Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Grain Refined Pr2Co14B Melt-Spun Ribbons
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
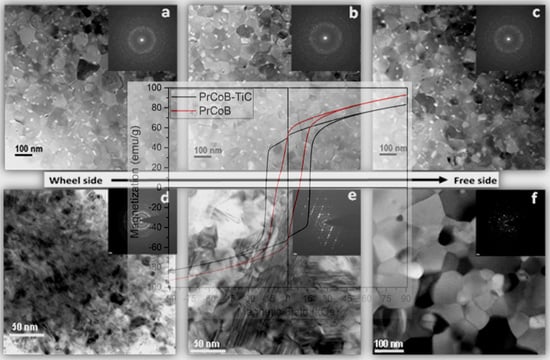
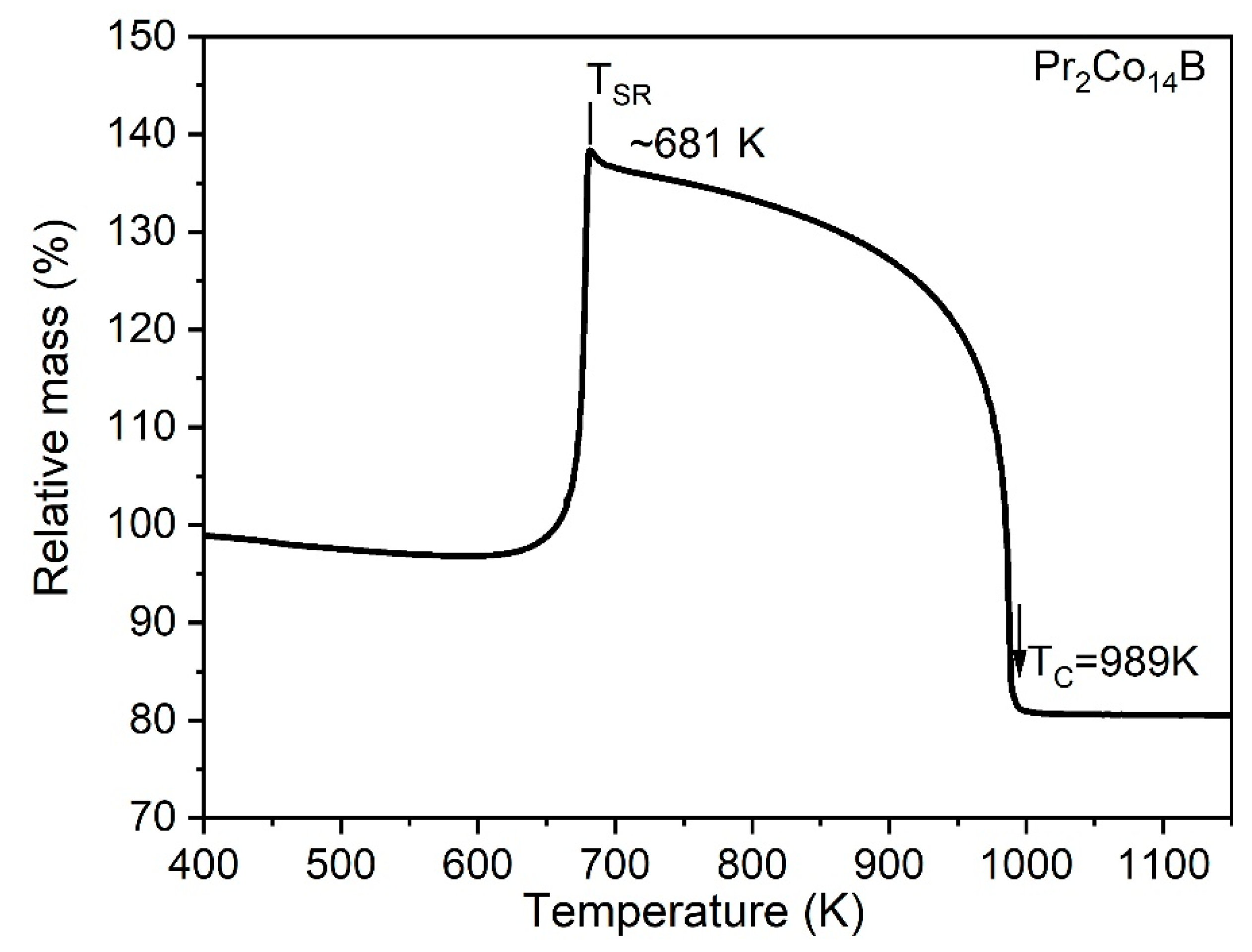
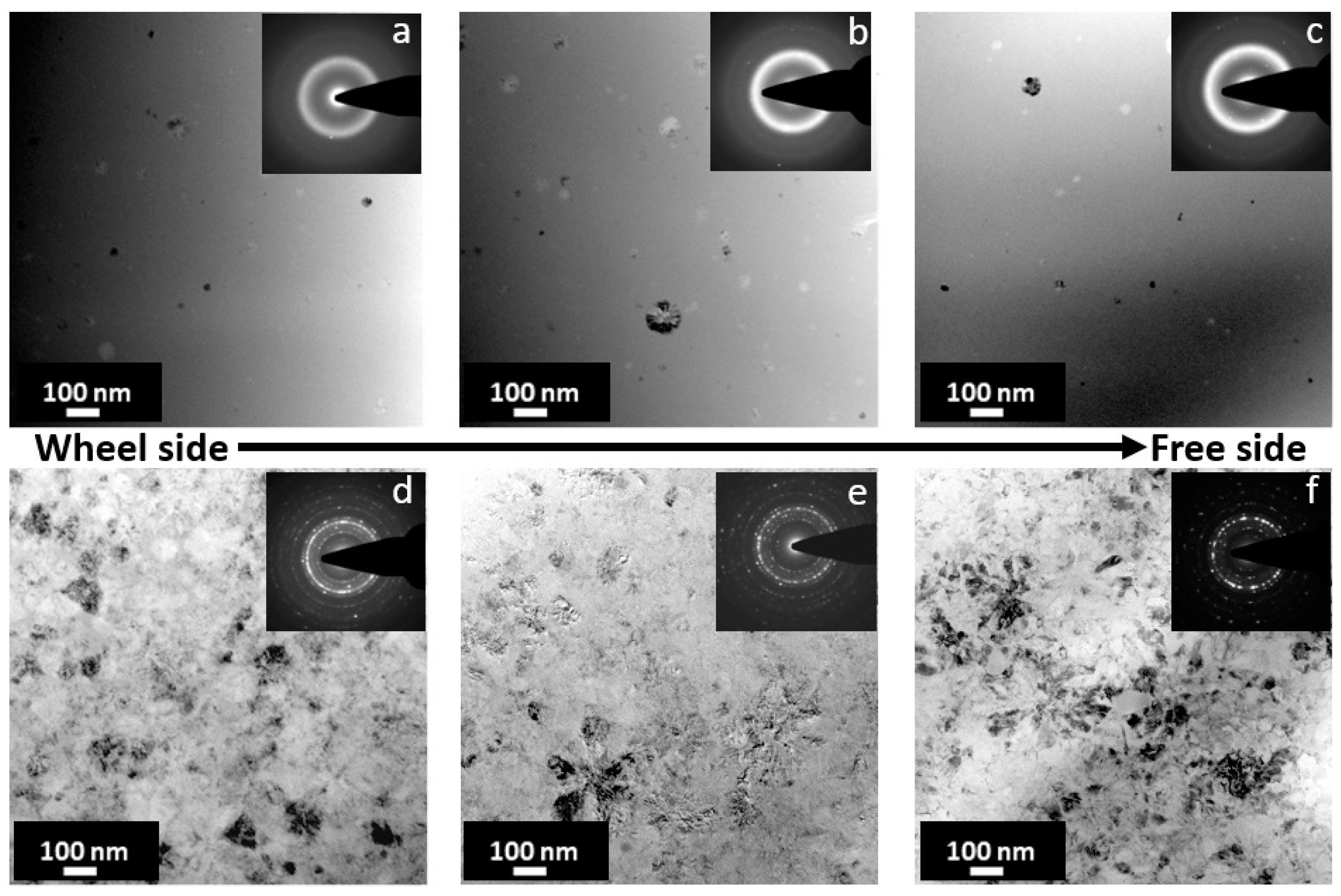
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herbst, J. R2Fe14B materials: Intrinsic properties and technological aspects. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1991, 63, 819–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagawa, M.; Fujimura, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Matsuura, Y.; Hiraga, K. Permanent magnet materials based on the rare earth-iron-boron tetragonal compounds. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1984, 20, 1584–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Morimoto, S. Comparison of dysprosium security strategies in Japan for 2010–2030. Resour. Policy 2014, 39, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Gao, R.W.; Sun, Y.; Han, G.B.; Wang, B. Study of high-coercivity sintered NdFeB magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 308, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrault, F.; Arnold, D.P.; Zana, I.; Galle, P.; Allen, M.G. High temperature operation of multi-watt, axial-flux, permanent-magnet microgenerators. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 148, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.T.; Ohkubo, T.; Hono, K. Structure and chemical compositions of the grain boundary phase in Nd-Fe-B sintered magnets. Acta Mater. 2016, 115, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Yasui, A.; Kotani, Y.; Fukagawa, T.; Nishiuchi, T.; Iwai, H.; Akiya, T.; Ohkubo, T.; Gohda, Y.; Hono, K.; et al. Direct observation of ferromagnetism in grain boundary phase of Nd-Fe-B sintered magnet using soft x-ray magnetic circular dichroism. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 202404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Liu, Z.W.; Zhong, X.C.; Zhang, G.Q. Properties improvement and structural optimization of sintered NdFeB magnets by non-rare earth compound grain boundary diffusion. Mater. Des. 2015, 86, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, K.-H.; Kim, T.-H.; Lee, S.-R.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, M.-W.; Jang, T.-S. Magnetic and microstructural characteristics of DyF3/DyHx dip-coated Nd–Fe–B sintered magnets. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 612, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, A.M.; Hu, X.C.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. Mechanochemical synthesis of fine R2Fe14BHx and R2Fe14B powders with R=Nd or Nd–Dy. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 574, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucar, H.; Parker, D.S.; Nlebedim, I.C.; McCallum, R.W.; McCall, S.K.; Paranthaman, M.P. Strategic coating of NdFeB magnets with Dy to improve the coercivity of permanent magnets. Adv. Mater. Res. 2015, 4, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Ma, T.; Zhang, P.; Jin, J.; Yan, M. Coercivity enhancement of NdFeB sintered magnets by low melting point Dy32.5Fe62Cu5.5 alloy modification. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 355, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodewald, W.; Katter, M. Properties and Applications of High Performance Magnets. VACUUMSCHMELZE GmbH Co. KG. (n.d.) Available online: https://www.vacuumschmelze.de/fileadmin/documents/pdf/fipublikationen/Paper_HPMA_2004_Magnets.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2018).
- EEC. Neodymium Iron Boron Magnets. Electron Energy Corp. (n.d.) Available online: http://www.electronenergy.com/neodymium-iron-boron-magnets/ (accessed on 12 November 2018).
- Manthey, N. Samsung SDI to Reduce Cobalt in Its Batteries to Zero. Electrive.Com. 2018. Available online: https://www.electrive.com/2018/02/12/samsung-sdi-reduce-cobalt-batteries-zero/ (accessed on 12 November 2018).
- Bailey, M.P. Cabot to Develop Low-Cobalt Cathodes for DOE’s Lithium-Ion Battery Research Project. Chemical Engineering. 2018. Available online: https://www.chemengonline.com/cabot-to-develop-low-cobalt-cathodes-for-does-lithium-ion-battery-research-project/?printmode=1 (accessed on 12 November 2018).
- Christodoulou, C.N.; Massalski, T.B.; Wallace, W.E. Magnetic hardening of the Pr2Co14B-based rapidly quenched alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1993, 125, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S. Rare Earth Permanent Magnet Alloys’ High Temperature Phase Transformation: In Situ and Dynamic Observation and Its Application in Material Design; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Christodoulou, C.N.; Wallace, W.E.; Massalski, T.B. Magnetic hardening of Pr-Co-B sintered magnets (abstract). J. Appl. Phys. 1990, 66, 2749–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschow, K.H.J.; de Mooij, D.B.; Sinnema, S.; Radwanski, R.J.; Franse, J.J.M. Magnetic and crystallographic properties of ternary rare earth compounds of the type R2Co14B. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1985, 51, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimao, M.; Ido, H.; Kido, G.; Ohashi, K. Magnetic properties of R2Co14B (R = rare earth). IEEE Trans. Magn. 1987, 23, 2722–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuerst, C.D.; Herbst, J.F.; Pinkerton, F.E. Magnetic hardening of Pr2Co14B. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 64, 5556–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Wu, Y.Q.; Dennis, K.W.; Kramer, M.J.; Anderson, I.E.; McCallum, R.W. Effect of TiC addition on microstructure and magnetic properties for MRE2(Fe,Co)14B melt-spun ribbons (MRE=Nd+Y+Dy). J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 08B510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.J.; Li, C.P.; Dennis, K.W.; McCallum, R.W.; Sellers, C.H.; Branagan, D.J.; Lewis, L.H.; Wang, J.Y. Effect of TiC additions to the microstructure and magnetic properties of Nd9.5Fe84.5B6 melt-spun ribbons. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 83, 6631–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucar, H.; Nlebedim, I.C.; Paranthaman, M.P.; McCallum, R.W. Evolution of structural and magnetic properties due to nanocrystallization of mechanically milled amorphous Pr-Co-B powders. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 233901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedziwiatr, A.T.; Wallace, W.E. Spin arrangements in R2Co14B compounds (R = rare earth). Solid State Commun. 1986, 60, 653–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branagan, D.J.; McCallum, R.W. Precipitation phenomenon in stoichiometric Nd2Fe14B alloys modified with titanium and titanium with carbon. J. Alloys Compd. 1995, 230, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkulova, G.Y.; Margulies, L.; Dennis, K.W.; McCallum, R.W. The temperature dependence of coercivity in nanocrystalline Nd–Fe–B–(TiC) magnets. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 4738–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, R.W. Determination of the saturation magnetization, anisotropy field, mean field interaction, and switching field distribution for nanocrystalline hard magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 292, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.C.; Wu, C.H.; Chang, T.D.; Wang, F.H.; De Boer, F.R. Structure and magnetic properties of cobalt-rich Pr-Co-B alloys. J. Less Common Met. 1988, 144, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jongh, L.J.; Bartolomé, J.; Greidanus, F.J.A.M.; de Groot, H.J.M.; Stipdonk, H.L.; Buschow, K.H.J. Magnetic properties of PrCo2 and its ternary hydride PrCo2H4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1981, 25, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedziwiatr, A.T.; Wallace, W.E. Spin reorientations in R2Fe14-xCoxB systems (R = Pr, Nd and Er). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1987, 65, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Guo, S.; Wang, J.; Lee, D.; Yan, A. The microstructure and magnetization behaviors of (Pr8.2Fe86.12xCoxB5.7)0.99Zr0.01 (x = 0–10) nanocomposite magnets. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 07A756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nlebedim, I.C.; Huang, M.; Sun, K.; Zhou, L.; McCallum, R.W.; Kramer, M.J. Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Grain Refined Pr2Co14B Melt-Spun Ribbons. Magnetochemistry 2019, 5, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry5010006
Nlebedim IC, Huang M, Sun K, Zhou L, McCallum RW, Kramer MJ. Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Grain Refined Pr2Co14B Melt-Spun Ribbons. Magnetochemistry. 2019; 5(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry5010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleNlebedim, I. C., M. Huang, K. Sun, L. Zhou, R. W. McCallum, and M. J. Kramer. 2019. "Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Grain Refined Pr2Co14B Melt-Spun Ribbons" Magnetochemistry 5, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry5010006
APA StyleNlebedim, I. C., Huang, M., Sun, K., Zhou, L., McCallum, R. W., & Kramer, M. J. (2019). Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Grain Refined Pr2Co14B Melt-Spun Ribbons. Magnetochemistry, 5(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry5010006