry, and concentration of WB particles are shown in Table 2.
The obtained results showed that the δ-endotoxin concentrations ranged between 0.04 and 1.93 mg/mL, culture pH between 5.54 and 7.98, and DMC between 36.82 and 65.94%. For δ-endotoxins, the highest production level was seen in run 14 (0, 0, +α), in which the parameters were set to a WB granule size of 437 µm, agitation of 200 rpm, and a WB concentration of 73.6 g/L (Table 1 and Table 2). However, in this run, both the pH and DMC were low (6.46 and 43.84%, respectively). The highest pH was obtained in run 10 (+α, 0, 0), but was accompanied by a low δ-endotoxin concentration (0.41 mg/mL) and DMC (36.82%). As for the highest DMC, it was observed in run 9 (−α, 0, 0), the only run in which both the δ-endotoxin concentration and DMC were high (1.64 mg/mL and 65.94%), but with a low pH of 6.26.
In the following section, each response parameter was detailed following RSM analysis.
3.1.1. Response Parameter: δ-Endotoxins Concentration
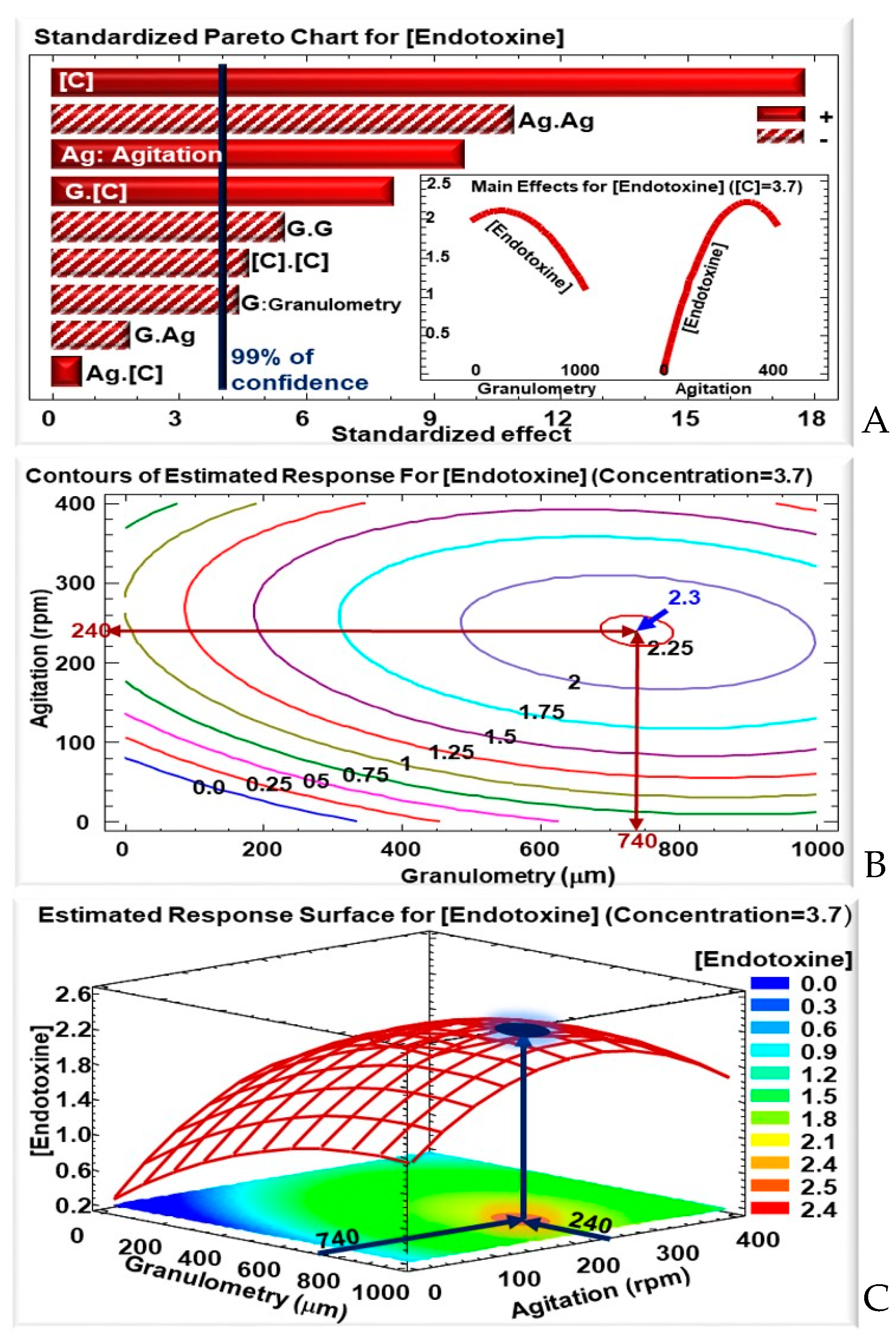
The key to B. thuringiensis biopesticidal activity are δ-endotoxins. Therefore, the concentration of B. thuringiensis sv. kurstaki Lip δ-endotoxins is one of the response parameters adopted in the RSM approach. Our results showed that several factors had significant effects on the δ-endotoxins concentration. On one hand, shaking speed (agitation) and WB concentration both had significant positive linear effects (represented by Ag and C, respectively, in Figure 1A). This means that the δ-endotoxin concentration will increase with an increase in agitation and WB concentration. For the former, its effect on bacterial growth and δ-endotoxin yield could be attributed to two main factors. First, agitation improves aeration in the culture, which will lead to a higher biomass production, and hence higher δ-endotoxin concentration and spore counts [31,32]. Second, agitation can prevent WB particles from aggregating, an aforementioned phenomenon that can reduce the bacteria’s access to nutrients by reducing the WB particles’ specific surface (SS). In summary, continuous mixing helps maintain chemical and physical homogeneity [33].
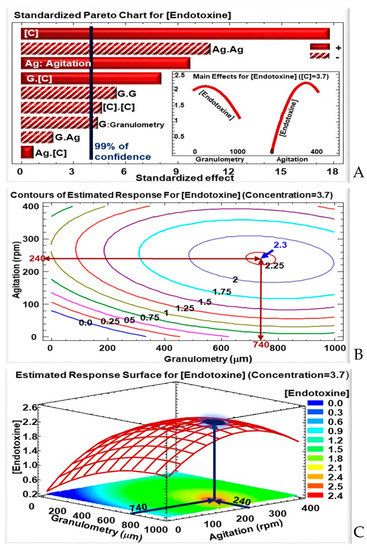
Figure 1.
For the δ-endotoxin concentration: (A) Standardized Pareto chart—columns that surpass the vertical line indicate factors with significant effects on the δ-endotoxins concentration at a confidence rate of 99%; the insert shows the effects of the variation in granulometry and concentration on δ-endotoxins concentration with a fixed WB concentration of 3.7 g/50 mL. (B) Contours of the estimated response—the blue and red arrows indicate the maximum δ-endotoxins concentration of around 2.3 mg/mL and for an agitation of 240 rpm and a granulometry of 740 μm. (C) 3D representation of the estimated response surface for a fixed WB concentration of 3.7 g/50 mL, as a function of WB granulometry and agitation; the colors show areas with similar responses with the optimum shown in the blue projected spot, highlighted by the blue arrows.
However, both these factors—agitation and WB concentration—had negative quadratic effects (Ag.Ag and C.C) on δ-endotoxin concentration, meaning that (i) there is an optimum to be reached between the two extremes (−α; +α); and (ii) an excess in agitation and/or WB concentration will negatively affect the δ-endotoxin concentration (Figure 1A). In fact, an excess of WB in the media will favor vegetative growth over sporulation: with an abundance of nutrients to their disposal, bacteria will not be under “food stress” and will continue to replicate in a vegetative way. Moreover, an excess in WB concentration could risk overcrowding the culture media, making it difficult for bacteria to access the nutrients provided by the WB particles.
On the other hand, WB particles granulometry had negative linear (G) and quadratic (G.G) effects, as shown in the corresponding Pareto chart (Figure 1A). Several phenomena come into play concerning granulometry. On one hand there is a competition between lowering the size of the WB to have higher SS, but not having particles too small that are at a high risk for forming aggregates and losing accessibility to nutrients. The right balance will be reliant of an adequate granule size. On the other hand, the smaller particles recovered after sifting are usually rich in residual starch from the grain-milling process, and larger size granules will retain less starch than smaller ones. Starch is a major source of carbon, allowing for a better biomass production.
Interestingly, a positive effect was seen in the interaction between WB granulometry and concentration (G.C). This means that δ-endotoxin production will be favored at a higher granulometry, if it is accompanied by a high WB concentration. In other words, a high WB concentration will help circumvent the negative effect observed previously with an increase in WB particle size.
Based on the results of the response parameters of Lip in WB media under various granulometry, agitation, and WB concentration (Table 2), it was noted that the highest δ-endotoxins concentration was obtained for a +α WB concentration, i.e., 3.7 g/50 mL. Therefore, for the remainder of the analysis, the WB concentration will be fixed at 3.7 g/50 mL, while varying the agitation and WB granulometry.
In these conditions, the optimal culture conditions for δ-endotoxin production, for a fixed WB concentration of 3.7 g/50 mL, were determined at a granulometry of 740 µm and agitation of 240 rpm. In these optimal conditions, according to the RSM model, the δ-endotoxin concentration reaches a maximum of around 2.25 mg/mL (Table 3). These results are also shown by the 2- and 3-dimensional representation of the δ-endotoxin concentration variation, as a function of agitation and WB granulometry, as shown by the contours of the iso-response (Figure 1B) and the estimated response surface (Figure 1C), respectively. The modeled δ-endotoxin concentration would be 2.25-fold higher than the one reached with the fully synthetic Anderson medium, or the one with WB at 3% [25].

Table 3.
Optimal culture conditions for a maximum δ-endotoxin concentration of 2.25 mg/mL.
3.1.2. Response Parameter: Culture pH
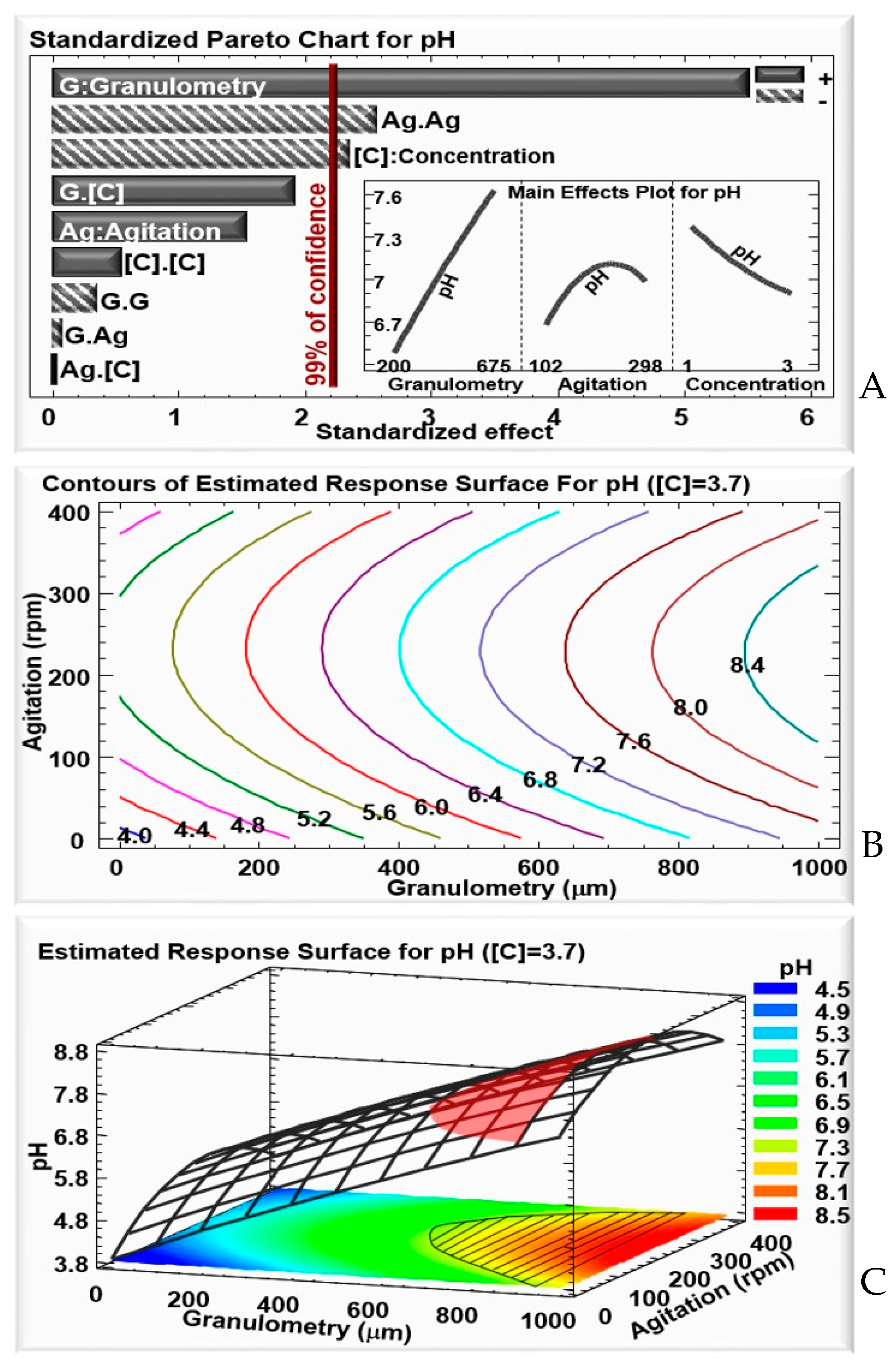
The culture media’s initial pH, as well as its variation during the culture, play a key role in bacterial growth and crystal production. For the first 15 h of culture, the bacteria are in the exponential phase—that of vegetative growth—and the pH will decrease due to the production of acetate by the bacteria. Afterwards, the bacteria enter the stationary phase, during which spores and parasporal crystals are produced and released in the culture medium, accompanied by an increase in pH due the consumption of the acetate [34]. In fact, it was previously shown that the optimum for δ-endotoxin production is a culture pH between 6.5 and 7.5, with a slight shift towards an alkaline pH at the end of the sporulation phase, due to cell lysis and release of alkaline metabolites [35]. As per previous experiments, in unbuffered medium, at a pH lower than 6, crystal production is partially inhibited. In fact, after a 48-h culture, for a pH of 5.54, a lot of Lip cells remained in vegetative state, unlike the culture in which the pH reached between 6.5 and 7.5, where almost all cells completed the sporulation and crystal production phase (Supplementary Figure S1). This was also observed in our study, where the δ-endotoxin concentration reached a maximum of 0.88 mg/mL in runs where the final culture pH remained under 6 (Table 2). This was also reported by Abdel-hameed et al. (2001) [31].
According to the RSM results, as shown in the Pareto chart (Figure 2A), on one hand the WB granulometry had a positive linear effect (G) on pH variation. A higher pH was obtained at the end of the culture in large-size WB granules. Smaller-size granules are richer in starch, leading to the production of acetate, and a lower pH. In turn, larger-size granules will push the bacteria towards sporulation and cellular lysis, and hence a higher pH, up to 7.6, as shown in the granulometry effects plot for pH (Figure 2A). On the other hand, the agitation and WB concentration had less significant negative quadratic (Ag.Ag) and linear (C) effects.
Figure 2.
For culture pH: (A) Standardized Pareto chart—columns that surpass the vertical line indicate factors with significant effects on culture pH at a confidence rate of 99%; the insert shows the effects of the variation of granulometry and concentration on culture pH with a fixed WB concentration of 3.7 g/50 mL. (B) Contours of the estimated response. (C) 3D representation of the estimated response surface for a fixed WB concentration of 3.7 g/50 mL, as a function of WB granulometry and agitation. Colors show areas with similar responses, with the optimum shown in red.
Given that the highest δ-endotoxins concentration was observed with a WB concentration of 3.7 g/50 mL, in the following analysis, this concentration was fixed, while agitation and WB granulometry were varied, to observe their effect on culture pH evolution.
The contours for the estimated response (Figure 2B), and the estimated response surface graph (Figure 2C), both show variation in pH, according to the granulometry and agitation. A low granulometry does not favor an increase in pH after 48 h of culture. However, a granulometry above 600 μm, regardless of the agitation, shows an increase in pH, up to 8.5, meaning that, at a higher granulometry, the cells are more likely to enter the sporulation phase, during which a spore and parasporal crystal are released into the culture medium after cell lysis.
3.1.3. Response Parameter: Dry-Matter Consumption Percentage
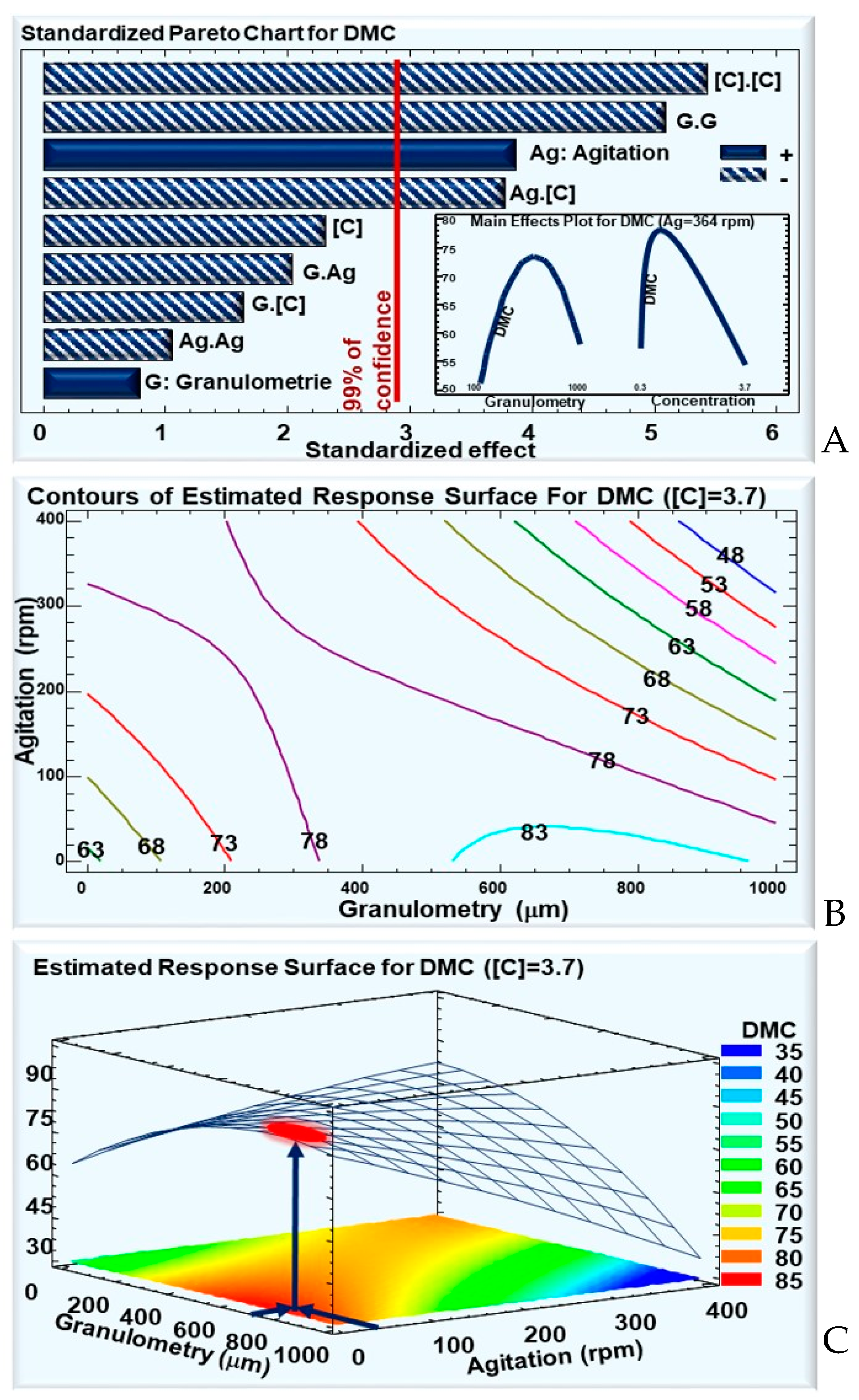
The monitoring of dry-matter consumption (DMC) before and after a 48-h culture allows the tracking of WB consumption by the B. thuringiensis sv. kurstaki strain Lip throughout its growth and sporulation phases. As shown in the Pareto chart, the WB concentration and granulometry had significant quadratic negative effects (C.C and G.G), whereas agitation had a positive linear one (Ag) (Figure 3A). Moreover, a negative interaction effect is seen between the agitation and concentration (Ag.C). This means that DMC increases at a high agitation, when the WB concentration is low, and decreases at a high agitation when the WB concentration is elevated.
Figure 3.
For dry-matter consumption: (A) Standardized Pareto chart—columns that surpass the vertical line indicate factors with significant effects on DMC at a confidence rate of 99%; the insert shows the effects of the variation in granulometry and concentration on DMC with a fixed WB concentration of 3.7 g/50 mL. (B) Contours of the estimated response. (C) 3D representation of the estimated response surface for a fixed WB concentration of 3.7 g/50 mL, as a function of WB granulometry and agitation. Colors show areas with similar responses, with the optimum shown in red and highlighted by the blue arrows.
The contour of estimated response (Figure 3B) and the estimated response surface (Figure 3C), for a fixed WB concentration of 3.7 g/50 mL, showed that the optimal DMC, up to ca. 83%, is for a low agitation, under 100 rpm, and a granulometry of around 650 μm (Figure 3C). However, even though DMC reflects bacterial growth and use of the culture medium, it does not necessarily mean sporulation and δ-endotoxin production.
3.2. Optimum Parameters Selection
Three response parameters—δ-endotoxin concentration, culture pH, and DMC percentage—were taken into consideration during the search for optimal culture conditions in WB-based media. The factors included in the culture conditions were the WB particles granulometry and concentration as well as the flask’s shaking speed or agitation.
First, for a fixed WB concentration of 3.7 g/50 mL, the optimum for both δ-endotoxin concentration (2.25 mg/mL) and culture pH (7.3–8.1) are shown by the regions highlighted in blue and in green, respectively (Figure 4A). An overlay between the two regions signifies conditions where the best outcomes can be obtained for both parameters. This optimum can be reached for a granulometry ranging between 680 and 900 μm, and agitation between 170 and 270 rpm (Figure 4A).
Figure 4.
Overlay plots for optimization of the three response parameters: (A): δ-endotoxin concentration and culture pH, and (B): δ-endotoxin concentration and DMC, for a fixed WB concentration of 3.7 g/50 mL, as a function of WB granulometry and agitation.
However, as shown in Figure 4B, there is no overlay between the δ-endotoxin concentration optimum (blue) and the DMC (red). This can be explained by previous results that showed the vastly different conditions needed for each parameter, the main variant in this case being the agitation. A high production of δ-endotoxins (ca. 2.25 mg/mL) and a high DMC could both be reached at a granulometry ranging from 680 to 900 μm. However, the former requires an agitation speed between 170 and 270 rpm, whereas the latter does not.
At an industrial level, and during biopesticide production, the ultimate goal is to have the best bacterial growth and, most importantly, δ-endotoxin yield. For the latter, we were able to determine in this study, at the flask level, the optimal conditions for a maximum toxin yield in a WB-based culture medium: a granulometry ranging between 680 and 900 μm, and agitation between 170 and 270 rpm, for a WB concentration of 3.7 g/50 mL.
4. Conclusions
The biopesticide market, particularly that of B. thuringiensis-based products, is growing exponentially [10]. Finding natural alternatives to synthetic culture media will not only help reduce costs, but also help make biopesticides even more environmentally friendly. The studied WB-based medium was proven to be such a replacement, providing all the necessary components for B. thuringiensis growth and δ-endotoxin production. In this study, using RSM, we were able to evaluate and model the optimal WB granulometry, concentration, and culture agitation conditions. This was done using shake-flask experiments, with three response parameters in mind: δ-endotoxins concentration, culture pH, and dry-matter consumption.
This study constitutes the first step of the path to replacing synthetic media by a WB-based one, and this at an industrial level with large-scale production and downstream formulation. Several complementary studies evaluating the potential of WB media are well under way, including analysis of the WB based medium performance in bioreactors, as well as the fermentable fraction and the limiting factor of fermentation in a WB-based medium.
5. Patents
Kallassy Awad M., El Khoury M. and Louka N., (2017) New strain of Bacillus thuringiensis « Bacillus thuringiensis Lip MKA » isolated from Lebanese soil, as a biopesticidal agent; Conception, realisation and installation of bioreactors for its large-scale culture and production. Deposited: 15 November 2017; Published: December 2017.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fermentation8120666/s1, Figure S1: Microscopic observation of Lip spore formation after a 48-h culture at 30 °C with a final culture pH of 5.54 (A) and 7 (B).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.K.A.; methodology, J.A., F.D. and M.K.A.; software, J.A. and N.L.; validation, N.F., N.L. and M.K.A.; formal analysis, N.F., N.L. and M.K.A.; investigation, N.F. and J.A.; resources, M.K.A.; data curation, N.F. and N.L.; writing—original draft preparation, N.F. and M.K.A.; writing—review and editing, N.F., J.A., F.D., N.L. and M.K.A.; visualization, N.L.; supervision, M.K.A.; project administration, M.K.A.; funding acquisition, M.K.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the research council of Saint-Joseph University of Beirut CR-USJ under grant number FS65. F.D. mobility (Tunisia—Lebanon) was funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 funds: H2020-MSCA-RISE-2016 # 734921, and MKA mobility (Lebanon—France) was funded by « Allocation de perfectionnement à la formation-recherche, November 2021» from the « Agence Universitaire de la Francophonie ».
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Luc Fillaudeau for scientific exchange and discussions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Aktar, W.; Sengupta, D.; Chowdhury, A. Impact of pesticides use in agriculture: Their benefits and hazards. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2009, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilliom, R.J. Pesticides in U.S. streams and groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3408–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topaz, T.; Egozi, R.; Suari, Y.; Ben-Ari, J.; Sade, T.; Chefetz, B.; Yahel, G. Environmental risk dynamics of pesticides toxicity in a Mediterranean micro-estuary. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsini, E.; Sokooti, M.; Galli, C.L.; Moretto, A.; Colosio, C. Pesticide induced immunotoxicity in humans: A comprehensive review of the existing evidence. Toxicology 2013, 307, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, L.G.; Giordano, G.; Guizzetti, M.; Vitalone, A. Neurotoxicity of pesticides: A brief review. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou Zeid, M.I.; Jammoul, A.M.; Melki, K.C.; Jawdah, Y.A.; Kallassy Awad, M. Suggested policy and legislation reforms to reduce deleterious effect of pesticides in Lebanon. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intelligence, M. Biopesticides Marke—Growth, Trends, COVID-19 Impact, and Forecasts (2021–2026). 2020. Available online: https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/global-biopesticides-market-industry (accessed on 3 August 2022).
- Kumar, J.; Ramlal, A.; Mallick, D.; Mishra, V. An Overview of Some Biopesticides and Their Importance in Plant Protection for Commercial Acceptance. Plants 2021, 10, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damalas, C.A.; Koutroubas, S.D. Current status and recent developments in biopesticide use. Agriculture 2018, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, A. Biopesticides: Present Status and the Future Prospects. J. Fertil. Pestic. 2015, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soberón, M.; Monnerat, R.; Bravo, A. Mode of Action of Cry Toxins from Bacillus thuringiensis and Resistance Mechanisms. In Microbial Toxins—Toxinology; Gopalakrishnakone, P., Stiles, B., Alape-Girón, A., Dubreuil, J., Mandal, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, L.; Muñoz, D.; Berry, C.; Murillo, J.; Caballero, P. Bacillus thuringiensis Toxins: An Overview of Their Biocidal Activity. Toxins 2014, 6, 3296–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayad, N.; Patiño-Navarrete, R.; Kambris, Z.; Antoun, M.; Osta, M.; Chopineau, J.; Mahillon, J.; El Chamy, L.; Sanchis, V.; Kallassy Awad, M. Characterization and Whole Genome Sequencing of AR23, a Highly Toxic Bacillus thuringiensis Strain Isolated from Lebanese Soil. Curr. Microbiol. 2019, 76, 1503–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayad, N.; Kambris, Z.; El Chamy, L.; Mahillon, J.; Kallassy Awad, M. A novel anti-dipteran Bacillus thuringiensis strain: Unusual Cry toxin genes in a highly dynamic plasmid environment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 87, e02294-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Khoury, M.; Azzouz, H.; Chavanieu, A.; Abdelmalak, N.; Chopineau, J.; Kallassy Awad, M. Isolation and characterization of a new Bacillus thuringiensis strain Lip harboring a new cry1Aa gene highly toxic to Ephestia kuehniella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) larvae. Arch. Microbiol. 2014, 196, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Dyer, D.; Bulla, L. Genome sequence of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki strain HD-1. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Song, L.; Shu, C.; Wang, P.; Deng, C.; Peng, Q.; Lereclus, D.; Wang, X.; Huang, D.; Zhang, J.; et al. Complete Genome Sequence of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki Strain HD73. Genome Announc. 2013, 1, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, N.; He, J.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, G.; Li, M.; Sun, M.; Yu, Z. Prevalence and diversity of insertion sequences in the genome of Bacillus thuringiensis YBT-1520 and comparison with other Bacillus cereus group members. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 310, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadaoui, I.; Rouis, S.; Jaoua, S. A new Tunisian strain of Bacillus thuringiensis kurstaki having high insecticidal activity and δ-endotoxin yield. Arch. Microbiol. 2009, 191, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, P.S.V.; Ravinder, T.; Jaidev, C. Cost-effective production of Bacillus thuringiensis by solid-state fermentation. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2005, 88, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndao, A. Mise a L’Echelle de la Production du Biopesticide Bacillus thuringiensis Var. Kurstaki Avec Comme Substrat des Eaux Usées d’Amidon; Université du Québec: Quebec City, QC, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Nickerson, K.W.; Bulla, L.A. Physiology of Spore-forming Bacteria Associated with Insects: Minimal Nutritional Requirements for Growth, Sporulation, and Parasporal Crystal Formation of Bacillus thuringiensis. Appl. Microbiol. 1974, 28, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel, M.D.; Tyagi, R.D.; Valero, J.R. Wastewater treatment sludge as a raw material for the production of Bacillus thuringiensis based biopesticides. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3807–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, M. Antioxidant Properties of Wheat Bran against Oxidative Stress. In Wheat and Rice in Disease Prevention and Health; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounsef, J.R.; Salameh, D.; Kallassy Awad, M.; Lteif, R.; Brandam, C. Evaluation of a cereal milling by-product for the low-cost production of Bacillus thuringiensis kurstaki in submerged fermentation. Eur. J. Biotechnol. Biosci. 2014, 1, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, T.B. Effects of Carbon: Nitrogen Ratio and Oxygen on the Growth Kinetics of Bacillus thuringiensis and Yield of Bioinsecticidal Crystal Protein. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Graduate Studies, University of Western Ontario, London, ON, Canada, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Kallassy, M.I.; Khoury, M.; Louka, N. New Strain of Bacillus Thuringiensis “Bacillus Thuringiensis Lip MKA” Isolated from Lebanese Soil as Biocontrol Agent (biopesticide) and Design, Construction and Installation of Bioreactors for Large Scale Production and Cultivation of This Strain. LEBANON Patent 2017/11-11298L, 15 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Loutfi, H.; Fayad, N.; Pellen, F.; Le Jeune, B.; Chakroun, M.; Benfarhat, D.; Lteif, R.; Kallassy, M.; Le Brun, G.; Abboud, M. Morphological Study of Bacillus thuringiensis Crystals and Spores. Appl Sci. 2021, 11, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abi-Khattar, A.M.; Rajha, H.N.; Abdel-Massih, R.M.; Habchi, R.; Maroun, R.G.; Debs, E.; Louka, N. “Intensification of Vaporization by Decompression to the Vacuum” (IVDV), a novel technology applied as a pretreatment to improve polyphenols extraction from olive leaves. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Hameed, A. Stirred tank culture of Bacillus thuringiensis H-14 for production of the mosquitocidal δ-endotoxin: Mathematical modelling and scaling-up studies. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 17, 857–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avignone-Rossa, C.; Arcas, J.; Mignone, C. Bacillus thuringiensis growth, sporulation and δ-endotoxin production in oxygen limited and non-limited cultures. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1992, 8, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jallouli, W.; Driss, F.; Fillaudeau, L.; Rouis, S. Review on biopesticide production by Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki since 1990: Focus on bioprocess parameters. Process. Biochem. 2020, 98, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Içgen, Y.; Içgen, B.; Ozcengiz, G. Regulation of crystal protein biosynthesis by Bacillus thuringiensis: I. Effects of mineral elements and pH. Res. Microbiol. 2002, 153, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanain, A.M. Development of a cheap media for Bacillus thuringiensis growth. Int. J. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 3, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).