Preparation, Characterization, and Application of Citrate-Functionalized Cobalt-Doped Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Rhodamine Dye and Lead Ion Sequestration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis, Surface Functionalization, and Characterization of the Co-Doped Iron Oxide MNPs
2.3. Rhodamine B and Lead (II) Ions Removal Using the Citrate-Functionalized MNPs
3. Results and Discussions
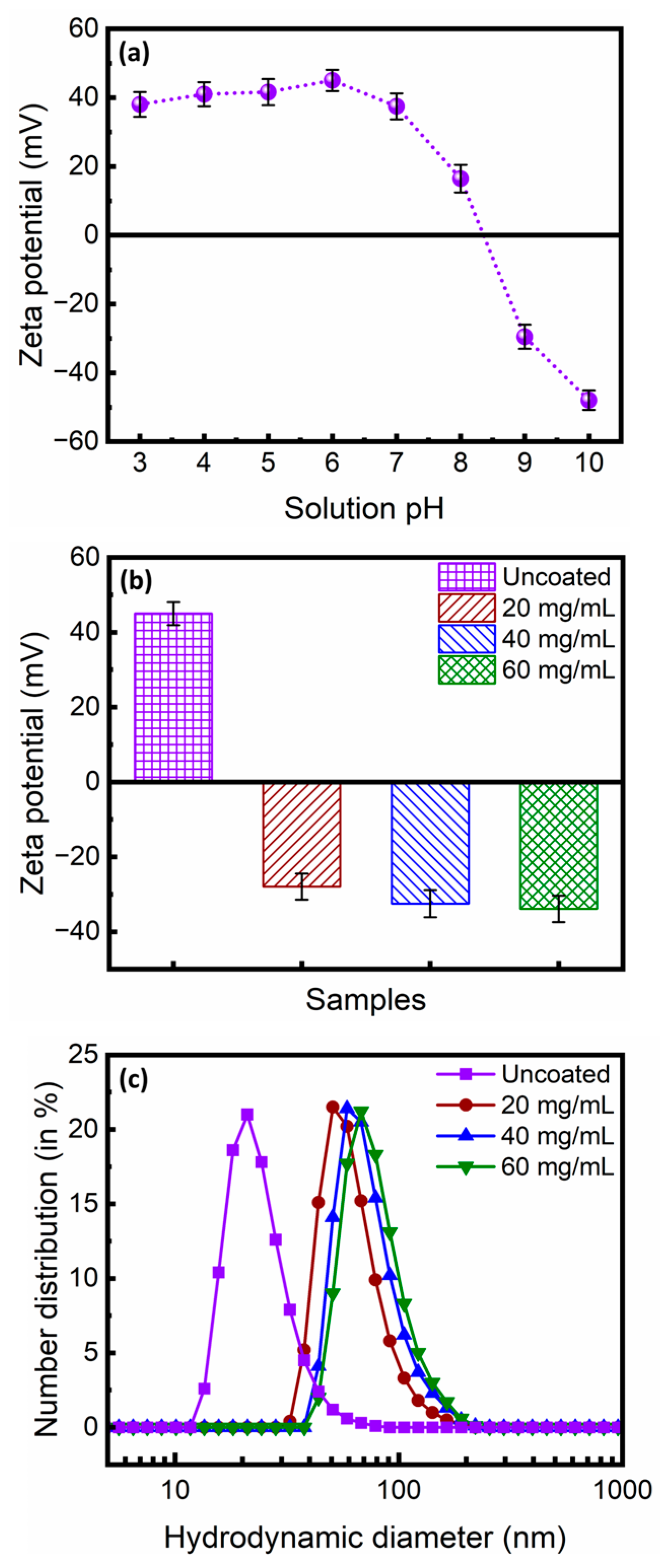
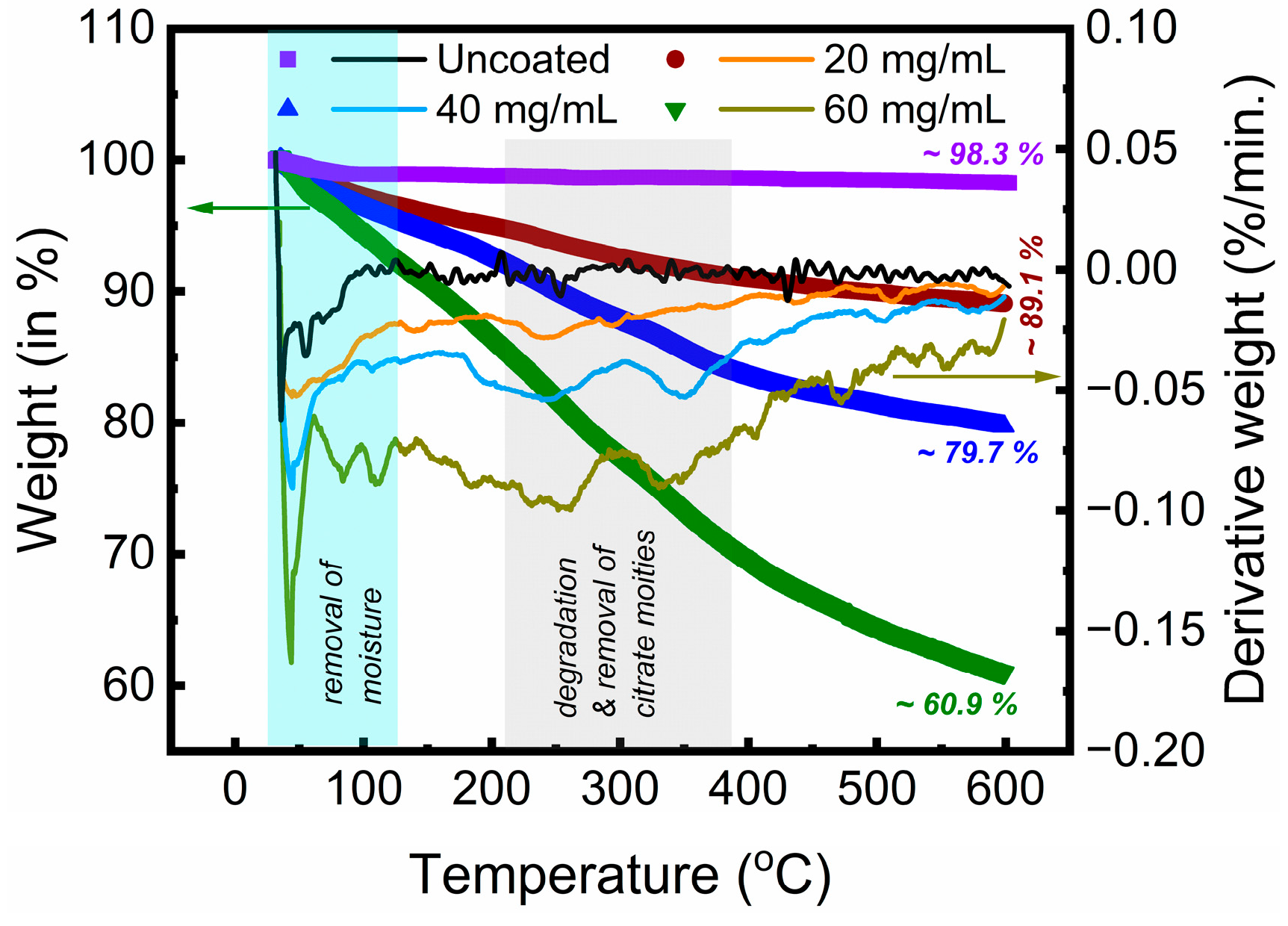
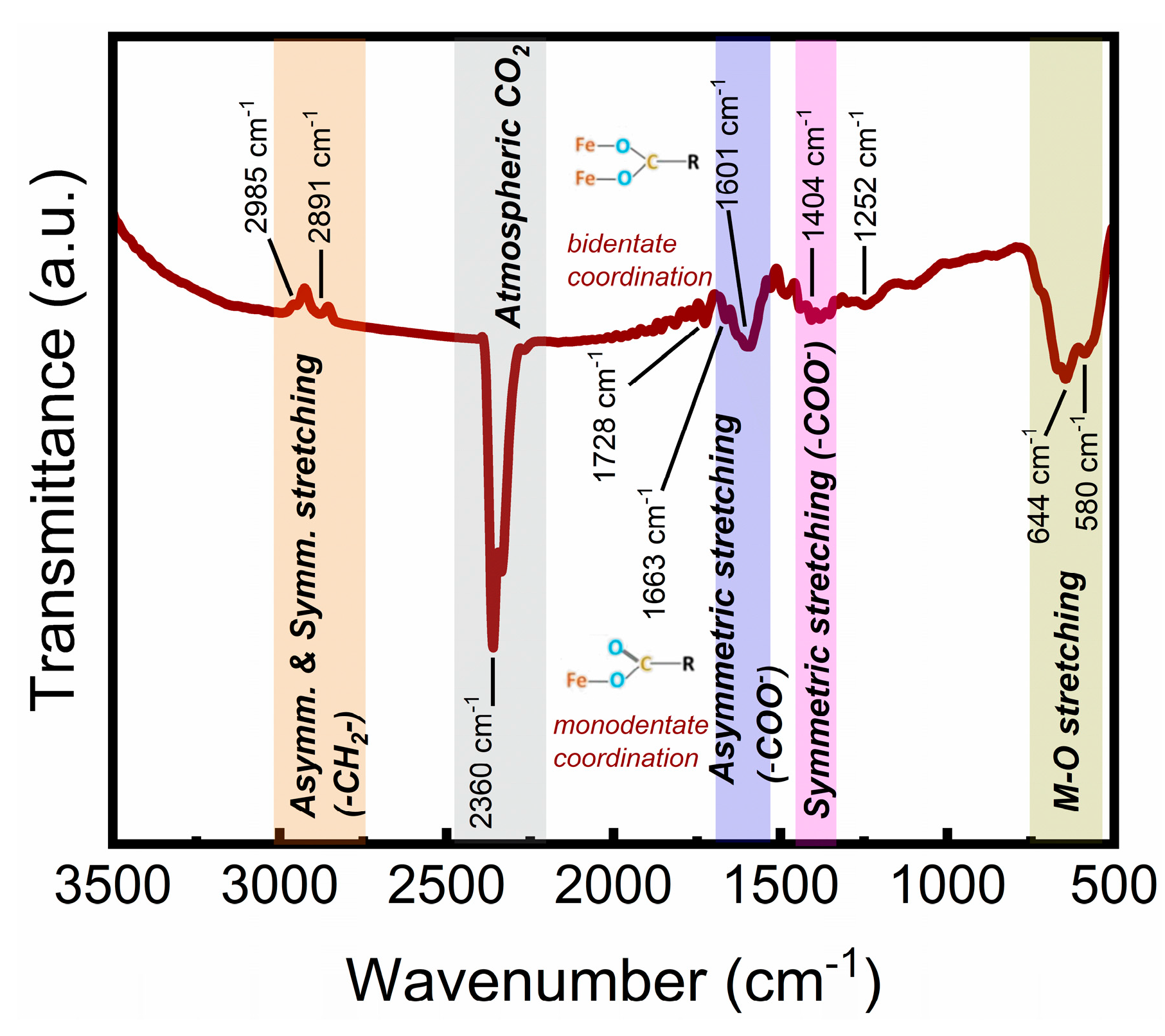
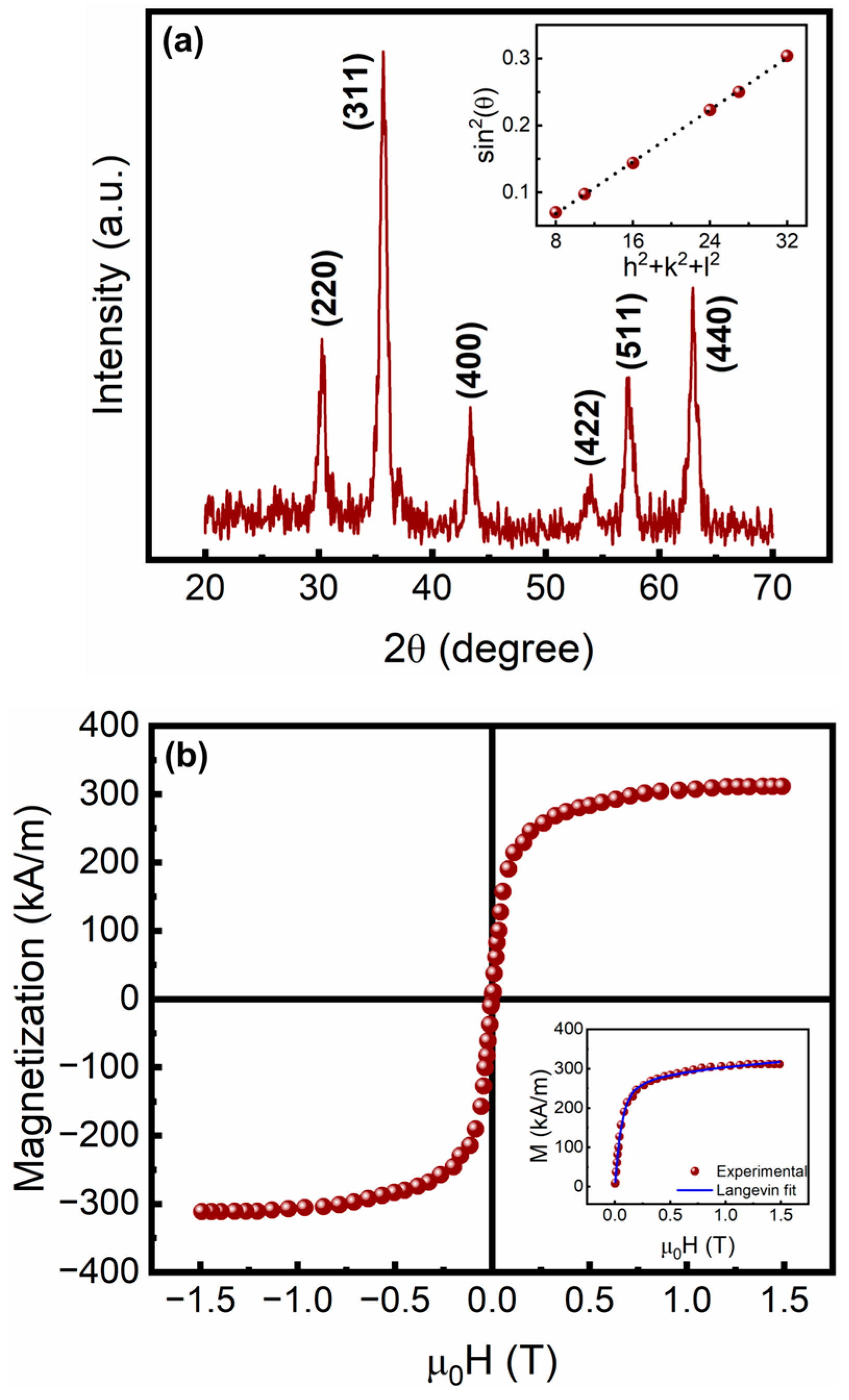
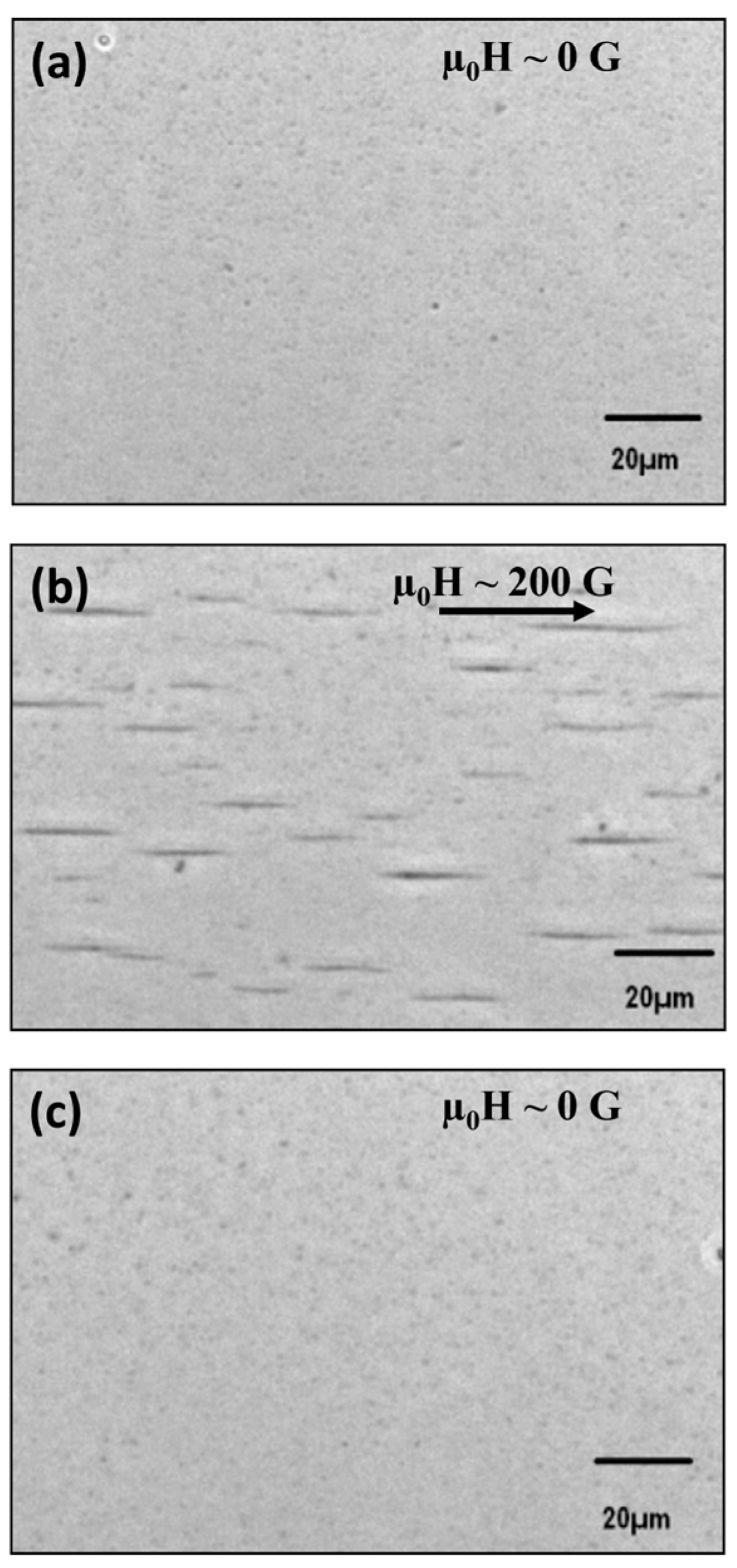
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of the Citrate-Functionalized MNPs
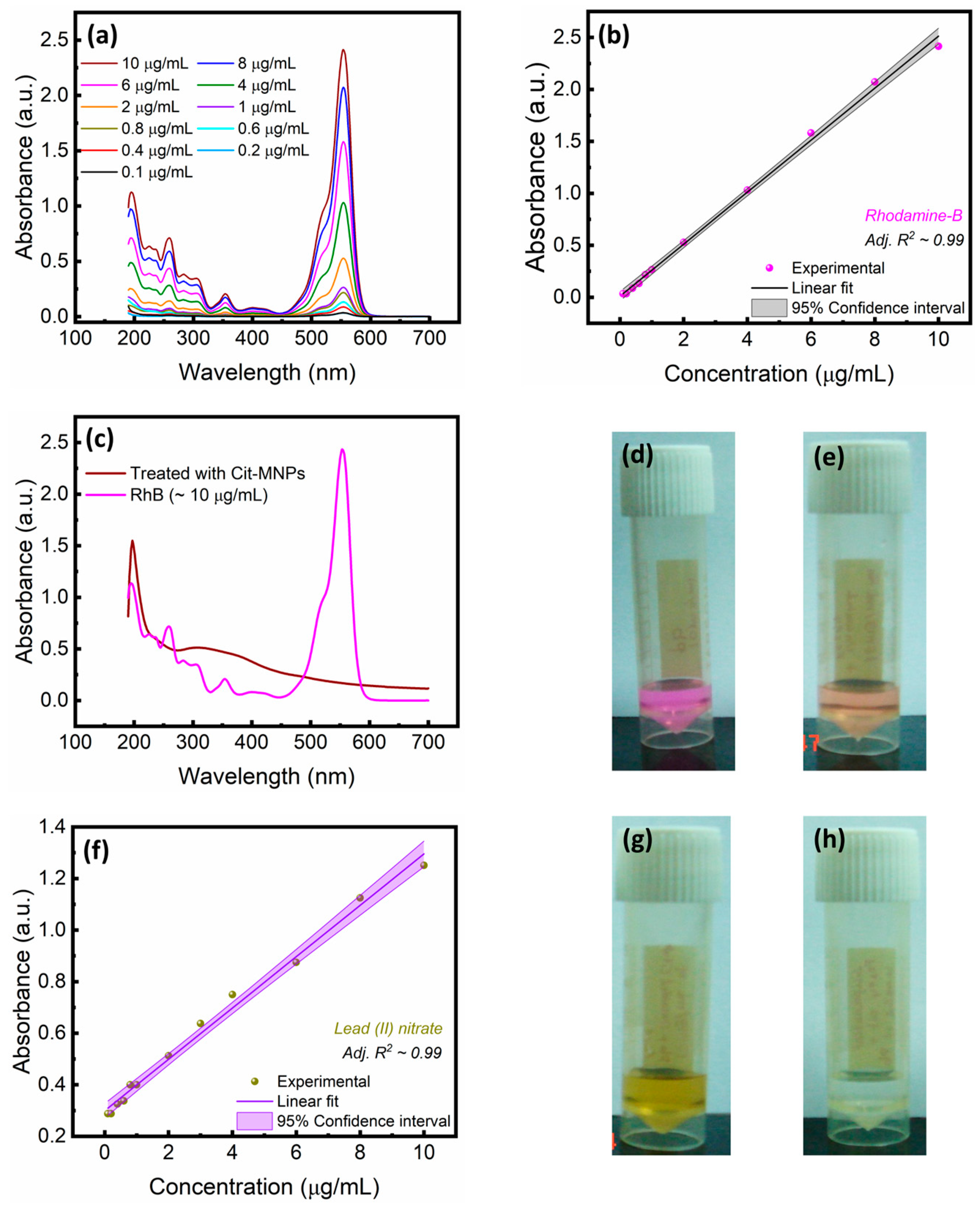
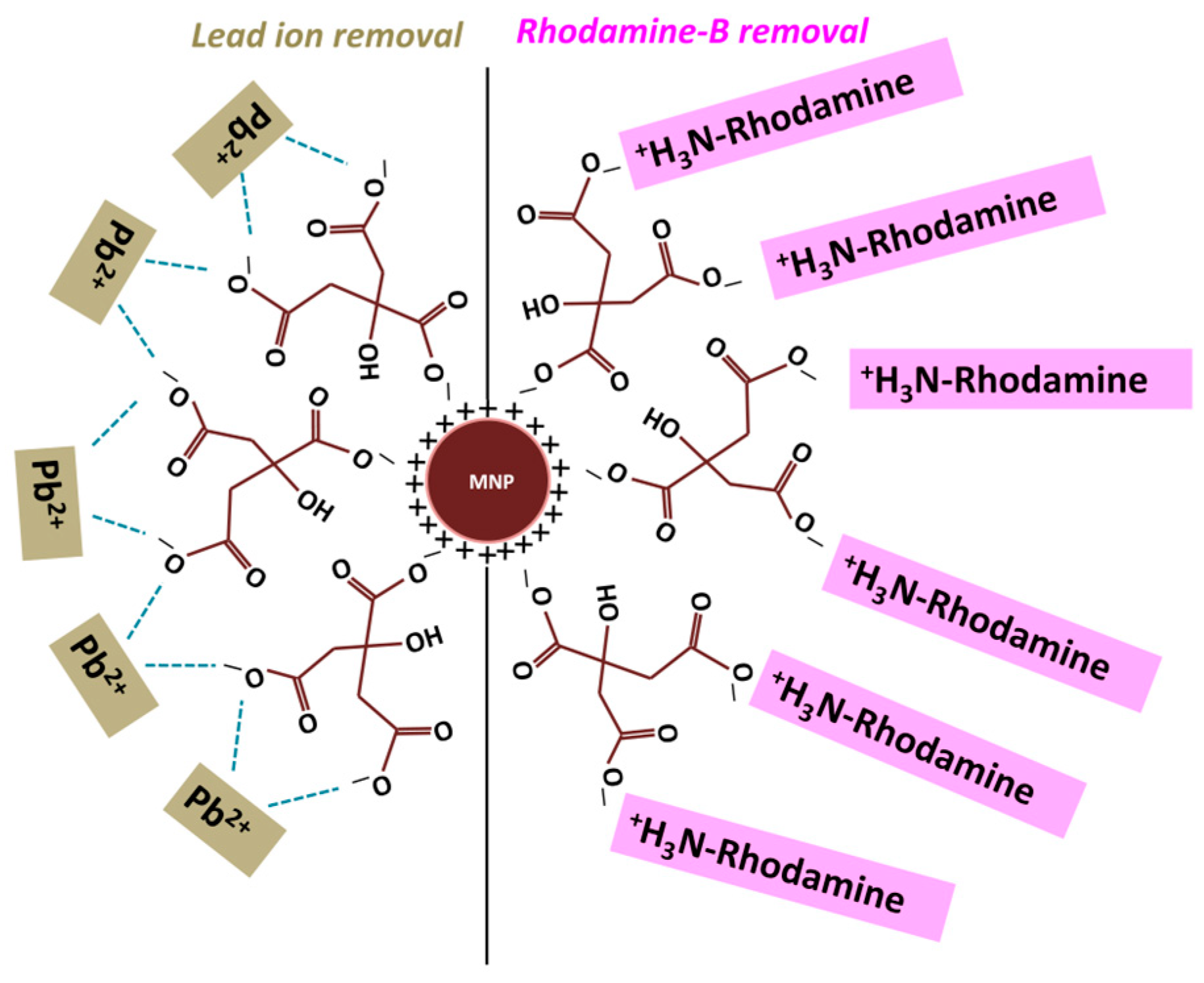
3.2. Citrate-Functionalized MNPs for the Sequestration of Rhodamine B Dye and Lead (II) Ions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soliz, J.R.; Ranjit, S.; Phillips, J.J.; Rosenberg, R.A.; Hauser, A.J. Magnetic and impedance analysis of Fe2O3 nanoparticles for chemical warfare agent sensing applications. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brojabasi, S.; Mahendran, V.; Lahiri, B.B.; Philip, J. Near infrared light absorption in magnetic nanoemulsion under external magnetic field. Opt. Commun. 2014, 323, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandy, M.; Lahiri, B.B.; Philip, J. Visual detection of defects in carbon steel using magnetic nanoemulsions: Effect of stabilizing moieties on the defect detection sensitivity. Sens. Actuators A 2020, 314, 112220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendravada, S.; Lahiri, B.B.; Jayakumar, S.; Sathyanarayana, A.T.; Vetrivendan, E.; Khan, F.; Vidya, R.; Philip, J.; Dasgupta, A. Hyaluronic acid-coated iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic fluid hyperthermia and methylene blue dye removal: Preparation, physicochemical characterization, and enhancing the heating efficiency. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 415, 126314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimundo, R.A.; Silva, V.D.; Ferreira, L.S.; Loureiro, F.J.A.; Fagg, D.P.; Macedo, D.A.; Gomes, U.U.; Soares, M.M.; Gomes, R.M.; Morales, M.A. NiFe alloy nanoparticles tuning the structure, magnetism, and application for oxygen evolution reaction catalysis. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutz, S.; Buske, N.; Landers, J.; Grafe, C.; Wende, H.; Clement, J.H. Biocompatible magnetic fluids of Co-doped iron oxide nanoparticles with tunable magnetic properties. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soetaert, F.; Korangath, P.; Serantes, D.; Fiering, S.; Ivkov, R. Cancer therapy with iron oxide nanoparticles: Agents of thermal and immune therapies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 163–164, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korolev, D.V.; Shulmeyster, G.A.; Istomina, M.S.; Nikiforov, A.I.; Aleksandrov, I.V.; Semenov, V.G.; Galagudza, M.M. Indocyanine green-containing magnetic liposomes for constant magnetic field-guided targeted delivery and theranostics. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harja, M.; Lupu, N.; Chiriac, H.; Herea, D.-D.; Buema, G. Studies on the removal of congo red dye by an adsorbent based on fly-ash@Fe3O4 mixture. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, S.; Lai, C.W.; Gan, S.; Zamiri, G.; Pivehzhani, O.A.; Johan, M.R. Application of efficient magnetic particles and activated carbon for dye removal from wastewater. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 20684–20697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daffalla, S.; Da’na, E.; Taha, A.; El-Aassar, M.R. Synthesis of a novel magnetic biochar from lemon peels via impregnation-pyrolysis for the removal of methyl orange from wastewater. Magnetochemistry 2024, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgreccia, E.; Rogalska, C.; Gonzalez, F.S.G.; Prosposito, P.; Burratti, L.; Knauth, P.; Vona, M.L.D. Heavy metal decontamination by ion exchange polymers for water purification: Counterintuitive cation removal by an anion exchange polymer. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 2776–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Noor, T.; Iqbal, N.; Yaqoob, L. Photocatalytic dye degradation from textile wastewater: A review. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 21751–21767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga, J.F.M.; Vodnik, D.; Kastelec, D.; Zupanc, M.; Dular, M.; Ortar, J.; Đurić, M.; Kaurin, A.; Mihelic, R.; Lestan, D. Removal of toxic metals from sewage sludge by EDTA and hydrodynamic cavitation and use of the sludge as fertilizer. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 923, 171444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Min, X.; Tang, C.-J.; Sillanpää, M.; Zhao, F. Recent advances in membrane filtration for heavy metal removal from wastewater: A mini review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fato, T.P.; Li, D.-W.; Zhao, L.-J.; Qiu, K.; Long, Y.-T. Simultaneous removal of multiple heavy metal ions from river water using ultrafine mesoporous magnetite nanoparticles. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 7543–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahoon, M.A.; Siddeeg, S.M.; Alsaiari, N.S.; Mnif, W.; Rebah, F.B. Effective heavy metals removal from water using nanomaterials: A review. Processes 2020, 8, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sana, S.S.; Haldhar, R.; Parameswaranpillai, J.; Chavali, M.; Kim, S.-C. Silver nanoparticles-based composite for dye removal: A comprehensive review. Clean. Mater. 2022, 6, 100161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha, J.; Suganthi, V.; Philip, J. Functionalization of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles with biotin and lawsone and their use in rhodamine dye and lead ion removal. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 5284–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.M.; Badawy, A.A.; Essawy, H.A. Improvement of dyes removal from aqueous solution by Nanosized cobalt ferrite treated with humic acid during coprecipitation. J. Nanostrc. Chem. 2019, 9, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, S.; Gul, Z.; Khatoon, J.; Shah, M.R.; Hamid, I.; Khan, I.A.T.; Aslam, F. Anionic azo dyes removal from water using amine-functionalized cobalt–iron oxide nanoparticles: A comparative time-dependent study and structural optimization towards the removal mechanism. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 1021–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumaran, T.; Philip, J. A facile approach to synthesis of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles with a uniform ultrathin layer of silicon carbide for organic dye removal. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 317, 114110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wasidi, A.S.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Simple synthesis and characterization of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for the successful adsorption of indigo carmine dye from aqueous media. Inorganics 2023, 11, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.S.; Khader, E.H.; Khudhur, R.H.; Abdulrahman, M.A.; Salih, I.K.; Albayati, T.M. Removal of anionic azo dye from wastewater using Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles adsorbents in a batch system. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 317, 100033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ren, X.; Chen, L. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic metal-organic framework for the adsorptive removal of Rhodamine B from aqueous solution. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 34, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaiari, N.S.; Osman, H.; Amari, A.; Tahoon, M.A. The synthesis of metal–organic-framework-based ternary nanocomposite for the adsorption of organic dyes from aqueous solutions. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, T. Magnetic nanomaterials: Greener and sustainable alternatives for the adsorption of hazardous environmental contaminants. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 362, 132338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoohestani, E.; Samari, F.; Homaei, A.; Yosuefinejad, S. A facile strategy for preparation of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles using Cordia myxa leaf extract and investigating its adsorption activity in dye removal. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabet, R.H.; Fouad, M.K.; Ali, I.A.; Sherbiney, S.A.E.; Tony, M.A. Magnetite-based nanoparticles as an efficient hybrid heterogeneous adsorption/oxidation process for reactive textile dye removal from wastewater matrix. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 103, 2636–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.; Badawy, A.M.; Seliem, A.Q.; Bendary, H.I.; Lima, E.C.; Al-Dossari, M.; EL-Gawaad, N.S.A.; Reis, G.S.; Mobarak, M.; Hassan, A.M.; et al. Macroscopic and microscopic levels of methylene blue adsorption on a magnetic bio-based adsorbent: In-depth study using experiments, advanced modeling, and statistical thermodynamic analysis. Magnetochemistry 2024, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurkan, V.; Von Nidda, H.-A.K.; Deisenhofer, J.; Lunkenheimer, P.; Loidl, A. On the complexity of spinels: Magnetic, electronic, and polar ground states. Phys. Rep. 2021, 926, 1–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.K.; Aggarwal, I.; Kumar, H.; Prasad, L.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, A.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Thuan, D.V.; Mishra, V. Magnetite nanoparticles as sorbents for dye removal: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2487–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, N.; Sen, S.; Biswas, G.; Saxena, A.; Haldar, P.K. Adsorption and desorption study of reusable magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles modified with Justicia adhatoda leaf extract for the removal of textile dye and antibiotic. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoso, W.A.; Haleem, N.; Baig, M.A.; Jamal, Y. Synthesis, characterization and heavy metal removal efficiency of nickel ferrite nanoparticles (NFN’s). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Baharinikoo, L.; Farahani, M.D.; Mahdizadeh, B.; Farizhandi, A.A.K. Experimental modelling studies on the removal of dyes and heavy metal ions using ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wasidi, A.S.; Abdelrahman, E.A.; Rehman, K.; Saad, F.A.; Munshi, A.M. Efficient removal of crystal violet and acid red 88 dyes from aqueous environments using easily synthesized copper ferrite nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Z.; Tanweer, M.S.; Alam, M. Reduced graphene oxide-modified spinel cobalt ferrite nanocomposite: Synthesis, characterization, and its superior adsorption performance for dyes and heavy metals. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 6376–6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, N.M.; Sheshmani, S.; Shahvelayati, A.S. Manganese ferrite-graphite oxide-chitosan nanocomposite for efficient dye removal from aqueous and textile wastewater under UV and sunlight irradiation. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, P.; Gahlawat, N.; Punia, P.; Kharbanda, S.; Ravelo, B.; Thakur, A. Cobalt nanoferrites: A review on synthesis, characterization, and applications. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2022, 35, 2639–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, M.D.; Obayomi, K.S.; Abdulkadir, M.B.; Iyaka, Y.A.; Olugbenga, A.G. Characterization of cobalt ferrite-supported activated carbon for removal of chromium and lead ions from tannery wastewater via adsorption equilibrium. Water Sci. Eng. 2020, 13, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez–Vargas, S.; Valle–Ascencio, L.; Mtz-Enriquez, A.I.; Glez-Rosas, A.J.; Vázquez–Hipólito, V.; Mijangos–Ricardez, O.F.; López–Luna, J. As(III) adsorption on co-precipitated cobalt substituted ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 539, 168389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadirvelu, K.; Karthika, C.; Vennilamani, N.; Pattabhi, S. Activated carbon from industrial solid waste as an adsorbent for the removal of Rhodamine-B from aqueous solution: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, S.S.; Babamale, H.F. A short review on the removal of rhodamine B dye using agricultural waste-based adsorbents. Asian J. Chem. Sci. 2020, 7, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Liu, X.; Kafuti, Y.S.; Kim, H.; Wang, J.; Peng, X.; Li, H.; Yoon, J. Fluorescent dyes based on rhodamine derivatives for bioimaging and therapeutics: Recent progress, challenges, and prospects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 5607–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Sharma, S.; Bhatt, U.; Soni, V. Toxic effects of Rhodamine B on antioxidant system and photosynthesis of Hydrilla verticillata. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2022, 3, 100069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, K.A.; Adegoke, O.R.; Araoye, A.O.; Ogunmodede, J.; Agboola, O.S.; Bello, O.S. Engineered raw, carbonaceous, and modified biomass-based adsorbents for Rhodamine B dye removal from water and wastewater. Bioresour Technol. Rep. 2022, 18, 101082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, A.L.; Ara, A.; Usmani, J.A. Lead toxicity: A review. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2015, 8, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, M.A.; Hezmee, M.N.M.; Haron, A.W.; Sabri, M.Y.M.; Rajion, M.A. The detrimental effects of lead on human and animal health. Vet. World 2016, 27, 660–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Silva, M.J.; Mijangos-Ricardez, O.F.; Vazquez-Hipolito, V.; Martinez-Vargas, S.; Lopez-Luna, J. Single and mixed adsorption of Cd(II) and Cr(VI) onto citrate-coated magnetite nanoparticles. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 57, 4008–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, S.S.; Gopinath, S.; Panneerselvam, G.; Antony, M.P.; Philip, J. High temperature phase transformation studies in magnetite nanoparticles doped with Co2+ ion. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 054320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumb, A.; Brechbiel, M.W.; Choyke, P.L.; Fugger, L.; Eggeman, A.; Prabhakaran, D.; Hutchinson, J.; Dobson, P.J. Synthesis and characterization of ultra-small superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles thinly coated with silica. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 335601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.J.; Mamun, M.-A. Spectrophotometric determination of lead in industrial, environmental, biological and soil samples using 2,5-dimercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole. Talanta 2001, 55, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, J.J.; Kawatra, S.K. Factors affecting zeta potential of iron oxides. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2013, 34, 269–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaminger, S.P.; Bauer, D.; Fraga-García, P.; Wagner, F.E.; Berensmeier, S. Oxidation of magnetite nanoparticles: Impact on surface and crystal properties. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2017, 19, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiremath, C.G.; Kariduraganavar, M.Y.; Hiremath, M.B. Synergistic delivery of 5-fluorouracil and curcumin using human serum albumin-coated iron oxide nanoparticles by folic acid targeting. Prog. Biomater. 2018, 7, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.-h.; Bao, J.-f.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.-x.; Chen, Z.-w.; Ren, L.; Zhou, X.; Ke, X.-b.; Chena, M.; Yang, A.-q. One-step synthesis of monodisperse, water-soluble ultra-small Fe3O4 nanoparticles for potential bioapplication. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 2133–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Lotina, A.; Portela, R.; Baeza, P.; Alcolea-Rodriguez, V.; Villarroel, M.; Avila, P. Zeta potential as a tool for functional materials development. Catalysis Today 2023, 423, 113862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha, J.; Philip, J. Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial property of Fe3O4-Cys-HNQ nanocomplex, with L-cysteine molecule as a linker. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 8047–8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraswathy, A.; Nazeer, S.S.; Jeevan, M.; Nimi, N.; Arumugam, S.; Harikrishnan, V.S.; Varma, P.R.H.; Jayasree, R.S. Citrate coated iron oxide nanoparticles with enhanced relaxivity for in vivo magnetic resonance imaging of liver fibrosis. Colloids Surf. B 2014, 117, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sun, Z.; Deng, Y.; Zou, Y.; Li, C.; Guo, X.; Xiong, L.; Gao, Y.; Li, F.; Zhao, D. Highly water-dispersible biocompatible magnetite particles with low cytotoxicity stabilized by citrate groups. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 5875–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassallo, M.; Martella, D.; Barrera, G.; Celegato, F.; Coïsson, M.; Ferrero, R.; Olivetti, E.S.; Troia, A.; Sozeri, H.; Parmeggiani, C.; et al. Improvement of hyperthermia properties of iron oxide nanoparticles by surface coating. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 2143–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, R.D. Infrared spectra of ferrites. Phys. Rev. 1955, 99, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, C.; Shen, C.; Yang, T.; Bao, L.; Tian, J.; Ding, H.; Li, C.; Gao, H.-J. Large-scale Fe3O4 nanoparticles soluble in water synthesized by a facile method. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 11336–11339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Lahiri, B.B.; Srujana, M.; Vidya, R.; Philip, J. Induction heating of magnetic nanoparticles: Role of thermo-physical properties of the coating moieties. Colloids Surf. A 2024, 692, 133982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.G.; Liu, X.C.; Chen, M.F. In situ ATR-FTIR investigation and theoretical calculation of the interactions of chromate and citrate on the surface of haematite (a-Fe2O3). RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 41011–41016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plekhanov, M.S.; Thomä, S.L.J.; Magerl, A.; Appel, M.; Zobel, M. Quasi-elastic neutron scattering of citrate-capped iron oxide nanoparticles: Distinguishing between ligand, water, and magnetic dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. C 2024, 128, 11661–11671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anila, I.; Lahiri, B.B.; Jacob Mathew, M.; Philip, J. Synthesis and magneto-structural properties of chitosan coated ultrafine cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for magnetic fluid hyperthermia in viscous medium. Ceram. Intl. 2022, 48, 22767–22781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranoo, S.; Lahiri, B.B.; Damodaran, S.P.; Philip, J. Tuning magnetic heating efficiency of colloidal dispersions of iron oxide nano-clusters by varying the surfactant concentration during solvothermal synthesis. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 360, 119444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, I.; Shokrollahi, H.; Doroodmand, M.M.; Safi, R. Magnetic and structural studies on CoFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation, normal micelles and reverse micelles methods. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 1854–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, B.B.; Ranoo, S.; Zaibudeen, A.W.; Philip, J. Magnetic hyperthermia in magnetic nanoemulsions: Effects of polydispersity, particle concentration and medium viscosity. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 441, 310–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslibeiki, B.; Eskandarzadeh, N.; Jalili, H.; Varzaneh, A.G.; Kameli, P.; Orue, I.; Chernenko, V.; Hajalilou, A.; Ferreira, L.P.; Cruz, M.M. Magnetic hyperthermia properties of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles: Effect of polymer coating and interparticle interactions. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 27995–28005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brojabasi, S.; Mahendran, V.; Lahiri, B.B.; Philip, J. Temperature dependent light transmission in ferrofluids. Optics Commun. 2015, 342, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, B.B.; Ranoo, S.; Philip, J. Effect of orientational ordering of magnetic nanoemulsions immobilized in agar gel on magnetic hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 451, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birtalan, E.; Rudat, B.; Kölmel, D.K.; Fritz, D.; Vollrath, S.B.L.; Schepers, U.; Bräse, S. Investigating rhodamine B-labeled peptoids: Scopes and limitations of its applications. Biopolymers 2011, 96, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koli, P.; Sharma, U. Exploratory insight into the stability of Rhodamine B and crude aqueous spinach extract-based photogalvanic cells: Comparing photo-stability of electrolytes for solar power and storage. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 2021, 8, 100086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangami, G.; Dharmaraj, N. UV–visible spectroscopic estimation of photodegradation of rhodamine-B dye using tin(IV) oxide nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2012, 97, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, B.E.; Metson, P. A field method for determination of lead fume. Analyst 1959, 84, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugaš, M.; Pauković, R. Microdetermination of lead as chromate by the ring-oven technique. Anal. Chimi. Acta 1970, 49, 356–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaper, D.G.M.; Kuksis, A. Determination of lead by dithizone in a single phase water–acetone system. Can. J. Chem. 2011, 35, 1278–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahat, A.; Hassan, H.M.A.; Azzazy, H.M.E.; El-Sharkawy, E.A.; Abdou, H.M.; Awual, M.R. Novel hierarchical composite adsorbent for selective lead(II) ions capturing from wastewater samples. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 332, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, J.; Su, C.; Lai, H.; Shen, P.; Cai, J.; Liu, D. Separation of copper-lead using 2,5-dimercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole as chalcopyrite depressant: Adsorption and hydrophilicity studies. Colloids Surf. A 2024, 702, 135041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Asthana, A.; Chakraborty, R.; Jain, B.; Singh, A.K.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Susan, M.A.B.H. Cationic dye removal using novel magnetic/activated charcoal/β-cyclodextrin/alginate polymer nanocomposite. Nanomater. 2020, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Lan, R.; He, L.; Liu, H.; Pei, X. A critical review of adsorption isotherm models for aqueous contaminants: Curve characteristics, site energy distribution and common controversies. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 329, 117104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Kim, J.H.; Park, H.; Kwak, C.; Yang, J.; Kim, J.; Ryu, S.Y.; Lee, J. Role of electrostatic interactions in the adsorption of dye molecules by Ti3C2-MXenes. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 6201–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jayakumar, S.; Lahiri, B.B.; Dasgupta, A. Preparation, Characterization, and Application of Citrate-Functionalized Cobalt-Doped Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Rhodamine Dye and Lead Ion Sequestration. Magnetochemistry 2025, 11, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11040024
Jayakumar S, Lahiri BB, Dasgupta A. Preparation, Characterization, and Application of Citrate-Functionalized Cobalt-Doped Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Rhodamine Dye and Lead Ion Sequestration. Magnetochemistry. 2025; 11(4):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11040024
Chicago/Turabian StyleJayakumar, Sangeetha, Barid Baran Lahiri, and Arup Dasgupta. 2025. "Preparation, Characterization, and Application of Citrate-Functionalized Cobalt-Doped Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Rhodamine Dye and Lead Ion Sequestration" Magnetochemistry 11, no. 4: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11040024
APA StyleJayakumar, S., Lahiri, B. B., & Dasgupta, A. (2025). Preparation, Characterization, and Application of Citrate-Functionalized Cobalt-Doped Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Rhodamine Dye and Lead Ion Sequestration. Magnetochemistry, 11(4), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11040024






