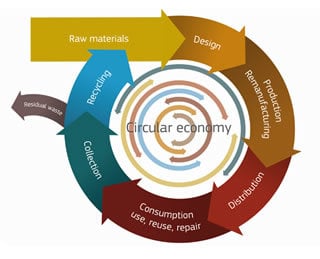
The EU Circular Economy and Its Relevance to Metal Recycling
Abstract
Share and Cite
Hagelüken, C.; Lee-Shin, J.U.; Carpentier, A.; Heron, C. The EU Circular Economy and Its Relevance to Metal Recycling. Recycling 2016, 1, 242-253. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling1020242
Hagelüken C, Lee-Shin JU, Carpentier A, Heron C. The EU Circular Economy and Its Relevance to Metal Recycling. Recycling. 2016; 1(2):242-253. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling1020242
Chicago/Turabian StyleHagelüken, Christian, Ji Un Lee-Shin, Annick Carpentier, and Chris Heron. 2016. "The EU Circular Economy and Its Relevance to Metal Recycling" Recycling 1, no. 2: 242-253. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling1020242
APA StyleHagelüken, C., Lee-Shin, J. U., Carpentier, A., & Heron, C. (2016). The EU Circular Economy and Its Relevance to Metal Recycling. Recycling, 1(2), 242-253. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling1020242