Balanced Standing on One Foot of Biped Robot Based on Three-Particle Model Predictive Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Motivation
1.3. Related Work
1.4. Contribution
- (1)
- The proposed TP-MPC method can generate feasible swing leg trajectories that balance the robot while standing on one foot. The WBC tracks the generated swing leg trajectories. As a result, the overall control scheme can resist large external disturbances.
- (2)
- The TP-MPC catches the main effects of the swing leg motion while being simple enough to operate at the same frequency as the WBC.
2. Three-Particle Model Predictive Control
2.1. Three-Particle Simplified Model
2.2. Tasks
2.3. Constraints
2.4. MPC Optimization Problem
2.4.1. Tasks
2.4.2. Constraints
2.4.3. The Quadratic Programming Problem
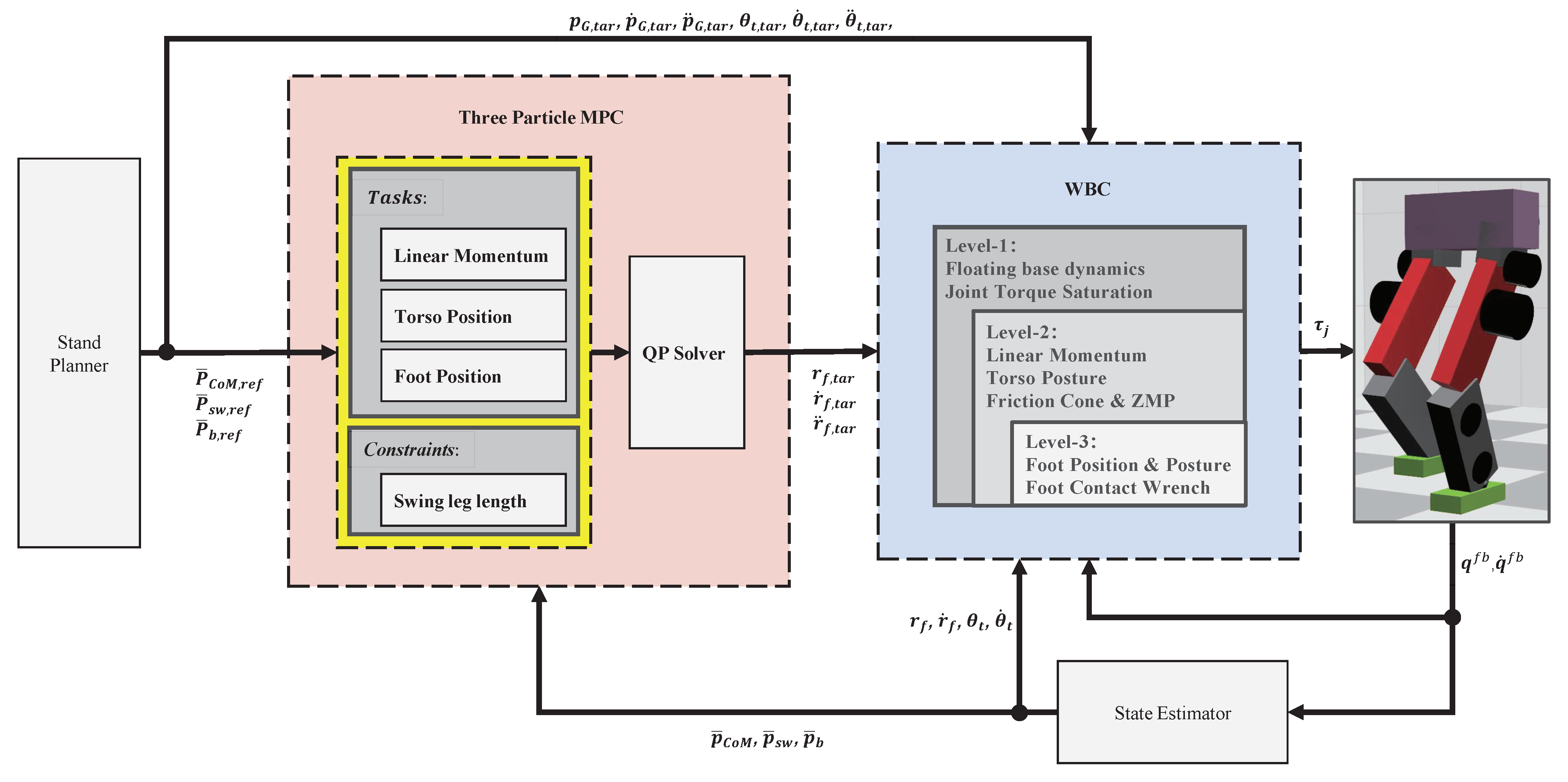
3. Hierarchical Whole-Body Control
3.1. Problem Formulation
3.2. Tasks
3.2.1. Floating Base Dynamics Task
3.2.2. Centroidal Dynamics Task
3.2.3. Torso Orientation Task
3.2.4. Feet Position and Orientation Task
3.2.5. Contact Wrench Task
3.3. Constraints
3.3.1. Joint Torque Constraint
3.3.2. ZMP Constraint
3.3.3. Foot Friction Cone Constraint
3.4. Control Framework
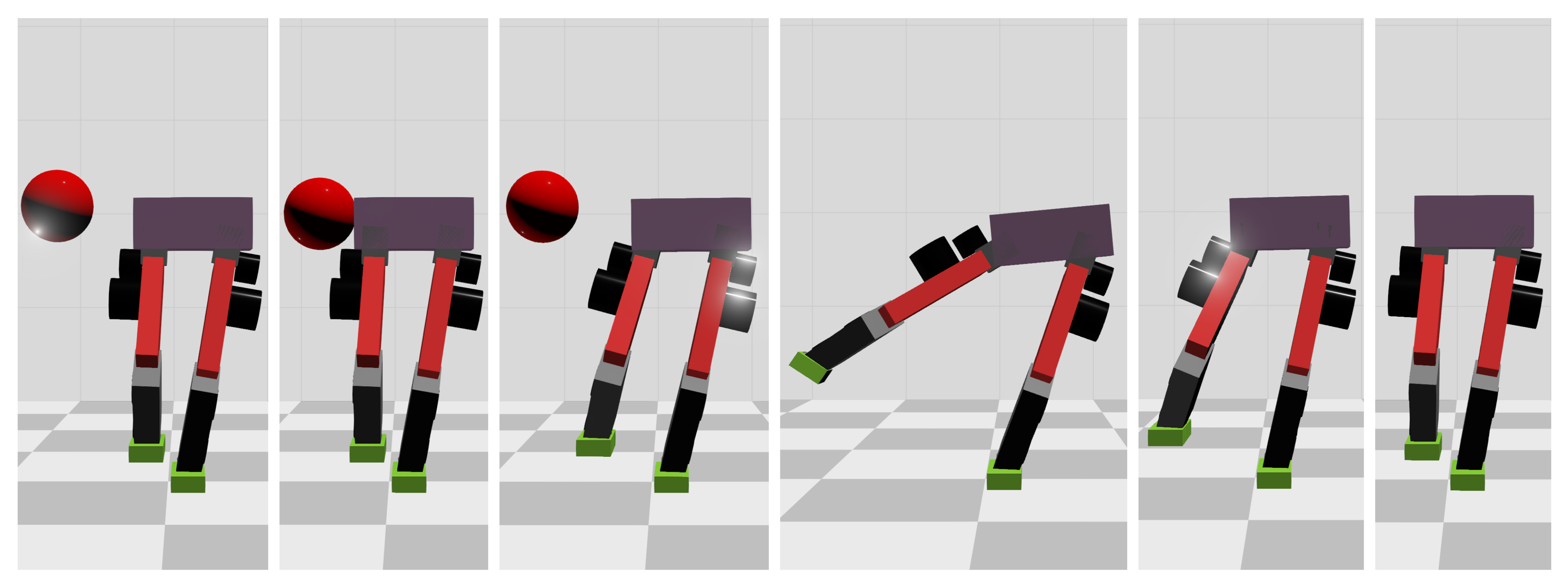
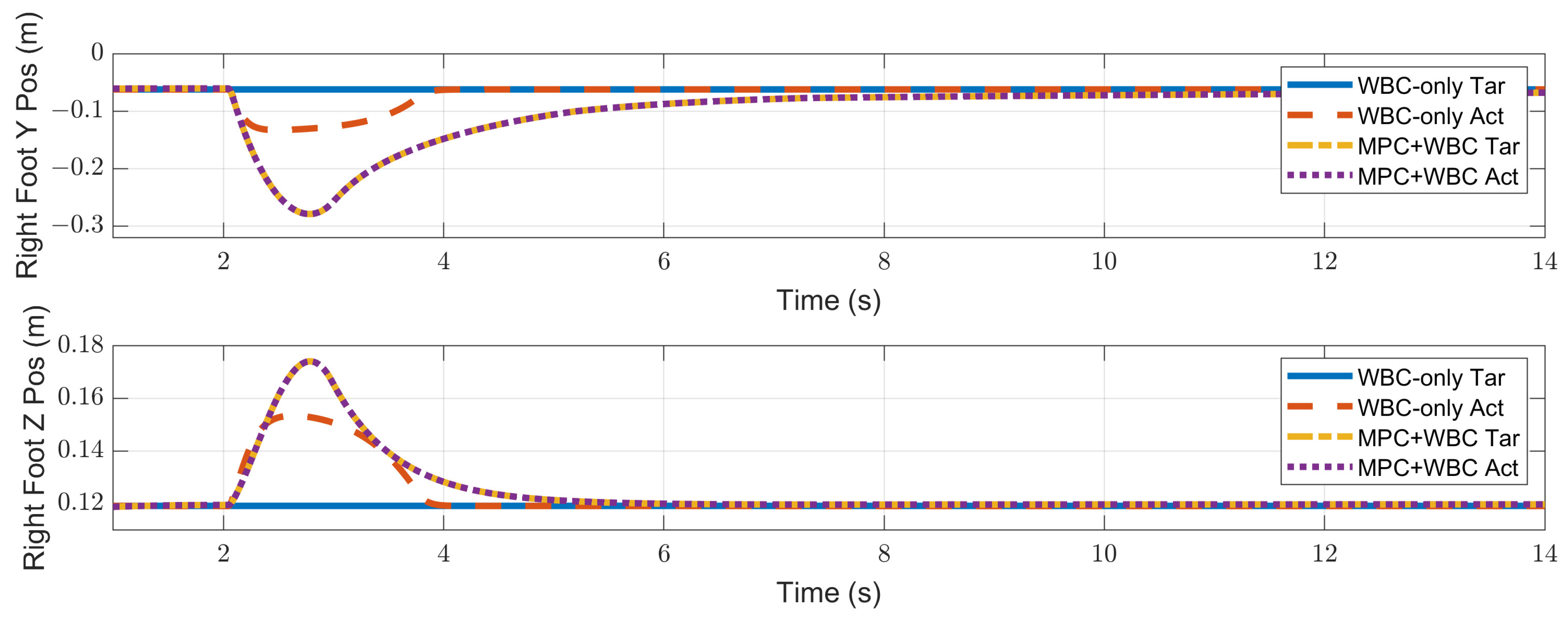
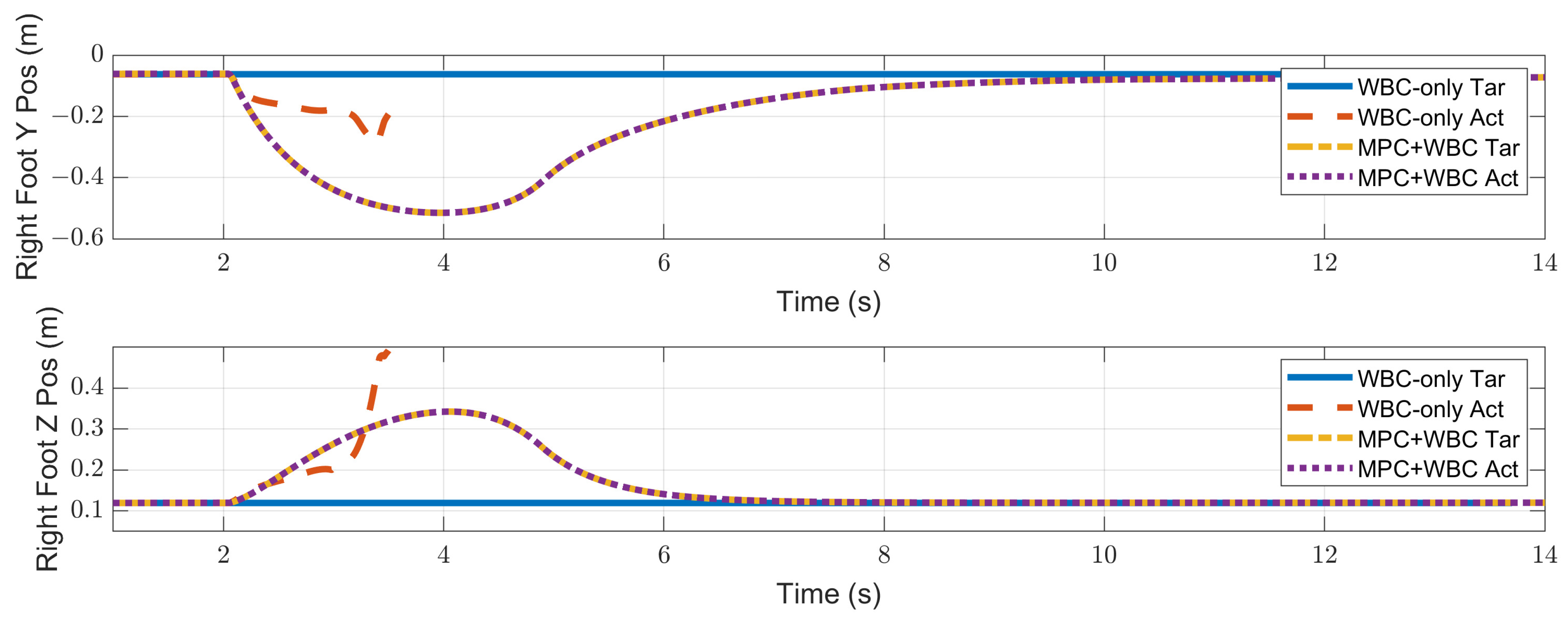
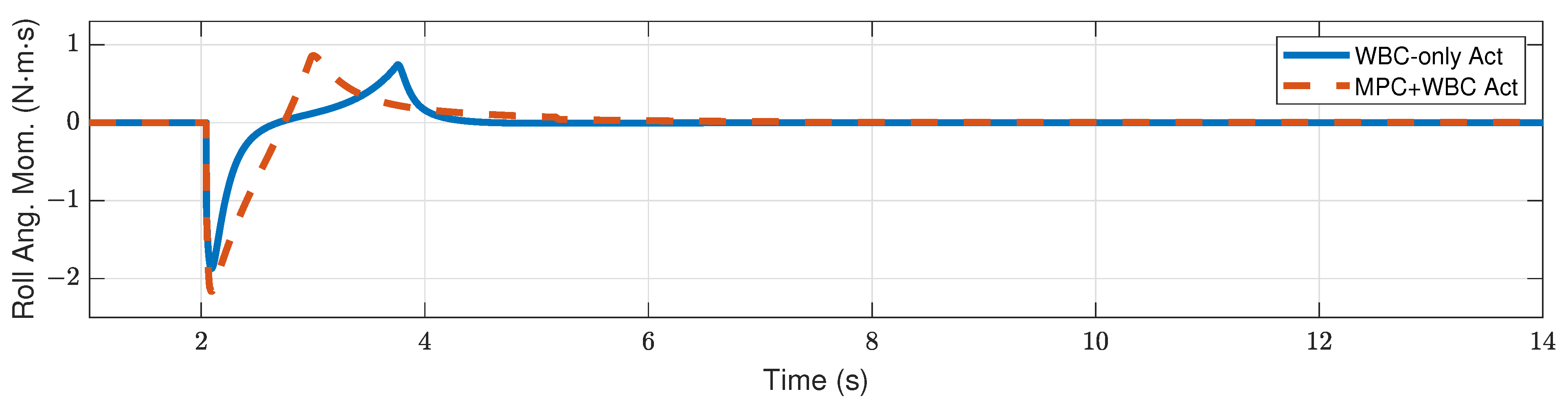
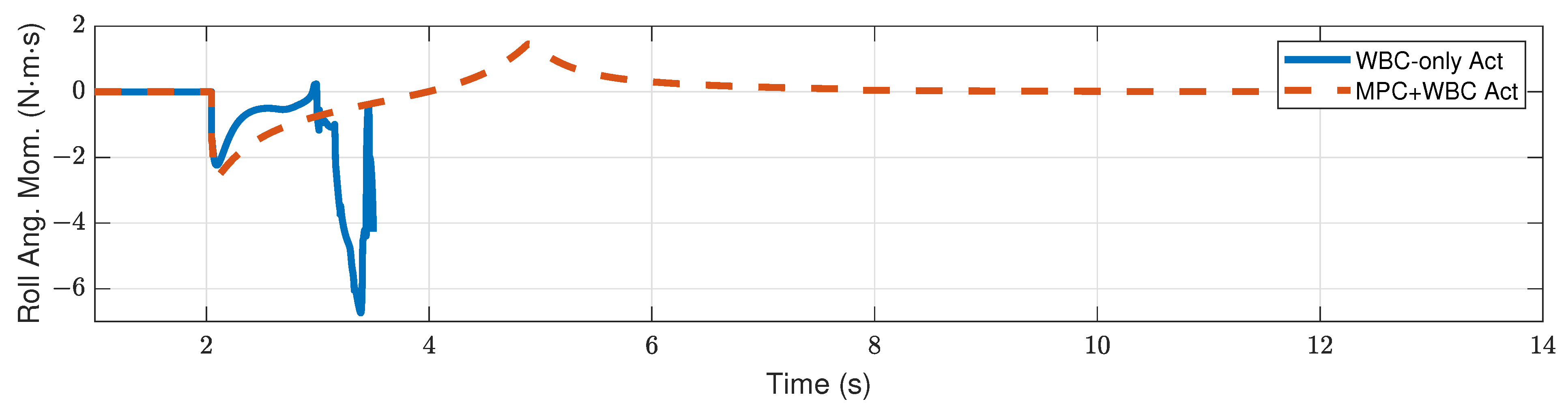
4. Simulation Results and Discussion
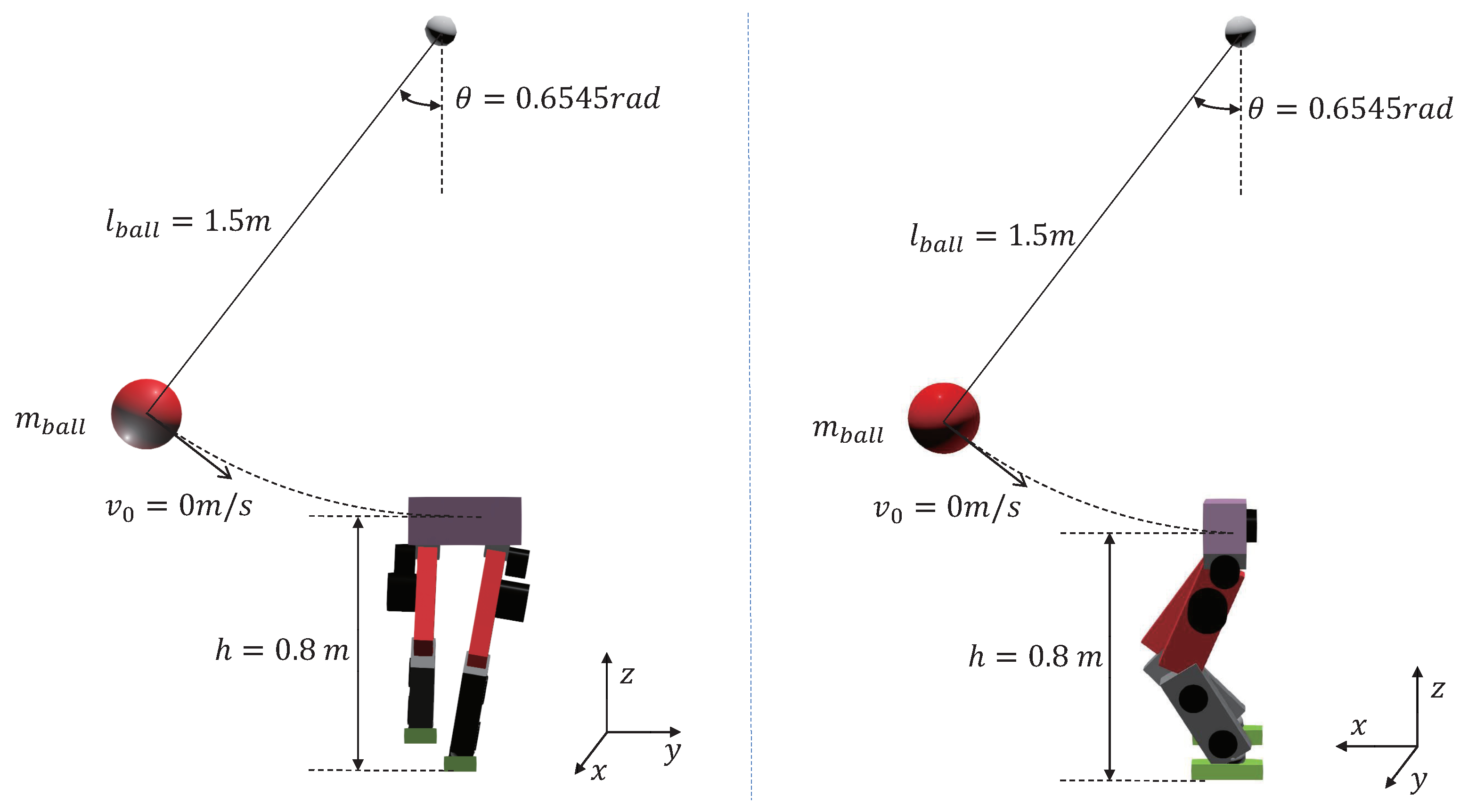
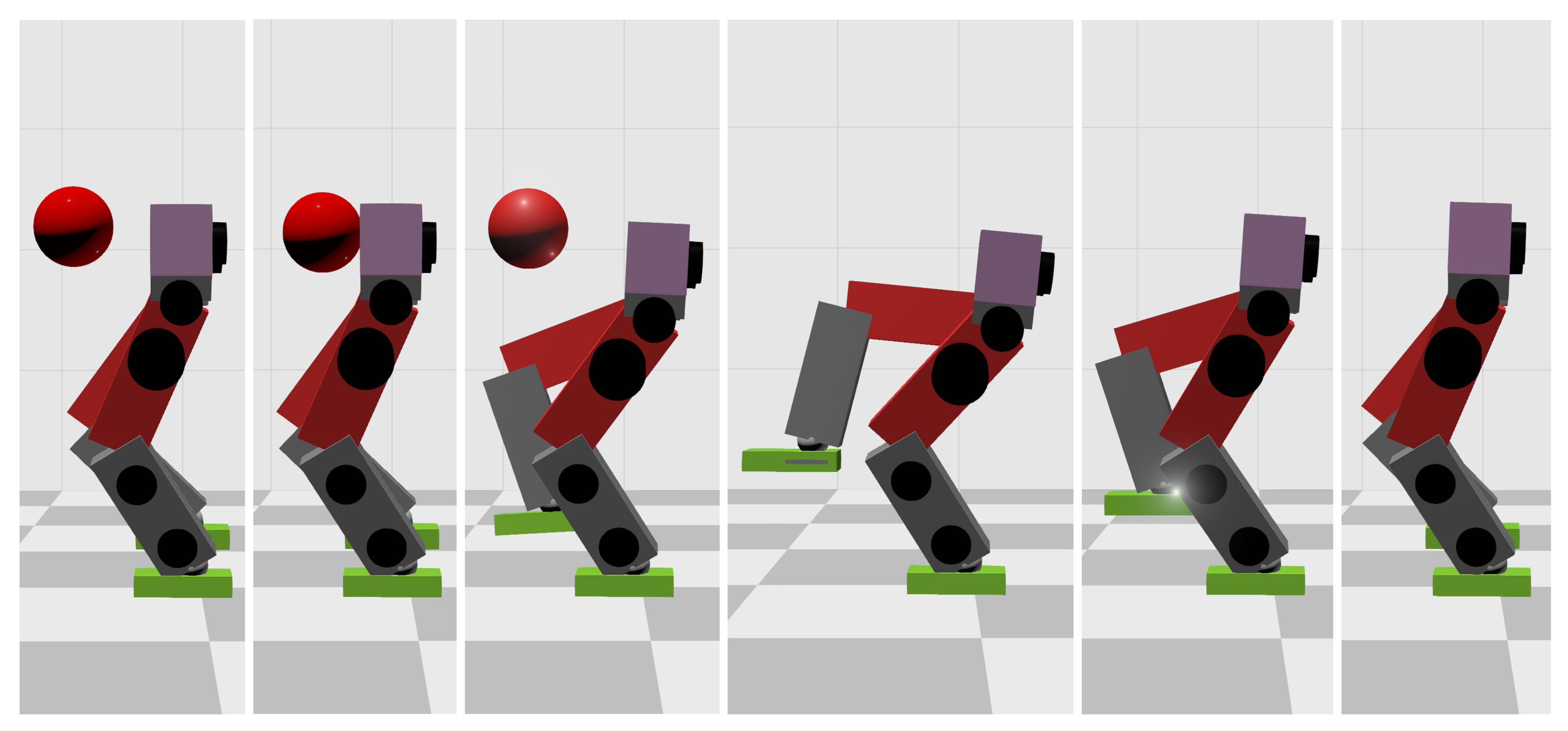
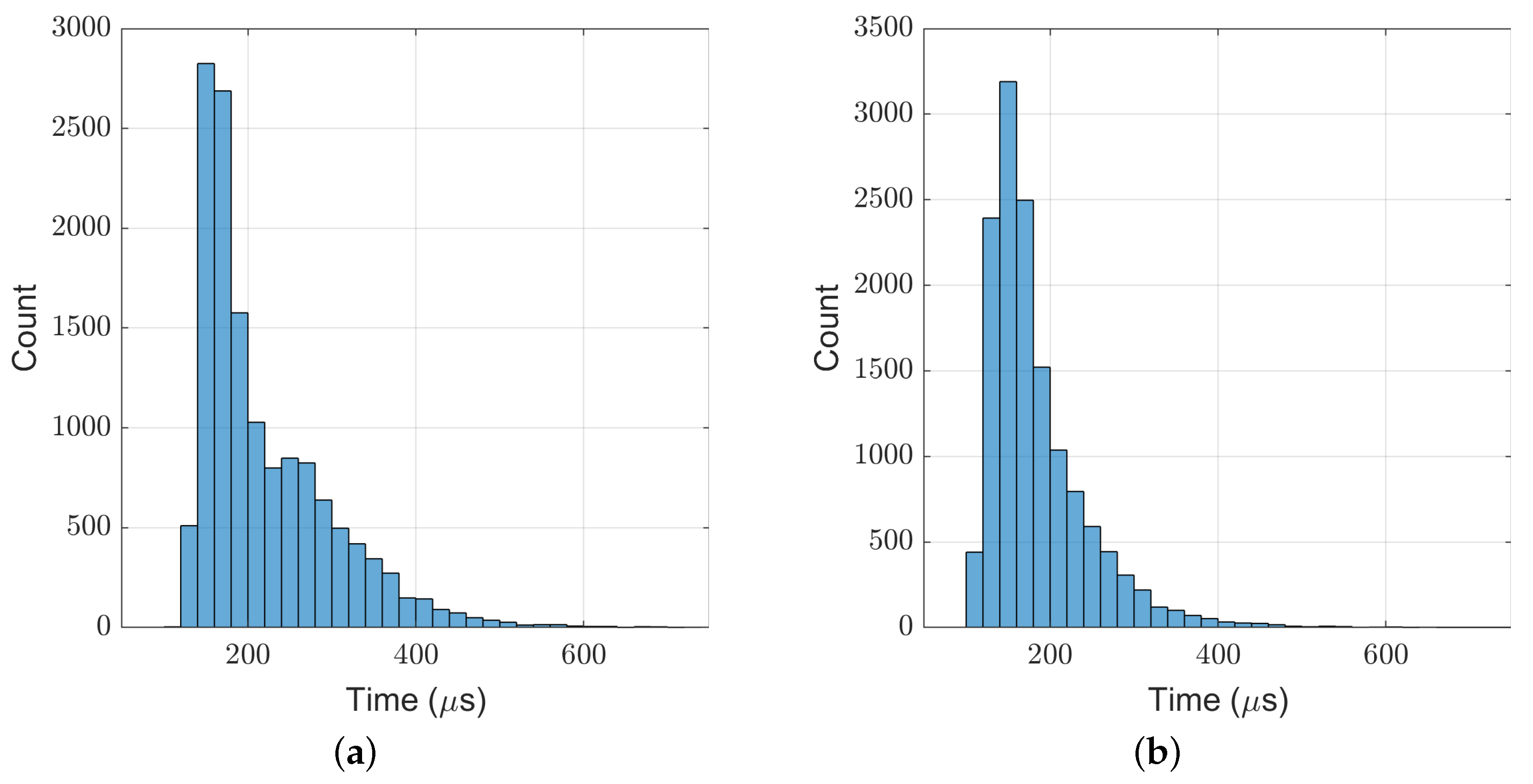
4.1. Simulation Setup
4.2. Results
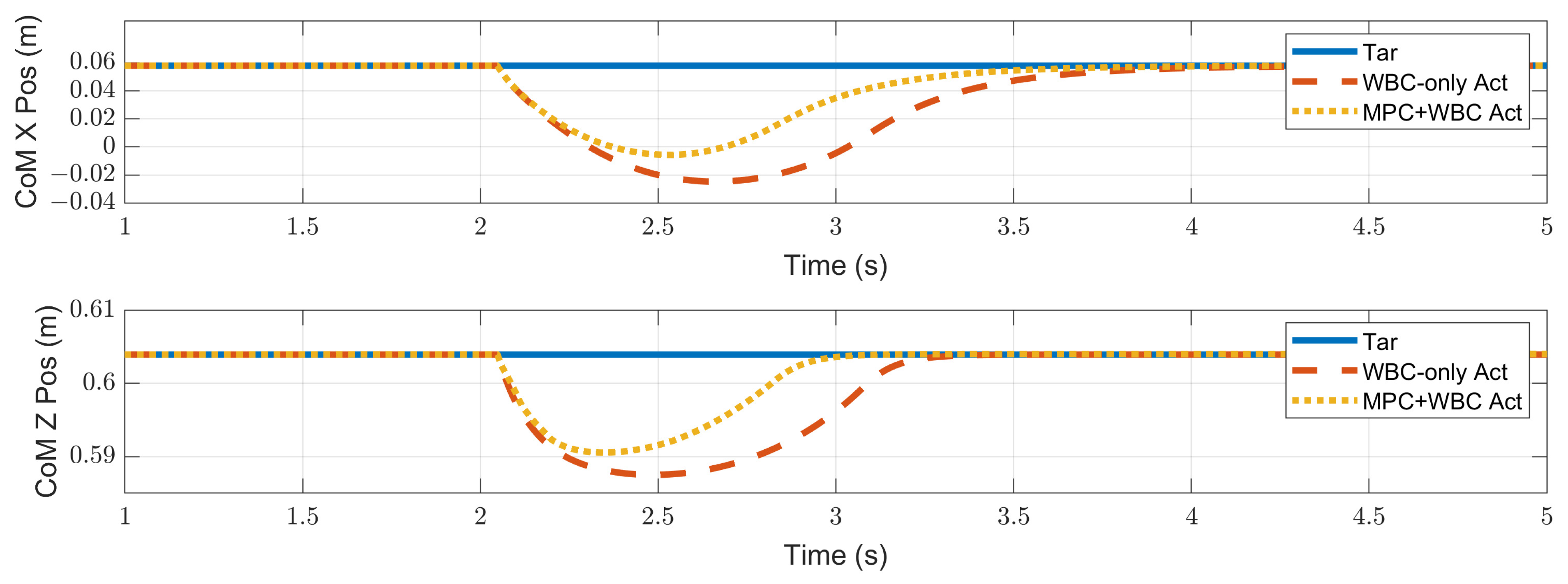
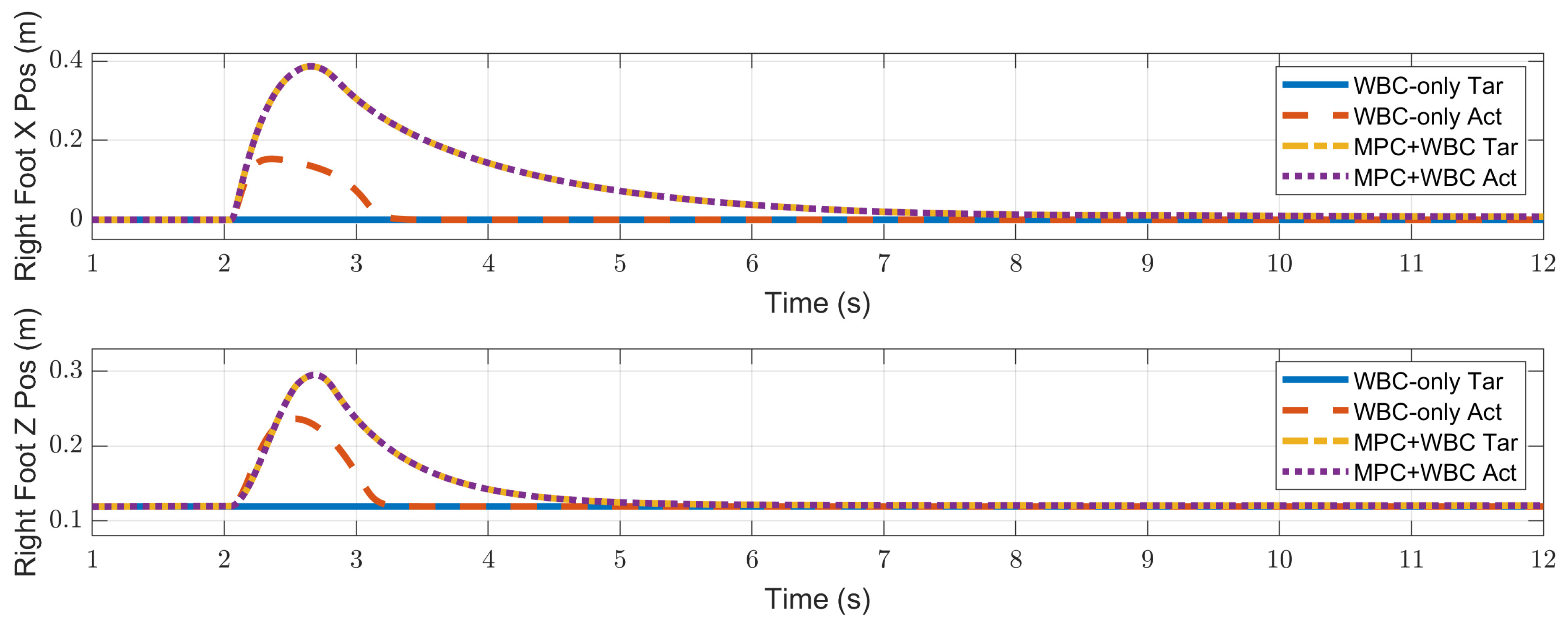
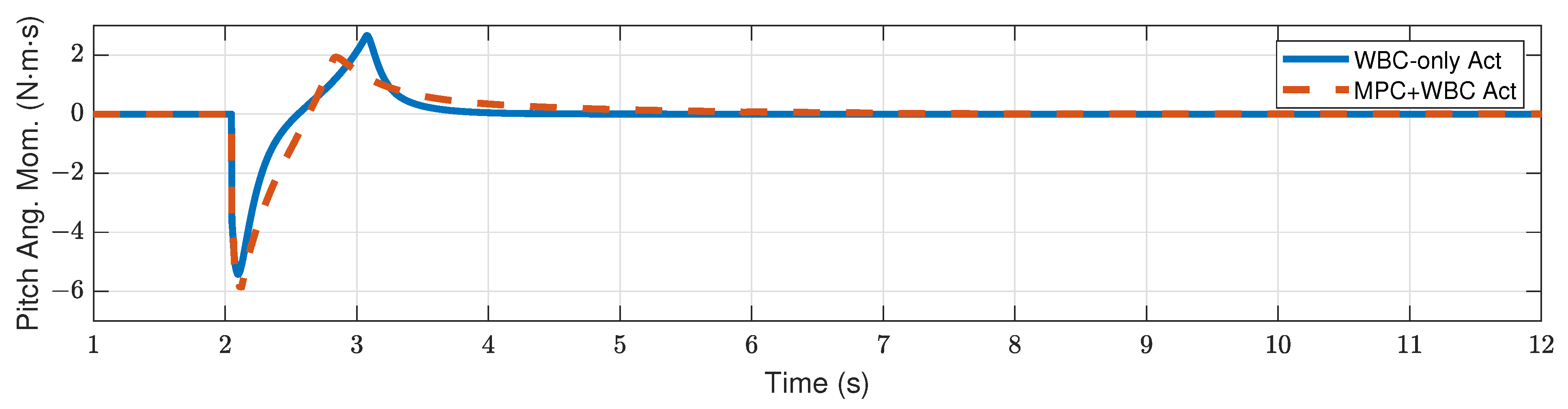
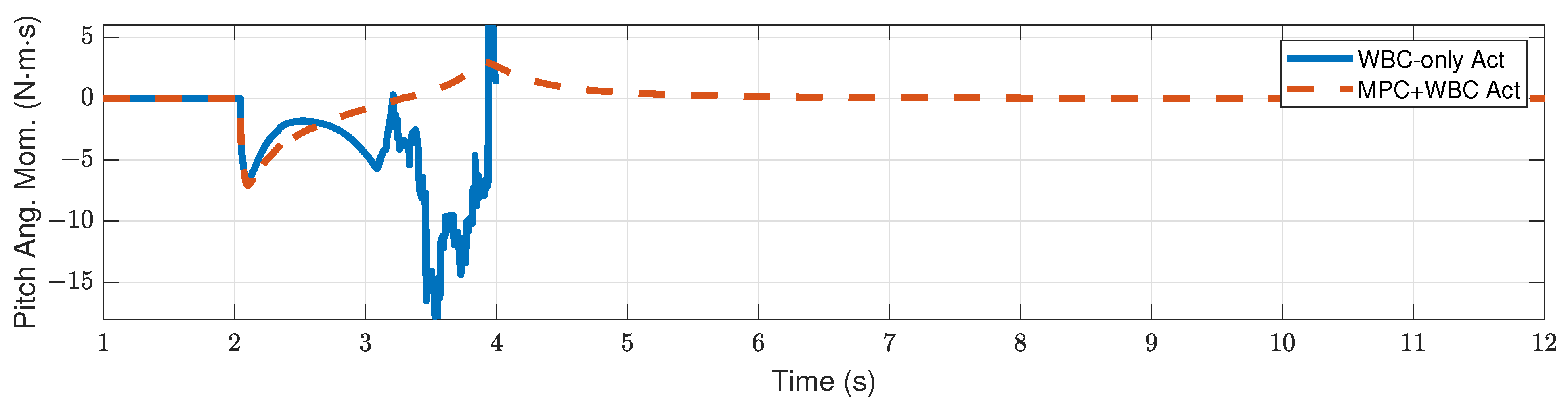
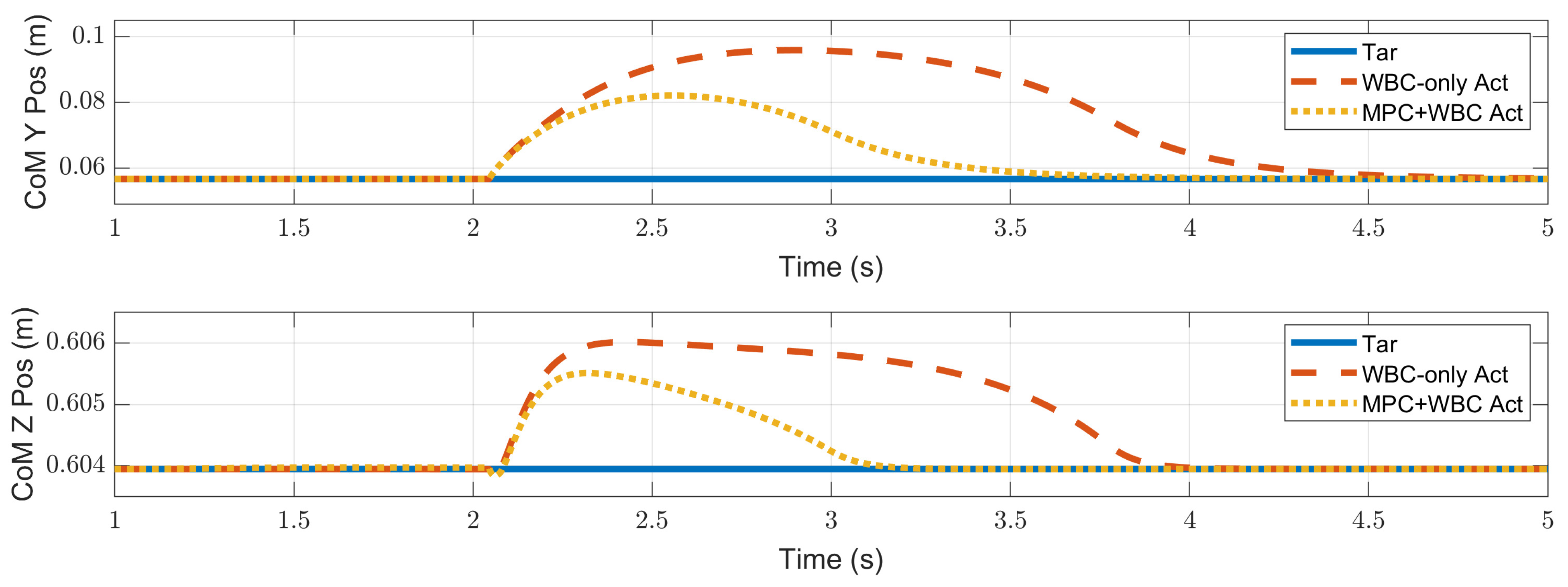
4.2.1. Frontal Impact
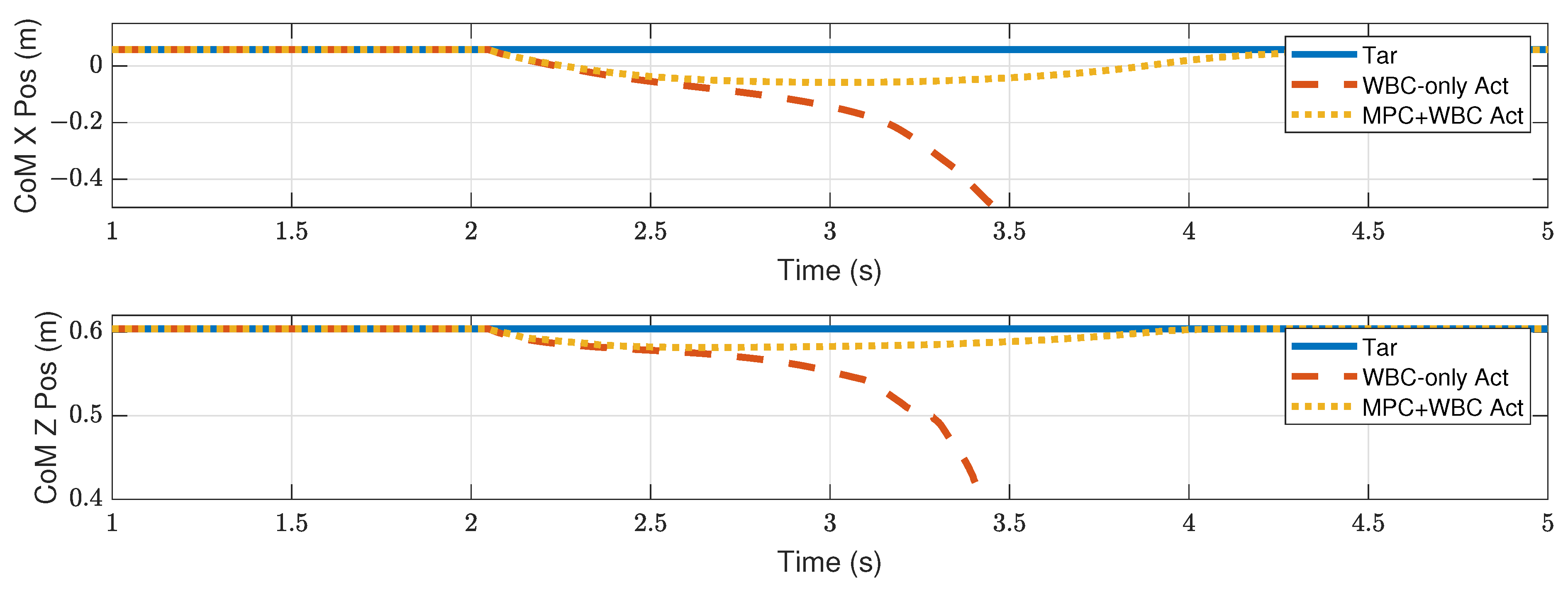
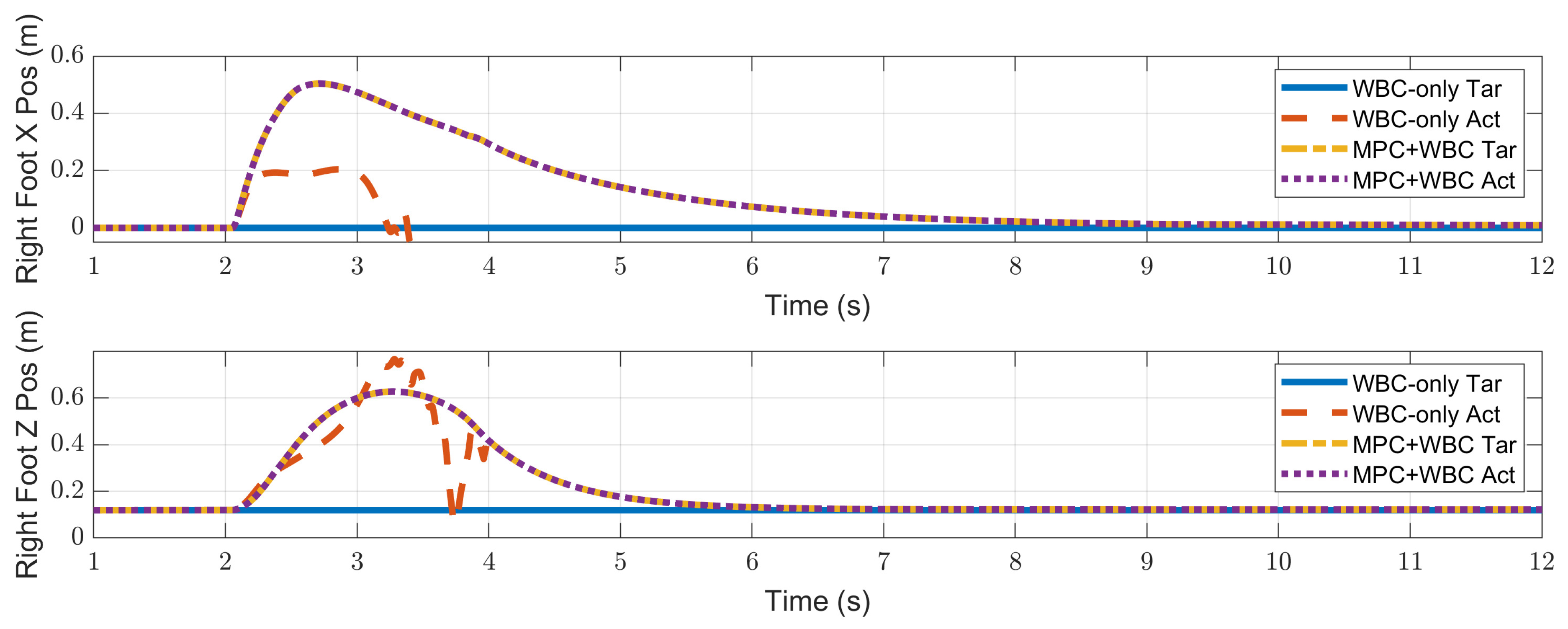
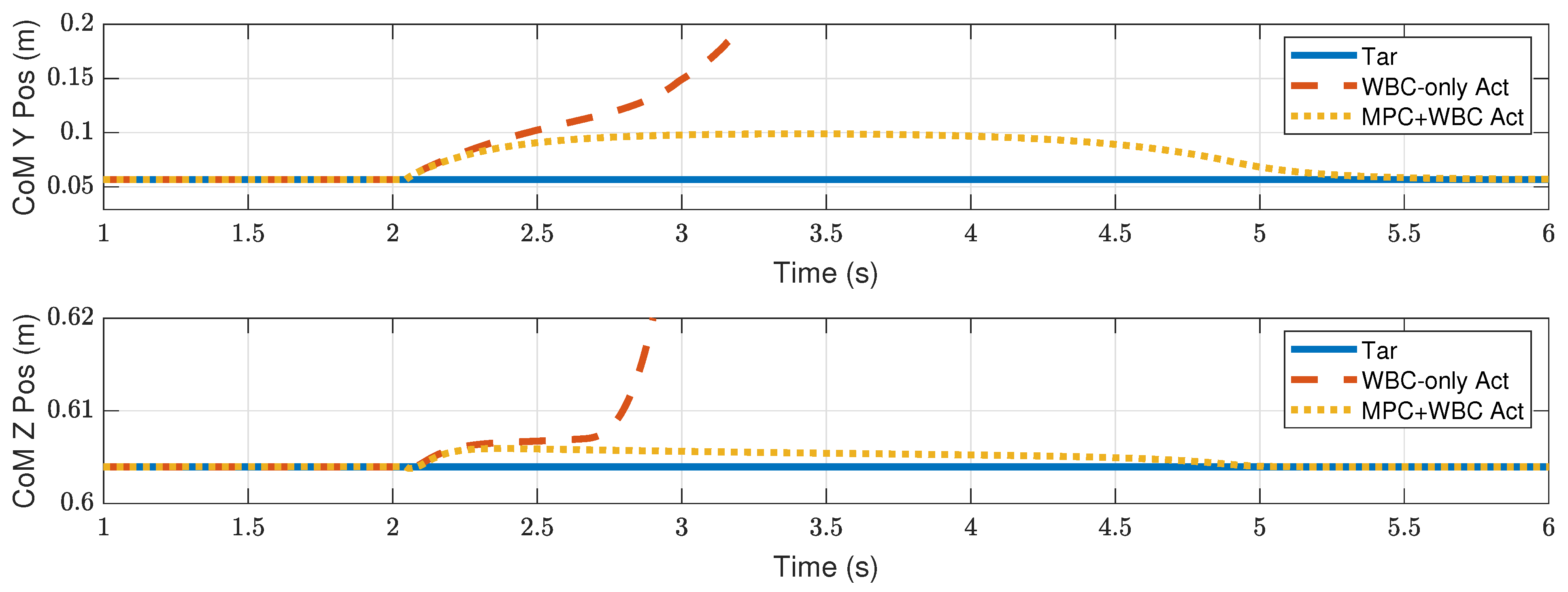
4.2.2. Side Impact
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, R.C.; Huang, C.W.; Hung, W.C. Bipedal robot push recovery control mimicking human reaction. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 14th International Workshop on Advanced Motion Control (AMC), Auckland, New Zealand, 22–24 April 2016; pp. 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficht, G.; Behnke, S. Direct Centroidal Control for Balanced Humanoid Locomotion. In Proceedings of the 25th Climbing and Walking Robots Conference, Ponta Delgada, Portugal, 12–14 September 2022; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 242–255. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, F.; Zhu, W.; Hayashibe, M. Balance stability augmentation for wheel-legged biped robot through arm acceleration control. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 54022–54031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentis, L.; Khatib, O. A whole-body control framework for humanoids operating in human environments. In Proceedings of the Proceedings 2006 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2006. ICRA 2006, Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 May 2006; pp. 2641–2648. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, X.; Wang, J.; Han, G.; Zhao, M. Mixed Control for Whole-Body Compliance of a Humanoid Robot. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 8331–8337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Di Carlo, J.; Katz, B.; Bledt, G.; Kim, S. Highly dynamic quadruped locomotion via whole-body impulse control and model predictive control. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.06586. [Google Scholar]
- Koenemann, J.; Del Prete, A.; Tassa, Y.; Todorov, E.; Stasse, O.; Bennewitz, M.; Mansard, N. Whole-body model-predictive control applied to the HRP-2 humanoid. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 3346–3351. [Google Scholar]
- Erez, T.; Lowrey, K.; Tassa, Y.; Kumar, V.; Kolev, S.; Todorov, E. An integrated system for real-time model predictive control of humanoid robots. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 13th IEEE-RAS International conference on humanoid robots (Humanoids), Atlanta, GA, USA, 15–17 October 2013; pp. 292–299. [Google Scholar]
- Farshidian, F.; Jelavic, E.; Satapathy, A.; Giftthaler, M.; Buchli, J. Real-time motion planning of legged robots: A model predictive control approach. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE-RAS 17th International Conference on Humanoid Robotics (Humanoids), Birmingham, UK, 15–17 November 2017; pp. 577–584. [Google Scholar]
- Neunert, M.; Stäuble, M.; Giftthaler, M.; Bellicoso, C.D.; Carius, J.; Gehring, C.; Hutter, M.; Buchli, J. Whole-body nonlinear model predictive control through contacts for quadrupeds. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 1458–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Pandala, A.; Park, H.W. Real-time model predictive control for versatile dynamic motions in quadrupedal robots. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 8484–8490. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, Q.; Powell, M.J.; Katz, B.; Carlo, J.D.; Kim, S. Optimized Jumping on the MIT Cheetah 3 Robot. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 7448–7454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajita, S.; Hirukawa, H.; Harada, K.; Yokoi, K. Introduction to Humanoid Robotics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 101. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, G.; Dosunmu-Ogunbi, O.; Gong, Y.; Grizzle, J. Terrain-Aware Foot Placement for Bipedal Locomotion Combining Model Predictive Control, Virtual Constraints, and the ALIP. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.14862. [Google Scholar]
- Bledt, G.; Kim, S. Implementing regularized predictive control for simultaneous real-time footstep and ground reaction force optimization. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 3–8 November 2019; pp. 6316–6323. [Google Scholar]
- Vukobratovic, M.; Frank, A.A.; Juricic, D. On the stability of biped locomotion. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1970, BME-17, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajita, S.; Tani, K. Study of dynamic biped locomotion on rugged terrain-derivation and application of the linear inverted pendulum mode. In Proceedings of the 1991 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, IEEE Computer Society, Sacramento, CA, USA, 9–11 April 1991; pp. 1405–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Pratt, J.; Carff, J.; Drakunov, S.; Goswami, A. Capture point: A step toward humanoid push recovery. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2006 6th IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, Genova, Italy, 4–6 December 2006; pp. 200–207. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Goswami, A. A momentum-based balance controller for humanoid robots on non-level and non-stationary ground. Auton. Robot. 2012, 33, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, J.; Dong, H.; Ren, X.; Huang, L.; Zhao, M. Dynamic Balancing of Humanoid Robot with Proprioceptive Actuation: Systematic Design of Algorithm, Software, and Hardware. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Jorgensen, S.J.; Lee, J.; Ahn, J.; Luo, J.; Sentis, L. Dynamic locomotion for passive-ankle biped robots and humanoids using whole-body locomotion control. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2020, 39, 936–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieber, P.B. Trajectory free linear model predictive control for stable walking in the presence of strong perturbations. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE 6th IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, Genova, Italy, 4–6 December 2006; pp. 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Nguyen, Q. Force-and-moment-based model predictive control for achieving highly dynamic locomotion on bipedal robots. In Proceedings of the 2021 60th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Austin, TX, USA, 14–17 December 2021; pp. 1024–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, R.C.; Chen, C.C. Biped Walking Trajectory Generator Based on Three-Mass With Angular Momentum Model Using Model Predictive Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boston Dynamics’ Humanoid Robot Atlas Shows Off Its Balancing Skills. Available online: https://laughingsquid.com/boston-dynamics-humanoid-robot-atlas-shows-off-its-balancing-skills/ (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- Kanoun, O.; Lamiraux, F.; Wieber, P.B.; Kanehiro, F.; Yoshida, E.; Laumond, J.P. Prioritizing linear equality and inequality systems: Application to local motion planning for redundant robots. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009; pp. 2939–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wensing, P.M.; Orin, D.E. Improved Computation of the Humanoid Centroidal Dynamics and Application for Whole-Body Control. Int. J. Humanoid Robot. 2016, 13, 1550039:1–1550039:23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Gao, J.; Lu, Y.; Cao, J.; Zuo, W.; Mu, T. Simulation of Improved Bipedal Running Based on Swing Leg Control and Whole-body Dynamics. In Proceedings of the 2021 6th International Conference on Robotics and Automation Engineering (ICRAE), Guangzhou, China, 19–22 November 2021; pp. 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Gao, J.; Shi, X.; Tian, D.; Jia, Z. Whole-Body Control Based on Landing Estimation for Fixed-Period Bipedal Walking on Stepping Stones. In Proceedings of the 2020 3rd International Conference on Control and Robots (ICCR), Tokyo, Japan, 26–29 December 2020; pp. 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, O. Webots: Professional Mobile Robot Simulation. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2004, 1, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Felis, M.L. RBDL: An efficient rigid-body dynamics library using recursive algorithms. Auton. Robot. 2017, 41, 495–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreau, H.; Kirches, C.; Potschka, A.; Bock, H.; Diehl, M. qpOASES: A parametric active-set algorithm for quadratic programming. Math. Program. Comput. 2014, 6, 327–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Priority | Tasks | Tasks Dimension | Constraints | Constraints Dimension |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Floating Base Dynamics | 6 | Joint Torque | 10 |
| 2 | Linear Momentum | 6 | ZMP | 9 |
| Torso Posture | Friction Cone | |||
| 3 | Foot Position & Posture | 16 | ||
| Contact Wrench |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Shi, J.; Huang, S.; Ge, Y.; Cai, W.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, M. Balanced Standing on One Foot of Biped Robot Based on Three-Particle Model Predictive Control. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7040244
Yang Y, Shi J, Huang S, Ge Y, Cai W, Li Q, Chen X, Li X, Zhao M. Balanced Standing on One Foot of Biped Robot Based on Three-Particle Model Predictive Control. Biomimetics. 2022; 7(4):244. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7040244
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yong, Jiyuan Shi, Songrui Huang, Yuhong Ge, Wenhan Cai, Qingkai Li, Xueying Chen, Xiu Li, and Mingguo Zhao. 2022. "Balanced Standing on One Foot of Biped Robot Based on Three-Particle Model Predictive Control" Biomimetics 7, no. 4: 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7040244
APA StyleYang, Y., Shi, J., Huang, S., Ge, Y., Cai, W., Li, Q., Chen, X., Li, X., & Zhao, M. (2022). Balanced Standing on One Foot of Biped Robot Based on Three-Particle Model Predictive Control. Biomimetics, 7(4), 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7040244





