Quorum-Sensing Inhibitors from Probiotics as a Strategy to Combat Bacterial Cell-to-Cell Communication Involved in Food Spoilage and Food Safety
Abstract
1. Introduction
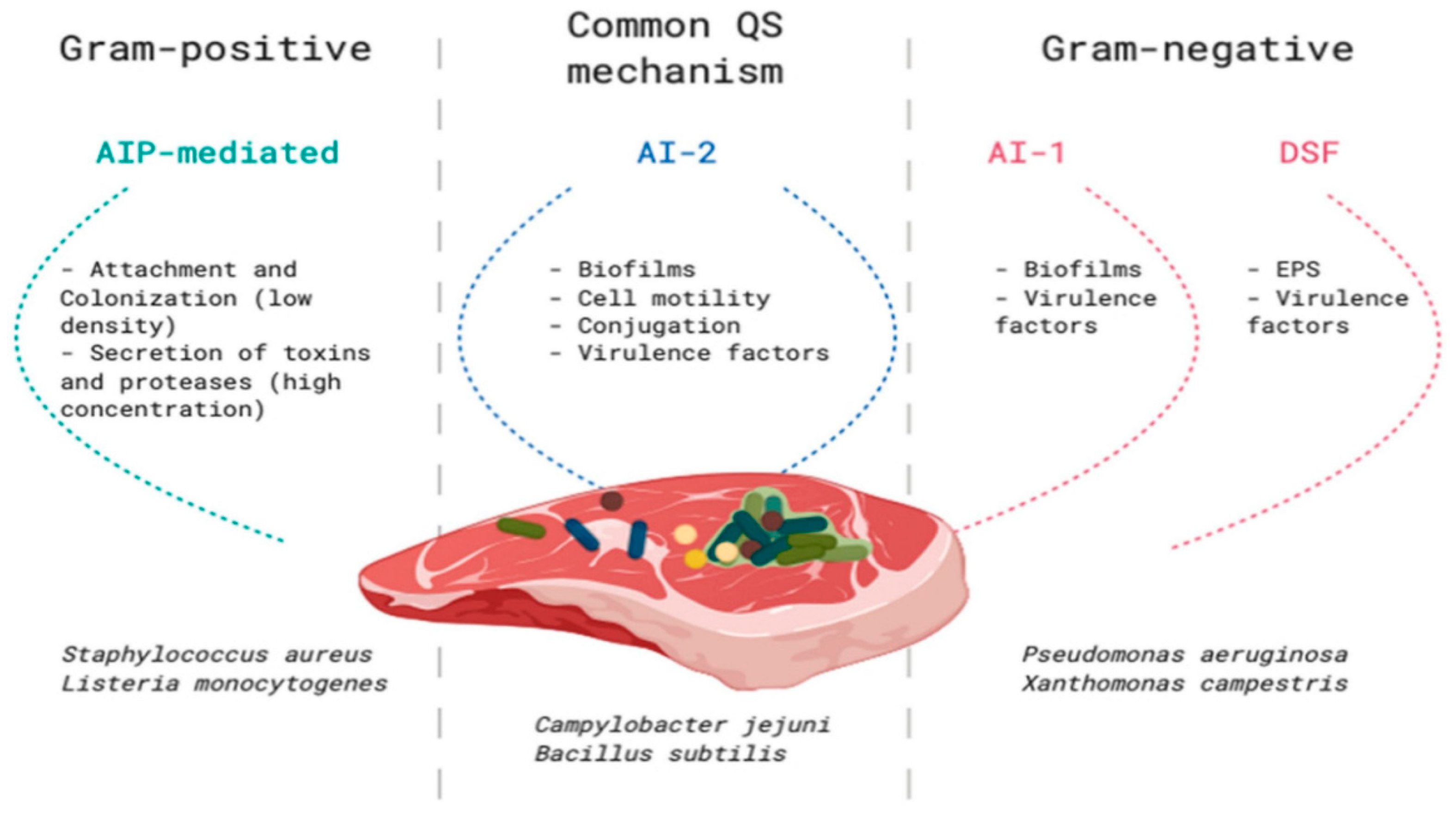
2. Microbial Communication
3. Quorum Sensing in Food Spoilage
4. Quorum Quenching and QS Inhibitors from Probiotics
| Probiotics | Bacteria Inhibited | QSI Mechanism | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | |||
| Bacillus | B. subtilis | L. monocytogenes E. coli Gardnerella vaginalis | Inhibits AI-2 activity and biofilm formation | [86] |
| B. cereus RC1 | Lelliottia amnigena seudomonas aeruginosa MTCC2297 | Inhibits pyocyanin production in P. aeruginosa and modulates the pathogenicity in L. amnigena | [87] | |
| B. subtilis R-18 | Serratia marcescens | The bacterial extract inhibits biofilm formation, protease, lipase, and hemolysin production | [88] | |
| B. subtilis BR4 | P. aeruginosa | Inhibits biofilm formation | [89] | |
| B. pumilus | P. aeruginosa PAO1 (las, rhl) S. marcescens (shl). | Reduces the accumulation of N-acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) and shows significant inhibition of LasA protease, LasB elastase, caseinase, pyocyanin, pyoverdin, and biofilm formation. | [90] | |
| Bifidobacterium | B. licheniformis DAHB1, | Vibrio parahaemolyticus | Inhibits biofilm formation in vitro and reduces shrimp intestinal colonization and mortality | [91] |
| B. licheniformis T-1 | Aeromonas hydrophila | Quorum-quenching gene ytnP encodes an acyl-homoserine lactone metallo-β-lactamase | [92] | |
| B. longum ATCC15707 | Escherichia coli 0157:H7 | Inhibits AI-2 and reduces biofilm formation | [18] | |
| Lactobacillus | L. acidophilus 30SC | E. coli O157:H7 | Inhibits AI-2 | [93] |
| L. plantarum M.2, L. curvatus B.67 | L. monocytogenes | Inhibits swimming motility, biofilm formation, and expression levels of target genes related to biofilm formation | [85] | |
| L. plantarum SBR04MA | Microbiota of activated sludge | Inhibits N-Hexanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (6-HSL) | [94] | |
| L. plantarum, | S. aureus | Reduces expression of some genes involved in biofilm formation | [95] | |
| L. acidophilus GP1B | Clostridium difficile | Reduces production of AI-2 molecules | [20] | |
| L. acidophilus La-5 | Escherichia coli 0157:H7 | Interferes with QS molecules and reduces adherence and colonization | [19] | |
| L. acidophilus NCFM | - | Not in pathogenic bacteria, but increases adherence of probiotic to intestinal cells by increasing AI-2 in LuxS system | [96] | |
| L. brevis 3M004 | P. aeruginosa | Inhibits biofilm formation | [97] | |
| L. casei | Streptococcus mutans | Inhibits QS genes vicKR and comCD | [98] | |
| L. casei ATCC 393, L. reuteri ATCC23272, L. plantarum ATCC14917 L. salivarius ATCC11741 | Streptococcus mutans | Inhibits acyl-homoserine lactone activity and blocks their synthesis | [98] | |
| L. fermentum Lim2 | Clostridium difficile | Reduces the AI-2 in QS gene luxS | [99] | |
| L. plantarum PA 100 | P. aeruginosa | Inhibits acyl-homoserine lactone activity and blocks their synthesis | [100] | |
| Streptococcus | S. salivarius | S. mutans | Inhibits biofilm formation in vitro when cultured with S. mutans | [101] |
| S. salivarius K12 | C. albicans | Inhibits C. albicans aggregation, biofilm formation, and dimorphism. | [102] | |
| S. salivarius 24SMB and S. oralis 89a | S. aureus, S. epidermidis, S. pyogenes, S. pneumoniae, M. catarrhalis and P. acnes | Inhibits biofilm formation in pathogens of the upper respiratory tract | [103] | |
5. Concluding Remarks and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nealson, K.H.; Platt, T.; Hastings, J.W. Cellular Control of the Synthesis and Activity of the Bacterial Luminescent System. J. Bacteriol. 1970, 104, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.C.; Miyashiro, T. Quorum Sensing in the Squid-Vibrio Symbiosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 16386–16401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padder, S.A.; Prasad, R.; Shah, A.H. Quorum sensing: A less known mode of communication among fungi. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 210, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahreen, S.; Mukhtar, H.; Imre, K.; Morar, A.; Herman, V.; Sharif, S. Exploring the Function of Quorum Sensing Regulated Biofilms in Biological Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Tian, P.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Chen, W. Quorum Sensing of Lactic Acid Bacteria: Progress and Insights. Food Rev. Int. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abisado, R.G.; Benomar, S.; Klaus, J.R.; Dandekar, A.A.; Chandler, J.R. Bacterial Quorum Sensing and Microbial Community Interactions. mBio 2018, 9, e02331-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Cooper, R.; Tsimring, L.S. Coexistence and Pattern Formation in Bacterial Mixtures with Contact-Dependent Killing. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, I.; Silva, L.R.; Giaouris, E.; Melo, L.; Simões, M. Quorum sensing in food spoilage and natural-based strategies for its inhibition. Food Res. Int. 2019, 127, 108754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizan, F.R.; Jahid, I.K.; Kim, M.; Lee, K.-H.; Kim, T.J.; Ha, S.-D. Variability in biofilm formation correlates with hydrophobicity and quorum sensing among Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates from food contact surfaces and the distribution of the genes involved in biofilm formation. Biofouling 2016, 32, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Sadiq, F.A.; Burmølle, M.; Liu, T.; He, G. Insights into Bacterial Milk Spoilage with Particular Emphasis on the Roles of Heat-Stable Enzymes, Biofilms, and Quorum Sensing. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faille, C.; Bénézech, T.; Midelet-Bourdin, G.; Lequette, Y.; Clarisse, M.; Ronse, G.; Ronse, A.; Slomianny, C. Sporulation of Bacillus spp. within biofilms: A potential source of contamination in food processing environments. Food Microbiol. 2014, 40, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.-H.; Beuchat, L.R. Biofilm Formation and Sporulation by Bacillus cereus on a Stainless Steel Surface and Subsequent Resistance of Vegetative Cells and Spores to Chlorine, Chlorine Dioxide, and a Peroxyacetic Acid–Based Sanitizer. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 2614–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsene, M.M.J.; Viktorovna, P.I.; Alla, M.V.; Mariya, M.A.; Sergei, G.V.; Cesar, E.; Davares, A.K.L.; Parfait, K.; Wilfrid, K.N.; Nikolay, T.S.; et al. Optimization of Ethanolic Extraction of Enantia chloranta Bark, Phytochemical Composition, Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles, and Antimicrobial Activity. Fermentation 2022, 8, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaouris, E.; Heir, E.; Hébraud, M.; Chorianopoulos, N.; Langsrud, S.; Møretrø, T.; Habimana, O.; Desvaux, M.; Renier, S.; Nychas, G.-J. Attachment and biofilm formation by foodborne bacteria in meat processing environments: Causes, implications, role of bacterial interactions and control by alternative novel methods. Meat Sci. 2014, 97, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.; Sousa, P.; Gaspar, A.; Vilar, S.; Borges, F.; Simões, M. Furvina inhibits the 3-oxo-C12-HSL-based quorum sensing system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and QS-dependent phenotypes. Biofouling 2017, 33, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, C.A.K.; Arnason, J.T. Mini Review of Phytochemicals and Plant Taxa with Activity as Microbial Biofilm and Quorum Sensing Inhibitors. Molecules 2015, 21, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skandamis, P.N.; Nychas, G.-J.E. Quorum Sensing in the Context of Food Microbiology. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 5473–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, J.W.; Kang, S.-G.; Oh, S.; Griffiths, M.W. Bifidobacterium spp. influences the production of autoinducer-2 and biofilm formation by Escherichia coli O157:H7. Anaerobe 2012, 18, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medellin-Peña, M.J.; Griffiths, M.W. Effect of Molecules Secreted by Lactobacillus acidophilus Strain La-5 on Escherichia coli O157:H7 Colonization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, B.; Oh, S.; Griffiths, M. Lactobacillus acidophilus modulates the virulence of Clostridium difficile. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 4745–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO/WHO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, World Health Organization). Probiotics in Food. In Health and Nutritional Properties and Guidelines for Evaluation; FAO Food and Nutrition Paper No. 85; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and World Health Organization: Rome, Italy, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Dong, Q.; Ma, Y.; Yang, S.; Aslam, M.Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z. Potential antimicrobial activities of probiotics and their derivatives against Listeria monocytogenes in food field: A review. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunaratnam, S.; Millette, M.; McFarland, L.V.; DuPont, H.L.; Lacroix, M. Potential role of probiotics in reducing Clostridioides difficile virulence: Interference with quorum sensing systems. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 153, 104798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuqua, W.C.; Winans, S.C. A LuxR-LuxI type regulatory system activates Agrobacterium Ti plasmid conjugal transfer in the presence of a plant tumor metabolite. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 2796–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jon Windsor, J.W. How Quorum Sensing Works. 2020. Available online: https://asm.org/Articles/2020/June/How-Quorum-Sensing-Works (accessed on 22 October 2022).
- Jaafar, F.N.; Al-Bayati, M.A.; Musafer, H.K.; Azeez, M.A.; Raheem, Z.K. Quorum Sensing and its Correlation with Virulence Factors. South Asian Res. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 4, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sionov, R.V.; Steinberg, D. Targeting the Holy Triangle of Quorum Sensing, Biofilm Formation, and Antibiotic Resistance in Pathogenic Bacteria. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Lahiri, D.; Nag, M.; Dey, A.; Pandit, S.; Sarkar, T.; Pati, S.; Kari, Z.A.; Ishak, A.R.; Edinur, H.A.; et al. Phytocompound Mediated Blockage of Quorum Sensing Cascade in ESKAPE Pathogens. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eduanis-Assaf, D.; Esteinberg, D.; Echai, Y.; Eshemesh, M. The LuxS Based Quorum Sensing Governs Lactose Induced Biofilm Formation by Bacillus subtilis. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Hou, K.; Valencak, T.G.; Luo, X.M.; Liu, J.; Wang, H. AI-2/LuxS Quorum Sensing System Promotes Biofilm Formation of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and Enhances the Resistance to Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in Germ-Free Zebrafish. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0061022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.A.; Petersen, F.C.; Scheie, A.A. AI-2/LuxS Is Involved in Increased Biofilm Formation by Streptococcus intermedius in the Presence of Antibiotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 4258–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teren, M.; Michova, H.T.; Vondrakova, L.; Demnerova, K. Molecules Autoinducer 2 and cjA and Their Impact on Gene Expression in Campylobacter jejuni. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, K.B.; Bassler, B.L. Interference with AI-2-mediated bacterial cell–cell communication. Nature 2005, 437, 750–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khera, R.; Mehdipour, A.R.; Bolla, J.R.; Kahnt, J.; Welsch, S.; Ermler, U.; Muenke, C.; Robinson, C.V.; Hummer, G.; Xie, H.; et al. Cryo-EM structures of pentameric autoinducer-2 exporter from Escherichia coli reveal its transport mechanism. EMBO J. 2022, 41, e109990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabidi, S.; Hoshiko, Y.; Maeda, T. Quorum quenching of autoinducer 2 increases methane production in anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 4763–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keizers, M.; Dobrindt, U.; Berger, M. A Simple Biosensor-Based Assay for Quantitative Autoinducer-2 Analysis. ACS Synth. Biol. 2022, 11, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemichód, A.; Skotarczak, B. QS—systems communication of Gram-positive bacterial cells. Acta Biol. 2017, 24, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilmann, C.; Götz, F. Cell–cell communication and biofilm formation in gram-positive bacteria. In Bacterial Signaling; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 1, pp. 7–22. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt, V.S. Quorum sensing mechanisms in gram positive bacteria. In Implication of Quorum Sensing System in Biofilm Formation and Virulence; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 297–311. [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead, N.A.; Barnard, A.M.; Slater, H.; Simpson, N.J.; Salmond, G.P. Quorum-sensing in Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 25, 365–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, G.; Ray, A.K. The talking language in some major Gram-negative bacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 2016, 198, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Ding, H.; Ke, W.; Wang, L. Quorum Sensing in Fungal Species. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 75, 449–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, A.; Herráez, M.; Costa-Gutierrez, S.B.; Molina-Henares, M.A.; Martínez, M.J.; Espinosa-Urgel, M.; Barriuso, J. The architecture of a mixed fungal–bacterial biofilm is modulated by quorum-sensing signals. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 2433–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, T.; Averesch, N.; Winter, G.; Plan, M.; Vickers, C.; Nielsen, L.; Krömer, J. Quorum-sensing linked RNA interference for dynamic metabolic pathway control in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab. Eng. 2015, 29, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, P.; Casadevall, A. Quorum sensing in fungi—A review. Med. Mycol. 2012, 50, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiang, J.; Lv, W.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Wan, P.; Jiang, L. Quorum sensing molecules in yeast wastewater treatment and their regulation of yeast cell morphology. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, P.; Nicola, A.M.; Nieves, E.; Paes, H.C.; Williamson, P.R.; Silva-Pereira, I.; Casadevall, A. Quorum Sensing-Mediated, Cell Density-Dependent Regulation of Growth and Virulence in Cryptococcus neoformans. mBio 2014, 5, e00986-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Chang, Y.C.; Nardone, G.; Kwon-Chung, K.J. TUP1 disruption in Cryptococcus neoformans uncovers a peptide-mediated density-dependent growth phenomenon that mimics quorum sensing. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 64, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewald, S.; Josephs, K.; Bölker, M. Genetic Analysis of Biosurfactant Production in Ustilago maydis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 3033–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affeldt, K.J.; Brodhagen, M.; Keller, N.P. Aspergillus Oxylipin Signaling and Quorum Sensing Pathways Depend on G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Toxins 2012, 4, 695–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amare, M.G.; Keller, N.P. Molecular mechanisms of Aspergillus flavus secondary metabolism and development. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2014, 66, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruppa, M. Quorum sensing and Candida albicans. Mycoses 2009, 52, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Fujita, M.; Feng, Q.; Clardy, J.; Fink, G.R. Tyrosol is a quorum-sensing molecule in Candida albicans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5048–5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singkum, P.; Muangkaew, W.; Suwanmanee, S.; Pumeesat, P.; Wongsuk, T.; Luplertlop, N. Suppression of the pathogenicity of Candida albicans by the quorum-sensing molecules farnesol and tryptophol. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 65, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosero-Hernández, E.D.; Moraga, J.; Collado, I.G.; Echeverri, F. Natural Compounds That Modulate the Development of the Fungus Botrytis cinerea and Protect Solanum lycopersicum. Plants 2019, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, D.A. Talking to Themselves: Autoregulation and Quorum Sensing in Fungi. Eukaryot. Cell 2006, 5, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumdar, S.; Mondal, S. Perspectives on Quorum sensing in Fungi. bioRxiv 2015, 019034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gram, L.; Ravn, L.; Rasch, M.; Bruhn, J.B.; Christensen, A.B.; Givskov, M. Food spoilage—Interactions between food spoilage bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 78, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammor, M.S.; Michailidis, C.; Nychas, G.-J. Insights into the Role of Quorum Sensing in Food Spoilage. J. Food Prot. 2008, 71, 1510–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, A.J.; Rai, V.R. Bacterial quorum sensing and food industry. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2011, 10, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepaniak, L. Dairy enzymology. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2004, 57, 153–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, U.; Viana, E.D.S.; Martins, M.; Vanetti, M.C.D. Detection of acylated homoserine lactones in gram-negative proteolytic psychrotrophic bacteria isolated from cooled raw milk. Food Control 2007, 18, 1322–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, A.B.; Riedel, K.; Eberl, L.; Flodgaard, L.R.; Molin, S.; Gram, L.; Givskov, M. Quorum-sensing-directed protein expression in Serratia proteamaculans B5a. Microbiology 2003, 149, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, N.; Ma, A.; Wang, Y. Quorum sensing system-regulated genes affect the spoilage potential of Shewanella baltica. Food Res. Int. 2018, 107, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gram, L.; Huss, H.H. The Microbiological Safety and Quality of Food; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 472–506. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaly, A.E.; Dave, D.; Budge, S.; Brooks, M.S. Fish Spoilage Mechanisms and Preservation Techniques: Review. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 7, 859–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, J.; Yu, H.; Han, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, M. Acyl-homoserine-lactones receptor LuxR of Shewanella baltica involved in the development of microbiota and spoilage of refrigerated shrimp. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 2795–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Wu, H.; Zhang, C.; Jie, J.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, M.; Wang, C. Spoilage of refrigerated Litopenaeus vannamei: Eavesdropping on Acinetobacter acyl-homoserine lactones promotes the spoilage potential of Shewanella baltica. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flodgaard, L.R.; Dalgaard, P.; Andersen, J.B.; Nielsen, K.F.; Givskov, M.; Gram, L. Nonbioluminescent Strains of Photobacterium phosphoreum Produce the Cell-to-Cell Communication Signal N-(3-Hydroxyoctanoyl)homoserine Lactone. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 2113–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegbeleye, O.; Odeyemi, O.A.; Strateva, M.; Stratev, D. Microbial spoilage of vegetables, fruits and cereals. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasch, M.; Andersen, J.B.; Nielsen, K.F.; Flodgaard, L.R.; Christensen, H.; Givskov, M.; Gram, L. Involvement of Bacterial Quorum-Sensing Signals in Spoilage of Bean Sprouts. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 3321–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandclément, C.; Tannières, M.; Moréra, S.; Dessaux, Y.; Faure, D. Quorum quenching: Role in nature and applied developments. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 40, 86–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.H.; Xu, J.L.; Li, X.Z.; Zhang, L.H. AiiA, an enzyme that inactivates the acylhomoserine lactone quorum-sensing signal and attenuates the virulence of Erwinia carotovora. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 3526–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butel, M.J. Probiotics, gut microbiota and health. Médecine Mal. Infect. 2014, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prazdnova, E.V.; Gorovtsov, A.V.; Vasilchenko, N.G.; Kulikov, M.P.; Statsenko, V.N.; Bogdanova, A.A.; Refeld, A.G.; Brislavskiy, Y.A.; Chistyakov, V.A.; Chikindas, M.L. Quorum-Sensing Inhibition by Gram-Positive Bacteria. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selhub, E.M.; Logan, A.C.; Bested, A.C. Fermented foods, microbiota, and mental health: Ancient practice meets nutritional psychiatry. J. Physiol. Anthr. 2014, 33, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsène, M.M.J.; Davares, A.K.L.; Andreevna, S.L.; Vladimirovich, E.A.; Carime, B.Z.; Marouf, R.; Khelifi, I. The use of probiotics in animal feeding for safe production and as potential alternatives to antibiotics. Veter.-World 2021, 14, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Ma, Y.; Liu, X.; Tian, C.; Zhong, X.; Zhao, L. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: Lactobacillus acidophilus for Treating Acute Gastroenteritis in Children. Nutrients 2022, 14, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Nogales, A.; Algieri, F.; Garrido-Mesa, J.; Vezza, T.; Utrilla, M.P.; Chueca, N.; Garcia, F.; Olivares, M.; Rodríguez-Cabezas, M.E.; Gálvez, J. Differential intestinal anti-inflammatory effects of Lactobacillus fermentum and Lactobacillus salivarius in DSS mouse colitis: Impact on microRNAs expression and microbiota composition. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1700144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Hong, K.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Lactobacillus fermentum and its potential immunomodulatory properties. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 56, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomi, A.; Iino, T.; Nonaka, C.; Miyazaki, K.; Ishikawa, F. Health benefits of fermented milk containing Bifidobacterium bifidum YIT 10347 on gastric symptoms in adults. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 2277–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, B.; Delgado, S.; Blanco-Míguez, A.; Lourenço, A.; Gueimonde, M.; Margolles, A. Probiotics, gut microbiota, and their influence on host health and disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600240. [Google Scholar]
- Mbarga, M.J.A.; Zangue DS, C.; Ngoune, T.L.; Nyasha, K.; Louis, K. Antagonistic effects of raffia sap with probiotics against pathogenic microorganisms. Foods Raw Mater. 2021, 9, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, I.; Mizan, F.R.; Roy, P.K.; Nahar, S.; Toushik, S.H.; Ashrafudoulla, M.; Jahid, I.K.; Lee, J.; Ha, S.-D. Listeria monocytogenes biofilm inhibition on food contact surfaces by application of postbiotics from Lactobacillus curvatus B.67 and Lactobacillus plantarum M.2. Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis-Teixeira, F.B.D.; Alves, V.F.; Martinis, E.C.P.D. Growth, viability and architecture of biofilms of Listeria monocytogenes formed on abiotic surfaces. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2017, 48, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroni, G. Probiotics in Treating Pathogenic Biofilms. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/17732 (accessed on 31 October 2022).
- Kachhadia, R.; Kapadia, C.; Singh, S.; Gandhi, K.; Jajda, H.; Alfarraj, S.; Ansari, M.J.; Danish, S.; Datta, R. Quorum Sensing Inhibitory and Quenching Activity of Bacillus cereus RC1 Extracts on Soft Rot-Causing Bacteria Lelliottia amnigena. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 25291–25308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, K.R.; Srinivasan, S.; Ravi, A.V. Inhibition of quorum sensing-mediated virulence in Serratia marcescens by Bacillus subtilis R-18. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 120, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boopathi, S.; Vashisth, R.; Mohanty, A.K.; Jia, A.; Sivakumar, N.; Arockiaraj, J. Bacillus subtilis BR4 derived stigmatellin Y interferes Pqs-PqsR mediated quorum sensing system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Basic Microbiol. 2022, 62, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithya, C.; Aravindraja, C.; Pandian, S.K. Bacillus pumilus of Palk Bay origin inhibits quorum-sensing-mediated virulence factors in Gram-negative bacteria. Res. Microbiol. 2010, 161, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algburi, A.; Zehm, S.; Netrebov, V.; Bren, A.B.; Chistyakov, V.; Chikindas, M.L. Subtilosin Prevents Biofilm Formation by Inhibiting Bacterial Quorum Sensing. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2016, 9, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinoj, G.; Vaseeharan, B.; Thomas, S.; Spiers, A.; Shanthi, S. Quorum-Quenching Activity of the AHL-Lactonase from Bacillus licheniformis DAHB1 Inhibits Vibrio Biofilm Formation In Vitro and Reduces Shrimp Intestinal Colonisation and Mortality. Mar. Biotechnol. 2014, 16, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Peng, M.; Tong, W.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Z. The Quorum Quenching Bacterium Bacillus licheniformis T-1 Protects Zebrafish against Aeromonas hydrophila Infection. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 12, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Oh, S.; Song, M.; Choe, J.H.; Whang, K.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Oh, S. Influences of quorum-quenching probiotic bacteria on the gut microbial community and immune function in weaning pigs. Anim. Sci. J. 2018, 89, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampouris, I.D.; Karayannakidis, P.D.; Banti, D.C.; Sakoula, D.; Konstantinidis, D.; Yiangou, M.; Samaras, P.E. Evaluation of a novel quorum quenching strain for MBR biofouling mitigation. Water Res. 2018, 143, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, B.; Azcarate-Peril, M.; Klaenhammer, T. Role of autoinducer-2 on the adhesion ability of Lactobacillus acidophilus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 107, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Li, Q.; Wu, B.; Hu, M. RNA-seq-based transcriptomic analysis of AHL-induced biofilm and pyocyanin inhibition in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Lactobacillus brevis. Int. Microbiol. 2022, 25, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasfi, R.; Abd El-Rahman, O.A.; Zafer, M.M.; Ashour, H.M. Probiotic Lactobacillus sp. inhibit growth, biofilm formation and gene expression of caries-inducing Streptococcus mutans. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 1972–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, C.; Lim, J.; Kim, B.; Park, D.; Oh, S. Suppressive effect of Lactobacillus fermentum Lim2 on Clostridioides difficile 027 toxin production. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdéz, J.C.; Peral, M.C.; Rachid, M.; Santana, M.; Perdigón, G. Interference of Lactobacillus plantarum with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in vitro and in infected burns: The potential use of probiotics in wound treatment. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2005, 11, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, S.; Yonezawa, H.; Motegi, M.; Nakao, R.; Yoneda, S.; Watanabe, H.; Yamazaki, T.; Senpuku, H. Inhibiting effects of Streptococcus salivarius on competence-stimulating peptide-dependent biofilm formation by Streptococcus mutans. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2009, 24, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, M.; Rismayuddin, N.A.R.; Mat Yassim, A.S.; Ahmad, H.; Abdul Wahab, R.; Dashper, S.; Arzmi, M.H. Streptococcus salivarius K12 inhibits Candida albicans aggregation, biofilm formation and dimorphism. Biofouling 2021, 37, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidossi, A.; De Grandi, R.; Toscano, M.; Bottagisio, M.; De Vecchi, E.; Gelardi, M.; Drago, L. Probiotics Streptococcus salivarius 24SMB and Streptococcus oralis 89a interfere with biofilm formation of pathogens of the upper respiratory tract. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Davares, A.K.L.; Arsene, M.M.J.; Viktorovna, P.I.; Vyacheslavovna, Y.N.; Vladimirovna, Z.A.; Aleksandrovna, V.E.; Nikolayevich, S.A.; Nadezhda, S.; Anatolievna, G.O.; Nikolaevna, S.I.; et al. Quorum-Sensing Inhibitors from Probiotics as a Strategy to Combat Bacterial Cell-to-Cell Communication Involved in Food Spoilage and Food Safety. Fermentation 2022, 8, 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8120711
Davares AKL, Arsene MMJ, Viktorovna PI, Vyacheslavovna YN, Vladimirovna ZA, Aleksandrovna VE, Nikolayevich SA, Nadezhda S, Anatolievna GO, Nikolaevna SI, et al. Quorum-Sensing Inhibitors from Probiotics as a Strategy to Combat Bacterial Cell-to-Cell Communication Involved in Food Spoilage and Food Safety. Fermentation. 2022; 8(12):711. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8120711
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavares, Anyutoulou K. L., Mbarga M. J. Arsene, Podoprigora I. Viktorovna, Yashina N. Vyacheslavovna, Zhigunova A. Vladimirovna, Vasilyeva E. Aleksandrovna, Senyagin A. Nikolayevich, Sachivkina Nadezhda, Gizinger O. Anatolievna, Sharova I. Nikolaevna, and et al. 2022. "Quorum-Sensing Inhibitors from Probiotics as a Strategy to Combat Bacterial Cell-to-Cell Communication Involved in Food Spoilage and Food Safety" Fermentation 8, no. 12: 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8120711
APA StyleDavares, A. K. L., Arsene, M. M. J., Viktorovna, P. I., Vyacheslavovna, Y. N., Vladimirovna, Z. A., Aleksandrovna, V. E., Nikolayevich, S. A., Nadezhda, S., Anatolievna, G. O., Nikolaevna, S. I., & Sergueïevna, D. M. (2022). Quorum-Sensing Inhibitors from Probiotics as a Strategy to Combat Bacterial Cell-to-Cell Communication Involved in Food Spoilage and Food Safety. Fermentation, 8(12), 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8120711







