Green Magnetic Nanoparticles CoFe2O4@Nb5O2 Applied in Paracetamol Removal
Abstract
1. Introduction
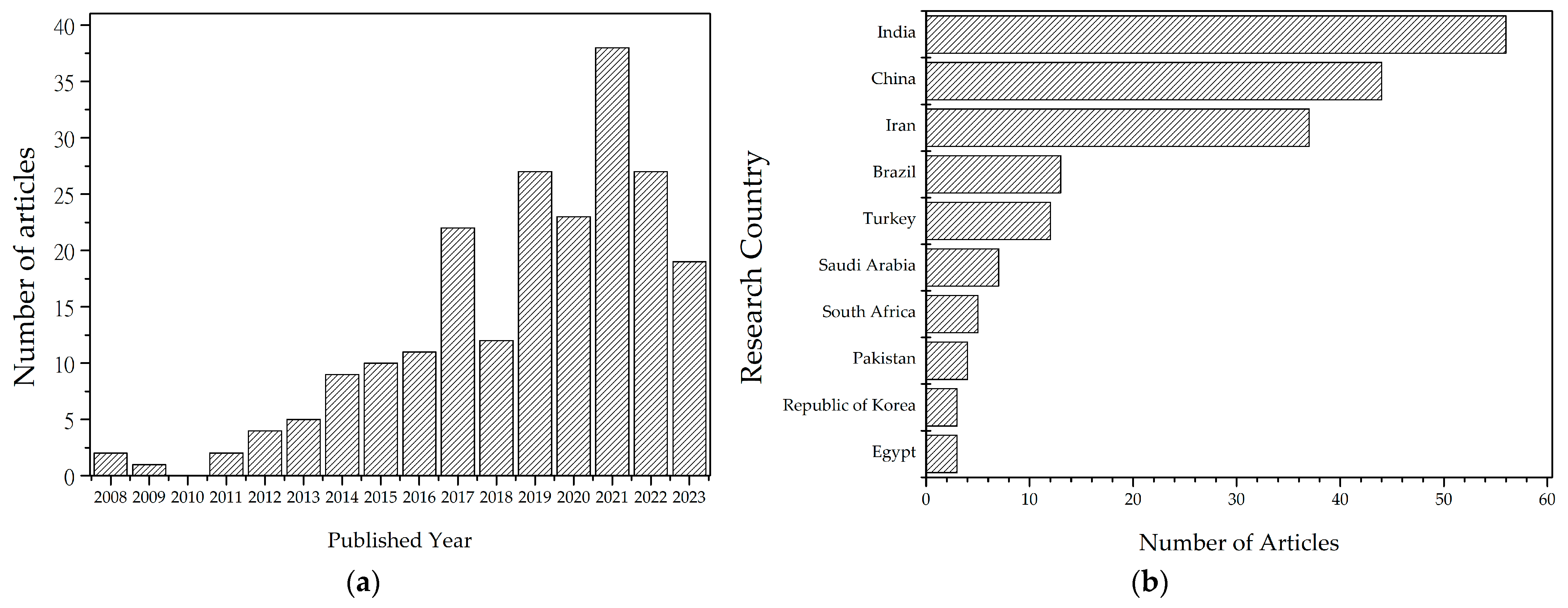
2. Bibliometric Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
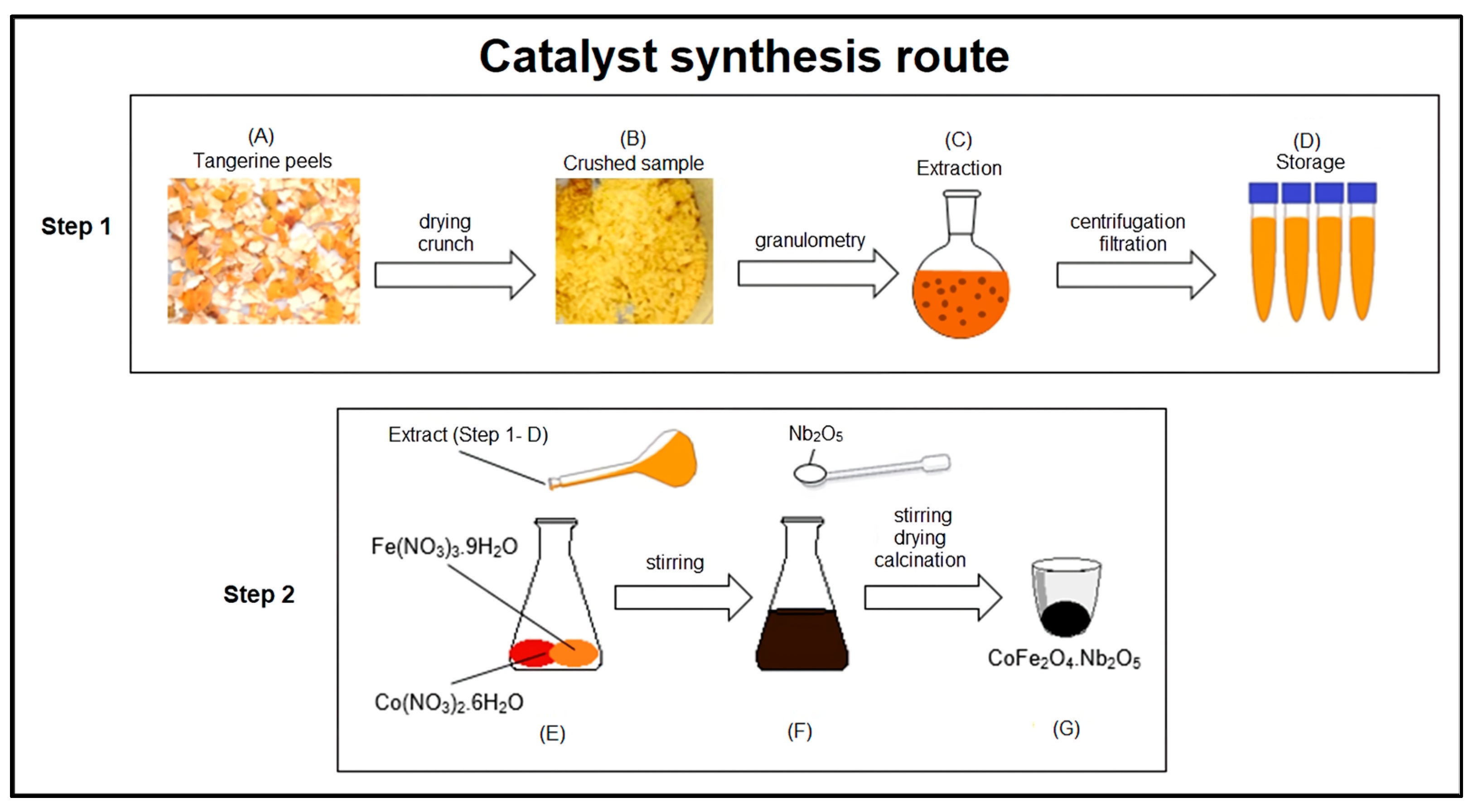
3.2. Catalysts Preparation
3.2.1. Tangerine Peel Extract
3.2.2. Magnetic Demonstration
3.3. Characterization Techniques
3.3.1. Surface and Pore Analyzer
3.3.2. Photoacoustic Spectroscopy
3.3.3. Point of Zero Charge (pHpzc)
3.3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS)
3.3.5. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
3.3.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy
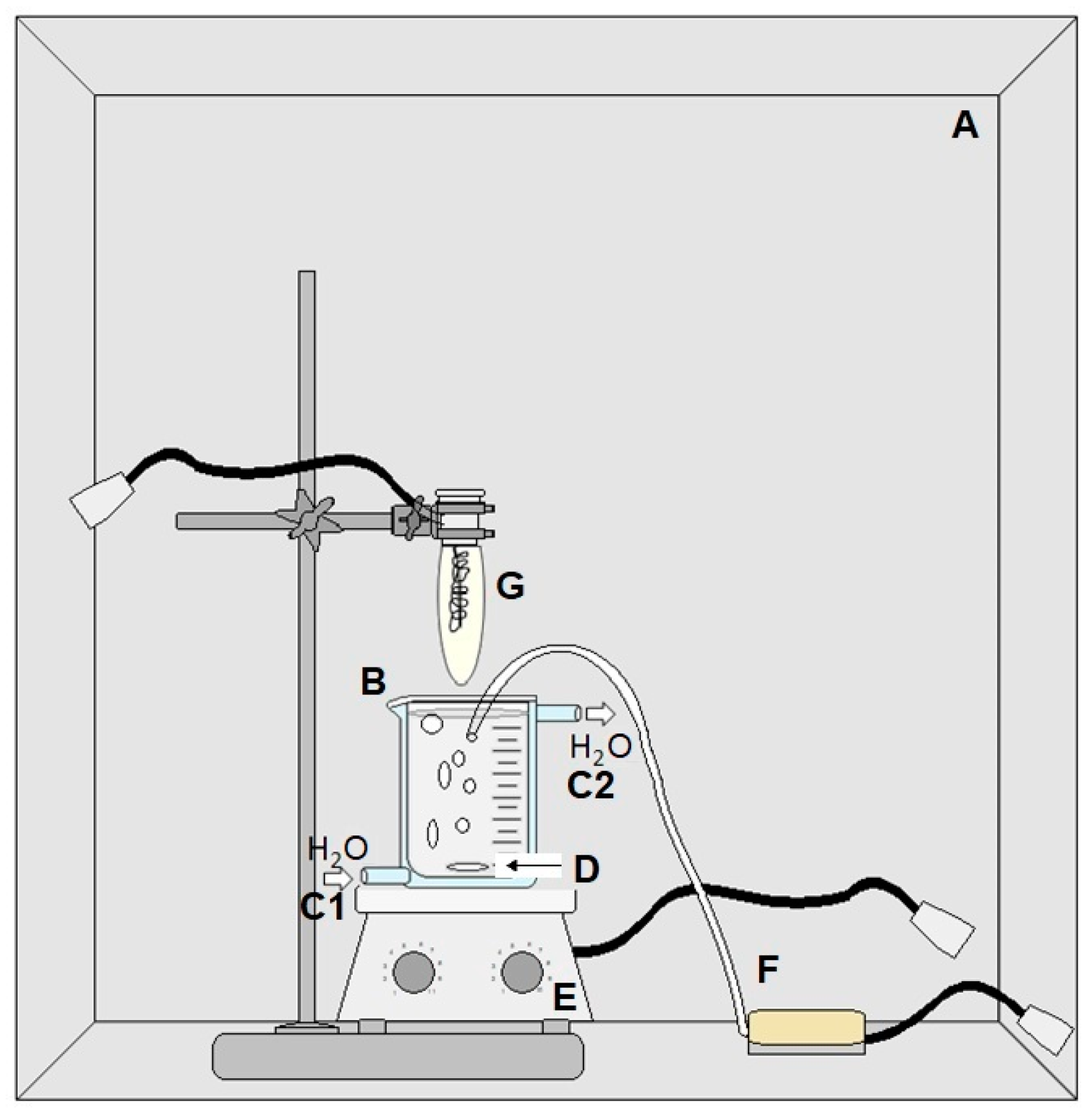
3.3.7. Photocatalysis
- The pH of the paracetamol solution (21.7 ± 1.9 mg·L−1) was adjusted;
- The paracetamol solution was placed in the reactor (B), which was established in the photocatalytic chamber (A);
- A jacketed reactor maintained a constant temperature of approximately 298 K. To keep the flow of water in the reactor jacket (C1 and C2), an ultra-thermostatic bath was used (SL 152/10, SOLAB);
- Magnetic stirring (D) using a magnetic stirring plate (C-MAG HS 7, IKA) (E) and constant airflow (F) started;
- The catalyst was added to the solution, and samples were taken at 0, 15, 30, 45, 60, 90, 120, 180, and 240 min;
- The mercury lamp (G) 250 Watts was lit, remaining on until the end of the reaction;
- All nine samples of all reactions were analyzed using HPLC applying the calibration curve made initially as a reference.
4. Results and Discussion
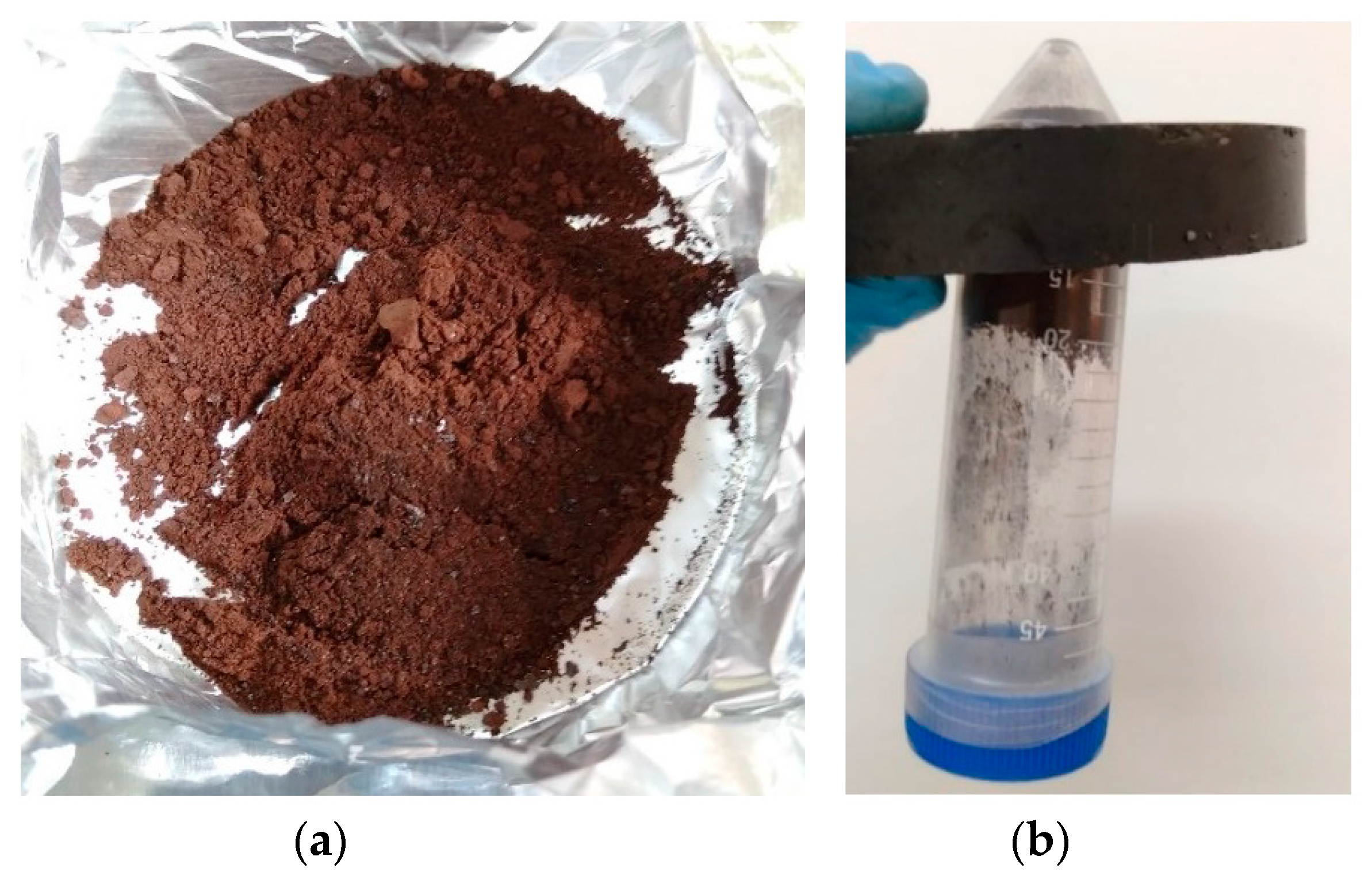
4.1. Catalyst Preparation
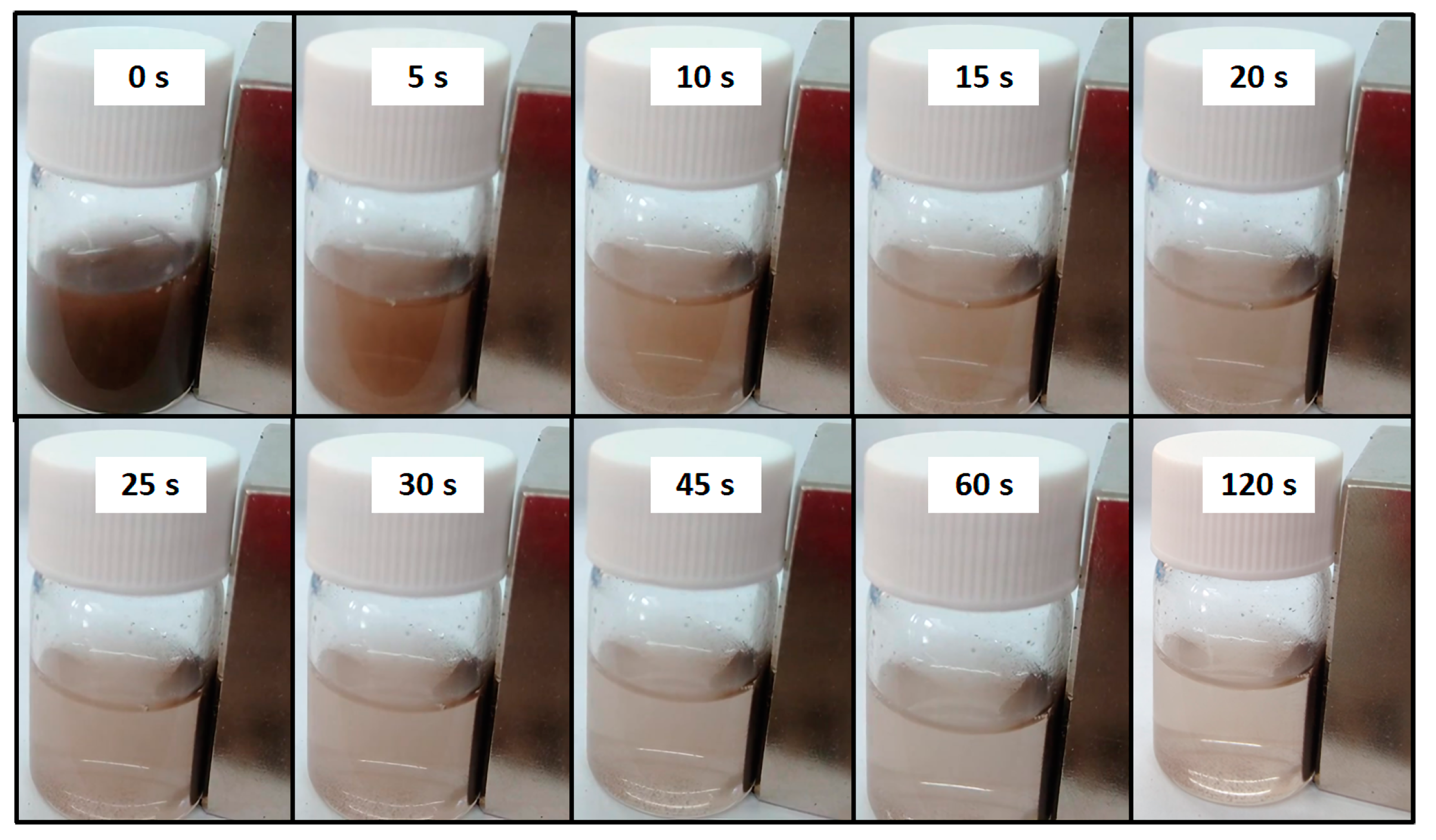
4.2. Magnetic Demonstration
4.3. Characterization Techniques
4.3.1. Surface and Pore Analyzer
4.3.2. Photoacoustic Spectroscopy
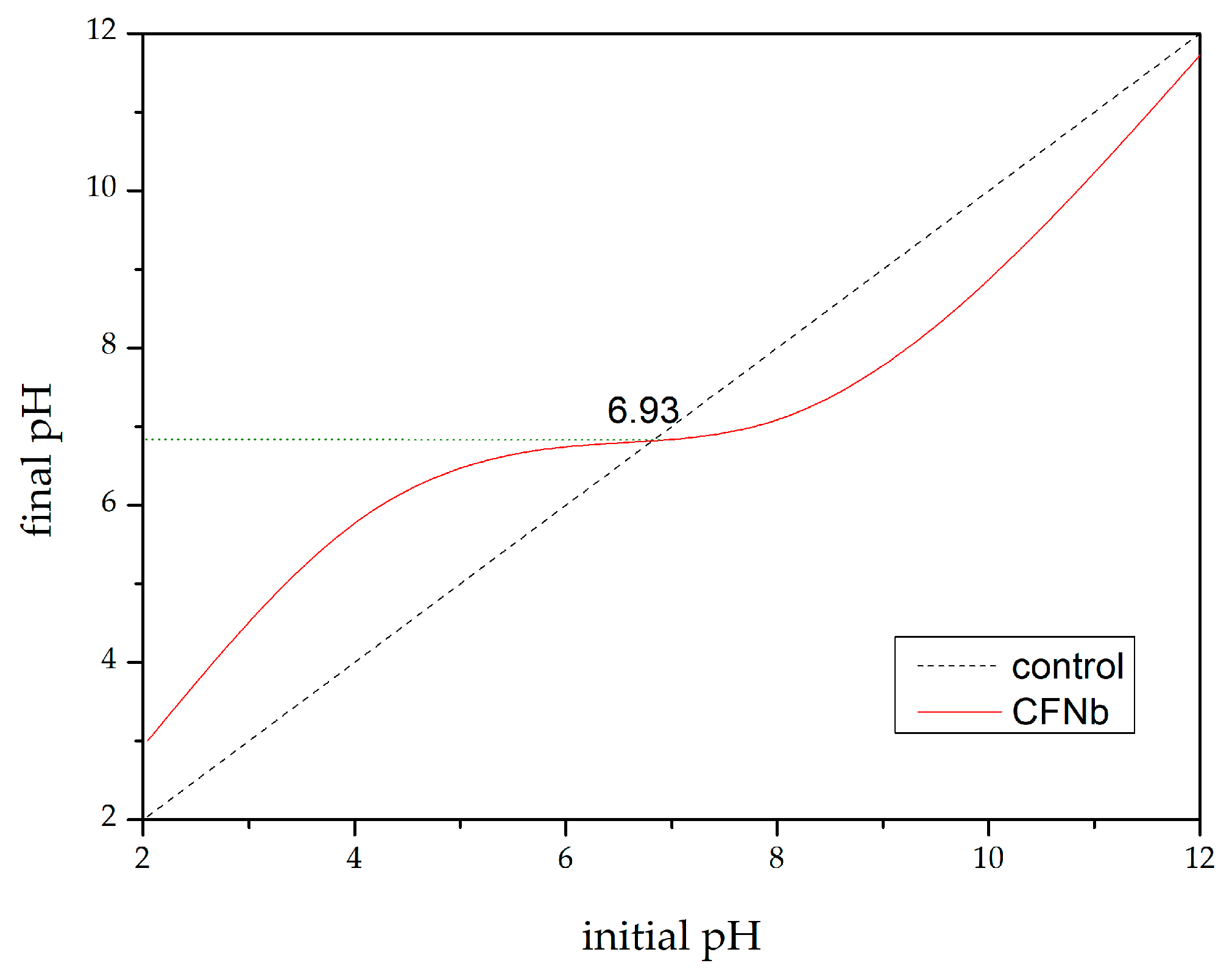
4.3.3. Point of Zero Charge (pHpzc)
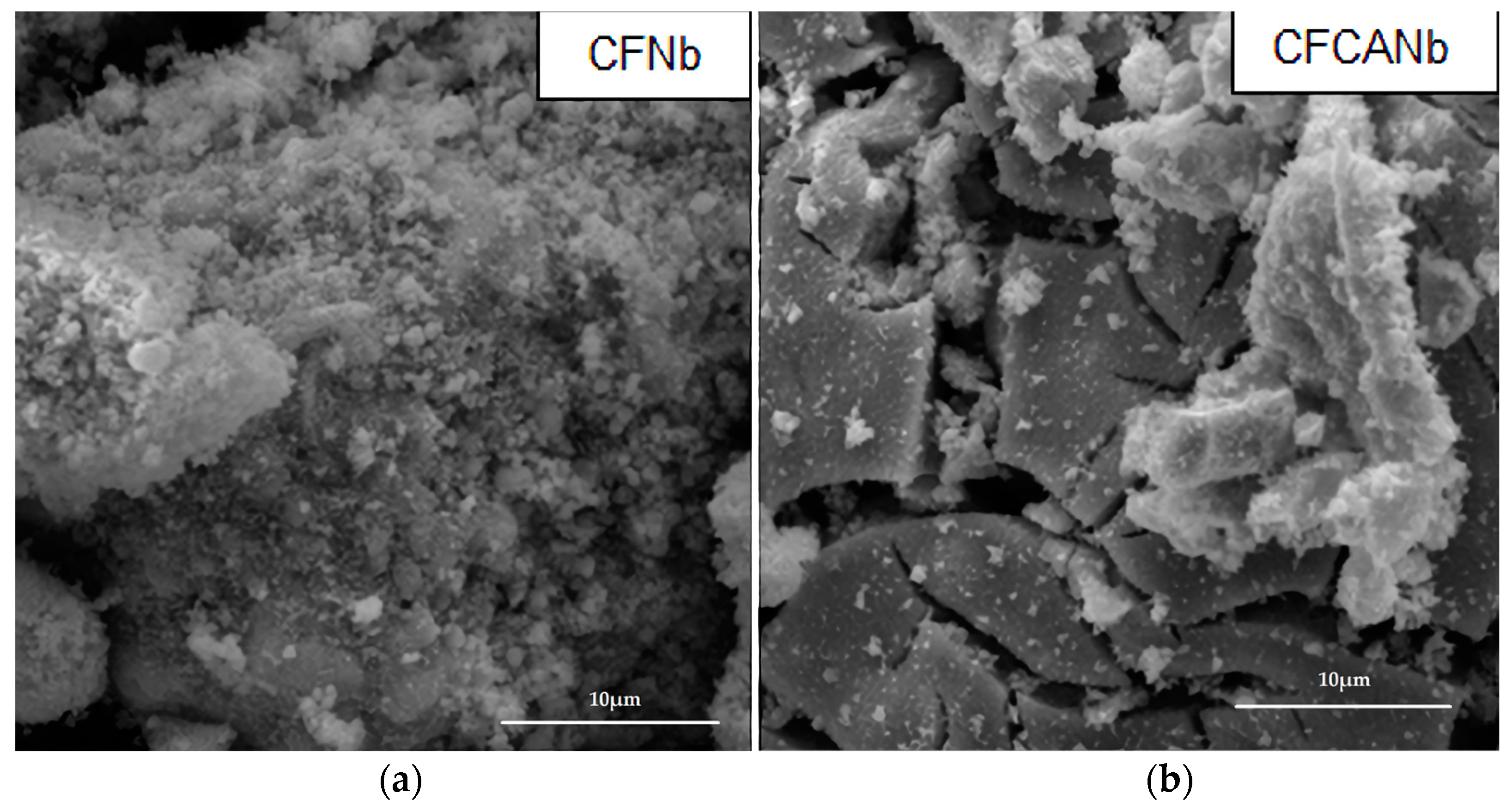
4.3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS)
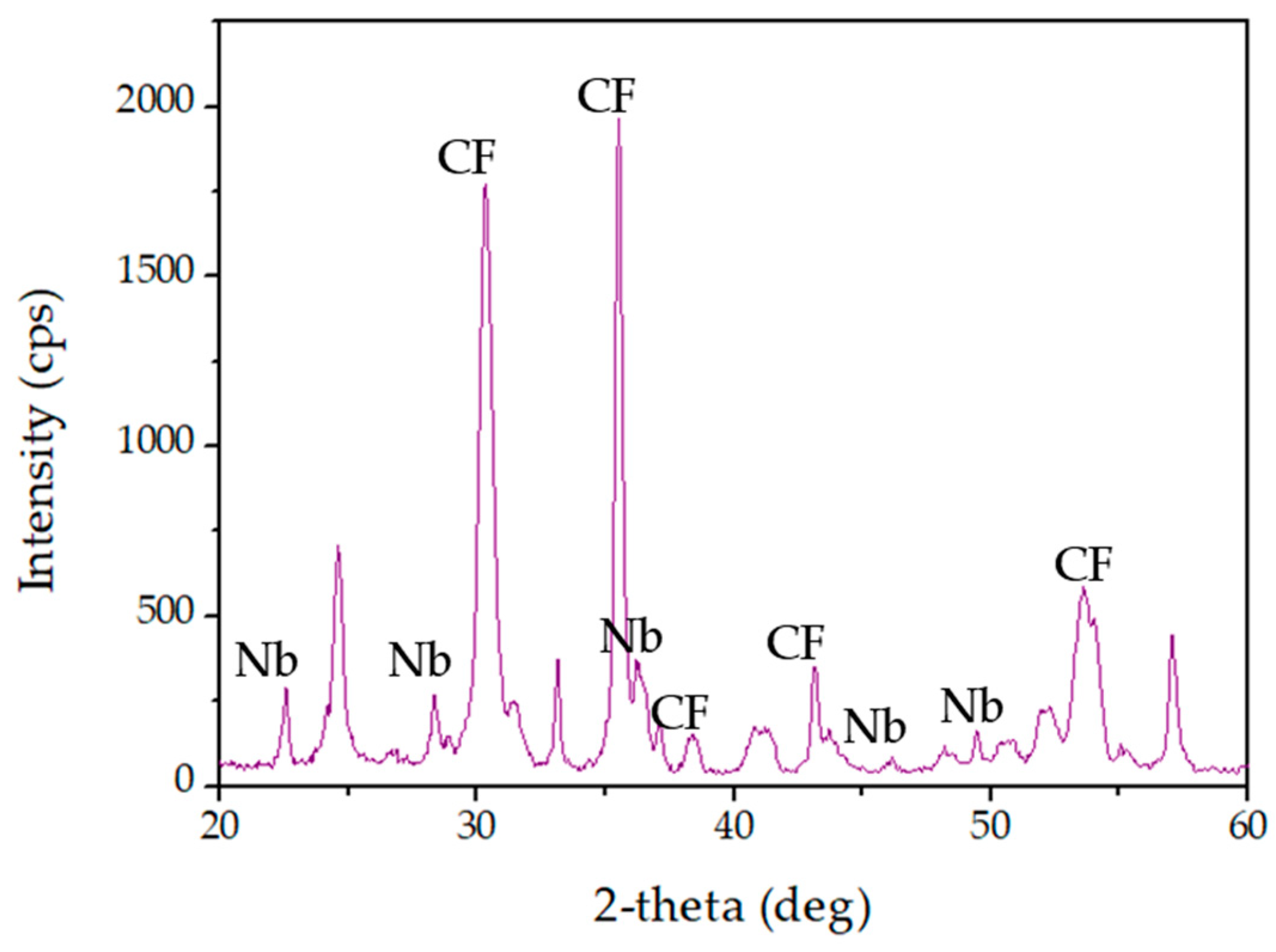
4.3.5. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
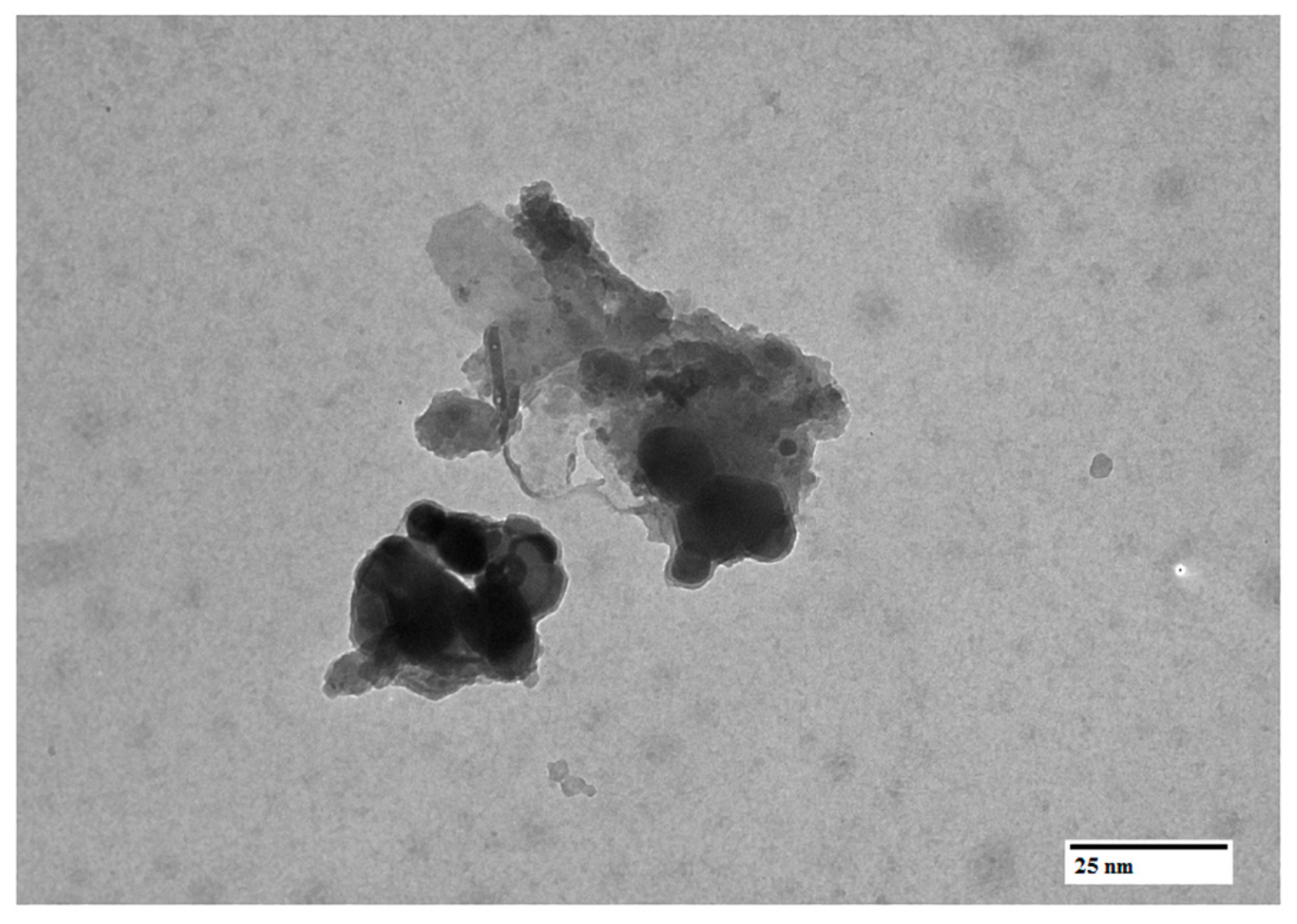
4.3.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy
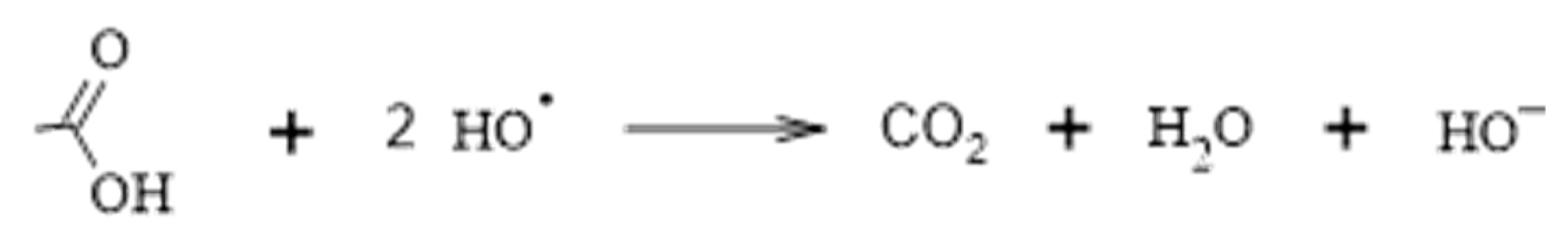
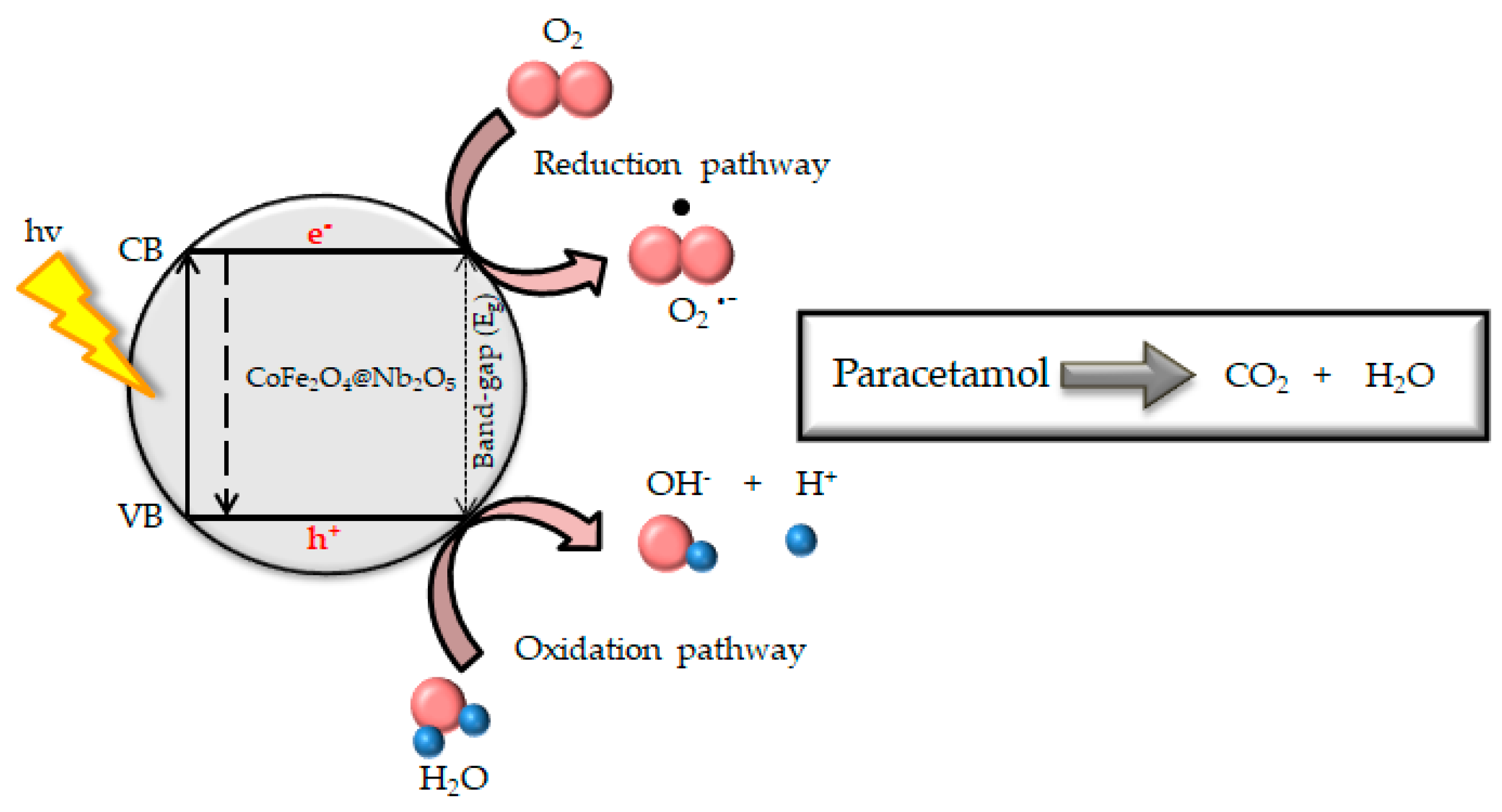
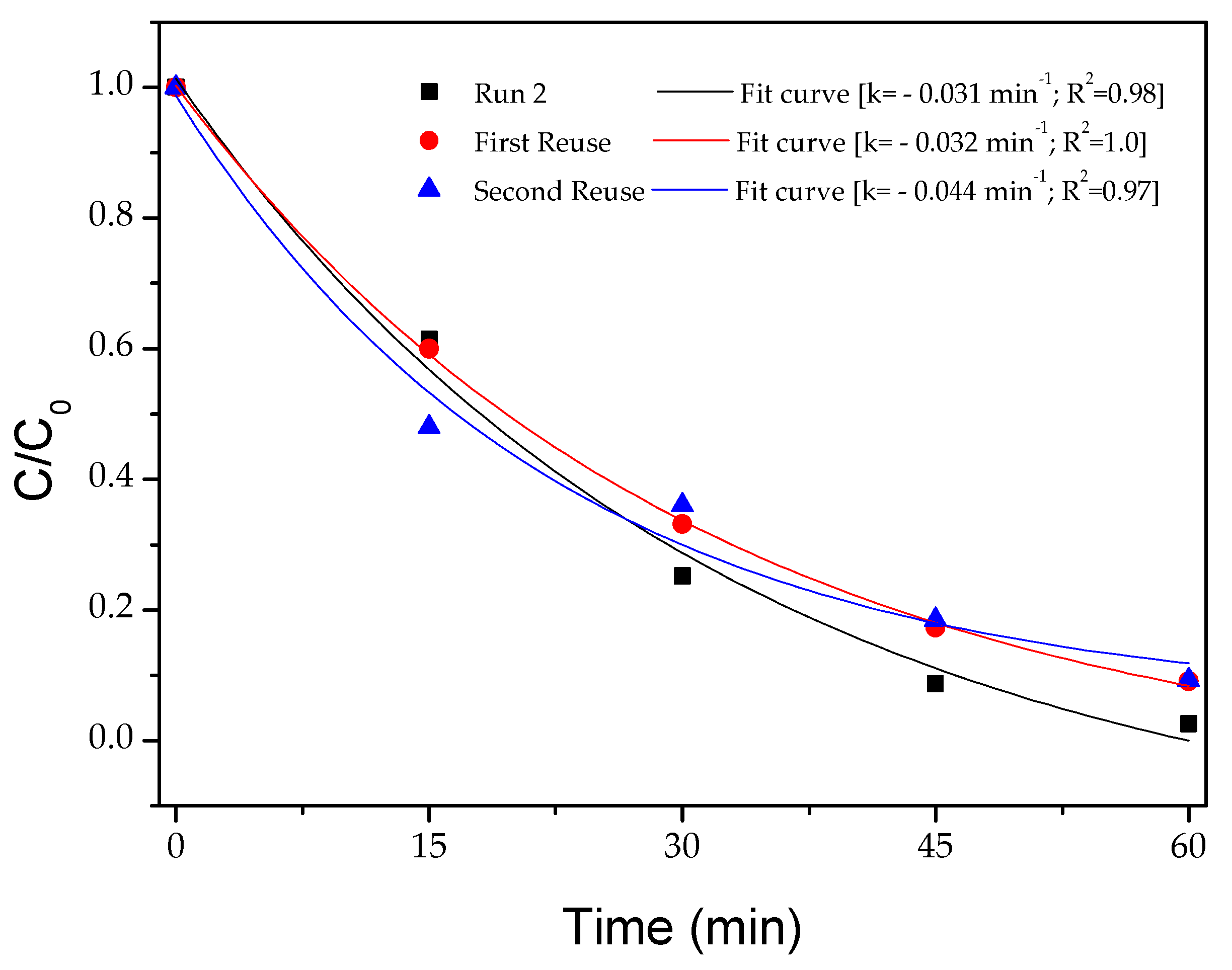
4.3.7. Photocatalysis
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van Santen, R.A. Theoretical Heterogeneous Catalysis; World Scientific: Singapore, 1991; Volume 5, ISBN 9810203845. [Google Scholar]
- Bhaduri, S.; Mukesh, D. Homogeneous Catalysis: Mechanisms and Industrial Applications, 1st ed.; Wiley Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 0471372218. [Google Scholar]
- Ertl, G.; Knözinger, H.; Schüth, F.; Weitkamp, J. Handbook of Heterogeneous Catalysis; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; Volume 1, ISBN 9783527312412. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, J.R.H. Heterogeneuos Catalysis: Fundamentals and Applications, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; ISBN 978-0-444-53363-0. [Google Scholar]
- Dupont, J. A Catálise No Brasil Nos Últimos 25 Anos: Uma História de Sucesso. Quim. Nova 2002, 25, 12–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameta, R.; Ameta, S.C. Nanoparticles and Catalysis, 1st ed.; Astruc, D., Ed.; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; ISBN 9783527315727. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, R.S.; Silva, A.M.T.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Faria, J.L.; Gomes, H.T. The Role of Cobalt in Bimetallic Iron-Cobalt Magnetic Carbon Xerogels Developed for Catalytic Wet Peroxide Oxidation. Catal. Today 2017, 296, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, M.; Yamini, Y.; Rezaee, M. Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Stabilization, Functionalization, Characterization, and Applications. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2010, 7, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessica, R.P. Oliveira Development and Functionalization of Magnetic Nanocomposites for Cancer Treatment. Master’s Thesis, Instituto Politécnico de Bragança, Bragança, Portugal, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Basics of Green Chemistry. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/greenchemistry/basics-green-chemistry#:~:text=Definition (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Anastas, P.; Warner, J. 12 Principles of Green Chemistry. Available online: https://www.acs.org/content/acs/en/greenchemistry/principles/12-principles-of-green-chemistry.html (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Kharissova, O.V.; Kharisov, B.I.; Oliva González, C.M.; Méndez, Y.P.; López, I. Greener Synthesis of Chemical Compounds and Materials. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 191378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, V.V.; Makarova, S.S.; Love, A.J.; Sinitsyna, O.V.; Dudnik, A.O.; Yaminsky, I.V.; Taliansky, M.E.; Kalinina, N.O. Biosynthesis of Stable Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Aqueous Extracts of Hordeum Vulgare and Rumex Acetosa Plants. Langmuir 2014, 30, 5982–5988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmuş, A.; Çolak, H.; Karaköse, E. Production and Examination of ZnO Thin Film for First Time Using Green Synthesized Method from Aqueous Citrus Reticulata Peel Extract. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 809, 151813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, D.; Arias, V.; Zhang, Y.; Cabot, A.; Agudelo, A.C.; Cadavid, D. Low-Cost Tangerine Peel Waste Mediated Production of Titanium Dioxide Nanocrystals: Synthesis and Characterization. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 13, 100285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingasu, D.; Mindru, I.; Patron, L.; Calderon-Moreno, J.M.; Mocioiu, O.C.; Preda, S.; Stanica, N.; Nita, S.; Dobre, N.; Popa, M.; et al. Green Synthesis Methods of CoFe2O4 and Ag-CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles Using Hibiscus Extracts and Their Antimicrobial Potential. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F.E.; Lemos, L.V.; Migliano, A.C.C.; Machado, J.P.B.; Pullar, R.C. Structural and Complex Electromagnetic Properties of Cobalt Ferrite (CoFe2O4) with an Addition of Niobium Pentoxide. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, M.; Shanker, U. Removal of Chlorpyrifos, Thiamethoxam, and Tebuconazole from Water Using Green Synthesized Metal Hexacyanoferrate Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 10878–10893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, N.V.; Yang, Y.; Teranishi, T.; Thi, C.M.; Cao, Y.; Nogami, M. Synthesis and Magnetism of Hierarchical Iron Oxide Particles. Mater. Des. 2015, 86, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, B.J.; Ravina, M.; Saravanakumar, B.; Ravi, G.; Ganesh, V.; Ravichandran, S.; Yuvakkumar, R. Ferrimagnetism in Cobalt Ferrite (CoFe2O4) Nanoparticles. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2018, 14, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.; Salavati-Niasari, M.; Akbari, A.; Gholami, T. Removal of Malachite Green (a Toxic Dye) from Water by Cobalt Ferrite Silica Magnetic Nanocomposite: Herbal and Green Sol-Gel Autocombustion Synthesis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 24846–24860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.S.; Rodrigues, R.O.; Silva, A.M.T.; Tavares, P.B.; Carvalho, A.M.C.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Faria, J.L.; Gomes, H.T. Hybrid Magnetic Graphitic Nanocomposites towards Catalytic Wet Peroxide Oxidation of the Liquid Effluent from a Mechanical Biological Treatment Plant for Municipal Solid Waste. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 219, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonu; Dutta, V.; Sharma, S.; Raizada, P.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Kumar Gupta, V.; Singh, P. Review on Augmentation in Photocatalytic Activity of CoFe2O4 via Heterojunction Formation for Photocatalysis of Organic Pollutants in Water. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2019, 23, 1119–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzi, G.G.; Lopes, M.F.; Andrade, D.I.; Napoli, J.S.; Parolin, A.; Fávaro, Y.B.; Kounaris Fuziki, M.E.; de Almeida, L.N.B.; Josué, T.G.; Dias, D.T.; et al. Functioned Catalysts with Magnetic Core Applied in Ibuprofen Degradation. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 2158–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.; Akbari, A.; Ahmadi, M.; Pardakhti, A.; Salavati-Niasari, M. Synthesis and in Vitro Evaluation of a Novel Magnetic Drug Delivery System; Proecological Method for the Preparation of CoFe2O4 Nanostructures. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 249, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhou, F.; Zheng, L.; Wang, G.; Gao, J.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, L.; Fu, B.; et al. Mesoporous Superparamagnetic Cobalt Ferrite Nanoclusters: Synthesis, Characterization and Application in Drug Delivery. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 498, 166222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefeni, K.K.; Mamba, B.B.; Msagati, T.A.M. Magnetite and Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles Used as Seeds for Acid Mine Drainage Treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 333, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.K.; Marques, R.G.; Machado, N.R.C.F.; Santos, O.A.A. Evaluation of Nb2O5 and Ag/Nb2O5 in the Photocatalytic Degradation of Dyes from Textile Industries. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2002, 19, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, D.C.; Cavalcante, R.P.; Jorge, J.; Martines, M.A.U.; Oliveira, L.C.S.; Casagrande, G.A.; Machulek, A., Jr. Synthesis and Characterization of Mesoporous Nb2O5 and Its Application for Photocatalytic Degradation of the Herbicide Methylviologen. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2016, 27, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Han, X.; Astorsdotter, J.; Farrauto, R. Catalysts Promoted with Niobium Oxide for Air Pollution Abatement. Catalysts 2017, 7, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, E.; Fidelis, M.Z.; Fuziki, M.E.; Malikoski, R.M.; Mastsubara, M.C.; Imada, R.E.; Diaz de Tuesta, J.L.; Gomes, H.T.; Anziliero, M.D.; Baldykowski, B.; et al. Degradation of Emerging Contaminants: Effect of Thermal Treatment on nb2o5 as Photocatalyst. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2021, 419, 113484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidelis, M.; Abreu, E.; Dos Santos, O.; Chaves, E.; Brackmann, R.; Dias, D.; Lenzi, G. Experimental Design and Optimization of Triclosan and 2.8-Diclorodibenzeno-p-Dioxina Degradation by the Fe/Nb2O5/UV System. Catalysts 2019, 9, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoleão, D.C.; Elias, L.; Carneiro, M.; De Almeida, J.B.; Vitória, R.; Sales, D.L.; Lins, V. Degradação Do Contaminante Emergente Paracetamol Empregando Processos Oxidativos Avançados. Rev. Eletrônica Gestão Educ. Tecnol. Ambient. 2015, 19, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, D.; Zhou, C.; Bin Hashim, M.H.; Hang, T.M.; Gin, K.Y.-H.; Wang, C.-H.; Neoh, K.G. Emerging Pharmaceutical and Organic Contaminants Removal Using Carbonaceous Waste from Oil Refineries. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Rangabhashiyam, S.; Verma, P.; Singh, P.; Devi, P.; Kumar, P.; Hussain, C.M.; Gaurav, G.K.; Kumar, K.S. Environmental and Health Impacts of Contaminants of Emerging Concerns: Recent Treatment Challenges and Approaches. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Berrones, K.; Bernal-Jácome, L.; Díaz de León-Martínez, L.; Flores-Ramírez, R. Emerging Pollutants (EPs) in Latin América: A Critical Review of under-Studied EPs, Case of Study -Nonylphenol-. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paumo, H.K.; Dalhatou, S.; Katata-Seru, L.M.; Kamdem, B.P.; Tijani, J.O.; Vishwanathan, V.; Kane, A.; Bahadur, I. TiO2 Assisted Photocatalysts for Degradation of Emerging Organic Pollutants in Water and Wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 331, 115458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, R.N.; Pedroso, B.; dos Santos, C.B.; Picinin, C.T.; Kovaleski, J.L. Methodi Ordinatio 2.0: Revisited under Statistical Estimation, and Presenting FInder and RankIn. Qual. Quant. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, O.J.; Soto-Robles, C.A.; Gómez-Gutiérrez, C.M.; Vilchis-Nestor, A.R.; Castro-Beltrán, A.; Olivas, A.; Luque, P.A. Fruit Peel Extract Mediated Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1147, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.; Rodrigues, R.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.; Marchesi, L.; Koneracka, M.; Jurikova, A.; Zavisova, V.; Gomes, H. Carbon-Based Magnetic Nanocarrier for Controlled Drug Release: A Green Synthesis Approach. C 2018, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3P-instrument BET Surface Area. Available online: https://www.3p-instruments.com/measurement-methods/bet-surface-area/#measurement-methods-bet-surface-area. (accessed on 16 December 2020).
- Shimadzu ABC’s of Photoacoustic Spectroscopy. Available online: https://www.shimadzu.com/an/service-support/technical-support/analysis-basics/ftirtalk/talk7.html. (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Poghossian, A.A. Determination of the PHpzc of Insulators Surface from Capacitance–Voltage Characteristics of MIS and EIS Structures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1997, 44, 551–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.; Belessiotis, G.V.; Arfanis, M.K.; Athanasekou, C.; Philippopoulos, A.I.; Mitsopoulou, C.A.; Romanos, G.E.; Falaras, P. Surfactant Effects on the Synthesis of Redox Bifunctional V2O5 Photocatalysts. Materials 2020, 13, 4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panalytical, M. X-ray Analysis. Available online: https://www.malvernpanalytical.com/br/products/technology/xray-analysis (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Tan, C.; Gao, N.; Fu, D.; Deng, J.; Deng, L. Efficient Degradation of Paracetamol with Nanoscaled Magnetic CoFe2O4 and MnFe2O4 as a Heterogeneous Catalyst of Peroxymonosulfate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 175, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavasso, I.; Poggi, C.; Petrucci, E. Enhanced Degradation of Paracetamol by Combining UV with Electrogenerated Hydrogen Peroxide and Ozone. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 34, 101102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masudi, A.; Jusoh, N.W.C.; Jusoh, R.; Jaafar, N.F.; Jalil, A.A.; Firdausi, A.; Hartanto, D. Equidistant Crystal Distortion Arrangement of Copper Doped Magnetite for Paracetamol Degradation and Optimization with Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 250, 122995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bian, Z. Photocatalytic Degradation of Paracetamol on Pd–BiVO4 under Visible Light Irradiation. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, G.; Borlaf, M.; López-Muñoz, M.J.; Fariñas, J.C.; Rodrigues Neto, J.B.; Moreno, R. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Nb2O5 for Photocatalytic Application of Nanopowders and Thin Films. J. Mater. Res. 2017, 32, 3271–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, Q.; Uchaker, E.; Cao, X.; Cao, G. Comparison of Amorphous, Pseudohexagonal and Orthorhombic Nb2O5 for High-Rate Lithium Ion Insertion. CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 2532–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.-Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, J.; Cha, L.-M.; Dou, Y.-H.; Ma, J.-M. Fabrication of Nb2O5/C Nanocomposites as a High Performance Anode for Lithium Ion Battery. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017, 28, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.S.; Gallo, J.; Bañobre-López, M.; Silva, A.M.T.; Faria, J.L.; Gomes, H.T. Enhanced Performance of Cobalt Ferrite Encapsulated in Graphitic Shell by Means of AC Magnetically Activated Catalytic Wet Peroxide Oxidation of 4-Nitrophenol. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 376, 120012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianoș, R. Highly Sinterable Cobalt Ferrite Particles Prepared by a Modified Solution Combustion Synthesis. Mater. Lett. 2014, 135, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, N.N.; Earnshaw, A. Chemistry of the Elements, 2nd ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Chavarriaga, E.A.; Lopera, A.A.; Franco, V.; Bergmann, C.P.; Alarcón, J. Gel Combustion Synthesis and Magnetic Properties of CoFe2O4, ZnFe2O4, and MgFe2O4 Using 6-Aminohexanoic Acid as a New Fuel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 497, 166054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, O.; Sattayamuk, D.; Saelee, T.; Yamashita, H.; Kuwahara, Y.; Mori, K.; Praserthdam, P.; Praserthdam, S. A Closer Look inside TiO2 (P25) Photocatalytic CO2/HCO3− Reduction with Water. Methane Rate and Selectivity Enhancements. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 128141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolzon, L.B.; Prado, A.G.S. Effect of Protonation and Deprotonation on Surface Charge Density of Nb2O5. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 106, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, A.; Sarani, M.; Najafidoust, A.; Mehrabani, M.; Zadeh, F.A.; Varma, R.S. Photocatalytic Performance and Cytotoxic Activity of Green-Synthesized Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 2022, 149, 111706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khawaga, A.M.; Elsayed, M.A.; Fahim, Y.A.; Shalaby, R.E. Promising Photocatalytic and Antimicrobial Activity of Novel Capsaicin Coated Cobalt Ferrite Nanocatalyst. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Weng, X.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Green Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles by Various Tea Extracts: Comparative Study of the Reactivity. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 130, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harshiny, M.; Iswarya, C.N.; Matheswaran, M. Biogenic Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles Using Amaranthus Dubius Leaf Extract as a Reducing Agent. Powder Technol. 2015, 286, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, S.; Pacheco, J.G.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Albergaria, J.T.; Delerue-Matos, C. Characterization of Green Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles Produced with Tree Leaf Extracts. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 533, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnama, B.; Wijayanta, A.T. Suharyana Effect of Calcination Temperature on Structural and Magnetic Properties in Cobalt Ferrite Nano Particles. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2019, 31, 956–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjia, M.; Oubaha, M.; Prescott, T.; Olabi, A.G. Development of Cobalt Ferrite Powder Preparation Employing the Sol–Gel Technique and Its Structural Characterization. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 506, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Xue, D. Large-Scale Fabrication of H2(H2O)Nb2O6 and Nb2O5 Hollow Microspheres. Mater. Res. Bull. 2010, 45, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- He, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lu, W.; Yang, S.; Wu, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Gu, H.; Wang, J. Hydrothermal Growth and Optical Properties of Nb2O5 Nanorod Arrays. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 8185–8190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawa Eblagon, K.; Malaika, A.; Ptaszynska, K.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Figueiredo, J.L. Impact of Thermal Treatment of Nb2O5 on Its Performance in Glucose Dehydration to 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural in Water. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Tan, R.; Kuang, Z.; Cui, C.; Wei, Z.; Deng, X.; Yan, Z.; Feng, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, C.; et al. Controlling the Morphology, Size and Phase of Nb2O5 Crystals for High Electrochemical Performance. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 1785–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.; Kim, K.; Kim, J.-H. Spherical Sb Core/Nb2O5-C Double-Shell Structured Composite as an Anode Material for Li Secondary Batteries. Energies 2020, 13, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakubu, A.; Abbas, Z.; Ibrahim, N.; Hashim, M. Effect of Temperature on Structural, Magnetic and Dielectric Properties of Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles Prepared via Co-Precipitation Method. Phys. Sci. Int. J. 2015, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaz, K.; Mumtaz, A.; Hasanain, S.K.; Ceylan, A. Synthesis and Magnetic Properties of Cobalt Ferrite (CoFe2O4) Nanoparticles Prepared by Wet Chemical Route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 308, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabal, M.A.; Al-Juaid, A.A.; El-Rashed, S.; Hussein, M.A. Synthesis and Characterization of Nano-Sized CoFe 2 O 4 via Facile Methods: A Comparative Study. Mater. Res. Bull. 2017, 89, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, K.B.; Chaves, E.S.; Kosera, V.S.; Lenzi, G.G. Barium Removal by Photocatalytic Process: An Alternative for Water Treatment. J. Water Process. Eng. 2018, 22, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrino, F.; Camera-Roda, G.; Loddo, V.; Palmisano, G.; Augugliaro, V. Combination of Ozonation and Photocatalysis for Purification of Aqueous Effluents Containing Formic Acid as Probe Pollutant and Bromide Ion. Water Res. 2014, 50, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mukherjee, D.; Ray, A.; Barghi, S. Mechanism of Acetyl Salicylic Acid (Aspirin) Degradation under Solar Light in Presence of a TiO2-Polymeric Film Photocatalyst. Processes 2016, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wahab, A.-M.; Al-Shirbini, A.-S.; Mohamed, O.; Nasr, O. Photocatalytic Degradation of Paracetamol over Magnetic Flower-like TiO2 /Fe2O3 Core-Shell Nanostructures. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2017, 347, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
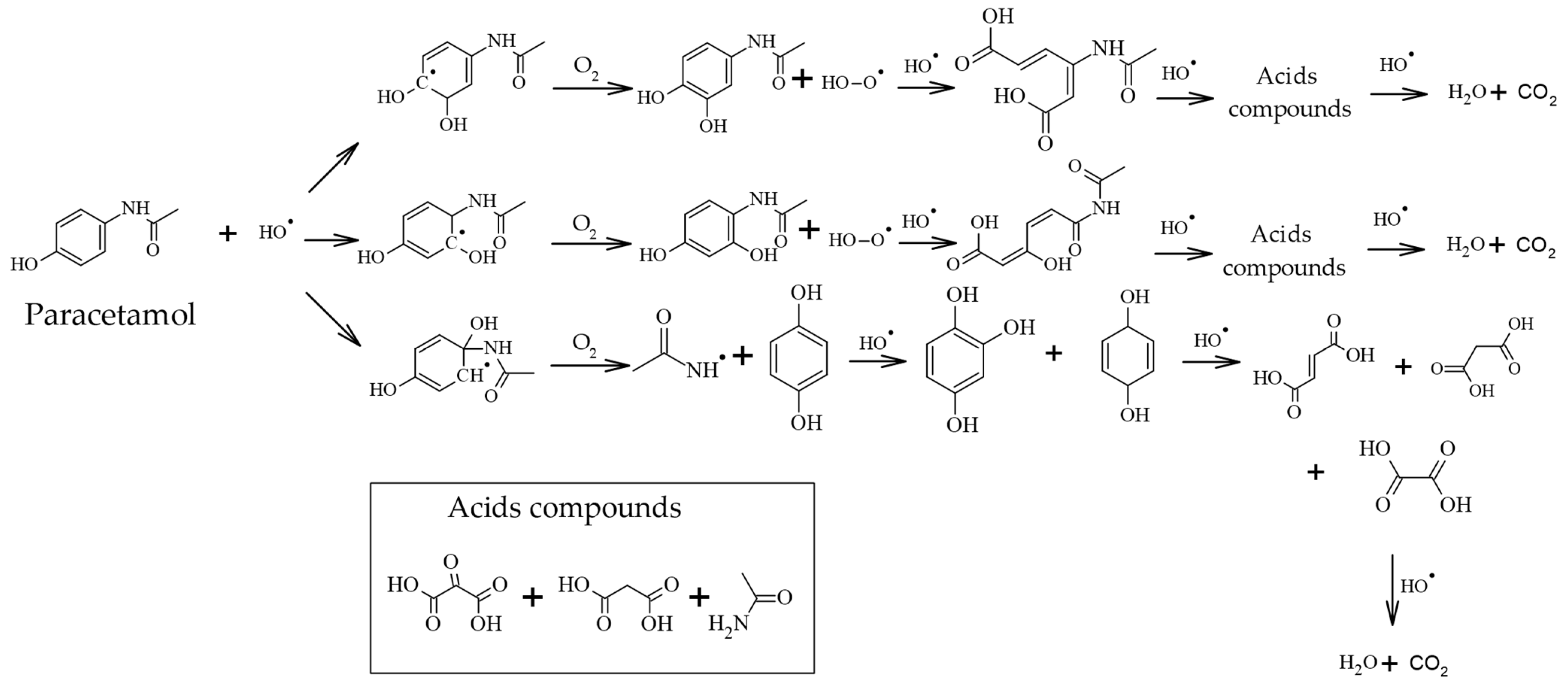
- Moctezuma, E.; Leyva, E.; Aguilar, C.A.; Luna, R.A.; Montalvo, C. Photocatalytic Degradation of Paracetamol: Intermediates and Total Reaction Mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 243, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




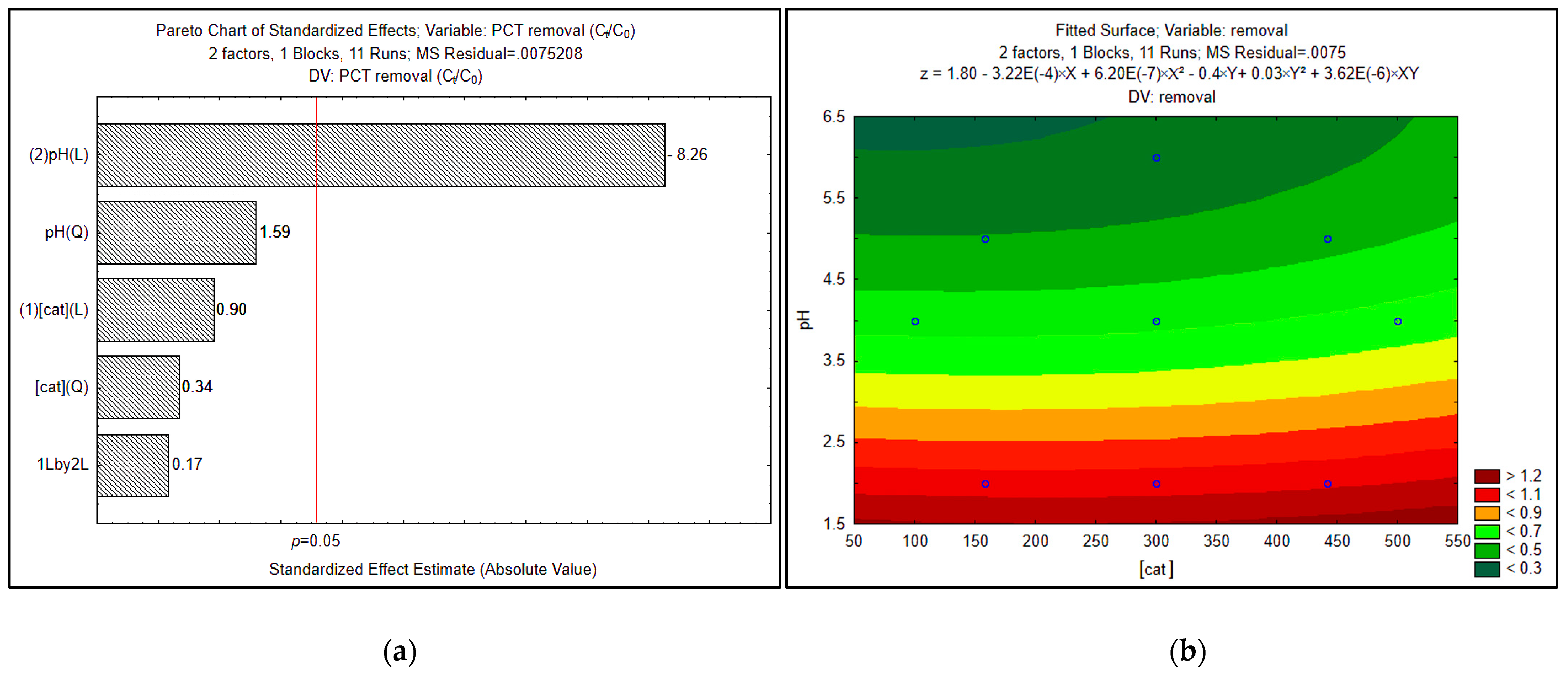

| Run | pH | Catalyst Concentration (mg·L−1) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.00 (−1.41) | 300.00 (0.00) |
| 2 | 2.59 (−1.00) | 441.42 (+1.00) |
| 3 | 2.59 (−1.00) | 158.58 (−1.00) |
| 4 | 4.00 (0.00) | 500.00 (+1.41) |
| 5 | 4.00 (0.00) | 300.00 (0.00) |
| 6 | 4.00 (0.00) | 300.00 (0.00) |
| 7 | 4.00 (0.00) | 300.00 (0.00) |
| 8 | 4.00 (0.00) | 100.00 (−1.41) |
| 9 | 5.41 (+1.00) | 441.42 (+1.00) |
| 10 | 5.41 (+1.00) | 158.58 (−1.00) |
| 11 | 6.00 (+1.41) | 300.00 (0.00) |
| Compound | Calculated Lattice | Standard Lattice |
|---|---|---|
| CoFe2O4 | 8.38 Å | 8.38 Å |
| TT-Nb2O5 | 3.53 Å | 3.61 Å |
| T-Nb2O5 | 25.38 Å | 29.17 Å |
| Acid | Formic Acid | Hydrochloric Acid |
|---|---|---|
| Reaction Time | 4 h | 4 h |
| Run | Paracetamol Removal (%) | Paracetamol Removal (%) |
| 1 | 33 | 100 |
| 2 | 74 | 100 |
| 3 | 100 | 100 |
| 4 | 13 | 100 |
| 5 | 31 | 100 |
| 6 | 18 | 100 |
| 7 | 18 | 100 |
| 8 | 18 | 100 |
| 9 | 14 | 100 |
| 10 | 11 | 98 |
| 11 | 22 | 97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, J.R.P.; Ribas, L.S.; Napoli, J.S.; Abreu, E.; Diaz de Tuesta, J.L.; Gomes, H.T.; Tusset, A.M.; Lenzi, G.G. Green Magnetic Nanoparticles CoFe2O4@Nb5O2 Applied in Paracetamol Removal. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9080200
Oliveira JRP, Ribas LS, Napoli JS, Abreu E, Diaz de Tuesta JL, Gomes HT, Tusset AM, Lenzi GG. Green Magnetic Nanoparticles CoFe2O4@Nb5O2 Applied in Paracetamol Removal. Magnetochemistry. 2023; 9(8):200. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9080200
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Jessica R. P., Laura S. Ribas, Jose S. Napoli, Eduardo Abreu, Jose L. Diaz de Tuesta, Helder T. Gomes, Angelo M. Tusset, and Giane G. Lenzi. 2023. "Green Magnetic Nanoparticles CoFe2O4@Nb5O2 Applied in Paracetamol Removal" Magnetochemistry 9, no. 8: 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9080200
APA StyleOliveira, J. R. P., Ribas, L. S., Napoli, J. S., Abreu, E., Diaz de Tuesta, J. L., Gomes, H. T., Tusset, A. M., & Lenzi, G. G. (2023). Green Magnetic Nanoparticles CoFe2O4@Nb5O2 Applied in Paracetamol Removal. Magnetochemistry, 9(8), 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9080200