NIR Spectroscopy Assessment of Quality Index of Fermented Milk (Laban) Drink Flavored with Date Syrup during Cold Storage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Sensory Evaluation of Laban Drinks
2.3. Measurements of Physicochemical Properties of Laban Drinks
2.4. Quality Index (Qi) Assessment
2.5. Quality Index Assessment Using NIR Technique
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Sensory Evaluation
3.1.1. Best Sample Selection
3.1.2. Shelf-Life Sensory Evaluation
3.2. Physicochemical Properties during Shelf Life
3.3. Quality Index Modeling
3.4. Modeling Quality Index Using the NIR Technique
3.4.1. Partial Least Squares Regression (PLSR)
3.4.2. Artificial Neural Networks (ANN)
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simoneliene, A.; Treciokiene, E.; Lukosiunaite, G.; Vysniauskas, G.; Kasparaviciute, E. Rheology, technology, and sensory charavterestics of fortified drink products with fibers. Balt. Conf. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 72, 294–297. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, J.; Hutchings, S.; Fang, Z.; Bandara, N.; Gamlath, S.; Ajlouni, S.; Ranadheera, C. Microbial, physico-chemical and sensory characteristics of mango juice-enriched probiotic dairy drinks. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2020, 73, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- General Authority for Statistics. 2022. Agriculture Statistics 2021. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.sa (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Yanes, M.; Durán, L.; Costell, E. Effect of hydrocolloid type and concentration on flow behaviour and sensory properties of milk beverages model systems. Food Hydrocoll. 2002, 16, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, H.; Griffiths, M. Major advances in fresh milk and milk products: Fluid milk products and frozen des-serts. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debon, J.; Prudêncio, E.S.; Petrus, J.C.C. Rheological and physico-chemical characterization of prebiotic microfiltered fermented milk. J. Food Eng. 2010, 99, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Sucre, M.O.; Vélez-Ruiz, J.F. Physicochemical, rheological and stability characterization of a caramel flavored yogurt. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 51, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, F.K. Utilization of date syrup as a tablet binder, comparative study. Saudi Pharm. J. 2010, 18, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashaswini, N.; Arunkumar, H. Process optimization for the preparation of date syrup blended yoghurt. J. Res. Agric. Anim. Sci. 2016, 4, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Hamza, H.; Ben Miloud, N.; Jemni, M.; Slei, A.; M’Barak, S. Gamma irradiated date syrup for sucrose substitution in yogurt: Effect on physicochemical properties, antioxidant capacity and sensory evaluation. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 59, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhamdan, A.M.; Al Juhaimi, F.Y.; Hassan, B.H.; Ehmed, K.A.; Ahmed, I.A.M. Physicochemical, Microbiological, and Sensorial Quality Attributes of a Fermented Milk Drink (Laban) Fortified with Date Syrup (Dibs) during Cold Storage. Foods 2021, 10, 3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, P. A model for overall description of food quality. Food Qual. Prefer. 1995, 6, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardello, A.V. Food quality: Relativity, context and consumer expectations. Food Qual. Prefer. 1995, 6, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, J.A. Quality measurement of fruits and vegetables. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 1999, 15, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliffe, M.; Panozzo, J. The Application of Near Infrared Spectroscopy to Evaluate Malting Quality. J. Inst. Brew. 1999, 105, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nørgaard, L.; Lagerholm, M.; Westerhaus, M. Artificial Neural Networks and Near Infrared Spectroscopy—A Case Study on Protein Content in Whole Wheat Grain. FOSS. 2013. Available online: http://www.foss.dk/campaign/-/media/242657904D734CE9B0652C3D885776AE.ashx (accessed on 19 July 2022).
- Hernández-Jiménez, M.; Hernández-Ramos, P.; Martínez-Martín, I.; Vivar-Quintana, A.M.; González-Martín, I.; Revilla, I. Comparison of artificial neural networks and multiple regression tools applied to near infrared spectroscopy for predicting sensory properties of products from Quality Labels. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, K.; McGlone, V.; Han, D. The uses of near infra-red spectroscopy in postharvest decision support: A review. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 163, 111139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, K.B.; Blasco, J.; Zude-Sasse, M.; Sun, X. Visible-NIR ‘point’ spectroscopy in postharvest fruit and vegetable assessment: The science behind three decades of commercial use. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 168, 111246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.; Mazzoni, L.; Gagliardi, F.; Balducci, F.; Duca, D.; Toscano, G.; Mezzetti, B.; Capocasa, F. Application of the Non-Destructive NIR Technique for the Evaluation of Strawberry Fruits Quality Parameters. Foods 2020, 9, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Subedi, P.; Walker, R.; Walsh, K.B. NIRS prediction of dry matter content of single olive fruit with consideration of variable sorting for normalisation pre-treatment. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 163, 111140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhamdan, A.M.; Atia, A. Non-destructive method to predict Barhi dates quality at different stages of maturity utilising near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, S2950–S2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayuela, J.A.; Camino, M.D.C.P. Prediction of quality of intact olives by near infrared spectroscopy. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2010, 112, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parpinello, G.; Nunziatini, G.; Rombolà, A.; Gottardi, F.; Versari, A. Relationship between sensory and NIR spectroscopy in consumer preference of table grape (cv Italia). Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2013, 83, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inarejos-García, A.; Gómez-Alonso, S.; Fregapane, G.; Salvador, M.D. Evaluation of minor components, sensory characteristics and quality of virgin olive oil by near infrared (NIR) spectroscopy. Food Res. Int. 2013, 50, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Solah, V.; Wei, Y.; Wu, G.; Wang, X.; Crosbie, G.; Fenton, H. Sensory evaluation of Chinese white salted noodles and steamed bread made with Australian and Chinese wheat flour. Cereal Chem. 2019, 96, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhamdan, A.M.; Fickak, A.; Atia, A.R. Evaluation of sensory and texture profile analysis properties of stored Khalal Barhi dates nondestructively using Vis/NIR spectroscopy. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e13215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Tan, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z. Rapid monitoring of flavonoid content in sweet tea (Lithocarpus litseifolius (Hance) Chun) leaves using NIR spectroscopy. Plant Methods 2022, 18, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zuo, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, J.; Ban, L.; Yang, H.; Bai, Z. Development and Validation of Near-Infrared Methods for the Quantitation of Caffeine, Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, and Moisture in Green Tea Production. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2021, 2021, 9563162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandiselvam, R.; Kaavya, R.; Monteagudo, S.I.M.; Divya, V.; Jain, S.; Khanashyam, A.C.; Kothakota, A.; Prasath, V.A.; Ramesh, S.V.; Sruthi, N.U.; et al. Contemporary Developments and Emerging Trends in the Application of Spectroscopy Techniques: A Particular Reference to Coconut (Cocos nucifera L.). Molecules 2022, 27, 3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, C.D.S.; Vimercati, W.C.; Macedo, L.L.; Ferreira, A.; Prezotti, L.C.; Teixeira, L.J.Q.; Saraiva, S.H. Predicting the Electric Conductivity and Potassium Leaching of Coffee by NIR Spectroscopy Technique. Food Anal. Methods 2020, 13, 2312–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Reinoso, D.; Purwanto, Y.; Budiastra, I.; Sutrisno Kuroki, S.; Widodo, S.; Kamanga, B. Determination of α-guaiene and azulene chemical content in patchouli aromatic oil (Pogostemon cablin Benth.) from Indonesia by Near-infrared spectroscopy. Indian J. Nat. Prod. Resour. 2021, 12, 256–262. [Google Scholar]
- Ghooshkhaneh, N.G.; Golzarian, M.R.; Mamarabadi, M. Spectral pattern study of citrus black rot caused by Alternaria alternata and selecting optimal wavelengths for decay detection. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 1694–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawless, H.; Heymann, H. Sensory Evaluation of Food Science Principles and Practices, 2nd ed.; Springer: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2010; Chapter 1. [Google Scholar]
- Jayalakshmi, T.; Santhakumaran, A. Statistical Normalization and Back Propagationfor Classification. Int. J. Comput. Theory Eng. 2011, 3, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, P.J.M.; Faraj, R.H. Data Normalization and Standardization: A Technical Report. Mach. Learn. Tech. Rep. 2014, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranya, C.; Manikandan, G. A study on normalization techniques for privacy preserving data mining. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2013, 5, 2701–2704. [Google Scholar]
- Camarinha-Matos, L.M.; Falcão, A.J.; Vafaei, N.; Najdi, S. Technological Innovation for Cyber-Physical Systems. In Proceedings of the 7th IFIP WG 5.5/SOCOLNET Advanced Doctoral Conference on Computing, Electrical and Industrial Systems, DoCEIS 2016, Costa de Caparica, Portugal, 11–13 April 2016; Volume 470, pp. 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordey, T.; Joas, J.; Davrieux, F.; Chillet, M.; Léchaudel, M. Robust NIRS models for non-destructive prediction of mango internal quality. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 216, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumiyati; Munawar, A.A.; Suhandy, D. Fast, simultaneous and contactless assessment of intact mango fruit by means of near infrared spectroscopy. AIMS Agric. Food 2021, 6, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silalahi, D.D.; Reaño, C.E.; Lansigan, F.P.; Panopio, R.G.; Bantayan, N.C. Using Genetic Algorithm Neural Network on Near Infrared Spectral Data for Ripeness Grading of Oil Palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) Fresh Fruit. Inf. Process. Agric. 2016, 3, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrita, L.; Fossen, T.; Andersen, M. Colour and stability of the six common anthocyanidin 3-glucosides in aqueous solutions. Food Chem. 2000, 68, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani-López, E.; Palou, E.; López-Malo, A. Probiotic viability and storage stability of yogurts and fermented milks prepared with several mixtures of lactic acid bacteria. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 2578–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ścibisz, I.; Ziarno, M.; Mitek, M. Color stability of fruit yogurt during storage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 1997–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Son, Y.-J.; Kwon, S.H.; Kim, S.-K. Biochemical and antioxidant activity of yogurt supplemented with paprika juice of different colors. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2020, 40, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristo, E.; Biliaderis, C.; Tzanetakis, N. Modelling of rheological, microbiological and acidification properties of a fermented milk product containing a probiotic strain of Lactobacillus paracasei. Int. Dairy J. 2003, 13, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damin, M.R.; Minowa, E.; Alcântara, M.R.; Oliveira, M.N. Effect of Cold Storage on Culture Viability and Some Rheological Properties of Fermented Milk Prepared with Yogurt and Probiotic Bacteria. J. Texture Stud. 2008, 39, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukić, D.V.; Vukić, V.R.; Milanović, S.D.; Ilicić, M.D.; Kanurić, K.G. Modeling of rheological characteristics of the fermented dairy products obtained by novel and traditional starter cultures. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 2180–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djaoud, K.; Boulekbache-Makhlouf, L.; Yahia, M.; Mansouri, H.; Mansouri, N.; Madani, K.; Romero, A. Dairy dessert processing: Effect of sugar substitution by date syrup and powder on its quality characteristics. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singham, P.; Birwal, P.; Yadav, B. Importance of Objective and Subjective Measurement of Food Quality and Their Inter-Relationship. J. Food Process. Technol. 2015, 6, 1000488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitbeck, M. Second Derivative Infrared Spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 1981, 35, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, T.; Marsico, A.D.; Perniola, R. Use of Artificial Neural Networks and NIR Spectroscopy for Non-Destructive Grape Texture Prediction. Foods 2022, 11, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, A. Uses of Derivative Spectroscopy, Application Note. Publication # 5963-3940E Agilent Technologies. 1995, pp. 1–8. Available online: https://www.whoi.edu/cms/files/derivative_spectroscopy (accessed on 19 July 2022).
- Bakeev, K. Process Analytical Technology Spectroscopic Tools and Implementation Strategies for the Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industries; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava, R.; Levin, I. Spectrochemical Analysis Using Infrared Multichannel Detectors; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irudayaraj, J.; Reh, C. Nondestructive Testing of Food Quality; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciurczak, E.; Workman, J.; Burns, D. Handbook of Near-Infrared Analysis, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-1-13857-648-3. [Google Scholar]
- FD 150-1:2018; Expiration Dates for Food Products—Part 1: Mandatory Expiration Dates. SFDA Standard: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2018; p. 8.
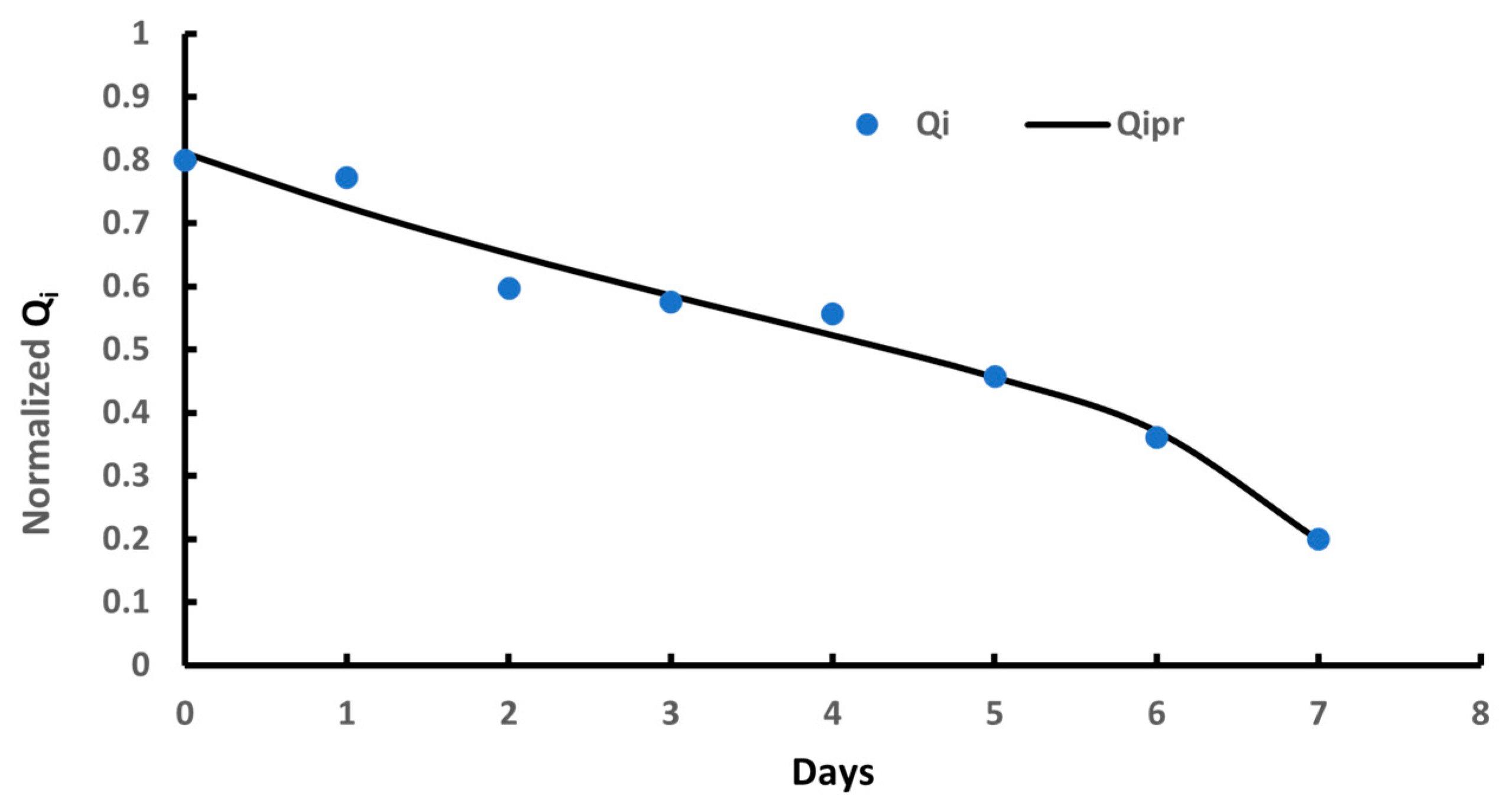
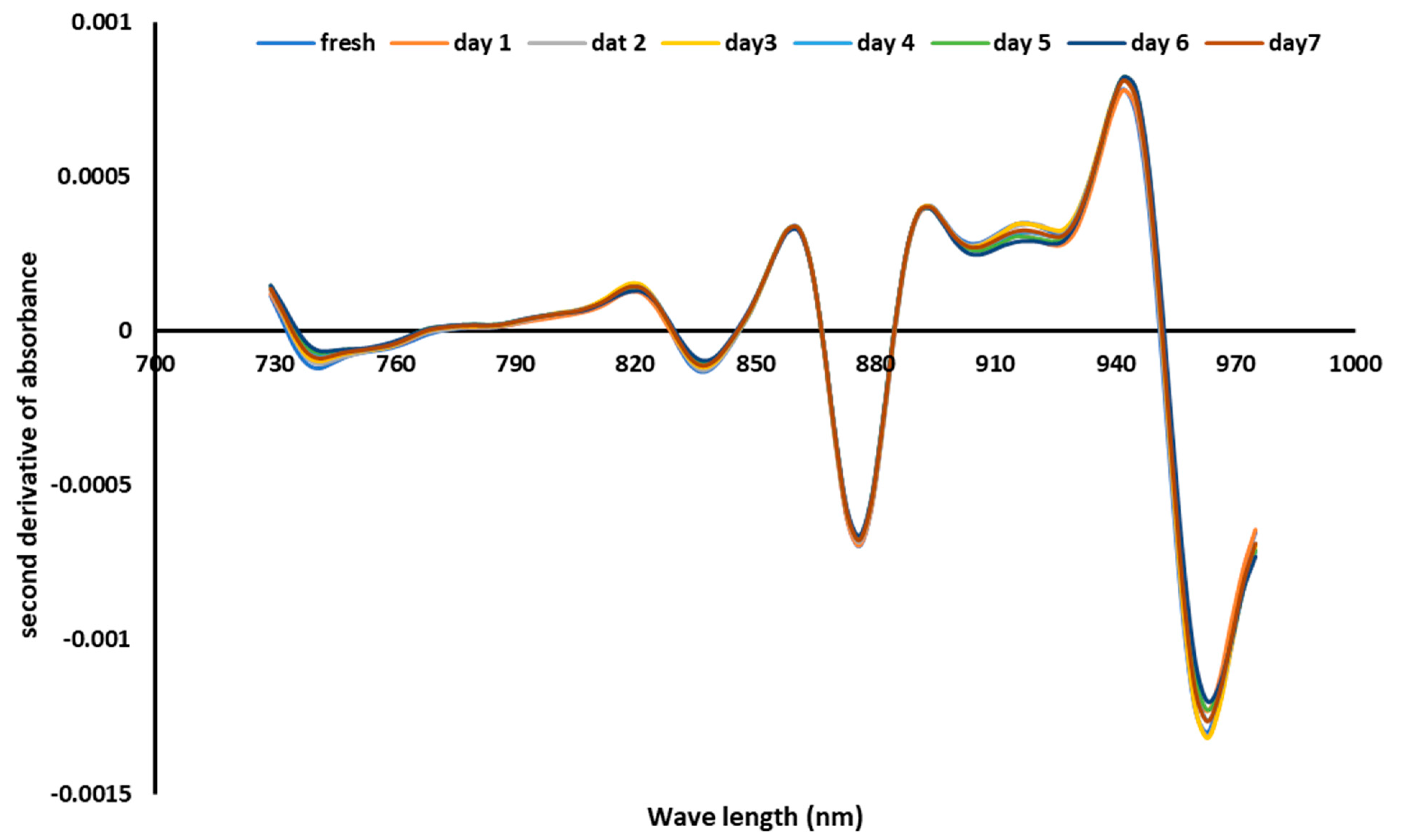
| Added Date Syrup g/100 g Laban Drink | Texture | Flavor | Taste | Color | Acceptance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 7.92A ± 1.22 | 7.56A ± 1.18 | 7.67A ± 1.02 | 7.53A ± 1.20 | 7.72A ± 1.00 |
| 12.5 | 7.28A ± 1.79 | 6.67A ± 1.39 | 6.64A ± 1.11 | 7.11A ± 0.98 | 7.17A ± 1.08 |
| 10 | 6.72A ± 1.50 | 6.03A ± 1.40 | 6.25A ± 1.16 | 6.75B ± 1.11 | 6.00B ± 0.68 |
| 7.5 | 6.19B ± 1.50 | 5.39B ± 1.36 | 5.42B ± 1.00 | 6.50B ± 1.18 | 6.06B ± 1.01 |
| 5 | 5.39C ± 1.65 | 4.83B ± 1.36 | 4.53C ± 1.20 | 5.67C ± 1.20 | 5.28C ± 1.00 |
| 2.5 | 4.19C ± 1.02 | 3.67B ± 1.24 | 3.39C ± 1.45 | 4.78C ± 1.96 | 4.11C ± 1.09 |
| Day | Texture | Flavor | Taste | Color | Acceptance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 7.31A ± 1.22 | 6.67A ± 1.18 | 6.67A ± 1.02 | 7.19A ± 1.20 | 7.17A ± 1.00 |
| 1 | 7.28A ± 1.79 | 6.64A ± 1.39 | 6.58A ± 1.11 | 7.11A ± 0.98 | 7.17A ± 1.08 |
| 2 | 6.11B ± 1.50 | 6.00B ± 1.40 | 6.00B ± 1.16 | 6.36B ± 1.11 | 6.00B ± 0.68 |
| 3 | 5.94B ± 1.50 | 5.86B ± 1.36 | 5.88B ± 1.00 | 6.14B ± 1.18 | 5.94B ± 1.01 |
| 4 | 5.25C ± 1.65 | 5.25C ± 1.36 | 5.33C ± 1.20 | 5.58C ± 1.20 | 5.28C ± 1.00 |
| 5 | 4.75D ± 1.02 | 4.81CD ± 1.24 | 4.81C ± 1.45 | 4.94D ± 1.96 | 4.78D ± 1.09 |
| 6 | 4.27E ± 1.12 | 4.33DE ± 1.17 | 4.25D ± 1.02 | 4.19E ± 1.22 | 4.25E ± 1.14 |
| 7 | 4.08E ± 1.08 | 4.19E ± 1.13 | 4.06D ± 1.52 | 4.03E ± 1.33 | 4.11E ± 1.17 |
| Day | pH | TSS (Brix) | μ (mPas−1) | ΔE | BI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 4.76A ± 0.005 | 16.47A ± 0.001 | 240.65A ± 0.01 | 0.00A ± 0.000 | 1.01D ± 0.001 |
| 1 | 4.76B ± 0.005 | 16.47A ± 0.001 | 240.65A ± 0.01 | 1.11G ± 0.002 | 1.11B ± 0.002 |
| 2 | 4.75B ± 0.006 | 16.47A ± 0.001 | 239.48B ± 0.02 | 1.30F ± 0.010 | 1.30C ± 0.010 |
| 3 | 4.73C ± 0.005 | 16.47A ± 0.001 | 235.36C ± 0.01 | 2.59E ± 0.014 | 2.59h ± 0.014 |
| 4 | 4.71C ± 0.005 | 16.46A ± 0.001 | 235.00C ± 0.01 | 3.38D ± 0.002 | 3.38F ± 0.002 |
| 5 | 4.69D ± 0.006 | 16.46A ± 0.001 | 234.35D ± 0.03 | 3.79D ± 0.001 | 3.79C ± 0.001 |
| 6 | 4.67E ± 0.005 | 16.46A ± 0.001 | 232.34E ± 0.03 | 4.58C ± 0.004 | 4.58A ± 0.004 |
| 7 | 4.61F ± 0.033 | 16.40A ± 0.001 | 229.70F ± 0.01 | 4.62B ± 0.008 | 4.62E ± 0.008 |
| Parameter | Calibration | Cross-Validation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSRC | R2 | RMSECV | |
| TSS | 0.989 | 0.666 | 0.919 | 0.766 |
| pH | 0.912 | 0.715 | 0.902 | 0.785 |
| μ | 0.911 | 2.140 | 0.910 | 1.940 |
| ΔE | 0.971 | 1.004 | 0.921 | 0.989 |
| BI | 0.890 | 0.988 | 0.891 | 0.911 |
| Qi | 0.801 | 0.111 | 0.791 | 0.301 |
| Parameter | Calibration | Cross-Validation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSRC | R2 | RMSECV | |
| TSS | 0.991 | 0.866 | 0.989 | 0.712 |
| pH | 0.900 | 0.755 | 0.902 | 0.715 |
| μ | 0.910 | 1.840 | 0.910 | 1.140 |
| ΔE | 0.960 | 1.104 | 0.959 | 0.999 |
| BI | 0.900 | 0.688 | 0.898 | 0.611 |
| Qi | 0.921 | 0.311 | 0.921 | 0.311 |
Short Biography of Authors
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alhamdan, A.M. NIR Spectroscopy Assessment of Quality Index of Fermented Milk (Laban) Drink Flavored with Date Syrup during Cold Storage. Fermentation 2022, 8, 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8090438
Alhamdan AM. NIR Spectroscopy Assessment of Quality Index of Fermented Milk (Laban) Drink Flavored with Date Syrup during Cold Storage. Fermentation. 2022; 8(9):438. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8090438
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlhamdan, Abdullah M. 2022. "NIR Spectroscopy Assessment of Quality Index of Fermented Milk (Laban) Drink Flavored with Date Syrup during Cold Storage" Fermentation 8, no. 9: 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8090438
APA StyleAlhamdan, A. M. (2022). NIR Spectroscopy Assessment of Quality Index of Fermented Milk (Laban) Drink Flavored with Date Syrup during Cold Storage. Fermentation, 8(9), 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8090438







