Abstract
The assembly properties of three known spin crossover iron(III) complexes 1–3, at the air–water interface, are reported. All three complexes are amphiphiles, each bearing a pair of Cn alkyl chains on the polyamino Schiff base sal2trien ligand (n = 6, 12, or 18). Complex 1 is water-soluble but complexes 2 and 3 form Langmuir films, and attempts were made to transfer the film of the C18 complex 3 to a glass surface. The nature of the assembly of more concentrated solutions of 3 in water was investigated by light scattering, cryo-SEM (scanning electron microscopy), and TEM (transmission electron microscopy), all of which indicated nanoparticle formation. Lyophilization of the assembly of complex 3 in water yielded a powder with a markedly different magnetic profile from the powder recovered from the initial synthesis, notably, the spin crossover was almost completely quenched, and the thermal behavior was predominantly low spin, suggesting that nanoparticle formation traps the system in one spin state.
1. Introduction
The continuing pressure to intensify hard drive bit densities has prompted research into molecular alternatives to the current methodology of using nanoislands of magnetic metal oxides, which are now starting to reach the superparamagnetic size limit [1,2]. Molecular switching phenomena which could be harnessed for this purpose include changes in redox state [3,4,5], spin state [6,7,8], conformation [9,10,11], or shape [12,13]. Spin state change is a particularly appealing vehicle for molecular switching, as it is often accompanied by significant hysteresis [14,15], and synthetic routes to spin transition systems tend to be relatively facile. In addition, there exist many external perturbation methods to effect a spin state change including thermal [16,17,18], irradiation [19,20,21], magnetic field [22,23], pressure [24,25,26], or electric [27,28] inputs, and an equally wide range of detection methods, including measurement of magnetic properties [29], vibrational [21,30,31] and electronic [32,33,34] spectroscopic signatures, conductance [35], or surface plasmonic response [36]. This activity has intensified research into assembly protocols for spin crossover (SCO) complexes, and methods to prepare thin films [37,38], nanocrystals [39,40], and nanoparticles [41,42,43,44,45,46] have all been reported in recent years. Ligand design is important in preparing a SCO complex for a particular assembly method, and we have concentrated our design efforts into modification of the FeIIIsal2trien SCO cation by attachment of one or more alkyl chains onto both phenoxy rings [47,48,49], or onto each of the secondary amine groups [50,51,52]. Such amphiphilic complexes show markedly different magnetic behavior to the parent complex in both the solid state and in solution, and these and related Mn(III) SCO systems [53], may be candidates for Langmuir–Blodgett (LB) [54,55] monolayer formation and transfer to a surface.
Generally, SCO properties of many alkylated Fe(II) complexes have also been reported [56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71], with fewer examples in Fe(III) [72], and these may show a variety of solution and solid state properties [67,68,69,70,71], including some with a wide thermal SCO hysteresis [67]. Clérac et al. have recently reported an Fe(II) SCO complex decorated with long alkyl chains with a wide thermal hysteresis around room temperature (RT), demonstrating that a spin transition and the presence of a monotropic phase leads to magnetic tristability at RT [73]. In crystalline phases, entropy-driven conformational isomerization of alkyl chains, such as anti/gauche changes or order/disorder transitions, can also affect magnetic properties and promote spin state switching, as strikingly illustrated in a Co(II) compound featuring a “reverse” spin transition [74].
We are interested in the potential for depositing SCO amphiphiles on surfaces using the LB technique [54,55], since it provides precise control of the monolayer thickness, as well as homogeneous deposition of the monolayer over large areas and the possibility to make multilayer structures with varying layer composition [75,76]. In 1988, Kahn et al. reported the first fabrication of thin films of SCO compounds using LB techniques [77], and Clérac et al. showed, in 2004, that the fabrication of LB films of triazole-based polymers which exhibit SCO behavior is possible [78]. The first magnetic characterization of the SCO in an LB film has been reported for a semi-fluorinated Fe(II) compound, which exhibits similar bulk and thin film magnetic properties [79]. In addition, light-induced excited spin state trapping (LIESST) has been observed for an iron(II) compound organized as an LB film, where the LIESST population and relaxation are faster for the LB film than for the powder [80]. Most of the recent studies on SCO amphiphiles concentrate on Fe(II)- and Co(II)-containing coordination centers [81,82,83,84,85]. Recently, Brooker et al. showed a close to ideal transfer ratio of Langmuir films onto a glass support in the first upstroke using an Fe(II) SCO compound [86], but in the subsequent downstroke, the first layer was quantitatively desorbed onto the air–water interface, suggesting only moderate adhesion of the complex to the support.
Amphiphilic iron(III) complexes, 1–3 [50,51,52,87], with C6, C12, and C18 appended chains, all show solid state spin crossover, and we now report their Langmuir isotherm behavior and the results of attempts to transpose these to a glass surface. The nature of the assembly, 3 in aqueous solution, is also probed by scanning and transmission electron microscopy, and the magnetic properties of the powdered sample of 3 recovered by lyophilization are compared with those of the initial sample.
2. Results
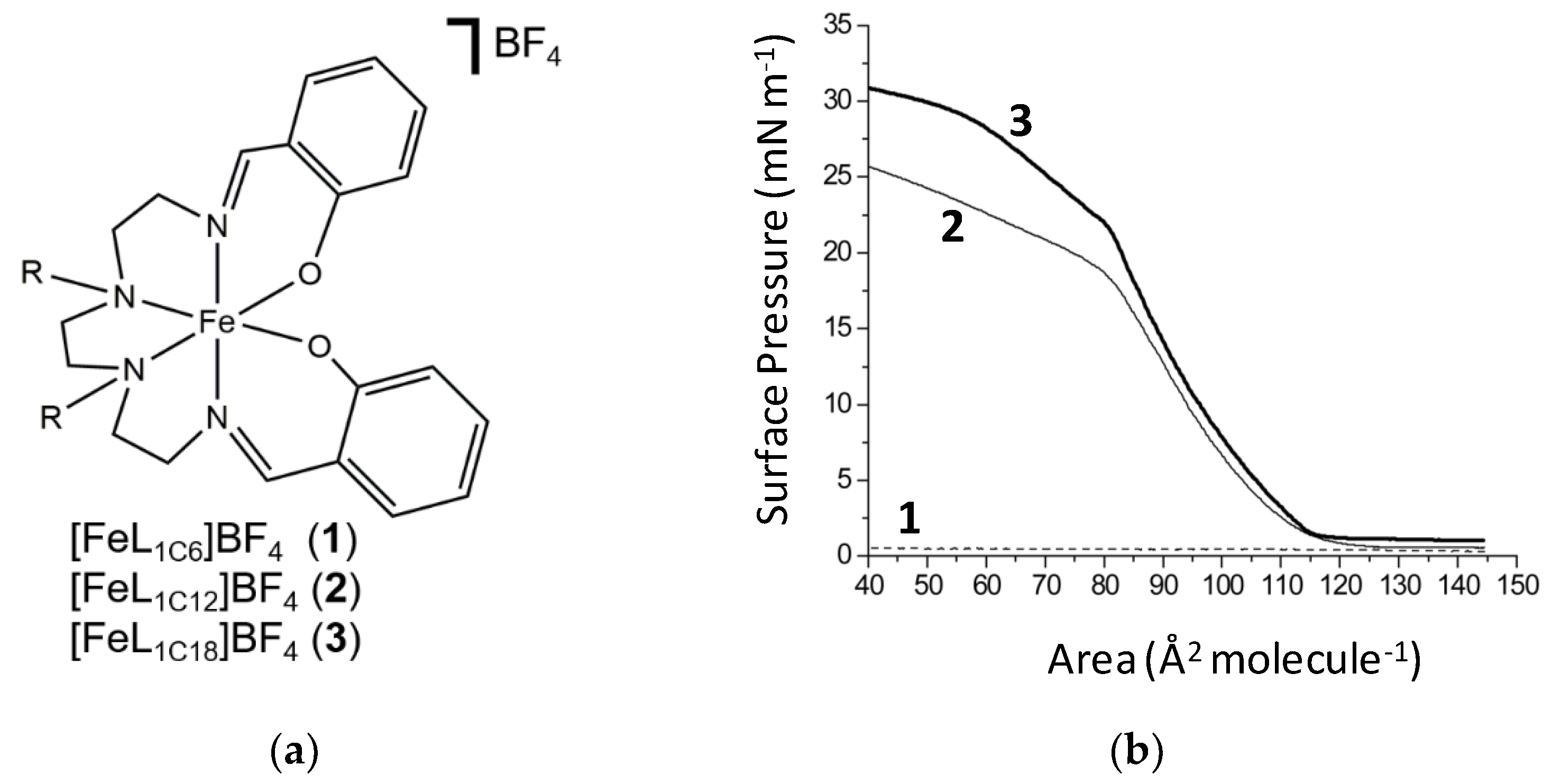
Amphiphilic complexes 1–3, Figure 1, were prepared as described elsewhere [50], and the potential for self-assembly as a Langmuir monolayer at the air–water interface was assessed for all three. An important criterion for monolayer formation is water insolubility, and the solubility of all three was initially assessed visually. The bis-C6 complex 1 readily formed a purple solution in water, but the longer bis-C12 and bis-C18 analogues 2 and 3 were insoluble under ambient conditions. In line with these observations, complex 1 does not form a Langmuir film, Figure 1, presumably due to its solubility in water. Such behavior was observed previously for the FeIIsal2trien derivative with C6 chains appended on the phenolate ring [47,48,49].
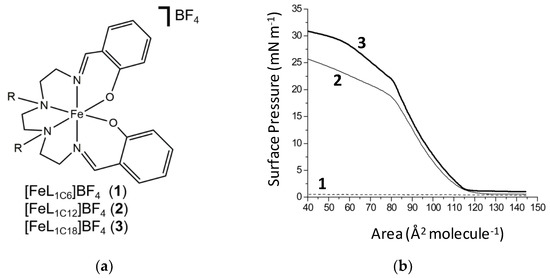
Figure 1.
Schematic structure of 1–3 (a) and pressure-area isotherms for complexes 1–3 showing chain length dependence (b).
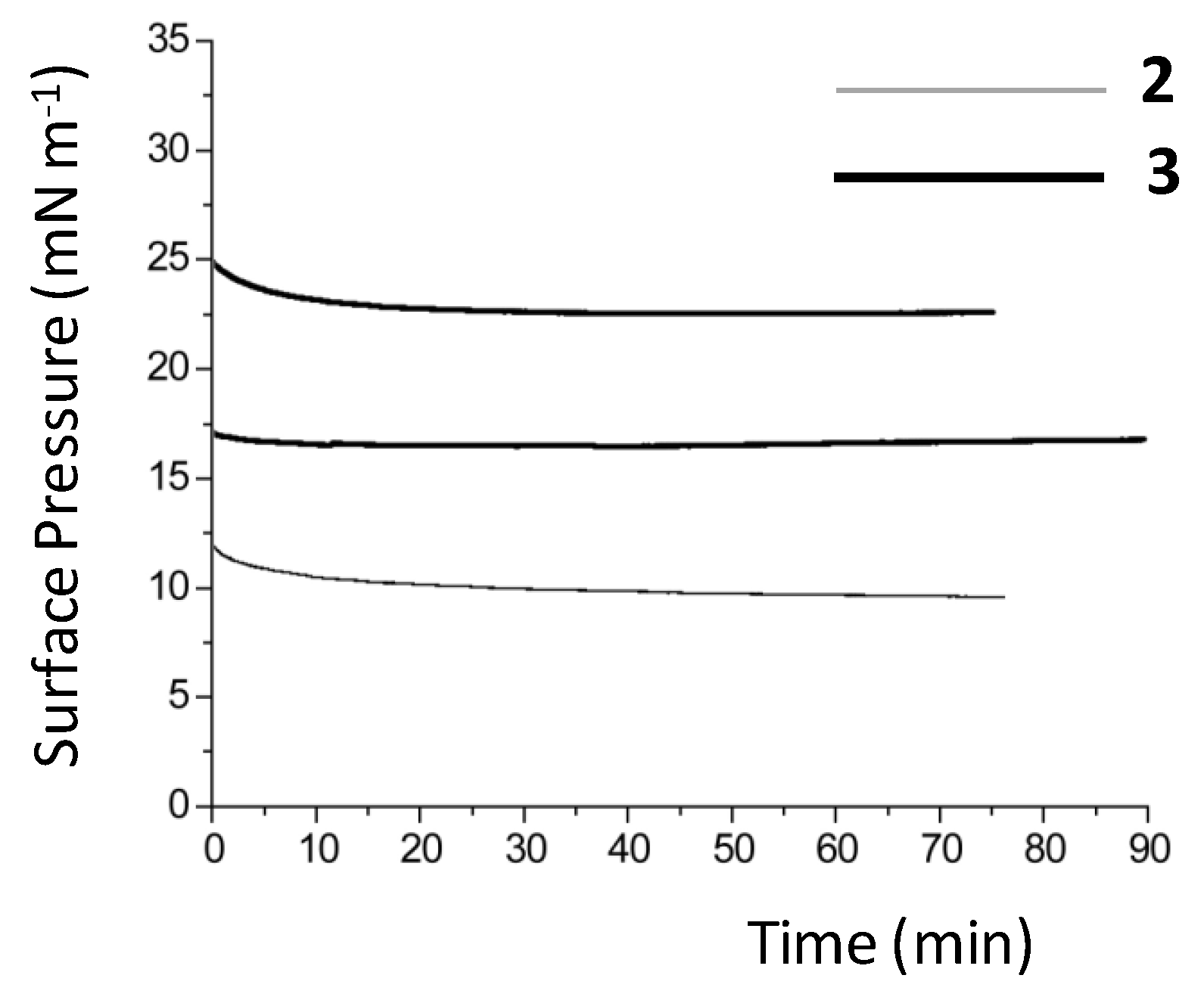
By contrast, compounds 2 and 3, which are water-insoluble, form Langmuir monolayers at the air–water interface, and the corresponding pressure–area isotherms show that the packing process is rather gradual, Figure 1. The area occupied by one surfactant in the Langmuir monolayer is estimated at 85 Å2 per molecule at the maximum packing density, given that this is the area/molecule at which the film collapses for both complexes. The accessible surface pressure of 20–25 mN m−1 is, therefore, low, and the condensed phase for both compounds begins at 115 Å2 per molecule, and is sharply defined, in particular, for complex 3. Studies of the stability of the monolayers formed for both 2 and 3 were performed, Figure 2. From this, it can be concluded that both compounds form stable monolayers over a period longer than 90 min.
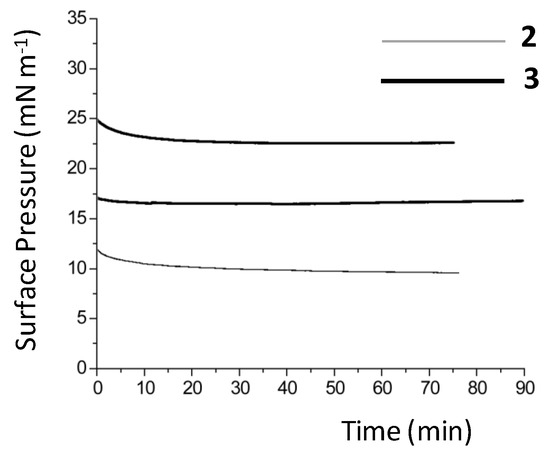
Figure 2.
Time-dependence of film stability for complexes 2 and 3 at a fixed barrier position. The stability of complex 3 was measured at two different surface pressures.
Comparison of the behavior of compounds 1–3, which have alkyl chains appended to the NH backbone, with analogues where the alkyl chains are appended on the phenolate donors [48], allows us to conclude that similar maximum packing density is reached in both series. The pressure–area isotherms for N-functionalized complexes are less steep, indicating less ordered arrangements, possibly due to backfolding of the alkyl chains. Both types of complexes (N-functionalized and O-functionalized) do not show clear evidence of the transition from the condensed phase to the solid phase, before gradually collapsing. Lower collapse pressures for compounds 2 and 3, and the fact that the surface pressures start to rise at a larger area per molecule, might be attributed to the reduced amphiphilicity conferred by substitution on the NH backbone, rather than the phenolate ring. Besides this, no differences in terms of time stability were observed between the two types of Fe(III) amphiphiles.
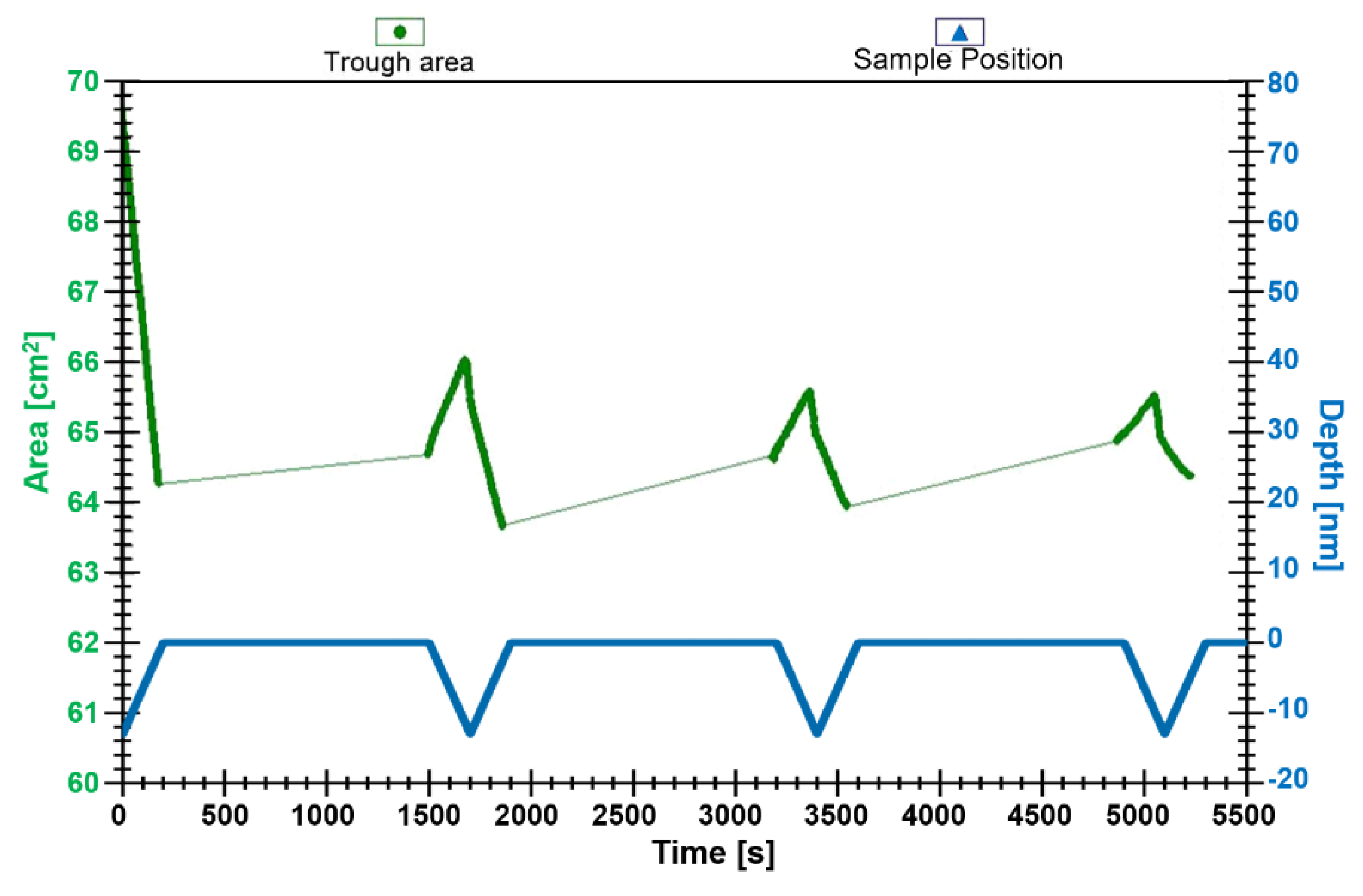
Attempts to transfer the C18 amphiphilic compound 3 onto a glass support using the Langmuir–Blodgett (LB) technique were made using the vertical dipping method [54,55]. After holding the monolayer at a constant surface pressure of 4 mN/m, and allowing the monolayer to equilibrate for 10 min, the glass substrate was submerged. The dipper speed was maintained at 4 mm/min for upward and downward motion and, before each downstroke, the wafer was allowed to dry for 20 min in air. Interestingly, layers are only observed to be transferred to the glass surface upon upstroke, and the initial transfer ratio upon upstroke is high (0.9). In the downstroke, the layer is partially transferred back from the support to the air–water interface, as indicated by the negative transfer ratio and the third and fourth deposition cycles show a noticeable decrease in the transfer ratio, see Figure 3.
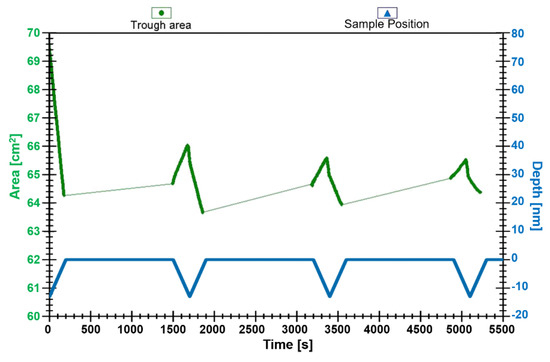
Figure 3.
Plot of transfer ratio for attempted transfer and deposition of complex 3 onto a glass support at 4 mN m−1. Emersion and immersion are indicated by a solid line. The transferred layer was allowed to dry for 20 min after each emersion.
In subsequent cycles, the material deposited upon upstroke is completely removed upon downstroke. The profile obtained for the attempts at surface transfer and deposition of C18 amphiphile, compound 3, suggests that only a Langmuir–Blodgett monolayer can be fabricated, rather than multilayers. The monolayer showed good stability upon air drying, and attempts were made to record the variable temperature Raman spectra of the deposited layer. However, the absence of any signal suggests that the sample size on the glass support is too small.
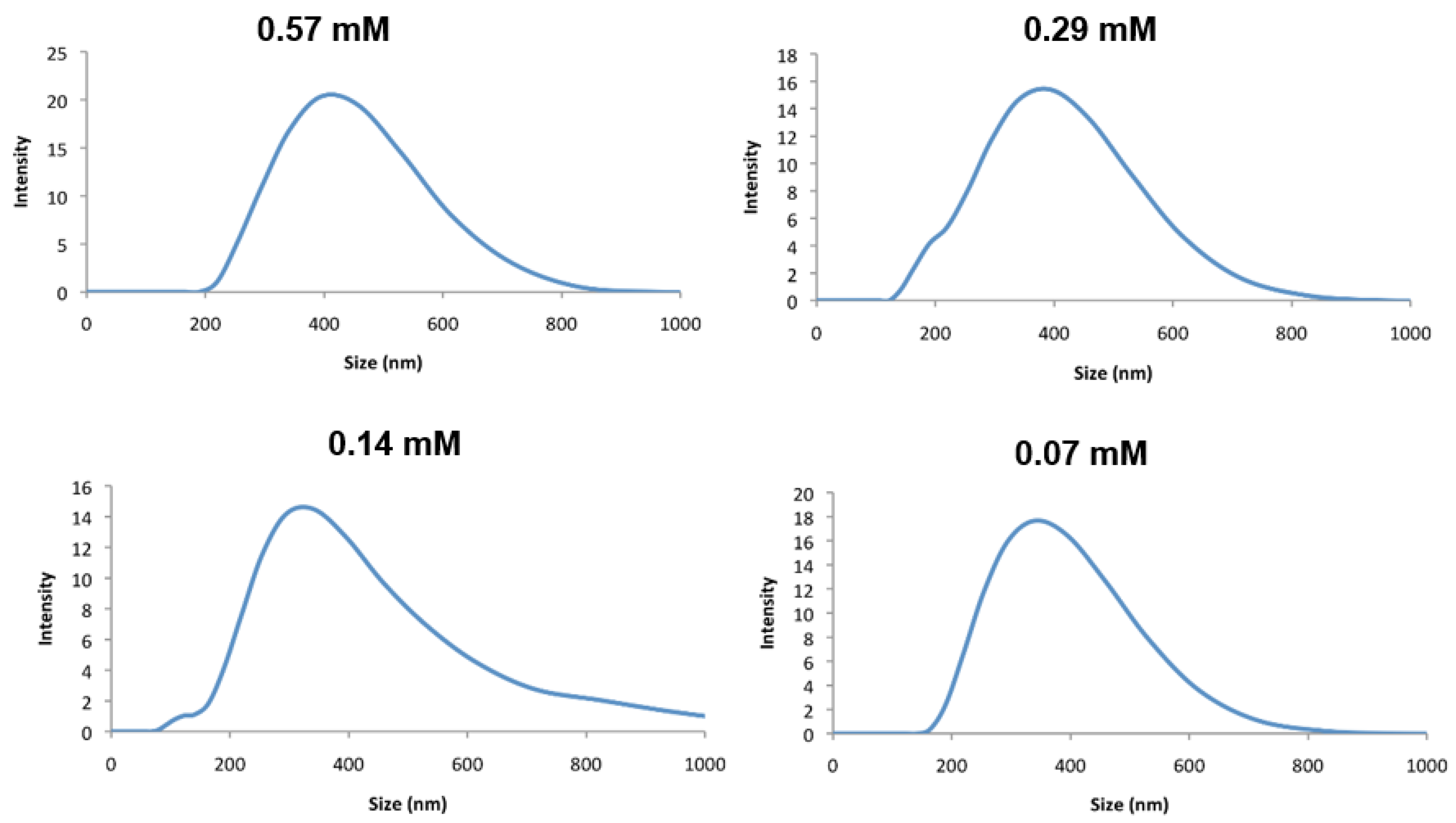
Initial solubility tests of the bis-C12 and bis-C18 complexes, 2 and 3, indicated that both were insoluble in water. Suspensions of excess solid of each in water were then subjected to prolonged sonication to encourage micellar formation with the aim of recovering the solution particles by lyophilization for magnetic characterization. Sonication had no effect on complex 2, but yielded a purple suspension in the case of 3, which, after filtering, yielded a transparent purple solution, which was further investigated by light scattering and electron microscopy. The maximum concentration of the assembly of 3 that could be achieved at room temperature was 0.57 mM (this was estimated by evaporating the solvent and weighing the residue). At this concentration, dynamic light scattering (DLS) indicated an average particle size of 350 nm with a polydispersity of 0.22; see Figure 4.
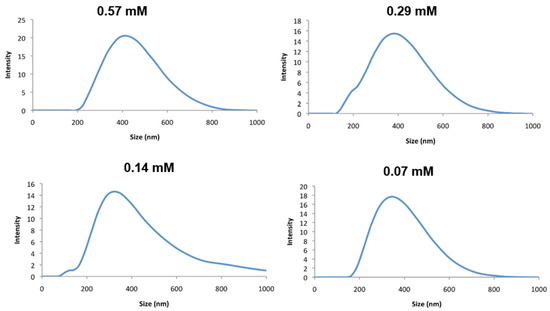
Figure 4.
Plot of particle size distribution of complex 3 in water at indicated concentrations measured by DLS.
Stepwise dilution up to one-eighth of this concentration caused a relatively small variation in particle size (Figure 4 and Table 1), suggesting only a small concentration dependence but a relatively high polydispersity.

Table 1.
Particle size of 3 in water measured by dynamic light scattering.
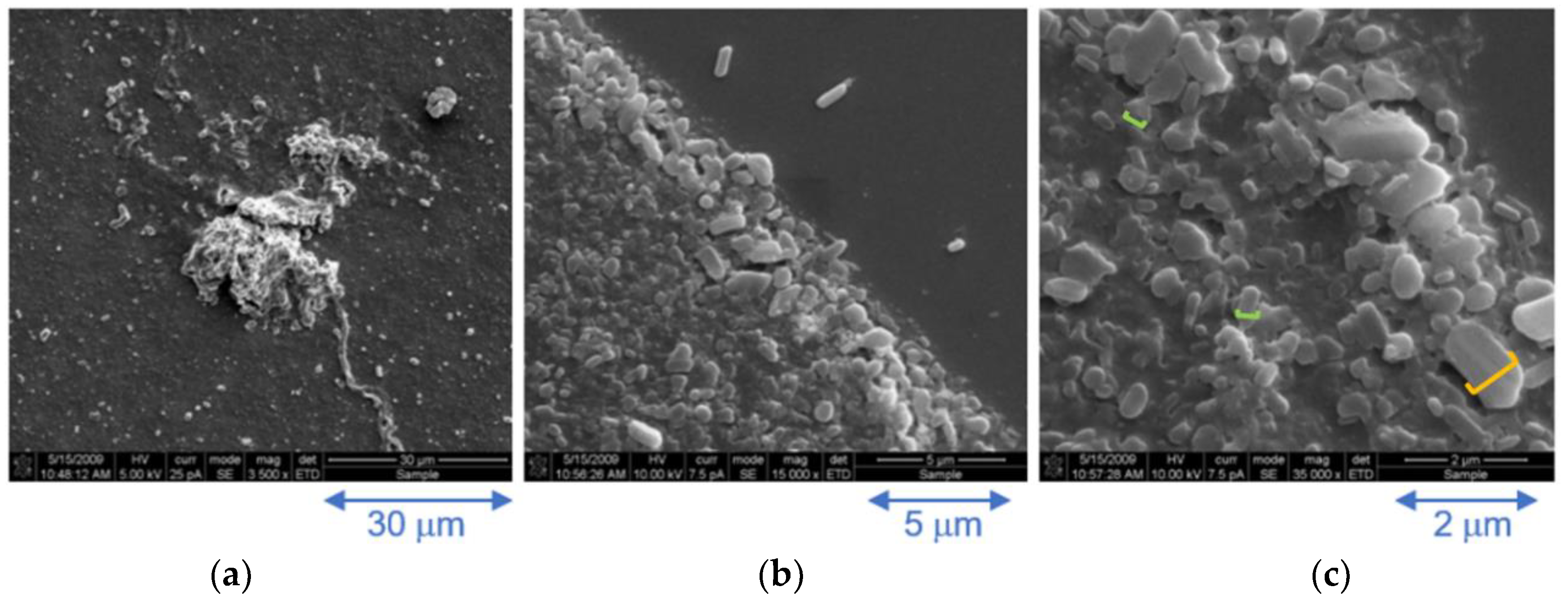
Cryo-SEM images, recorded on a further diluted 3.0 × 10−5 M frozen solution assembly of 3, reveal a range of particles sizes, Figure 5a–c. The majority of particles are of the order of 300 nm (0.3 microns, green line in Figure 5c) but can grow to around 800 nm (0.8 microns, orange line in Figure 5c) which matches the particle sizes obtained by DLS, Figure 4. Larger particles are also discernible, suggesting that the nano-sized particles aggregate into larger particles on the micron scale, Figure 5a. At higher magnification, these are revealed to be comprised of smaller polydispersive oblong-shaped particles ranging from around 0.5–2 microns in width, Figure 5c.
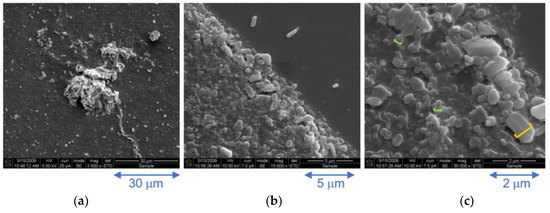
Figure 5.
Cryo-SEM images of a 0.03 mM aqueous solution of complex 3 at increasing magnification; (a) ×3500, (b) ×15,000 and (c) ×35,000.
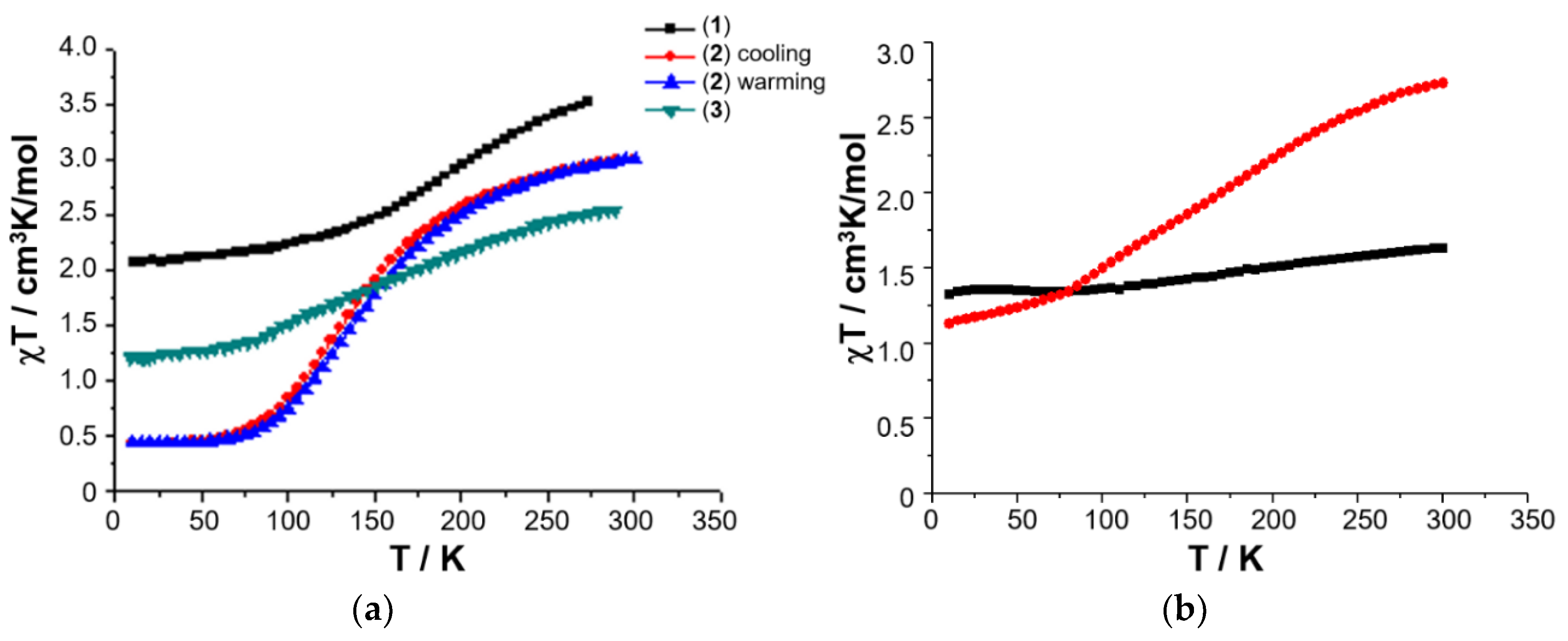
Freshly prepared powdered samples of complexes 1–3 all show a gradual spin crossover, Figure 6 [50,52] and, given the interest in preparing nanoparticles of SCO complexes, it was of interest to investigate if the nanosized micellar particles of 3 could be harvested by freeze-drying, in order to probe their magnetic characteristics.
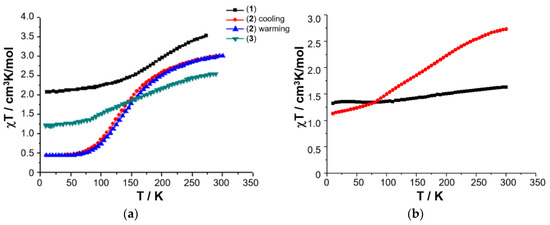
Figure 6.
Temperature-dependence of the χT product for 1–3 (a), and variable temperature χmT of solid sample of [FeL1C18]BF4, 3 (red circles), and freeze-dried sample of [FeL1C18]BF4, 3 (black squares), extracted from freeze-dried aqueous assembly of 3 (b). Magnetic data originally published in [50,52].
A 0.03 mM assembly of 3 in water was therefore prepared using sonication and heating, and the resulting solution gravity-filtered to remove all traces of insoluble material as before. The resulting clear solution was then frozen in a Dewar of liquid nitrogen, before being placed under vacuum for 24 h. The recovered dry powder was collected, and its magnetic susceptibility recorded on a SQUID magnetometer. The solid obtained from lyophilization of the aqueous solution of 3 shows a completely different magnetic profile to that of the original solid, Figure 7b, with an almost temperature independent χmT where the high spin (HS) fraction falls from 29% at RT down to 21% at 10 K (assuming χmT = 0.50 cm3 mol−1 K for low spin (LS) Fe(III) with a small orbital contribution and spin only χmT = 4.38 cm3 mol−1 K for HS Fe(III)). Elemental analysis reveals that the composition of the solid sample of lyophilized 3 is different from the freshly prepared anhydrous powder as revealed by the difference between the experimental and calculated values: Exp. (Calc.): C 62.38 (67.26); H 9.40 (9.68); N 3.11 (5.60). The challenges in effectively pumping off all the water mean that the freeze-dried sample may be hydrated and would, therefore, be expected to have a different magnetic profile.
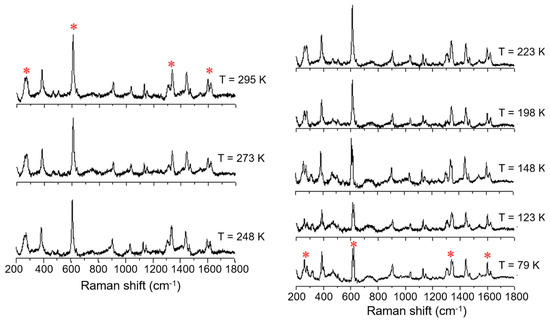
Figure 7.
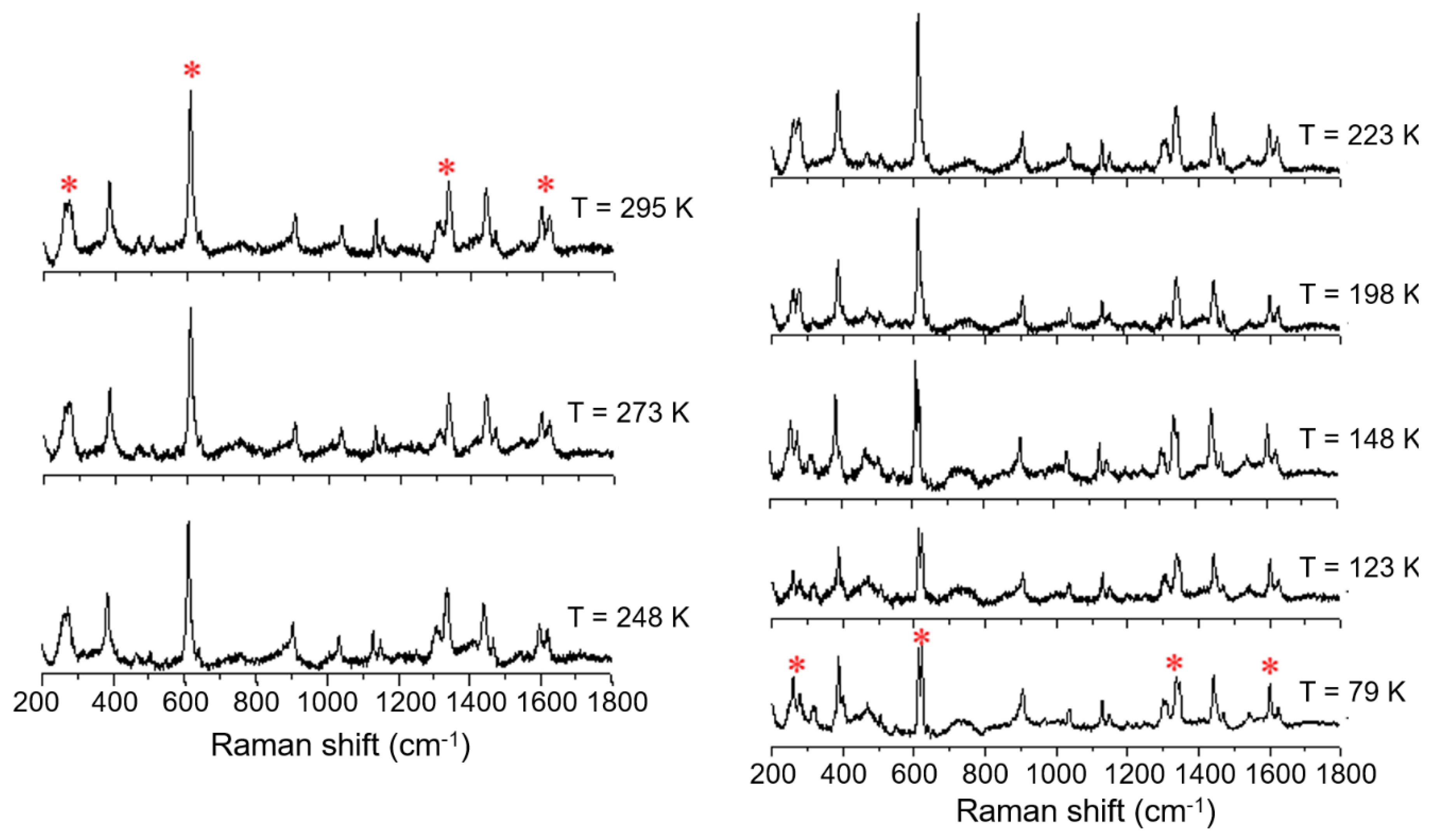
Variable temperature Raman spectra of [FeL1C6]BF4, 1, using laser excitation at 785 nm in the temperature range of 79 K to 295 K.
An investigation into differences in the vibrational modes of all three compounds was made by Raman spectroscopy using an excitation wavelength of 785 nm (4 mW) in a temperature range between 79 K to 295 K. The variable temperature Raman spectra of the C6 alkylated compound (1) show six main modes which change upon cooling from 295 K to 79 K; (Figure 7, indicated by *). The most temperature-responsive Raman modes are identified as 266, 271, 611, 1335, 1599, and 1619 cm−1 at room temperature, and can be associated with the high spin state. These vibrational modes remain practically unchanged down to 223 K. Further cooling to 198 K shows a change in some modes: the mode at 1619 cm−1, attributed primarily to phenyl ring stretch, decreases in intensity, the mode at 1335 cm−1 splits into two distinct vibrational modes, and the mode at 611 cm−1 starts to decrease in relative intensity, giving rise to a new mode at around 620 cm−1. Finally, the broad Raman features at 266 and 271 cm−1 start to resolve, showing that the population of LS species is increasing. The Raman spectrum at 79 K shows significant shifts of between 5 and 20 cm−1, and the key features now appear at 259, 279, 613, 623, 1338, 1348, and 1600 cm−1. It is known from the magnetic profile of compound 1 that, at this temperature, there is a mixture of HS and LS species, and the Raman spectrum at this temperature also confirms this observation, with retention of features from the higher temperature spectrum.
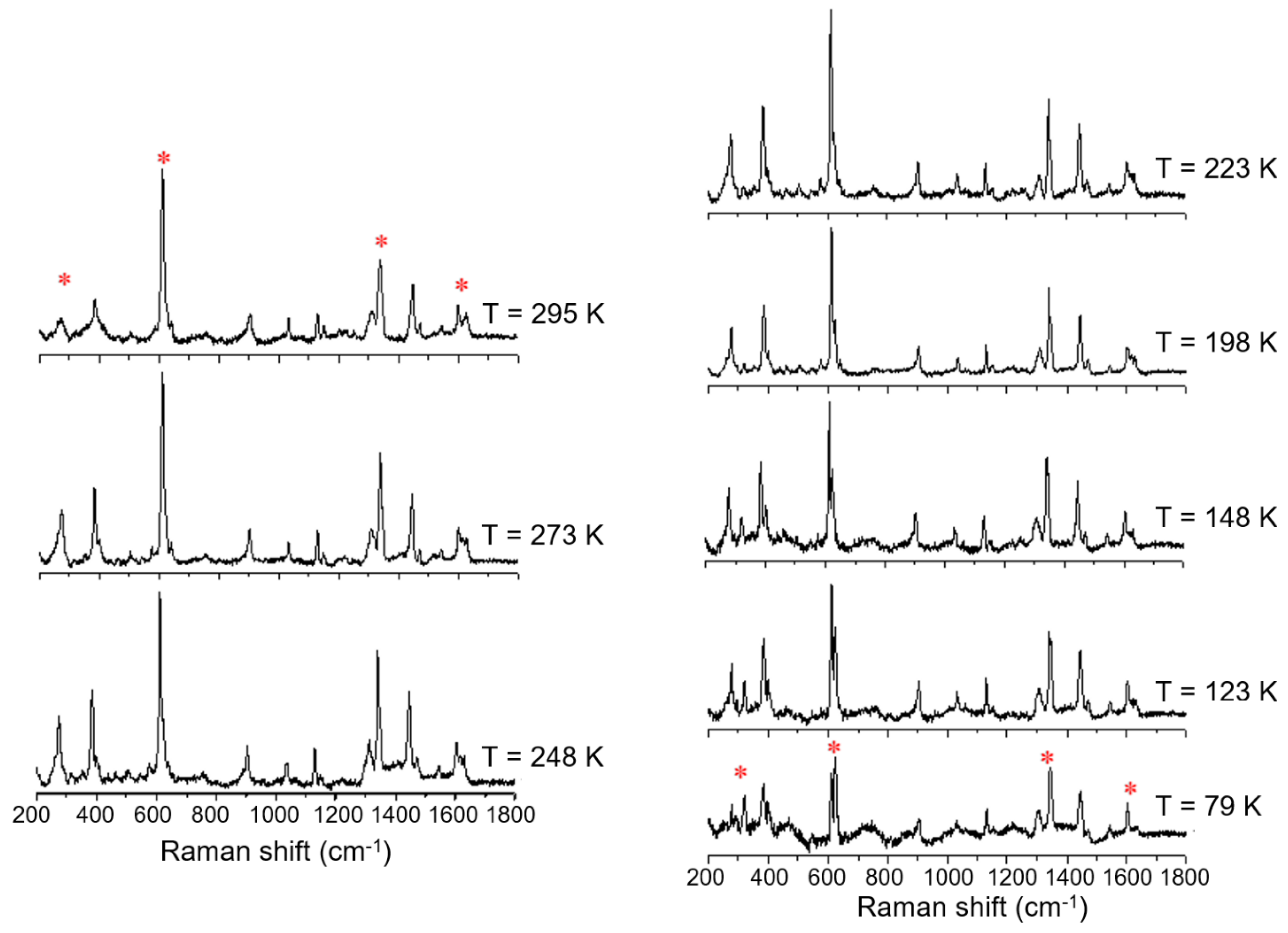
The magnetic plot of the C18 amphiphile, compound 3, shows that it has a very gradual thermal spin transition, which is incomplete at both ends of the temperature range, Figure 6. Raman spectra of this complex also show six main modes which change upon cooling from 295 K to 79 K, which is highlighted in Figure 8. As observed before, at RT, the main modes which undergo a change with temperature are at 268, 272, 612, 625, 1338, 1598, and 1626 cm−1. These vibrational modes change gradually over the measured range, which is in good agreement with the very gradual change the magnetic plot of this compound presents. At 79 K, compound 3 shows vibrational modes at 319, 612, 624, 1346, and 1605 cm−1. The major change observed with temperature was for the vibrational modes at 268 and 272 cm−1, which merge, and a new vibrational mode at 319 cm−1 appears. This spectral region is expected to be dominated by metal–ligand deformation modes that are expected to be profoundly affected by the metal spin state transition. It should be also noted that the vibrational mode, attributed to Fe(III)–O stretch around 623 cm−1, which is characteristic of the LS state, vide infra, never disappears, which is in good agreement with the magnetic result for compound 3.
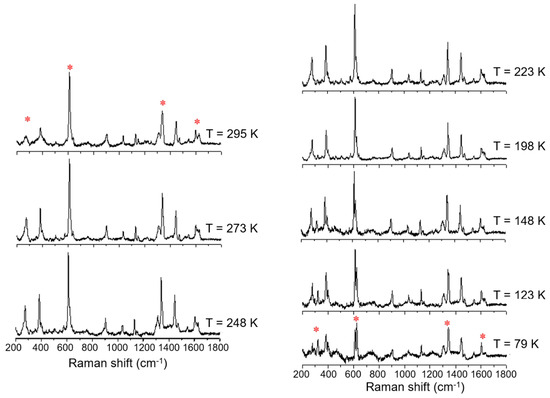
Figure 8.
Variable temperature Raman spectra of [FeL1C18]BF4, 3, using laser excitation at 785 nm in the temperature range of 79 K to 295 K.
Salts of [Fe(sal)2trien]+ are well studied and well characterized for HS, LS, and SCO electronic configurations, and reports of spectroscopic behavior in solution have been published [88,89]. This cation is known to have two distinct absorbance bands: one corresponding to the HS electronic state (≈500 nm), and a second one corresponding to the LS electronic state (≈650 nm). Resonance Raman (rRaman) for the HS state using laser excitation at 532 nm, and for the LS state at 633 nm, can be used to maximize the enhancement achieved by using laser excitation with energy close to the metal-to-ligand charge transfer (MLCT) band. Besides this enhancement of the main modes, less predominant modes can be unobservable when using rRaman, whereas Raman may highlight these modes and should also be used for spectroscopic characterization. We have used Raman spectroscopy with a laser excitation at 785 nm, and rRaman with a laser excitation at 532 nm, which is in resonance with the high-spin UV–vis maximum absorbance band. Raman and rRaman spectra of compounds 1–3 were recorded using these two different laser lines (LL), one at 532 nm (green laser) and a second at 785 nm (red laser), and both were determined at RT and at 79 K using a 50× magnification lens. The Raman spectra of 2 were reported elsewhere before [52], but will be included for completeness. The sample was dispersed on a glass slide, and the variable temperature Raman and rRaman, which are shown in Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11 for compound 1–3. Spectra obtained using 532 nm excitation laser produces enhanced rRaman spectra, but do not permit the observation of thermal spin transition. On the other hand, the spectra obtained using the out-of-resonance 785 nm excitation laser lose the enhancement but permit the observation of the thermal spin transition between HS and LS electronic states.
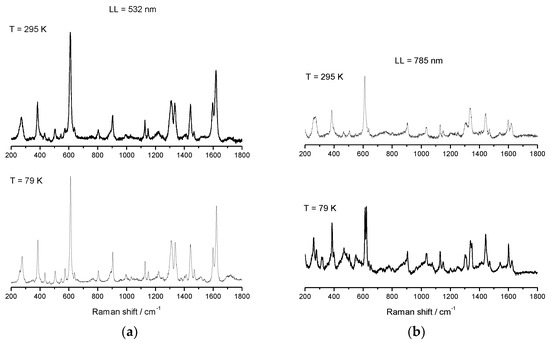
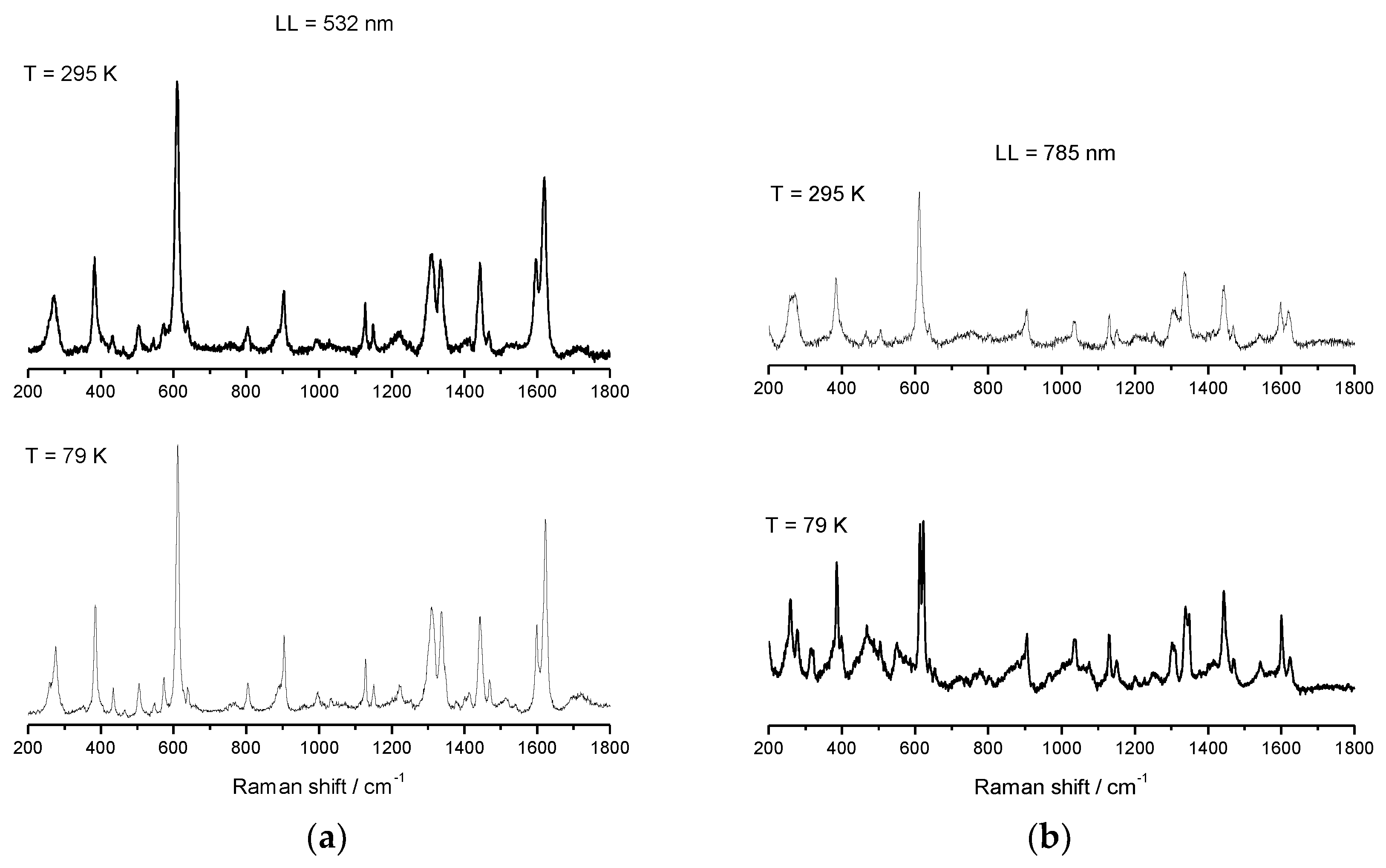
Figure 9.
Variable temperature rRaman spectra of [FeL1C6]BF4, 1, using laser ex 532 nm (a) and variable temperature Raman spectra of [FeL1C6]BF4, 1, using laser excitation of 785 nm (b).
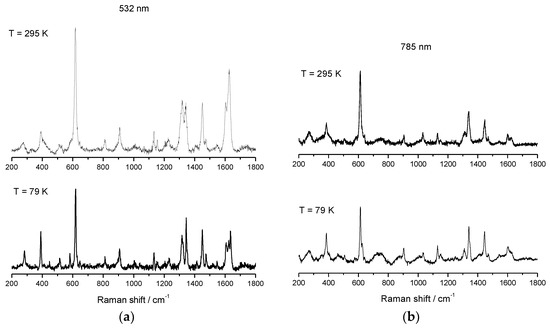
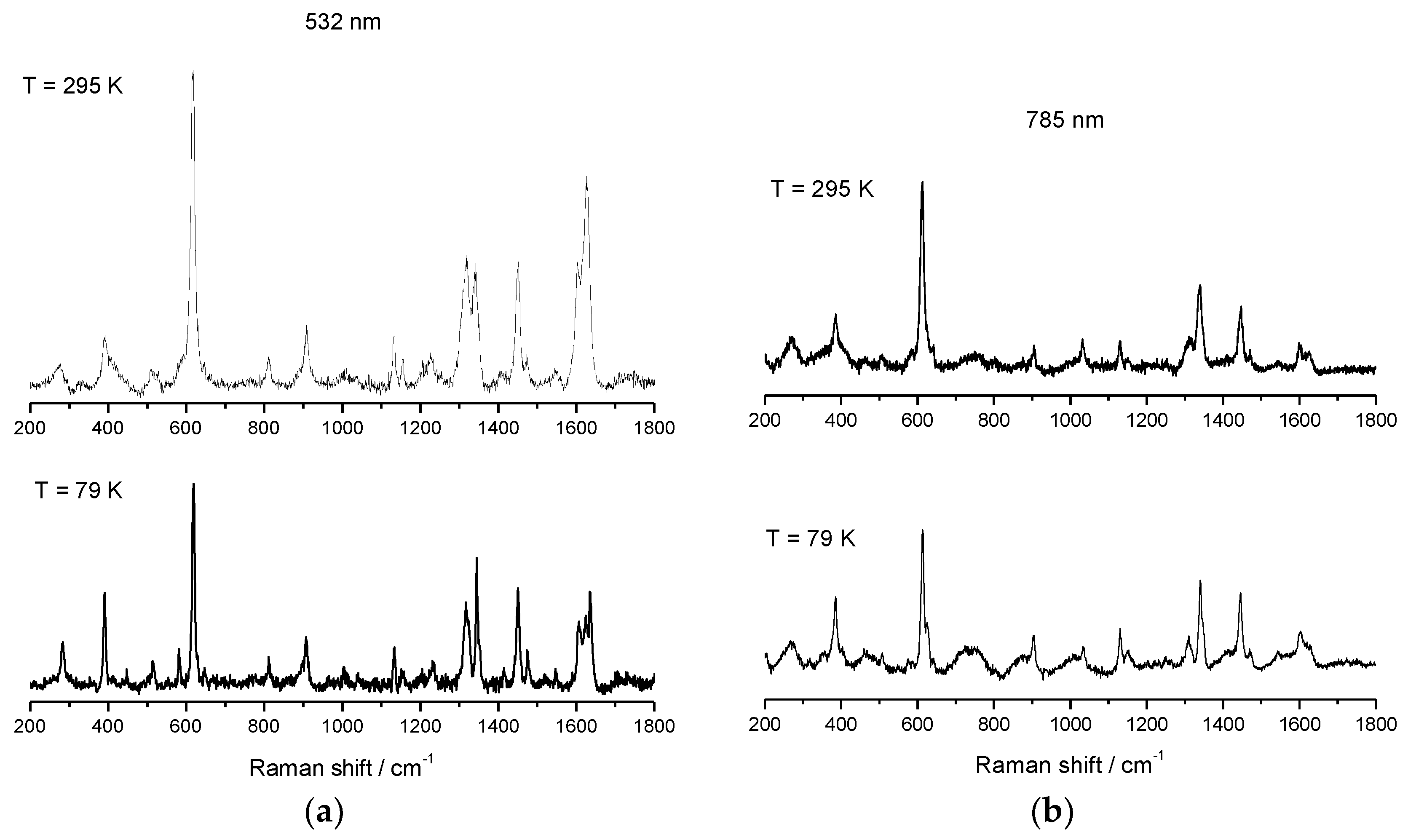
Figure 10.
Variable temperature rRaman spectra of [FeL1C12]BF4, 2, using laser excitation of 532 nm (a) and variable temperature Raman spectra of [FeL1C12]BF4, 2, using laser excitation of 785 nm (b) [52].
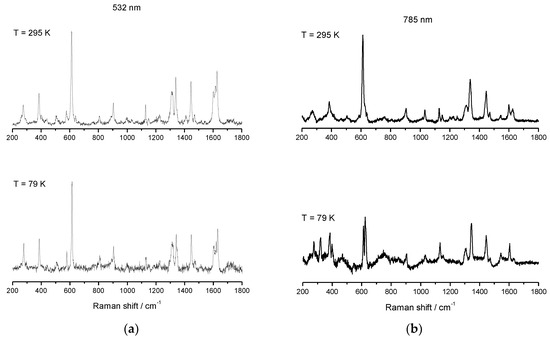
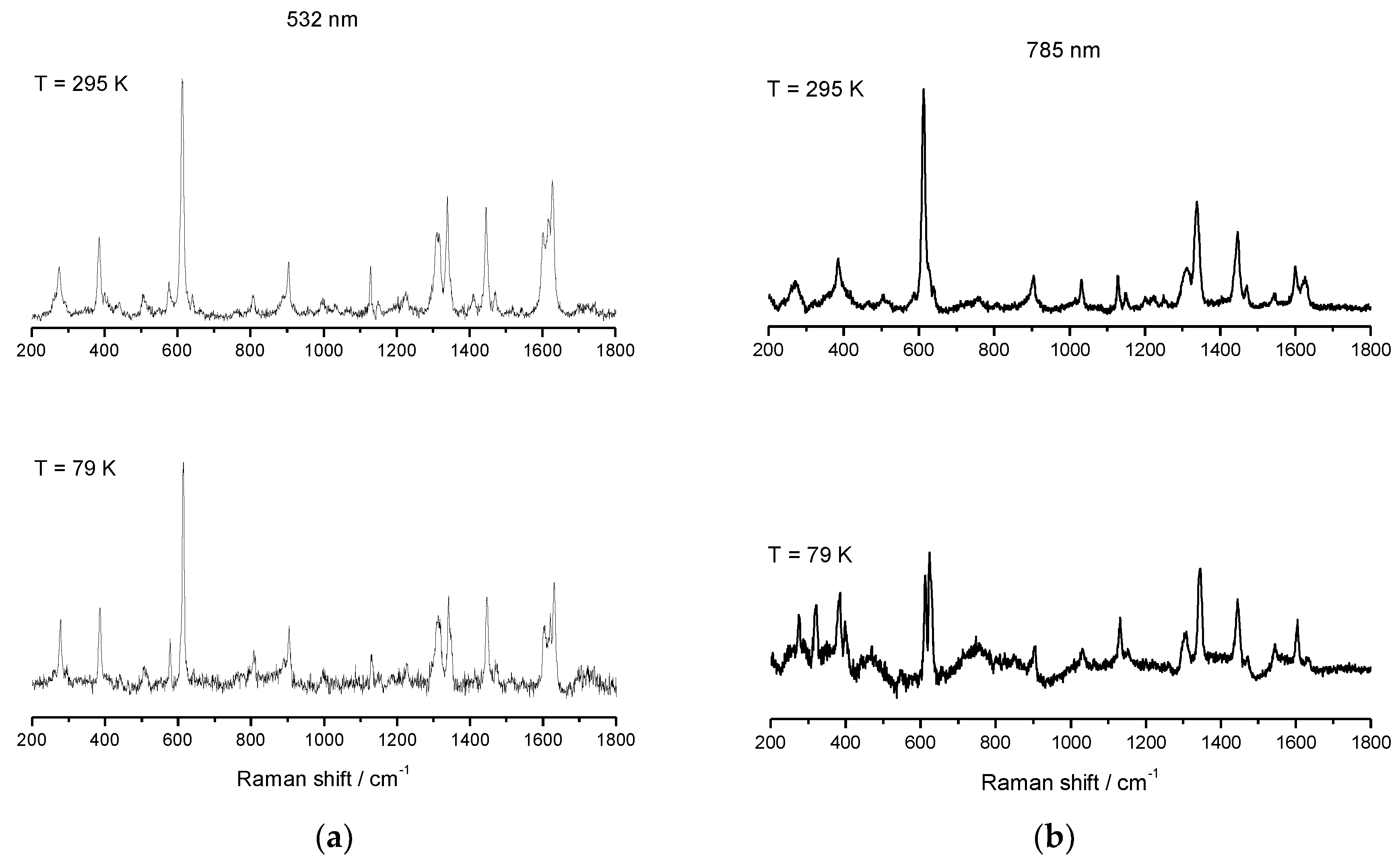
Figure 11.
Variable temperature rRaman spectra of [FeL1C18]BF4, (3), using laser excitation of 532 nm (a) and variable temperature Raman spectra of [FeL1C18]BF4, (3), using laser excitation 785 nm (b).
Variable temperature rRaman spectra of 1 using 532 nm excitation show characteristic features for HS Fe(III), which remain unchanged upon cooling, see Figure 9 and Table 2. When the laser line was changed from 532 nm to 785 nm, the appearance of a new mode at 623 cm−1 (which corresponds to υ(Fe–O)) was observed upon cooling to 79 K i.e., indicative of a spin transition. The main υ(Fe–O) HS mode at 608 cm−1 also becomes less intense due to the increase in LS population on cooling. From comparison of the results obtained for both Raman and rRaman experiments, it was clear that while using rRaman produces an enhancement of the vibrational modes, some very important structural information might be less noticeable, or even undetectable, which does not happen if non-resonance Raman is used to characterize and follow thermal spin changes.

Table 2.
Representative Raman shifts and IR stretches of compounds 1–3.
The υ(Fe–O) vibrational mode of 2 using 532 nm excitation shows characteristic features of HS Fe(III) at 615 cm−1 and 618 cm−1, see Figure 10, which can be assigned to 68% HS character at RT. On cooling to 79 K, a single feature is observable at 618 cm−1, see Table 2. In the Raman experiment with 785 nm laser excitation, a more distinct separation between modes at 613 and 623 cm−1 at 79 K could be observed, although the complete appearance of the mode at 623 cm−1 at low temperature and the complete disappearance of the mode at 613 cm−1 at low temperature was not observed. The appearance of the new mode at 623 cm−1 at 79 K was attributed to the LS signature which, at 79 K, was estimated at 95% from the magnetic data. The absence of the mode at 1627 cm−1, corresponding to υ(C=N) at 79 K, also indicates a thermal spin transition.
Variable temperature rRaman spectra of 3 at 295 K with 532 nm excitation show two features at 611 and 614 cm−1, Figure 11, which can be attributed to a mixture of both HS and LS Fe(III) electronic states with 53% HS character at this temperature; see Table 2. On cooling to 79 K, no significant change was observed, and the same vibrational modes were identified, revealing, once again, that rRaman enhances the signals obtained but can, sometimes, omit relevant information. In the rRaman experiment with 785 nm excitation, a more distinct separation between the modes at 613 and 623 cm−1 could be observed, as seen in Figure 9, and the absence of the υ(C=N) mode at 1627 cm−1, upon cooling to 79 K, indicates a thermal spin transition. It should be noted from the magnetic measurement that, at both ends of temperature range, the complete population of both HS and LS was never attained and, therefore, Raman modes characteristic of both HS and LS should be present at RT and 79 K.
3. Discussion
We have investigated the behavior of three known SCO iron(III) complexes which host hydrophobic alkyl chains varying from C6 to C18. The ability of these compounds to form monolayers at the air–water interface was investigated, and we have found that the C6 compound 1 does not form monolayers at the air–water interface, due to partial solubility of the compound in water. On the other hand, the C12 and C18 amphiphilic compounds 2 and 3 do form stable monolayers at the air–water interface over a long period of time (>90 min). Besides forming stable monolayers at the air–water interface, the Langmuir isotherms of both compounds do not show a steep increase in surface pressure with compression, indicating that the arrangements at the air–water interface are not very ordered, possibly due to backfolding of the alkyl chains. Attempts to transfer the monolayer formed at the air–water interface by the C18 amphiphilic compound 3, onto a glass support, resulted in the transfer of only one layer. This indicates that it is only possible to fabricate a Langmuir–Blodgett monolayer of compound 3. Characterization of the transferred LB monolayer by Raman spectroscopy was not possible, due to insufficient material being deposited on the glass surface. We have also observed that the longer amphiphilic compound 3 forms micellar aggregates in aqueous solution, and that lyophilization of micellar aggregates yields a hydrated product with a magnetic profile that is almost temperature independent, with a predominance of the LS electronic state.
4. Materials and Methods
Pressure–area isotherms and time stability were measured at 25 °C on a KSV MiniMicro Langmuir–Blodgett trough (Biolin Scientific, Espoo, Finland ), with a surface area between 1700 and 8700 mm2. Water was purified with a Barnstead Nanopure system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, UK), and its resistivity was measured to be higher than 18 MΩ cm. Chloroform (puriss. p.a. ≥99.8%, Fluka, was used as spreading solvent. Typically drops of the surfactant solution (20 μL, 0.50 mM) were deposited using a microsyringe on the water subphase. After letting the solvent evaporate for 30 min, the barriers were compressed at 6 mm min−1 (3 cm2 min−1), and the surface pressure was monitored using a platinum Wilhelmy plate. Variable temperature magnetic susceptibility measurements were performed on a Magnetic Property Measurement System (MPMS XL-7) (Quantum Design, CA, USA) sample with Superconducting Quantum Interference Device (SQUID). Dynamic light scattering was measured using a Malvern PCS-4700 instrument (Malvern Panalytical, Malvern, UK) equipped with a 256-channel correlator. The 488.0 nm line of a Coherent Innova-70 Ar ion laser was used as the incident beam with 250 mW laser power, and the employed scattering angles, θ, were 90°. The temperature was maintained at 25 °C with an external circulator. Data analysis was performed according to standard procedures and interpreted through a cumulant expansion of the field autocorrelation function to the second order. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was carried out using a JEOL 2000FX 200 kV instrument (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan) instrument equipped with a LaB6 filament, angle PGT EDXS detector and Gatan slow-scan and wide-angle TV-rate cameras. This instrument has a high-tilt pole piece with a point resolution of 0.3 nm and ±60° double-tilt capability using the Gatan low-background double-tilt holder. Cryo-SEM measurements were completed using an FEI Dual-beam Cryo-focused Ion Beam Scanning Electron Microscope. The Raman spectra were acquired on a confocal Labram HR microscope from Horiba coupled to a 532 nm diode (5 mW) or 785 nm solid state laser source (4 mW) using a 100× (N.A. = 0.90) Olympus objective. The Raman band of a silicon wafer at 520 cm−1 and Rayleigh line were used to calibrate the spectrometer, and the accuracy of the spectral measurement was estimated to be better than 1 cm−1. Measurements at low temperature were carried out in a temperature-controlled stage (THMS 600 from Linkam Scientific Instruments (Linkam Scientific Instruments, Tadworth, UK). The Raman spectra were recorded over the temperature range 295–77 K. The acquisition time for all spectra was set to 6 s, unless otherwise stated. Spectra were background corrected using a 4-point polynomial generated using LabSpec software (Horiba Scientific, Kyoto, Japan).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.G.M. and M.A.; Methodology, T.E.K., G.M., B.O., M.A.; Formal Analysis, P.N.M., B.G., T.L., B.O. and C.G.; Investigation, P.N.M., B.G., T.L., B.O. and C.G.; Resources, G.G.M., T.E.K., G.M. and M.A.; Data Curation, G.G.M., T.E.K., G.M. and M.A.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, G.G.M. and P.N.M.; Writing—Review & Editing, G.G.M., P.N.M., I.A.K.; Visualization, P.N.M., T.L., C.G., I.A.K.; Supervision, G.G.M., T.E.K., G.M. and M.A.; Project Administration, G.G.M.; Funding Acquisition, G.G.M. and M.A.
Funding
This research was funded by the Irish Research Council for Science, Engineering (IRCSET) and the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) under the ERA-Chemistry programme (studentships to P.N.M and C.G.); by the award of an IRCSET Government of Ireland Research Scholarship (to B.G.); by generous financial support from Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (to P.N.M.); by support from University College Dublin and the Irish Higher Education Authority (to G.G.M.); by the Irish Research Council (IRC) for the GOIPD/2016/503 fellowship [I.A.K.]; by Science Foundation Ireland for Investigator Project Award 12/IP/1703 (to G.G.M). The generous support of COST Actions CM1305, ECOSTBio, CA15128, MOLSPIN and CA15107, MultiCOMP is gratefully acknowledged.
Acknowledgments
We thank K. Dawson (UCD Centre for Bionano Interactions (CBNI)) for the use of DLS facilities and Eugene Mahon (UCD CBNI) for useful discussions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Weller, D.; Moser, A. Thermal effect limits in ultrahigh-density magnetic recording. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1999, 35, 4423–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skumryev, V.; Stoyanov, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hadjipanayis, G.; Givord, D.; Nogués, J. Beating the superparamagnetic limit with exchange bias. Nature 2003, 423, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leoni, T.; Guillermet, O.; Walch, H.; Langlais, V.; Scheuermann, A.; Bonvoisin, J.; Gauthier, S. Controlling the Charge State of a Single Redox Molecular Switch. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 216103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swart, I.; Sonnleitner, T.; Repp, J. Charge State Control of Molecules Reveals Modification of the Tunneling Barrier with Intramolecular Contrast. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 1580–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repp, J.; Meyer, G.; Olsson, F.E.; Persson, M. Controlling the Charge State of Individual Gold Adatoms. Science 2004, 305, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Létard, J.-F.; Guionneau, P.; Goux-Capes, L. Towards Spin Crossover Applications. Top. Curr. Chem. 2004, 235, 221–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusso, J.L.; Clements, O.P.; Haddon, R.C.; Itkis, M.E.; Leitch, A.A.; Oakley, R.T.; Reed, R.W.; Richardson, J.F. Bistabilities in 1,3,2-Dithiazolyl Radicals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 8256–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norel, L.; Rota, J.-B.; Chamoreau, L.-M.; Pilet, G.; Robert, V.; Train, C. Spin Transition and Exchange Interaction: Janus Visions of Supramolecular Spin Coupling between Face-to-Face Verdazyl Radicals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7128–7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balzani, V.; Credi, A.; Venturi, M. Molecular Devices and Machines—A Journey into the Nano World; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2003; ISBN 3527305068. [Google Scholar]
- Spruell, J.M.; Paxton, W.F.; Olsen, J.-C.; Benítez, D.; Tkatchouk, E.; Stern, C.L.; Trabolsi, A.; Friedman, D.C.; Goddard, W.A.; Stoddart, J.F. A Push-Button Molecular Switch. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 11571–11580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, H.-R.; Vignon, S.A.; Celestre, P.C.; Perkins, J.; Jeppesen, J.O.; Di Fabio, A.; Ballardini, R.; Gandolfi, M.T.; Venturi, M.; Balzani, V.; et al. Redox-Controllable Amphiphilic [2] Rotaxanes. Chem. Eur. J. 2004, 10, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallini, M.; Biscarini, F.; Léon, S.; Zerbetto, F.; Bottari, G.; Leigh, D.A. Information Storage Using Supramolecular Surface Patterns. Science 2003, 299, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigh, D.A.; Morales, M.Á.F.; Pérez, E.M.; Wong, J.K.Y.; Saiz, C.G.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Carmichael, A.J.; Haddleton, D.M.; Brouwer, A.M.; Buma, W.J.; et al. Patterning through Controlled Submolecular Motion: Rotaxane-Based Switches and Logic Gates that Function in Solution and Polymer Films. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3062–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krober, J.; Codjovi, E.; Kahn, O.; Groliere, F.; Jay, C. A spin transition system with a thermal hysteresis at room temperature. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 9810–9811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, B.; Bauer, W.; Obel, J. An Iron(II) Spin-Crossover Complex with a 70 K Wide Thermal Hysteresis Loop. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 10098–10101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halcrow, M.A. Spin-Crossover Materials; Halcrow, M.A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd: Oxford, UK, 2013; ISBN 9781118519301. [Google Scholar]
- Gütlich, P.; Garcia, Y.; Spiering, H. Spin Transition Phenomena. In Magnetism: Molecules to Materials IV; Miller, J.S., Drillon, M., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2003; pp. 271–344. [Google Scholar]
- Gütlich, P.; Garcia, Y.; Goodwin, H.A. Spin crossover phenomena in Fe(II) complexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2000, 29, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGravey, J.J.; Lawthers, I. Photochemically-induced perturbation of the 1 A ⇌ 5 T equilibrium in Fe(II) complexes by pulsed laser irradiation in the metal-to-ligand charge-transfer absorption band. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1982, 906–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, A. Light-Induced Spin Crossover and the High-Spin → Low-Spin Relaxation. In Spin Crossover in Transition Metal Compounds II; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bonhommeau, S.; Molnár, G.; Galet, A.; Zwick, A.; Real, J.-A.; McGarvey, J.J.; Bousseksou, A. One Shot Laser Pulse Induced Reversible Spin Transition in the Spin-Crossover Complex [Fe(C4H4N2){Pt(CN)4}] at Room Temperature. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4069–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousseksou, A.; Negre, N.; Goiran, M.; Salmon, L.; Tuchagues, J.-P.; Boillot, M.-L.; Boukheddaden, K.; Varret, F. Dynamic triggering of a spin-transition by a pulsed magnetic field. Eur. Phys. J. B 2000, 13, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousseksou, A.; Boukheddaden, K.; Goiran, M.; Consejo, C.; Boillot, M.-L.; Tuchagues, J.-P. Dynamic response of the spin-crossover solid Co(H2(fsa)2en)(py)2 to a pulsed magnetic field. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 65, 172412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ksenofontov, V.; Gaspar, A.B.; Gütlich, P. Pressure Effect Studies on Spin Crossover and Valence Tautomeric Systems. In Spin Crossover in Transition Metal Compounds III; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Niel, V.; Muñoz, M.C.; Gaspar, A.B.; Galet, A.; Levchenko, G.; Real, J.A. Thermal-, Pressure-, and Light-Induced Spin Transition in Novel Cyanide-Bridged FeII-AgI Bimetallic Compounds with Three-Dimensional Interpenetrating Double Structures {FeIILx[Ag(CN)2]2}⋅G. Chem. Eur. J. 2002, 8, 2446–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeftić, J.; Hauser, A. Pressure Study of the Thermal Spin Transition and the High-Spin → Low-Spin Relaxation in the R-3 and P-1 Crystallographic Phases of [Zn1- xFex(ptz)6](BF4)2 Single Crystals (x = 0.1, 0.32, and 1; ptz = 1-n-propyltetrazole). J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 10262–10270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamachi, T.; Gruber, M.; Davesne, V.; Bowen, M.; Boukari, S.; Joly, L.; Scheurer, F.; Rogez, G.; Yamada, T.K.; Ohresser, P.; et al. Robust spin crossover and memristance across a single molecule. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopakumar, T.G.; Matino, F.; Naggert, H.; Bannwarth, A.; Tuczek, F.; Berndt, R. Electron-Induced Spin Crossover of Single Molecules in a Bilayer on Gold. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 6262–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gütlich, P.; Goodwin, H.A. Spin Crossover—An Overall Perspective. In Spin Crossover in Transition Metal Compounds I; Gütlich, P., Goodwin, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bousseksou, A.; McGarvey, J.J.; Varret, F.; Real, J.A.; Tuchagues, J.-P.; Dennis, A.C.; Boillot, M.L. Raman spectroscopy of the high- and low-spin states of the spin crossover complex Fe(phen)2(NCS)2: An initial approach to estimation of vibrational contributions to the associated entropy change. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2000, 318, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayagaki, T.; Tanaka, K. Photoinduced Phase Transition to a New Macroscopic Spin-Crossover-Complex Phase. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 2886–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gütlich, P.; Hauser, A.; Spiering, H. Thermal and Optical Switching of Iron(II) Complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1994, 33, 2024–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, A.; Vef, A.; Adler, P. Intersystem crossing dynamics in Fe(II) coordination compounds. J. Chem. Phys. 1991, 95, 8710–8717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, A. Intersystem crossing in Fe(II) coordination compounds. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1991, 111, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Stocker, M.; Gieb, K.; Müller, P.; Haryono, M.; Student, K.; Grohmann, A. Spin-State Patterns in Surface-Grafted Beads of Iron(II) Complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 1159–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Félix, G.; Abdul-Kader, K.; Mahfoud, T.; Gural’skiy, I.A.; Nicolazzi, W.; Salmon, L.; Molnár, G.; Bousseksou, A. Surface Plasmons Reveal Spin Crossover in Nanometric Layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15342–15345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousseksou, A.; Molnár, G.; Salmon, L.; Nicolazzi, W. Molecular spin crossover phenomenon: Recent achievements and prospects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3313–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallini, M. Status and perspectives in thin films and patterning of spin crossover compounds. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 11867–11876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boldog, I.; Gaspar, A.B.; Martínez, V.; Pardo-Ibañez, P.; Ksenofontov, V.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Gütlich, P.; Real, J.A. Spin-Crossover Nanocrystals with Magnetic, Optical, and Structural Bistability Near Room Temperature. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 6433–6437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volatron, F.; Catala, L.; Rivière, E.; Gloter, A.; Stéphan, O.; Mallah, T. Spin-Crossover Coordination Nanoparticles. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 6584–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Létard, J.-F.; Nguyen, O.; Daro, N. Nanoparticules d’un composé à transition de. spin Patent FR2894581, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Coronado, E.; Galán-Mascarós, J.R.; Monrabal-Capilla, M.; García-Martínez, J.; Pardo-Ibáñez, P. Bistable Spin-Crossover Nanoparticles Showing Magnetic Thermal Hysteresis near Room Temperature. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 1359–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarev, A.; Salmon, L.; Guari, Y.; Nicolazzi, W.; Molnár, G.; Bousseksou, A. Cooperative spin crossover phenomena in [Fe(NH2trz)3](tosylate)2 nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 8011–8013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galán-Mascarós, J.R.; Coronado, E.; Forment-Aliaga, A.; Monrabal-Capilla, M.; Pinilla-Cienfuegos, E.; Ceolin, M. Tuning Size and Thermal Hysteresis in Bistable Spin Crossover Nanoparticles. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 5706–5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forestier, T.; Mornet, S.; Daro, N.; Nishihara, T.; Mouri, S.; Tanaka, K.; Fouché, O.; Freysz, E.; Létard, J.-F. Nanoparticles of iron(II) spin-crossover. Chem. Commun. 2008, 4327–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larionova, J.; Salmon, L.; Guari, Y.; Tokarev, A.; Molvinger, K.; Molnár, G.; Bousseksou, A. Towards the Ultimate Size Limit of the Memory Effect in Spin-Crossover Solids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 8236–8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandolfi, C.; Moitzi, C.; Schurtenberger, P.; Morgan, G.G.; Albrecht, M. Improved Cooperativity of Spin-Labile Iron(III) Centers by Self-Assembly in Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14434–14435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandolfi, C.; Miyashita, N.; Kurth, D.G.; Martinho, P.N.; Morgan, G.G.; Albrecht, M. Organization of spin- and redox-labile metal centers into Langmuir and Langmuir–Blodgett films. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 4508–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandolfi, C.; Morgan, G.G.; Albrecht, M. A magnetic iron(III) switch with controlled and adjustable thermal response for solution processing. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 3726–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinho, P.N.; Harding, C.J.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Albrecht, M.; Morgan, G.G. Inducing Spin Crossover in Amphiphilic Iron(III) Complexes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 2010, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, P.N.; Ortin, Y.; Gildea, B.; Gandolfi, C.; McKerr, G.; O’Hagan, B.; Albrecht, M.; Morgan, G.G. Inducing hysteretic spin crossover in solution. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 7461–7463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinho, P.N.; Lemma, T.; Gildea, B.; Picardi, G.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Forster, R.J.; Keyes, T.E.; Redmond, G.; Morgan, G.G. Template Assembly of Spin Crossover One-Dimensional Nanowires. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 11995–11999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandolfi, C.; Cotting, T.; Martinho, P.N.; Sereda, O.; Neels, A.; Morgan, G.G.; Albrecht, M. Synthesis and self-assembly of spin-labile and redox-active manganese(III) complexes. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 1855–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blodgett, K.B. Monomolecular Films of Fatty Acids on Glass. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1934, 56, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blodgett, K.B.; Langmuir, I. Built-Up Films of Barium Stearate and Their Optical Properties. Phys. Rev. 1937, 51, 964–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, F.; Liu, T.; Yuan, M.; Wang, Z.-M.; Gao, S. Spin Crossover in a Series of Iron(II) Complexes of 2-(2-Alkyl-2H-tetrazol-5-yl)-1,10-phenanthroline: Effects of Alkyl Side Chain, Solvent, and Anion. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 2541–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayami, S.; Danjobara, K.; Shigeyoshi, Y.; Inoue, K.; Ogawa, Y.; Maeda, Y. Crystal structure and mesogenic property of an iron(II) complex with a terpyridine derivative ligand. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2005, 8, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, H.S.; Moubaraki, B.; Paradis, N.; Chastanet, G.; Létard, J.-F.; Batten, S.R.; Murray, K.S. 2,2′-Dipyridylamino-based ligands with substituted alkyl chain groups and their mononuclear-M(II) spin crossover complexes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 7845–7857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, S.; Kawasaki, T.; Okabayashi, J.; Kitazawa, T. 2D Spin-Crossover Coordination Polymer Fe(hexyl-nicotinate)2[Au(CN)2]2. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2016, 89, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredyuk, M.; Gaspar, A.B.; Ksenofontov, V.; Galyametdinov, Y.; Kusz, J.; Gütlich, P. Does the Solid−Liquid Crystal Phase Transition Provoke the Spin-State Change in Spin-Crossover Metallomesogens? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seredyuk, M. Iron(II) metallomesogens based on symmetrical tripod ligands. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2012, 380, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredyuk, M.; Gaspar, A.B.; Ksenofontov, V.; Galyametdinov, Y.; Kusz, J.; Gütlich, P. Iron(II) Metallomesogens Exhibiting Coupled Spin State and Liquid Crystal Phase Transitions near Room Temperature. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 2089–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vologzhanina, A.V.; Belov, A.S.; Novikov, V.V.; Dolganov, A.V.; Romanenko, G.V.; Ovcharenko, V.I.; Korlyukov, A.A.; Buzin, M.I.; Voloshin, Y.Z. Synthesis and Temperature-Induced Structural Phase and Spin Transitions in Hexadecylboron-Capped Cobalt(II) Hexachloroclathrochelate and Its Diamagnetic Iron(II)-Encapsulating Analogue. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 5827–5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voloshin, Y.Z.; Varzatskii, O.A.; Stash, A.I.; Belsky, V.K.; Bubnov, Y.N.; Vorontsov, I.I.; Potekhin, K.A.; Antipin, M.Y.; Polshin, E.V. Template synthesis, structure and unusual series of phase transitions in clathrochelate iron(II) α-dioximates and oximehydrazonates formed by capping with functionalized boron-containing agents. Polyhedron 2001, 20, 2721–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.-K.; Li, Z.-H.; Zhu, W.; Li, T.; Li, Z.; Ren, X.; Gu, Z.-G. Molecular isomerism induced Fe(II) spin state difference based on the tautomerization of the 4(5)-methylimidazole group. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 4218–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchen, J.A.; White, N.G.; Jameson, G.N.L.; Tallon, J.L.; Brooker, S. Effect of Counteranion X on the Spin Crossover Properties of a Family of Diiron(II) Triazole Complexes [FeII2(PMAT)2](X)4. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 4586–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlamp, S.; Weber, B.; Naik, A.D.; Garcia, Y. Cooperative spin transition in a lipid layer like system. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 7152–7154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlamp, S.; Thoma, P.; Weber, B. New Octahedral, Head-Tail Iron(II) Complexes with Spin Crossover Properties. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 2012, 2759–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlamp, S.; Dankhoff, K.; Weber, B. Amphiphilic iron(II) complexes with short alkyl chains – crystal packing and spin transition properties. N. J. Chem. 2014, 38, 1965–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlamp, S.; Lochenie, C.; Bauer, T.; Kempe, R.; Weber, B. Iron(II) Spin-Crossover Complexes with Schiff Base Like Ligands and N-Alkylimidazoles. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 2015, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlamp, S.; Thoma, P.; Weber, B. Influence of the Alkyl Chain Length on the Self-Assembly of Amphiphilic Iron Complexes: An Analysis of X-ray Structures. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 6462–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakaya, M.; Shimayama, K.; Takami, K.; Hirata, K.; Amolegbe, S.; Nakamura, M.; Lindoy, L.; Hayami, S. Structures and Magnetic Properties of Iron(III) Complexes with Long Alkyl Chains. Crystals 2014, 4, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario-Amorin, D.; Dechambenoit, P.; Bentaleb, A.; Rouzières, M.; Mathonière, C.; Clérac, R. Multistability at Room Temperature in a Bent-Shaped Spin-Crossover Complex Decorated with Long Alkyl Chains. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayami, S.; Shigeyoshi, Y.; Akita, M.; Inoue, K.; Kato, K.; Osaka, K.; Takata, M.; Kawajiri, R.; Mitani, T.; Maeda, Y. Reverse Spin Transition Triggered by a Structural Phase Transition. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4899–4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talham, D.R. Conducting and Magnetic Langmuir−Blodgett Films. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 5479–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, A.B.; Seredyuk, M. Spin crossover in soft matter. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2014, 268, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruaudel-Teixier, A.; Barraud, A.; Coronel, P.; Kahn, O. Spin transition in a magnetic Langmuir-Blodgett film. Thin Solid Films 1988, 160, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubeau, O.; Agricole, B.; Clérac, R.; Ravaine, S. Triazole-Based Magnetic Langmuir−Blodgett Films: Paramagnetic to Spin-Crossover Behavior. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 15110–15116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyer, H.; Dupart, E.; Gómez-García, C.J.; Mingotaud, C.; Delhaès, P. First Magnetic Observation of a Spin Crossover in a Langmuir-Blodgett Film. Adv. Mater. 1999, 11, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Létard, J.F.; Nguyen, O.; Soyer, H.; Mingotaud, C.; Delhaès, P.; Kahn, O. First Evidence of the LIESST Effect in a Langmuir−Blodgett Film. Inorg. Chem. 1999, 38, 3020–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodenthin, Y.; Pietsch, U.; Möhwald, H.; Kurth, D.G. Inducing Spin Crossover in Metallo-supramolecular Polyelectrolytes through an Amphiphilic Phase Transition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 3110–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchen, J.A.; White, N.G.; Gandolfi, C.; Albrecht, M.; Jameson, G.N.L.; Tallon, J.L.; Brooker, S. Room-temperature spin crossover and Langmuir–Blodgett film formation of an iron(II) triazole complex featuring a long alkyl chain substituent: The tail that wags the dog. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 6464–6466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gütlich, P.; Gaspar, A.B.; Garcia, Y. Spin state switching in iron coordination compounds. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 342–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayami, S. Amphiphilic and Liquid Crystalline Spin-Crossover Complexes. In Spin-Crossover Materials; John Wiley & Sons Ltd: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 321–345. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyoshi, R.; Kuroiwa, K.; Alao Amolegbe, S.; Nakaya, M.; Ohtani, R.; Nakamura, M.; Lindoy, L.F.; Hayami, S. Supramolecular architectures self-assembled using long chain alkylated spin crossover cobalt(II) compounds. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 4685–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feltham, H.L.C.; Johnson, C.; Elliott, A.B.S.; Gordon, K.C.; Albrecht, M.; Brooker, S. “Tail” Tuning of Iron(II) Spin Crossover Temperature by 100 K. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 2902–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzpatrick, A.J.; Martinho, P.N.; Gildea, B.J.; Holbrey, J.D.; Morgan, G.G. Robust Room Temperature Hysteresis in an Fe(III) Spin Crossover Metallomesogen. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 2016, 2025–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tweedle, M.F.; Wilson, L.J. Variable spin iron(III) chelates with hexadentate ligands derived from triethylenetetramine and various salicylaldehydes. Synthesis, characterization, and solution state studies of a new 2T ⇌ 6A spin equilibrium system. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 4824–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrano, C.J.; Carrano, M.W.; Sharma, K.; Backes, G.; Sanders-Loehr, J. Resonance Raman spectra of high- and low-spin ferric phenolates. Models for dioxygenases and nitrile hydratase. Inorg. Chem. 1990, 29, 1865–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).