Cloning and Characterization of Cellulase from Paenibacillus peoriae MK1 Isolated from Soil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Isolation and Identification of a Cellulase-Producing Strain
2.3. Bacterial Strain, Plsmids, and Cloning
2.4. Culture Conditions for Enzyme Expression and Enzyme Purification
2.5. Determination of Molecular Mass
2.6. Enzyme Assay
2.7. Effects of pH, Temperature, and Metal Ions
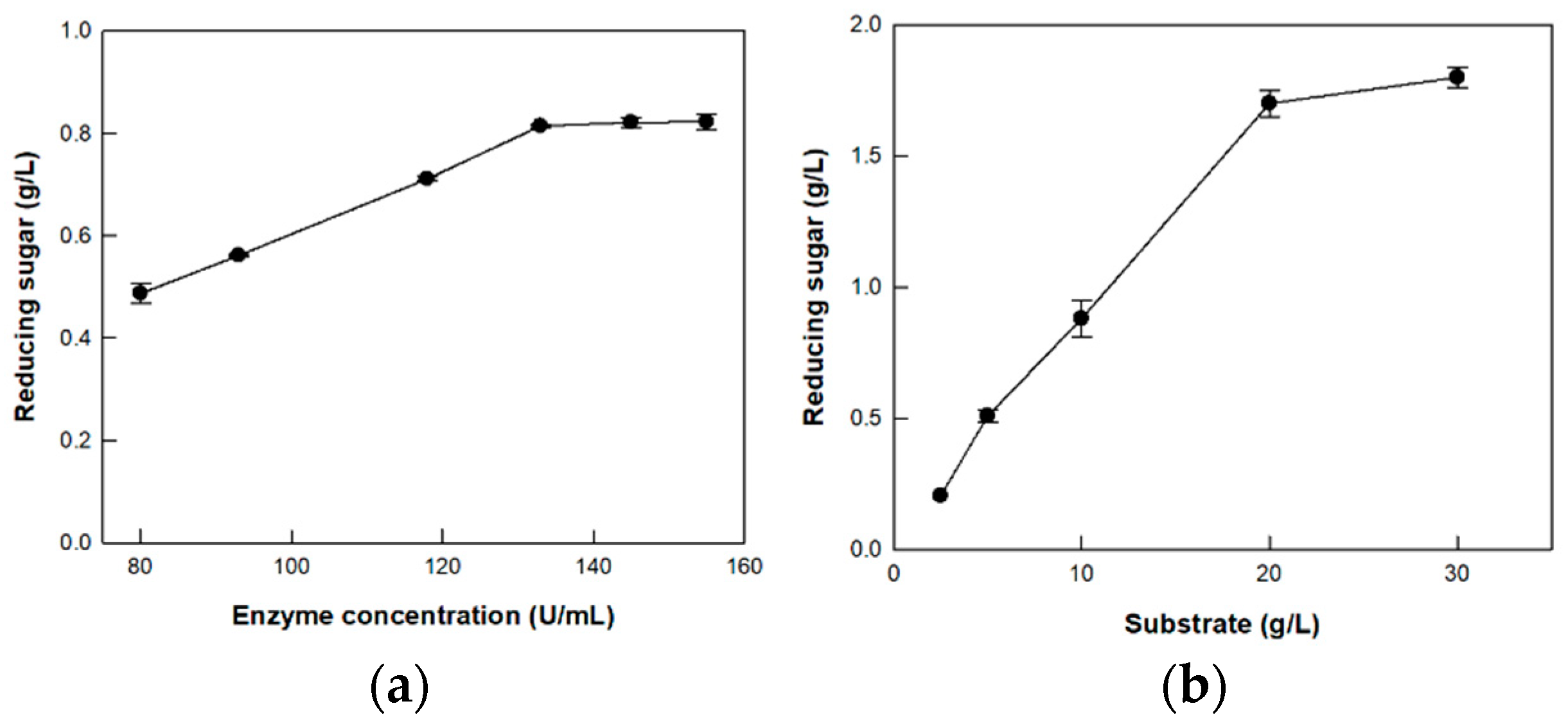
2.8. Optimization of Enzyme and Substrate Concentrations
2.9. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cloning, Expression, and Purification of Cellulase from Isolated Strain
3.2. Effect of Metal Ions on the Activity of Cellulase from P. peoriae MK1
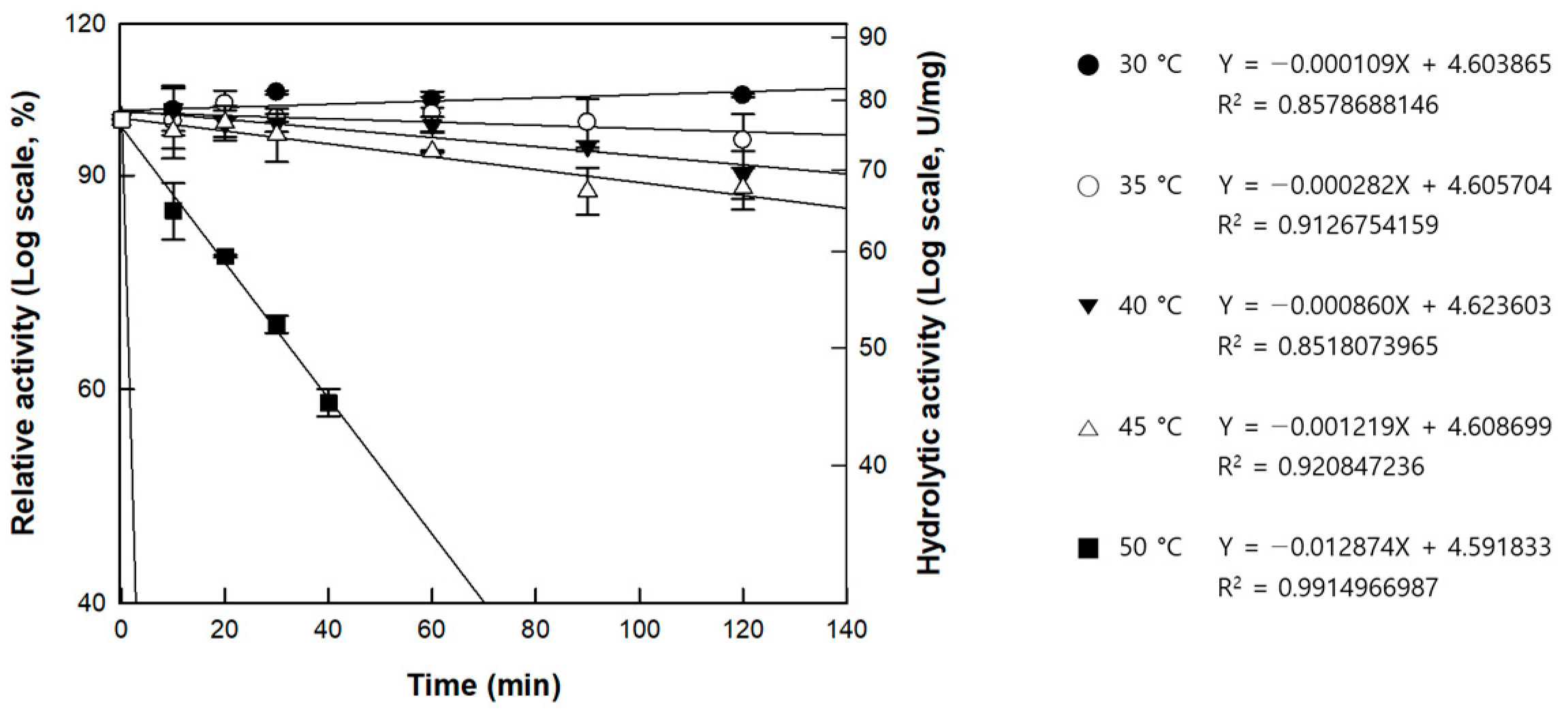
3.3. Effects of pH and Temperature on the Activity of Cellulase from P. peoriae MK1
3.4. Substrate Specificity of Cellulase from P. peoriae MK1
3.5. Hydrolysis of CM-Cellulose by Cellulase from P. peoriae MK1 on the Optimized Enzyme and Substrate Concentrations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lynd, L.R.; Laser, M.S.; Bransby, D.; Dale, B.E.; Davison, B.; Hamilton, R.; Himmel, M.; Keller, M.; McMillan, J.D.; Sheehan, J.; et al. How biotech can transform biofuels. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynd, L.R.; Weimer, P.J.; van Zyl, W.H.; Pretorius, I.S. Microbial cellulose utilization: Fundamentals and biotechnology. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2002, 66, 506–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, B.C. Alpha-L-arabinofuranosidases: Biochemistry, molecular biology and application in biotechnology. Biotechnol. Adv. 2000, 18, 403–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukumaran, R.K.; Singhania, R.R.; Pandey, A. Microbial cellulases-production, applications and challenges. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2005, 64, 832–844. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhad, R.C.; Gupta, R.; Singh, A. Microbial cellulases and their industrial applications. Enzyme Res. 2011, 2011, 280696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Srivastava, M.; Mishra, P.; Singh, P.; Ramteke, P. Application of cellulases in biofuels industries: An overview. J. Biofuels Bioenergy 2015, 1, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.S.; Ray, R.C. Solid state fermentation for production of microbial cellulases: Recent advances and improvement strategies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 86, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Srivastava, M.; Mishra, P.K.; Gupta, V.K.; Molina, G.; Rodriguez-Couto, S.; Manikanta, A.; Ramteke, P.W. Applications of fungal cellulases in biofuel production: Advances and limitations. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2379–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, M.; Naguib, M.; Abdel Rehim, M.; Ali, K. Immobilization of β-galactosidase on carrageenan gel via bio-inspired polydopamine coating. J. Text. Color. Polym. 2018, 15, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Sarkar, P.K.; Mohiuddin, A.K.M.; Suzauddula, M. Optimization of fermentation condition for cellulase enzyme production from Bacillus sp. Malays. J. Halal Res. 2019, 2, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawadza, C.; Hatti-Kaul, R.; Zvauya, R.; Mattiasson, B. Purification and characterization of cellulases produced by two Bacillus strains. J. Biotech. 2000, 83, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nochur, S.V.; Roberts, M.F.; Demain, A.L. True cellulase production by Clostridium thermocellum grown on different carbon sources. Biotech. Lett. 1993, 15, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Vinha, F.N.M.; Gravina-Oliveira, M.P.; Franco, M.N.; Macrae, A.; da Silva Bon, E.P.; Nascimento, R.P.; Coelho, R.R.R. Cellulase production by Streptomyces viridobrunneus SCPE-09 using lignocellulosic biomass as inducer substrate. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 164, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohail, M.; Siddiqi, R.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, S.A. Cellulase production from Aspergillus niger MS82: Effect of temperature and pH. New Biotech. 2009, 25, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Resch, M.G.; Podkaminer, K.; Yang, S.; Baker, J.O.; Donohoe, B.S.; Wilson, C.; Klingeman, D.M.; Olson, D.G.; Decker, S.R.; et al. Dramatic performance of Clostridium thermocellum explained by its wide range of cellulase modalities. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, D.; Lin, D.; Gong, C.; Peng, C.; Yao, S. Expression of a bifunctional cellulase with exoglucanase and endoglucanase activities to enhance the hydrolysis ability of cellulase from a marine Aspergillus niger. Process Biochem. 2017, 52, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasani, H.; Umretiya, N.; Dharajiya, D.; Kapuria, M.; Shah, S.; Patel, J. Isolation, optimization and production of cellulase by Aspergillus niger from agricultural waste. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 10, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar]
- Saratale, G.D.; Saratale, R.G.; Chang, J.-S. Chapter 9—Biohydrogen from renewable resources. In Biohydrogen; Pandey, A., Chang, J.-S., Hallenbecka, P.C., Larroche, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 185–221. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, G.L. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.H.; Chang, J.; Lee, Y.S.; Fang, S.J.; Choi, Y.L. Gene cloning of endoglucanase Cel5A from cellulose-degrading Paenibacillus xylanilyticus KJ-03 and purification and characterization of the recombinant enzyme. Protein J. 2012, 31, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.M.; Hong, S.J.; Math, R.K.; Islam, S.M.; Kim, J.O.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, H.; Yun, H.D. Cloning of two cellulase genes from endophytic Paenibacillus polymyxa GS01 and comparison with cel 44C-man 26A. J. Basic Microbiol. 2008, 48, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, H.; Kasana, R.C.; Dutt, S.; Gulati, A. Cloning and expression of low temperature active endoglucanase EG5C from Paenibacillus sp. IHB B 3084. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 259–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Kim, B.K.; Lee, B.H.; Jo, K.I.; Lee, N.K.; Chung, C.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Lee, J.W. Purification and characterization of cellulase produced by Bacillus amyoliquefaciens DL-3 utilizing rice hull. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, S.; Kushwah, J.; Tiwari, R.; Kumar, R.; Somvanshi, V.S.; Nain, L.; Saxena, A.K. Cloning and expression of β-1, 4-endoglucanase gene from Bacillus subtilis isolated from soil long term irrigated with effluents of paper and pulp mill. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Yang, W.; Meng, F.; Ji, S.; Xin, H.; Cao, B. Characterization of an acidic cellulase produced by Bacillus subtilis BY-4 isolated from gastrointestinal tract of Tibetan pig. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2015, 56, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asha, B.M.; Revathi, M.; Yadav, A.; Sakthivel, N. Purification and characterization of a thermophilic cellulase from a novel cellulolytic strain, Paenibacillus barcinonensis. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 22, 1501–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.H.; Tsai, C.H.; Lin, P.H.; Chang, K.C.; Tu, J.; Wang, Y.N.; Yang, C.Y. Characterization and pulp refining activity of a Paenibacillus campinasensis cellulase expressed in Escherichia coli. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 7882–7888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.-L.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, M.; Wu, Y.; Feng, J.-X. Isolation, screening, and identification of cellulolytic bacteria from natural reserves in the subtropical region of China and optimization of cellulase production by Paenibacillus terrae ME27-1. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 512497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.M.; Yin, Y.R.; Li, W.J. Cloning, expression and characterization of a novel GH5 exo/endoglucanase of Thermobifida halotolerans YIM 90462(T) by genome mining. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 120, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Strain | Molecular Mass (kDa) | Metal Ion | pH | Temperature (°C) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. amyloiquefaciens | 54 | Ca2+ | 7.0 | 50 | [23] |
| B. subtilis | 55 | NR * | 8.0 | 50–60 | [24] |
| B. subtilis BY-4 | 55 | Mg2+ | 4.5 | 60 | [25] |
| Paenibacillus sp. | 63.5 | Co2+ | 5.0 | 40 | [22] |
| P. barcinonensis | 58.6 | Fe2+ | 7.0 | 35 | [26] |
| P. campinasensis | 38 | NR * | 6.0–7.0 | 60 | [27] |
| P. peoriae MK1 | 65 | Cu2+ | 5.0 | 40 | This study |
| P. polymyxa | 61 | NR * | 6.0 | 50 | [21] |
| P. terrae | NR | NR * | 5.5 | 50 | [28] |
| P. xylanilyticus | 64 | Cu2+ | 6.0 | 40 | [20] |
| T. halotolerans | 49.6 | Ca2+ | 8.0 | 50 | [29] |
| Temperature (°C) | kd (min−1) | t1/2 (h) |
|---|---|---|
| 30 | 1.09 × 10−4 | 105.6 |
| 35 | 2.82 × 10−4 | 41.0 |
| 40 | 8.60 × 10−4 | 13.4 |
| 45 | 1.22 × 10−3 | 9.5 |
| 50 | 1.29 × 10−2 | 0.9 |
| Substrate | Enzyme Unit (U/mg) |
|---|---|
| CM-cellulose | 77.0 ± 0.03 |
| Swollen cellulose | 15.4 ± 0.01 |
| Sigmacell cellulose | 10.6 ± 0.03 |
| α-Cellulose | 6.3 ± 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.J.; Shin, K.-C.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, Y.-S.; Park, C.-S. Cloning and Characterization of Cellulase from Paenibacillus peoriae MK1 Isolated from Soil. Fermentation 2023, 9, 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100873
Kim SJ, Shin K-C, Kim DW, Kim Y-S, Park C-S. Cloning and Characterization of Cellulase from Paenibacillus peoriae MK1 Isolated from Soil. Fermentation. 2023; 9(10):873. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100873
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Sang Jin, Kyung-Chul Shin, Dae Wook Kim, Yeong-Su Kim, and Chang-Su Park. 2023. "Cloning and Characterization of Cellulase from Paenibacillus peoriae MK1 Isolated from Soil" Fermentation 9, no. 10: 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100873
APA StyleKim, S. J., Shin, K.-C., Kim, D. W., Kim, Y.-S., & Park, C.-S. (2023). Cloning and Characterization of Cellulase from Paenibacillus peoriae MK1 Isolated from Soil. Fermentation, 9(10), 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100873






