Abstract
In this study, a novel green tea/Mg-functionalized magnetic nano-adsorbent, denoted as GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs, was developed and applied to the extraction of Methylene Blue (MB) from water-based solutions. The GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs were synthesized by incorporating green tea extracts (GTE) and Mg species onto the surface of Fe3O4 nanoparticles using a hydrothermal method. Characterization analyses corroborated the successful functionalization of the Fe3O4 surface with GTE and Mg species, resulting in a superparamagnetic adsorbent equipped with abundant surface functional groups, which promoted MB adsorption and facilitated magnetic separation. Batch experiments revealed that different operating parameters had an impact on the adsorption behavior, such as adsorbent dosage, pH, coexisting ions, contact time, the initial MB concentration, and temperature. The investigations of adsorption kinetics and isotherms emphasized that the MB adsorption onto GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs was an exothermic process dominated by chemisorption. The experimental adsorption capacity of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs for MB surpassed 174.93 mg g−1, markedly superior to the performance of numerous other adsorbents. Ultimately, the utilized GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs could be effectively regenerated through acid pickling, retaining over 76% of its original adsorption capacity after six adsorption–desorption cycles, which suggested that GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs was a suitable adsorbent for eliminating MB from effluent.
1. Introduction
The escalating discharge of dye-containing effluents into water bodies via human activities, including leather tanning, printing, and textile production, has turned the decontamination of dye-polluted water into an urgent global challenge [1,2]. For instance, during the dyeing process in the textile industry, 2–15% of the used dyes are lost in the effluent, which not only contributes to unacceptable water pollution but also poses a significant hazard to aquatic life, even to humans [3,4]. A common cationic dye employed in fabric valorization processes is methylene blue (MB). In humans and animals, excessive exposure to MB can cause a number of illnesses, including allergies, gastrointestinal disorders, diarrhea and nausea, tachycardia, and respiratory distress [5]. To comply with the associated health and environmental concerns, numerous effective and eco-friendly approaches, such as electrochemical treatment, flocculation, membrane separation, and adsorption, have been imperatively developed to eliminate the water contamination caused by dyes [6]. Among these processes, the adsorption process is favored for its ease of operation, high efficiency at low energy consumption, and robustness to variations in water quality [7].
A multitude of adsorbents have been developed in the interim to absorb cationic dyes. Owing to its unique physicochemical properties (e.g., well-developed porous structures and rich functional groups on the surface), biomass is considered a promising class of porous adsorbents with a high capability of removing a variety of organic and inorganic pollutants from water [8]. Among biomass, green tea has garnered interest as an inexpensive and readily accessible adsorbent material. It was discovered that green tea performs well when it comes to dye adsorption. The biological components of tea leaves can encapsulate and shield the adsorbent, increasing its stability in an aqueous environment. Furthermore, the uniform encirclement of the biological matrix around the adsorbent allows for the augmentation of its surface pore count, while sufficient pore filling can also improve the adsorption efficiency of MB.
However, the application of raw biomass without modifications is still restricted in practical water treatment due to its non-optimal pore sizes, which results in a relatively poor adsorption capacity, necessitating an excessive dosage of adsorbent to achieve the desired level of contaminant removal [9]. Additionally, achieving both high uptake and a high adsorption rate simultaneously for larger molecules or ions is still challenging with most raw biomass due to the low accessibility of porous surfaces and the large diffusion distance within the unimodal pores [6]. To address these issues, various physical and chemical modifications of impregnating nano-sized metal oxide (e.g., Mg, Mn, Al, Fe, etc.) into raw biomass have been developed to reduce the diffusion path lengths and provide easier access to the porous regions by varying the surface properties and pore structure, thereby improving the adsorption efficiency and reducing the amount of adsorbent required for effective water treatment [10]. For instance, the loading of nontoxic MgO nanoparticles into biomass through a chemical pretreatment process can significantly enlarge the adsorbent’s porosity and increase the number of available binding sites, which results in a superior adsorption capacity toward dye, surpassing that of the raw biomass and even other commercially available adsorbents [10,11]. Despite the promoted adsorption capability of the MgO-modified biomass, the challenge of recycling the used adsorbent from solutions remains unresolved, which limits the widespread application of MgO-modified biomass adsorbents in wastewater treatment.
As a solution, incorporating a magnetic core into the adsorbent can achieve effective and fast separation and collection using an external magnetic field [12]. Magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles are commonly used as the magnetic core for the preparation of various magnetic adsorbents because of their typical superparamagnetic behavior, high stability, affordability, and low toxicity [13]. Cai et al. [14] prepared Fe3O4@Ti-SiO2 (FTS), a new magnetic adsorbent with superior pore volume, specific surface area, thermal stability, and surface charge. Fe3O4 nanoparticles worked in concert to enhance the adsorbent’s ability to selectively adsorb cationic dyes from complex wastewater, leading to a maximum adsorption capacity of 336.74 mg g−1 for MB. Hinsene et al. effectively synthesized a ternary recyclable rice husk biochar (Fe3O4-ZnO/RBC-DES), which was a biopolymer-based magnetic nanocomposites doped with Fe3O4-ZnO nanoparticles and deep eutectic solvents [15]. The nano-adsorbent surface was modified with more potent active adsorption sites. Furthermore, the incorporation of the metal oxide nanocomposites (i.e., Fe3O4-ZnO) significantly facilitated the removal of contaminants. Inspired by the advantages of Fe3O4 nanoparticles, integrating them into MgO-modified biomass is expected to enhance the dye adsorption capacity and facilitate the easy separation of the used adsorbent along with the adsorbed dye from water through the application of an external magnetic field.
In this study, a magnetic MgO-modified biomass adsorbent, named GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs, is synthesized using green tea, MgO, and Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Methylene blue is chosen as a typical dye with a large heterocyclic aromatic structure to assess the adsorption capacity of the prepared GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs [13]. Characterization analysis is carried out to thoroughly investigate the physicochemical properties of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs. Subsequently, the mechanisms underlying the MB adsorption are clarified, and the effects of different operational parameters, including adsorbent dosage, reaction pH, coexisting ions, contact time, and temperature, on the process of adsorption, are assessed through a series of kinetic, isotherm, and thermodynamic experiments. Lastly, studies utilizing desorption-adsorption cycles were conducted to evaluate the capacity of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs for regeneration and recovery.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
Dried green tea leaves, sourced from the Chongqing Yongchuan District Tea Industry Association, were finely pulverized using a high-speed blender and then stored in a refrigerator maintained at a temperature of 277.15 K before utilization. Chemicals and reagents, including nanoiron tetraoxide, methylene blue, magnesium sulfate, sodium acetate, anhydrous ethanol, sodium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid, sodium chloride, potassium chloride, calcium chloride, sodium nitrate, and sodium sulfate, etc., were analytically pure and utilized exactly as supplied. Unless specified otherwise, all solutions were made with deionized water (DI-water, 18.2 MΩ cm) from a Taisite water purification system.
2.2. Adsorbent Preparation
Green tea extracts (GTE) preparation: 80 g of pulverized green tea leaves were ultrasonically dispersed into 100 mL DI water, and then the above mixture was transferred into a beaker with a cover (500 mL). The above mixture was heated at 353 K for 1 h and then filtered (0.45 mm) to obtain the green filtrate. The obtained GTE was transferred to a brown bottle and stored in the refrigerator (277.15 K).
GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NP preparation: 10 g CH3COONa and 3 g MgSO4 7H2O were ultrasonically dissolved in 20 mL DI water. Subsequently, the above solution was introduced dropwise into a 200 mL three-necked flask that already contained 0.9 g of commercial Fe3O4 nanoparticles (particle size 50–100 nm) and 80 mL of GTE solution. The above mixture within the flask was then subjected to vigorous stirring (300 rpm) and heated at 353.15 K for 3 h. Once cooled to room temperature, the solids in suspension were magnetically separated and subsequently washed three times with ethanol and DI water. After washing, the solids were dried in a vacuum oven for a duration of 24 h at 353.15 K. The final product was a black adsorbent material designated as GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs.
2.3. Characterizations
The prepared GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs underwent a comprehensive characterization process. This involved the use of various instruments: a scanning electron microscope equipped with an energy dispersive spectrometer (SEM-EDS, TM4000Plus II, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan), an X-ray powder diffractometer (XRD, PANalytical X’Pert Powder, Spectris Pte. Ltd., Almelo, The Netherlands), a Fourier infrared spectroscope (FT-IR, IRTracer100, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan), an X-ray photoelectron spectrometer (XPS, ESCALAB250Xi, Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA), a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM, PPMS DynaCool 9, Quantum Design, San Diego, CA, USA), a zeta potential analyzer (Zetasizer Nano ZS90, London, UK; Malvern, PA, USA), and an N2 sorption analyzer (Quadrasorb 2MP, Quantachrome, Boca Raton, FL, USA). Detailed analysis methods, along with their corresponding parameters, are outlined in Text S1.
2.4. Batch Adsorption Experiments
To investigate the adsorption kinetics, formulate adsorption isotherms, and evaluate the adsorption capacity of MB onto GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs, batch adsorption experiments were conducted. Briefly, a stock solution of MB was created by dissolving MB powders directly in DI water, which was then diluted to achieve predetermined concentrations prior to the reactions. The pH of the solution was brought to the necessary level by adding 0.2 M H2SO4 and 0.2 M NaOH solutions. Then, 0.15 g L−1 of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs was added to 50 mL of each solution with the intended MB concentration. The reaction vessels were placed on an orbital shaking incubator set at 400 rpm and agitated for 180 min at a steady temperature. At specified intervals, aliquots were collected, immediately filtered using a 0.22 μm filter, and subsequently neutralized with 1 mL of a 40 mM phosphate buffer solution (pH 6) before undergoing analysis. All experiments were repeated three times.
Residual MB concentrations in the samples were quantified by measuring the absorbance at a wavelength of 664 nm using a UV-vis spectrophotometer (TU-1901, provided by Shanghai Jinghong Experimental Equipment Co., Shanghai, China). To assess the effect of pH on adsorption efficiency, the pH was adjusted within a wide range of 1 to 11 using 0.2 M H2SO4 and 0.2 M NaOH solutions. Additionally, the influence of commonly co-existing ions on adsorption performance was evaluated by introducing various concentrations (0.1 to 200 mM) of Na+, K+, Ca2+, Cl−, NO3−, and SO42− into the reaction mixture. The adsorption capacity (qe) was determined by utilizing the following Equation (1).
where C0 and Ce are the initial and equilibrium MB concentrations in solution, respectively; M is the mass of the adsorbent; and V is the volume of the reaction solution.
To gain a deeper understanding of the adsorption kinetics, the Pseudo-First-Order (PFO), Pseudo-Second-Order (PSO), and Intra-Particle Diffusion models were utilized to analyze the experimental kinetic data. For the adsorption isotherm experiments, the adsorbent dosage was fixed at 0.3 g L−1, and the MB concentration spanned from 20 to 100 mg L−1. The above reaction solution was shaken (at 400 rpm) at a constant temperature of 288.15, 298.15, 308.15, and 318.15 K for 20 h, respectively. For a more comprehensive understanding of the adsorption behavior, the Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin isotherm models were applied to analyze the experimental adsorption data. The related equations and parameters are expressed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Kinetic and equilibrium isotherm models.
Where qt (mg g−1) and qe (mg g−1) are the amount of MB adsorbed on GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs at any time t (min) and equilibrium, respectively; k1 (min−1), k2 (g mg−1 min−1), and k3 (g mg−1 min−0.5) are the rate constants for the PFO, PSO, and Intra-Particle Diffusion models, respectively; C (mg g−1) is the model constant for the boundary layer thickness. qm (mg g−1) is the maximum adsorption of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs; Ce (mg L−1) is the concentration of residual MB in solution at equilibrium; kL (L mg−1), kF (mg g−1), and bT (J mol−1) are the constants for the Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin models, respectively; n is the Freundlich heterogeneity factor; and f (L mg−1) is the maximum binding energy constant for the Temkin model.
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs
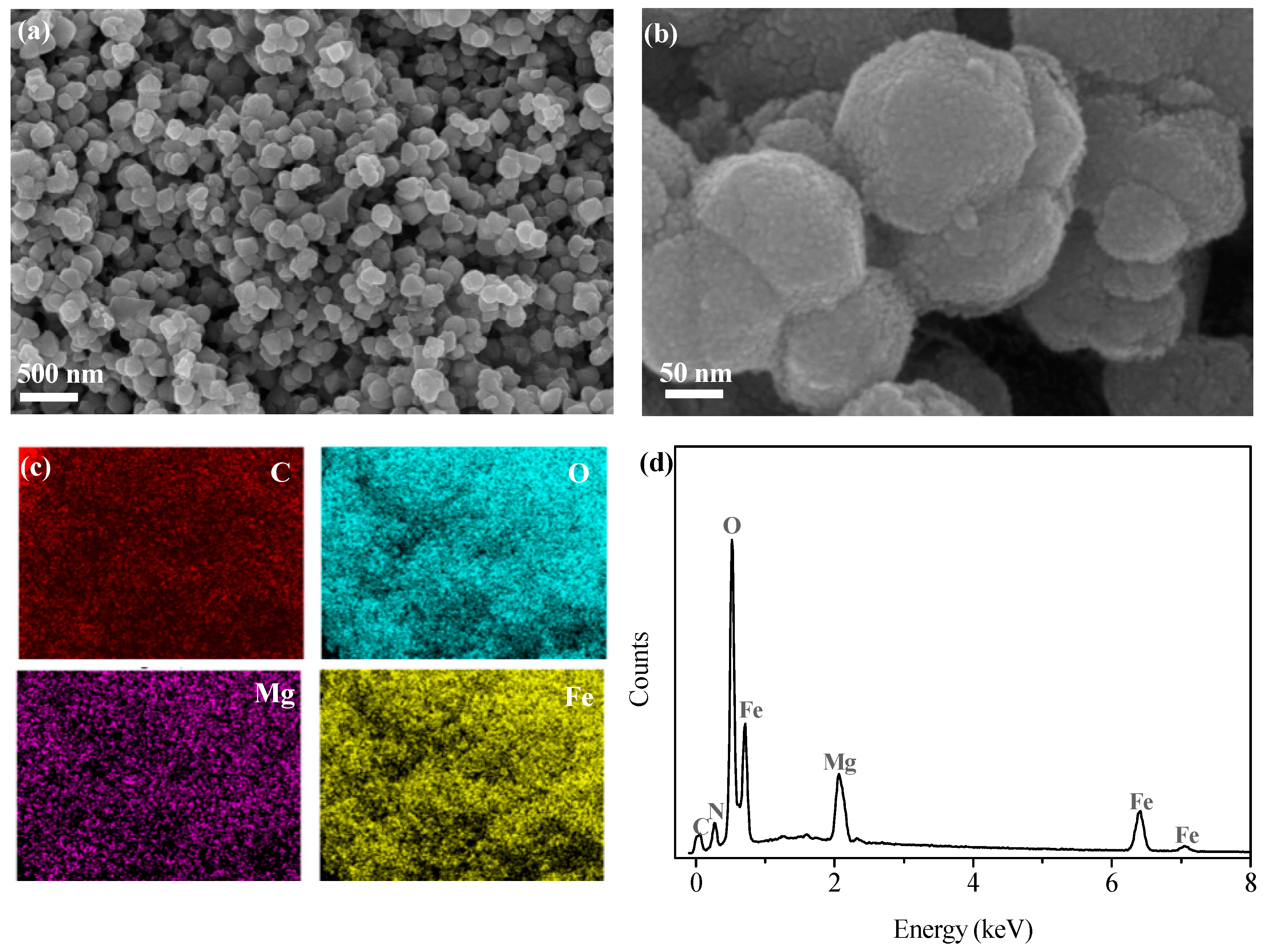
The SEM image of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NP particles, as depicted in Figure 1a, revealed the highly uniform distribution of spherical particles without significantly aggregating into large clusters. The particle size of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NP particles was approximately 50–100 nm. The possible surface modification with GTE and Mg resulted in the rough surface of the absorbent (Figure 1b), which likely increased the specific surface area (SBET) and supplied more active sites for MB adsorption. The EDS image (Figure 1c), along with the corresponding element signals, displayed the highly uniform distribution of C, O, Mg, and Fe elements, which implied the successful loading of GTE and MgO onto the surface of Fe3O4.
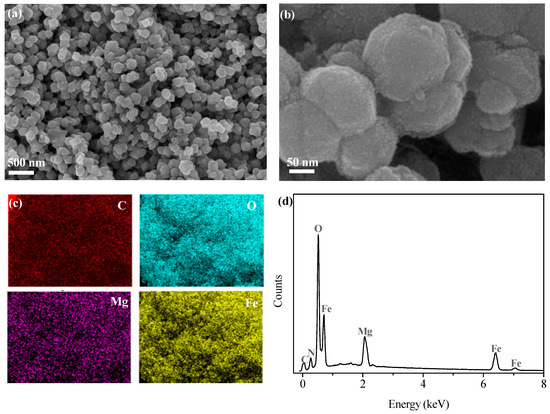
Figure 1.
(a,b) SEM images of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs, (c) EDS mapping image, and (d) spectrum of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs.
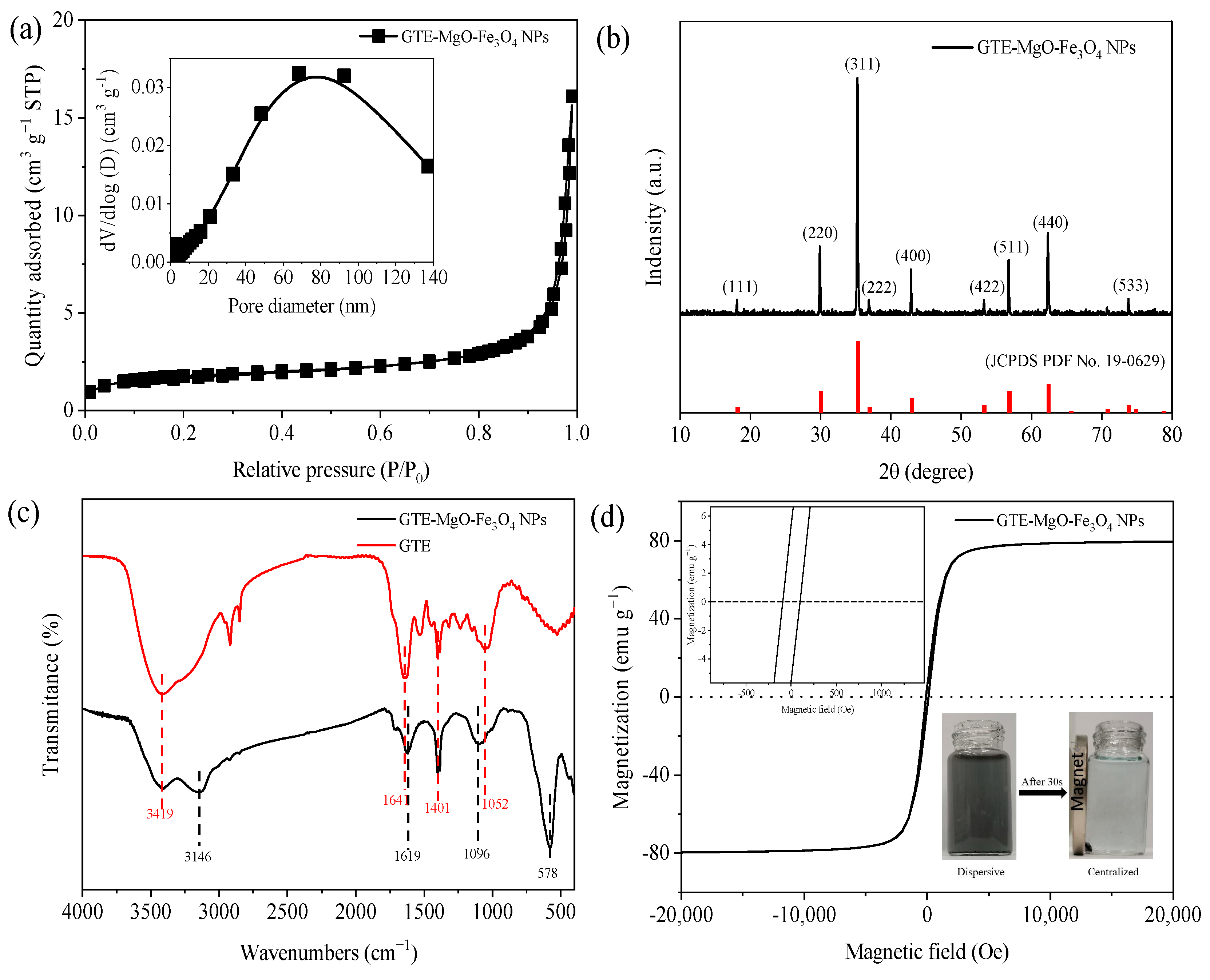
Based on the N2 adsorption–desorption isotherm depicted (Figure 2a), the prepared GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs had an SBET of 36.54 m2 g−1 with an average pore diameter of 10.18 nm. Besides, the bimodal pore size distribution with the predominant pore sizes at around 2.32 and 68.40 nm suggested a complex porous structure that could facilitate efficient adsorption by providing a variety of sites for MB to bind. The crystallinity of the GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs surface was characterized by XRD (Figure 2b). The sharp and intense diffraction peaks represented crystallographic planes (111), (220), (311), (222), (400), (422), (511), (440), and (533), which were well indexed to the crystal structure of Fe3O4 (JCPDS PDF No. 19-0629) [16], indicating that the GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs was possibly endowed with magnetic properties. Furthermore, the presence of Mg1s and Fe2p peaks in the XPS (Figure S1) suggests that MgO and Fe3O4 have been partially bonded to the adsorbent. Notably, no obvious diffraction peaks belonging to organic copolymers and Mg species emerged, which suggested the low content or highly amorphous state of these additives on the GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs surface [17]. Compared with GTE, the peaks assigned to the oxygen-associated functional groups in the range of 940–1750 cm−1 obviously shifted in GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs (Figure 2c) [18]. For instance, the peaks corresponding to C−O (1641 cm−1) and C=C/C=O bonds (1052 cm−1) moved to 1619 and 1096 cm−1, respectively [19,20]. This shift illustrates the complexation reaction that occurs between metal species (such as Fe and Mg) and the oxygen-containing functional groups present in GTE [21]. The novel peak observed at 3146 cm−1 was attributed to the stretching vibration of O−H linked to metal elements, specifically Mg and Fe [22]. The new adsorption detected at 578 cm−1 was related to the stretching vibration of metal–oxygen bonds in Mg−O or Fe−O complexes [23,24], confirming that the Fe/Mg species complexed with the functional groups of GTE by sharing an oxygen atom [25], which resulted in the formation of chelate bonds or bidentate bridge coordination bonds [26]. Magnetic field-dependent behavior of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs was measured by VSM, and the result (Figure 2d) revealed a narrow S-shaped hysteresis loop with negligible remanence and coercivity, exhibiting the distinctive features of magnetic Fe3O4. Thus, although the modification with GTE and MgO likely varied the structure of Fe3O4, GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs still possessed a superparamagnetic characteristic with a high saturation magnetization intensity of 78.16 emu g−1, which assisted its effective dispersion in the aqueous solution to adsorb MB and also facilitated its magnetic separation under an external magnetic field. Furthermore, the point of zero charge (pHpzc) of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs determined from the zeta potential curve in the pH range of 1 to 11 was ~1.65 (Figure S2, being much lower than that of Fe3O4 (common pHpzc range of 6–8), which was probably ascribed to the high oxygen-containing group on the GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs surface [27].
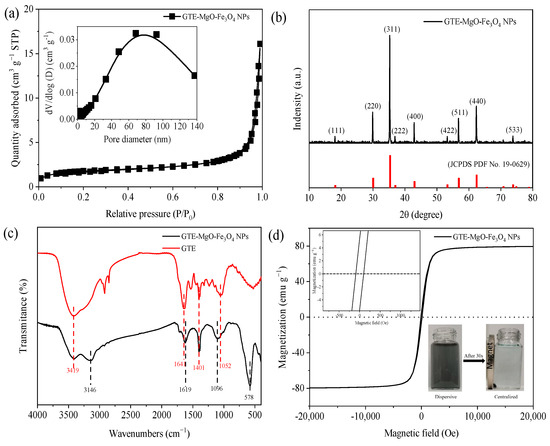
Figure 2.
Characterization analysis: (a) nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherm; (b) XRD pattern; (c) FT-IR spectra; (d) magnetic field-dependent behavior of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs.
3.2. Influencing Factors
3.2.1. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage
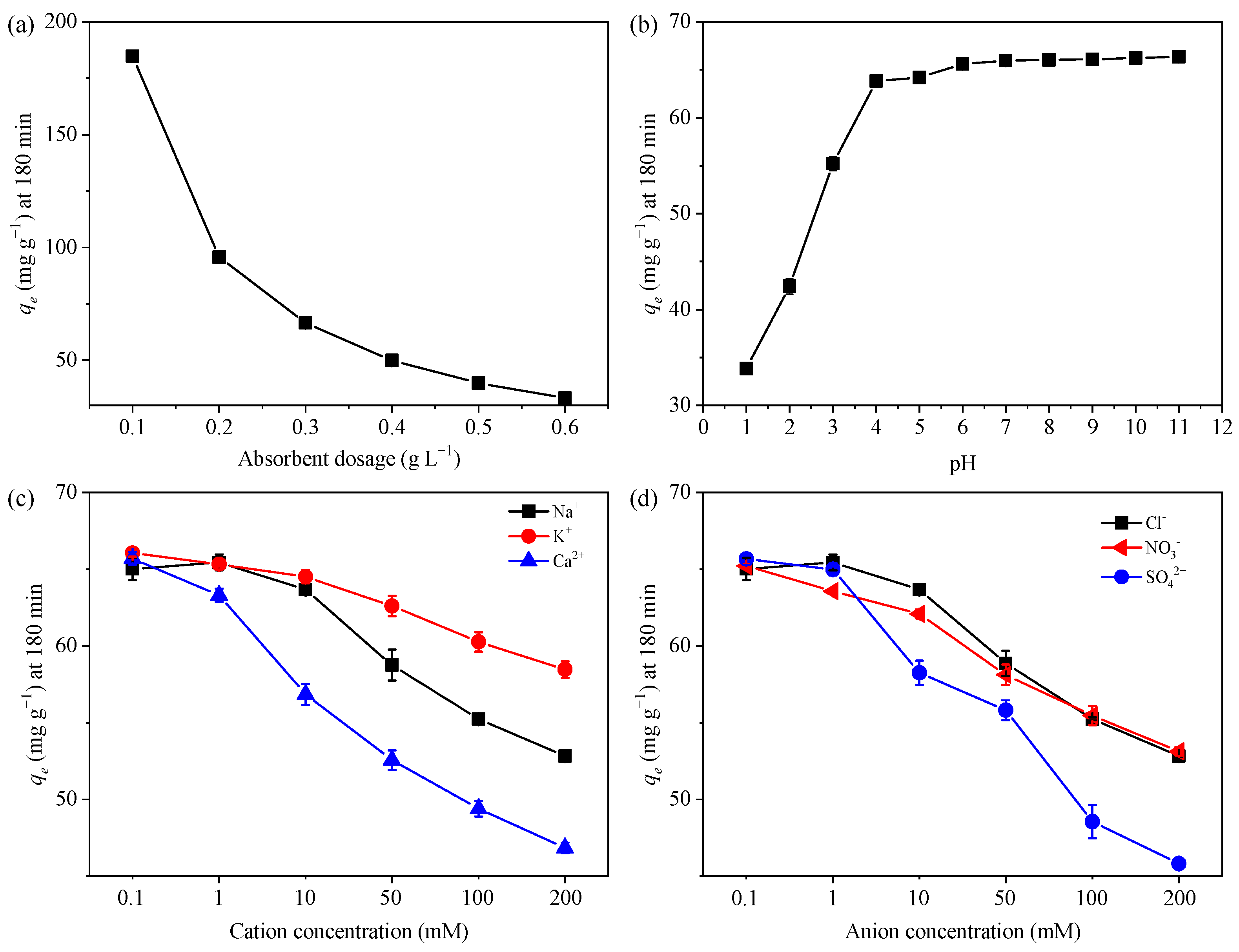
The MB adsorption at different dosages of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs was displayed in Figure 3a. As the quantity of adsorbent was gradually increased to ≥0.3 g L−1, the removal efficiency rose steadily to exceed 99.8%. This significant enhancement can be attributed to the augmented adsorption sites provided by the elevated amount of adsorbent used. Nevertheless, the adsorption capacity generally dropped when the adsorbent dosage increased, suggesting the insufficient utilization of overdosing adsorbent. Given the high removal efficiency and economy, 0.3 g L−1 of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs was appropriately employed in the following experiments.
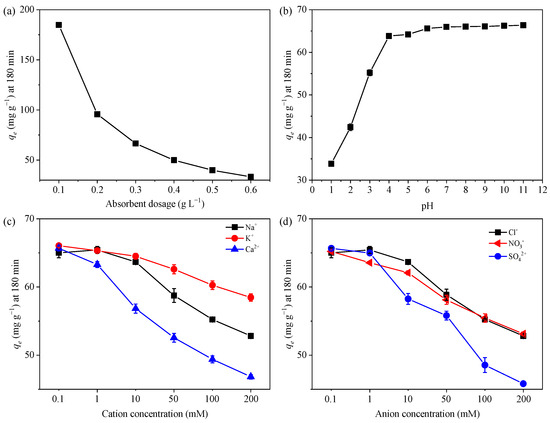
Figure 3.
Effect of (a) adsorbent dosage (0.1–0.6 g L−1), (b) pH (1–11), (c) cations (0.1–200 mM Na+, K+, and Ca2+), and (d) anions (0.1–200 mM Cl−, NO3−, and SO42−) on the MB adsorption by GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs, respectively. General conditions: [GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs] = 0.3 g L−1, [MB] = 20 mg L−1, pH0 = 6.0, temperature = 298.15 K, contact time = 180 min.
3.2.2. Effect of pH
The solution pH was widely considered a pivotal factor that impacts the adsorption process, primarily because it significantly altered the adsorption–desorption interaction by modifying the surface charge of the adsorbent [28]. As presented in Figure 3b, the adsorption capacity increased to reach a plateau with the increment of the initial solution pH from 1 to 11. The hydrolysis of the functional groups (e.g., hydroxyl (-OH) and carboxyl (-COOH)) was highly pH-dependent, resulting in the variation of the adsorbent surface charge in a specific range of pH, which in turn altered the adsorption–desorption interaction [29]. When the pH exceeded the point of zero charge (pHpzc), deprotonation of the surface groups took place, resulting in a powerful electrostatic attraction between the negatively charged surface of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs and the positively charged MB cations. Meanwhile, the enhanced deprotonation of potential active sites (e.g., OH) at higher pH endowed GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs with a strong affinity for MB fixation [17]. Conversely, when the pH was less than the point of zero charge (pHpzc), the positively charged surface hindered the adsorption capacity of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs for MB because of intense electrostatic repulsion. Additionally, under more acidic conditions, the elevated concentration of H+ ions in the solution amplified the rivalry between H+ and MB for the active sites on the adsorbent’s surface, thereby reducing the adsorption capacity as well (33.83 mg g−1 at pH 1) [6]. Regardless, at a pH of 4 or higher, both the adsorption capacity and removal efficiency exceeded 64 mg g−1 and 98%, respectively. This suggests that GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs hold promise for the broad application of MB removal across a wide pH range.
3.2.3. Effect of Coexisting Ions
The influence of coexisting ions on the MB adsorption by GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs was also evaluated by adding coexisting cations (i.e., Na+, K+, and Ca2+) and anions (i.e., Cl−, NO3−, and SO42−). Among these ions (Figure 3c,d), the positively charged cations seemed to be more adverse to the MB adsorption compared with the negatively charged anions. This difference might be explained by the fact that cations and MB competitively occupy similar sporting sites [30]. It has been reported that high ionic strength could significantly disrupt physisorption or the formation of outer-sphere complexes because the increased ions in solution competed for adsorption sites on the surface and screened the electrostatic interactions between the adsorbent and adsorbate. However, the adsorption capacity just decreased to >50 mg g−1 even in the presence of 0.1 to 200 mM Na+ and Cl− ions, which implied that the adsorption process encompassed not just weaker physical interactions (physisorption) but also stronger chemical bonding between the adsorbate and the adsorbent, referred to as chemisorption [3].
3.3. Effect of Contact Time and Initial MB Concentration: Adsorption Kinetics
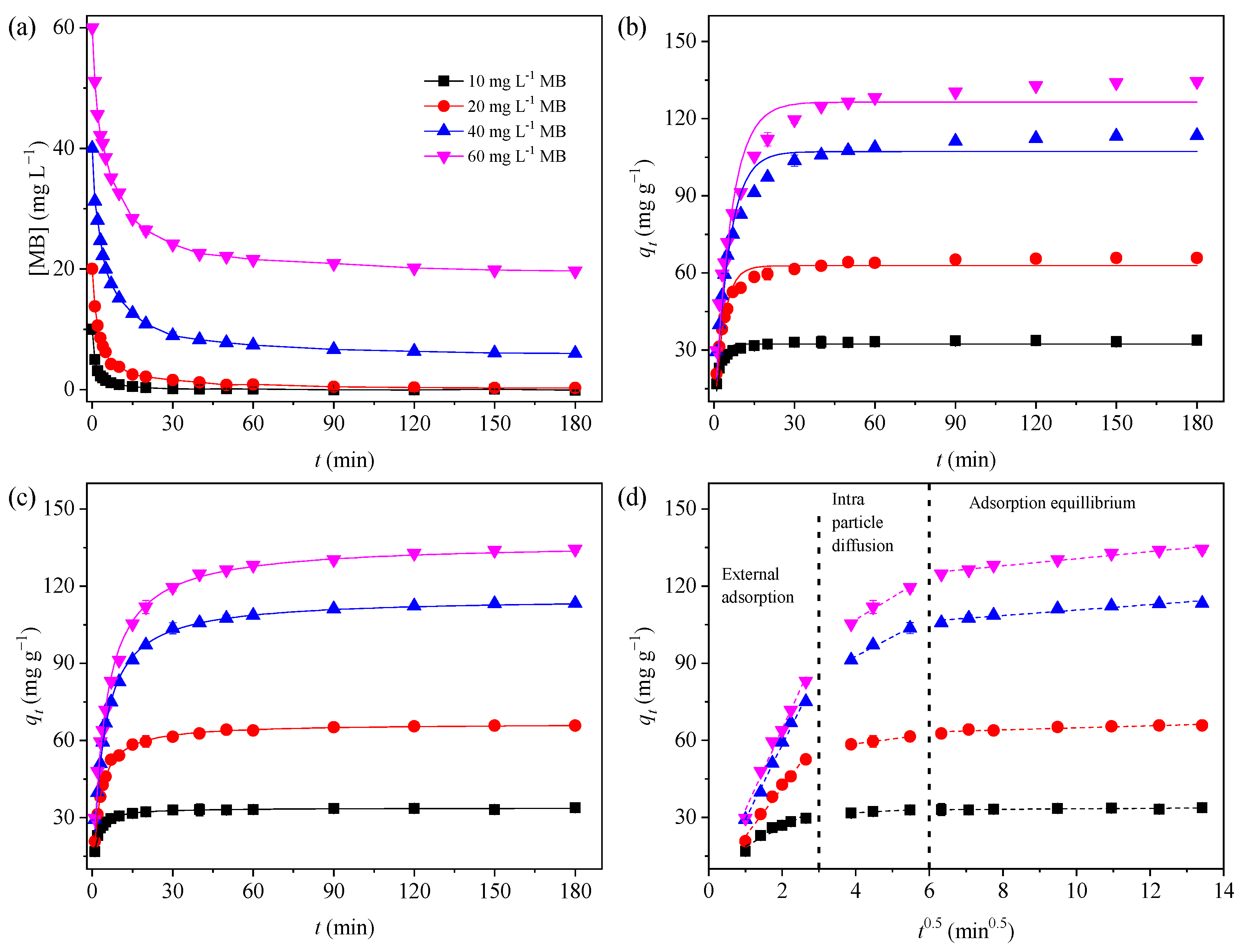
The kinetics curve for the MB adsorption on the GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs over time at various initial MB concentrations (10–60 mg L−1) was investigated, and results were presented in Figure 4a. GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs exhibited an effective and rapid MB removal capability, resulting in less than 1.0% of MB remaining in the processed solution within a 180-minute timeframe, provided that the initial MB concentration was ≤20 mg L−1. With the increment of MB concentration to ≥40 mg L−1, the removal efficiency dropped to a certain extent, which indicated that the fixed dosage of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs at 0.3 g L−1 could not supply enough adsorption sites for the removal of too high-concentrated MB (e.g., ≥40 mg L−1). Notably, the MB adsorption operated rapidly in the first 5 min of contact time because of the abundance of unused binding sites, achieving about 60% of the maximum adsorption capacity. Subsequently, the MB adsorption gradually slowed down with prolonged contact time and eventually reached adsorption equilibrium at ≥150 min of contact time. The observed slowdown stage could be explained by (i) the gradual drop in the concentration gradient between the solution and adsorbent or (ii) the ongoing surface available adsorption site saturation, which most likely causes the repulsive forces among the adsorbed MB [31]. Moreover, to delineate the adsorption kinetics, the adsorption data was fitted with both the PFO and PSO models (Figure 4b,c) [30]. The kinetic parameters derived from these fittings are enumerated in Table S1. In contrast to the PFO model, the PSO model exhibited superior fitting correlation coefficients (R2 ≥ 0.99). Additionally, the qe values computed using the PSO model aligned more closely with the experimental qe values across all examined initial MB concentrations. Hence, the PSO model provided a more precise description of the adsorption kinetic data than the PFO model. This suggests that the adsorption of MB by GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs might involve physisorption or electron exchange between the adsorbate and the adsorbent [6]. Additionally, the rate constant (k2) gradually decreased with the increment of the initial concentration of MB, which might be caused by the stronger mass transfer resistance at higher MB concentrations [32].
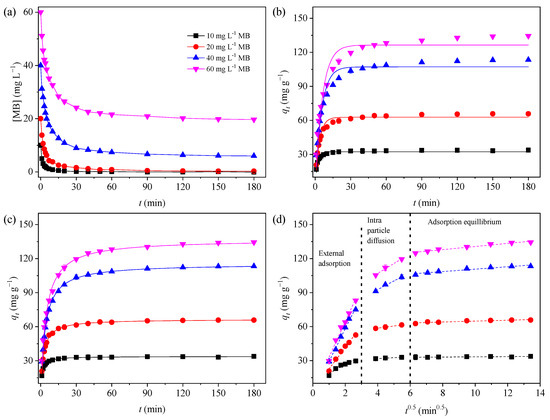
Figure 4.
Adsorption kinetic data (a) and their fitted models of MB to GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs: (b) PFO, (c) PSO, and (d) Intra-Particle Diffusion models. Conditions: [GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs] = 0.3 g L−1, [MB] = 10–60 mg L−1, pH0 = 6.0, temperature = 298.15 K.
To further understand the mechanism and the rate-limited phase of the MB adsorption process by GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs, the Intra-Particle Diffusion model was chosen to fit the adsorption kinetic data. As seen in Figure 4d, the MB adsorption process at all tested initial MB concentrations could be linearly fitted to three different stages. The first stage (external mass transfer) was the rate-controlling step with the rapid adsorption of MB from the bulk solution to the adsorbent surface, leading to the saturation of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs surface adsorption sites, which was associated with boundary diffusion [33]. Then, the rapid adsorption of MB on the adsorbent surface expanded the diffusion barrier, resulting in a slow intra-particle diffusion stage [30]. Subsequently, the following MB adsorption was strongly limited by the pronounced mass transfer resistance and the boundary layer effects, which further curtailed the diffusion of MB into the internal pores of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs [29]. Moreover, none of the fitting curves intersected the origin of the coordinate system, indicating that the adsorption behavior was not solely governed by intra-particle diffusion. Besides, it was probably influenced by both liquid film diffusion and surface adsorption mechanisms [34]. Furthermore, as the initial MB concentration increased, the diffusion rate constants for both the first and second stages augmented, suggesting that the interaction between the adsorbent and adsorbate intensifies at elevated MB concentrations due to a powerful mass transfer driving force. Similarly, the rate constant for the adsorption equilibrium phase rose with an increase in the initial MB concentration, signifying that a longer contact duration was necessary to attain adsorption equilibrium at higher MB concentrations.
3.4. Effect of Initial MB Concentration and Temperature: Adsorption Isotherms
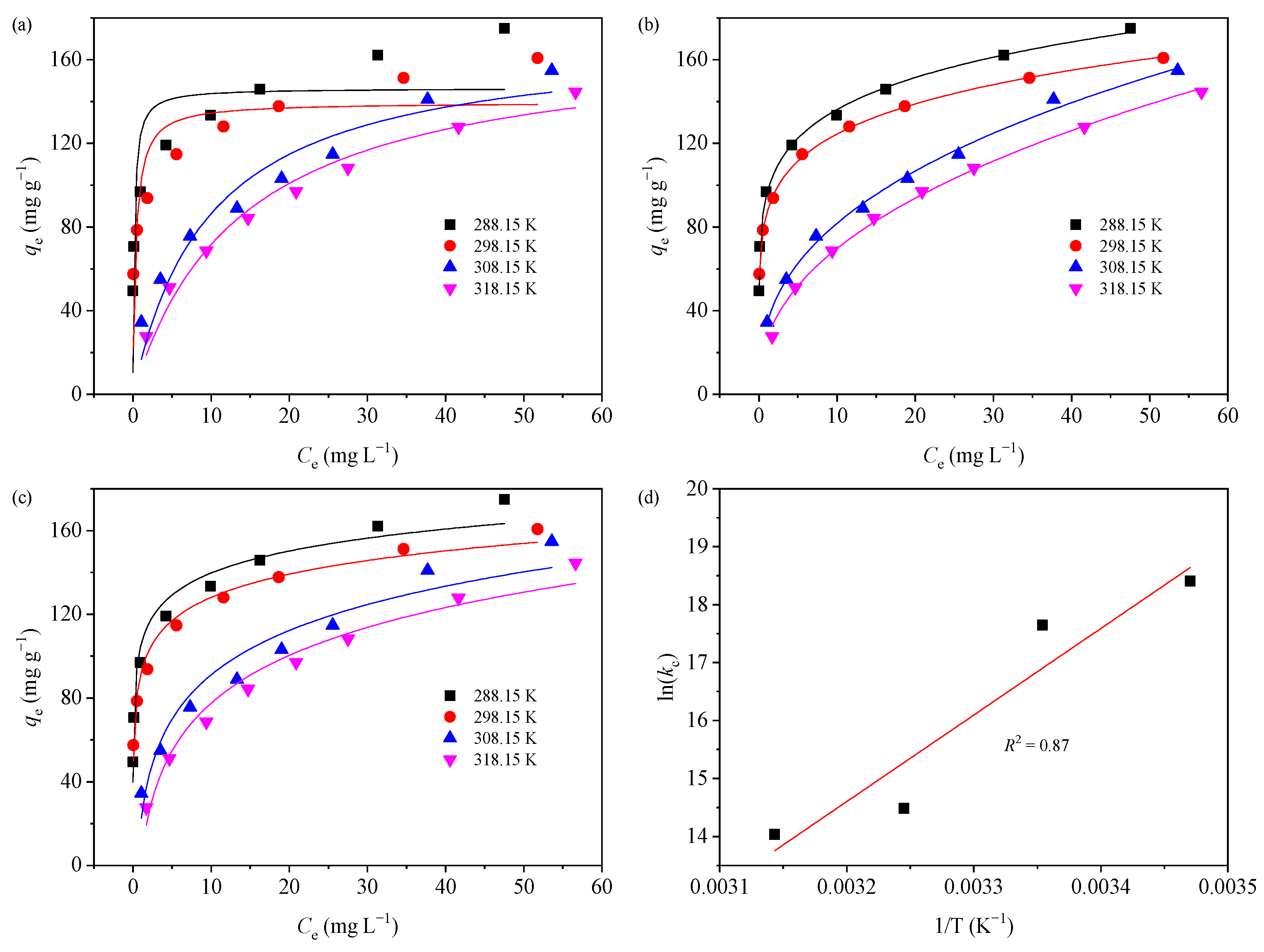
The adsorption behavior of MB (10–100 mg L−1) on GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs at four different reaction temperatures (288.15, 298.15, 308.15, and 318.15 K) was explored. The adsorption capacity rose at all tested temperatures, as illustrated in Figure 3a, in response to an increase in initial MB concentrations. This phenomenon may be explained by a larger concentration gradient between the adsorbent and bulk solution at higher MB concentrations, which increases MB mass transfer at the liquid–solid interface [9]. At the peak initial MB concentration (100 mg L−1), the experimental adsorption capacity recorded at 288.15 K stood at 174.93 mg g−1. Nevertheless, as the reaction temperature rose from 298.15 to 318.15 K, the adsorption capacity diminished. For example, at the peak initial MB concentration (100 mg L−1), the experimental adsorption capacity recorded at 288.15 K stood at 174.93 mg g−1. However, this progressively fell to 160.75 mg g−1 at 298.15 K, 154.79 mg g−1 at 308.15 K, and 144.59 mg g−1 at 318.15 K, respectively.
In order to gain additional insight into the behavior of adsorption, three isotherm models, including the Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin models, were fitted to the experimental adsorption data at various reaction temperatures (Table 1). The fitting curves were presented in Figure 5a–c, and the related isotherm parameters were listed in Table S2. According to the R2 values for different isotherm models, the experimental adsorption data at various temperatures were better described by the Freundlich model compared to the Langmuir model, indicative of the multilayer adsorption of MB molecules on the heterogeneous GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs surface [35]. The large amplitude of the Freundlich exponent (n) was often used to assess the degree of favorability of the adsorption process [36]. All the obtained n values were in the range of 1–10, evidencing that GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs were favorable and useful for adsorbing MB at various temperatures. Notably, the Temkin model also well described the adsorption data at different temperatures with all R2 ≥ 0.94, also indicating the multilayer adsorption for MB removal on the GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs surface [30]. Further, the heat of adsorption (bT) obtained from the Temkin model was all > 1 and gradually decreased with the increment of reaction temperature, implying an exothermic process for the MB adsorption by GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs [30].
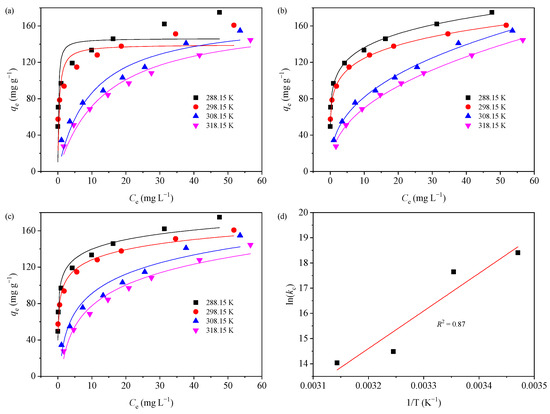
Figure 5.
Isotherm analysis of MB adsorption on GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs: (a) Langmuir, (b) Freundlich, and (c) Temkin models; (d) Van’t Hoff’s diagram. Conditions: [GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs] = 0.3 g L−1, [MB] = 10–100 mg L−1, pH0 = 6.0, temperature = 288.15–318.15 K, contact time = 20 h.
In order to ascertain the spontaneity and character of the adsorption behavior, the Van’t Hoff Equation Equations (2)–(4) were used to compute the thermodynamic parameters [30], which comprised Gibbs free energy (ΔG0, kJ mol−1), enthalpy change (ΔH0, kJ mol−1), and entropy change (ΔS0, kJ mol−1).
where kc (L g−1) is the thermodynamic equilibrium constant; C0 (mol L−1) is the standard concentration; Madsorbate is the molecular weight of MB; and γ is the coefficient of activity.
ΔG0 = −RTlnkc
lnkc = −ΔH0/RT + ΔS0/R
kc = kL × Madsorbate × 103 × C0/γ
The values of ΔG0, ΔH0, and ΔS0 (Table S3) were calculated based on the slopes and intercepts derived from the plot of lnkc vs. 1/T (Figure 5d). The negative ΔG0 values suggested that the adsorption of MB onto GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs is a favorable and spontaneous process. The reduction in the absolute value of ΔG0 with the up-regulation of reaction temperature indicated that the MB removal by GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs operated through an exothermic adsorption process, which was further supported by the negative ΔH0 value. This was probably ascribed to the complex interplay between the MB and the assorted surfaces of the adsorption sites [27]. Furthermore, the negative ΔS0 value indicated a reduction in randomness at the solid–liquid interface throughout the adsorption process [30].
3.5. Desorption of MB and Recyclability of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs
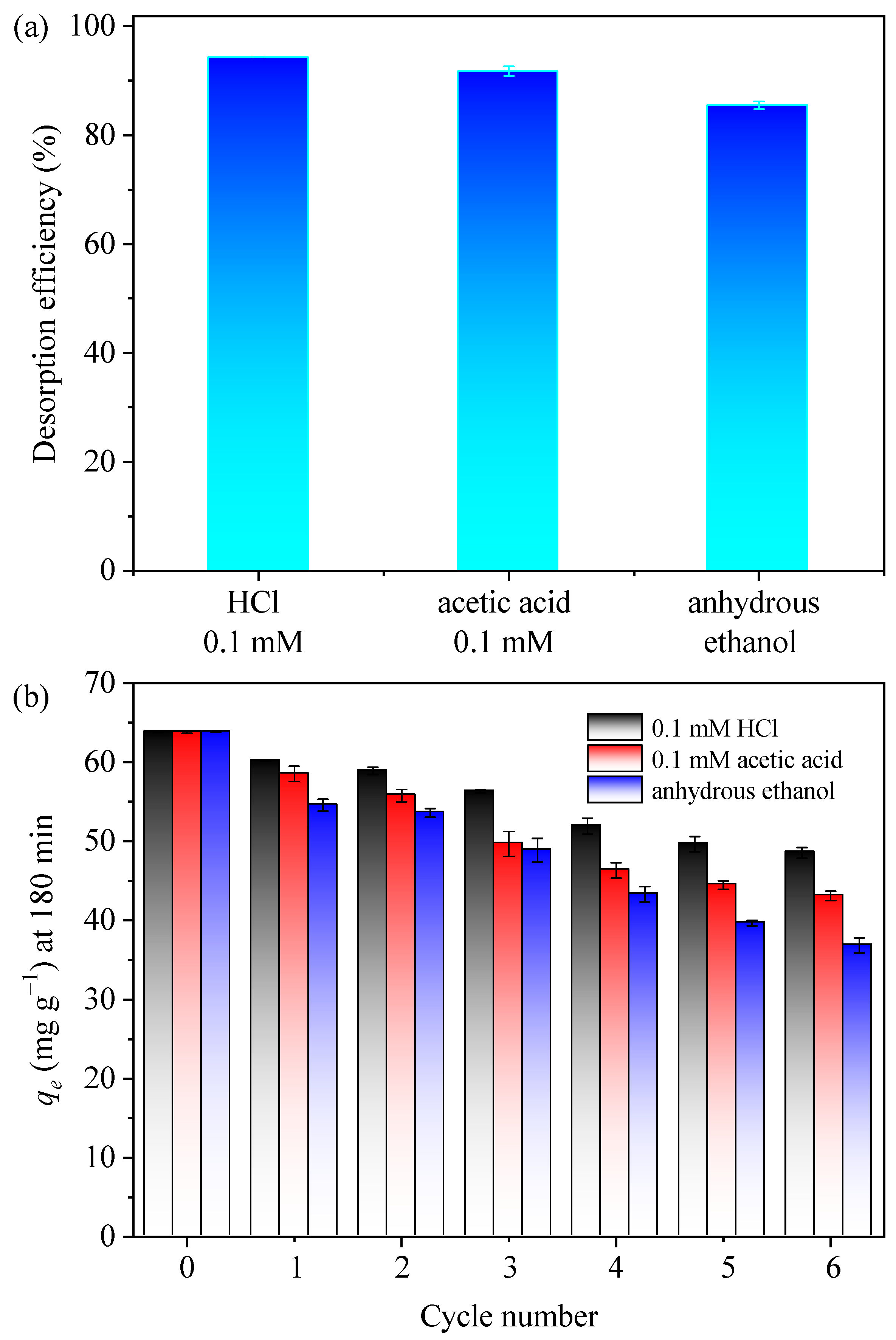
As stability and recyclability were the critical factors in assessing the environmental and economic viability of adsorbents, we first adopted three kinds of common eluents, including 0.1 mM HCl, 0.1 mM acetic acid, and anhydrous ethanol, in the desorption experiments, and the desorption efficiency (the ratio of the desorbed MB over the adsorbed MB) is presented in Figure 6a. The desorption efficiencies were found to be 94.3%, 91.7%, and 85.5% for 0.1 mM HCl, 0.1 mM acetic acid, and anhydrous ethanol, respectively, demonstrating that all three eluents were capable of effectively desorbing MB, with 0.1 mM HCl exhibiting the highest efficiency, followed by acetic acid and then anhydrous ethanol. Therefore, all three eluents were further employed in the cycles of the adsorption–desorption process (Figure 6b). Regenerating the used adsorbent with anhydrous ethanol led to a notable reduction in adsorption capacity, which was probably attributed to its relatively inferior efficiency in desorbing chemically bonded MB. Meanwhile, the desorption of MB using acetic acid involved a competitive complexation mechanism, which led to a gradual decline in the number of available adsorption sites as the frequency of desorption cycles increased, consequently resulting in a substantial diminishment of the adsorptive capacity. Since the adsorption capacity dwindled with decreasing pH (Figure 3b), indicating an acidic condition (lower than the pHpzc) created by 0.1 mM HCl could efficiently desorbed the MB from the used GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs. As shown in Figure 6b, despite a gradual reduction in the MB adsorption capacity of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs with each adsorption–desorption cycle when using a 0.1 mM HCl solution, the remaining adsorption capacity was more than 48.5 mg g−1 after six cycles, and the adsorption regeneration efficiency was 76.10% when compared to the initial adsorption (the 0th cycle). After six cycles, the adsorption capacities of the other two resolving solutions were slightly lower, at 43.09 mg g−1 for 0.1 mol L−1 CH3COOH and 36.82 mg g−1 for anhydrous ethanol. These findings indicated the effective separation of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs without any appreciable loss of adsorbent mass using a magnetic field and demonstrated the ease of reuse with efficient MB removal when employing a 0.1 mM HCl solution as the eluent.
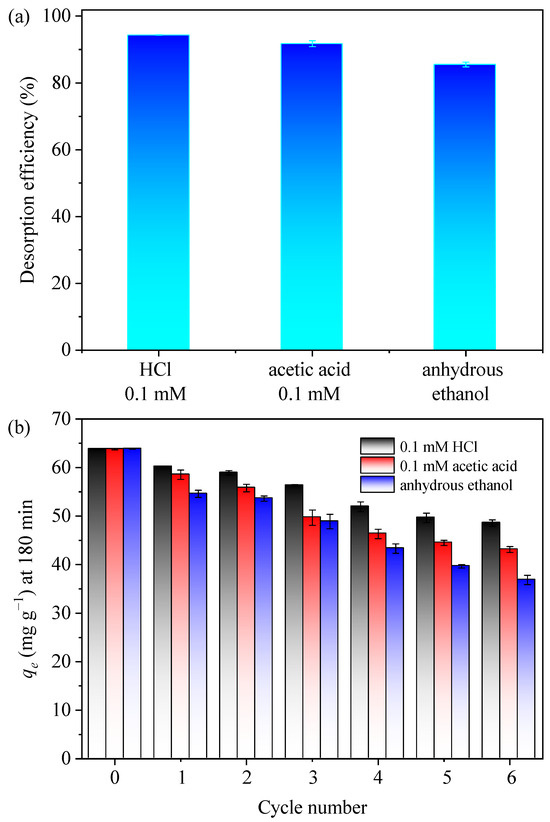
Figure 6.
(a) desorption performance with different eluents (0.1 mM HCl, 0.1 mM acetic acid, or anhydrous ethanol); (b) adsorption capacity of used GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs that was regenerated by 0.1 mM HCl, 0.1 mM acetic acid, and anhydrous ethanol, respectively. Conditions: [GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs] = 0.3 g L−1, [MB] = 20 mg L−1, pH0 = 6.0, temperature = 298.15 K, contact time = 180 min.
3.6. Comparison with the Literature
To assess the performance of Fe3O4@GT@Mg NPs for the adsorption of MB removal, a comparison was made with other adsorbents that have been reported for the same purpose, including biomass matrix adsorbents, magnetic nanocomposite adsorbents, and biomass-based magnetic nanocomposite adsorbents (Table S4) [37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44]. The results illustrated the Fe3O4@GT@Mg NPs’ high removal rate and adsorption capacity, which were generated throughout the current testing. In addition, Fe3O4@GT@Mg NPs were produced in an environmentally responsible way and exhibited exceptional magnetic separation properties. They may, therefore, considerably reduce the pollution that adsorbents release into the environment both during their manufacture and use. As a result, Fe3O4@GT@Mg NPs were efficient adsorbents for removing MB from wastewater.
4. Conclusions
In this study, a modified magnetic adsorbent named GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs was successfully fabricated by impregnating GTE and Mg species onto the surface of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Its efficacy in removing MB from aqueous solutions has been documented. Characterization analyses confirmed that the resultant GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs possessed robust magnetic properties and an abundance of surface functional groups. Batch adsorption experiments illustrated that GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs could effectively adsorb MB over a relatively broad pH range (pH ≥ 4). The MB adsorption behavior exhibited a moderate sensitivity to high ionic strength, implying that both physisorption and chemisorption contributed to the overall adsorption process. Further investigation into the adsorption kinetics and isotherms highlighted chemisorption as the predominant mechanism for MB adsorption by GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs, which was noted for its exothermic characteristics. The adsorption capacity of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs for MB, as determined experimentally, surpassed 174.93 mg g−1. This value outweighed the adsorption capacities exhibited by numerous other adsorbents. Moreover, GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs demonstrated exceptional stability and regenerative capabilities, maintaining over 76% of its initial adsorption capacity even after six cycles of adsorption–desorption. In summary, GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs are excellent green adsorbents for methylene blue removal, and their environmentally friendly production broadens the range of adsorbent materials available and offers a new approach to plant resource utilization. Our future work will be more concentrated on the mechanism analysis (for example, the predominated functional groups for MB fixation) and the further optimization of other synthesis conditions (for example, the amounts of added GTE, MgSO4, and NaOAc).
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/magnetochemistry10050031/s1. Text S1: Characterization Techniques; Figure S1: The XPS fully scanned spectra of GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs.; Figure S2: Zeta potential curve for GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs; Table S1: Kinetic model parameters for the MB adsorption by GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs; Table S2: Isotherm model parameters for the MB adsorption by GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs; Table S3: Thermodynamic parameters for MB adsorption by GTE-MgO-Fe3O4 NPs; Table S4: The maximum adsorption capacities (qmax) of various adsorbents for MB.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.L. and W.D.; methodology, Y.H.; software, S.L.; validation, W.L., H.L. and H.Z.; formal analysis, H.Z.; investigation, H.L.; resources, W.D.; data curation, W.L.; writing—original draft preparation, H.L.; writing—review and editing, W.D.; visualization, Y.H.; supervision, H.Z.; project administration, H.L.; funding acquisition, W.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 52370161) and the Natural Science Foundation of the Chongqing Science & Technology Commission (grant number CSTB2022NSCQ-MSX1430).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All the data used in this study are available within this article. Further inquiries can be directed to the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Forgacs, E.; Cserhati, E.; Oros, G. Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: A review. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 953–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moharrami, P.; Motamedi, E. Application of cellulose nanocrystals prepared from agricultural wastes for synthesis of starch-based hydrogel nanoNPs: Efficient and selective nanoadsorbent for removal of cationic dyes from water. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 313, 123661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eren, M.A.; Arslanoğlu, H.; Çiftçi, H. Production of microporous Cu-doped BTC (Cu-BTC) metal-organic framework composite materials, superior adsorbents for the removal of methylene blue (basic blue 9). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.J.; Ashiq, M.N. Adsorption of dyes from aqueous solutions on activated charcoal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 139, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazetta, A.L.; Vargas, A.M.M.; Nogami, E.M.; Kunita, M.H.; Guilherme, M.R.; Martins, A.C.; Silva, T.L.; Moraes, J.C.G.; Almeida, V.C. NaOH-activated carbon of high surface area produced from coconut shell: Kinetics and equilibrium studies from the methylene blue adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 174, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Budarin, V.L.; Clark, J.H.; North, M.; Wu, X. Rapid and efficient adsorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution by hierarchically porous, activated starbons®: Mechanism and porosity dependence. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagub, M.T.; Sen, T.K.; Afroze, S.; Ang, H.M. Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Tan, X.; Liu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Hu, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, B. Production of biochars from ca impregnated ramie biomass (Boehmeria nivea (L.) Gaud.) and their phosphate removal potential. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 5871–5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wei, Q.; Tian, C.; Li, D.; Li, H.; Qin, G.; Hu, K.; Zhang, Q. Preparation of biomass carbon NPs MgO@ZnO@BC and its adsorption and removal of Cu(II) and Pb(II) in wastewater. Molecules 2023, 28, 6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.J. Synthesis of novel magnesium ferrite (MgFe2O4)/biochar magnetic NPs and its adsorption behavior for phosphate in aqueous solutions. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Shi, B. Conversion of tannery solid waste to an adsorbent for high-efficiency dye removal from tannery wastewater: A road to circular utilization. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thines, K.R.; Abdullah, E.C.; Mubarak, N.M.; Ruthiraan, M. Synthesis of magnetic biochar from agricultural waste biomass to enhancing route for waste water and polymer application: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, R.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y. Polymer-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and methylene blue adsorption. Materials 2018, 11, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.S.; Zhang, L.; Wei, J.; Hou, Y.R.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, S.L.; Jia, Z.F.; Su, X.D. Ultra-efficient and selective adsorption of cationic dyes by Ti-doped SiO2 functionalized hydrophilic Fe3O4 nanoparticles with superior structural stability. J. Water Process. Eng. 2024, 57, 104729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinsene, H.; Bhawawet, N.; Imyim, A. Rice husk biochar doped with deep eutectic solvent and Fe3O4/ZnO nanoparticles for heavy metal and diclofenac removal from water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 339, 126638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifthikar, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, T.; Wang, H.; Khan, A.; Jawad, A.; Sun, T.; Jiao, X.; Chen, Z. Highly efficient lead distribution by magnetic sewage sludge biochar: Sorption mechanisms and bench applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, J.; He, C.; Lyu, W.; Zhang, W.; Yan, W.; Yang, L. Development of rare earth element doped magnetic biochars with enhanced phosphate adsorption performance. Colloid Surf. A 2019, 561, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Wan, C.; Liu, J.; Gao, J.; Yu, F.; Zhang, J.; Cai, Z. Iron nanoparticles in situ encapsulated in biochar-based carbon as an effective catalyst for the conversion of biomass-derived syngas to liquid hydrocarbons. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 1631–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Ho, S.; Huang, X.; Wang, D.; Yang, F.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Cao, X.; Ma, F. Magnetic nanoscale zerovalent iron assisted biochar: Interfacial chemical behaviors and heavy metals remediation performance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 9673–9682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.M.; Mandal, B.K.; Kumar, K.S.; Reddy, P.S.; Sreedhar, B. Biobased Green method to synthesise palladium and iron nanoparticles using terminalia chebula aqueous extract. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 102, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazetta, A.L.; Pezoti, O.; Bedin, K.C.; Silva, T.L.; Junior, A.P.; Asefa, T.; Almeida, V.C. Magnetic activated carbon derived from biomass waste by concurrent synthesis: Efficient adsorbent for toxic dyes. Acs Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1058–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, W.; Feng, L.; Wu, L.; Lv, J.; Du, W. Characteristics and mechanisms of phosphorous adsorption by peanut shell-derived biochar modified with magnesium chloride by ultrasonic-assisted impregnation. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 43102–43110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asilturk, M.; Sayilkan, F.; Arpac, E. Effect of Fe3+ ion doping to TiO2 on the photocatalytic degradation of malachite green dye under UV and Vis-irradiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A-Chem. 2009, 203, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Tiwari, D.; Kim, D. Phosphate adsorption/desorption kinetics and P bioavailability of Mg-biochar from ground coffee waste. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 37, 101484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirtiu, C.M.; Raychoudhury, T.; Ghoshal, S.; Moores, A. Systematic comparison of the size, surface characteristics and colloidal stability of zero valent iron nanoparticles pre- and post-grafted with common polymers. Colloids Surf. A 2011, 390, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Du, Y.; Ma, J. Novel synthesis of carbon spheres supported nanoscale zero-valent iron for removal of metronidazole. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 390, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasannamedha, G.; Kumar, P.S.; Mehala, R.; Sharumitha, T.J.; Surendhar, D. Enhanced adsorptive removal of sulfamethoxazole from water using biochar derived from hydrothermal carbonization of sugarcane bagasse. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.; Zheng, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, X.; Wu, Y.; Xiao, W. Activation of MnFe2O4 by sulfite for fast and efficient removal of arsenic (III) at circumneutral ph: Involvement of Mn (III). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Dong, W.; Zhang, L.; Kong, Q.; Wang, W. Efficient adsorption of sulfamethazine onto modified activated carbon: A plausible adsorption mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, P.; Lei, X.; Taylor, K.; Holmes, W.; Yan, H.; Cao, D.; Zappi, M.E.; Gang, D.D. Evaluation of the adsorption of sulfamethoxazole (SMX) within aqueous influents onto customized ordered mesoporous carbon (OMC) adsorbents: Performance and elucidation of key adsorption mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Hu, X.; Fu, D.; Lam, F.L.Y. Adsorption removal of Acid Black 1 from aqueous solution using ordered mesoporous carbon. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 294, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, N.; Khani, H.; Gupta, V.K.; Amereh, E.; Agarwal, S. Adsorption process of methyl orange dye onto mesoporous carbon material-kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 362, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, H.H.; Demarchi, C.A.; Rodrigues, C.A.; Greneche, J.M.; Nedelko, N.; Ślawska-Waniewska, A. Adsorption of As (III) on chitosan-Fe-crosslinked complex (Ch-Fe). Chemosphere 2011, 82, 278283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, H.J.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Arumugam, T.K.; Radhakrishnan, S.; Vasudevan, D. An efficient removal of crystal violet dye from waste water by adsorption onto tlac/chitosan composite: A novel low cost adsorbent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 96, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Liu, M.; Yuan, B.; He, J.; Wu, P.; Liu, C.; Jiang, W. Separation of vanadium and chromium by selective adsorption by titanium-based microspheres. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Lan, R.; He, L.; Liu, H.; Pei, X. A critical review of adsorption isotherm models for aqueous contaminants: Curve characteristics, site energy distribution and common controversies. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 329, 117104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.K.; Senapati, K.K.; Sarma, K.C. Synthesis of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated with green tea polyphenols and their use for removal of dye pollutant from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2214–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, N.K.; Siddiqui, S.I.; Tara, N.; Hashmi, A.A.; Chaudhry, S.A. Psidium guajava leave-based magnetic nanocomposite γ-FeO@GL: A green technology for methylene blue removal from water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabakaran, E.; Pillay, K.; Brink, H. Hydrothermal synthesis of magnetic-biochar nanocomposite derived from avocado peel and its performance as an adsorbent for the removal of methylene blue from wastewater. Mater. Today Sustain. 2022, 18, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayantong, A.R.B.; Shih, Y.J.; Ong, D.C.; Abarca, R.R.M.; Dong, C.D.; de Luna, M.D.G. Adsorptive removal of dye in wastewater by metal ferrite-enabled graphene oxide nanocomposites. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirak, M.; Abdollahiyan, A.; Eftekhari-Sis, B.; Saraei, M. Carboxymethyl cellulose coated Fe3O4@SiO2 core-shell magnetic nanoparticles for methylene blue removal: Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. Cellulose 2017, 25, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harimu, L.; Wahyuni, S.; Nasrudin, N. Fabrication of chitosan/Fe3O4 nanocomposite as adsorbent for reduction methylene blue contents. Ind. J. Chem. 2022, 22, 878–886. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, J.; Garg, V.K.; Gupta, R.K. Removal of Methylene Blue from aqueous solution by Fe3O4@Ag/SiO2 nanospheres: Synthesis, characterization and adsorption performance. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 250, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Azazy, M.; El-Shafie, A.S.; Yousef, B.A. Green Tea waste as an efficient adsorbent for Methylene Blue: Structuring of a novel adsorbent using full factorial design. Molecules 2021, 26, 6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).