Abstract
Agroforestry is being promoted as a feasible land use management to improve understory economic benefits. However, there are few studies on species selection and the comprehensive evaluation of soil quality change in rhizoma bletillae (Bletilla striata) agroforestry systems. The soil quality index (SQI) and minimum dataset (MDS) methods can reflect the overall condition and were effective tools for understanding different cultivation systems. In this study, we evaluated the soil quality of four cultivation models (including three agroforestry systems: PeB, moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis)–rhizoma bletillae; PoB, plane trees (Platanus orientali)–rhizoma bletillae; CcB, pecan trees (Carya cathayensis)–rhizoma bletillae; and CK, rhizoma bletillae monoculture. The total dataset (TDS) consisted of 15 soil parameters containing physical, chemical, and biological characteristics. The results showed that soil organic carbon (SOC), total nitrogen (TN), and total phosphorus (TP) were finally selected and established as the MDS. Agroforestry could significantly influence soil quality. Compared with CK, the SQI in CcB significantly increased and decreased in PeB and PoB. Soil water content (SWC), nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N), dissolved organic carbon (DOC), SOC, TN, and TP contents were higher in CcB than in the other cultivation models. Based on various soil indicators and SQI analysis, the CcB was the best in improving soil quality. These findings showed that the soil quality index based on the MDS can be used as an effective indicator for agroforestry systems selection. It provides theoretical guidance for the practice of bionic cultivation and the sustainable management of rhizoma bletillae.
1. Introduction
Soil is an essential carrier of material exchange and nutrient cycling in forest ecosystems, providing necessary nutrients and water for plant growth and development [1]. In ecosystems, soil quality refers to the comprehensive capacity of soil to maintain crop productivity, safeguard environmental quality, and promote the health of plants and animals [2,3]. With the increasing emphasis on land quality and service functions, soil quality evaluation has received widespread attention. Soil quality is closely related to many factors, such as land use practices and soil and vegetation types [4,5]. However, soil quality cannot be determined by the evaluation of a single measured parameter. It is generally assessed indirectly on a time or spatial scale by combining diversified soil functional attributes based on different soil characteristics [6]. The Soil Quality Index (SQI) method is one of the most frequently utilized approaches for soil quality assessment [7], which is obtained by integrating different soil property indices. Larson and Pierce [8] conceptualized the minimum dataset, using principal component analysis to filter extensive indicators, effectively reducing redundancy and maximizing the extraction of soil functional information. Nortcliff [9] emphasized the necessity for soil quality indicators to take into account soil functioning and suggested a common set of soil quality indices within the standardized soil quality attributes. Andrews et al. [10] confirmed the high consistency between the total dataset (TDS) and minimum dataset (MDS) in evaluating soil quality.
Agroforestry systems are land use systems and technologies that intentionally integrate woody perennials with other cultivated plants on the same land management unit and manage them at a certain spatial and temporal scale [11,12]. This practice has contributed to the improvement of land utilization and has proved to be an effective land management strategy [13]. It provides a wide range of soil multiple functions for social development and has good ecological and economic benefits. There is increasing evidence that agroforestry systems can enhance soil quality by regulating the carbon- and nitrogen-fixing capacity of soil microorganisms, reducing water loss, and promoting nutrient cycling [14,15]. Lorenz [12] believed that planting high root biomass to above-ground biomass ratio or nitrogen-fixing tree species is conducive to improving carbon sequestration and soil organic carbon (SOC) stability in the agroforestry systems. Suarez [16] compared the soil quality of cacao agroforestry systems with pastures and secondary forests and found that cacao-based agroforestry systems not only maintained the key ecological functions of degraded grassland soil but also restored the soil quality. Compared with monoculture, the input of fresh soil organic matter in agroforestry increased, and the soil had higher microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen, which provided abundant carbon sources for microbial metabolism and thus improved soil fertility conditions [17]. It can be seen that species composition in agroforestry systems has a significant impact on soil function and quality [18]. However, with the extension of practice time, the positive influence of agroforestry on soil multifunction was gradually weakened [11]. There might be a competitive effect between the root systems of trees and understory crops, reducing the availability of soil moisture and nutrients [19]. Tree shading might also lead to lower crop yields [20]. The competition in agroforestry significantly affected both plant growth and productivity, such as the rubber agroforestry system [18]. To mitigate the competitive pressure on plant roots, a variety of approaches have been explored and implemented, including optimizing the planting density between trees and crops, adjusting the spacing between them, and carefully selecting plant species with different root structures and nutritional needs [21,22]. However, most methods are not always effective. Therefore, it is necessary to select the appropriate species collocation and realize the complementary use of resources to form sustainable and highly productive agroforestry systems.
Rhizoma bletillae (Bletilla striata) is a perennial medicinal plant growing in forests, widely distributed in the Yangtze River Basin in China, the Korean Peninsula, and Japan. Its pseudobulbs contain polysaccharides, terpenoids, phenanthrene derivatives, and other chemical components [14]. It has high medicinal and economic value. Due to overexploitation and environmental degradation, the natural growth of rhizoma bletillae has been unable to meet the market demand. Moreover, this species was listed as a second-class protected wild plant in China in 2021. Therefore, understory bionic cultivation is an effective measure to promote the sustainable production of Bletilla pseudobulbs and the sustainable management of forestry because it can take into account the efficient utilization of medicinal plants to achieve the goal of making up for the long with the short. In the southern region of Anhui, China, mechanized agriculture is often not feasible in steep mountainous terrain, which makes it urgent to develop and utilize land-friendly agroforestry systems. The area is dominated by low mountains and hills, is highly compatible with the optimal growing environment for rhizoma bletillae, and provides a unique environmental foundation for bionic cultivation. Current research on the cultivation of rhizoma bletillae has focused on soil nutrient availability, changes in bacterial community composition, and metabolic components [23,24]. Research on soil quality evaluation under the agroforestry systems is relatively scarce. Therefore, here, our major objectives are (1) to develop an SQI for the study district and (2) to evaluate the soil quality of the different agroforestry systems, identifying the best agroforestry practice for the cultivation of rhizoma bletillae.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The experimental area is located in Guangde City, Anhui Province, China (31°01′49″ N, 119°23′37″ E) (Figure 1a). This area is situated in the subtropical humid climate zone, known for its stable climatic characteristics, with a mean annual temperature (MAT) of 15.4 °C. Additionally, the area is blessed with abundant rainfall, boasting mean annual precipitation (MAP) of 1328 mm. The maximum relative humidity is 83%. The soil type is yellowish-red soil, which is classified as Alfisols according to the FAO classification [25], clayey in texture, and weakly acidic. The study area is rich in forest resources, with a forest coverage of 58.4%. In addition, there are large areas of economic plants such as moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis), Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata), and Vernicia fordii.
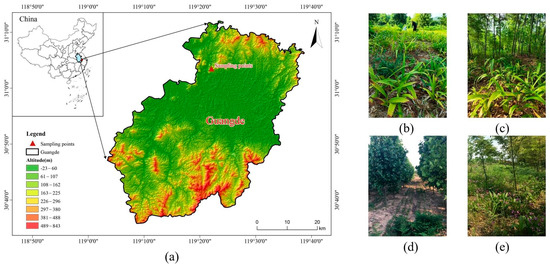
Figure 1.
Location map and sample plots of the study area. (a) is the location map, (b–e) are the sample plots of rhizoma bletillae monoculture, moso bamboo–rhizoma bletillae, plane trees–rhizoma bletillae, and pecan trees–rhizoma bletillae, respectively.
2.2. Experimental Design and Soil Sampling
In the study area, a total of 170 ha of rhizoma bletillae monoculture and agroforestry with the different tree species was established. Before intercropping, the stand density was reduced by thinning, the canopy was 0.5~0.6, and then the forest land reclamation was carried out; the depth was about 30 cm. Then, 22.5 t organic fertilizer was applied per hectare before planting. After planting, weeding was performed 2~3 times in the first three years, and then extensive management, without any additional fertilization and use of pesticides. The 0.5-year-old seedlings of rhizoma bletillae were planted with a spacing of 30 cm × 40 cm in both monoculture and agroforestry systems. In August 2023, the actual surveys were conducted in the experimental area. Rhizoma bletillae monoculture was used as control (CK). The agroforestry systems of moso bamboo–rhizoma bletillae (PeB), plane trees (Platanus orientalis)–rhizoma bletillae (PoB), and pecan trees (Carya cathayensis)–rhizoma bletillae (CcB) were selected for comparative analyses. The cultivation and management practices were consistent across the different systems. Among them, rhizoma bletillae had been planted for three years, and the planting density was about 50,000 plants per hectare. Bamboo forests were natural forests, and plane trees and pecan trees were planted for 7~8 years with 4 m × 5 m spacing. The planting density of rhizoma bletillae in the agroforestry stands were about 40% of that in monoculture. Six replicate plots were set up in size of 20 m × 20 m for each treatment. In each sample plot, three sub-samples were collected from 0 to 20 cm using an “S” shaped mixed sampling method and then mixed into one sample. Samples were transported to the laboratory, where they were passed through a 2 mm sieve to remove impurities like litter, fine roots, and gravel in preparation for the analysis of soil indicators.
2.3. Soil Indicator Measurements
A total of 15 soil indicators were measured and included in TDS according to their applicability in soil quality assessment. The soil water content (SWC) was measured by the drying method (105 °C) to constant weight, about 24 h [26]. Soil pH was determined with a pH meter (FE28-Standard, Mettler Toledo, Zurich, Switzerland) after mixing evenly according to the ratio of deionized water/soil ratio of 2.5:1 [27].
The available nitrogen (NH4+-N and NO3−-N) was extracted with 1 mol·L−1 KCl solution and subsequently quantified by a continuous flow injection analyzer (Futura, Alliance, Paris, France). For dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and nitrogen (DON), a 0.5 mol·L−1 K2SO4 solution was used for extraction, followed by analysis with a TOC/TN analyzer (Multi C/N 3100, Analytik Jena, Jena, Germany). Microbial biomass carbon (MBC) and nitrogen (MBN) were determined by the chloroform fumigation method [28]. SOC and total nitrogen (TN) were measured with an elemental analyzer (EA3000, Leeman, Hudson, USA). Total phosphorus (TP) was determined after high-temperature digestion with a mixture of HNO3 and HClO4 in a 3:1 ratio using a continuous flow injection analyzer (Futura, Alliance, Paris, France). After the same high-temperature digestion, the concentrations of K and Mg were analyzed by atomic absorption spectrophotometer (PinAAcle D900, PerkinElmer, Massachusetts, USA).
Since carbon and nitrogen isotope compositions (δ13C and δ15N) can reflect C and N transformation and decomposition processes within soil ecosystems [29], they are highly influenced by the environment [30]. The abundance of δ13C and δ15N were determined using an isotope ratio mass spectrometer (DeltaV Advantage, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.4. Soil Quality Evaluation Method
In this study, the standard scoring function (SSF) and soil quality index (SQI) method were used for evaluation, consistent with methodologies from prior studies [27,31]. The MDS indicator selection principles are as follows: firstly, factor dimension reduction analysis was conducted on the TDS-selected indicators, retaining principal components (PC) with eigenvalues ≥ 1. Soil indicators with absolute loadings ≥ 0.5 in each PC were divided into one group [32]. Secondly, the Norm values of each group of indicators were calculated, and the indicators with Norm values in the top 10% of each group were selected [32]. Generally, the higher the Norm value of an indicator, the stronger the indicator explains the overall soil quality information. Lastly, when multiple indicators were retained within a single PC, correlation coefficients were further utilized to assess whether these variables were redundantly included in the MDS [27]. The formula for calculating the Norm value is presented below.
where Nik represents the comprehensive loading value of the i-th variable on the k PC corresponding to eigenvalues ≥ 1, Uik represents the loading value of the i-th variable on the k PC, and λk represents the eigenvalue of the k-th PC.
Following the selection of MDS indicators, the next step involved computing soil quality scores by the standard scoring function (SSF) method. Given the differences in the units of measurement of the soil indicators, the data need to be normalized. Each soil indicator was converted and normalized by using the standard scoring function method [33]. Indicators were categorized into “more is better” (Formula (2)) and “less is better” (Formula (3)) types based on the sensitivity of soil quality [33]. According to the impact of different indicators on soil quality and plant growth, the indicators selected in this study were used in Formula (2). Soil pH was weakly acidic in different agroforestry systems. Bletilla striata was suitable for growing in weakly alkaline soil [34]; therefore, pH was used in Formula (2). The formulas were as follows.
where S represents the linear score of the soil indicator, Xi represents the measured value of the soil indicator, and Ximin and Ximax represent the minimum and maximum values of the indicator, respectively.
Finally, the scores and weights of the evaluation indicators were weighted to calculate the soil quality index (SQI). The formula is as follows.
where Wi represents the weight of each evaluation indicator, Si represents the linear score of the evaluation indicator, and n represents the number of evaluation indicators. SQI is between 0 and 1; the closer the index is to 1, the better the soil quality.
2.5. Statistical Analyses
All data analyses were performed using Excel 2019 and SPSS 22.0 [35]. Soil indicators of the different agroforestry systems were analyzed and tested using one-way ANOVA, and the least significant difference (LSD), where p < 0.05 was considered a statistical difference. Correlations between soil indicators were quantified using Spearman coefficients. Principal component analysis (PCA) combined with Norm value was adopted to select the soil indicators to establish the MDS. To verify the degree of soil quality explained by the MDS, a linear method was utilized to fit the relationship between the MDS and TDS. All figures were plotted using Origin 2021 [36].
3. Results
3.1. Soil Characteristics of Different Agroforestry Systems
Agroforestry significantly changed the soil properties (Table 1). Specifically, the SWC was significantly greater in CcB than in CK (p < 0.05). The pH value was 5.84 in PeB, which was markedly higher compared to the other systems (p < 0.05). The contents of NO3−-N, DOC, SOC, TN, and TP were higher in CcB than in other systems (p < 0.05). Compared with CK, the contents of DOC, DON, TP, and K were decreased in PoB, while NO3−-N, DOC, and DON contents were decreased in PeB (p < 0.05). From the perspective of biological indicators, CcB had elevated MBC and MBN contents compared to CK, but these were considerably lower in PeB (p < 0.05). A comprehensive evaluation of these indicators showed that the soil properties were markedly improved in CcB relative to other agroforestry systems and CK.

Table 1.
Statistics of soil quality indicators in different systems (Mean ± SE).
3.2. Indicators Selection for MDS
The PCA revealed that the first three principal components, PC1 (36.80%), PC2 (30.64%), and PC3 (11.89%), together explained 79.34% of the total variance (Table 2). This suggests that these components retain the original variability of the whole dataset and have strong explanations. According to the MDS establishment rule, the high-weight indicators exhibited significant correlations (r > 0.6, Figure 2). PC1 selected TN (2.126) with the highest Norm value as the MDS indicator. Similarly, SOC (Norm value: 2.155) and TP (Norm value: 2.017) were selected as representative indicators by PC2 and PC3, respectively. Ultimately, TN, SOC, and TP, among the soil indicators of different models, constitute the MDS for evaluating soil quality.

Table 2.
Load matrix and Norm value for each indicator.
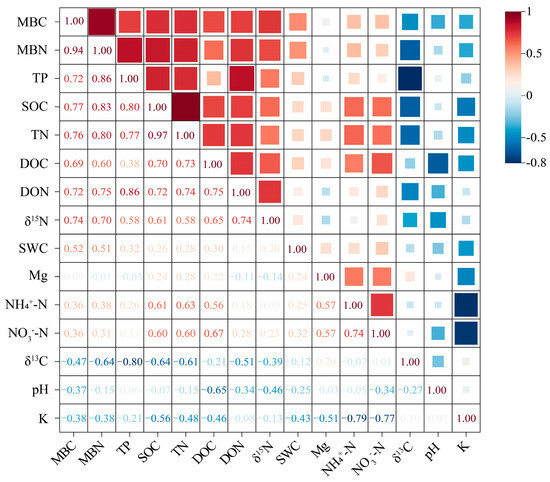
Figure 2.
Correlation coefficients between soil quality evaluation indicators. Significant correlation at r > 0.6.
3.3. Soil Quality Evaluation
The linear fitting of TDS-SQI and MDS-SQI was carried out. The linear fitting coefficient R2 was 0.910 (Figure 3a), showing a very significant positive correlation (p < 0.01). This indicated that the chosen MDS could better reflect the soil quality evaluation information of all dataset indicators under the different systems, and the evaluation results were of high accuracy. The MDS weight values were ranked as follows: SOC (0.355), TN (0.353), and TP (0.292) (Table 3).
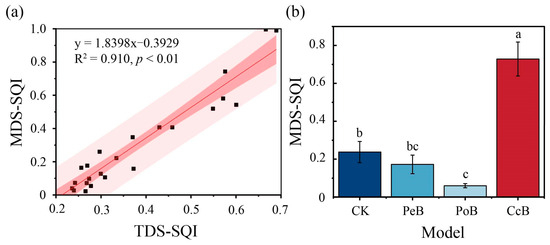
Figure 3.
The linear relationship between TDS-SQI and MDS-SQI (a) and the soil quality index values for different agroforestry systems with rhizoma bletillae (b). Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between systems (p < 0.05). The confidence interval is 95%.

Table 3.
Common-factor variance and weights for TDS and MDS soil indicators.
SQIs of the different agroforestry systems were in the order of CcB (0.728) > CK (0.238) > PeB (0.172) > PoB (0.060) (Figure 3b). Compared with CK, the SQI of PoB and PeB were significantly reduced (p < 0.05), while the SQI of CcB was significantly increased by 206.49% (p < 0.05). The agroforestry system CcB had the highest SQI, which was significantly better than the others. It suggested that CcB can effectively improve soil quality.
4. Discussion
The agroforestry system was superior to the monoculture system in improving the physicochemical properties and soil quality to a certain extent [31,37]. This was influenced by a combination of many factors, such as plant growth, land use practices, and management measures [38,39,40]. This has been verified in multiple agroforestry ecosystems [41,42]. In this study, we found that the contents of SWC, NO3−-N, DOC, SOC, TN, and TP were significantly higher in the agroforestry system of pecan trees–rhizoma bletillae than those in the monoculture system, indicating that there may be a complementary effect in the nutrient utilization process and the interaction between pecan trees and rhizoma bletillae. The changes in light and temperature conditions, the input of high-quality litterfall, and the increase in root exudates in the agroforestry systems favored soil organic matter accumulation and nutrient cycling, improving soil quality [43]. Improving microclimatic conditions and soil fertility can favor the development and growth of microorganism communities. Compared with the monoculture, the MBC and MBN contents in the agroforestry system of pecan trees–rhizoma bletillae increased significantly. This might be attributed to the increased species diversity in agroforestry, which increased soil organic matter and nutrient availability, providing diverse habitats for the growth of soil microorganisms [44]. Soil organic matter content and nutrient availability were positively correlated with soil microbial biomass [45]. This result is consistent with the findings of Ngaba et al.’s [46] meta-analysis, which found that agroforestry significantly increased microbial biomass and enzyme activity across all surveyed climate types. Furthermore, it has been demonstrated in the study that the root systems of trees in agroforestry were more developed and could capture leached C and N from the deep soil layer, which is known as the nutrient pumping effect [47]. This can also explain the increase of nutrient elements in the surface soil layer in the agroforestry system of pecan trees and rhizoma bletillae. The results of a trial conducted on the degraded rangelands in Colombia showed that agroforestry systems increased soil fertility by 42% [16]. Zou et al. [48] found that rubber–Dracaena cochinchinensis and rubber–Camellia sinensis agroforestry systems significantly increased SOC and TN contents. This result reinforces the advantages of agroforestry.
In numerous agroforestry systems, intercropping contributes to the enhancement of soil nutrients [15,49]. However, as the intensity of competition increases, the negative effects of interspecific competition gradually offset this positive impact, causing a sharp decline in soil nutrient concentrations [50]. The competitive influence between trees and understory crops might vary depending on soil moisture, fertilization, tree species, and planting density [51]. In this study, we found that the contents of DOC, DON, MBC, and MBN in the agroforestry systems of moso bamboo–rhizoma bletillae and plane trees–rhizoma bletillae were significantly lower than those in the monoculture. There might be ecological niche overlap between understory crops and trees, which intensified the negative effects of interspecific competition [48,52]. It has been reported that in agroforestry systems, the nutrient acquisition strategies at the tree–crop interface are primarily determined by the root structure [47,53]. The root structure of different species varies considerably [54]. Compared to medicinal crops, the unique root structure and functional traits of trees form the foundation of agroforestry. A previous study has found that agroforestry has an impact on the distribution of species root structure, which explains the interspecific competition effect to a certain extent [55]. Zhang et al. [56] studied the effect of interspecific interaction between jujube trees (Ziziphus jujuba) and cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) on root distribution and morphology, and found that the roots of jujube were more developed and spread under the crop, while the roots of cotton plants were shallower in the soil profile. The longer the distance of cotton roots, the less the impact of jujube trees. In this study, Moso bamboo has well-developed roots, especially its underground rhizome system, which occupies a large space. Additionally, Moso bamboo grows fast with dense standing culms and close canopy; both the above- and below-ground parts may have some inhibitory effects on the growth of rhizoma bletillae. The large leaves and dense canopy of plane trees have a strong shading effect, and its root system is mainly distributed in the topsoil. The root distribution space overlaps with rhizoma bletillae. This spatial distribution pattern in the agroforestry systems increases the competition between the tree and perennial medicinal crops. Strong belowground competition not only affects the aboveground growth but may also cause excessive consumption of soil nutrients and water and result in a decrease in soil quality. For example, Zhang et al. [37] found that the agroforestry of bamboo and rhizoma bletillae significantly reduced the contents of total organic carbon, pH, and available nitrogen of rhizosphere soil. Agroforestry can change soil quality, but the effect varies according to tree species selection.
Assessing soil quality changes induced by management practices is essential for ensuring forest sustainability. Given that plant growth faces various soil factors with different effects, it is crucial to pinpoint and develop a concise set of soil parameters. This approach aims to gather precise information on soil quality conditions more efficiently and cost-effectively. Numerous previous studies have found that the PCA method is an effective tool for screening data information [57,58]. Based on PCA, we set up the MDS. The high consistency between the TDS and MDS further verifies the representativeness and applicability of our indicator screening (Figure 2). Our results showed a high sensitivity for soil quality evaluation using this MDS dataset. Many studies confirmed the effectiveness of the MDS method [59,60]. For example, Guo et al. [61] utilized four commonly used methods to assess soil quality in the lower Yellow River irrigation area. Considering both the precision of assessment and the economic costs associated with soil data acquisition, they found that the MDS method was the most accurate and practical. In addition, we only select SOC, TN, and TP as MDS indicators from 15 parameters. This is mainly because SOC is a representative index reflecting soil fertility and soil quality. Many studies have confirmed that SOC has a significant effect on soil properties and crop growth [12,62]. TN and TP are also essential elements that affect plant growth [63,64,65]. It has been found that the selection frequency of SOC in global soil quality evaluation in the past 30 years, from 1990 to 2019, was 97%. The selection frequency of soil pH, TN, and AP were all above 50%. The occurrence frequency of microbial biomass increased year by year [6]. In our study, microbial biomass changes were most pronounced in agroforestry compared to monoculture. It can be seen that microbial biomass is an early indicator of soil organic matter change. It shows that the indicators we selected are representative. In sum, our results confirm that the MDS method is a useful and practical tool for evaluating and monitoring soil quality because it is flexible and accurate.
5. Conclusions
Among the total of 15 soil indicators analyzed, the most representative indicators of the MDS selected were SOC, TN, and TP. Based on the MDS, the order of SQI in the different cultivation models ranked as pecan trees–rhizoma bletillae agroforestry > rhizoma bletillae monoculture > moso bamboo–rhizoma bletillae agroforestry > plane trees–rhizoma bletillae agroforestry. The two agroforestry systems of moso bamboo–rhizoma bletillae and plane trees–rhizoma bletillae are found to be unfavorable to the improvement of soil quality, while pecan trees–rhizoma bletillae can significantly improve soil quality and is the best agroforestry practice for the bionic cultivation of rhizoma bletillae in the region. Our findings suggest that species selection is important for improving soil quality in agroforestry practices.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.C. and X.X.; methodology, X.C.; software, X.C.; validation, X.C.; formal analysis, X.C.; investigation, X.C., Z.Z., H.D. and A.Z.; resources, X.X.; data curation, X.C.; writing—original draft preparation, X.C.; writing—review and editing, J.W. and X.X.; visualization, X.C.; supervision, X.X.; project administration, X.X.; funding acquisition, X.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFD0600105) and the Key Research and Development Program of Anhui Province (Grant No. 202007d06020010).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- van der Heijden, M.G.A. The unseen majority: Soil microbes as drivers of plant diversity and productivity in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doran, J.W. Soil health and global sustainability: Translating science into practice. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 88, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, R.E.; Upchurch, D.R.; Borlaug, N.E. Quality soil management or soil quality management: Performance versus semantics. Adv. Agron. 2003, 79, 1–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.Q.; Lv, Z.Q.; Liu, G.C. Assessing soil quality for sustainable cropland management based on factor analysis and fuzzy sets: A case study in the Lhasa River Valley, Tibetan Plateau. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.L.; Li, Z.W.; Liu, M.X.; Xu, C.H.; Zhang, R.F.; Luo, W. Effects of vegetation restoration on soil quality in degraded karst landscapes of southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2657–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, W.J.; Wu, L.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, J.D.; Xu, M.G. Advance in indicator screening and methodologies of soil quality evaluation. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2021, 54, 3043–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Medina, C.; Goyes-Vera, F.; Arteaga-Crespo, Y.; Garcia-Quintana, Y.; Changoluisa, D. A soil quality index for seven productive landscapes in the Andean-Amazonian foothills of Ecuador. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 2226–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, W.E.; Pierce, F. Conservation and enhancement of soil quality. In Evaluation for Sustainable Land Management in the Developing World; International Board for Soil Research and Management: Bangkok, Thailand, 1991; pp. 175–203. [Google Scholar]
- Nortcliff, S. Standardisation of soil quality attributes. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 88, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.S.; Mitchell, J.P.; Mancinelli, R.; Karlen, D.L.; Hartz, T.K.; Horwath, W.R.; Pettygrove, G.S.; Scow, K.M.; Munk, D.S. On-farm assessment of soil quality in California’s central valley. Agron. J. 2002, 94, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.F.; Gong, S.S.; Hou, Y.H.; Li, X.N.; Wang, C. The impacts of agroforestry on soil multi-functionality depending on practices and duration. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, K.; Lal, R. Soil organic carbon sequestration in agroforestry systems. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, P.K.R.; Kumar, B.M.; Nair, V.D. Agroforestry as a strategy for carbon sequestration. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2009, 172, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zeng, R.; Hu, L.L.; Maffucci, K.G.; Ren, X.D.; Qu, Y. In vivo wound healing and in vitro antioxidant activities of Bletilla striata phenolic extracts. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.M.; Xu, H.S.; Shi, J.; Wang, Z.; Lv, J.F.; Li, L.; Wang, X. Soil microbial composition, diversity, and network stability in intercropping versus monoculture responded differently to drought. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 365, 108915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, L.R.; Salazar, J.C.S.; Casanoves, F.; Bieng, M.A.N. Cacao agroforestry systems improve soil fertility: Comparison of soil properties between forest, cacao agroforestry systems, and pasture in the Colombian Amazon. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 314, 107349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardozo, F.M.; Carneiro, R.F.V.; Rocha, S.M.B.; Nunes, L.A.P.L.; dos Santos, V.M.; Feitoza, L.D.; de Araujo, A.S.F. The impact of pasture systems on soil microbial biomass and community-level physiological profiles. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Yang, B.; Zhu, X.A.; Ma, S.; Xie, E.H.; Zeng, H.H.; Li, C.; Wu, J.E. An increase in intercropped species richness improves plant water use but weakens the nutrient status of both intercropped plants and soil in rubber-tea agroforestry systems. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 284, 108353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivezić, V.; Yu, Y.; van der Werf, W. Crop yields in European agroforestry systems: A meta-analysis. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 606631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.A.; Osen, K.; Grass, I.; Holscher, D.; Tscharntke, T.; Wurz, A.; Kreft, H. Land-use history determines ecosystem services and conservation value in tropical agroforestry. Conserv. Lett. 2020, 13, e12740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langenberger, G.; Cadisch, G.; Martin, K.; Min, S.; Waibel, H. Rubber intercropping: A viable concept for the 21st century? Agrofor. Syst. 2017, 91, 577–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaupel, A.; Bednar, Z.; Herwig, N.; Hommel, B.; Moran-Rodas, V.E.; Beule, L. Tree-distance and tree-species effects on soil biota in a temperate agroforestry system. Plant Soil 2023, 487, 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.F.; Yin, R.Y.; Wang, H.L.; Chen, L.R.; Cao, X.Q.; Xu, X.N. Comparative analyses of functional traits based on metabolome and economic traits variation of Bletilla striata: Contribution of intercropping. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1147076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.L.; Cao, X.Q.; Fan, W.; Deng, P.F.; Xu, X.N. Effects of intercropping systems of Phyllostachys edulis and Bletilla striata on soil bacterial community composition and function. Agrofor. Syst. 2023, 97, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Guidelines for Soil Description, 4th ed.; FAO/ISRIC: Rome, Italy, 2006; pp. 67–82. [Google Scholar]
- AS 1289.2. 1.1; Methods of Testing Soils for Engineering Purposes, Soil Moisture Content Tests—Determination of the Moisture Content of a Soil-Oven Drying Method (Standard Method). SAI Global: Sydney, Australia, 2005.
- Huang, C.; Wang, Z.C.; Ren, X.L.; Ma, X.M.; Zhou, M.Y.; Ge, X.; Liu, H.; Fu, S.L. Evaluation of soil quality in a composite pecan orchard agroforestry system based on the smallest dataset. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.C.; Landman, A.; Pruden, G.; Jenkinson, D.S. Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: A rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1985, 17, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, J.A.; Craine, J.M.; Cramer, M.D. Correspondence between δ13C and δ15N in soils suggests coordinated fractionation processes for soil C and N. Plant Soil 2018, 423, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.R.; Wen, Z.Y.; Yin, R.Y.; Deng, P.F.; Gao, Y.; Xu, H.; Xu, X.N. Soil Organic Carbon turnover response to nitrogen and phosphorus additions in Eastern China: Evidence from stable carbon isotopes. Forests 2023, 14, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Lal, R.; Jiang, S. Soil quality index of a crosby silt loam in central Ohio. Soil Till Res. 2015, 146, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.S.; Carroll, C.R. Designing a soil quality assessment tool for sustainable agroecosystem management. Ecol. Appl. 2001, 11, 1573–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, G.D.; Ai, J.J.; Sun, Q.W.; Hou, L.Y.; Dong, Y.F. Soil quality assessment under different forest types in the Mount Tai, central Eastern China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 115, 106439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.J.; Lv, B.Q.; Wu, C.Q.; Hu, J.Y. Study on soil physical and chemical properties and soil enzyme activities of wild Bletilla striata habitat in Yanting, Sichuan. J. Sichuan For. Sci. Technol. 2023, 44, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows (Version 22.0); IBM Corp.: Armonk, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Origin(Pro), Version 2021; OriginLab Corporation: Northampton, MA, USA, 2021.
- Zhang, X.P.; Gao, G.B.; Wu, Z.Z.; Wen, X.; Zhong, H.; Zhong, Z.K.; Bian, F.Y.; Gai, X. Agroforestry alters the rhizosphere soil bacterial and fungal communities of moso bamboo plantations in subtropical China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 143, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.L.; Hayashi, K.; Ohigashi, K.; Shimura, M.; Kohyama, K. Developing characterization factors to quantify management impacts on soil quality of paddy fields within life cycle assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 238, 117890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panicoa, S.C.; Esposito, F.; Memoli, V.; Vitale, L.; Polimeno, F.; Magliulo, V.; Maisto, G.; De Marco, A. Variations of agricultural soil quality during the growth stages of sorghum and sunflower. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 152, 103569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirghaed, F.A.; Souri, B. Spatial analysis of soil quality through landscape patterns in the Shoor River Basin, Southwestern Iran. Catena 2022, 211, 106028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, R.; Dalling, J.W.; Harms, K.E.; Yavitt, J.B.; Stallard, R.F.; Mirabello, M.; Hubbell, S.P.; Valencia, R.; Navarrete, H.; Vallejo, M.; et al. Soil nutrients influence spatial distributions of tropical tree species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; Keiblinger, K.M.; Mooshammer, M.; Penuelas, J.; Richter, A.; Sardans, J.; Wanek, W. The application of ecological stoichiometry to plant-microbial-soil organic matter transformations. Ecol. Monogr. 2015, 85, 133–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, R.R.; Rozendaal, D.M.A.; Saputra, D.D.; Hairiah, K.; Roshetko, J.M.; van Noordijk, M. Balancing litterfall and decomposition in cacao agroforestry systems. Plant Soil 2022, 473, 251–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, E.J.; Tanner, E.V.J.; Cheesman, A.W. Increased litterfall changes fine root distribution in a moist tropical forest. Plant Soil 2006, 281, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yengwe, J.; Gebremikael, M.T.; Buchan, D.; Lungu, O.; De Neve, S. Effects of Faidherbia albida canopy and leaf litter on soil microbial communities and nitrogen mineralization in selected Zambian soils. Agrofor. Syst. 2018, 92, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngaba, M.J.Y.; Mgelwa, A.S.; Gurmesa, G.A.; Uwiragiye, Y.; Zhu, F.F.; Qiu, Q.Y.; Fang, Y.T.; Hu, B.; Rennenberg, H. Meta-analysis unveils differential effects of agroforestry on soil properties in different zonobiomes. Plant Soil 2024, 496, 589–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, M.E.; Borden, K.A. Nutrient acquisition strategies in agroforestry systems. Plant Soil 2019, 444, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.Y.; Luo, Y.H.; Burgess, K.S.; Tan, S.L.; Zheng, W.; Fu, C.N.; Xu, K.; Gao, L.M. Joint effect of phylogenetic relatedness and trait selection on the elevational distribution of Rhododendron species. J. Syst. Evol. 2021, 59, 1244–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Zhang, W.X.; Teng, C.; Pang, Z.Y.; Peng, Y.H.; Qiu, J.; Lei, J.W.; Su, X.H.; Zhu, W.X.; Ding, C.J. Intercropping changed the soil microbial community composition but no significant effect on alpha diversity. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1370996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.N.; Zeng, H.H.; Zhao, F.; Chen, C.F.; Jiang, X.J.; Zhu, X.A.; Wang, P.Y.; Wu, Z.X.; Liu, W.J. The nutrient status of plant roots reveals competition intensities in rubber agroforestry systems. Forests 2020, 11, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, R.F.; Reynolds, P.E. Ten-year responses of ponderosa pine plantations to repeated vegetation and nutrient control along an environmental gradient. Can. J. For. Res. 1999, 29, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrero, A.; Traba, J.; Tarjuelo, R. Increased density of conspecifics caused niche contraction in a multispecific passerine assemblage. Ecology 2024, 105, e4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobbágy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. The uplift of soil nutrients by plants: Biogeochemical consequences across scales. Ecology 2004, 85, 2380–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borden, K.A.; Thomas, S.C.; Isaac, M.E. Interspecific variation of tree root architecture in a temperate agroforestry system characterized using ground-penetrating radar. Plant Soil 2017, 410, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ahanbieke, P.; Wang, B.J.; Xu, W.L.; Li, L.H.; Christie, P.; Li, L. Root distribution and interactions in jujube tree/wheat agroforestry system. Agrofor. Syst. 2013, 87, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, B.J.; Gan, Y.W.; Duan, Z.P.; Hao, X.D.; Xu, W.L.; Li, L.H. Competitive interaction in jujube tree/cotton agroforestry system in Xinjiang province, northwestern China. Agrofor. Syst. 2019, 93, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.S.; Karlen, D.L.; Mitchell, J.P. A comparison of soil quality indexing methods for vegetable production systems in Northern California. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 90, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.B.; Darilek, J.L.; Huang, B.A.; Zhao, Y.C.; Sun, W.X.; Gu, Z.Q. Evaluating soil quality indices in an agricultural region of Jiangsu Province, China. Geoderma 2009, 149, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurmangozhinov, A.; Xue, W.; Li, X.Y.; Zeng, F.J.; Sabit, R.; Tusun, T. High biomass production with abundant leaf litterfall is critical to ameliorating soil quality and productivity in reclaimed sandy desertification land. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 263, 110373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.F.; Chen, Y.P.; Zhou, J.; Wang, K.B.; Wu, J.H. Soil quality should be accurate evaluated at the beginning of lifecycle after land consolidation for eco-sustainable development on the Loess Plateau. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 122244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.L.; Sun, Z.G.; Ouyang, Z.; Han, D.R.; Li, F.D. A comparison of soil quality evaluation methods for Fluvisol along the lower Yellow River. Catena 2017, 152, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fohrafellner, J.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; Murugan, R.; Valkama, E. Quality assessment of meta-analyses on soil organic carbon. Soil 2023, 9, 117–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.L.; Dai, Y.Z.; Cui, J.; Deng, P.F.; Fan, W.; Xu, X.N. Soil bacterial and fungal communities resilience to long-term nitrogen addition in subtropical forests in China. J. For. Res. 2024, 35, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClory, R.; Ellis, R.H.; Lukac, M.; Clark, J.; Mayoral, C.; Hart, K.M.; Plackett, A.R.G.; Mackenzie, A.R. Carbon dioxide enrichment affected flower numbers transiently and increased successful post-pollination development stably but without altering final acorn production in mature pedunculate oak (Quercus robur L.). J. For. Res. 2024, 35, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Lin, W.Y.; Hsiao, Y.M.; Chiou, T.J. Milestones in understanding transport, sensing, and signaling of the plant nutrient phosphorus. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 1504–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).