The Synthesis of Metal–Organic-Framework-Based Ternary Nanocomposite for the Adsorption of Organic Dyes from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of SiO2/MnFe2O4 Nanocomposite
2.3. Synthesis of SiO2/MnFe2O4/ZIF-8 Nanocomposite
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Synthesized Nanomaterials
3.2. Optimization of the Adsorption Parameters
3.3. Adsorption Isotherm
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics
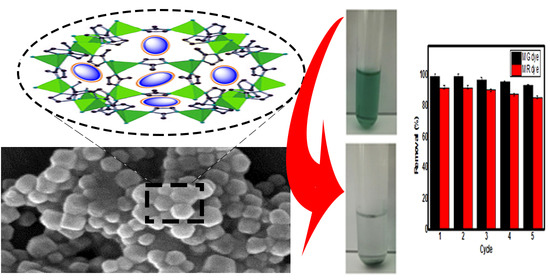
3.5. Regeneration and Reusability Study
3.6. Comparative Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qian, C.; Yin, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Bai, Z.; Jiao, T. Facile preparation and highly efficient photodegradation performances of self-assembled Artemia eggshell-ZnO nanocomposites for wastewater treatment. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 610, 125752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, F.M.; Amari, A.; Katubi, K.M.; Alsaiari, N.S.; Tahoon, M.A. The synthesis of nanocellulose-based nanocomposites for the effective removal of hexavalent chromium ions from aqueous solution. Open Chem. 2022, 20, 970–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgarahy, A.; Elwakeel, K.; Mohammad, S.; Elshoubaky, G. A critical review of biosorption of dyes, heavy metals and metalloids from wastewater as an efficient and green process. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 4, 100209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Jeevanantham, S.; Karishma, S.; Tajsabreen, B.; Yaashikaa, P.; Reshma, B. Effective water/wastewater treatment methodologies for toxic pollutants removal: Processes and applications towards sustainable development. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajoriya, S.; Saharan, V.K.; Pundir, A.S.; Nigam, M.; Roy, K. Adsorption of methyl red dye from aqueous solution onto eggshell waste material: Kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamic studies. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 4, 100180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Mitan, M.; Kim, H.; Vaya, D. Efficient photocatalytic degradation of Malachite green dye using facilely synthesized cobalt oxide nanomaterials using citric acid and oleic acid. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2021, 155, 110125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, D.; Bharadvaja, N. Phycoremediation of effluents containing dyes and its prospects for value-added products: A review of opportunities. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 41, 102080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velusamy, S.; Roy, A.; Sundaram, S.; Kumar Mallick, T. A review on heavy metal ions and containing dyes removal through graphene oxide-based adsorption strategies for textile wastewater treatment. Chem. Rec. 2021, 21, 1570–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.A.; Ahmad, N.; Bello, O.S. Modified durian seed as adsorbent for the removal of methyl red dye from aqueous solutions. Appl. Water Sci. 2015, 5, 407–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ismail, M.; Khan, M.; Khan, S.B.; Akhtar, K.; Khan, M.A.; Asiri, A.M. Catalytic reduction of picric acid, nitrophenols and organic azo dyes via green synthesized plant supported Ag nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 268, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, H.U.R.; Ahmad, K.; Naseem, H.A.; Parveen, S.; Ashfaq, M.; Rauf, A.; Aziz, T. Water stable graphene oxide metal-organic frameworks composite (ZIF-67@ GO) for efficient removal of malachite green from water. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 154, 112312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naresh, G.; Malik, J.; Meena, V.; Mandal, T.K. pH-mediated collective and selective solar photocatalysis by a series of layered Aurivillius perovskites. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 11104–11116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, J.; Radhakrishnan, R.C.; Johnson, J.K.; Joy, S.P.; Thomas, J. Ion-exchange mediated removal of cationic dye-stuffs from water using ammonium phosphomolybdate. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 242, 122488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahinkaya, E.; Tuncman, S.; Koc, I.; Guner, A.R.; Ciftci, S.; Aygun, A.; Sengul, S. Performance of a pilot-scale reverse osmosis process for water recovery from biologically-treated textile wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, M.; Javanbakht, V.; Esmaili, J. Synthesis of zeolite/nickel ferrite/sodium alginate bionanocomposite via a co-precipitation technique for efficient removal of water-soluble methylene blue dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, A.; Alzahrani, F.M.; Alsaiari, N.S.; Katubi, K.M.; Rebah, F.B.; Tahoon, M.A. Magnetic metal organic framework immobilized laccase for wastewater decolorization. Processes 2021, 9, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannaujia, R.; Prasad, V.; Rawat, P.; Rawat, V.; Thakur, A.; Majumdar, S.; Verma, M.; Rao, G.K.; Gupta, A.P.; Kumar, H. Facile synthesis of CuFe2O4 doped polyacrylic acid hydrogel nanocomposite and its application in dye degradation. Mater. Lett. 2019, 252, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demissie, H.; An, G.; Jiao, R.; Ritigala, T.; Lu, S.; Wang, D. Modification of high content nanocluster-based coagulation for rapid removal of dye from water and the mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 259, 117845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcyotto, F.; Wei, Q.; Macharia, D.K.; Huang, M.; Shen, C.; Chow, C.W. Effect of dye structure on color removal efficiency by coagulation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaiari, N.S.; Amari, A.; Katubi, K.M.; Alzahrani, F.M.; Rebah, F.B.; Tahoon, M.A. The Synthesis of Magnetic Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite for the Removal of Reactive Orange 12 Dye. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 9417542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, A.; Elboughdiri, N.; Ghernaout, D.; Lajimi, R.H.; Alshahrani, A.M.; Tahoon, M.A.; Rebah, F.B. Multifunctional crosslinked chitosan/nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot for wastewater treatment. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 4007–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, A.; Alzahrani, F.M.; Mohammedsaleh Katubi, K.; Alsaiari, N.S.; Tahoon, M.A.; Rebah, F.B. Clay-polymer nanocomposites: Preparations and utilization for pollutants removal. Materials 2021, 14, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaiari, N.S.; Amari, A.; Katubi, K.M.; Alzahrani, F.M.; Rebah, F.B.; Tahoon, M.A. Innovative magnetite based polymeric nanocomposite for simultaneous removal of methyl orange and hexavalent chromium from water. Processes 2021, 9, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahadat, M.; Isamil, S. Regeneration performance of clay-based adsorbents for the removal of industrial dyes: A review. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 24571–24587. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Fu, F. High-performance magnetic carbon materials in dye removal from aqueous solutions. J. Solid State Chem. 2016, 239, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Li, Z.; Duan, J.; He, X. Adsorption and photocatalytic degradation mechanism of magnetic graphene oxide/ZnO nanocomposites for tetracycline contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoli, C.P.; Ofomaja, A.E. Development of sustainable magnetic polyurethane polymer nanocomposite for abatement of tetracycline antibiotics aqueous pollution: Response surface methodology and adsorption dynamics. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 217, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, H.; Alhassan, S.M.; Ray, S.S. Efficient organic dye removal from wastewater by magnetic carbonaceous adsorbent prepared from corn starch. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 7119–7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasseh, N.; Arghavan, F.S.; Rodriguez-Couto, S.; Hossein Panahi, A. Synthesis of FeNi3/SiO2/CuS magnetic nano-composite as a novel adsorbent for Congo Red dye removal. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102, 2342–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, F.M.; Alsaiari, N.S.; Katubi, K.M.; Amari, A.; Ben Rebah, F.; Tahoon, M.A. Synthesis of polymer-based magnetic nanocomposite for multi-pollutants removal from water. Polymers 2021, 13, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, X.; Qin, D.; Da, W.; Hou, B.; Hao, C.; Wu, J. Construction of magnetic lignin-based adsorbent and its adsorption properties for dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yang, Y.W. Metal–organic frameworks for biomedical applications. Small 2020, 16, 1906846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, M. The applications of metal− organic frameworks in electrochemical sensors. ChemElectroChem 2018, 5, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bavykina, A.; Kolobov, N.; Khan, I.S.; Bau, J.A.; Ramirez, A.; Gascon, J. Metal–organic frameworks in heterogeneous catalysis: Recent progress, new trends, and future perspectives. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 8468–8535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmadijokani, F.; Mohammadkhani, R.; Ahmadipouya, S.; Shokrgozar, A.; Rezakazemi, M.; Molavi, H.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Arjmand, M. Superior chemical stability of UiO-66 metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for selective dye adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 399, 125346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Ng, H.Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, J. Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs)-boosted filtration membrane technology for water sustainability. APL Mater. 2020, 8, 040902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iman, K.; Shahid, M.; Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, M.; Sama, F. Topology, magnetism and dye adsorption properties of metal organic frameworks (MOFs) synthesized from bench chemicals. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 5299–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.-Q.; Yin, X.-B. Metal–organic frameworks with multiple luminescence emissions: Designs and applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, T.T.; Tran, M.T.; Feller, J.-F.; Castro, M.; Van Ngo, T.; Hassan, K.; Nine, M.J.; Losic, D. Graphene and metal organic frameworks (MOFs) hybridization for tunable chemoresistive sensors for detection of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) biomarkers. Carbon 2020, 159, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, B.M.; Madden, D.G.; Wheatley, A.E.; Fairen-Jimenez, D. Shaping the future of fuel: Monolithic metal–organic frameworks for high-density gas storage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 8541–8549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Su, S.; Luo, S.; Huang, R.; Jing, Y.; Luo, M. Photocatalytic nitrogen fixation of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) excited by ultraviolet light: Insights into the nitrogen fixation mechanism of missing metal cluster or linker defects. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 7801–7809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Pournara, A.; Kim, K.-H.; Bansal, V.; Rapti, S.; Manos, M.J. Metal-organic frameworks: Challenges and opportunities for ion-exchange/sorption applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 86, 25–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, H.D.; Walton, S.P.; Chan, C. Metal–Organic Frameworks for Drug Delivery: A Design Perspective. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 7004–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y. Recent progress in the design and synthesis of zeolite-like metal–organic frameworks (ZMOFs). Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 3450–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.R.; Yaghi, O.M. The pervasive chemistry of metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1213–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Férey, G. Hybrid porous solids: Past, present, future. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 191–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.F.; Fang, Y.; Luan, D.; Lou, X.W.D. Metal–organic frameworks derived functional materials for electrochemical energy storage and conversion: A mini review. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 1555–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, B.; Kim, K.-H.; Sonwani, R.K.; Szulejko, J.E.; Heynderickx, P.M. Removal of gaseous benzene by a fixed-bed system packed with a highly porous metal-organic framework (MOF-199) coated glass beads. Environ. Res. 2022, 208, 112655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayazit, Ş.S.; Yildiz, M.; Aşçi, Y.S.; Şahin, M.; Bener, M.; Eğlence, S.; Salam, M.A. Rapid adsorptive removal of naphthalene from water using graphene nanoplatelet/MIL-101 (Cr) nanocomposite. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 701, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.J.; Ampiaw, R.E.; Lee, W. Adsorptive removal of dyes from wastewater using a metal-organic framework: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-Y.; Yang, C.; Geng, Q.; Fan, H.-L.; Wang, B.-J.; Wu, M.-M.; Tian, Z. Adsorption of hydrogen sulfide by amine-functionalized metal organic framework (MOF-199): An experimental and simulation study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 497, 143815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedi, A.; Zarandi, M.B.; Nateghi, M.R. Highly efficient removal of dye pollutants by MIL-101(Fe) metal-organic framework loaded magnetic particles mediated by Poly L-Dopa. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, X.; Li, S.; Tang, W.; Chen, Y. Magnetic porous Fe3O4/carbon octahedra derived from iron-based metal-organic framework as heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 436, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, F.M.; Alsaiari, N.S.; Katubi, K.M.; Amari, A.; Tahoon, M.A. Synthesis, characterization, and application of magnetized lanthanum (III)-based metal-organic framework for the organic dye removal from water. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 3513829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Arabloo, M.; Abdi, J. Laccase immobilized manganese ferrite nanoparticle: Synthesis and LSSVM intelligent modeling of decolorization. Water Res. 2014, 67, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Fu, F.; Lu, J.; Ding, Z.; Tang, B.; Pang, J. Facile preparation of magnetic mesoporous MnFe2O4@ SiO2−CTAB composites for Cr (VI) adsorption and reduction. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, J.; Vossoughi, M.; Mahmoodi, N.M.; Alemzadeh, I. Synthesis of metal-organic framework hybrid nanocomposites based on GO and CNT with high adsorption capacity for dye removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 326, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laokul, P.; Amornkitbamrung, V.; Seraphin, S.; Maensiri, S. Characterization and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline CuFe2O4, NiFe2O4, ZnFe2O4 powders prepared by the Aloe vera extract solution. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2011, 11, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M. Manganese ferrite nanoparticle: Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic dye degradation ability. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 53, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, E.L.; Fernández, J.L.; Zamaro, J.M. Influence of the solvent in the synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) nanocrystals at room temperature. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 424, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Kazemian, H.; Rohani, S.; Huang, Y.; Song, Y. In situ high pressure study of ZIF-8 by FTIR spectroscopy. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 12694–12696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Jayaramulu, K.; Maji, T.K.; Rao, C. Hybrid nanocomposites of ZIF-8 with graphene oxide exhibiting tunable morphology, significant CO2 uptake and other novel properties. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 4947–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.-X.; Wang, F.; Meng, Y.-F.; Tang, Q.-H.; Liu, Z.-Q. Fabrication and characterization of manganese ferrite nanospheres as a magnetic adsorbent of chromium. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, F.; He, Y.; Lian, Z.; Xu, J. The impact of solution chemistry of electrolyte on the sorption of pentachlorophenol and phenanthrene by natural hematite nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noreen, S.; Bhatti, H.N.; Iqbal, M.; Hussain, F.; Sarim, F.M. Chitosan, starch, polyaniline and polypyrrole biocomposite with sugarcane bagasse for the efficient removal of Acid Black dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, N.; Bhatti, H.N.; Iqbal, M.; Noreen, S. Biopolymers composites with peanut hull waste biomass and application for Crystal Violet adsorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 94, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayomie, O.S.; Kandeel, H.; Shoeib, T.; Yang, H.; Youssef, N.; El-Sayed, M.M. Novel approach for effective removal of methylene blue dye from water using fava bean peel waste. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellahsen, N.; Varga, G.; Halyag, N.; Kertész, S.; Tombácz, E.; Hodúr, C. Pomegranate peel as a new low-cost adsorbent for ammonium removal. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, M.; Sharma, N.; Saxena, R. Highly efficient and rapid removal of a toxic dye: Adsorption kinetics, isotherm, and mechanism studies on functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 21, 100639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption isotherm models: Classification, physical meaning, application and solving method. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, E.A.; Khan, T.A. Adsorption of methyl red on activated carbon derived from custard apple (Annona squamosa) fruit shell: Equilibrium isotherm and kinetic studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 249, 1195–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadfarnia, S.; Shabani, A.H.; Moradi, S.; Emami, S. Methyl red removal from water by iron based metal-organic frameworks loaded onto iron oxide nanoparticle adsorbent. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 330, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Wang, B.; Chen, L.; Zhao, S. Simultaneous adsorption of methyl red and methylene blue onto biochar and an equilibrium modeling at high concentration. Chemosphere 2016, 163, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Mo, Z.; Li, L.; Chen, F.; Wu, Q.; Qi, L. Efficient removal of copper (II) and malachite green from aqueous solution by magnetic magnesium silicate composite. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2017, 62, 3036–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Xu, C.; Guan, H.; Li, L.; Fan, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, R. Magnetic metal organic frameworks (MOFs) composite for removal of lead and malachite green in wastewater. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 539, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, X.-P.; Fu, S.-Y.; Du, Y.-M.; Guo, J.-Z.; Li, B. Adsorption of methylene blue and malachite green from aqueous solution by sulfonic acid group modified MIL-101. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 237, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyi, A.A.; Jamil, S.N.; Abdullah, L.C.; Choong, T.S. Adsorption of malachite green dye from liquid phase using hydrophilic thiourea-modified poly (acrylonitrile-co-acrylic acid): Kinetic and isotherm studies. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 4321475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altintig, E.; Onaran, M.; Sarı, A.; Altundag, H.; Tuzen, M. Preparation, characterization and evaluation of bio-based magnetic activated carbon for effective adsorption of malachite green from aqueous solution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 220, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Dye | Langmuir | Freundlich | Pseudo-1st-Order | Pseudo-2nd-Order | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | 1/n | KF (mg/g)(L/mg)1/n | R2 | k1 (min−1) | qe | R2 | k2 (g/mg.h) | qe | R2 | |
| MG | 1000.03 | 0.077 | 0.990 | 0.396 | 8.715 | 0.963 | 0.062 | 445.248 | 0.991 | 0.001 | 555.55 | 0.999 |
| MR | 1111.12 | 0.040 | 0.979 | 0.501 | 7.338 | 0.965 | 0.160 | 141.70 | 0.941 | 0.001 | 476.20 | 0.999 |
| Adsorbent | Pollutant | Removal Capacity (mg/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2/MnFe2O4/ZIF-8 | MR | 1111.12 | This study |
| MIL-53 (Fe) DSAC | MR | 384.62 | [9] |
| K2CO3@activated carbon | MR | 226.90 | [72] |
| H3PO4@activated carbon | MR | 435.25 | [72] |
| 101(Fe)@PDopa@Fe3O4 | MR | 625.0 | [73] |
| Woody biochar | MR | 156.25 | [74] |
| SiO2/MnFe2O4/ZIF-8 | MG | 1000.03 | This study |
| Cu-MOFs/Fe3O4 | MG | 125.15 | [75] |
| MIL-101-SO3H | MG | 113.67 | [76] |
| 101(Fe)@Pdopa@Fe3O4 | MG | 676 | [77] |
| TU-poly(AN-co-AA) | MG | 269.54 | [78] |
| AC@Fe2O3 | MG | 311.40 | [79] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsaiari, N.S.; Osman, H.; Amari, A.; Tahoon, M.A. The Synthesis of Metal–Organic-Framework-Based Ternary Nanocomposite for the Adsorption of Organic Dyes from Aqueous Solutions. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8100133
Alsaiari NS, Osman H, Amari A, Tahoon MA. The Synthesis of Metal–Organic-Framework-Based Ternary Nanocomposite for the Adsorption of Organic Dyes from Aqueous Solutions. Magnetochemistry. 2022; 8(10):133. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8100133
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsaiari, Norah Salem, Haitham Osman, Abdelfattah Amari, and Mohamed A. Tahoon. 2022. "The Synthesis of Metal–Organic-Framework-Based Ternary Nanocomposite for the Adsorption of Organic Dyes from Aqueous Solutions" Magnetochemistry 8, no. 10: 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8100133
APA StyleAlsaiari, N. S., Osman, H., Amari, A., & Tahoon, M. A. (2022). The Synthesis of Metal–Organic-Framework-Based Ternary Nanocomposite for the Adsorption of Organic Dyes from Aqueous Solutions. Magnetochemistry, 8(10), 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8100133