Abstract
To investigate the effect of phenyllactic acid (PLA) on the dynamic changes of high-moisture stylo silage, fresh stylo was ensiled with addition of PLA at the levels of 0, 1% and 2% using lab-level silage bags, where samples were collected on days 3, 7, 14 and 30 of ensiling fermentation to analyze fermentation parameters, nitrogen distribution and bacterial community. The results showed that PLA addition at ensiling led to the increase (p < 0.01) in dry matter content, lactic acid concentration and Flieg’s score of stylo silage as well as the decrease (p < 0.01) in dry matter loss, pH value and coliform bacteria population, with butyric acid only detected in the control group. It also resulted in the increase (p < 0.01) in true protein content and its proportion as well as the decrease (p < 0.01) in ammonia-N content and its proportion, almost with linearly dose effect. Sequencing analysis revealed that PLA addition led to the increase (p < 0.05) in Sobs, Shannon, Chao and Ace of bacterial community in the stylo silage, where the relative abundance of Enterobacter, Clostridium, and Kosakonia was decreased, and that of Lactobacillus, Enterococcus and Pantoea was increased. Furthermore, Kosakonia, Terriglobus, Sphingomonas and Sphingopyxis had an important role in the bacterial interaction network. It is suggested that PLA application at the level of 1–2% could improve silage quality of stylo silage via modifying bacterial community.
1. Introduction
Stylo (Stylosanthes guianensis) is a tropical legume shrub widely grown for forage throughout the tropics and subtropics. Stylo is fairly palatable to livestock when mature and can grow on relatively infertile soils [1]. Stylo is a high-yielding forage legume that can produce 10–20 t DM/ha depending on soil fertility. Stylo is regarded as “tropical alfalfa” with crude protein content of 11–16% [2,3] and can be used as hay, silage or fed fresh. As to silage production, protein hydrolysis may be the main concern in legume silage, such as alfalfa silage and stylo silage, where generally more than half of protein in raw materials would be hydrolyzed during ensiling [4,5]. Due to its potentially negative effect on ruminant nitrogen nutrition, many measurements have been taken to prevent proteolysis in silage, including lowering moisture content by wilting or mixing drier materials [6], intensifying initial loading of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) [7,8], adding fermentation promotors (sugar, molasses or cellulase) or inhibitors (organic acids, protein binding agent) [9,10,11]. Overall, such additives or measurements could somewhat improve silage fermentation and protein preservation. However, compared to some intrinsic components such as nisin and organic acids, exogenous additives might have poorer promotion or inhibition selectivity and consistency. More recently, much effort has been made to develop functional LAB simultaneously producing organic acids, fibrolytic enzymes or antimicrobial substances [7,11,12]. Their application would be expected to not only promote silage fermentation but also improve its aerobic stability, even directly promoting animal health in a convenient and economical way.
Phenyllactic acid (PLA) has been recognized as a new type of biological preservative due to its high antimicrobial activity and broad antimicrobial spectrum, such as Listeria monocytes, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella spp., Candida spp., Rhodotorula spp., Aspergillus spp. and Penicillin spp. [2,13,14]. Moreover, PLA can be produced with phenylalanine (a common amino acid in animals and plants) as raw material via LAB fermentation, such as Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus plantarum and Leuconostoc mesenteroides [12,15,16]. Therefore, PLA is a promising antimicrobial agent for fermented foods and feeds in the perspective of safety and effectiveness. It is reported that PLA or PLA-tolerant LAB strains could effectively prevent alfalfa protein from degrading during ensiling period [12] and lead to the decrease in butyric acid and ammonia-N in timothy silage likely via favoring the growth of Lactobacillus curvatus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae as well as inhibiting the growth of lactic acid assimilating yeasts belonging to Issatchenkia [17]. The application of PLA or PLA-producing LAB in silage production is attracting increasing attention, but its effectiveness and mechanism still need further research. In consideration that the added PLA is mostly degraded in the mature silage [12], there is a need to figure out the dynamic changes of silage fermentation in order to achieve its proper and efficient utilization.
Therefore, the present study aimed to investigate the effect of PLA addition on the dynamic fermentation parameters, nitrogen fractions and bacterial community of stylo silage, where high moisture stylo silage ensiled with addition of PLA at the levels of 0, 1% and 2% were unsealed for samples collection on days 3, 7, 14 and 30 of ensiling fermentation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Material Preparation and Silage Processing
Fresh stylo (CIAT 184) was harvested at full bloom stage by its second cutting with a 10 cm stubble left, where the growth of stylo was managed with manual weeding but no fertilization. The whole plant was manually chopped into 1–2 cm using straw chopper in the lab. Immediately, the prepared forage was ensiled without (CK) or with addition of 1.0% or 2.0% PLA on a fresh matter (FM) basis, where PLA was added in the form of powder and evenly mixed in plastic basins. In total, 36 silage bags (3 treatments × 4 time-points × 3 replicates) were individually prepared using polythene plastic bags (20 cm by 30 cm; maximum capacity of 300 g), with 200 g raw material per bag. With initial weight recorded, all the prepared bag silages were stored in a carton and kept under natural condition (25–30 °C). To monitor the dynamic changes of silage fermentation, 3 bag silages of each treatment were unsealed for sample collection on days 3, 7, 14 and 30 of ensiling, respectively. All the samples were destined to the analyses of fermentation parameters, nitrogen fractions and bacterial community. Chemical composition and bacterial profile of the fresh stylo used in the present study are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Chemical composition and bacterial profile of fresh stylo.
2.2. Determination of Microbial Population, Fermentation Parameters and Chemical Composition
Bacteria solution was prepared by suspending silage sample in sterilized saline, and then lactic acid bacteria, coliform bacteria, yeasts and molds were separately cultivated with De Man, Rogosa, Sharpe (MRS), Violet Red Bile and Rose Bengal agar, and enumerated after incubating at 30 °C for 2–3 days.
Another silage sample was soaked with distilled water for the analyses of pH, ammonia-nitrogen (ammonia-N) and organic acids (lactic acid, acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid). The values of pH were measured by a glass electrode pH meter (PHS-3C, INESA Instrument, Shanghai, China); ammonia-N content was determined in colorimetry with a Thermo Scientific Varioskan LUX (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Shanghai, China) [18]; and individual organic acid was analyzed using high performance liquid chromatography equipped with Shodex RS Pak KC-811 column and SPD-20A detector (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) [19].
The remaining silage of each bag was oven-dried at 65 °C for 48 h to determine dry matter (DM) and then used for the analysis of nitrogen fractions (crude protein (CP), true protein and nonprotein-N) [20]. The raw material was also analyzed for the contents of neutral detergent fiber (NDF), acid detergent fiber (ADF) and acid detergent lignin (ADL) using an A220 Fiber Analyzer (ANKOM Technology Corp., Macedon, NY, USA) [21] as well as water soluble carbohydrate (WSC) concentration using the method of 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid colorimetry [22].
Furthermore, the comprehensive quality of silage was evaluated using Flieg’s evaluation system with the following equation [23]:
Flieg’s scores = 220 + (2 × DM% − 15) − 40 × pH
2.3. Bacterial Community Analysis by 16S rDNA Sequencing Technology
The DNA extraction and sequencing analysis were carried out with the help of Gene Denovo Co., Ltd. (Guangzhou, China). In brief, bacterial DNA was extracted with DNA extraction Kit (Omega Biotek, Norcross, GA, USA), and PCR amplification was conducted with the primers (341F: CCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG; 806R: GGACTACHVGGGTATCTAAT) targeting the V3–V4 regions of 16S rDNA according to the reported procedure [24]. Following purification and quantification, the amplicons were sequenced on Illumina Hiseq 2500 platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). The raw data were analyzed in steps as reported [8]. Paired-end clean reads were merged using FLSAH (v 1.2.11), and then noisy sequences were filtered with QIIME (v 1.9.1). Subsequently, chimera checking was performed using UCHIME algorithm. Operational taxonomic unit (OTU) with 97% identities was generated using UPARSE pipeline. Taxonomy assignment was performed using Ribosome Database Project (RDP) classifier (Version 2.2). The α-diversity and β-diversity were calculated in QIIME and then plotted in R software (Version 4.3.0). Spearman’s correlation coefficient was calculated, and then correlation heatmap and co-occurrence network were built in R software. The sequencing data reported in this study were archived in the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) with the accession number PRJNA 736346.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Mixed model was used to analyze the effects of PLA level, ensiling day and their interaction by statistical software SAS 9.3 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) using the following model:
where Yijk is the dependent variable; µ is the overall mean; Silobagk is the random effect of the k-th silobag; PLj is the effect of the i-th treatment; EDj is the effect of the j-th ensiling day; PLi × EDj is the interaction effect of the i-th treatment by the j-th ensiling day; and eijk is the residual error. For the repeated measures analysis, the covariance structure with unstructured type was used, and ensiling day was set as repeated subject with significance declared at the level of p < 0.05; LSD was used to evaluate the difference. The linear and quadratic effects of PLA level were also contrasted. The sequencing analysis was performed on OmicShare platform (http://www.omicshare.com/tools (10 December 2022).
Yijk = µ + Silobagk + PLj + EDj + PLi × EDj + eijk
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Phenyllactic Acid on Dynamic Fermentation Characteristics of Stylo Silage
Dynamic fermentation characteristics of stylo silage are presented in Table 2. The interaction effect of PLA level and days of ensiling was significant (p < 0.01) on DM content, LAB and coliform bacteria population and lactic acid concentration. The DM content, pH value and coliform bacteria population of stylo silage gradually decreased (p < 0.01) as ensiling fermentation prolonged, and PLA addition led to the increase (p < 0.01) in DM content, lactic acid concentration and Flieg’s score as well as the decrease (p < 0.01) in DM loss, pH value and coliform bacteria population, with significant dose effect (pL < 0.01, pQ < 0.01). Meanwhile, compared to the control group, PLA addition at the level of 2% resulted in the decrease in LAB population (p < 0.01) and acetic acid concentration across the ensiling process. Additionally, butyric acid was only detected in the control group, and the numbers of yeasts and molds were less than 2 log10 CFU/g FM in all the silage.

Table 2.
Dynamic fermentation characteristics of stylo silage ensiled with addition of phenyllactic acid.
3.2. Effect of Phenyllactic Acid on Dynamic Nitrogen Distribution of Stylo Silage
Dynamic changes of nitrogen fractions in stylo silage are showed in Table 3. The interaction effect of PLA level and days of ensiling was significant (p < 0.01) on ammonia-N content and its proportion. As ensiling fermentation went on, true protein content and its proportion gradually decreased (p < 0.01) in the stylo silage while ammonia-N content and its proportion increased (p < 0.01). The application of PLA at ensiling resulted in the linear increase (p < 0.01; pL < 0.01, pQ > 0.05) in true protein content and its proportion as well as the significant decrease (p < 0.01; pL < 0.01, pQ < 0.01) in ammonia-N content and its proportion.

Table 3.
Dynamic nitrogen fractions of stylo silage ensiled with addition of phenyllactic acid.
3.3. Effect of Phenyllactic Acid on Dynamic Bacterial Community of Stylo Silage
The variation of alpha diversity of bacterial community in stylo silage is presented in Table 4. In the 16S rDNA sequencing, Goods_coverage of all the silage was over 0.99. Alpha diversity indices Sobs, Chao and Ace declined (p < 0.05) in the prolonged silage while Shannon and Simpson increased (p < 0.05) in a whole tendency. The addition of 1% or 2% PLA at ensiling led to the increase (p < 0.05; pL < 0.01, pQ > 0.05) in Sobs, Shannon and Chao of bacterial community in the stylo silage.

Table 4.
Dynamics of bacterial alpha diversity of stylo silage ensiled with addition of phenyllactic acid.
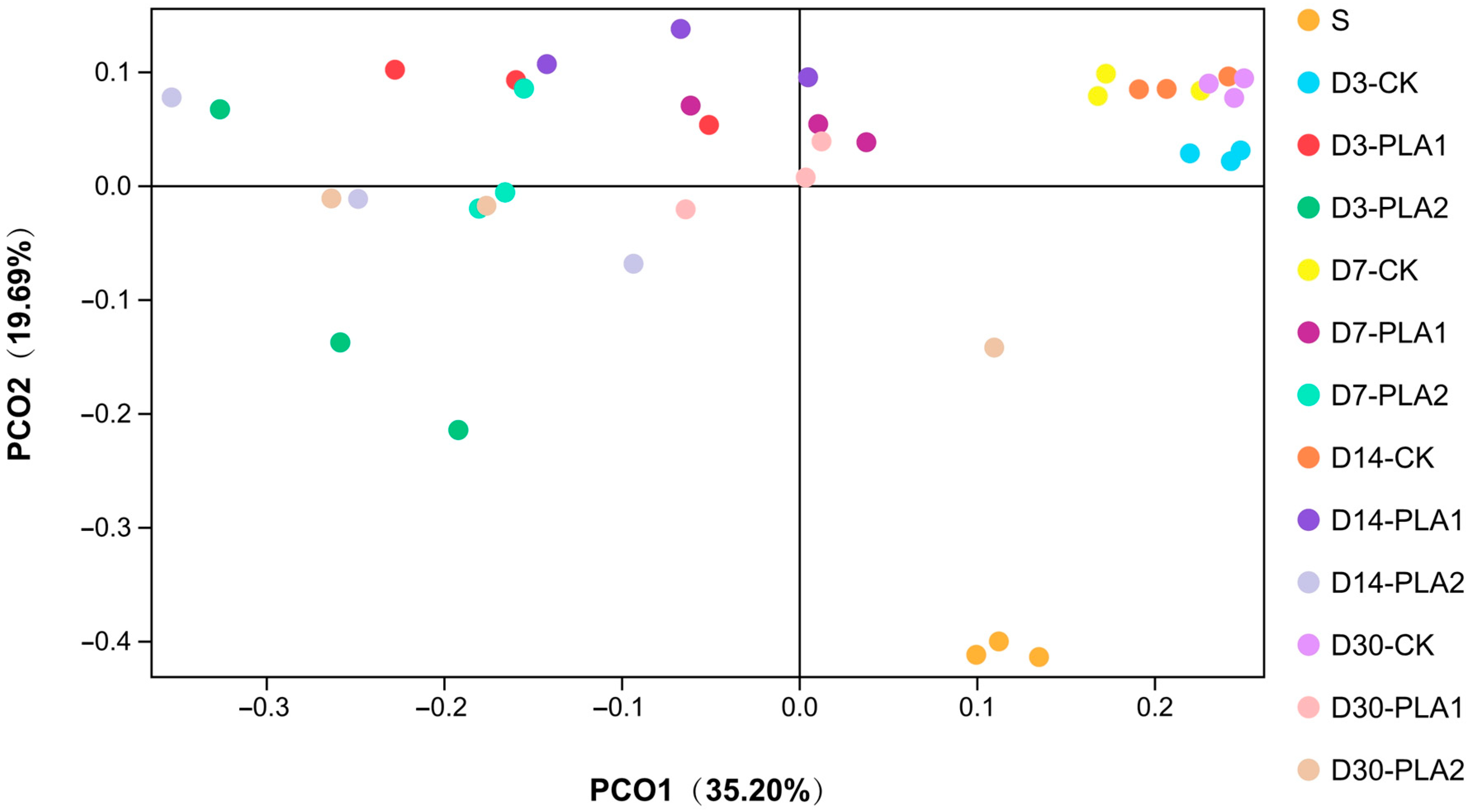
Furthermore, PCoA analysis (Figure 1) showed that samples of fresh stylo, CK group and PLA groups (1% or 2%) were separately clustered regardless of sampling time. Moreover, the samples of CK group at different timepoints varied in a narrow range while those of PLA groups were located in a wider range, especially for the 2% PLA addition.
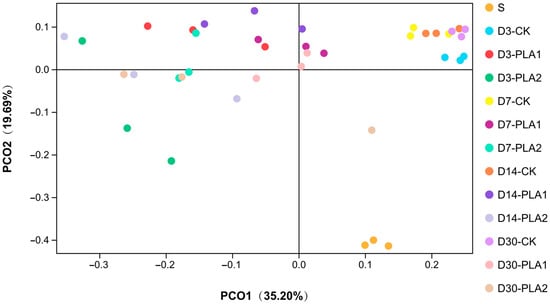
Figure 1.
Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) of bacterial community in stylo silage ensiled with addition of phenyllactic acid (S: fresh stylo; CK: blank control; PLA1 and PLA2: 1% or 2% phenyllactic acid addition).
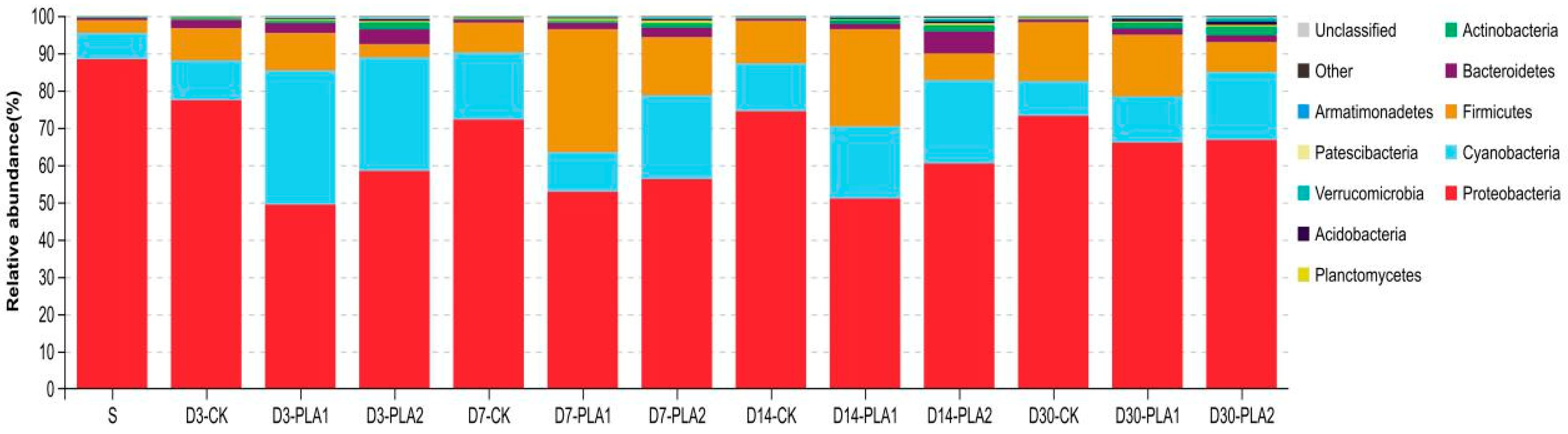
The relative abundance of bacterial community in stylo silage on the phylum level is illustrated in Figure 2. In fresh stylo and stylo silage, Proteobacteria (88.35%; 52.80–77.36%) was the most dominant phylum, followed by Firmicutes (3.41%; 3.53–32.96%), Cyanobacteria (7.00%; 9.33–35.91%) and Bacteroidetes (0.67%; 0.69–5.89%). In comparison, the abundance of Proteobacteria in stylo declined while that of Firmicutes, Cyanobacteria, Bacteroidetes and Actinobacteria increased after fermentation. Meanwhile, PLA addition (1% or 2%) led to the decrease of Proteobacteria abundance and the increase in Actinobacteria abundance. The addition of 1% PLA consistently resulted in the increase of Firmicutes abundance while the addition of 2% PLA consistently resulted in the increase of Cyanobacteria abundance.
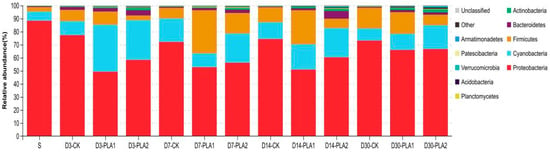
Figure 2.
Relative abundance of bacterial community on phylum level in stylo silage ensiled with addition of phenyllactic acid (S: fresh stylo; CK: blank control; PLA1 and PLA2: 1% or 2% phenyllactic acid addition).
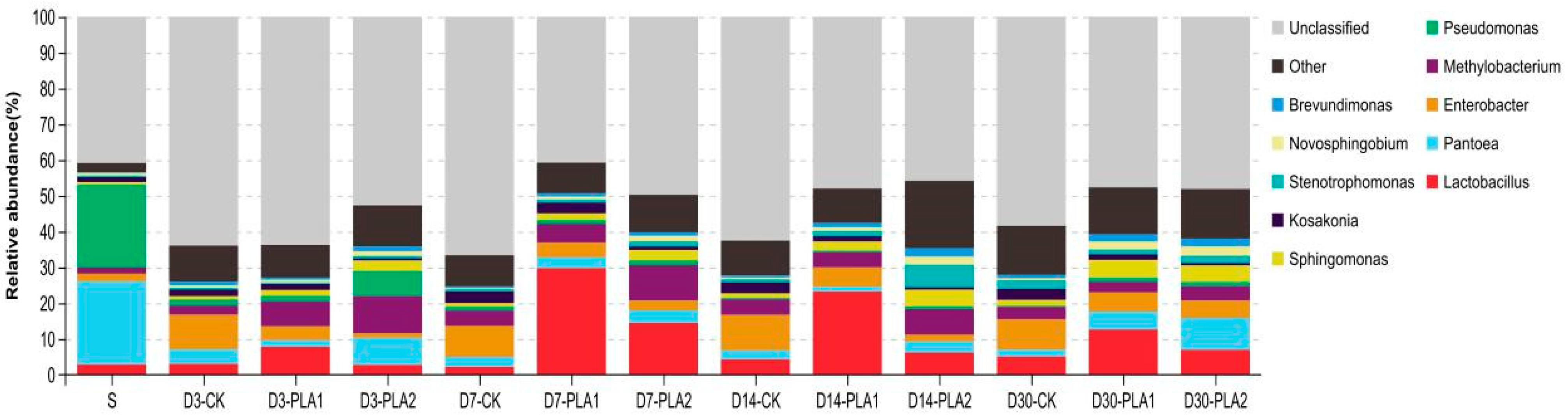
On the genus level, unclassified genus accounted for 40.88% of the bacterial community in fresh stylo, and the dominant classified genera were Pantoea (23.25%) and Pseudomonas (23.13%; Figure 3). As for the stylo silage, there was also 40.74–66.61% unclassified genus, and several genera coexisted in the silage, but the dominant genera were various in different treatment groups. Specifically, Enterobacter (8.48–9.90%) was the most abundant genus in the control silage, followed by Lactobacillus (2.20–5.10%), Pantoea (1.89–4.04%), Methylobacterium (2.55–4.23%) and Kosakonia (1.87–3.30%) across the ensiling fermentation. In comparison, Lactobacillus (7.85–29.79%) was the dominant genus in the stylo silage with 1% PLA addition, followed by Enterobacter (3.90–5.46%), Methylobacterium (2.98–6.91%), Pantoea (1.29–5.01%), Sphingomonas (1.67–4.91%) and Kosakonia (1.49–3.06%). The dominant genus of stylo silage ensiled with 2% PLA varied over the ensiling process, where the silages were mainly dominated by the growth of Methylobacterium (4.02–10.40%), Pantoea (3.10–8.94%), Sphingomonas (2.94–4.68%), Lactobacillus (2.76–14.47%), Enterobacter (1.23–4.80%).
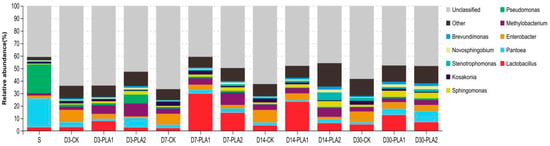
Figure 3.
Relative abundance of bacterial community on genus level in stylo silage ensiled with addition of phenyllactic acid (S: fresh stylo; CK: blank control; PLA1 and PLA2: 1% or 2% phenyllactic acid addition).
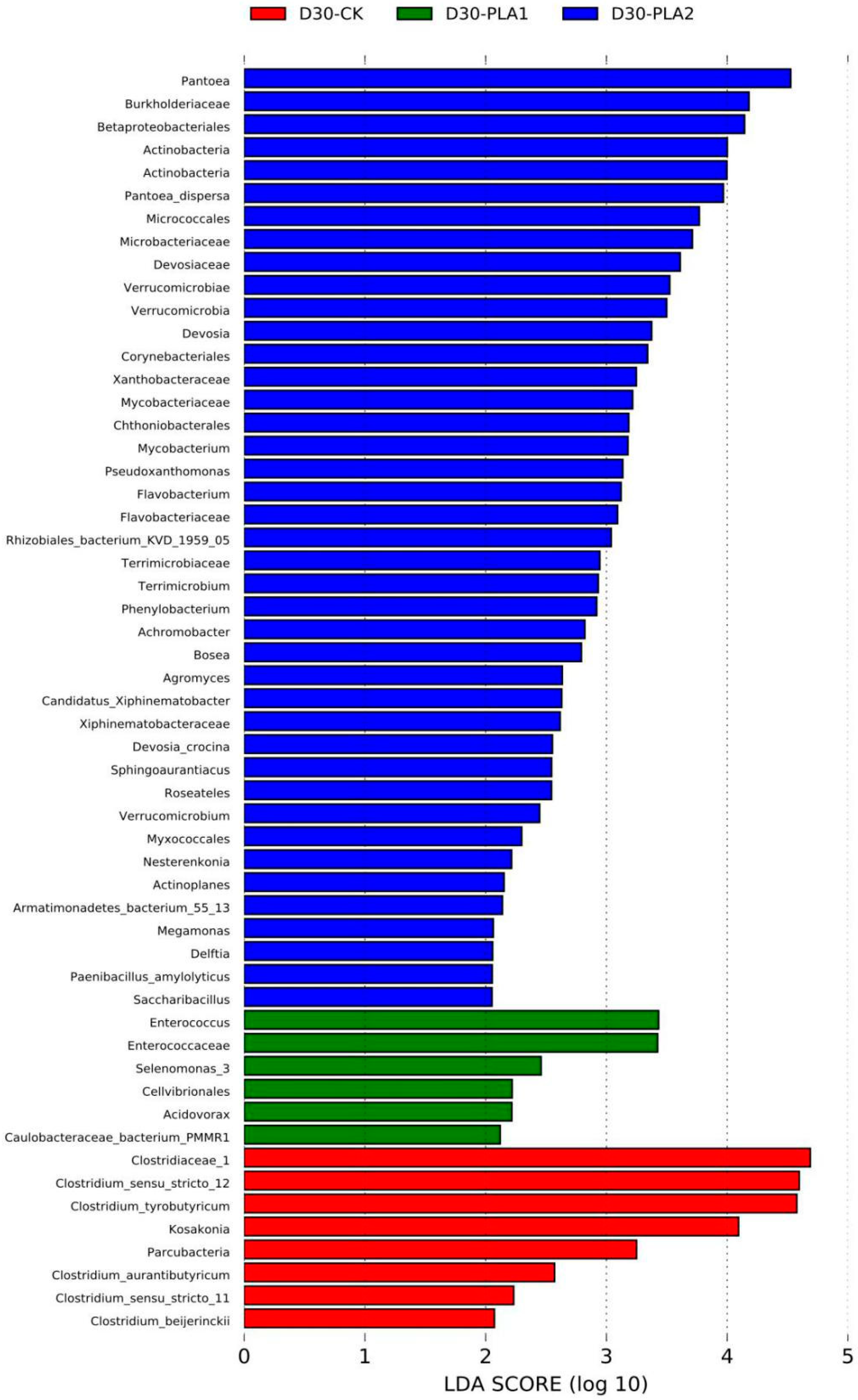
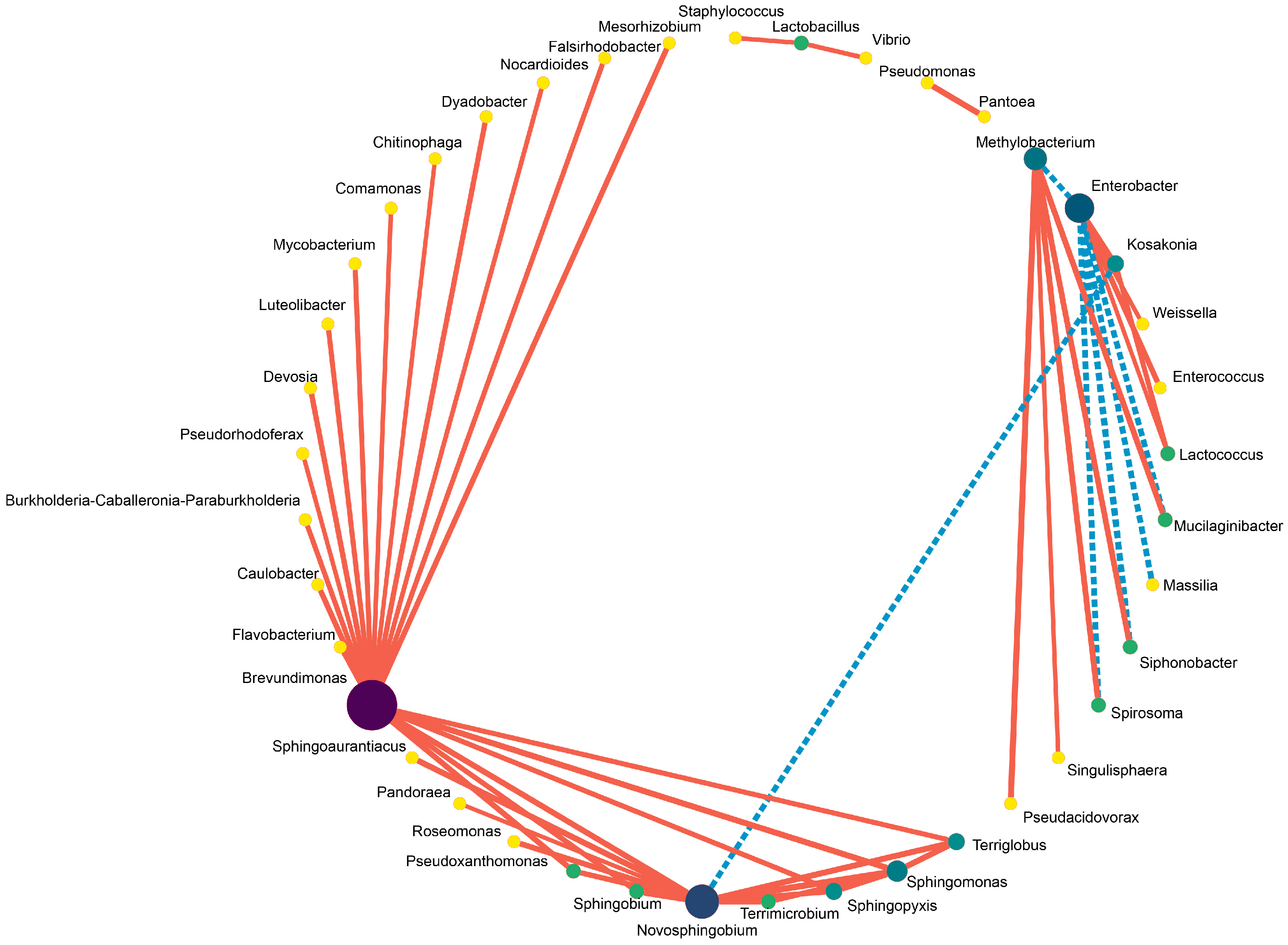
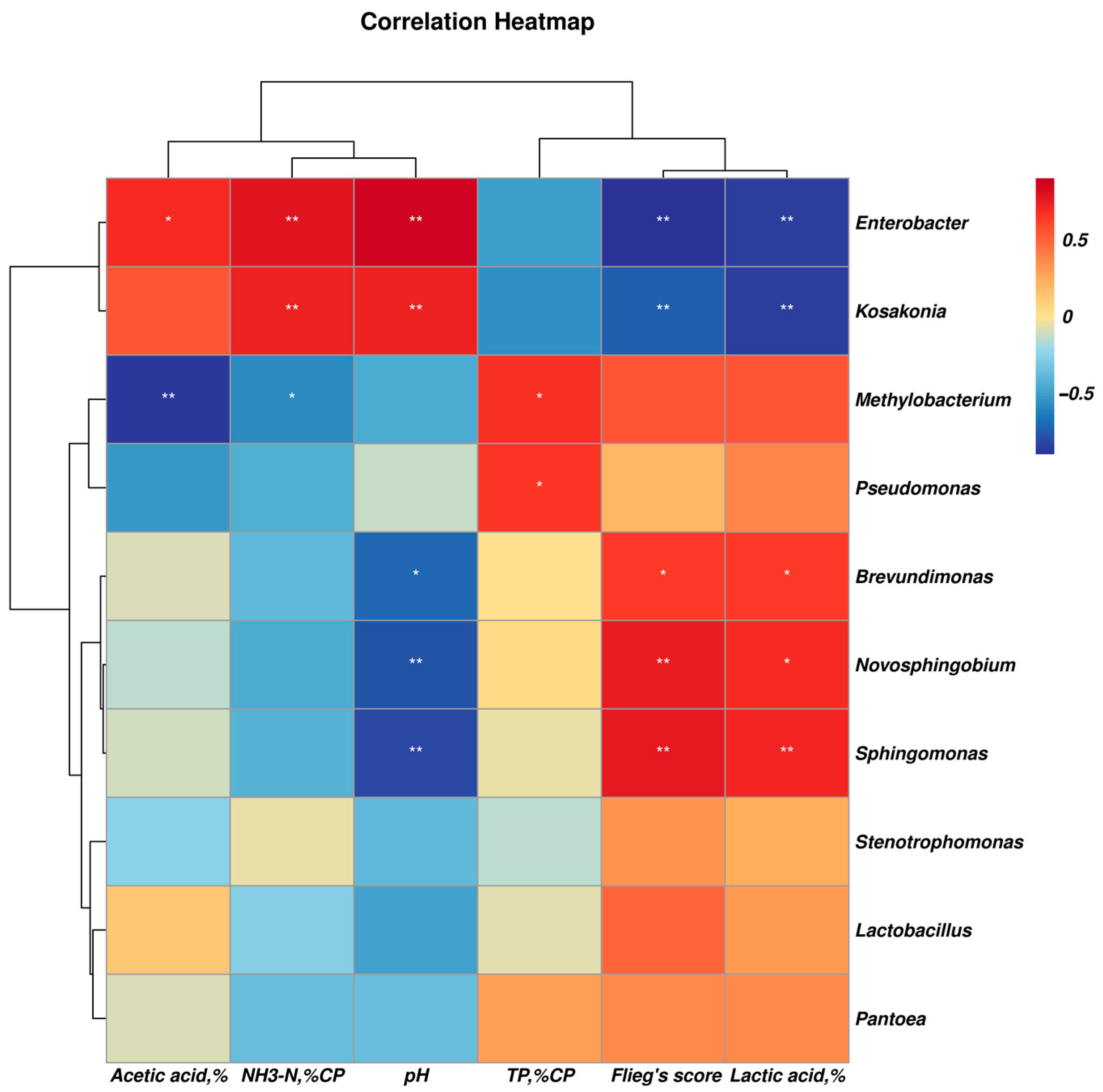
In comparison, the abundance of Clostridiaceae_1, Clostridium_sensu_stricto_12, Clostridium_tyrobutyricum, Clostridium_aurantibutyricum, Kosakonia, Parcubacteria, Clostridium_sensu_stricto_11 and Clostridium_beijerinckii was higher in the control silage relative to that of PLA-treated silages after 30 days of ensiling. The abundance of Enterococcus, Enterococcaceae, Selenomonas_3, Cellvibrionales, Acidovorax and Caulobacteraceae_bacterium_PMMR1 was relatively higher in 1% PLA-treated silages while there were tens of bacterial taxon higher in abundance found in 2% PLA-treated silages, such as Pantoea, Actinobacteria, Verrucomicrobia, Mycobacterium, Flavobacterium, Terrimicrobium (Figure 4). The co-occurrence network (Figure 5) revealed that Brevundimonas, Novosphingobium, Enterobacter and Methylobacterium were the top four genera in average abundance in the stylo silage, and they showed close interaction relationship with other genera. Kosakonia, Terriglobus, Sphingomonas and Sphingopyxis also had an important role in the interaction network. Furthermore, correlation heatmap (Figure 6) showed that the relative abundance of Enterobacter and Kosakonia was positively related to silage pH value (p < 0.01), ammonia-N proportion (p < 0.01) and acetic acid concentration (p < 0.05) and negatively related (p < 0.01) to silage lactic acid concentration and Flieg’s score, while the abundance of Brevundimonas (p < 0.05), Novosphingobium (p < 0.01) and Sphingomonas (p < 0.01) was negatively related to silage pH value and positively related to silage lactic acid concentration and Flieg’s score. Moreover, the abundance of Methylobacterium was negatively related to silage ammonia-N proportion (p < 0.05) and acetic acid concentration (p < 0.01), and silage true protein proportion positively correlated (p < 0.05) with the abundance of Methylobacterium and Pseudomonas.
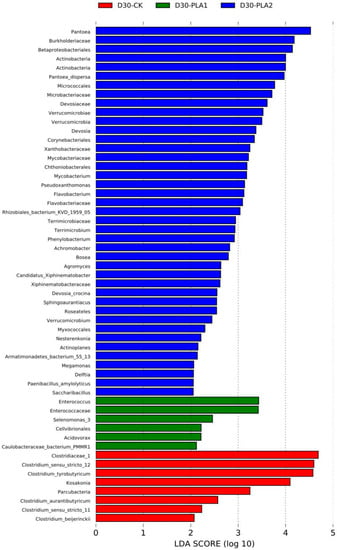
Figure 4.
Comparison of microbial variations in stylo silage ensiled with addition of phenyllactic acid using the LEfSe method (S: fresh stylo; CK: blank control; PLA1 and PLA2: 1% or 2% phenyllactic acid addition).
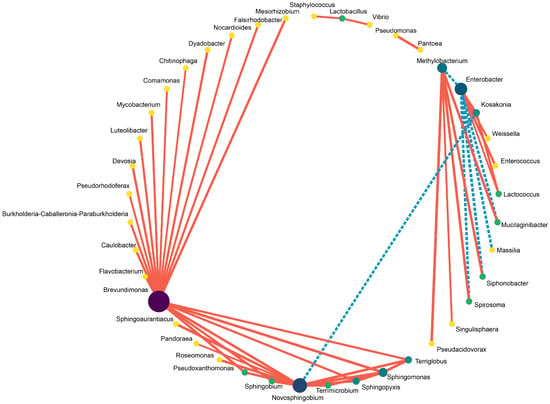
Figure 5.
Co-occurrence network of the main bacteria in stylo silage ensiled with addition of phenyllactic acid (The color of the dots represents the importance of the species, and the size of the dots represents the average abundance of the species. The solid red line indicates a positive correlation, and the dotted blue line denotes a negative correlation).
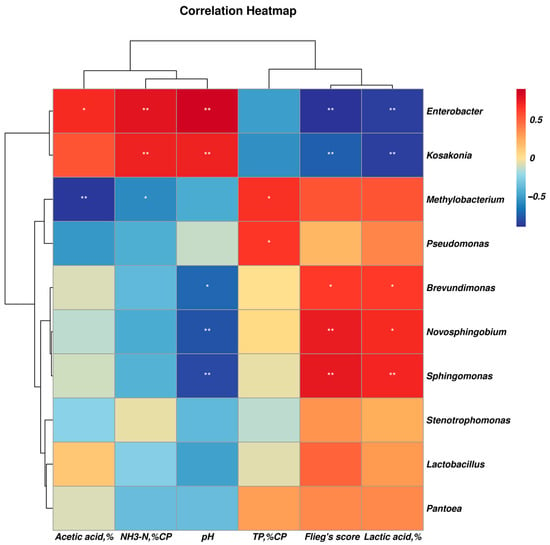
Figure 6.
Correlation heatmap of the main bacterial genera and silage characteristics (“*” denotes significant at the level of p < 0.05, and “**” denotes significant at the level of p < 0.01).
4. Discussion
4.1. General Characteristics of Fresh Stylo Used for Silage Production
Stylo is a common leguminous forage in tropical and subtropical areas, being a quality protein source for ruminants. In the present study, its protein content (13.35% DM) was somewhat low but would also meet the dietary protein concentration requirement for most grazing or feedlot beef cattle or sheep [25,26]. Meanwhile, its lignocellulose content is not too high, acting as an important source of dietary effective fiber. In general, true protein is higher in utilization efficiency for ruminants relative to nonprotein-N, especially nitrate-N or ammonia-N [27]. Thus, stylo is supposed to be a quality protein source in consideration of its true protein proportion of 82.13% CP, and much has been done to prevent its proteolysis during ensiling process. In principle, ensiling is a popular method to preserve moist forage via the anaerobic metabolism of LAB converting WSC into organic acids whereby lowering silage pH to inhibit the activity of spoilage organisms [27]. Epiphytic bacterial community, moisture content and WSC concentration might be the most important factors for silage fermentation. As reported, 5.0 log10 CFU/g FM and 60–70 g/kg DM are separately regarded as the thresholds of initial LAB population and WSC content at ensiling to produce quality silage [28,29], and the moisture content of high-quality silage is commonly in the range of 65–70% [30]. In the present study, epiphytic LAB population in the fresh stylo (6.05 log10 CFU/g FM) might be high enough, but the high population of coliform bacteria would compete for fermentation substrate [31]. Even worse, WSC content of fresh stylo (1.54% DM) was far behind the theoretical requirement, and the moisture content was too high, likely resulting in a high risk of large seepage losses, vigorous clostridial proliferation and slow pH decline.
4.2. Effect of Phenyllactic Acid on Dynamic Fermentation Characteristics of Stylo Silage
During the ensiling process, dry matter loss is mainly ascribed to the respiration of plant cell and the activities of aerobic or anaerobic microorganisms at the early stage. The addition of PLA at ensiling linearly reduced the DM loss of stylo silage. It might be owed to the antimicrobial activity of PLA likely altering bacterial community and metabolism [2,17]. With regard to fermentation parameters, silage pH is mainly dictated by the generation of lactate and the intrinsic buffering capacity of raw material, and pH 4.30–5.00 is acceptable for legume silage due to its low sugar content and high buffering capacity [32]. The application of PLA at ensiling resulted in the decline in silage pH value to an acceptable range (4.32–4.92). Moreover, it also led to the decrease in LAB and coliform bacteria population, especially when PLA was added at the level of 2%. In general, LAB actively grow under the pH values of 4.50–7.50 [33], and most undesirable bacteria in silage are usually inhibited at pH < 4.50 [34]. Thus, the present results could be interpreted as the acidity property and antimicrobial activity of PLA, and the resulting low pH condition inhibited the activity of silage microorganism, including LAB and undesirable organisms. Furthermore, the LAB number was not larger in PLA-treated silage relative to that in the control silage, but its lactic acid concentration was much higher. It might be due to the generated lactic acid further converting into acetic acid and butyric acid in the control silage [27], consequently resulting in less efficiency in pH decline and nutrient preservation. Additionally, the high butyric acid concentration (0.76% DM) of the control silage is undesired in that dietary butyric acid >0.5% DM might lead to reduced feed intake and other metabolic diseases in livestock feeding [35]. Overall, based on the discrimination of aggregative indicator Flieg’s score, integrating the data of silage DM content and pH value [23], the control silage was identified as poor quality, and 1% or 2% PLA-treated silage fell into the grade of good quality or very good quality. It is suggested that PLA addition at ensiling could improve the fermentation quality of high moisture stylo silage with dose effect.
4.3. Effect of Phenyllactic Acid on Dynamic Nitrogen Distribution of Stylo Silage
Generally speaking, dynamic changes of nonprotein-N and ammonia-N concentrations are commonly used to monitor the extent of proteolysis in silage. In the present study, almost half of protein in stylo was hydrolyzed during ensiling fermentation, and PLA addition could remarkably increase true protein proportion and decrease the proportion of ammonia-N in the mature silage. Considering that nonprotein-N, especially ammonia-N, is inferior in nitrogen retention relative to true protein for ruminant metabolism [36], the application of PLA at ensiling would improve the nutritional value of stylo silage, potentially with a better nitrogen utilization efficiency. Moreover, it is documented that a high ammonia-N concentration in silage likely has a negative effect on animal feed intake [32], where its recommended proportion is no more that 10% CP, better lower than 5% CP in mature silage [37]. During the ensiling process, plant protein is first hydrolyzed by plant proteases whereby generating free amino acids and peptides (collectively termed nonprotein-N), which are further degraded into ammonia, amines and ketonic acids by the deamination of microbial activity of undesirable bacteria such as Clostridium and Enterobacter [32]. Thus, PLA addition at ensiling not only lowered the protease activity but also inhibited microbial deamination activity. It might be interpreted that the low pH condition resulting from PLA addition would lower the activity of plant proteases, indicated by the higher true protein proportion. Meanwhile, the antimicrobial activity of PLA contributed to the alteration in bacterial community and, consequently, inhibiting microbial deamination activity, indicated by the lower ammonia-N proportion. To sum up, PLA addition at the level of 1% or 2% at ensiling would improve protein preservation in stylo silage.
4.4. Effect of Phenyllactic Acid on Dynamic Bacterial Community of Stylo Silage
As ensiling is a process of microbial competition, fermentation parameters and nutrient preservation status comprehensively reflect the result of silage fermentation. Making clear the succession of bacterial community would throw light on the variation mechanism of silage quality and its regulation [3]. Nowadays, 16S rDNA sequencing technology has become a common method to investigate bacterial community, such as microbial identification and community diversity. In the present study, Goods_coverage over 0.99 assured a good representativeness of sequencing data for the bacterial community in the stylo samples. The decline of alpha diversity indices Sobs, Chao and Ace in the prolonged silage suggests that the richness of bacterial community in stylo silage decreases as ensiling time is prolonged, especially 7 days later. It is inferred that the proliferation of kinds of microorganisms in stylo silage would be gradually inhibited by 3–7 days of ensiling fermentation. The increase of Shannon and Simpson indices suggests that the diversity of bacterial community in stylo silage increases as ensiling fermentation goes on. As Shannon and Simpson indices are affected by species richness and community evenness, the greater uniformity of each species should primarily account for the greater diversity of bacterial community in the stylo silage 7 days later [38]. As for the treatment effect, PLA addition increased the richness and diversity of the bacterial community in the stylo silage relative to the control silage, suggesting that PLA addition altered the succession of bacterial community in the stylo silage.
As illustrated by PCoA analysis, samples of fresh stylo, CK group and PLA groups were separately clustered in different quadrants regardless of sampling time. Moreover, the samples of CK group at different timepoints clustered closely in a narrow range while those of PLA groups varied in a wider range, especially for 2% PLA addition. It is suggested that bacterial community of stylo remarkably changes after ensiling fermentation, and the succession process of bacterial community in stylo silage is changed by the addition of PLA at ensiling, where bacterial community in the control silage does not experience much variation while that in the PLA-treated groups changes apparently as ensiling is prolonged. However, the overlap of the samples at different timepoints suggests that the succession of bacterial community is likely not remarkable enough during ensiling process.
In detail, Proteobacteria was the most dominant phylum both in fresh stylo and all the stylo silages, followed by Firmicutes, Cyanobacteria and Bacteroidetes, but their corresponding abundance was apparently different. Consistently, Ogunade et al. [39] drew a conclusion in a literature review that the majority of bacterial community in silage belonged to the phylum Firmicutes and Proteobacteria. The abundance of Proteobacteria declined while that of Firmicutes, Cyanobacteria, Bacteroidetes and Actinobacteria increased after fermentation. Inconsistently, our previous studies showed that Cyanobacteria dominated in fresh stylo and then was substituted by Proteobacteria and Firmicutes in stylo silage [4,40]. Such a discrepancy among studies might be due to the differences of stylo in growing condition and agronomic management, generating different epiphytic bacterial communities [41]. Relative to the control silage, PLA-treated silages were lower in Proteobacteria abundance and higher in Actinobacteria abundance. The decline of Proteobacteria abundance might be attributed to the low pH condition as Proteobacteria generally prefer the neutral environment [42]. It was reported that the abundance of Proteobacteria was positively correlated with ammonia-N content in soil or wastewater fermentation [43,44]. It is inferred that the improvement of protein preservation might somewhat correlate with the alteration of Proteobacteria. Moreover, the addition of 1% PLA consistently increased Firmicutes abundance while the addition of 2% PLA increased Cyanobacteria abundance. It is suggested that the individual abundance of some dominant phyla does change with the effect of PLA addition.
Furthermore, analysis of bacterial community on genus level also shows apparent difference. The identification ability of 16S rDNA V3-V4 sequencing was quite low in the present study in that almost half of bacterial genera were unclassified either in fresh stylo or stylo silage. It is indicated that more advanced technologies such as Helicos SMS, Pacific Bioscience SMRT sequencing or nanopore sequencing are needed to further make clear the bacterial community on genus level or specie level. As illustrated by histogram, bacterial community on genus level was quite different between fresh stylo and stylo silage, or among the different silage treatments. The dominant classified genera in fresh stylo were Pantoea and Pseudomonas while several genera such as Enterobacter, Lactobacillus, Pantoea, Methylobacterium, Sphingomonas and Kosakonia coexisted in stylo silage without a bacterial genus with overwhelming abundance, and the dominant genera differed in silage groups. It is inferred that LAB fail to establish dominance in the bacterial community of stylo silage, consequently resulting in poor fermentation quality. In comparison, Enterobacter was the most abundant genus in the control silage, followed by Lactobacillus, Pantoea, Methylobacterium and Kosakonia across the ensiling process. Lactobacillus was the dominant genus in 1% PLA-treated stylo silage, followed by Enterobacter, Methylobacterium, Pantoea, Sphingomonas and Kosakonia. The dominant genus of stylo silage ensiled with 2% PLA included Methylobacterium, Pantoea, Sphingomonas, Lactobacillus and Enterobacter.
Pantoea and Kosakonia are two new genera recently divided from the genus Enterobacter [45]. Generally, rapid suppression of enterobacteria is desired in silage production in the view that they would compete with LAB flora for nutrients and produce ammonia-N, acetic acid or butyric acid, even though nitrite and nitric oxide deriving from the reduction of NO3− by enterobacteria would potentially exert selective inhibition of clostridial growth [31]. As well, clostridia are undesirable bacteria in silage in consideration that they usually derive their energy from the fermentation of organic compounds such as carbohydrates and proteins. The most common clostridia in silage can be divided into three phenotypically relevant groups: proteolytic clostridia, Clostridium butyricum and Clostridium tyrobutyricum [31]. It is documented that feeding animals with the silage strong in clostridial activity likely results in the decrease in feed intake or the occurrence of ketosis [35]. Enterobacter and Clostridium are undesirable bacteria in silage fermentation, and their primary fermentation product is not lactic acid but acetic acid or butyric acid, where such a metabolic pathway is less efficient in pH decline and energy conversion [27]. Therefore, the dominance of these undesirable bacteria should be responsible for the poor fermentation quality of stylo silage. On the other hand, the LAB commonly found in silage such as Lactobacillus, Lactococcus, Enterococcus and Weissella failed to dominate the bacterial community in the stylo silage in view of their low abundance. In comparison, the lower abundance of Enterobacter and Clostridium as well as the higher abundance of Lactobacillus, Enterococcus and Pantoea would partly account for the improvement of silage quality in the PLA-treated groups, especially in the 1% PLA-treated group. Ogunade et al. [39] reported that Pantoea abundance is negatively related to silage ammonia-N concentrations, and the increased abundance of Pantoea would contribute to the decrease of ammonia-N concentration in silage.
Methylobacterium are obligately aerobic and facultative methylotrophic bacteria commonly found in soil and on surfaces of leaves and other plant parts [46]. Its abundance in stylo silage was increased by the addition of PLA, in line with the results of ensiling stylo with addition of gallic or vallic acid [4,5]. It might be due to the action of these silage additives as methy-donors to promote the proliferation of Methylobacterium bacteria. As well, Sphingomonas are Gram-negative aerobic Alpha-proteobacteria with an extensive metabolic capacity for aromatic compounds [47]. Their increased abundance in the PLA-treated silage might be due to the promotion of metabolic substrate. Meanwhile, Sphingomonas are reported to be common in agricultural byproduct silage and likely cause hydrolysis of soluble protein [48]. Thus, their increased abundance in silage might not be desired, but their exact roles in silage fermentation or other applications still need further research. Consistently, co-occurrence analysis revealed that Brevundimonas, Novosphingobium, Enterobacter and Methylobacterium were the most in average abundance and had close interaction relationship with other genera, suggesting that they played core roles in the succession and development of bacterial community in stylo silage. Kosakonia, Terriglobus, Sphingomonas and Sphingopyxis also had an important role in the interaction network. Correlation analysis revealed that the decrease in Enterobacter and Kosakonia as well as the increase in Brevundimonas, Novosphingobium, Sphingomonas and Methylobacterium would contribute to the improvement of silage fermentation quality and protein preservation. It is indicated that some additives or management methods aiming at the modification of these bacteria would help to improve silage quality.
5. Conclusions
The results of this study showed that DM loss, coliform bacteria population, pH value, butyric acid and ammonia-N concentration of stylo silage were decreased while lactic acid concentration, Flieg’s score and true protein proportion were increased by PLA application at ensiling time. Bacterial diversity increased in the silage, where the relative abundance of Enterobacter, Clostridium and Kosakonia decreased, and that of Lactobacillus, Enterococcus and Pantoea increased. To sum up, PLA application at the level of 1–2% could improve fermentation quality and protein preservation of stylo silage in short-term fermentation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.D. and L.H.; methodology, C.D., P.L. and X.W.; validation, L.H. and W.Z.; formal analysis, C.D. and P.L.; investigation, C.D., P.L. and X.W.; writing—original draft preparation, C.D.; writing—review and editing, C.D. and L.H.; visualization, X.W. and L.H.; supervision, L.H. and W.Z.; project administration, L.H.; funding acquisition, L.H. and W.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work received the financial support from Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 323QN260), Agricultural Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-39) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 32102562).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are openly available in the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) with the reference number [PRJNA 736346].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- HeuHeuzé, V.; Tran, G.; Boudon, A.; Labussière, E.; Bastianelli, D.; Lebas, F. Stylo (Stylosanthes guianensis). Feedipedia, a Programme by INRAE, CIRAD, AFZ and FAO. 2017. Available online: https://www.feedipedia.org/node/251 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Rajanikar, R.V.N.B. Phenyllactic acid: A green compound for food biopreservation. Food Control 2021, 128, 108184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Lv, H.; Xing, Y.; Wang, C.; You, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. The nutrients in Moringa oleifera leaf contribute to the improvement of stylo and alfalfa silage: Fermentation, nutrition and bacterial community. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Li, S.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Effects of vanillic acid on dynamic fermentation parameter, nitrogen distribution, bacterial community, and enzymatic hydrolysis of stylo silage. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 690801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Chen, N.; Lv, H.; Wang, C.; Zhou, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Gallic acid influencing fermentation quality, nitrogen distribution and bacterial community of high-moisture mulberry leaves and stylo silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 295, 122255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Li, Z.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X. Interactive effect of inoculant and dried jujube powder on the fermentation quality and nitrogen fraction of alfalfa silage. Anim. Sci. J. 2017, 88, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xie, Y.; Yu, Z.; Meng, G.; Wu, Z. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum expressing multifunctional glycoside hydrolases on the characteristics of alfalfa silage. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 19, 7983–7995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, L.; Xing, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, W.; Pian, R.; Yang, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Dynamics of bacterial community and Dynamics of bacterial community and fermentation quality during ensiling of wilted and unwilted Moringa oleifera leaf silage with or without lactic acid bacterial inoculants. Msphere 2019, 4, e00341-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, D.; Dong, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, B.; Shi, P.; Yan, J.; Zhuang, D.; Shao, T.; Wang, W.; Gu, M. Evaluating the fermentation quality and bacterial community of high-moisture whole-plant quinoa silage ensiled with different additives. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 3578–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, M.; Ilma, T.; Arto, H.; Marketta, R. Fermentation quality and bacterial ecology of red clover dominated silage modulated by different management factors. Front. Anim. Sci. 2022, 3, 1080535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J. Effects of different additives on fermentation quality, microbial communities, and rumen degradation of alfalfa silage. Fermentation 2022, 8, 660–669. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Xu, S.; Yun, Y.; Jia, T.; Yu, Z. Effect of 3-phenyllactic acid and 3-phenyllactic acid-producing lactic acid bacteria on the characteristics of alfalfa silage. Agriculture 2019, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieuleveux, V.; Lemarinier, S.; Guéguen, M. Antimicrobial spectrum and target site of D-3-phenyllactic acid. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1998, 40, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, W.; Yu, S.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, B. Recent research on 3-phenyllactic acid, a broad-spectrum antimicrobial compound. Appl. Microbiol. Biotech. 2012, 95, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prema, P.; Smila, D.; Palavesam, A.; Immanuel, G. Production and characterization of an antifungal compound (3-phenyllactic acid) produced by Lactobacillus plantarum strain. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2010, 3, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanina, B.A.; Graciela, F.; Luciana, G.C. Optimization of phenyllactic acid production by Pediococcus acidilactici CRL 1753. Application of the formulated bio-preserver culture in bread. Biol. Control 2018, 123, 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Chen, L.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, Q.; Chen, C. Effects of phenyllactic acid, lactic acid bacteria, and their mixture on fermentation characteristics and microbial community composition of timothy silage. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 743433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderick, G.A.; Kang, J.H. Automated simultaneous determination of ammonia and total amino acids in ruminal fluid and in vitro media. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Effect of applying lactic acid bacteria and cellulase on the fermentation quality, nutritive value, tannins profile and in vitro digestibility of Neolamarckia cadamba leaves silage. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 102, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licitra, G.; Hernandez, T.M.; Van Soest, P.J. Standardization of procedures for nitrogen fractionation of ruminant feeds. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1996, 57, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOA. Determination of soluble sugar in fruits and derived products—3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid colorimetry. In Agricultural Industry Standard of PRC NY/T 2742-2015; The Ministry of Agriculture: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Flieg, O. A key for the evaluation of silage samples. Futterb. Garfutterber. 1938, 1, 112–128. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; He, L.; Xing, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yang, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Fermentation quality and microbial community of alfalfa and stylo silage mixed with Moringa oleifera leaves. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 284, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NASEM. Nutrient Requirements of Beef Cattle: Eighth Revised Edition. In National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- NRC. Nutrient Requirements of Small Ruminants: Sheep, Goats, Cervids, and New World Camelids; National Academy of Science: Washintgton, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mcdonald, P.; Henderson, A.R.; Heron, S.J.E. The Biochemistry of Silage; Chalcombe Publications: Southampton, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; Bolsen, K.K.; Brent, B.E.; Hart, R.A.; Dickerson, J.T.; Feyerherm, A.M.; Aimutis, W.R. Epiphytic microflora on alfalfa and whole-plant corn. J. Dairy Sci. 1992, 75, 2484–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.H. Theoretical carbohydrate requirement for alfalfa silage production. Agron. J. 1962, 54, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyader, J.; Baron, V.; Beauchemin, K. Corn forage yield and quality for silage in short growing season areas of the Canadian prairies. Agronomy 2018, 8, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlow, G.; Muck, R.E.; Driehuis, F.; Elferink, S.J.W.H.; Spoelstra, S.F. Microbiology of Ensiling. In Silage Science and Technology; Buxton, D.R., Muck, R.E., Harrison, J.H., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA; Crop Science Society of America, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA; Soil Science Society of America, Inc. Publications: Madison, WI, USA, 2003; pp. 31–93. [Google Scholar]
- Kung, L.; Shaver, R.D.; Grant, R.J.; Schmidt, R.J. Silage review: Interpretation of chemical, microbial, and organoleptic components of silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4020–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutkins, R.W.; Nannen, N.L. pH Homeostasis in Lactic Acid Bacteria 1. J. Dairy Sci. 1993, 76, 2354–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, L.; Stokes, M.R.; Lin, C.J. Silage Additives. Silage Sci. Technol. 2003, 42, 305–360. [Google Scholar]
- Muck, R. Silage Microbiology and Its Control through Additives. Revista Brasileira Zootecnia 2010, 39, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabacco, E.; Borreani, G.; Crovetto, G.M.; Galassi, G.; Colombo, D.; Cavallarin, L. Effect of chestnut tannin on fermentation quality, proteolysis, and protein rumen degradability of alfalfa silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 4736–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N.; Li, S.; Zhao, S.; Wen, F.; Wang, J. Progress assessment of chemical indicators of silage. Chin. J. Anim. Husb. 2016, 52, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Grice, E.A.; Kong, H.H.; Conlan, S.; Deming, C.B.; Davis, J.; Young, A.C.; Segre, J.A. Topographical and temporal diversity of the human skin microbiome. Science 2009, 324, 1190–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunade, I.M.; Jiang, Y.; Cervantes, A.P.; Kim, D.H.; Oliveira, A.S.; Vyas, D.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Jeong, K.C.; Adesogan, A.T. Bacterial diversity and composition of alfalfa silage as analyzed by Illumina MiSeq sequencing: Effects of Escherichia coli O157: H7 and silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 2048–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Qiu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; He, L. Effect of tea polyphenols on the fermentation quality, protein preservation, antioxidant capacity and bacterial community of stylo silage. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 993750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, H.; Yan, Y.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Shuai, Y.; Feng, G.; Ran, Q.; Cai, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Microbial communities and natural fermentation of corn silages prepared with farm bunker-silo in Southwest China. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, D.J.; Krieg, N.R.; Staley, J.T. The proteobacteria, volume two, part B, the gammaproteo bacteria. In Berge’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd ed.; Garrity, G.M., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 382–400. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, J. Myriophyllum elatinoides growth and rhizosphere bacterial community structure under different nitrogen concentrations in swine wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, W.; Ni, Z.; Hashidoko, Y.; Shen, W. Ammonium nitrogen content is a dominant predictor of bacterial community composition in an acidic forest soil with exogenous nitrogen enrichment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Classification of Bacteria of the Genus Kosakonia Based on Genome-Wide Sequence Systems. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Doronina, N.V.; Trotsenko, Y.A.; Kuznetsov, B.B.; Tourova, T.P.; Salkinoja-Salonen, M.S. Methylobacterium suomiense sp. nov. and Methylobacterium lusitanum sp. nov., aerobic, pink-pigmented, facultatively methylotrophic bacteria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 773–776. [Google Scholar]
- White, D.C.; Sutton, S.D.; Ringelberg, D.B. The genus Sphingomonas: Physiology and ecology. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 1996, 7, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J.; Shen, Y.; Yang, J. The correlations and spatial characteristics of microbiome and silage quality by reusing of citrus waste in a family-scale bunker silo. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 226, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).