Study of Structural, Magnetic, and Mossbauer Properties of Dy2Fe16Ga1−xNbx (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 1.0) Prepared via Arc Melting Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strnat, K.J. Chapter 2—Rare earth-cobalt permanent magnets. In Handbook of Ferromagnetic Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1988; Volume 4, pp. 131–209. [Google Scholar]
- Isnard, O.; Miraglia, S.; Soubeyroux, J.L.; Fruchart, D. Neutron powder diffraction study of R2Fe17Hx compounds with R = Pr and Nd. Solid State Commun. 1992, 81, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautot, D.; Long, G.J.; Grandjean, F.; Isnard, O.; Miraglia, S. Hydrogen dynamics in the hydrides of Pr2Fe17 as revealed by Mössbauer spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 86, 2200–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, F.; Long, G.J.; Mishra, S.; Pringle, O.A.; Isnard, O.; Miraglia, S.; Fruchart, D. A Mössbauer effect study of the interstitial hydrides and nitride of Nd2Fe17. Hyperfine Interact. 1995, 95, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautot, D.; Long, G.J.; Grandjean, F.; Isnard, O.; Fruchart, D. An 57Fe Mössbauer spectral study of Gd2Fe17Hx (for x = 0, 3, and 5) and Sm2Fe17D5. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 202, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.J.; Marasinghe, G.K.; Mishra, S.; Pringle, O.A.; Hu, Z.; Yelon, W.B.; Middleton, D.P.; Buschow, K.H.J.; Grandjean, F. A Magnetic, Neutron Diffraction, and Mössbauer Spectral Study of the Nd2Fe17−xAlx Solid Solutions. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 76, 5383–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokorina, E.; Medvedev, M.V.; Nekrasov, I. Ab Initio Exchange Interactions and Magnetic Properties of Intermetallic Compound Gd2Fe17−xGax. Solid State Phenom. 2011, 168–169, 196–199. [Google Scholar]
- Dahal, J.N.; Ali, K.S.; Mishra, S.R.; Alam, J. Structural, Magnetic, and Mössbauer Studies of Transition Metal-Doped Gd2Fe16Ga0.5TM0.5 Intermetallic Compounds (TM = Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, Cu, and Zn). J. Magnetochem. 2018, 4, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.-G.; Cheng, Z.-H.; Gong, H.-Y.; Liang, B.; Yan, Q.-W.; Zhan, W.-S. Magnetic anisotropy of Dy2Fe17−xGax compounds. Solid State Commun. 1995, 95, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, J.N.; Ali, K.S.; Mishra, S.R.; Neupane, D. Effect of Ga and Zr Substitution on the Properties of Dy2Fe17−XZrX and Dy2Fe16Ga1−xZrx (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) Intermetallic Compounds Prepared via Arc Melting Process. J. Magnetochem. 2020, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorria, P.; Alvarez, P.; Marcos, J.S.; Llamazares, J.L.S.; Parez, M.J.; Blanco, J.A. Crystal structure, magnetocaloric effect and magnetovolume anomalies in nanostructured Pr2Fe17. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 1724–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isnard, O.; Guillot, M. Investigation of magnetic properties of Nd2Fe17 and Nd2Fe17Hx in high magnetic field. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 86, 5326–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, F.; Isnard, O.; Hautot, D.; Long, G.J. A structural, magnetic, and Mössbauer spectral study of Er2Fe17 and hydrides. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 63, 144061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, B.; Yuang, Y.; Wang, F. Anomalous thermal expansion and magnetic properties of Tm2Fe17−xCrx compounds. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 023915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunchin, A.; Iwasieczko, W. Enhancement of the magnetocaloric effect in the Lu2Fe17−xMnx system. Solid State Commun. 2010, 150, 1580–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, Z.; Kunchin, A.; Kamarad, J. Instability of the ferromagnetic ground state in Lu2Fe17−xMx[x = 0.5, 0.7]. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 07E310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shen, B.-G.; Zhang, P.; Cheng, Z.-H.; Zhang, J.; Gong, H.; Liang, B.; Sun, X.; Yan, Q. Effect of Ga substitution on the structure and magnetic properties of Ho2Fe17−xGax (x = 0–8) compounds. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 83, 3250–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dunlap, R.A. Effects of Al substitutions on the magnetic anisotropy of Sm2Fe17 compounds. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1993, 5, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, J.; Dowben, P.A.; Garrison, K. Evidence for imperfect ferromagnetic coupling between the Gd(0001) surface and the bulk. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1993, 5, L73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dunlap, R.A. Investigation of the hard-magnetic properties of Sm2Fe17 compounds with Ga substitution. Philos. Mag. B 1994, 69, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.J.; Mishra, S.R.; Pringle, O.A.; Yelon, W.B.; Hu, Z.; Grandjean, F.; Middleton, D.P.; Buschow, K.H.J. A magnetic, neutron diffraction and Mossbauer spectral study of the Ce2Fe17−xGax solid solution. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1997, 176, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Budnick, J.I.; Hines, W.A.; Shen, B.G.; Cheng, Z. Effect of Ga substitution on the Sm sublattice anisotropy in Sm2Fe17−xGax (0 < x < 8). J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 85, 4663–4665. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, B.; Ali, K.S.; Mishra, S.; Khanra, S.; Ghosh, K. A structural, magnetic and Mossbauer study of the Dy2Fe17−xNbx solid solutions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 353, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, T.A. Wmoss Mossbauer Spectral Analysis Software; Report; WEB Research Co.: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Rietveld, H.M. A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. J. Appl. Cryst. 1969, 2, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.X.; Altounican, Z.; Ryan, D.H. Cobalt site preferences in iron rare-earth-based compounds. Phy. Rev. B 1993, 47, 11230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulyanov, A.N.; Kim, J.S.; Shin, G.M.; Song, K.J.; Kang, Y.M.; Yoo, S.I. La0:7Ca0:3Mn0:95M0:05O3 manganites (M = Al, Ga, Fe, Mn, and In):Local structure and electron configuration effect on Curie temperature and magnetization. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2007, 388, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, K.G.; Rama Rao, K.V.S. Fe 57 Mossbauer investigation on (Er,Pr)2(Fe,Al)17 compounds and their nitrides. Phys. Rev. B 1997, 55, 15060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.P.; Li, H.S.; Sun, H.; Coey, J.M.D. A 5e Mossbauer study of a new series of rare-earth iron nitrides: R2Fe17N3- delta. J. Phys. Condens. Mater. 1991, 3, 3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.Z.; Ching, W.Y. Effects of Al substitution in Nd2Fe17 studied by first-principles calculations. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 76, 7046–7048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.Z.; Ching, W.Y. First-principles calculation of the electronic and magnetic properties of Nd2Fe17−xMx (M = Si, Ga) solid solutions. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 79, 5546–5549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekdadri, A.; Chami, R.; Saadi, A.; Lassri, H.; Omari, L.H. First-principle study of electronic and magnetic properties in cobalt-niobium alloys. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 37, 3813–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.R.; Ehrenberg, H.; Markandeyulu, G.; Varadaraju, U.; Venkatesan, M.; Suresh, K.; Murthy, V.; Schmidt, P.; Fuess, H. On the Structural and Magnetic Properties of R2Fe17−x(A,T)x (R = Rare Earth; A = Al, Si, Ga; T = Transition Metal) Compounds. Phys. Status Solidi 2002, 189, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neél, L. Propriétés magnétiques de l’état métallique et énergie d’interaction entre atoms magnétiques. Ann. Phys. 1936, 5, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Morrish, A.H. Negative exchange interactions and Curie temperatures for Sm2Fe17 and Sm2Fe17Ny. Phys. Rev. B 1997, 55, 3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bara, J.J.; Pedziwiatr, A.T.; Zarek, W. Investigations of crystal and magnetic properties of Dy-Fe intermetallic compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1982, 27, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeanu, M.; Plugaru, N.; Burzo, E. Effect of nitrogenation on the magnetic properties of Y2Fe17−xMx compounds, with M = Al, Ga or Si. Solid State Commun. 1994, 89, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isnard, O.; Hautot, D.; Long, G.L.; Grandjean, F. A structural magnetic and Mossbauer spectral study of Dy2Fe17 and hydrides. J. App. Phys. 2000, 88, 2750–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschow, K.H.J.; Wieringen, J.S.V. Crystal structure and magnetic properties of cerium-iron compounds. Phys. Status Solidi 1970, 42, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, L.M.; Rosenberg, E.; Shaulov, A.; Strnat, K. Mössbauer Study of Some 2–17 Lanthanide-Iron Compounds. J. Appl. Phys. 1970, 41, 910–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alp, E.E.; Umarji, A.M.; Malik, S.K.; Shenoy, G.K.; Huang, M.Q.; Boltich, E.B.; Wallace, W.E. 57Fe Mössbauer studies on Si-substituted Er2Fe17. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1987, 68, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Campbell, S.J.; Tegus, O.; Marquina, C.; Ibarra, M.R. Magnetovolume effect and magnetic properties of Dy2Fe17−xMnx. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 174423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, F.; Isnard, O.; Long, G.J. Magnetic and Mössbauer spectral evidence for the suppression of the magnetic spin reorientation in Tm2Fe17 by deuterium. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 65, 064429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.J.; Isnard, O.; Grandjean, F. A Mössbauer spectral study of the magnetic properties of Ho2Fe17 and Ho2 Fe17D3.8. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 91, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
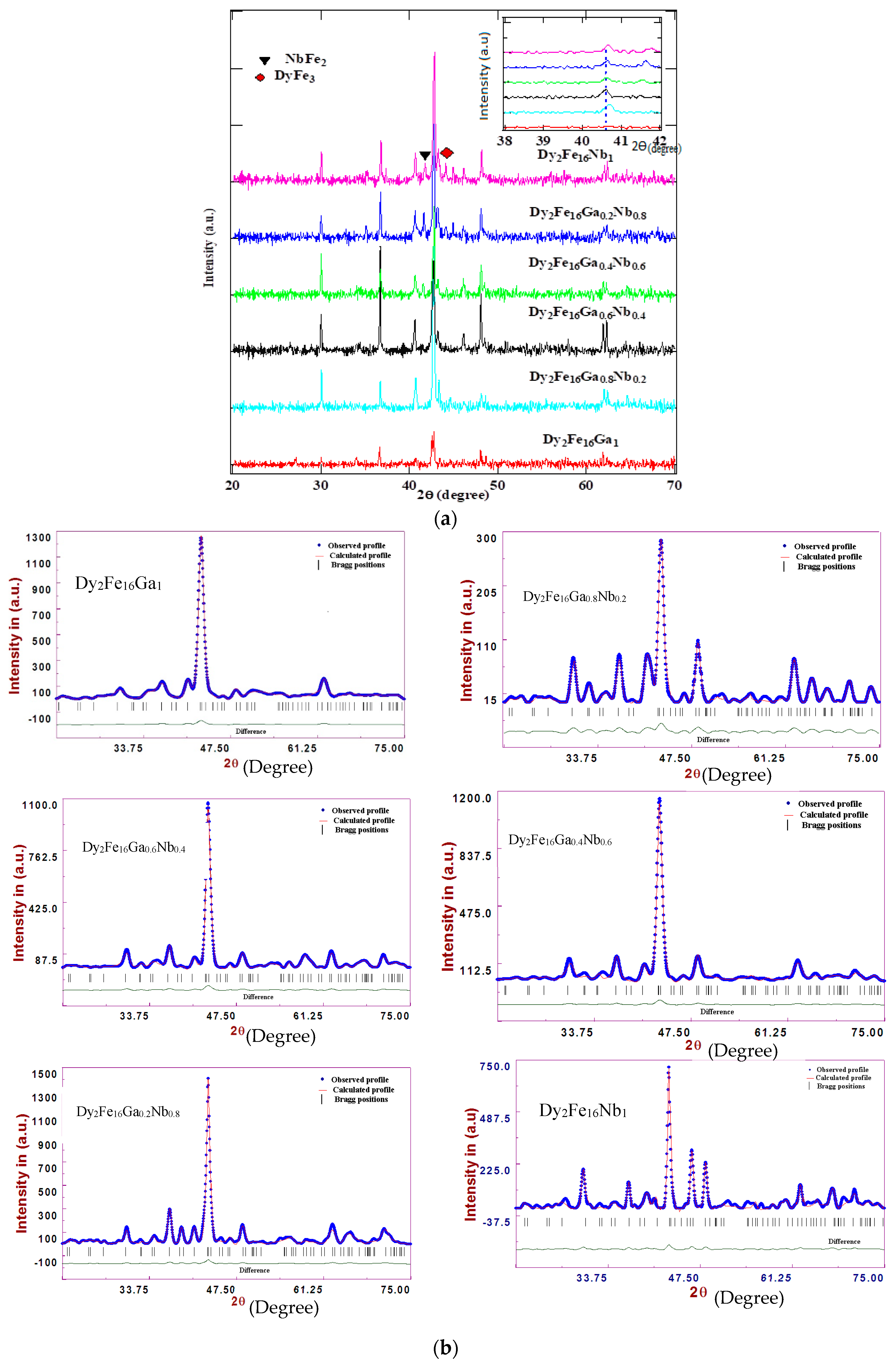


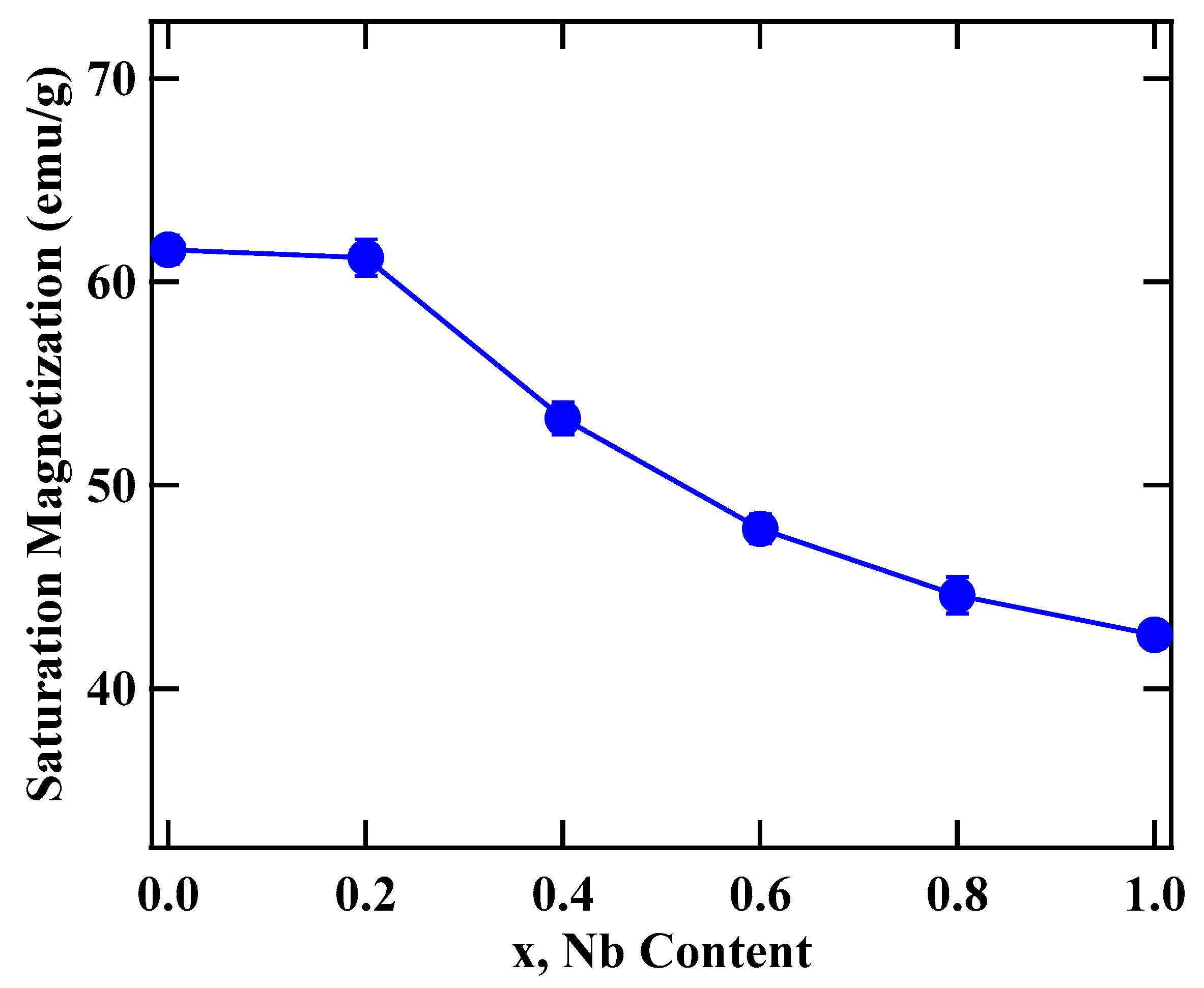

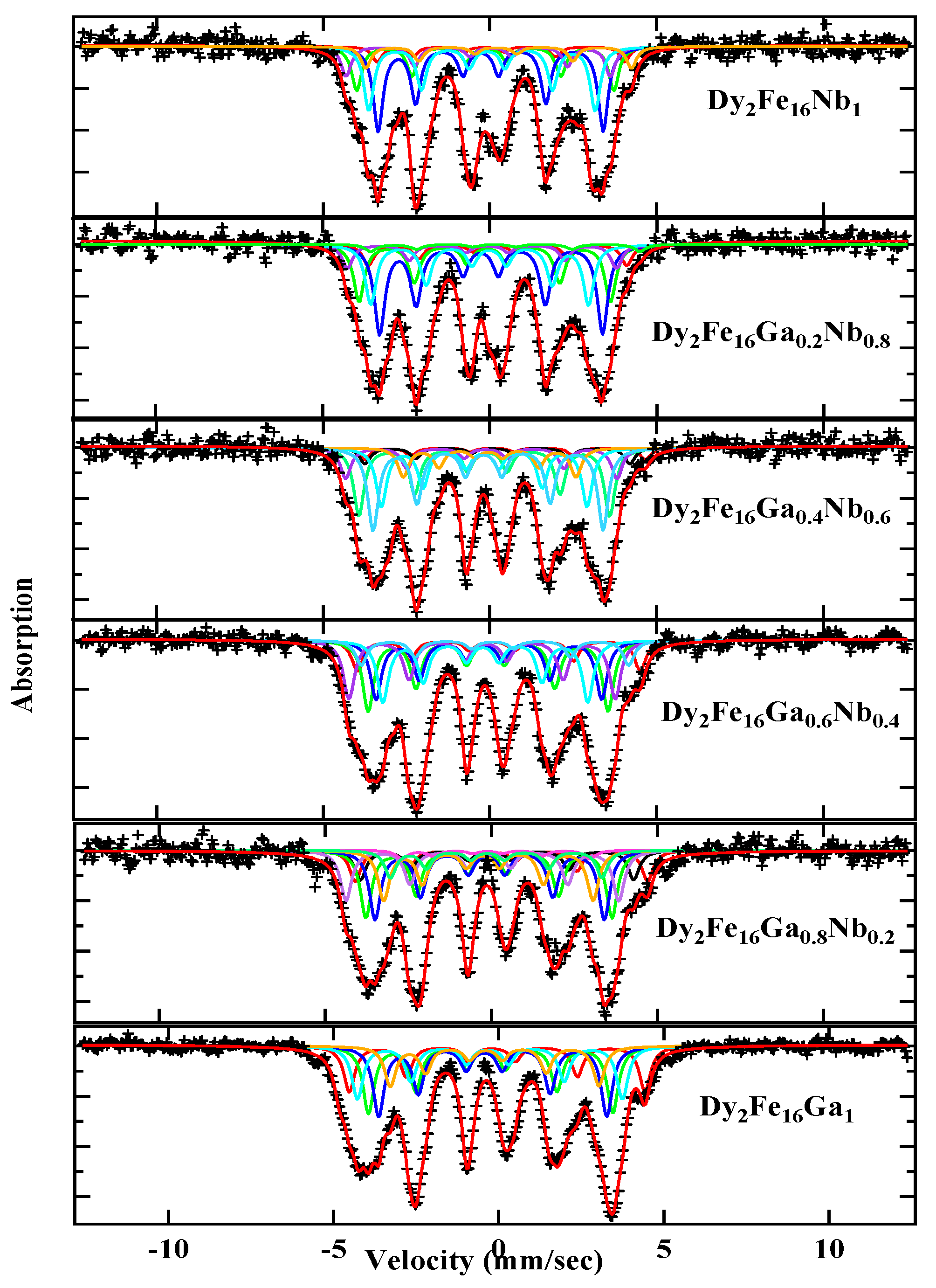

| x | a (Å) | c (Å) | Volume (Å3) | c/a | 6c(4f-4f) (Å) | 6g-12j (Å) | 6g-12k (Å) | 12j-12j (Å) | 12k-12k (Å) | Ms (emu/g) | Tc (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 8.4632(4) | 8.2902(5) | 514.01(3) | 0.979 | 2.4166(53) | 2.4312(12) | 2.4799(21) | 2.4589(31) | 2.4102(22) | 61.5(7) | 488(3) |
| 0.2 | 8.4863(6) | 8.3241(3) | 519.15(9) | 0.981 | 2.4181(22) | 2.4322(18) | 2.4956(8) | 2.4609(27) | 2.4281(32) | 61.1(9) | 489(5) |
| 0.4 | 8.4710(8) | 8.3667(8) | 519.94(1) | 0.988 | 2.4195(32) | 2.4335(14) | 2.5312(16) | 2.4625(9) | 2.4299(35) | 53.2(8) | 502(8) |
| 0.6 | 8.4879(6) | 8.3400(9) | 520.34(6) | 0.982 | 2.4286(42) | 2.4344(21) | 2.6901(15) | 2.4656(21) | 2.4325(32) | 47.8(7) | 523(7) |
| 0.8 | 8.4798(2) | 8.3596(3) | 520.56(7) | 0.986 | 2.4289(37) | 2.4343(7) | 2.7521(12) | 2.4673(18) | 2.4375(27) | 44.5(9) | 481(7) |
| 1.0 | 8.5098(3) | 8.3054(5) | 520.86(2) | 0.976 | 2.4293(4) | 2.4355(21) | 2.8801(23) | 2.4732(32) | 2.4399(29) | 42.6(6) | 460(6) |
| x | 4f | 4e | 6g1 | 6g2 | 12j1 | 12j2 | 12k1 | 12k2 | Doublet | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HF (kOe) | 0.0 | 278.7 | 249.7 | 230.1 | 214.9 | 260.0 | 218.1 | 196.4 | 220.0 | |
| 0.2 | 274.1 | 256.2 | 230.8 | 215.0 | 255.7 | 196.3 | 174.4 | 198.4 | ||
| 0.4 | 264.2 | 250.0 | 224.1 | 210.8 | 248.6 | 191.4 | 176.7 | 190.3 | ||
| 0.6 | 262.0 | 247.1 | 234.2 | 214.8 | 253.3 | 192.1 | 170.1 | 191.5 | ||
| 0.8 | 248.0 | 251.01 | 234.2 | 207.9 | 250.6 | 202.9 | 165.9 | 192.7 | ||
| 1.0 | 240.0 | 248.2 | 240.2 | 210.1 | 246.8 | 200.1 | 169.4 | 190.0 | 19.5 | |
| IS (mm/s) | 0.0 | −0.126 | −0.301 | −0.309 | −0.309 | −0.422 | −0.422 | −0.254 | −0.254 | |
| 0.2 | 0.166 | 0.059 | −0.097 | −0.0975 | −0.173 | −0.173 | 0.019 | 0.019 | ||
| 0.4 | 0.210 | 0.119 | −0.092 | −0.092 | −0.175 | −0.175 | 0.081 | 0.081 | ||
| 0.6 | 0.264 | 0.152 | −0.117 | −0.117 | −0.191 | −0.191 | −0.015 | −0.015 | ||
| 0.8 | 0.171 | 0.301 | −0.117 | −0.117 | −0.16 | −0.160 | −0.028 | −0.028 | ||
| 1.0 | 0.080 | 0.220 | −0.124 | −0.124 | −0.159 | −0.159 | −0.093 | −0.093 | −0.211 | |
| QS (mm/s) | 0 | 0.158 | 0.010 | 0.133 | 0.259 | −0.418 | −0.48 | 0.259 | −0.58 | |
| 0.2 | 0.27 | 0.216 | 0.04683 | 0.088 | −0.198 | 0.166 | 0.246 | 0.264 | ||
| 0.4 | 0.206 | 0.060 | 0.07976 | 0.124 | −0.119 | 0.080 | 0.200 | 0.153 | ||
| 0.6 | 0.384 | 0.154 | −0.0932 | 0.137 | −0.129 | 0.046 | 0.024 | 0.156 | ||
| 0.8 | 0.320 | 0.33 | −0.0683 | 0.313 | −0.156 | −0.286 | 0.102 | 0.190 | ||
| 1.0 | 0.420 | 0.081 | −0.0349 | 0.297 | −0.381 | −0.153 | 0.039 | 0.089 | 0.035 | |
| Area (%) | 0.0 | 13.70 | 14.90 | 20.00 | 21.00 | 10.53 | 5.59 | 10.9 | 3.93 | |
| 0.2 | 9.14 | 8.68 | 19.63 | 20.24 | 15.74 | 15.82 | 2.39 | 8.25 | ||
| 0.4 | 8.55 | 5.92 | 18.46 | 20.00 | 16.12 | 15.05 | 5.87 | 9.66 | ||
| 0.6 | 3.42 | 4.64 | 19.73 | 22.70 | 8.92 | 15.96 | 8.43 | 15.93 | ||
| 0.8 | 6.33 | 2.14 | 17.02 | 26.60 | 7.15 | 14.83 | 10.8 | 15.24 | ||
| 1.0 | 4.27 | 6.02 | 12.14 | 26.80 | 8.22 | 17.75 | 8.46 | 16.42 | 8.86 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dahal, J.N.; Ali, K.S.S.; Mishra, S.R. Study of Structural, Magnetic, and Mossbauer Properties of Dy2Fe16Ga1−xNbx (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 1.0) Prepared via Arc Melting Process. Magnetochemistry 2021, 7, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7030042
Dahal JN, Ali KSS, Mishra SR. Study of Structural, Magnetic, and Mossbauer Properties of Dy2Fe16Ga1−xNbx (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 1.0) Prepared via Arc Melting Process. Magnetochemistry. 2021; 7(3):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7030042
Chicago/Turabian StyleDahal, Jiba N., Kalangala Sikkanther Syed Ali, and Sanjay R. Mishra. 2021. "Study of Structural, Magnetic, and Mossbauer Properties of Dy2Fe16Ga1−xNbx (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 1.0) Prepared via Arc Melting Process" Magnetochemistry 7, no. 3: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7030042
APA StyleDahal, J. N., Ali, K. S. S., & Mishra, S. R. (2021). Study of Structural, Magnetic, and Mossbauer Properties of Dy2Fe16Ga1−xNbx (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 1.0) Prepared via Arc Melting Process. Magnetochemistry, 7(3), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7030042






