Precise Identification of Vitis vinifera L. Varieties Using Cost-Effective NGS-Based SNP Genotyping
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and DNA Extraction
2.2. PCR Amplification
2.3. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Grapevine Varieties
3.2. Genotyping Analysis
3.2.1. Protocol Validation
3.2.2. Variety Identification
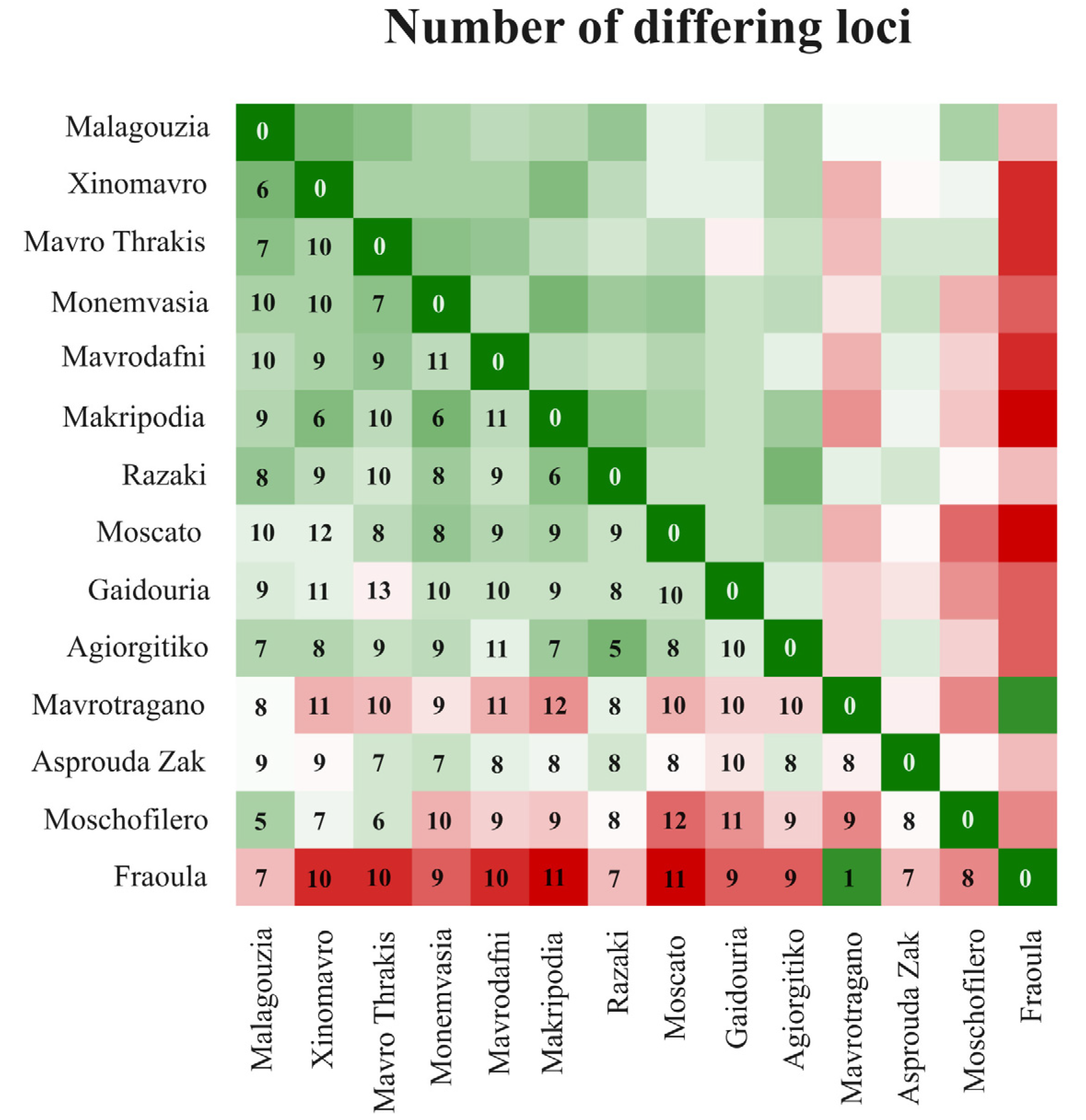
3.2.3. Comparison with Other Greek Varieties
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tympakianakis, S.; Trantas, E.; Avramidou, E.V.; Ververidis, F. Vitis vinifera Genotyping Toolbox to Highlight Diversity and Germplasm Identification. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1139647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsal, G.; Méndez, J.J.; Mateo, J.M.; Ferrer, S.; Canals, J.M.; Zamora, F.; Fort, F. Molecular Characterization of Vitis vinifera L. Local Cultivars from Volcanic Areas (Canary Islands and Madeira) Using SSR Markers. Oeno One 2019, 53, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohary, D.; Hopf, M.; Weiss, E. Domestication of Plants in the Old World: The Origin and Spread of Domesticated Plants in Southwest Asia, Europe, and the Mediterranean Basin; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- McGovern, P.E. The Search for the Origins of Viniculture. In The Origins and Ancient History of Wine; McGovern, P., Fleming, S., Katz, S.H., Eds.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Duan, S.; Xia, Q.; Liang, Z.; Dong, X.; Margaryan, K.; Musayev, M.; Goryslavets, S.; Zdunić, G.; Bert, P.F.; et al. Dual Domestications and Origin of Traits in Grapevine Evolution. Science 2023, 379, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aradhya, M.K.; Dangl, G.S.; Prins, B.H.; Boursiquot, J.M.; Walker, M.A.; Meredith, C.P.; Simon, C.J. Genetic Structure and Differentiation in Cultivated Grape, Vitis vinifera L. Genet. Res. 2003, 81, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmaso, M.; Faes, G.; Segala, C.; Stefanini, M.; Salakhutdinov, I.; Zyprian, E.; Toepfer, R.; Stella Grando, M.; Velasco, R. Genome Diversity and Gene Haplotypes in the Grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.), as Revealed by Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms. Mol. Breed. 2004, 14, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vouillamoz, J.F.; Grando, M.S. Genealogy of Wine Grape Cultivars: “Pinot” Is Related to “Syrah”. Heredity 2006, 97, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myles, S.; Boyko, A.R.; Owens, C.L.; Brown, P.J.; Grassi, F.; Aradhya, M.K.; Prins, B.; Reynolds, A.; Chia, J.M.; Ware, D.; et al. Genetic Structure and Domestication History of the Grape. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3530–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaryan, K.; Melyan, G.; Röckel, F.; Töpfer, R.; Maul, E. Genetic Diversity of Armenian Grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) Germplasm: Molecular Characterization and Parentage Analysis. Biology 2021, 10, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laucou, V.; Launay, A.; Bacilieri, R.; Lacombe, T.; Adam-Blondon, A.F.; Bérard, A.; Chauveau, A.; De Andrés, M.T.; Hausmann, L.; Ibáñez, J.; et al. Extended Diversity Analysis of Cultivated Grapevine Vitis vinifera with 10K Genome-Wide SNPs. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouby, L.; Figueiral, I.; Bouchette, A.; Rovira, N.; Ivorra, S.; Lacombe, T.; Pastor, T.; Picq, S.; Marinval, P.; Terral, J.F. Bioarchaeological Insights into the Process of Domestication of Grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) during Roman Times in Southern France. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e0063195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambino, G.; Dal Molin, A.; Boccacci, P.; Minio, A.; Chitarra, W.; Avanzato, C.G.; Tononi, P.; Perrone, I.; Raimondi, S.; Schneider, A.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing and SNV Genotyping of “Nebbiolo” (Vitis vinifera L.) Clones. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Töpfer, R.; Sudharma, K.N.; Kecke, S.; Marx, G.; Eibach, R.; Maghradze, D.; Maul, E. The Vitis International Varietey Catalogue (VIVC)—New Design and More Information. In Proceedings of the XXXIst World Congress of Vine and Wine, Verona, Italy, 15–20 June 2008; p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Greek Ministry of Rural Development and Food; Hellenic Republic, Ministry of Rural Development and Food, General Directorate of Agriculture, Directorate of Propagating Material of Cultivated Plant Species and Plant Genetic Resources: Athens, Greece, 2023.
- Jaillon, O.; Aury, J.M.; Noel, B.; Policriti, A.; Clepet, C.; Casagrande, A.; Choisne, N.; Aubourg, S.; Vitulo, N.; Jubin, C.; et al. The Grapevine Genome Sequence Suggests Ancestral Hexaploidization in Major Angiosperm Phyla. Nature 2007, 449, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, H.B.; Dilli, Y.; Oncu-Oner, T.; Ünal, A. Exploring Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of a Large Grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) Germplasm Collection in Türkiye. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1121811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- This, P.; Lacombe, T.; Thomas, M.R. Historical Origins and Genetic Diversity of Wine Grapes. Trends Genet. 2006, 22, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.; Maltese, F.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. Metabolic Constituents of Grapevine and Grape-Derived Products. Phytochem. Rev. 2010, 9, 357–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrakaki, M.; Biniari, K. Genotyping and Phenotyping of Twenty Old Traditional Greek Grapevine Varieties (Vitis vinifera L.) from Eastern and Western Greece. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 209, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.C.; Boso, S.; Gago, P.; Muñoz-Organero, G.; De Andrés, M.T.; Gaforio, L.; Cabello, F.; Santiago, J.L. Value of Two Spanish Live Grapevine Collections in the Resolution of Synonyms, Homonyms and Naming Errors. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2018, 24, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrakakis, M.N.; Biniari, K. Genetic Study of Grape Cultivars Belonging to the Muscat Family by Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA Markers. Vitis 1998, 37, 119–122. [Google Scholar]
- Biniari, K.; Stavrakaki, M. Genetic Study of Native Grapevine Varieties of Northern, Western and Central Greece with the Use of Ampelographic and Molecular Methods. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2019, 47, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrakakis, M.N. Ampelography; Tropi Publications: Athens, Greece, 2010. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, L.; Cavagnaro, P.; Boursiquot, J.M.; Agüero, C. Molecular Characterization of Bonarda-Type Grapevine Vitis vinifera Cultivars from Argentina, Italy, and France. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2008, 59, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespan, M.; Migliaro, D.; Larger, S.; Pindo, M.; Palmisano, M.; Manni, A.; Manni, E.; Polidori, E.; Sbaffi, F.; Silvestri, Q.; et al. Grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) Varietal Assortment and Evolution in the Marche Region (Central Italy). Oeno One 2021, 55, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, M.A.; Nawaz, M.A.; Shahid, M.Q.; Doğan, Y.; Comertpay, G.; Yıldız, M.; Hatipoğlu, R.; Ahmad, F.; Alsaleh, A.; Labhane, N.; et al. DNA Molecular Markers in Plant Breeding: Current Status and Recent Advancements in Genomic Selection and Genome Editing. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2018, 32, 261–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrul, A.; Baranov, A.; Kai, Y.; Lazarevski, M.; Palibin, T.V.; Prosmoserdov, N.N. Origin and Classification of Cultured Grape; Pischepromizdat: Moscow, Russia, 1946; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Koyama, K.; Kamigakiuchi, H.; Iwashita, K.; Mochioka, R.; Goto-Yamamoto, N. Polyphenolic Diversity and Characterization in the Red–Purple Berries of East Asian Wild Vitis Species. Phytochemistry 2017, 134, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royo, J.B.; Cabello, F.; Miranda, S.; Gogorcena, Y.; Gonzalez, J.; Moreno, S.; Itoiz, R.; Ortiz, J.M. The Use of Isoenzymes in Characterization of Grapevines (Vitis vinifera, L.). Influence of the Environment and Time of Sampling. Sci. Hortic. 1997, 69, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondini, L.; Noorani, A.; Pagnotta, M.A. Assessing Plant Genetic Diversity by Molecular Tools. Diversity 2009, 1, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzulli, S.; Doligez, A.; Bellin, D. Molecular Mapping of Grapevine Genes; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 9783030186005. [Google Scholar]
- Emanuelli, F.; Lorenzi, S.; Grzeskowiak, L.; Catalano, V.; Stefanini, M.; Troggio, M.; Myles, S.; Martinez-Zapater, J.M.; Zyprian, E.; Moreira, F.M.; et al. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure Assessed by SSR and SNP Markers in a Large Germplasm Collection of Grape. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, S.; Dangl, G.S.; Edwards, K.J.; Meredith, C.P. A Microsatellite Marker Based Framework Linkage Map of Vitis vinifera L. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 108, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, S.; Llaca, V.; May, G.D. Genotyping-by-Sequencing in Plants. Biology 2012, 1, 460–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Zhang, N.; Yang, Y.; Jin, Q.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; et al. NGS-Based Multi-Allelic InDel Genotyping and Fingerprinting Facilitate Genetic Discrimination in Grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Horticulturae 2024, 10, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broccanello, C.; Chiodi, C.; Funk, A.; McGrath, J.M.; Panella, L.; Stevanato, P. Comparison of Three PCR-Based Assays for SNP Genotyping in Plants. Plant Methods 2018, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słomka, M.; Sobalska-Kwapis, M.; Wachulec, M.; Bartosz, G.; Strapagiel, D. High Resolution Melting (HRM) for High-Throughput Genotyping-Limitations and Caveats in Practical Case Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polidoros, A.N. HRM Efficiency and Limitations for High-Throughput SSR Genotyping: A Case Study Using Grapevine Flavor-Linked Markers. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2019, 17, 12625–12631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammadov, J.; Aggarwal, R.; Buyyarapu, R.; Kumpatla, S. SNP Markers and Their Impact on Plant Breeding. Int. J. Plant Genom. 2012, 2012, 728398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossa, J.; Beyene, Y.; Semagn, K.; Pérez, P.; Hickey, J.M.; Chen, C.; Campos, G.d.L.; Burgueño, J.; Windhausen, V.S.; Buckler, E.; et al. Genomic Prediction in Maize Breeding Populations with Genotyping-by-Sequencing. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2013, 3, 1903–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myles, S.; Chia, J.M.; Hurwitz, B.; Simon, C.; Zhong, G.Y.; Buckler, E.; Ware, D. Rapid Genomic Characterization of the Genus Vitis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e0008219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Paslier, M.-C.; Choisne, N.; Scalabrin, S.; Bacilieri, R.; Berard, A.; Bounon, R.; Boursiquot, J.-M.; Bras, M.; Brunel, D.; Chauveau, A.; et al. The GrapeReSeq 18K Vitis Genotyping Chip. In Proceedings of the IX International Symposium on Grapevine Physiology and Biotechnology, Santiago, Chile, 21–26 April 2013; pp. 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- De Lorenzis, G.; Chipashvili, R.; Failla, O.; Maghradze, D. Study of Genetic Variability in Vitis vinifera L. Germplasm by High-Throughput Vitis18kSNP Array: The Case of Georgian Genetic Resources. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercati, F.; De Lorenzis, G.; Brancadoro, L.; Lupini, A.; Abenavoli, M.R.; Barbagallo, M.G.; Di Lorenzo, R.; Scienza, A.; Sunseri, F. High-Throughput 18K SNP Array to Assess Genetic Variability of the Main Grapevine Cultivars from Sicily. Tree Genet. Genomes 2016, 12, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas, J.A.; Ibáñez, J.; Lijavetzky, D.; Vélez, D.; Bravo, G.; Rodríguez, V.; Carreño, I.; Jermakow, A.M.; Carreño, J.; Ruiz-García, L.; et al. A 48 SNP Set for Grapevine Cultivar Identification. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrakaki, M.; Biniari, K. Ampelographic and Genetic Characterization of Grapevine Varieties (Vitis vinifera L.) of the “Mavroudia” Group Cultivated in Greece. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2017, 45, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsivelikas, A.L.; Avramidou, E.V.; Ralli, P.E.; Ganopoulos, I.V.; Moysiadis, T.; Kapazoglou, A.; Aravanopoulos, F.A.; Doulis, A.G. Genetic Diversity of Greek Grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) Cultivars Using Ampelographic and Microsatellite Markers. Plant Genet. Resour. Characterisation Util. 2022, 20, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hvarleva, T.; Hadjinicoli, A.; Atanassov, I.; Atanassov, A.; Ioannou, N. Genotyping Vitis vinifera L. Cultivars of Cyprus by Microsatellite Analysis. Vitis—J. Grapevine Res. 2005, 44, 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Maul, E.; Röckel, F. Vitis International Variety Catalogue. Available online: www.vivc.de (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Shi, X.; Cao, S.; Wang, X.; Huang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W.; Leng, X.; Peng, Y.; Wang, N.; et al. The Complete Reference Genome for Grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) Genetics and Breeding. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhad061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tegopoulos, K.; Fountas, D.V.; Andronidou, E.M.; Bagos, P.G.; Kolovos, P.; Skavdis, G.; Pergantas, P.; Braliou, G.G.; Papageorgiou, A.C.; Grigoriou, M.E. Assessing Genetic Diversity and Population Differentiation in Wild Hop (Humulus lupulus) from the Region of Central Greece via SNP-NGS Genotyping. Diversity 2023, 15, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M.; et al. Twelve Years of SAMtools and BCFtools. Gigascience 2021, 10, giab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing Mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast Gapped-Read Alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Robinson, J.T.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): High-Performance Genomics Data Visualization and Exploration. Brief. Bioinform. 2013, 14, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenALEx 6.5: Genetic Analysis in Excel. Population Genetic Software for Teaching and Research-an Update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (ITOL) v3: An Online Tool for the Display and Annotation of Phylogenetic and Other Trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W242–W245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babicki, S.; Arndt, D.; Marcu, A.; Liang, Y.; Grant, J.R.; Maciejewski, A.; Wishart, D.S. Heatmapper: Web-Enabled Heat Mapping for All. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W147–W153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basalekou, M.; Kyraleou, M.; Kallithraka, S. Chapter 38: Authentication of Wine and Other Alcohol-Based Beverages-Future Global Scenario. In Future Foods Gloal. Trends Opportunities and. Sustainability Challeneges; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 669–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atak, A. Climate Change and Adaptive Strategies on Viticulture (Vitis spp.). Open Agric. 2024, 9, 20220258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, H. Viticulture and Winemaking under Climate Change. Agronomy 2019, 9, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniatis, G.; Tani, E.; Katsileros, A.; Avramidou, E.V.; Pitsoli, T.; Sarri, E.; Gerakari, M.; Goufa, M.; Panagoulakou, M.; Xipolitaki, K.; et al. Genetic and Epigenetic Responses of Autochthonous Grapevine Cultivars from the ‘Epirus’ Region of Greece upon Consecutive Drought Stress. Plants 2024, 13, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banilas, G.; Korkas, E.; Kaldis, P.; Hatzopoulos, P. Olive and Grapevine Biodiversity in Greece and Cyprus—A Review. In Climate Change, Intercropping, Pest Control and Beneficial Microorganisms: Climate Change, Intercropping, Pest Control and Beneficial Microorganisms; Lichtfouse, E., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 401–428. ISBN 978-90-481-2716-0. [Google Scholar]

| S/N | Variety | Origin | VIVC | S/N | Variety | Origin | VIVC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Malagouzia | Central Greece | 7158 | 11 | Mavrotragano | Aegean Islands | 40,210 |
| 2 | Xinomavro | Macedonia | 13,284 | 12 | Asprouda Zakinthou | Ionian Islands | 708 |
| 3 | Mavro Thrakis | Thrace | 7539 | 13 | Moschofilero | Peloponnese | 8068 |
| 4 | Monemvasia | Peloponnese | 7925 | 14 | Fraoula | Peloponnese | 9226 |
| 5 | Mavrodafni | Ionian Islands | 7258 | 15 | Plyto | Crete | 9563 |
| 6 | Makripodia | Ionian Islands | 40,198 | 16 | Cardinal | USA | 2091 |
| 7 | Razaki | Unknown | 8790 | 17 | Victoria | Romania | 13,031 |
| 8 | Moscato | Aegean Islands | 8193 | 18 | Monastrell | Spain | 7915 |
| 9 | Gaidouria | Aegean Islands | 4998 | 19 | Merlot | France | 7657 |
| 10 | Agiorgitiko | Peloponnese | 102 |
| PCR Reaction | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) | Product Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 (Amplicons 1–5) | CAGCGAATCCCTACACGTCC | TCCAATTTCGTGCCCTCTGA | 72 bp |
| GAACATAAGGCCTCGAGTCTC | AGTGACCGAGGATAACACGG | 150 bp | |
| AAGTTGAGCTGGGAGATGGAG | TTCCAATAGGAGGGAATAGCGA | 226 bp | |
| GGGATACCCGATCAGCATGAAA | TCCAATGGGTGGACTTCAACA | 352 bp | |
| ACGGATCAAAATGAATGGCTTTG | CCCACAAGATTCTAAGTTCGCC | 236 bp | |
| R2 (Amplicons 6–10) | TCAAGTGAGCAAGGTGCACTAA | CTCTTTTGAACATTCTTGTGAGCC | 189 bp |
| ATAGGAAGCTGTGCTGAGTTGC | AGCATGGTTTCCAAAAACAGGG | 368 bp | |
| AAGTGCTTACACTGTGGCCC | ATTCATCGCCCCATACACGC | 83 bp | |
| GTTGGGGCTTAATGTACCCACTT | GCAACACATGGGAAAGGTGTG | 207 bp | |
| CACAAGCTTTTCCAGAGACACC | ATTGTTGGGCACAAATACGCT | 115 bp | |
| R3 (Amplicons 11–14) | CACAGCGAATGGAAACCGTG | AAATCTCTTCCGACGCCGTT | 242 bp |
| GCAACAGAGAACCAGATTACTATGC | AGATTCATCCCACTTGACCCAAA | 319 bp | |
| CCCACCCTCGACAATCTTTG | AAGAAGTGTATGGACCTGTTGGAT | 158 bp | |
| AGCATTATGTAGCATCATTCTTCCC | GTGGGGTTAACAGTTACACTAGA | 73 bp |
| SNP | RefSeq Accession | Chromosome | Amplicon Coordinates | SNP Position | Alleles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NC_081805.1 | 1 | 12,492,482 to 12,492,553 | 12,492,522 | T/C |
| 2 | NC_081807.1 | 3 | 3,694,974 to 3,695,084 | 3,695,042 | T/C |
| 3 | NC_081812.1 | 8 | 14,069,394 to 1,4069,619 | 14,069,512 | T/C |
| 4 | NC_081813.1 | 9 | 5,730,489 to 5,730,840 | 5,730,661 | T/C |
| 5 | NC_081815.1 | 11 | 5,380,240 to 5,380,475 | 5,380,410 | A/C |
| 6 | NC_081817.1 | 13 | 16,648,039 to 16,648,227 | 16,648,069 | T/C |
| 7 | NC_081818.1 | 14 | 4,382,939 to 4,383,306 | 4,383,127 | A/G |
| 8 | NC_081817.1 | 14 | 4,964,985 to 4,965,067 | 4,965,016 | T/G |
| 9 | NC_081819.1 | 15 | 21,381,119 to 21,381,325 | 21,381,247 | T/G |
| 10 | NC_081819.1 | 15 | 21,816,380 to 21,816,494 | 21,816,458 | T/G |
| 11 | NC_081820.1 | 16 | 20,981,581 to 20,981,822 | 20,981,646 | A/G |
| 12 | NC_081820.1 | 16 | 22,887,648 to 22,887,966 | 22,887,819 | A/G |
| 13 | NC_081821.1 | 17 | 594,944 to 595,101 | 595,010 | A/G |
| 14 | NC_081822.1 | 18 | 11,492,825 to 11,492,897 | 11,492,868 | T/C |
| Locus | Variety | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plyto | Cardinal | Victoria | Monastrell | Merlot | ||||||
| VIVC | This Study | VIVC | This Study | VIVC | This Study | VIVC | This Study | VIVC | This Study | |
| 1 | CC | CC | CC | CC | CC | CC | TC | TC | CC | CC |
| 2 | TT | TT | CC | CC | CC | CC | TC | TC | CC | CC |
| 3 | TC | TC | TC | TC | TT | TT | CC | CC | CC | CC |
| 4 | CC | CC | CC | CC | CC | CC | CC | CC | TT | TT |
| 5 | CC | CC | CC | CC | CC | CC | AC | AC | AC | AC |
| 6 | TC | TC | TC | TC | TC | TC | TC | TC | TT | TT |
| 7 | AG | AG | AG | AG | AG | AG | AG | AG | AA | AA |
| 8 | TG | TG | TG | TG | TG | TG | TG | TG | TG | TG |
| 9 | TT | TT | TG | TG | TG | TG | TG | TG | GG | GG |
| 10 | TG | TG | TG | TG | TT | TT | GG | GG | GG | GG |
| 11 | AG | AG | AA | AA | AA | AA | GG | GG | AA | AA |
| 12 | GG | GG | AG | AG | AA | AA | AA | AA | AG | AG |
| 13 | AG | AG | GG | GG | AG | AG | GG | GG | AA | AA |
| 14 | TC | TC | TT | TT | TC | TC | TC | TC | CC | CC |
| Locus | N | Na | Ne | I | Ho | He | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 59 | 2.000 | 1.921 | 0.672 | 0.390 | 0.479 | 0.187 |
| 2 | 59 | 2.000 | 1.999 | 0.693 | 0.542 | 0.500 | −0.085 |
| 3 | 59 | 2.000 | 1.921 | 0.672 | 0.458 | 0.479 | 0.045 |
| 4 | 59 | 2.000 | 1.995 | 0.692 | 0.441 | 0.499 | 0.116 |
| 5 | 59 | 2.000 | 1.995 | 0.692 | 0.373 | 0.499 | 0.252 |
| 6 | 59 | 2.000 | 1.995 | 0.692 | 0.475 | 0.499 | 0.048 |
| 7 | 59 | 2.000 | 2.000 | 0.693 | 0.525 | 0.500 | −0.051 |
| 8 | 59 | 2.000 | 1.999 | 0.693 | 0.475 | 0.500 | 0.051 |
| 9 | 59 | 2.000 | 1.986 | 0.690 | 0.508 | 0.496 | −0.024 |
| 10 | 59 | 2.000 | 1.998 | 0.693 | 0.492 | 0.499 | 0.016 |
| 11 | 59 | 2.000 | 1.933 | 0.676 | 0.542 | 0.483 | −0.124 |
| 12 | 59 | 2.000 | 1.991 | 0.691 | 0.492 | 0.498 | 0.012 |
| 13 | 59 | 2.000 | 1.933 | 0.676 | 0.542 | 0.483 | −0.124 |
| 14 | 59 | 2.000 | 1.986 | 0.690 | 0.576 | 0.496 | −0.161 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tegopoulos, K.; Polychronidou, S.-V.; Voumvouraki, A.; Kolovos, P.; Skavdis, G.; Grigoriou, M.Ε. Precise Identification of Vitis vinifera L. Varieties Using Cost-Effective NGS-Based SNP Genotyping. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11040375
Tegopoulos K, Polychronidou S-V, Voumvouraki A, Kolovos P, Skavdis G, Grigoriou MΕ. Precise Identification of Vitis vinifera L. Varieties Using Cost-Effective NGS-Based SNP Genotyping. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(4):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11040375
Chicago/Turabian StyleTegopoulos, Konstantinos, Sonia-Vasiliki Polychronidou, Anastasia Voumvouraki, Petros Kolovos, George Skavdis, and Maria Ε. Grigoriou. 2025. "Precise Identification of Vitis vinifera L. Varieties Using Cost-Effective NGS-Based SNP Genotyping" Horticulturae 11, no. 4: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11040375
APA StyleTegopoulos, K., Polychronidou, S.-V., Voumvouraki, A., Kolovos, P., Skavdis, G., & Grigoriou, M. Ε. (2025). Precise Identification of Vitis vinifera L. Varieties Using Cost-Effective NGS-Based SNP Genotyping. Horticulturae, 11(4), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11040375





