Improving Expression of Pepsinogen A from Homo sapiens in Aspergillus niger by Using a Multi-Copy Gene Knock-in Strategy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Culture Conditions
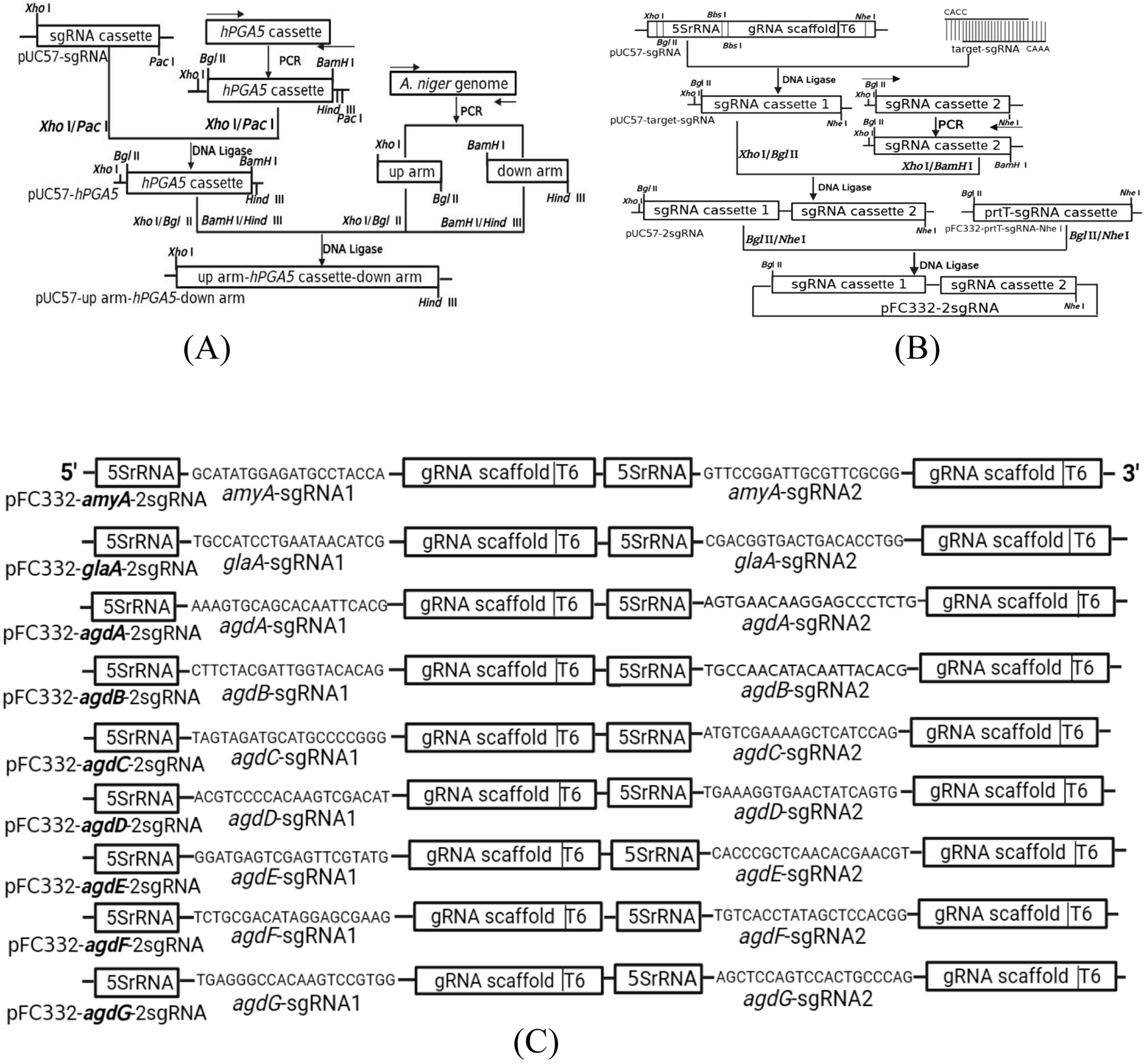
2.2. Construction of Recombinant Plasmid
2.3. Transformation and Expression
2.4. Assay of Pepsin Activity
3. Results
3.1. Free Expression of hPGA
3.2. Construction and Screening of Recombinant hPGA Strains
3.3. Expression of Recombinant hPGA at Different Integration Sites
3.4. Expression of Recombinant hPGA with Different Copy Numbers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herriott, R.M. Isolation, crystallization, and properties of swine pepsinogen. J. Gen. Physiol. 1938, 21, 501–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plebani, M.; Szabo, O.S. Pepsinogens in Health and Disease. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1993, 30, 273–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-M.; Li, J.-X.; Zhang, G.-Y.; Li, X.-H.; Gu, H. The value of serum pepsinogen levels for the diagnosis of gastric diseases in Chinese Han people in midsouth China. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furihata, C. Human gastric cancer risk screening: From rat pepsinogen studies to the ABC method. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2021, 97, 462–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gritti, I.; Banfi, G.; Roi, G. Pepsinogens: Physiology, pharmacology pathophysiology and exercise. Pharmacol. Res. 2000, 41, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Narita, Y.; Oda, S.-I.; Moriyama, A.; Takenaka, O.; Kageyama, T. Purification and characterization of goat pepsinogens and pepsins. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999, 122, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samloff, I.M. Slow moving protease and the seven pepsinogens. Electrophoretic demontration of the existence of eight proteolytic fractions in human gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology 1969, 57, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, Y.; Oda, S.-I.; Moriyama, A.; Takenaka, O.; Kageyama, T. Pepsinogens and Pepsins from House Musk Shrew, Suncus murinus: Purification, Characterization, Determination of the Amino-Acid Sequences of the Activation Segments, and Analysis of Proteolytic Specificities. J. Biochem. 1997, 121, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Yada, R.Y. Expression of soluble cloned porcine pepsinogen A in Escherichia coli. Biochem. J. 1996, 315 Pt 2, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimasu, A.M.; Ahn, J.-K.; Tanaka, T.; Yada, R.Y. Soluble expression and purification of porcine pepsinogen from Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr. Purif. 2002, 25, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Rudolph, R.; Söhling, B. A novel fusion protein system for the production of native human pepsinogen in the bacterial periplasm. Protein Expr. Purif. 2006, 47, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleißner, A.; Dersch, P.; Fleissner, A. Expression and export: Recombinant protein production systems for Aspergillus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 1255–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Pan, L.; Wang, B. Efficient Over-expression and Application of High-performance Pectin Lyase by Screening Aspergillus niger Pectin Lyase Gene Family. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2018, 23, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekmouche, Y.; Zhou, S.; Cusano, A.M.; Record, E.; Lomascolo, A.; Robert, V.; Simaan, A.J.; Rousselot-Pailley, P.; Ullah, S.; Chaspoul, F.; et al. Gram-scale production of a basidiomycetous laccase in Aspergillus niger. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2014, 117, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, B.; Pan, L. Heterologous expression and characterization of Penicillium citrinum nuclease P1 in Aspergillus niger and its application in the production of nucleotides. Protein Expr. Purif. 2019, 156, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Yu, D.; Lin, X.; Wang, B.; Pan, L. Improving expression of thermostable trehalase from Myceliophthora sepedonium in Aspergillus niger mediated by the CRISPR/Cas9 tool and its purification, characterization. Protein Expr. Purif. 2020, 165, 105482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, B.; Ye, Y.; Pan, L. High level expression and characterization of tannase tan7 using Aspergillus niger SH-2 with low-background endogenous secretory proteins as the host. Protein Expr. Purif. 2018, 144, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benghazi, L.; Record, E.; Suárez, A.; Gomez-Vidal, J.A.; Martínez, J.; de la Rubia, T. Production of the Phanerochaete flavido-alba laccase in Aspergillus niger for synthetic dyes decolorization and biotransformation. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zheng, P.; Zhang, K.; Cairns, T.C.; Meyer, V.; Sun, J.; Ma, Y. 5S rRNA Promoter for Guide RNA Expression Enabled Highly Efficient CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing in Aspergillus niger. ACS Synth. Biol. 2019, 8, 1568–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.-Q.; Liu, G.-N.; Ji, R.-Y.; Shi, K.; Song, P.; Ren, L.-J.; Huang, H.; Ji, X.-J. CRISPR/Cas9-based genome editing of the filamentous fungi: The state of the art. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 7435–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Wang, B.; He, P.; Lin, Y.; Pan, L. Genomic analysis of the aconidial and high-performance protein producer, industrially relevant Aspergillus niger SH2 strain. Gene 2014, 541, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nødvig, C.S.; Nielsen, J.B.; Kogle, M.E.; Mortensen, U.H. A CRISPR-Cas9 System for Genetic Engineering of Filamentous Fungi. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhao, B.; Lu, J.; Gui, L.; Lu, F.; Li, M. An efficient marker-free genome editing method for Aspergillus niger. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 4744–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hartingsveldt, W.; Mattern, I.E.; Van Zeijl, C.M.J.; Pouwels, P.H.; van den Hondel, C.A. Development of a homologous transformation system for Aspergillus niger based on the pyrG gene. Mol. Genet. Genom. 1987, 206, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carrière, F.; et al. INFOGEST static in vitro simulation of gastrointestinal food digestion. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Jiang, X.; Dong, Z.; Huang, J.; Chen, X. Identification of two integration sites in favor of transgene expression in Trichoderma reesei. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.-N.; Cai, F.-R.; Dong, X.-R.; Huang, Z.-B.; Tao, Y.; Huang, J.; Dong, Z.-Y. Improved production of heterologous lipase in Trichoderma reesei by RNAi mediated gene silencing of an endogenic highly expressed gene. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 109, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flagfeldt, D.B.; Siewers, V.; Huang, L.; Nielsen, J. Characterization of chromosomal integration sites for heterologous gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 2009, 26, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorer, C.A.; Clare, J.J.; McCombie, W.R.; Romanos, M.A.; Sreekrishna, K. Rapid Selection Using G418 of High Copy Number Transformants of Pichia pastoris for High–level Foreign Gene Expression. Nat. Biotechnol. 1994, 12, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimel, K. Unfolded protein response in filamentous fungi—Implications in biotechnology. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevalainen, K.H.; Te′O, V.S.J.; Bergquist, P.L. Heterologous protein expression in filamentous fungi. Trends Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Strain | Genotype | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | An_1-1 | 41683 (ΔamyA(05), glaA::2hPGA5) |
| 2 | An_1-2 | 41683 (ΔamyA(12), glaA::2hPGA5) |
| 3 | An_1-3 | 41683 (ΔamyA(05,12), glaA::3hPGA5) |
| 4 | An_1-4 | 41683 (ΔamyA(05)::hPGA5) |
| 5 | An_1-5 | 41683 (ΔamyA(12)::hPGA5) |
| 6 | An_1-6 | 41683 (ΔglaA::hPGA5) |
| 7 | An_2-1 | 41683 (ΔagdA::hPGA5) |
| 8 | An_2-2 | 41683 (ΔagdF::hPGA5) |
| 9 | An_2-3 | 41683 (ΔagdA, D::2hPGA5) |
| 10 | An_2-4 | 41683 (ΔagdA, D, E, F::4hPGA5) |
| 11 | An_2-5 | 41683 (ΔagdE::hPGA5) |
| 12 | An_2-6 | 41683 (ΔagdA, E::2hPGA5) |
| 13 | An_2-7 | 41683 (ΔagdD, E::2hPGA5) |
| 14 | An_2-8 | 41683 (ΔagdE, F::2hPGA5) |
| 15 | An_2-9 | 41683 (ΔagdA, D, E::3hPGA5) |
| 16 | An_2-10 | 41683 (ΔagdB::hPGA5) |
| 17 | An_2-11 | 41683 (ΔagdC::hPGA5) |
| 18 | An_2-12 | 41683 (ΔagdB, C::2hPGA5) |
| 19 | An_2-13 | 41683 (ΔagdB, G::2hPGA5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Gui, L.; Chen, B.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, F.; Li, M. Improving Expression of Pepsinogen A from Homo sapiens in Aspergillus niger by Using a Multi-Copy Gene Knock-in Strategy. Fermentation 2023, 9, 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9060538
Chen J, Gui L, Chen B, Sun Y, Zhao Y, Lu F, Li M. Improving Expression of Pepsinogen A from Homo sapiens in Aspergillus niger by Using a Multi-Copy Gene Knock-in Strategy. Fermentation. 2023; 9(6):538. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9060538
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jie, Ling Gui, Boyu Chen, Yuang Sun, Yongcan Zhao, Fuping Lu, and Ming Li. 2023. "Improving Expression of Pepsinogen A from Homo sapiens in Aspergillus niger by Using a Multi-Copy Gene Knock-in Strategy" Fermentation 9, no. 6: 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9060538
APA StyleChen, J., Gui, L., Chen, B., Sun, Y., Zhao, Y., Lu, F., & Li, M. (2023). Improving Expression of Pepsinogen A from Homo sapiens in Aspergillus niger by Using a Multi-Copy Gene Knock-in Strategy. Fermentation, 9(6), 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9060538





