Identification of the Oleosin Genes and Functional Analysis of CeOle4 Gene in Cyperus esculentus L.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Treatment
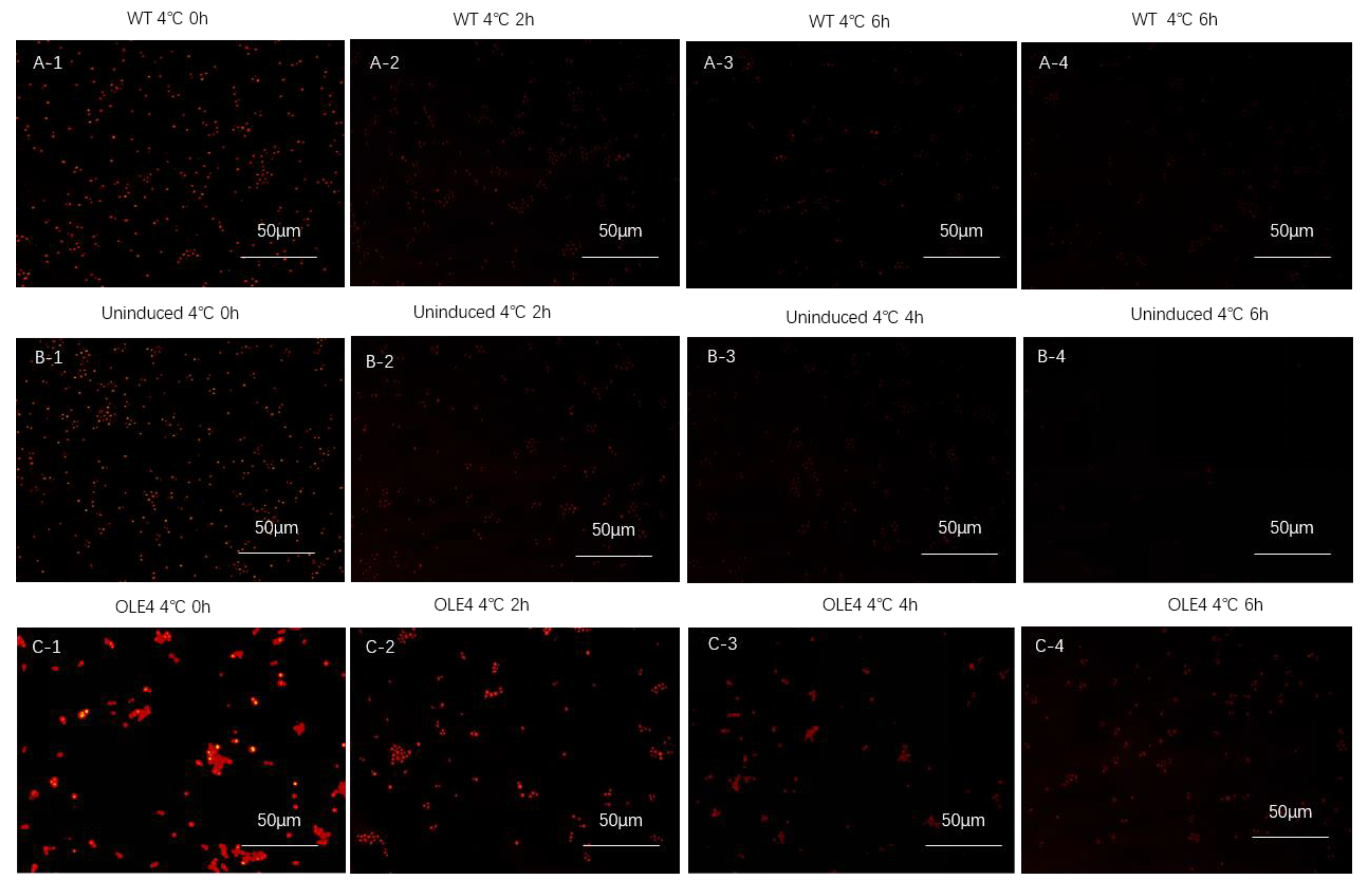
2.2. Nile Red Staining
2.3. RNA Isolation and qRT-PCR Analysis
2.4. Identification and Characterization of Oleosin Genes
2.5. Cloning and Vector Construction of CeOle4 Genes in Tiger Nut
2.6. Transformation and Observation of Tobacco Leaf Cells
2.7. Induced Expression of Target Protein in Yeast Cell
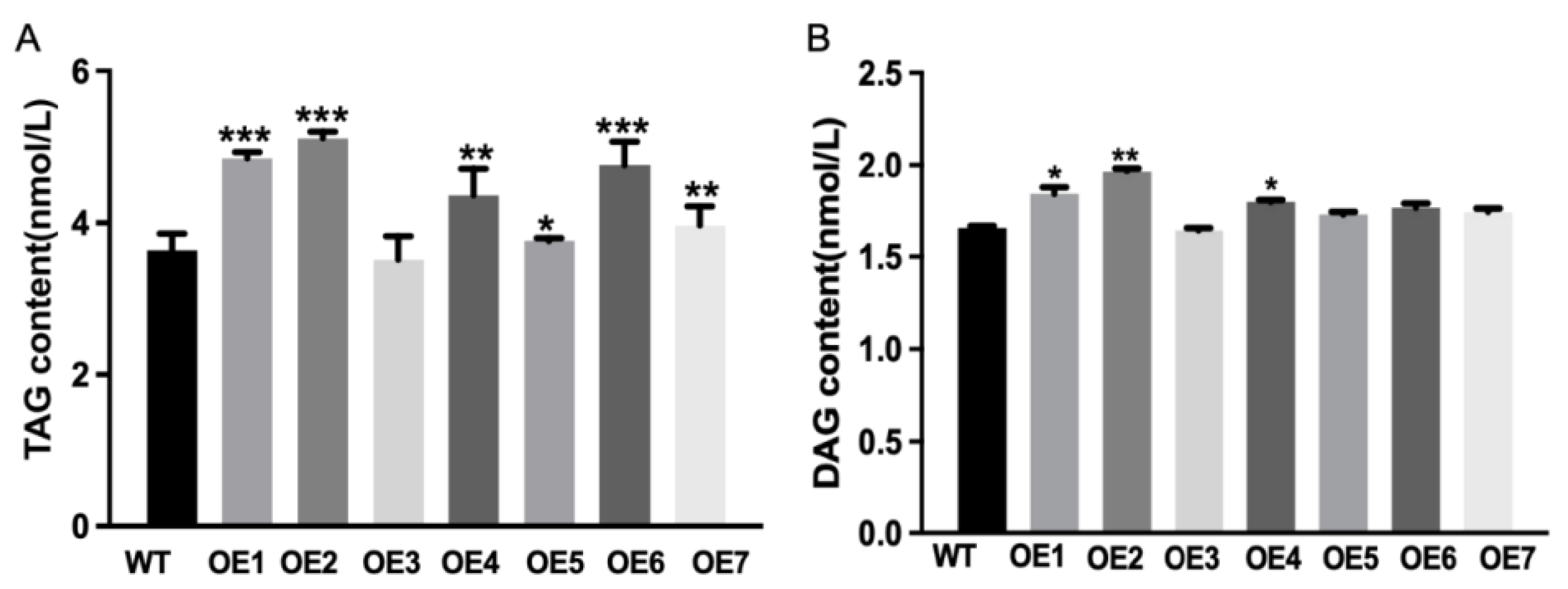
2.8. TAG and DAG Content Detection
2.9. Western Blotting Analysis Target Protein Expression
2.10. CeOle4-Overexpressed Transgenic Camelina Sativa and Expression Analysis
2.11. Observation of Phenotype of Transgenic Camelina Sativa
2.12. Data Analysis
3. Results
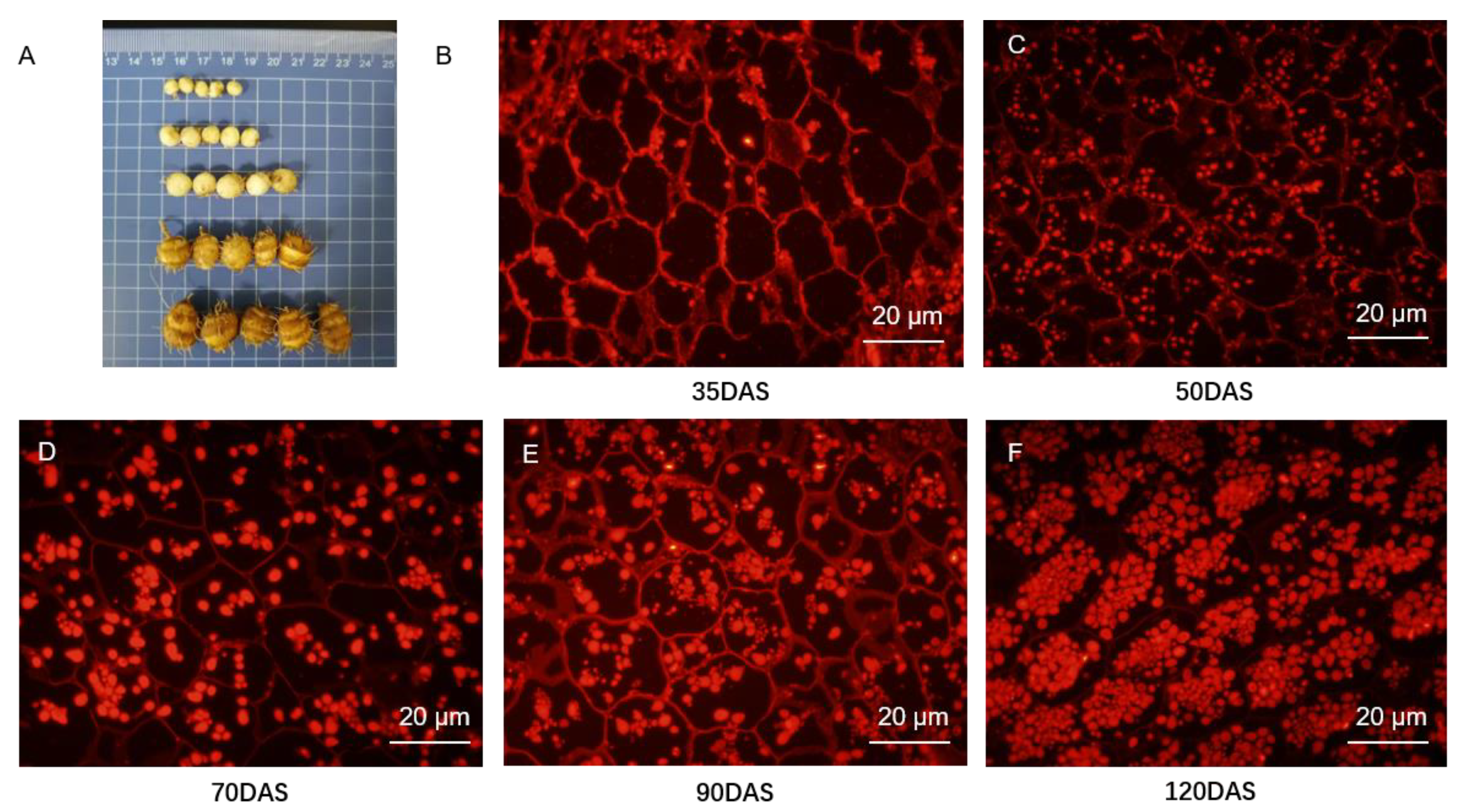
3.1. Lipid Droplets Accumulation during Tuber Development
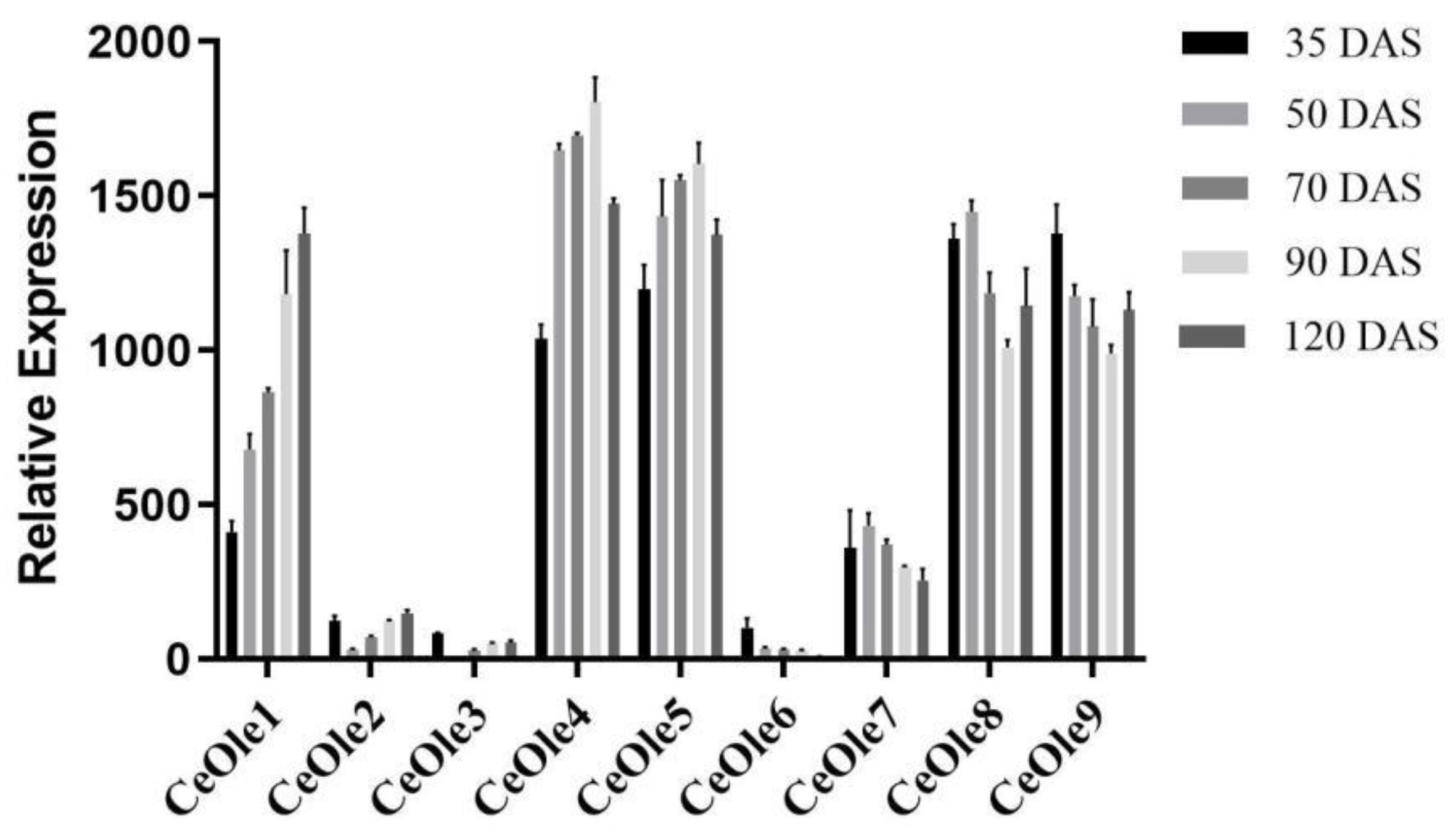
3.2. Gene Expression Analysis of CeOleosin Family
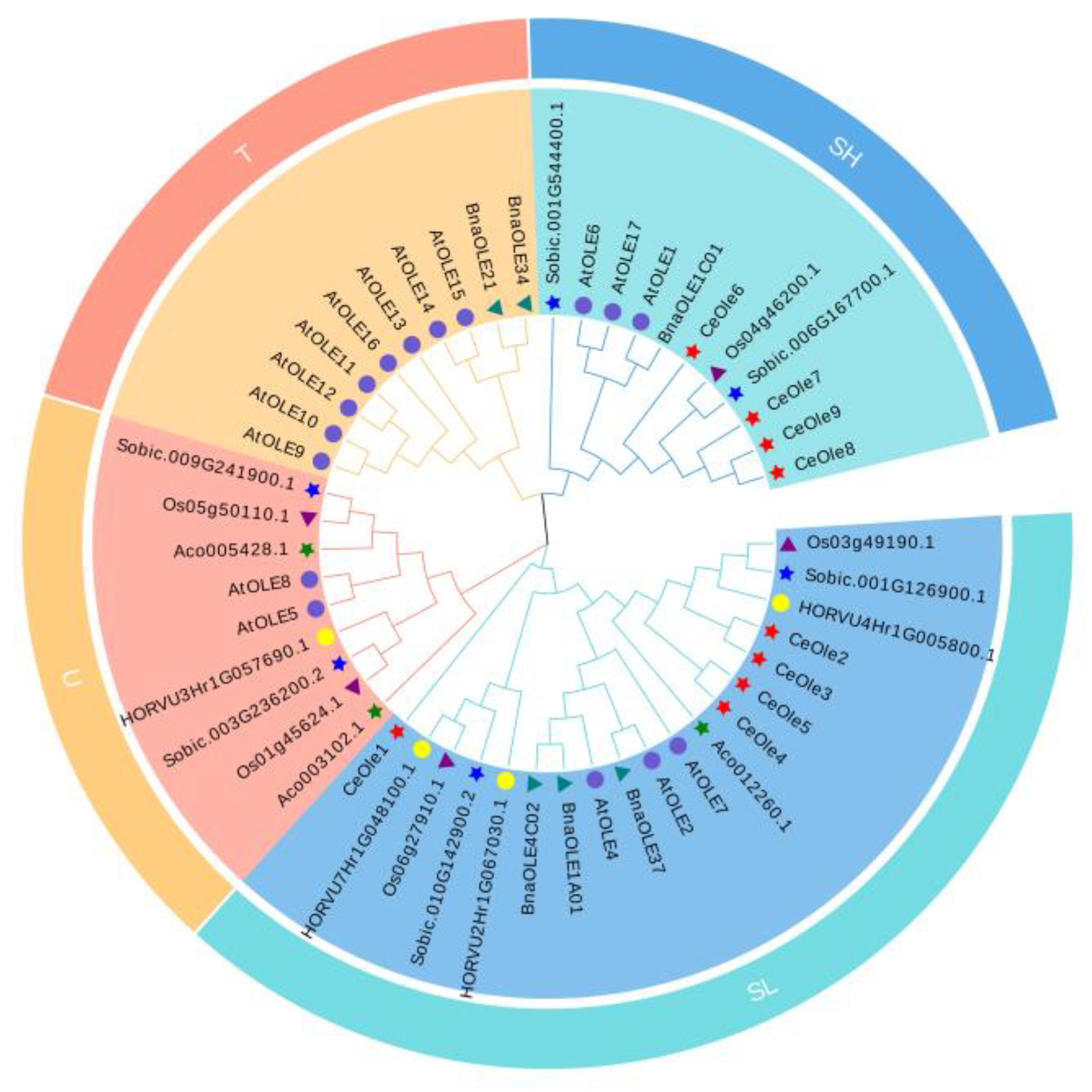
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of Oleosin Family Members
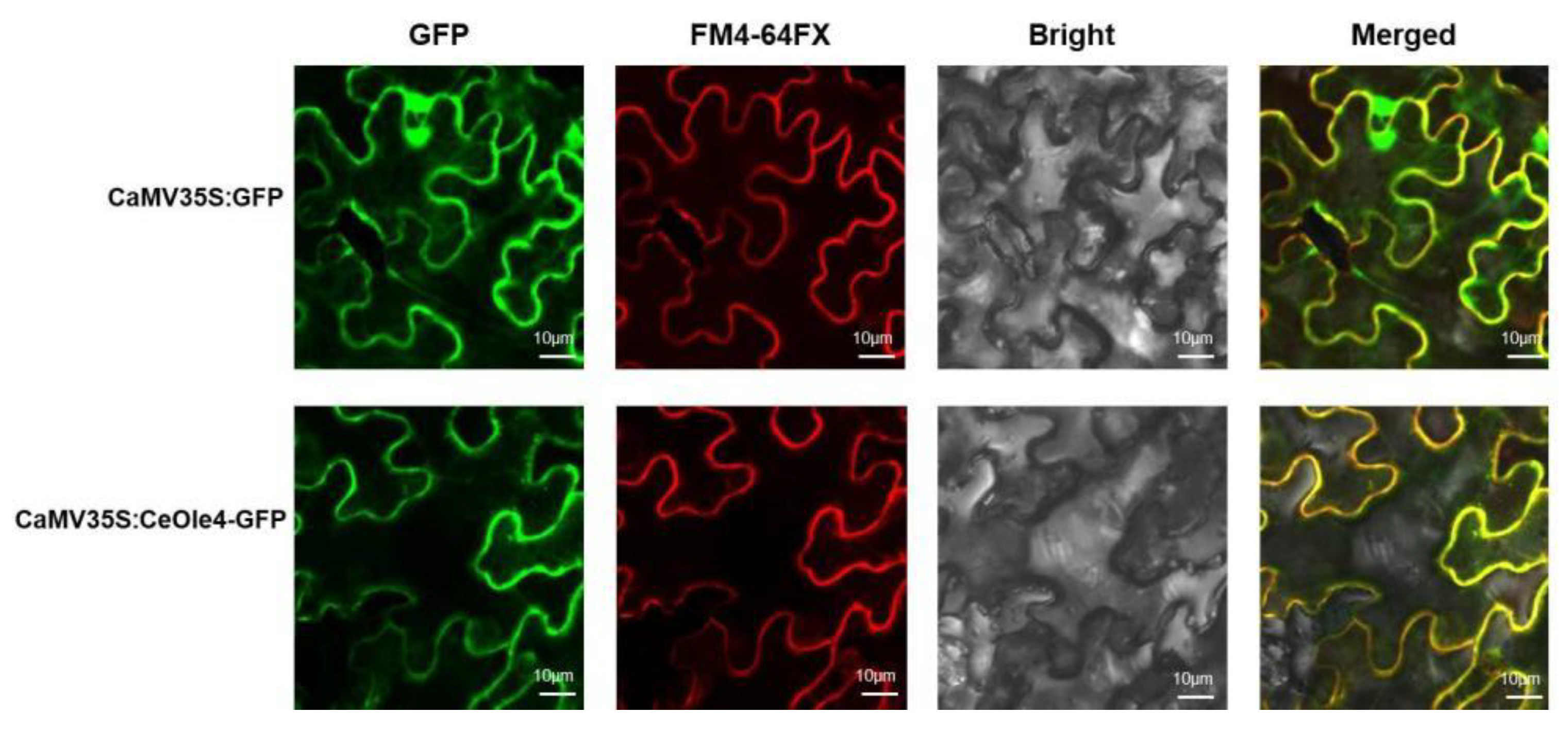
3.4. Subcellular Location of CeOle4
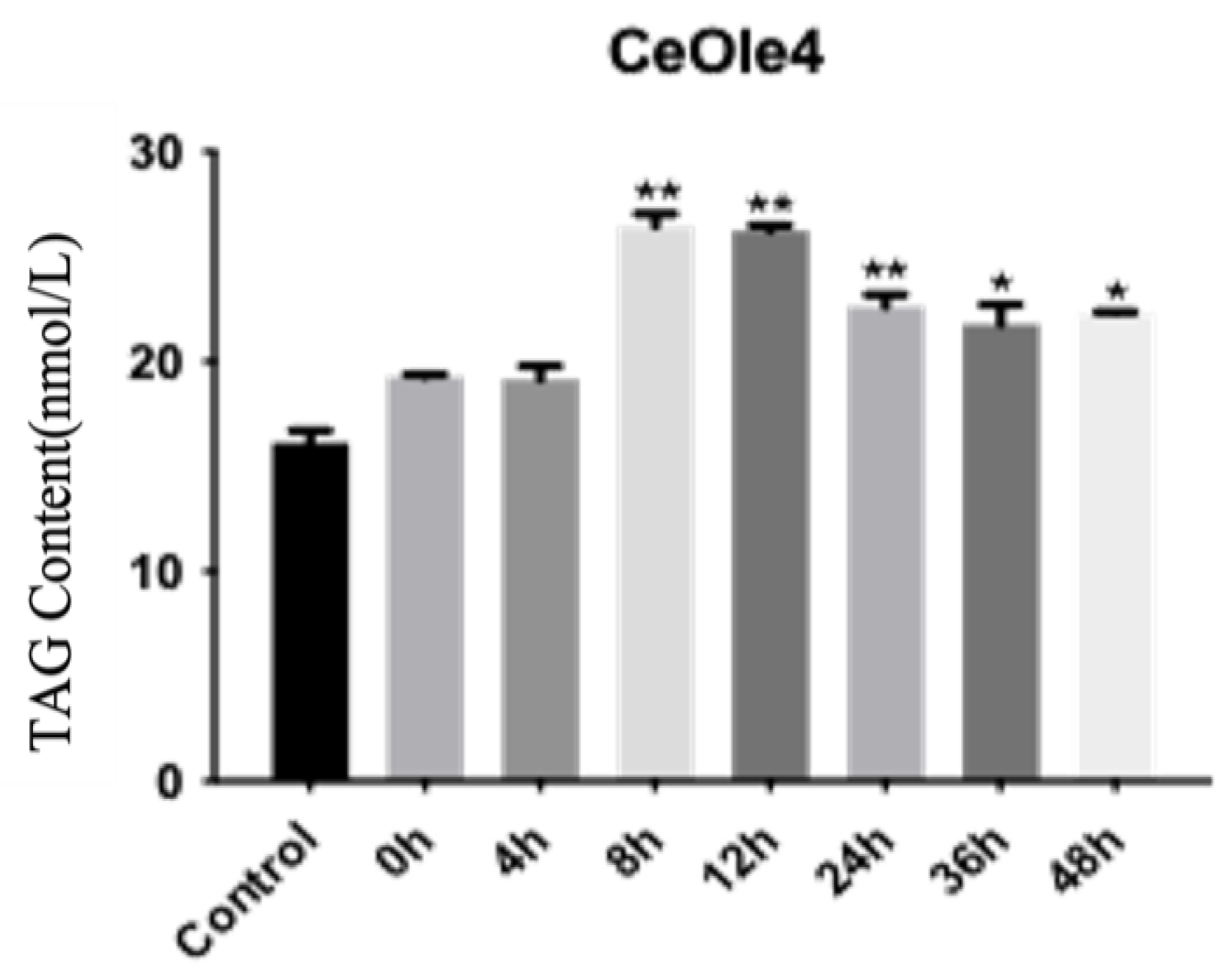
3.5. Exogenous Expression of CeOleosin4 and Function Analysis
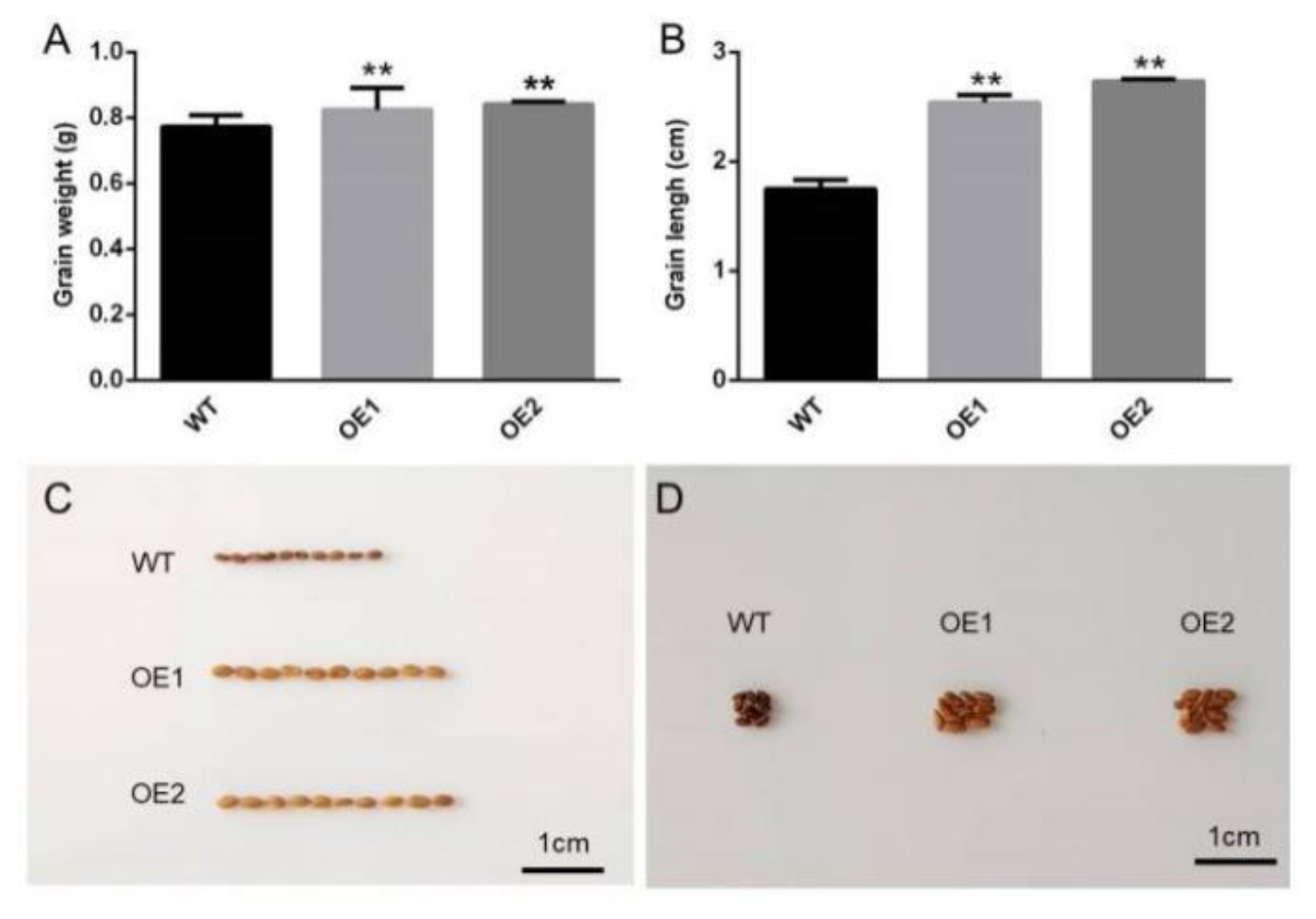
3.6. Analysis of Agronomic Traits in Transgenic Camelina Sativa Seeds
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Castro, O.; Gargiulo, R.; Del Guacchio, E.; Caputo, P.; De Luca, P. A molecular survey concerning the origin of Cyperus esculentus (Cyperaceae, Poales): Two sides of the same coin (weed vs. crop). Ann. Bot. 2015, 115, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onuoha, N.O.; Ogbusua, N.O.; Okorie, A.N.; Ejike, C. Tigernut (Cyperus esculentus L.) “milk” as a potent “nutri-drink” for the prevention of acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in a murine model. J. Intercult. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 6, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avicor, S.W.; Wajidi, M.F.F.; Achoribo, E.S.; Ong, M.T.; Hamzah, S.N. Tiger nut (Cyperus esculentus) as a potential phytoinsecticide: Larvicidal activity of crude extracts on Aedes aegypti and Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae). Trop. Biomed. 2021, 38, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, S. Tiger nut (Cyperus esculentus L.) oil: A review of bioactive compounds, extraction technologies, potential hazards and applications. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, C.; Guan, S.; Pu, Y.; Gao, F. Tiger Nut (Cyperus esculentus L.): Nutrition, Processing, Function and Applications. Foods 2022, 11, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibitoye, O.B.; Aliyu, N.O.; Ajiboye, T.O. Tiger nut oil-based diet improves the lipid profile and antioxidant status of male Wistar rats. J. Food Biochem. 2018, 42, e12587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adenowo, A.F.; Kazeem, M.I. Tiger Nut as A Functional Food, Pharmacological and Industrial Agent: A Mini Review. Ann. Sci. Technol. 2020, 5, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abell, B.M.; Holbrook, L.A.; Abenes, M.; Murphy, D.J.; Hills, M.J.; Moloney, M.M. Role of the proline knot motif in oleosin endoplasmic reticulum topology and oil body targeting. Plant Cell 1997, 9, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.H.C. Plant Lipid Droplets and Their Associated Proteins: Potential for Rapid Advances. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 1894–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.J. Storage lipid bodies in plants and other organisms. Prog. Lipid Res. 1990, 29, 299–324. [Google Scholar]
- Jolivet, P.; Acevedo, F.; Boulard, C.; d’Andréa, S.; Faure, J.D.; Kohli, A.; Nesi, N.; Valot, B.; Chardot, T. Crop seed oil bodies: From challenges in protein identification to an emerging picture of the oil body proteome. Proteomics 2013, 13, 1836–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzen, J.; Cao, Y.; Laurent, P.; Ratnayake, C.; Huang, A. Lipids, Proteins, and Structure of Seed Oil Bodies from Diverse Species. Plant Physiol. 1993, 101, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, E.; Baumberger, S.; Axelos, M.A.; Chardot, T. Oleosins of Arabidopsis thaliana: Expression in Escherichia coli, purification, and functional properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 5245–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.H. Oleosins and oil bodies in seeds and other organs. Plant Physiol. 1996, 110, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.Q.; Wang, X.F.; Gao, S.P. Progress on the functional role of oleosin gene family in plants. Yi Chuan 2022, 44, 1128–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Guan, L.; Du, L.; Guo, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Jiang, C.; et al. Expression of a functional recombinant oleosin-human hyaluronidase hPH-20 fusion in Arabidopsis thaliana. Protein Expr. Purif. 2014, 103, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargiotidou, A.; Deli, D.; Galanopoulou, D.; Tsaftaris, A.; Farmaki, T. Low temperature and light regulate delta 12 fatty acid desaturases (FAD2) at a transcriptional level in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 2043–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthibane, V.; Rajakumari, S.; Venkateshwari, V.; Iyappan, R.; Rajasekharan, R. Oleosin is bifunctional enzyme that has both monoacylglycerol acyltransferase and phospholipase activities. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 1946–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jing, M.; Ahmad, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, N.; Wang, F.; et al. Tracing Key Molecular Regulators of Lipid Biosynthesis in Tuber Development of Cyperus esculentus Using Transcriptomics and Lipidomics Profiling. Genes 2021, 12, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escorcia, W.; Ruter, D.L.; Nhan, J.; Curran, S.P. Quantification of Lipid Abundance and Evaluation of Lipid Distribution in Caenorhabditis elegans by Nile Red and Oil Red O Staining. JoVE 2018, 133, e57352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Quan, W.; Wang, D.; Cui, J.; Wang, T.; Lin, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, N.; Dong, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Fatty Acid Desaturase (FAD) Genes in Camelina sativa (L.) Crantz. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Zhang, H.; Gao, S.; Lercher, M.J.; Chen, W.H.; Hu, S. Evolview v2: An online visualization and management tool for customized and annotated phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W236–W241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Yang, X.; Xiao, C.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Li, S.; Lü, S.; Hu, H. GDSL lipase occluded stomatal pore 1 is required for wax biosynthesis and stomatal cuticular ledge formation. New Phytol. 2020, 228, 1880–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Kang, J. Generation of transgenic plants of a potential oilseed crop Camelina sativa by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Plant Cell Rep. 2008, 27, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, M.; Jameel, A.; Qiang, W.D.; Ahmad, N.; Liu, W.C.; Wang, F.W.; Li, H.Y. Overexpression of GmCAMTA12 Enhanced Drought Tolerance in Arabidopsis and Soybean. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffan, S.; Sparks, C.; Huttly, A.; Hyde, L.; Martignago, D.; Mead, A.; Hanley, S.J.; Wilkinson, P.A.; Barker, G.; Edwards, K.J.; et al. Wheat with greatly reduced accumulation of free asparagine in the grain, produced by CRISPR/Cas9 editing of asparagine synthetase gene TaASN2. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 1602–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Yin, Y.; Liu, S.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, K.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, W.; Chao, H.; Li, M. Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of oleosin genes in Brassica napus L. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthibane, V.; Iyappan, R.; Vijayakumar, A.; Venkateshwari, V.; Rajasekharan, R. Serine/threonine/tyrosine protein kinase phosphorylates oleosin, a regulator of lipid metabolic functions. Plant Physiol. 2012, 159, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, R.; Chen, F.; Liu, C.; Duan, X. Composition and Rheological Properties of Peanut Oil Bodies from Aqueous Enzymatic Extraction. J. Oleo Sci. 2021, 70, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilaru, A.; Cao, X.; Dabbs, P.B.; Sung, H.J.; Rahman, M.M.; Thrower, N.; Zynda, G.; Podicheti, R.; Ibarra-Laclette, E.; Herrera-Estrella, L.; et al. Oil biosynthesis in a basal angiosperm: Transcriptome analysis of Persea Americana mesocarp. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.D.; Huang, A.H. Bioinformatics Reveal Five Lineages of Oleosins and the Mechanism of Lineage Evolution Related to Structure/Function from Green Algae to Seed Plants. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Liu, J.; Guo, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, L.; Ali, K.; Qiang, F.; Wen, Y.; Li, W.; et al. Kinase regulators evolved into two families by gain and loss of ability to bind plant steroid receptors. Plant Physiol. 2023, 191, 1167–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostron, K.A.; Lawrence, C.L. Nile Red Staining of Neutral Lipids in Yeast. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1560, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajakumari, S.; Daum, G. Multiple functions as lipase, steryl ester hydrolase, phospholipase, and acyltransferase of Tgl4p from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 15769–15776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arisz, S.A.; Heo, J.Y.; Koevoets, I.T.; Zhao, T.; van Egmond, P.; Meyer, A.J.; Zeng, W.; Niu, X.; Wang, B.; Mitchell-Olds, T.; et al. DIACYLGLYCEROL ACYLTRANSFERASE1 Contributes to Freezing Tolerance. Plant Physiol. 2018, 177, 1410–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.; Han, D.; Li, Y.; Sommerfeld, M.; Hu, Q. Phospholipid:diacylglycerol acyltransferase is a multifunctional enzyme involved in membrane lipid turnover and degradation while synthesizing triacylglycerol in the unicellular green microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 3708–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigh, L.; Maresca, B.; Harwood, J.L. Does the membrane’s physical state control the expression of heat shock and other genes? Trends Biochem. Sci. 1998, 23, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, C.; Zhang, B.; Wang, R. Research progress on plant noncoding RNAs in response to low-temperature stress. Plant Signal Behav. 2022, 17, 2004035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.S.; Wang, L.D.; Chen, P.W.; Chen, L.J.; Tzen, J.T. Genomic cloning of 18 kDa oleosin and detection of triacylglycerols and oleosin isoforms in maturing rice and postgerminative seedlings. J. Biochem. 1998, 123, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Yao, M.; He, X.; Xiong, X.; Guan, M.; Liu, Z.; Guan, C.; Qian, L. Transcriptome and Regional Association Analyses Reveal the Effects of Oleosin Genes on the Accumulation of Oil Content in Brassica napus. Plants 2022, 11, 3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tao, J.J.; Lu, L.; Jiang, Z.H.; Wei, J.J.; Wu, C.M.; Yin, C.C.; Li, W.; Bi, Y.D.; et al. GmJAZ3 interacts with GmRR18a and GmMYC2a to regulate seed traits in soybean. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2023, 65, 1983–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niñoles, R.; Arjona, P.; Azad, S.M.; Hashim, A.; Casañ, J.; Bueso, E.; Serrano, R.; Espinosa, A.; Molina, I.; Gadea, J. Kaempferol-3-rhamnoside overaccumulation in flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase tt7 mutants compromises seed coat outer integument differentiation and seed longevity. New Phytol. 2023, 238, 1461–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzarowska, U.; Ruß, A.K.; Joubès, J.; Batsale, M.; Szymański, J.P.; Thirumalaikumar, V.; Luzarowski, M.; Wu, S.; Zhu, F.; Endres, N.; et al. Hello darkness, my old friend: 3-KETOACYL-COENZYME A SYNTHASE4 is a branch point in the regulation of triacylglycerol synthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 1984–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angeli, S.; Falasca, G.; Matteucci, M.; Altamura, M.M. Cold perception and gene expression differ in Olea europaea seed coat and embryo during drupe cold acclimation. New Phytol. 2013, 197, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, N.; Suzuki, C.; Yamashita, Y.; Senda, M. A pubescence color gene enhances tolerance to cold-induced seed cracking in yellow soybean. Breed. Sci. 2021, 71, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Y.; Luan, S.; Liu, X.; Yang, Q.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, F.; et al. Identification of the Oleosin Genes and Functional Analysis of CeOle4 Gene in Cyperus esculentus L. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10090945
Dong Y, Cui Y, Wang Y, Luan S, Liu X, Yang Q, Liu W, Li X, Wang N, Wang F, et al. Identification of the Oleosin Genes and Functional Analysis of CeOle4 Gene in Cyperus esculentus L. Horticulturae. 2024; 10(9):945. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10090945
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Yuanyuan, Yuling Cui, Yijin Wang, Shiyu Luan, Xinyi Liu, Qi Yang, Weican Liu, Xiaowei Li, Nan Wang, Fawei Wang, and et al. 2024. "Identification of the Oleosin Genes and Functional Analysis of CeOle4 Gene in Cyperus esculentus L." Horticulturae 10, no. 9: 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10090945
APA StyleDong, Y., Cui, Y., Wang, Y., Luan, S., Liu, X., Yang, Q., Liu, W., Li, X., Wang, N., Wang, F., Gu, L., & Xue, P. (2024). Identification of the Oleosin Genes and Functional Analysis of CeOle4 Gene in Cyperus esculentus L. Horticulturae, 10(9), 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10090945





