Reclaimed Carbon and Flax Fibre Composites: Manufacturing and Mechanical Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodologies
2.1. Materials
2.2. Specimen Manufacturing Overview
2.3. Tensile Test
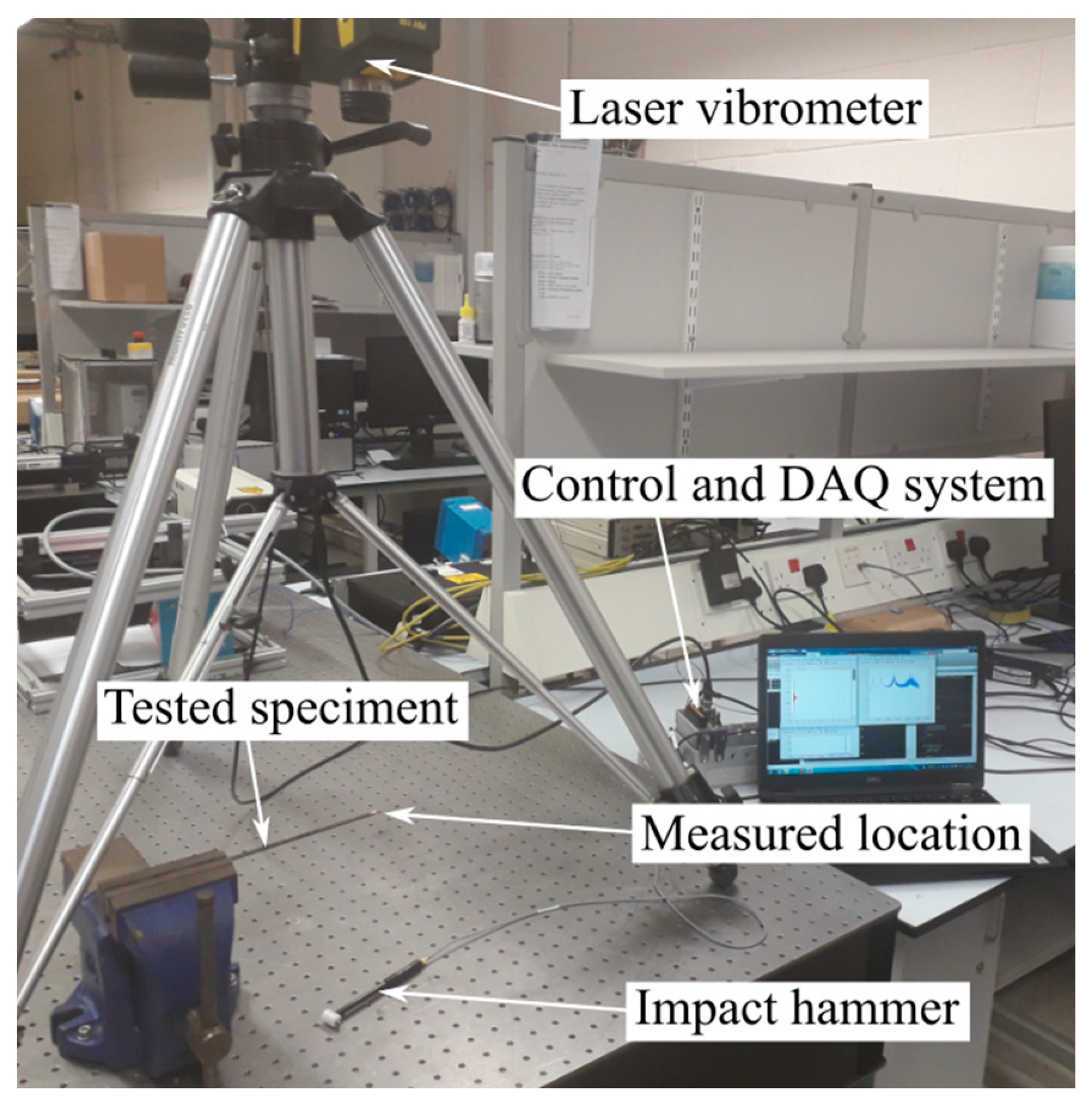
2.4. Vibration Damping Measurement
3. The HiPerDiF Process for Natural Fibre Processing
3.1. Fibre Water Absorption and Drying
3.2. Flax Fibres Processing Trials Tensile Test
4. Intermingled Flax/rCF Hybrid Composites Behaviour
4.1. Tensile Test Results
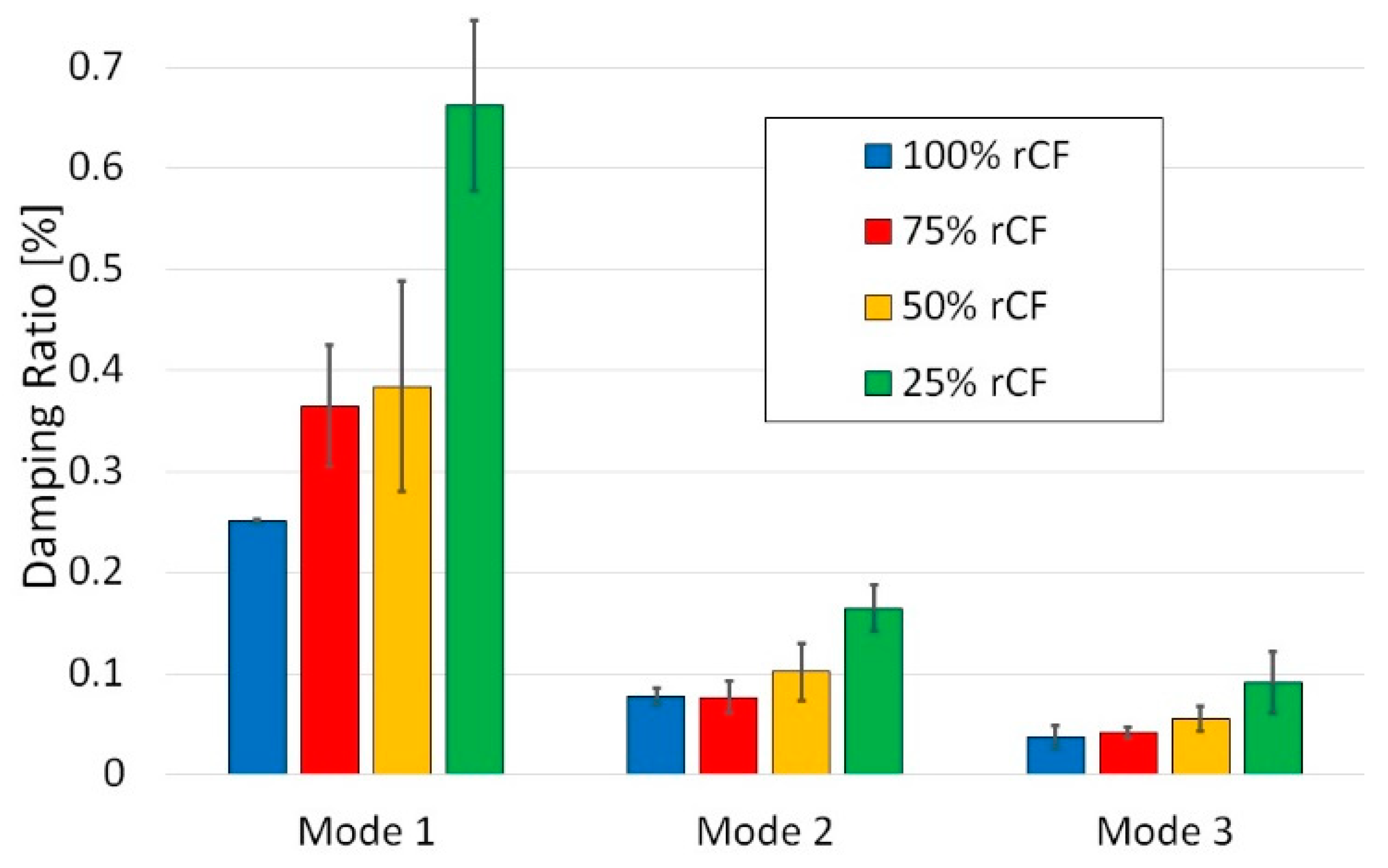
4.2. Vibration Damping Test Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Commission Directive (EU). 2017/2096 of 15 November 2017 Amending Annex II to Directive 2000/53/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council on End-of Life Vehicles (Text with EEA Relevance); EU: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Longana, M.L.; Aryal, P.; Yu, H.; Potter, K.D. The High Performance Discontinuous Fibre (HiPerDiF) Method for Carbon-Flax Hybrid Composites Manufacturing. In Proceedings of the ICCM21 21st International Conference on Composite Materials, Xi’an, China, 20–25 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sanjay, M.R.; Madhu, P.; Jawaid, M.; Senthamaraikannan, P.; Senthil, S.; Pradeep, S. Characterization and properties of natural fiber polymer composites: A comprehensive review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 566–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.B.; Chouw, N.; Jayaraman, K. Flax fibre and its composites—A review. Compos. Part B. Eng. 2014, 56, 296–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pil, L.; Bensadoun, F.; Pariset, J.; Verpoest, I. Why are designers fascinated by flax and hemp fibre composites? Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 83, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wambua, P.; Ivens, J.; Verpoest, I. Natural fibres: Can they replace glass in fibre reinforced plastics? Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhu, H.; Njuguna, J.; Abhyankar, H. Recent development of flax fibres and their reinforced composites based on different polymeric matrices. Materials 2013, 6, 5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oksman, K. Mechanical properties of natural fibre mat reinforced thermoplastic. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2000, 7, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassan, J.; Bledzki, A.K. Possibilities to improve the properties of natural fiber reinforced plastics by fiber modification—Jute polypropylene composites. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2000, 7, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilholt, H.; Lawther, J.M. Natural organic fibers. In Comprehensive Composite Materials Encyclopaedia; Chou, T.-W., Ed.; Elsevier Science: Oxford, UK, 2000; Volume 1, Chapter 10; pp. 303–325. ISBN 0-08-043719-2. [Google Scholar]
- Di Landro, L.; Lorenzi, W. Mechanical properties and dynamic mechanical analysis of thermoplastic-natural fiber/glass reinforced composites. Macromol. Symp. 2009, 286, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Landro, L.; Lorenzi, W. Static and dynamic properties of thermoplastic matrix/natural fiber composites. J. Biobased. Mater. Bioenergy 2009, 3, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buksnowitz, C.; Adusumalli, R.; Pahler, A.; Sixta, H.; Gindl, W. Acoustical properties of Lyocell, hemp, and flax composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Comp. 2010, 29, 3149–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genc, G.; El Hafidi, A.; Gning, P.B. Comparison of the mechanical properties of flax and glass fiber composite materials. J. Vibroeng. 2012, 14, 572–581. [Google Scholar]
- Duc, F.; Bourban, P.E.; Plummer, C.J.G.; Manson, J.A.E. Damping of thermoset and thermoplastic flax fibre composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 64, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, F.; Bourban, P.E.; Manson, J.A.E. The role of twist and crimp on the vibration behaviour of flax fibre composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 102, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guen, M.-J.; Newman, R.H.; Fernyhough, A.; Staiger, M.P. Tailoring the vibration damping behaviour of flax fibre-reinforced epoxy composite laminates via polyol additions. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 67, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, S.; Krishnaraj, V.; Kumar, M.S.; Zitoune, R. Sound and vibration damping properties of flax fiber reinforced composites. Procedia Eng. 2014, 97, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, H.; Rebiere, J.L.; Makni, A.; Taktak, M.; El Mahi, A.; Haddar, M. Numerical and experimental characterization of the dynamic properties of flax fiber reinforced composites. Int. J. Appl. Mech. 2016, 8, 1650068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, H.; El Mahi, A.; Rebiere, J.L.; Taktak, M.; Haddar, M. Characterization of the vibrational behaviour of flax fibre reinforced composites with an interleaved natural viscoelastic layer. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 128, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.Z.; Jayaraman, K.; Mace, B.R. Vibration damping of flax fibre-reinforced polypropylene composites. Fiber Polym. 2017, 18, 2187–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.Z.; Jayaraman, K.; Mace, B.R. Influence of damping on the bending and twisting modes of flax fibre-reinforced polypropylene composite. Fiber Polym. 2018, 19, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hafidi, A.; Gning, P.B.; Piezel, B.; Belaid, M.; Fontaine, S. Determination of dynamic properties of flax fibres reinforced laminate using vibration measurements. Polym. Test. 2017, 57, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveux, G.; Dandy, L.O.; Leeke, G.A. Current status of recycling of fibre reinforced polymers: Review of technologies, reuse and resulting properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 72, 61–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.O.; Schulte, K.; Grove-Nielsen, E. CFRP-recycling following a pyrolysis route: Process optimization and potentials. J. Compos. Mater. 2009, 43, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, S.J.; Kelly, R.M.; Kennerley, J.R.; Rudd, C.D.; Fenwick, N.J. A fluidised-bed process for the recovery of glass fibres from scrap thermoset composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2000, 60, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, E.; Kingman, S.; Wong, K.H.; Rudd, C.; Pickering, S.; Hilal, N. Microwave heating as a means for carbon fibre recovery from polymer composites: A technical feasibility study. Mater. Res. Bull. 2004, 39, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveux, G.; Dandy, L.O.; Leeke, G.A. Degradation of a model epoxy resin by solvolysis routes. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2015, 118, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinero-Hernanz, R.; Dodds, C.; Hyde, J.; Garcia-Serna, J.; Poliakoff, M.; Lester, E.; Cocero, M.J.; Kingman, S.; Pickering, S.; Wong, K.H. Chemical recycling of carbon fibre reinforced composites in nearcritical and supercritical water. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, S.; Pinho, S.T. Recycling carbon fibre reinforced polymers for structural applications: Technology review and market outlook. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 378–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wood, K. Carbon Fiber Reclamation: Going Commercial. Available online: https://www.compositesworld.com/articles/carbon-fiber-reclamation-going-commercial (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- Pickering, S.J. Carbon fibre recycling technologies: What goes in and what comes out? In Proceedings of the Carbon Fibre Recycling and Reuse, Hamburg, Germany, 3–4 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.H.; Turner, T.A.; Pickering, S.J.; Warrior, N.A. The potential for fibre alignment in the manufacture of polymer composites from recycled carbon fibre. In Proceedings of the SAE AeroTech Congress and Exhibition, Seattle, WA, USA, 22–24 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Potter, K.D. Method and Apparatus for Aligning Discontinuous Fibres. UK Patent 1,306,762, 15 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Potter, K.D.; Wisnom, M.R. A novel manufacturing method for aligned discontinuous fibre composites (High Performance-Discontinuous Fibre method). Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 65, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longana, M.L.; Ong, N.; Yu, H.N.; Potter, K.D. Multiple closed loop recycling of carbon fibre composites with the HiPerDiF (High Performance Discontinuous Fibre) method. Compos. Struct. 2016, 153, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longana, M.L.; Yu, H.N.; Jalavand, M.; Wisnom, M.R.; Potter, K.D. Aligned discontinuous intermingled reclaimed/virgin carbon fibre composites for high performance and pseudo-ductile behaviour in interlaminated carbon-glass hybrids. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 143, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longana, M.L.; Yu, H.; Hamerton, I.; Potter, K.D. Development and application of a quality control and property assurance methodology for reclaimed carbon fibers based on the HiPerDiF (High Performance Discontinuous Fibre) method and interlaminated hybrid specimens. Adv. Manuf. Polym. Comp. 2018, 4, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bachmann, J.; Wiedemann, M.; Wierach, P. Flexural mechanical properties of hybrid epoxy composites reinforced with nonwoven made of flax fibres and recycled carbon fibres. Aerospace 2018, 5, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, B.; Yu, X.; Gong, H.; Soutis, C. Flecural properties of wet-laid hybrid nonwoven recycled carbon and flax fibre composites in poly-lactic acid matrix. Aerospace 2018, 5, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assarar, M.; Zouari, W.; Sabhi, H.; Ayad, R.; Berthelot, J.M. Evaluation of the damping of hybrid carbon-flax reinforced composites. Compos. Struct. 2015, 132, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, J.; Amiri, A.; Ulven, C. Hybridized carbon and flax fiber composites for tailored performance. Mater. Des. 2016, 102, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guen, M.J.; Newman, R.H.; Fernyhough, A.; Emms, G.W.; Staiger, M.P. The damping–modulus relationship in flax–carbon fibre hybrid composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 89, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueppel, M.; Rion, J.; Dransfeld, C.; Fischer, C.; Masania, K. Damping of carbon fibre and flax fibre angle-ply composite laminates. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 146, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, K.; Lessard, L. Dynamic properties of hybrid composite hollow cylinders: Application for mountain bicycle handlebars. Des. Manuf. Appl. Compos. 2015, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Amiri, A.; Krosbakken, T.; Schoen, W.; Theisen, D.; Ulven, C.A. Design and manufacturing of a hybrid flax/carbon fiber composite bicycle frame. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part P J. Sports Eng. Technol. 2018, 232, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbon-Flax Hybrid Structures for Automotive Applications. Available online: https://carbioproject.com/ (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- Yu, H.; Longana, M.L.; Jalalvand, M.; Wisnom, M.R.; Potter, K.D. Hierarchical pseudo-ductile hybrid composites combining continuous and highly aligned discontinuous fibres. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 105, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.N.; Longana, M.L.; Jalalvand, M.; Wisnom, M.R.; Potter, K.D. Pseudo-ductility in intermingled carbon/glass hybrid composites with highly aligned discontinuous fibres. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 73, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finley, J.M.; Yu, H.; Longana, M.L.; Pimenta, S.; Shaffer, M.S.P.; Potter, K.D. Exploring the pseudo-ductility of aligned hybrid discontinuous composites using controlled fibre-type arrangements. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 107, 592–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewins, D.J. Modal Testing: Theory, Practice and Application; Research Studies Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]









| Fibre Property | rCF | Flax | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length | (mm) | 3 | 3 |
| Density | (g/cm3) | 1.8 | 1.4 |
| Stiffness | (GPa) | 205 (±11%) | N.A. |
| Strength | (MPa) | 4080 (±20%) | N.A. |
| Failure Strain | (%) | 2.00 (±19%) | N.A. |
| Cost | (€/kg) | 10 | 0.7 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Longana, M.L.; Ondra, V.; Yu, H.; Potter, K.D.; Hamerton, I. Reclaimed Carbon and Flax Fibre Composites: Manufacturing and Mechanical Properties. Recycling 2018, 3, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling3040052
Longana ML, Ondra V, Yu H, Potter KD, Hamerton I. Reclaimed Carbon and Flax Fibre Composites: Manufacturing and Mechanical Properties. Recycling. 2018; 3(4):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling3040052
Chicago/Turabian StyleLongana, Marco L., Vaclav Ondra, HaNa Yu, Kevin D. Potter, and Ian Hamerton. 2018. "Reclaimed Carbon and Flax Fibre Composites: Manufacturing and Mechanical Properties" Recycling 3, no. 4: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling3040052
APA StyleLongana, M. L., Ondra, V., Yu, H., Potter, K. D., & Hamerton, I. (2018). Reclaimed Carbon and Flax Fibre Composites: Manufacturing and Mechanical Properties. Recycling, 3(4), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling3040052






