Transformation Pathways of Ferromagnetic Mn-Al-Ga-Ni
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
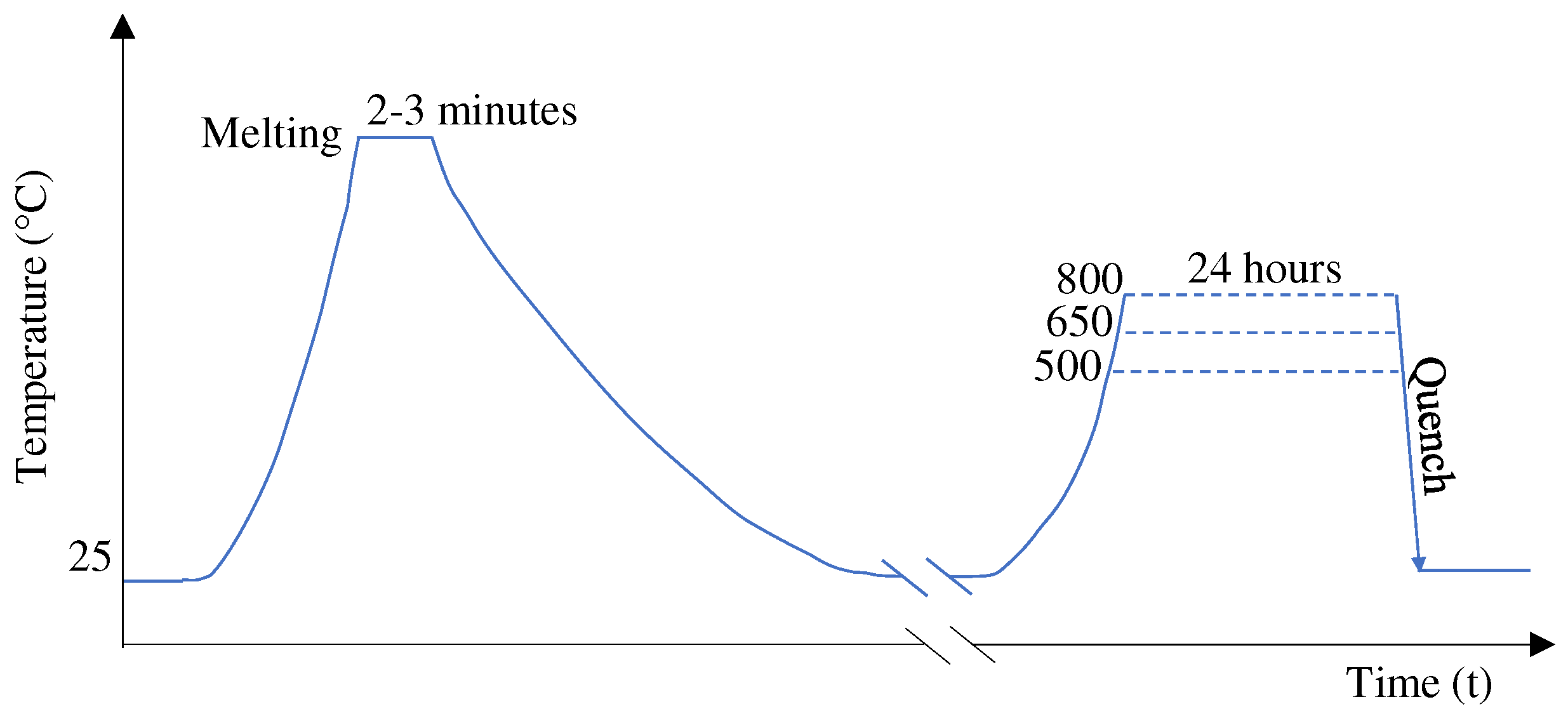
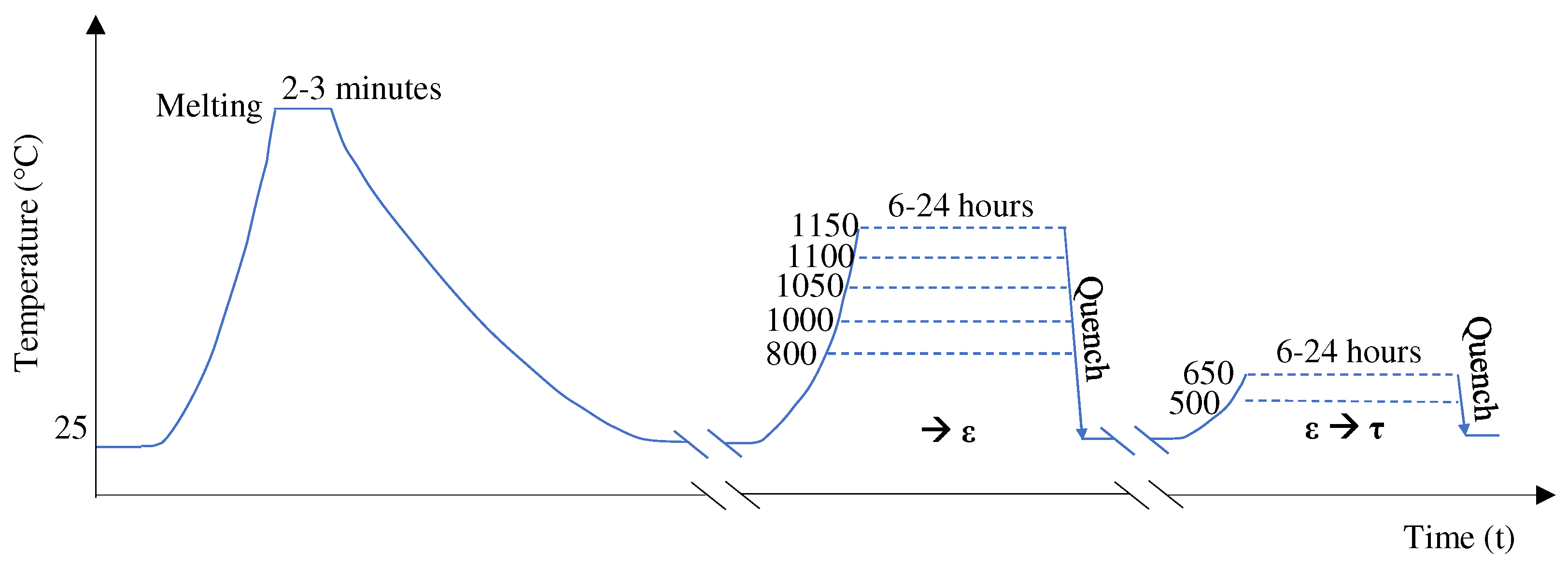
2.1. Heat Treatment: One and Two Step
2.2. Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Ternary Mn-Al-Ga One-Step Heat Treatment
3.2. Ternary Mn-Al-Ga Two-Step Heat Treatment
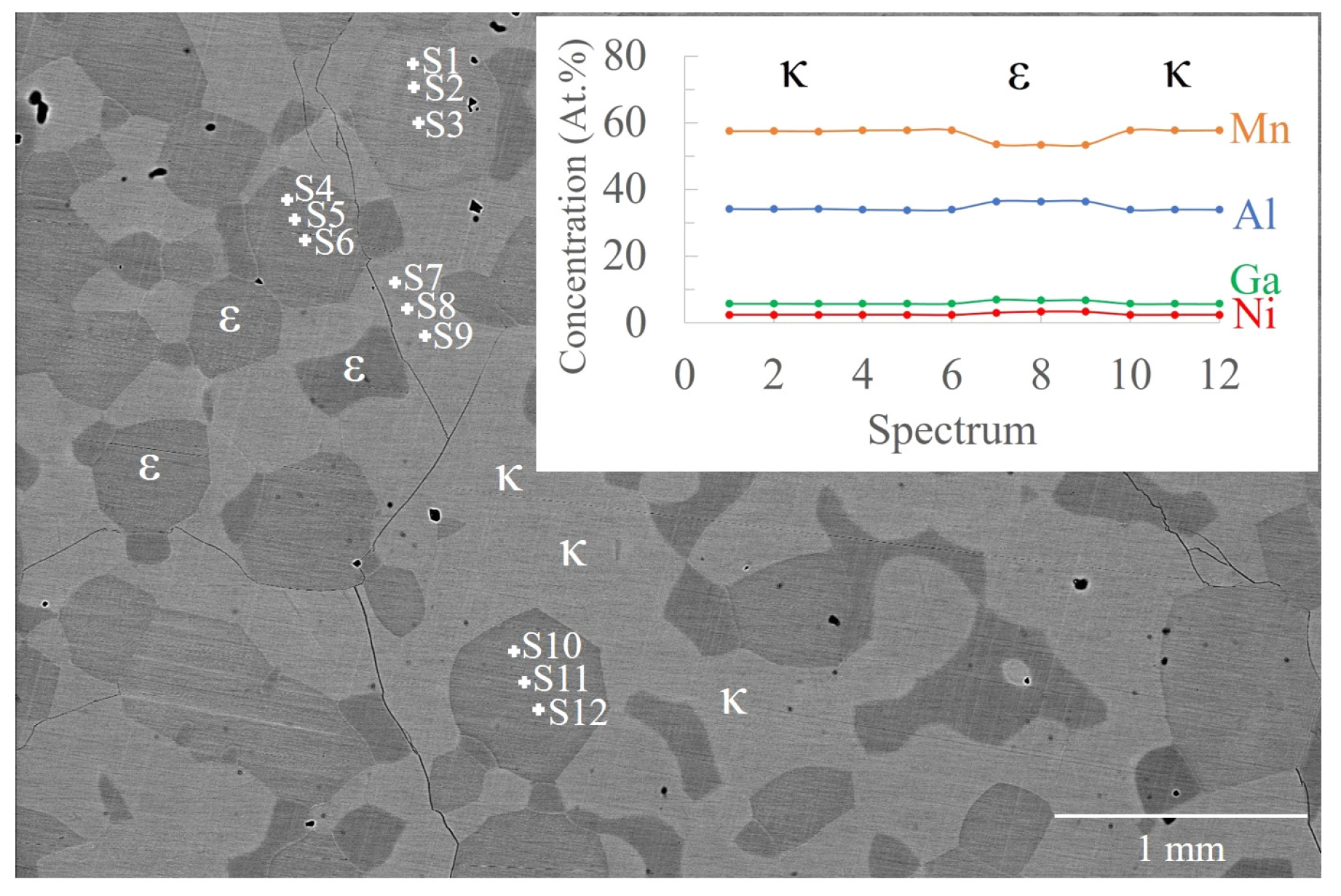
3.3. Mn-Al-Ga-Ni One-Step Heat Treatment
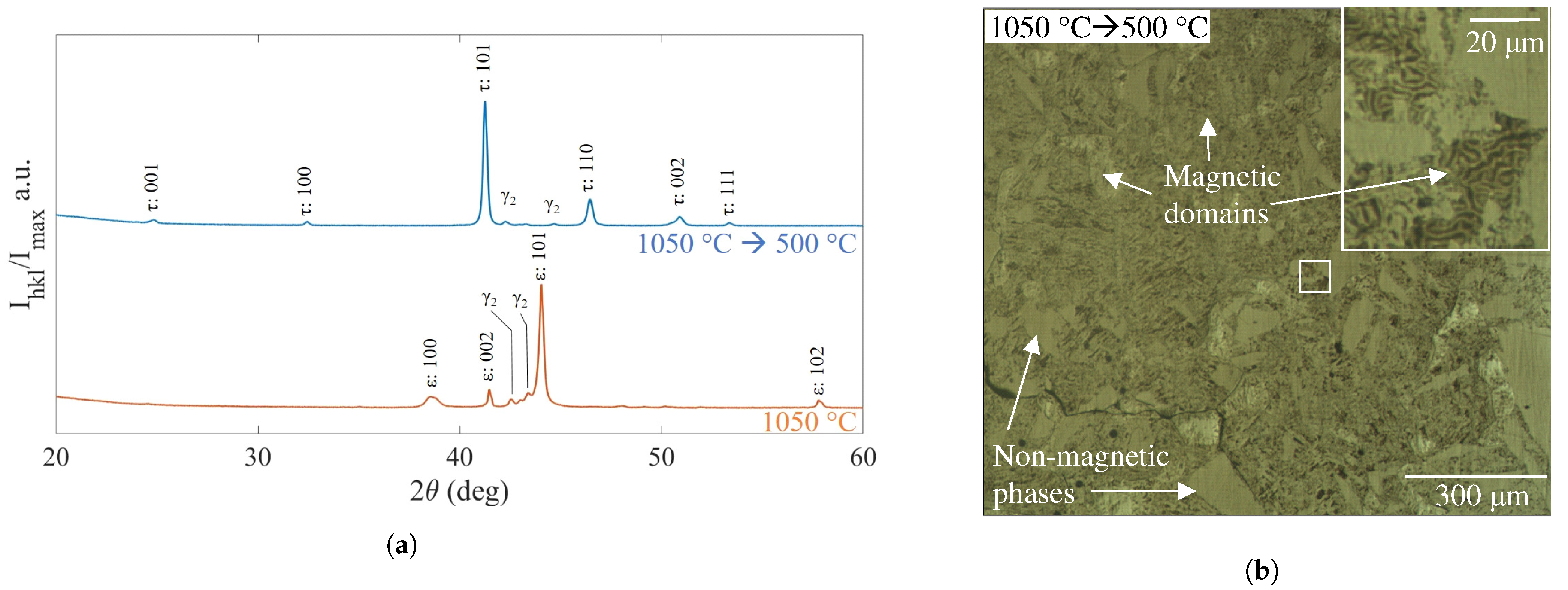
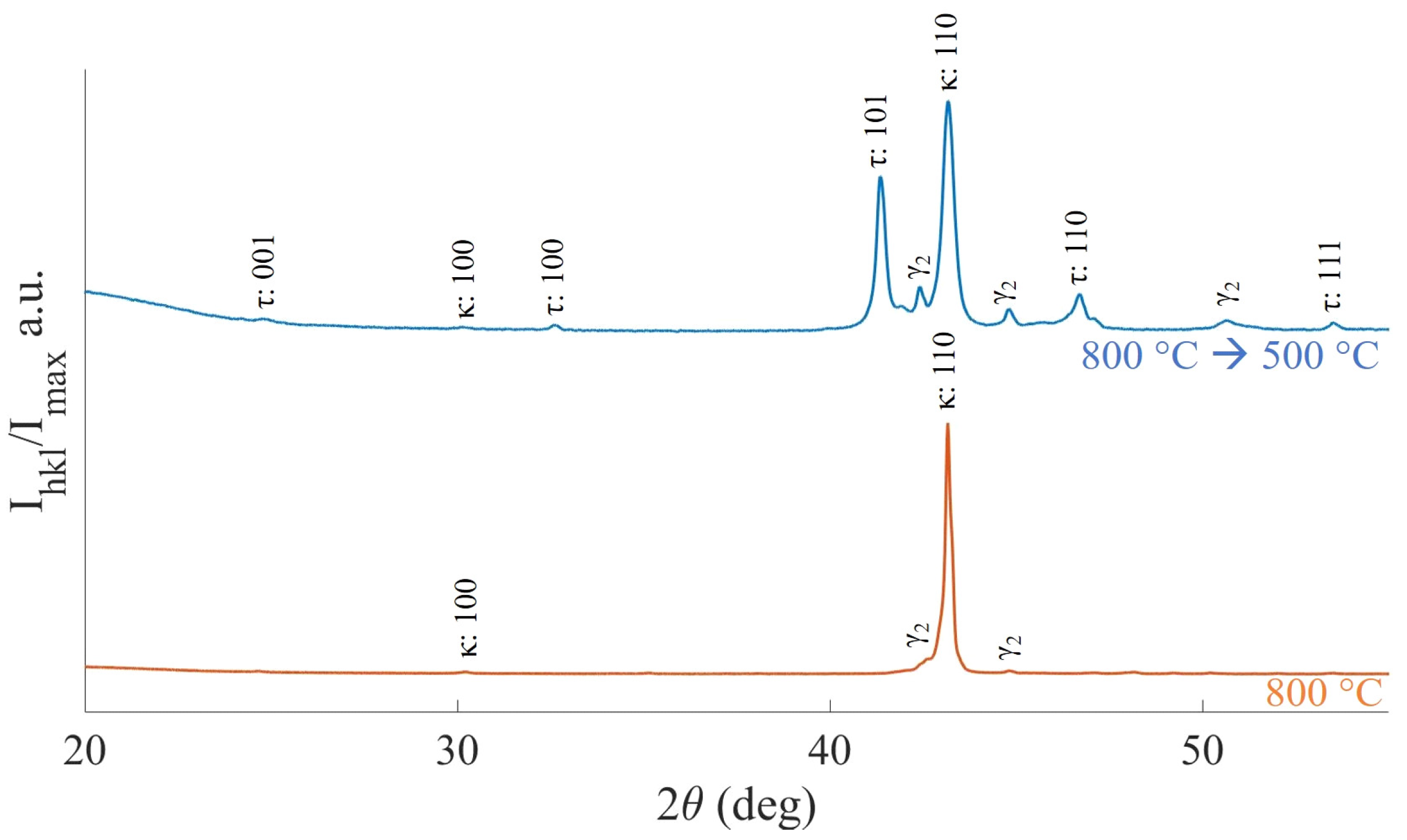
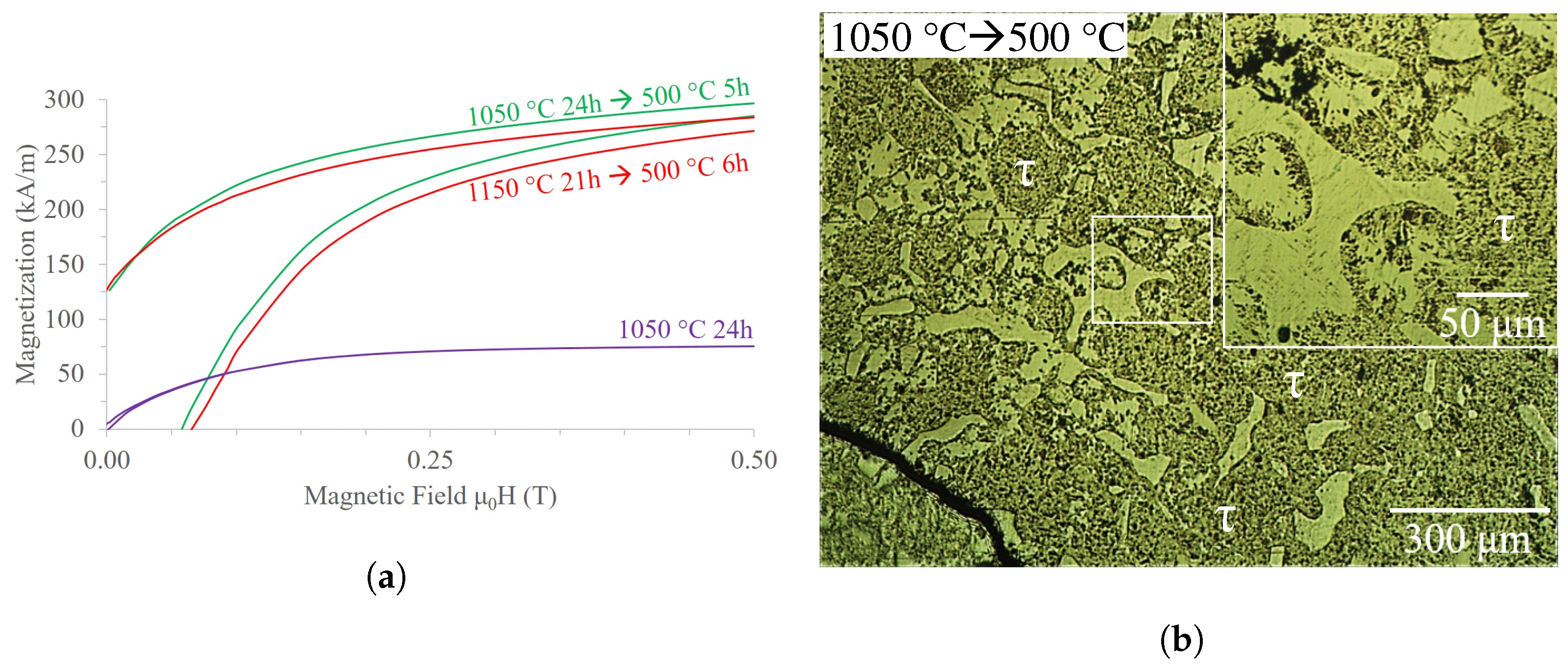
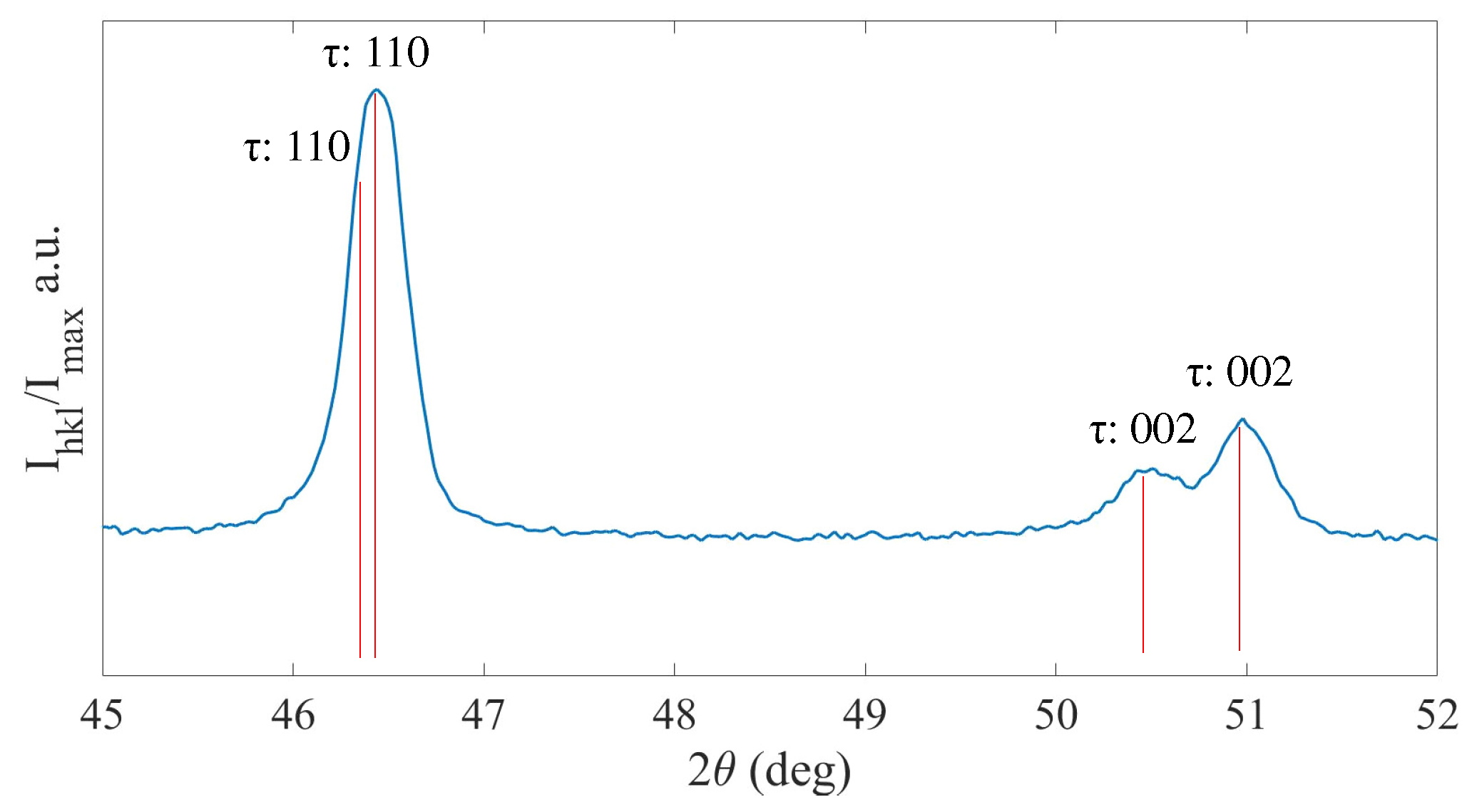
3.4. Mn-Al-Ga-Ni Two-Step Heat Treatment
4. Discussion
4.1. Phase Stability and Phase Transformations of Binary Mn-Al
4.2. Ternary Mn-Al-Ga
4.3. Mn-Al-Ga-Ni: Heat Treatments and Phase Transformations
4.4. Magnetic Properties
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patel, K.; Zhang, J.; Ren, S. Rare-earth-free high energy product manganese-based magnetic materials. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 11701–11718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, T.; Baker, I. Manganese-based permanent magnet materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2022, 124, 100872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Kramer, M.; Zhou, L.; Liu, F.; Gabay, A.; Hadjipanayis, G.; Balasubramanian, B.; Sellmyer, D. Current progress and future challenges in rare-earth-free permanent magnets. Acta Mater. 2018, 158, 118–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Hong, Y.; Bae, S.; Lee, J.; Jalli, J.; Abo, G.; Neveu, N.; Kim, S.; Choi, C.; Lee, J. Saturation magnetization and crystalline anisotropy calculations for MnAl permanent magnet. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 09A731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kōno, H. On the ferromagnetic phase in manganese-aluminum system. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1958, 13, 1444–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasko, A.; Mazaleyrat, F.; Lobue, M.; Fazakas, E.; Varga, L. Hard magnetic properties of melt-spun Mn-Al-C alloys. Epj Web Conf. 2013, 40, 06008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardias, R.; Szilva, A.; Bergman, A.; Marco, I.D.; Katsnelson, M.; Lichtenstein, A.; Nordström, L.; Klautau, A.; Eriksson, O.; Kvashnin, Y.O. The Bethe-Slater curve revisited; new insights from electronic structure theory. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L. Microstructure, Texture and Magnetic Properties of Powder Extruded Rare-Earth-Free MnAl-C-Ni Permanent Magnets. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universitat Dresden, Dresden, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, M.; Morisako, A.; Kohshiro, N. Crystal Structure and Magnetic Properties of Mn-Al-Ni Ferromagnetic Films. IEEE Transl. J. Magn. Jpn. 1991, 6, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mican, S.; Benea, D.; Hirian, R.; Gavrea, R.; Isnard, O.; Pop, V.; Coldea, M. Structural, electronic and magnetic properties of the Mn50Al46Ni4 alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 401, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlmann, M.; Koo, J.; Wise, J. Mn-Al-C for permanent magnets. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 2542–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboya, I.; Sugihara, M. The Magnetic Properties of the κ Phase in Mn–Al–Co System. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1962, 17, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Nielsch, K.; Woodcock, T.G. Enhanced thermal stability of the τ-phase in MnAl-C alloys with Ni additions. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 871, 159554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mix, T.; Bittner, F.; Müller, K.H.; Schultz, L.; Woodcock, T. Alloying with a few atomic percent of Ga makes MnAl thermodynamically stable. Acta Mater. 2017, 128, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mix, T.; Woodcock, T. Advanced thermal stability investigations of the Mn-Al-Ga system. Results Mater. 2020, 5, 100068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wu, Y.; Jiao, Z.; Jia, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, C. Evolution of intrinsic magnetic properties in L10 Mn-Al alloys doped with substitutional atoms and correlated mechanism: Experimental and theoretical studies. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2019, 11, 064008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yang, W.; Shao, Z.; Tian, G.; Zhou, D.; Chen, X.; Xia, Y.; Xie, L.; Liu, S.; Du, H.; et al. Structural evolution and magnetic properties of L10-type Mn54.5Al45.5−xGax (x = 0.0, 15.0, 25.0, 35.0, 45.5) phase. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 680, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moze, O.; Pareti, L.; Ermakov, A. Neutron diffraction and magnetic investigations of Ga substituted MnAl permanent magnet materials. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 63, 4616–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, R.; Zhao, S.; Skokov, K.P.; Maccari, F.; Aubert, A.; Gutfleisch, O.; Wang, J.; et al. Roadmap towards optimal magnetic properties in L10-MnAl permanent magnets. Acta Mater. 2023, 245, 118654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J. New permanent magnets; manganese compounds. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2014, 26, 064211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, S.; Ohtani, T.; Kato, N.; Kojima, K.; Sakamoto, Y.; Konno, I.; Tsukahara, M.; Kubo, T. Crystal transformation and orientation of Mn-Al-C hard magnetic alloy. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, American Institute of Physics, San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–6 December 1974; Volume 24, pp. 768–769. [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Broek, J.; Donkersloot, H.; Van Tendeloo, G.; Van Landuyt, J. Phase transformations in pure and carbon-doped Al45Mn55 alloys. Acta Metall. 1979, 27, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mix, T. Die L10-Struktur in Mn-Ga- und Mn-Al-Ga-Legierungen: Magnetische Eigenschaften und Phasenumwandlungen. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universitat Dresden, Dresden, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sologubenko, A.; Müllner, P.; Heinrich, H.; Kostorz, G. On the plate-like τ-phase formation in MnAl-C alloys. Z. Met. 2004, 95, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanar, C.; Wiezorek, J.; Soffa, W.; Radmilovic, V. Massive transformation and the formation of the ferromagnetic L10 phase in manganese-aluminum-based alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. 2002, 33, 2413–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, V.V.; Maccari, F.; Radulov, I.A.; Kovalevsky, A.; Katz-Demyanetz, A.; Bamberger, M. Microstructure and magnetic properties of Mn-Al-C permanent magnets produced by various techniques. Manuf. Rev. 2021, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiles, D. Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]



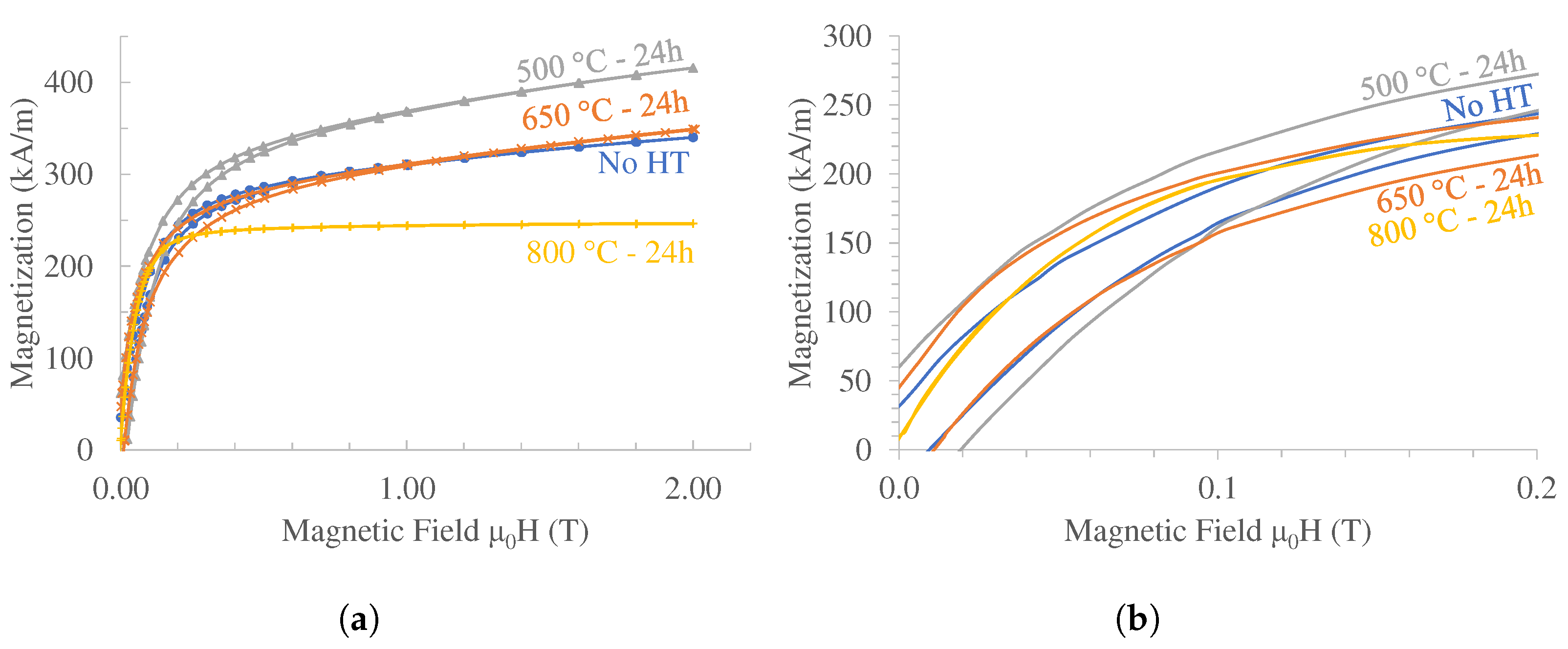
| Sample | Nom. Comp. (at.-%) | Mn (g) | Al (g) | Ga (g) | Al73.5Ni26.5 (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn-Al-Ga a | Mn55Al39.4Ga5.6 | 33.8 | 11.9 | 4.4 | - |
| Mn-Al-Ga-Ni a | Mn52Al39.4Ga5.6Ni3 | 31.9 | 9.3 | 4.4 | 4.5 |
| Nominal Composition | Phase | Mean Composition (at.-%) | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | Al | Ga | |||
| Mn55Al39.375Ga5.625 | 54.3 | 40.2 | 5.5 | [14] | |
| Mn55Al39.4Ga5.6 | 54.2 | 40.1 | 5.72 | - | |
| Mn55Al38.57Ga6.43 | 2 | 51.6 | 41.3 | 7.0 | [14] |
| Mn55Al39.4Ga5.6 | 2 | 50.9 | 41.2 | 7.9 | - |
| Sample | Heat | M2T | Mr | Hc | XV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment a | (kA m−1) | (kA m−1) | (T) | (10−3) | |
| Mn-Al-Ga b | No HT | 287 | - | - | - |
| 500 °C-24 h | 482 | - | - | - | |
| Mn-Al-Ga c | No HT | 280 | 34.8 | 0.02 | - |
| 500 °C-24 h | 450 | 80.6 | 0.02 | - | |
| 650 °C-24 h | 445 | 71.5 | 0.02 | - | |
| 800 °C-24 h | 2 | - | - | 1.22 | |
| 1050 °C-24 h | 6 | - | - | 3.91 | |
| 1150 °C-24 h | 7 | - | - | - |
| Sample | Heat Treatment a | M2T (kA m−1) | Mr (kA m−1) | Hc (T) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn-Al-Ga-Ni | No HT | 351 | 32 | 0.01 |
| 500 °C-24 h | 416 | 60 | 0.02 | |
| 650 °C-24 h | 349 | 46 | 0.01 | |
| 800 °C-24 h | 246 | - | - |
| Sample | Heat Treatment a | M2T (kA m−1) | Mr (kA m−1) | Hc (T) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn-Al-Ga-Ni | 1150 °C-21 h → 500 °C-6 h | 361 | 131 | 0.07 |
| 1100 °C-14 h → 500 °C-6 h | 311 | - | - | |
| 1100 °C-6 h → 500 °C-5 h | 260 | 61 | 0.03 | |
| 1050 °C-24 h → 500 °C-5 h | 377 | 126 | 0.06 | |
| 1000 °C-6 h → 500 °C-6 h | 321 | - | - | |
| 800 °C-24 h → 500 °C-24 h | 339 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palmer, S.; Martin, J.; Lindquist, P.; Müllner, P. Transformation Pathways of Ferromagnetic Mn-Al-Ga-Ni. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9050128
Palmer S, Martin J, Lindquist P, Müllner P. Transformation Pathways of Ferromagnetic Mn-Al-Ga-Ni. Magnetochemistry. 2023; 9(5):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9050128
Chicago/Turabian StylePalmer, Shane, John Martin, Paul Lindquist, and Peter Müllner. 2023. "Transformation Pathways of Ferromagnetic Mn-Al-Ga-Ni" Magnetochemistry 9, no. 5: 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9050128
APA StylePalmer, S., Martin, J., Lindquist, P., & Müllner, P. (2023). Transformation Pathways of Ferromagnetic Mn-Al-Ga-Ni. Magnetochemistry, 9(5), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9050128






