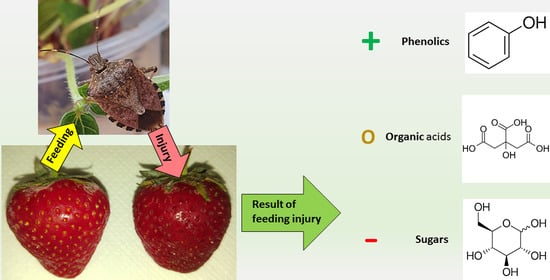
Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (Halyomorpha halys Stål.) Attack Induces a Metabolic Response in Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) Fruit
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Growing Conditions
2.2. Extraction of Sugars and Organic Acids
2.3. Extraction of Phenolics
2.4. Chemicals
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Visual Appearance of Strawberry
3.2. Sugars
3.3. Organic Acids
3.4. Phenolics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rot, M. First Record of Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (Halyomorpha halys (Stål, 1855)) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in Slovenia. Acta Entomol. Slov. 2018, 26, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Schumm, Z.R.; Alston, D.G.; Spears, L.R.; Manlove, K. Impact of Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) Feeding on Tart Cherry (Rosales: Rosaceae) Quality and Yield in Utah. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 2328–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bariselli, M.; Bugiani, R.; Maistrello, L. Distribution and damage caused by Halyomorpha halys in Italy. EPPO Bull. 2016, 46, 332–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoebeke, E.R.; Carter, M.E. Halyomorpha halys (Stal) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae): A polyphagous plant pest from Asia newly detected in North America. Proc. Entomol. Soc. Wash. 2003, 105, 225–237. [Google Scholar]
- Zamljen, T.; Veberic, R.; Hudina, M.; Slatnar, A. The Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (Halyomorpha halys Stål.) Influences Pungent and Non-Pungent Capsicum Cultivars’ Pre- and Post-Harvest Quality. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiman, N.G.; Parker, J.E.; Rodriguez-Saona, C.; Walton, V.M. Characterizing Damage of Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in Blueberries. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaby, K.; Mazur, S.; Nes, A.; Skrede, G. Phenolic compounds in strawberry (Fragaria x ananassa Duch.) fruits: Composition in 27 cultivars and changes during ripening. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesari, M.; Maistrello, L.; Ganzerli, F.; Dioli, P.; Rebecchi, L.; Guidetti, R. A pest alien invasion in progress: Potential pathways of origin of the brown marmorated stink bug Halyomorpha halys populations in Italy. J. Pest Sci. 2015, 88, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medal, J.; Smith, T.; Cruz, A.S. Biology of the Brown Marmorated Stink Bug Halyomorpha halys (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) in the Laboratory. J. Fla. Entomol. 2013, 96, 1209–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-H.; Wright, S.E.; Leskey, T.C. Impact of Insecticide Residue Exposure on the Invasive Pest, Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae): Analysis of Adult Mobility. J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wermelinger, B.; Wyniger, D.; Forster, B. First records of an invasive bug in Europe: Halyomorpha halys Stal (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae), a new pest on woody ornamentals and fruit trees? Mitt.-Schweiz. Entomol. Ges. 2007, 81, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Giusti, M.M.; Parker, J.; Salamanca, J.; Rodriguez-Saona, C. Frugivory by Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) Alters Blueberry Fruit Chemistry and Preference by Conspecifics. Environ. Entomol. 2016, 45, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weber, N.; Veberic, R.; Mikulic-Petkovsek, M.; Stampar, F.; Koron, D.; Munda, A.; Jakopic, J. Metabolite accumulation in strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) fruits and runners in response to Colletotrichum nymphaeae infection. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2015, 92, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- War, A.R.; Paulraj, M.G.; Ahmad, T.; Buhroo, A.A.; Hussain, B.; Ignacimuthu, S.; Sharma, H.C. Mechanisms of plant defense against insect herbivores. Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 1306–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaur, H.; Salh, P.K.; Singh, B. Role of defense enzymes and phenolics in resistance of wheat crop (Triticum aestivum L.) towards aphid complex. J. Plant Interact. 2017, 12, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Short, B.; Khrimian, A.; Leskey, T. Pheromone-based decision support tools for management of Halyomorpha halys in apple orchards: Development of a trap-based treatment threshold. J. Pest Sci. 2017, 90, 1191–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamljen, T.; Zupanc, V.; Slatnar, A. Influence of irrigation on yield and primary and secondary metabolites in two chilies species, Capsicum annuum L. and Capsicum chinense Jacq. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 234, 106104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, N.; Zupanc, V.; Jakopic, J.; Veberic, R.; Mikulic-Petkovsek, M.; Stampar, F. Influence of deficit irrigation on strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) fruit quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medic, A.; Zamljen, T.; Slatnar, A.; Hudina, M.; Veberic, R. Is Juglone the Only Naphthoquinone in Juglans regia L. with Allelopathic Effects? Agriculture 2021, 11, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medic, A.; Jakopic, J.; Solar, A.; Hudina, M.; Veberic, R. Walnut (J. regia) Agro-Residues as a Rich Source of Phenolic Compounds. Biology 2021, 10, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enomoto, H.; Takahashi, S.; Takeda, S.; Hatta, H. Distribution of Flavan-3-ol Species in Ripe Strawberry Fruit Revealed by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization-Mass Spectrometry Imaging. Molecules 2020, 25, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hassan, W.H.B.; Abdelaziz, S.; Al Yousef, H.M. Chemical Composition and Biological Activities of the Aqueous Fraction of Parkinsonea aculeata L. Growing in Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajdzanoska, M.; Gjamovski, V.; Stefova, M. HPLC-DAD-ESI-MSn identification of phenolic compounds in cultivated strawberry from Macedonia. Maced. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2010, 29, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ju, W.-T.; Kwon, O.C.; Kim, H.-B.; Sung, G.-B.; Kim, H.-W.; Kim, Y.-S. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of flavonoids from 12 species of Korean mulberry leaves. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 1789–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mullen, W.; Boitier, A.; Stewart, A.J.; Crozier, A. Flavonoid metabolites in human plasma and urine after the consumption of red onions: Analysis by liquid chromatography with photodiode array and full scan tandem mass spectrometric detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1058, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panighel, A.; De Rosso, M.; Dalla Vedova, A.; Flamini, R. Putative identification of new p-coumaroyl glycoside flavonoids in grape by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography/high-resolution mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 29, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spínola, V.; Pinto, J.; Castilho, P.C. Identification and quantification of phenolic compounds of selected fruits from Madeira Island by HPLC-DAD–ESI-MSn and screening for their antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagun, S.; Collins, E.; Martin, C.; Nolan, E.J.; Horzempa, J. Alarm Odor Compounds of the Brown Marmorated Stink Bug Exhibit Antibacterial Activity. J. Pharmacogn. Nat. Prod. 2016, 2, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milivojević, J.; Maksimović, V.; Nikolić, M.; Bogdanović, J.; Maletić, R.; Milatović, D. Chemical and Antioxidant Properties of Cultivated and Wild Fragaria and Rubus Berries. J. Food Qual. 2011, 34, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos Sánchez, N.; Salas-Coronado, R.; Hernandez-Carlos, B.; Villanueva, C. Shikimic Acid Pathway in Biosynthesis of Phenolic Compounds. In Plant Physiological Aspects of Phenolic Compounds; Intech: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weber, N.; Schmitzer, V.; Jakopic, J.; Stampar, F. First fruit in season: Seaweed extract and silicon advance organic strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) fruit formation and yield. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 242, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.E.; Zhao, X.; Carey, E.E.; Welti, R.; Yang, S.-S.; Wang, W. Phytochemical phenolics in organically grown vegetables. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2005, 49, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veluri, R.; Weir, T.; Bais, H.; Stermitz, F.; Vivanco, J. Phytotoxic and Antimicrobial Activities of Catechin Derivatives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, C.; Unsicker, S.B.; Fellenberg, C.; Constabel, C.P.; Schmidt, A.; Gershenzon, J.; Hammerbacher, A. Flavan-3-ols Are an Effective Chemical Defense against Rust Infection. Plant Physiol. 2017, 175, 1560–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lev-Yadun, S.; Gould, K.S. Role of Anthocyanins in Plant Defence. In Anthocyanins: Biosynthesis, Functions, and Applications; Winefield, C., Davies, K., Gould, K., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer, H.M.; Rentzsch, M.; Breuer, M. Anthocyanins Reduce Fungal Growth in Fruits. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2008, 3, 1934578X0800300808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gantner, M.; Najda, A.; Piesik, D. Effect of phenolic acid content on acceptancof hazel cultivars by filbert aphid. Plant Prot. Sci. 2019, 55, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Control | Halyomorpha halys | Indirect Halyomorpha halys | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sucrose | 10.20 ± 0.41 | a * | 6.01 ± 0.62 | b | 6.62 ± 0.44 | b |
| Glucose | 21.82 ± 0.40 | a | 18.63 ± 0.83 | b | 19.61 ± 0.42 | b |
| Fructose | 21.91 ± 0.45 | a | 19.62 ± 0.76 | b | 20.02 ± 0.35 | ab |
| Total sugars | 53.93 ± 0.52 | a | 44.26 ± 0.56 | b | 46.25 ± 0.44 | b |
| Control | Halyomorpha halys | Indirect Halyomorpha halys | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Citric acid | 8.15 ± 0.92 | a * | 6.85 ± 0.32 | a | 6.23 ± 0.27 | a |
| Malic acid | 3.86 ± 0.35 | a | 3.95 ± 0.24 | a | 3.23 ± 0.22 | a |
| Shikimic acid | 0.05 ± 0.01 | ab | 0.06 ± 0.00 | a | 0.04 ± 0.00 | b |
| Fumaric acid | 0.02 ± 0.00 | a | 0.02 ± 0.00 | a | 0.02 ± 0.00 | a |
| Total organic acid | 12.08 ± 1.4 | a | 10.88 ± 1.8 | a | 9.52 ± 0.7 | a |
| Control | Halyomorpha halys | Indirect Halyomorpha halys | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total elgaic acid derivatives | 326.0 ± 12.0 | b * | 487.8 ± 26.2 | a | 307.6 ± 21.8 | b |
| bis-HHDP-glucose | 85.0 ± 4.7 | b | 132.3 ± 10.3 | a | 71.0 ± 3.2 | b |
| bis-HHDP-hexose | 154.0 ± 11.4 | b | 222.3 ± 24.8 | a | 152.6 ± 17.8 | b |
| ellagic acid deoxyhexoside | 11.0 ± 0.5 | b | 15.9 ± 0.9 | a | 13.2 ± 1.2 | ab |
| Flavanols | 398.1 ± 13.5 | a | 436.4 ± 29.2 | a | 375.2 ± 16.8 | a |
| procyanidin dimer 1 | 115.5 ± 8.6 | a | 149.7 ± 3.6 | a | 137.1 ± 10.6 | a |
| procyanidin dimer 2 | 137.0 ± 7.6 | a | 124.8 ± 6.8 | ab | 104.9 ± 8.0 | b |
| procyanidin trimer | 78.5 ± 2.9 | a | 78.5 ± 7.4 | a | 79.5 ± 8.1 | a |
| propelargonidin dimer | 12.1 ± 1.4 | a | 10.5 ± 3.1 | a | 10.2 ± 2.6 | a |
| epicatechin | 38.6 ± 4.5 | b | 52.9 ± 12.5 | a | 29.7 ± 5.3 | b |
| catechin | 16.4 ± 0.8 | ab | 19.6 ± 0.4 | a | 13.5 ± 2.0 | b |
| Flavone | ||||||
| apigenin rhamnoside | 1.10± 0.1 | a | 1.0 ± 0.0 | a | 0.9 ± 0.1 | a |
| Flavonols | 21.7 ± 1.2 | a | 20.4 ± 1.4 | ab | 15.7 ± 1.9 | b |
| kaempferol-3-coumaroyl glucoside | 0.2 ± 0.0 | a | 0.1 ± 0.0 | a | 0.2 ± 0.0 | a |
| quercetin-3-glucuronide | 0.5 ± 0.1 | a | 0.3 ± 0.0 | a | 0.4 ± 0.1 | a |
| kaempferol-3-glucoside | 12.2 ± 0.7 | a | 9.4 ± 1.0 | ab | 7.4 ± 1.0 | b |
| quercetin-3-malonyl glucoside | 1.3 ± 0.1 | b | 1.9 ± 0.1 | a | 1.1 ± 0.1 | b |
| kaempferol-3- glucuoronide | 4.7 ± 0.3 | a | 4.6 ± 0.2 | a | 4.1 ± 0.5 | a |
| isorhamnetin-3- glucuronide | 0.7 ± 0.1 | a | 0.2 ± 0.1 | b | 0.3 ± 0.1 | b |
| kaempferol-3-acetyl glucoside | 2.3 ± 0.1 | b | 3.5 ± 0.1 | a | 2.2 ± 0.1 | b |
| Hydroxycinnamic acids | 310.1 ± 3.9 | b | 401.7 ± 5.4 | a | 354.1 ± 11.9 | ab |
| p-cumaroyl hexoside 1 | 12.6 ± 0.3 | ab | 14.3 ± 0.6 | a | 11.4 ± 0.5 | b |
| p-cumaroyl hexoside 2 | 3.4 ± 0.1 | a | 2.8 ± 0.4 | a | 1.4 ± 0.2 | b |
| p-cumaroyl hexoside 3 | 3.2 ± 0.3 | a | 3.6 ± 0.5 | a | 2.5 ± 0.5 | a |
| cinnamic acid hexoside | 190.4 ± 2.3 | a | 182.7 ± 4.1 | ab | 163.1 ± 10.7 | b |
| caffeoylhexose | 0.9 ± 0.0 | a | 0.9 ± 0.0 | a | 0.6 ± 0.1 | b |
| caffeic acid derivate | 0.5 ± 0.1 | b | 1.3 ± 0.0 | a | 0.5 ± 0.1 | b |
| ferulic acid hexose derivate | 87.0 ± 2.2 | b | 133.1 ± 5.7 | a | 83.9 ± 3.0 | b |
| p-coumaroylhexose | 4.4 ± 0.1 | b | 5.2 ± 0.1 | a | 4.1 ± 1.1 | b |
| cinnamic acid-3 acetylhexoside | 4.3 ± 0.3 | a | 3.52 ± 0.20 | a | 3.5 ± 0.4 | a |
| Hydroxybenzoic acids | ||||||
| ellagic acid | 4.2 ± 0.8 | a | 4.87 ± 0.46 | a | 2.9 ± 0.1 | a |
| Anthocyanins | 640.8 ± 18.9 | b | 1040.95 ± 48.07 | a | 683.5 ± 38.9 | b |
| Cyanidin-3-glucoside | 38.8 ± 0.6 | b | 57.98 ± 3.79 | a | 36.3 ± 5.4 | b |
| Pelargonidin-3-glucoside | 413.4 ± 15.1 | b | 672.37 ± 34.84 | a | 420.7 ± 20.4 | b |
| Pelargonidin-3-malonylglucoside | 14.4 ± 0.7 | b | 21.23 ± 1.77 | a | 18.3± 1.1 | b |
| Pelargonidin-3-rutinoside | 174.3 ± 4.5 | b | 289.59 ± 11.14 | a | 208.4 ± 16.7 | ab |
| Total analyzed phenolics | 1625.2 ± 28.5 | b | 2226.64 ± 58.60 | a | 1589.6 ± 53.0 | b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weber, N.C.; Razinger, J.; Jakopič, J.; Schmitzer, V.; Hudina, M.; Slatnar, A.; Veberič, R.; Štampar, F.; Zamljen, T. Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (Halyomorpha halys Stål.) Attack Induces a Metabolic Response in Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) Fruit. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 561. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7120561
Weber NC, Razinger J, Jakopič J, Schmitzer V, Hudina M, Slatnar A, Veberič R, Štampar F, Zamljen T. Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (Halyomorpha halys Stål.) Attack Induces a Metabolic Response in Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) Fruit. Horticulturae. 2021; 7(12):561. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7120561
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeber, Nika Cvelbar, Jaka Razinger, Jerneja Jakopič, Valentina Schmitzer, Metka Hudina, Ana Slatnar, Robert Veberič, Franci Štampar, and Tilen Zamljen. 2021. "Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (Halyomorpha halys Stål.) Attack Induces a Metabolic Response in Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) Fruit" Horticulturae 7, no. 12: 561. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7120561
APA StyleWeber, N. C., Razinger, J., Jakopič, J., Schmitzer, V., Hudina, M., Slatnar, A., Veberič, R., Štampar, F., & Zamljen, T. (2021). Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (Halyomorpha halys Stål.) Attack Induces a Metabolic Response in Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) Fruit. Horticulturae, 7(12), 561. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7120561