Design and Optimization of UAV Aerial Recovery System Based on Cable-Driven Parallel Robot
Abstract
1. Introduction
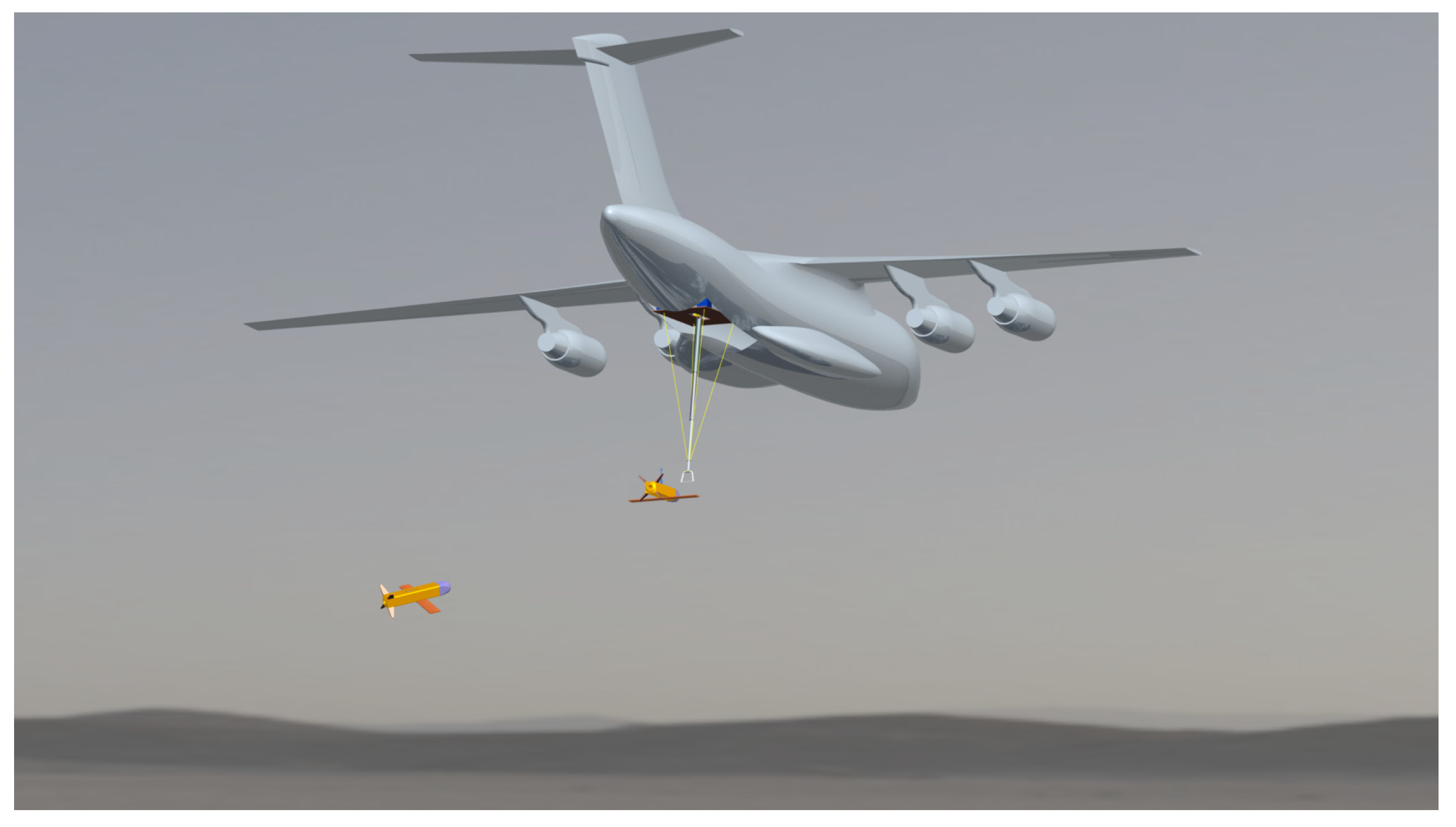
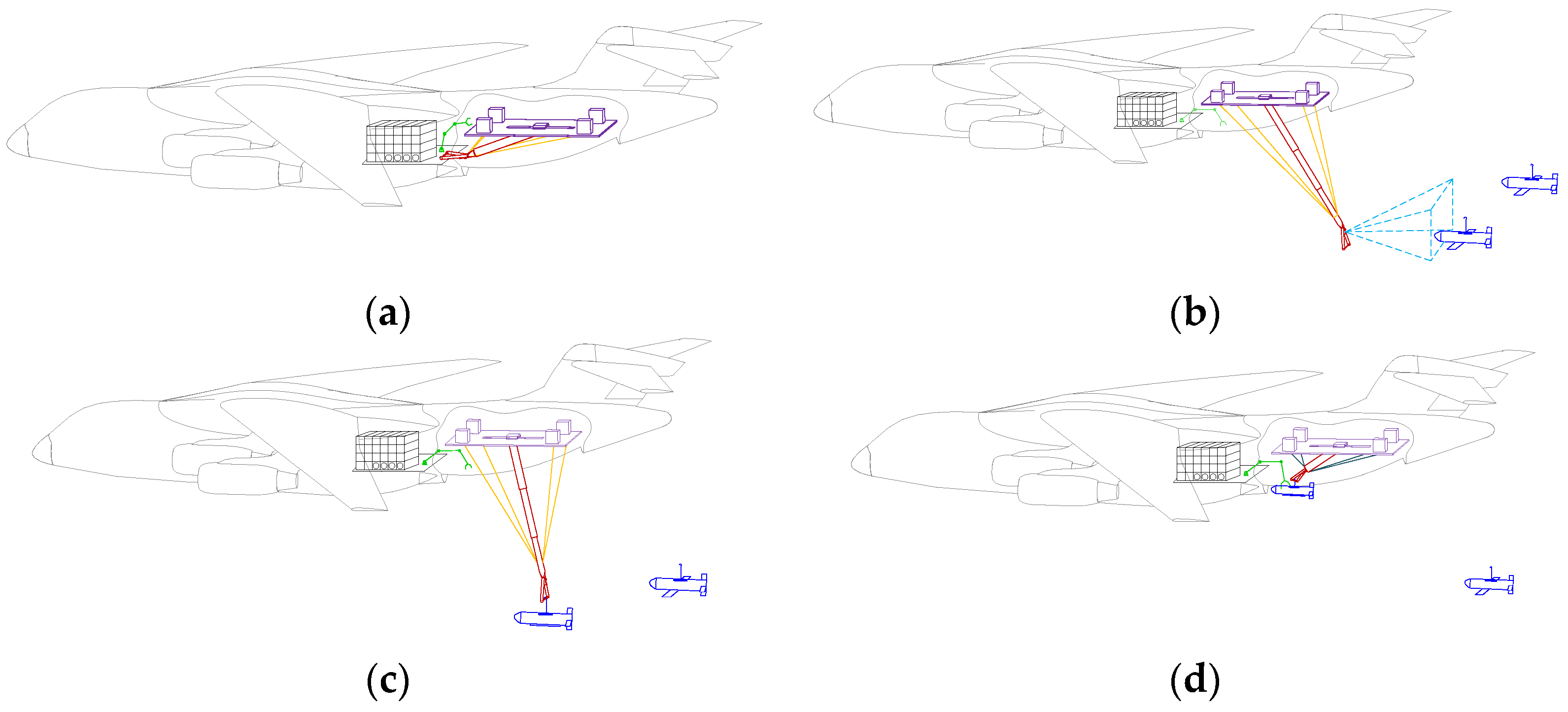
2. Design of UAV Aerial Recovery System
3. Modeling and Workspace
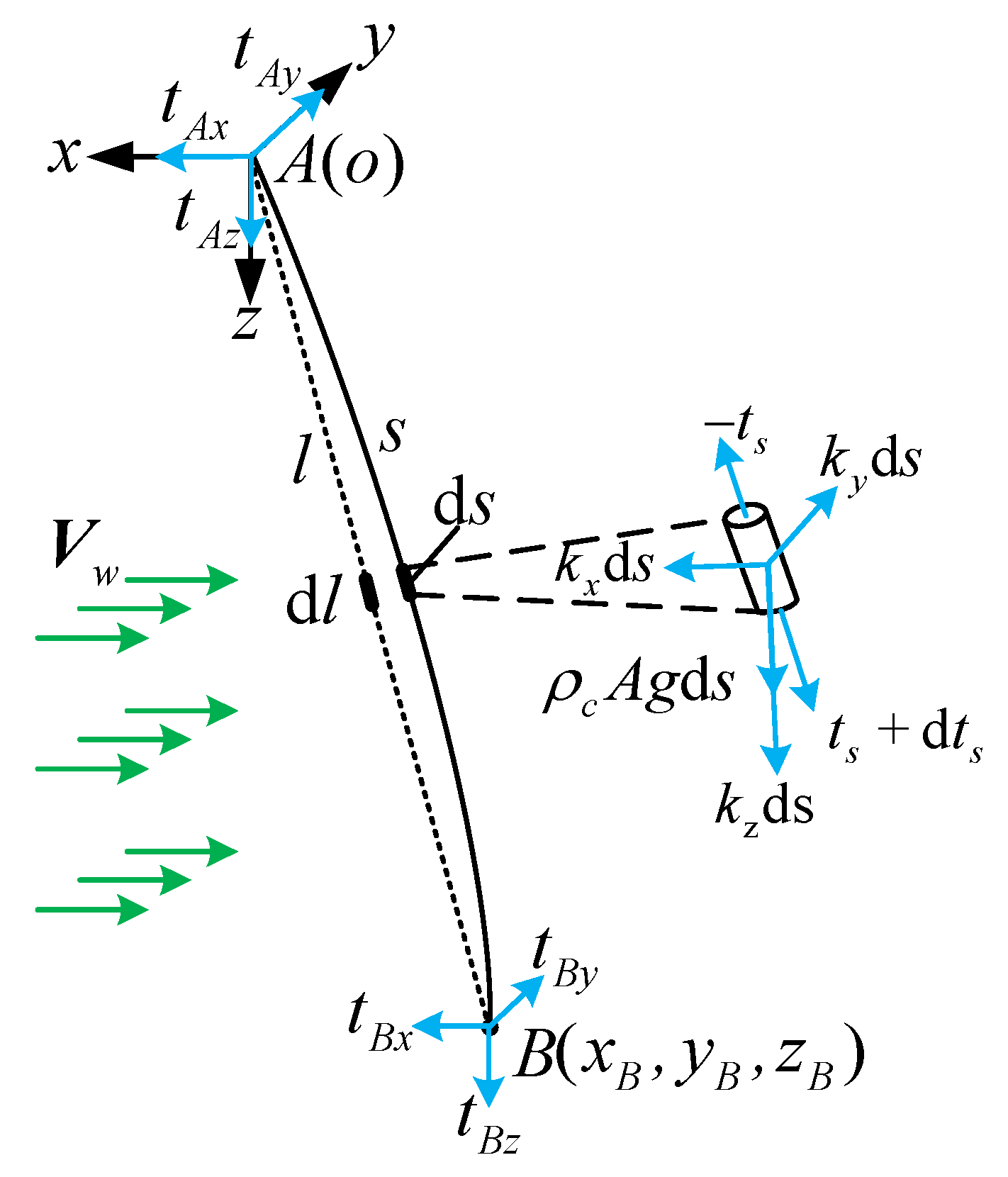
3.1. Spatial Cable Modeling Considering the Elasticity, Mass, and Aerodynamic Force
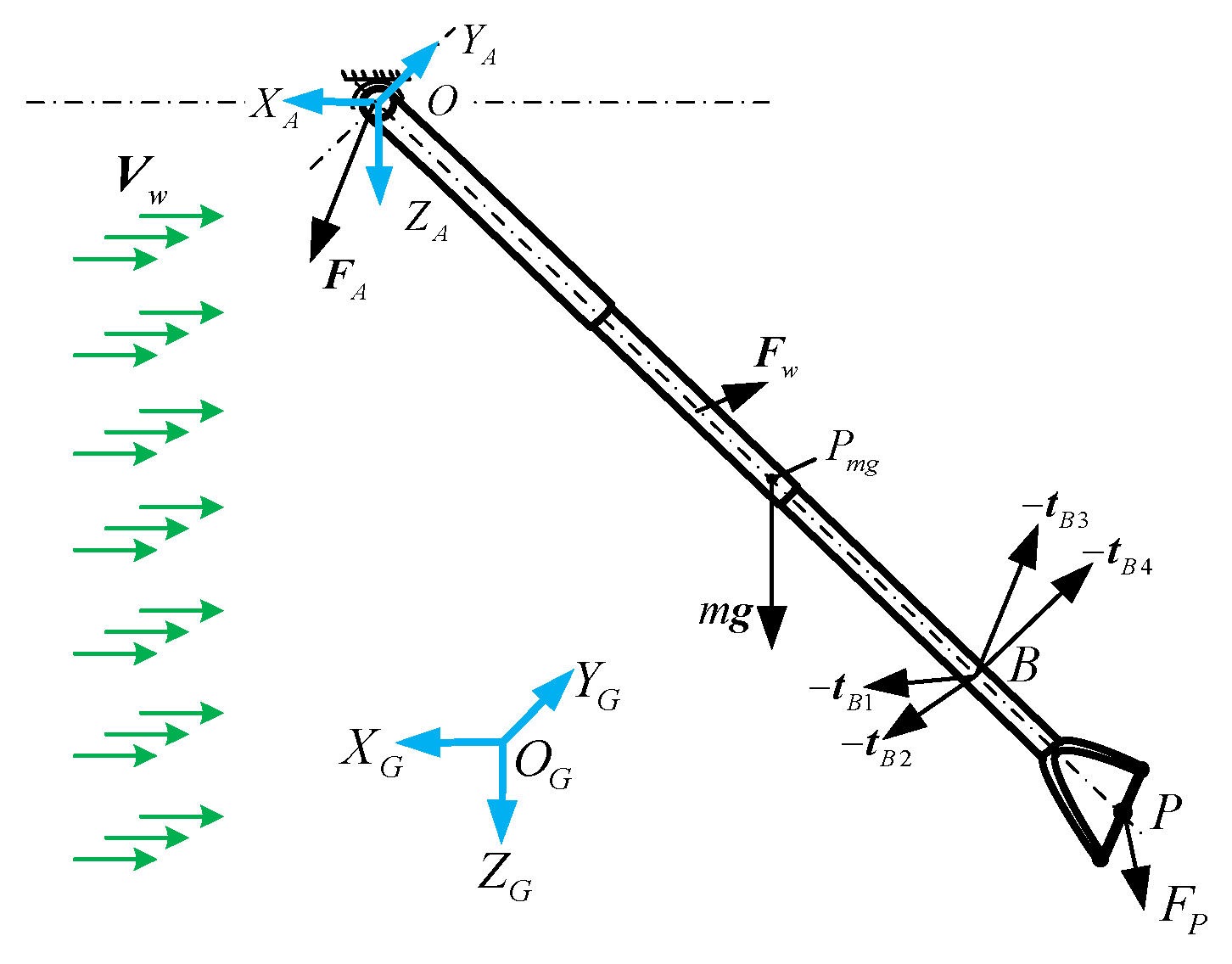
3.2. Static Equilibrium Equation
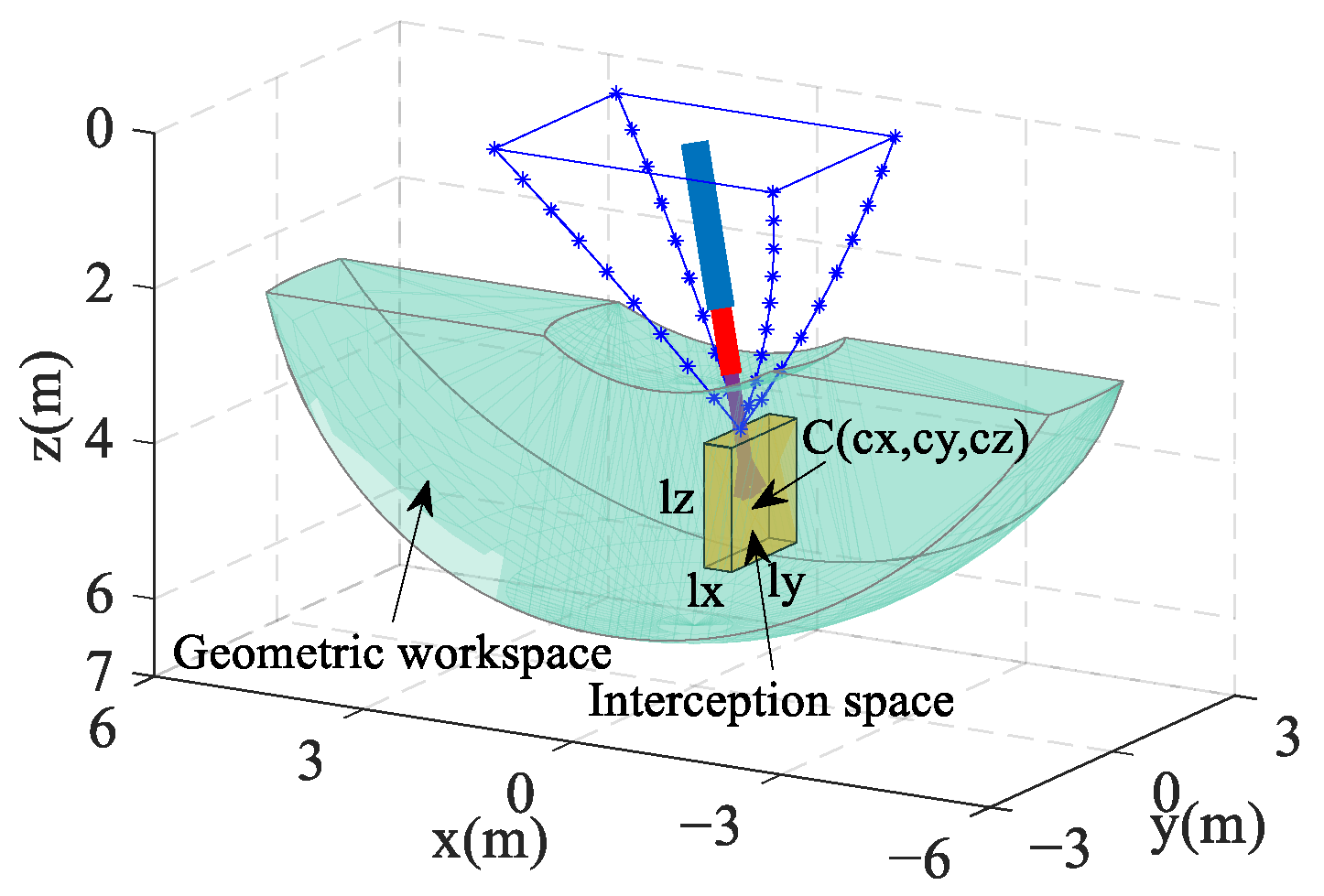
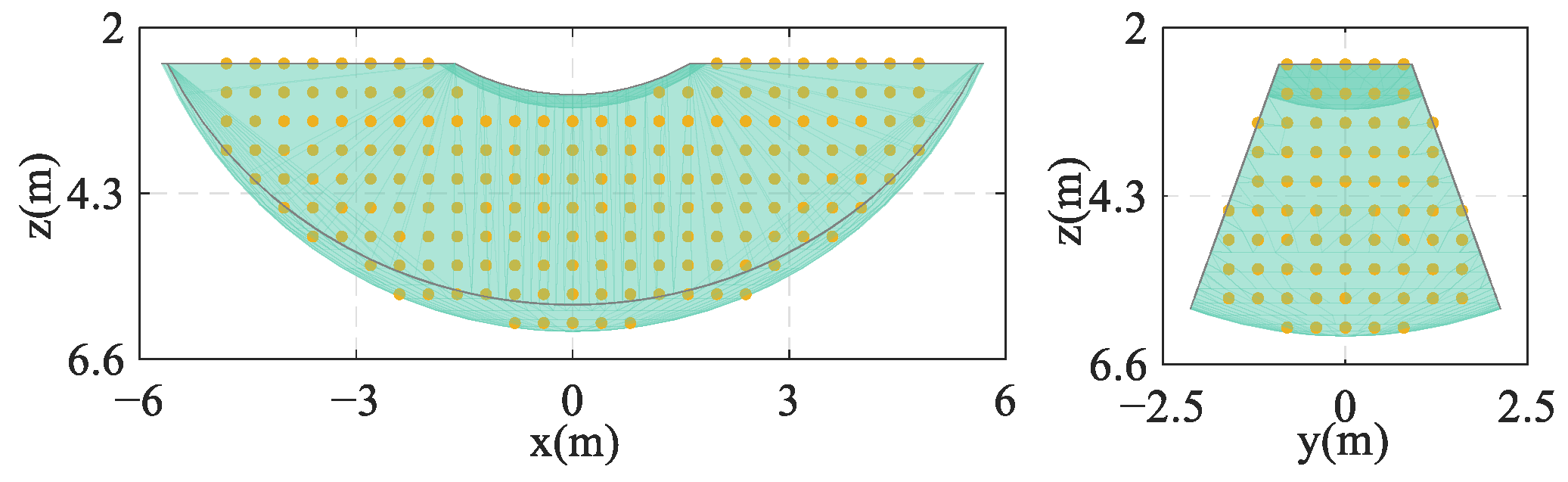
3.3. Workspace and Interception Space
4. Simulation Analysis of Cable and DCPR
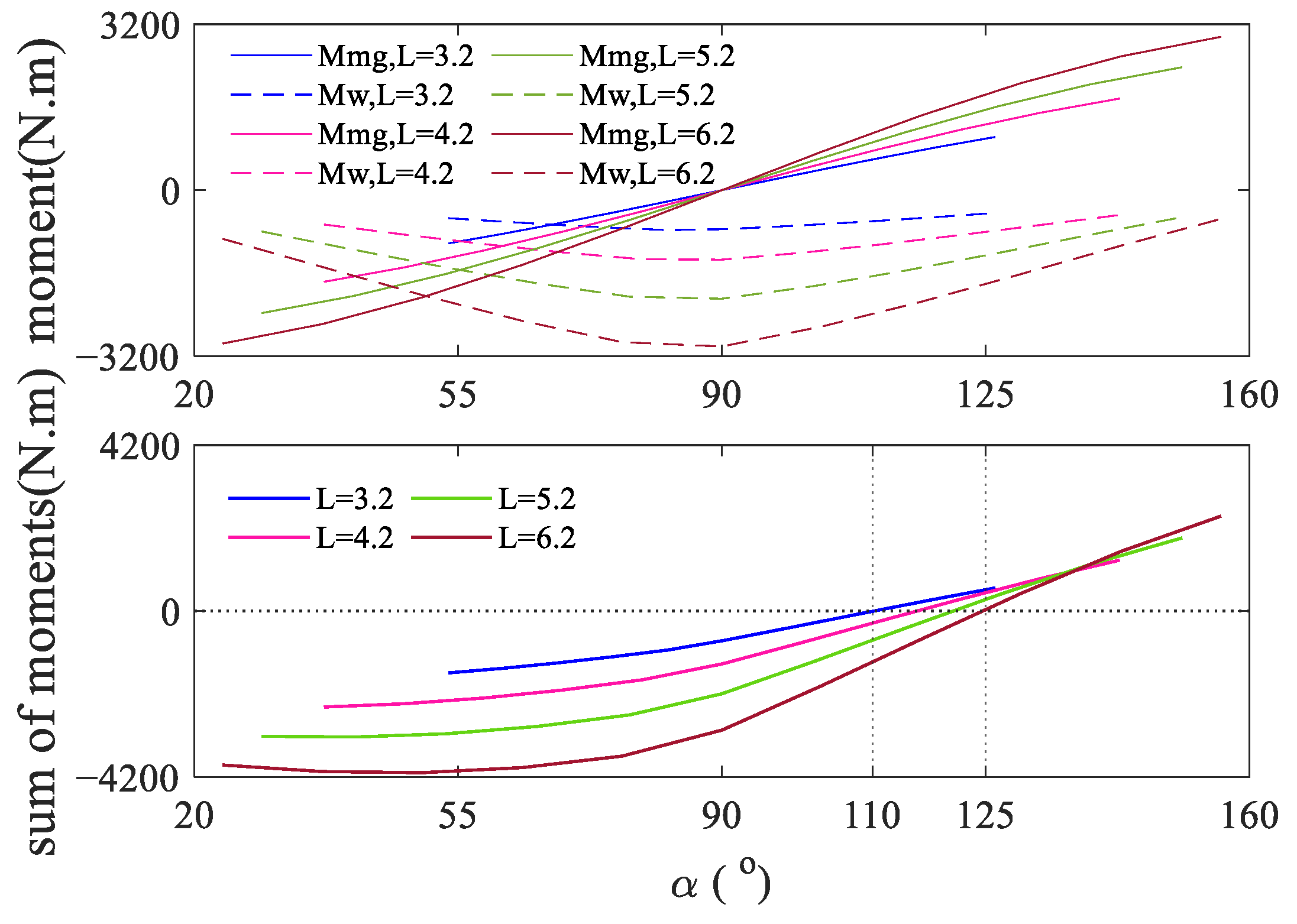
4.1. Cable Analysis
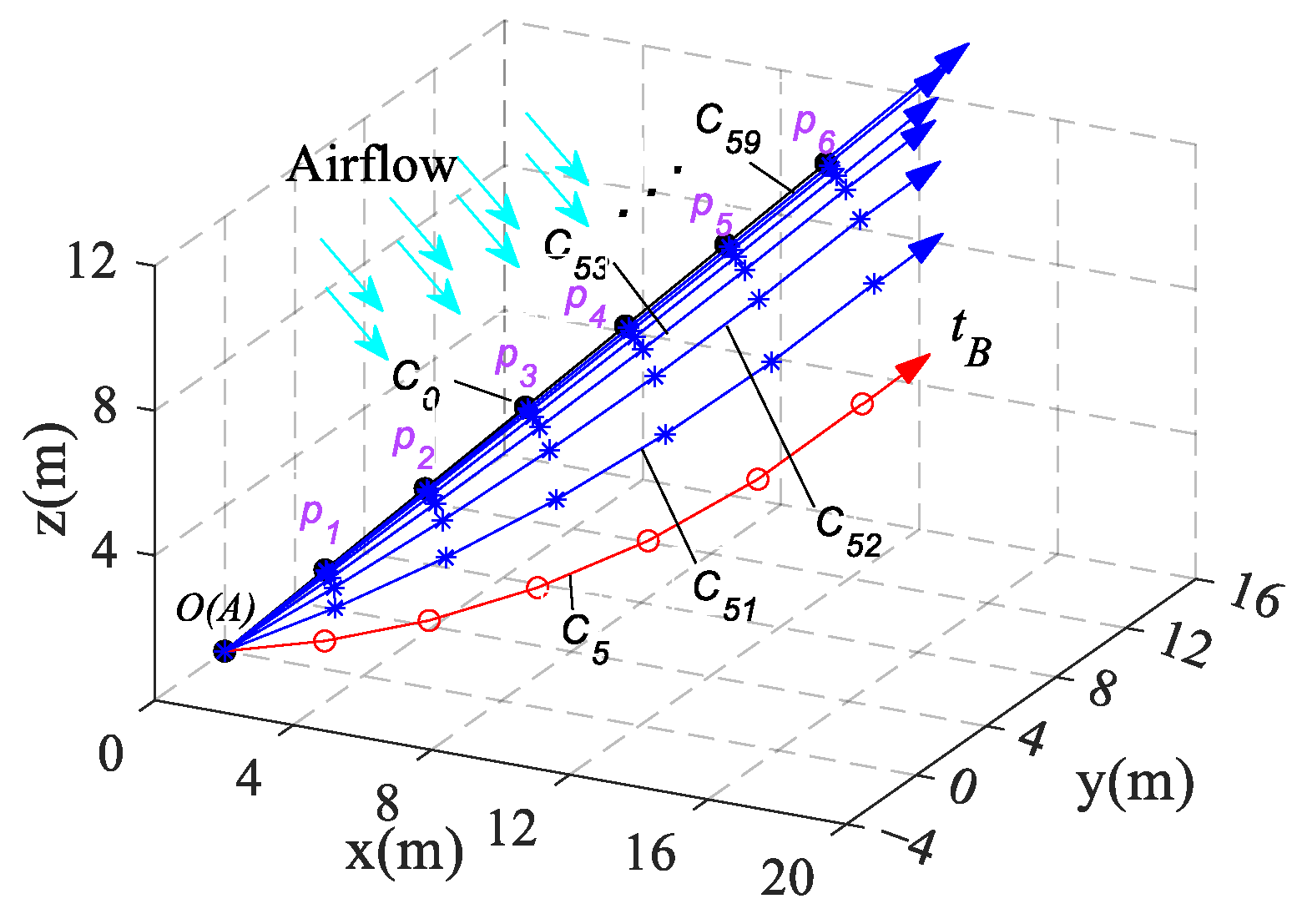
4.1.1. Analysis of the Effect of Airflow on Cable Configuration
4.1.2. Analysis of the Effect of Tension on Cable Configuration
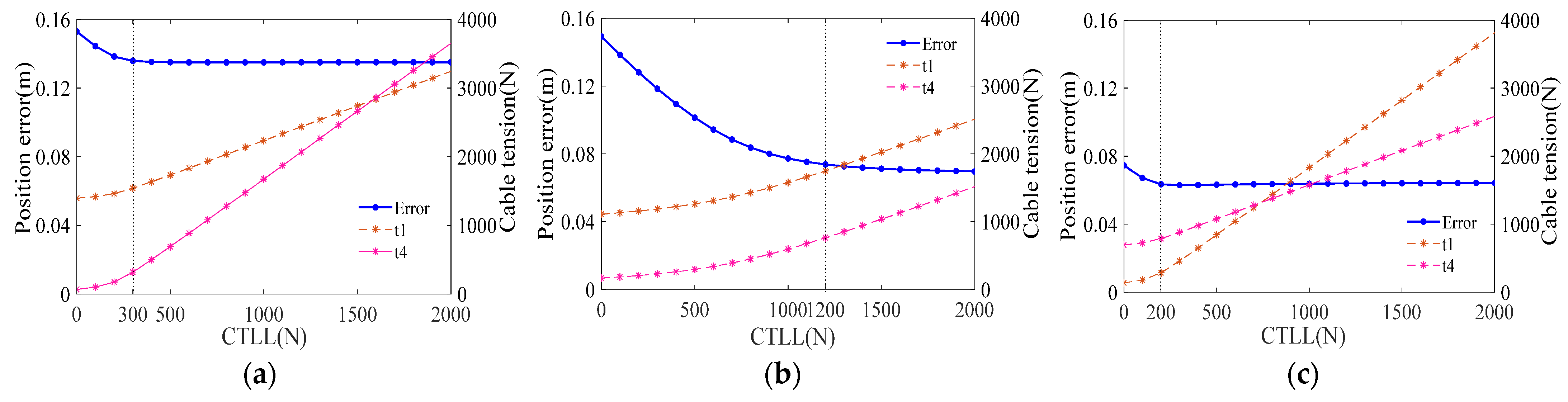
4.2. Position Error and Power Consumption Analysis in CDPR
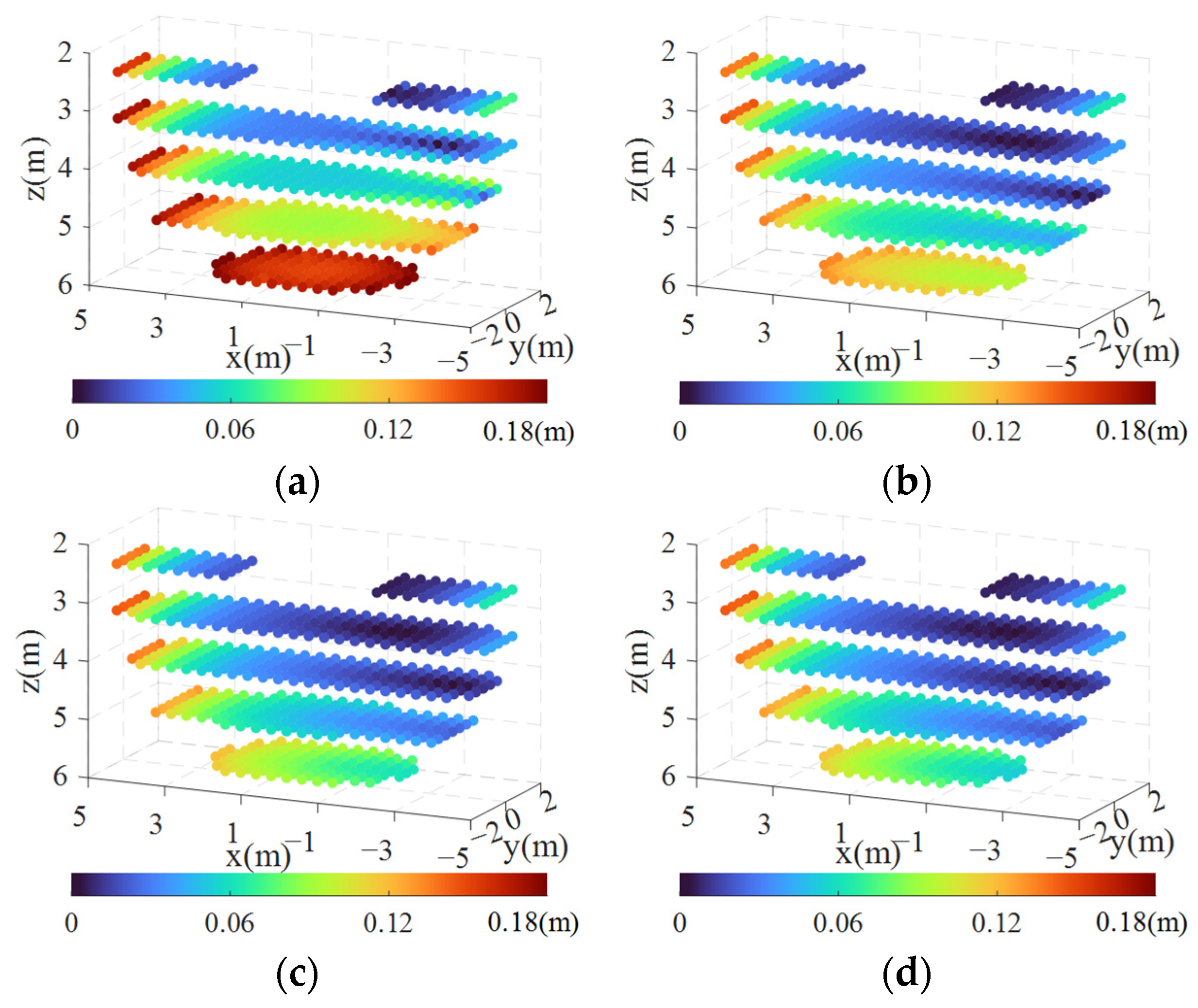
4.2.1. Position Error Analysis
4.2.2. Power Consumption Analysis
5. Multi-Objective Optimization of the UAV Aerial Recovery System
5.1. Optimization Objective Function
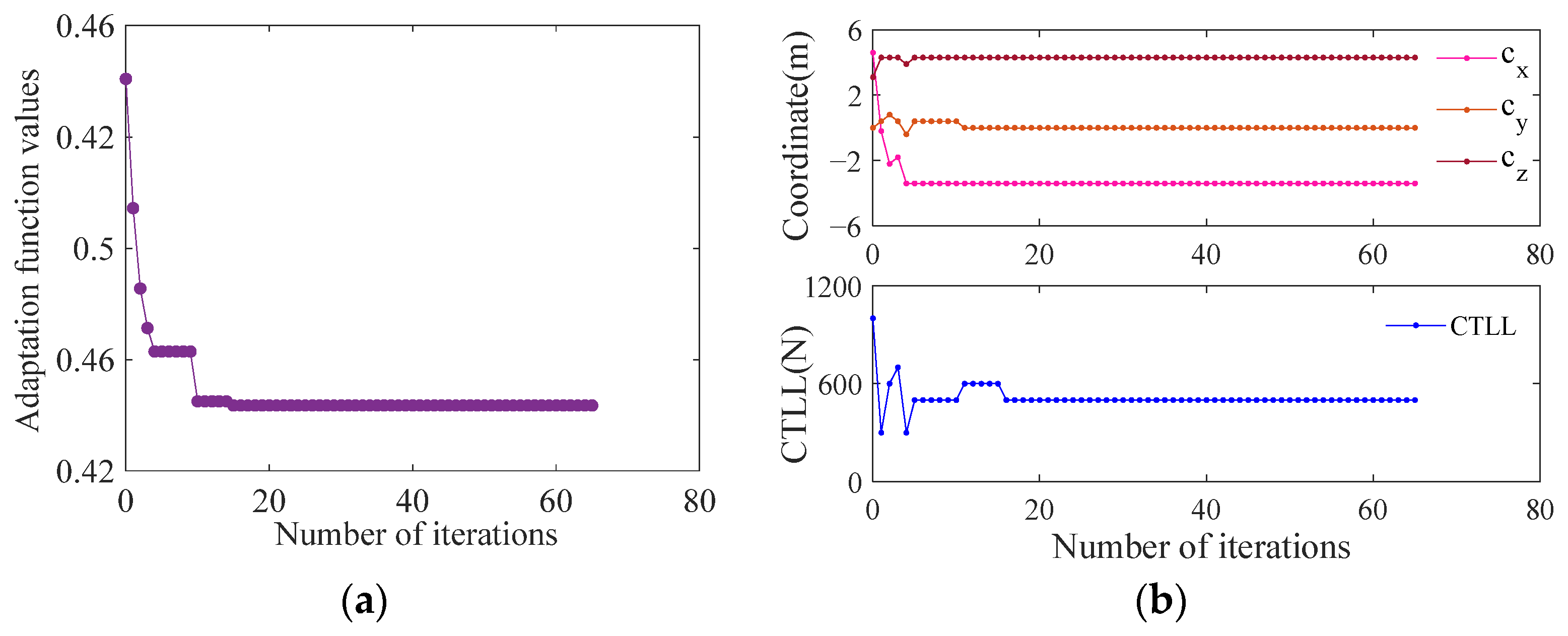
5.2. Optimization Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UAV | unmanned aerial vehicle; |
| CDPR | cable-driven parallel robot; |
| CTLL | cable tension lower limit; |
| DARPA | Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency; |
| MOP | multiple-objective problems; |
| DM | decision maker; |
| PF | Pareto Front; |
| TOPSIS | technique to order of preference by similarity to ideal solution; |
| GA | genetic algorithms; |
| PSO | particle swarm optimization; |
| DE | differential evolution; |
| ACO | ant colony optimization; |
| MOSA | multi-objective simulated annealing. |
Appendix A
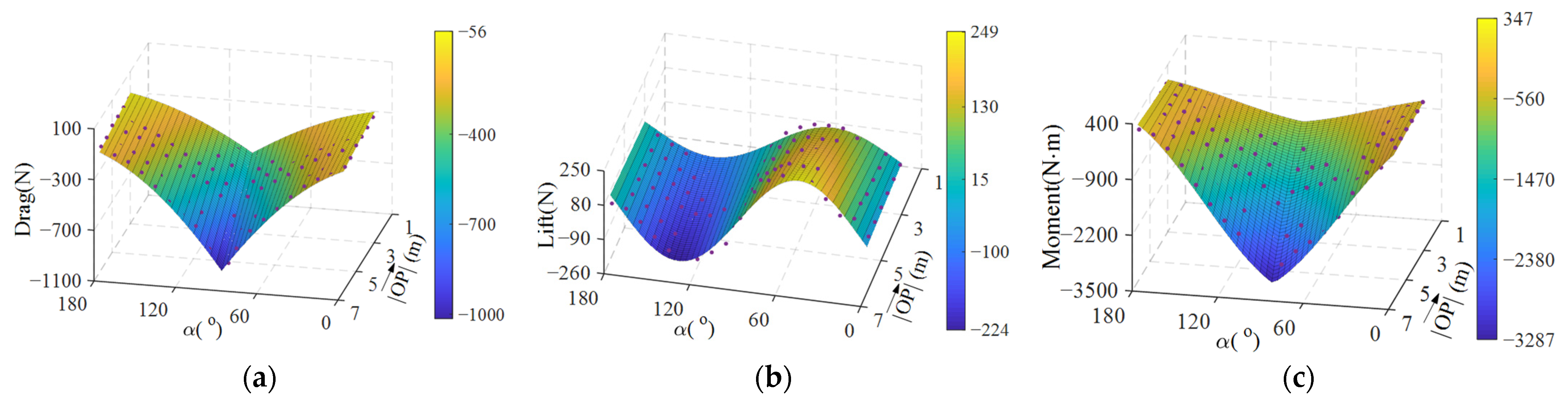
- Data fitting for and

- 2.
- Data fitting for and
References
- Telli, K.; Kraa, O.; Himeur, Y.; Ouamane, A.; Boumehraz, M.; Atalla, S.; Mansoor, W. A Comprehensive Review of Recent Research Trends on Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). Systems 2023, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Fu, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. A Comprehensive Survey on UAV Communication Channel Modeling. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 107769–107792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Xu, J.; Jin, S. A survey of prototype and experiment for UAV communications. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2021, 64, 140301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, A.; Sangaiah, A.K. A review on object detection in unmanned aerial vehicle surveillance. Int. J. Cogn. Comput. Eng. 2021, 2, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidaliyeva, U.; Ilipbayeva, L.; Taissariyeva, K.; Smailov, N.; Matson, E.T. Advances and Challenges in Drone Detection and Classification Techniques: A State-of-the-Art Review. Sensors 2023, 24, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idalene, A.; Boukhdir, K.; Medromi, H. UAV Control Architecture: Review. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2019, 10, 652–657. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.H.; Xiong, X.Z.; Yan, Y.H. UAV Formation Trajectory Planning Algorithms: A Review. Drones 2023, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsan, S.A.H.; Othman, N.Q.H.; Li, Y.; Alsharif, M.H.; Khan, M.A. Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs): Practical aspects, applications, open challenges, security issues, and future trends. Intell. Serv. Robot. 2023, 16, 109–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezza, D.; Andujar, M. The State-of-the-Art of Human–Drone Interaction: A Survey. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 167438–167454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Rao, B.; Wang, W. UAV Swarm Intelligence: Recent Advances and Future Trends. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 183856–183878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailon-Ruiz, R.; Lacroix, S. Wildfire remote sensing with UAVs: A review from the autonomy point of view. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Athens, Greece, 1–4 September 2020; pp. 412–420. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.W.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.Z.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, J.D.; Xu, Z. A review of rule-based collision avoidance technology for autonomous UAV. Sci. China-Technol. Sci. 2023, 66, 2481–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.Q.; Liu, H.P.; Wang, Y.F.; Liu, C.L. A Comprehensive Review for Typical Applications Based Upon Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Platform. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 9654–9666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafat, M.Y.; Alam, M.M.; Moh, S. Vision-Based Navigation Techniques for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles: Review and Challenges. Drones 2023, 7, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamola, V.; Kotesh, P.; Agarwal, A.; Naren; Gupta, N.; Guizani, M. A Comprehensive Review of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Attacks and Neutralization Techniques. Ad Hoc Netw. 2021, 111, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.J.; Yan, J.G.; Liu, Y. Improved Digital Model of Parafoil-Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Accurate Recycling System. In Proceedings of the IEEE Chinese Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference (CGNCC), Nanjing, China, 12–14 August 2016; pp. 1857–1863. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, H.Y.; Zhang, M.X.; Gu, F.; Chu, L.L.; Zhang, G.Y.; Du, X.T.; He, Y.Q. Fully Automated Control System for Recovery of Fixed-wing UAV. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (IEEE ROBIO), Sanya, China, 27–31 December 2021; pp. 1642–1649. [Google Scholar]
- Huh, S.; Shim, D.H. A vision-based landing system for small unmanned aerial vehicles using an airbag. Control Eng. Pract. 2010, 18, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Shi, H.; Wang, H. The object recognition and adaptive threshold selection in the vision system for landing an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Information and Automation, Zhuhai/Macau, China, 22–24 June 2009; pp. 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Z.K.; Li, C.T.; Zhen, Z.Y. Anti-disturbance constrained control of the air recovery carrier via an integral barrier Lyapunov function. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 106157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochstetler, R.D.; Bosma, J.; Chachad, G. Lighter-Than-Air (LTA) “AirStation”—Unmanned Aircraft System (UAS) Carrier Concept. In Proceedings of the 16th AIAA Aviation Technology, Integration, and Operations Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 13–17 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Voskuijl, M.; Said, M.R.; Pandher, J.; Tooren, M.J.V.; Richards, B. In-flight deployment of morphing UAVs—A method to analyze dynamic stability, controllability and loads. In Proceedings of the AIAA Aviation 2019 Forum, Dallas, TX, USA, 17–21 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Berti, A.; Merlet, J.-P.; Carricato, M. Solving the Direct Geometrico-Static Problem of 3-3 Cable-Driven Parallel Robots by Interval Analysis: Preliminary Results. In Cable-Driven Parallel Robots; Bruckmann, T., Pott, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 251–268. [Google Scholar]
- Barbazza, L.; Oscari, F.; Minto, S.; Rosati, G. Trajectory planning of a suspended cable driven parallel robot with reconfigurable end effector. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2017, 48, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korayem, M.H.; Yousefzadeh, M.; Susany, S. Dynamic Modeling and Feedback Linearization Control of Wheeled Mobile Cable-Driven Parallel Robot Considering Cable Sag. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2017, 42, 4779–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.Q.; Gouttefarde, M.; Company, O.; Pierrot, F. On the Simplifications of Cable Model in Static Analysis of Large-Dimension Cable-Driven Parallel Robots. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots & Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J. Workspace and Stiffness Analysis of 3D Printing Cable-Driven Parallel Robot with a Retractable Beam-Type End-Effector. Robotics 2020, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueners, D.; Chanal, H.; Bouzgarrou, B.C. Stiffness optimization of a cable driven parallel robot for additive manufacturing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 843–849. [Google Scholar]
- Izard, J.B.; Dubor, A.; Hervé, P.-E.; Cabay, E.; Culla, D.; Rodriguez, M.; Barrado, M. Large-scale 3D printing with cable-driven parallel robots. Constr. Robot. 2017, 1, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, X.; Ma, H.; Liu, K. Design and Experimental Research of Movable Cable-Driven Lower Limb Rehabilitation Robot. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 2315–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennaiem, F.; Laribi, M.A.; Sandoval, J.; Bennour, S.; Mlika, A.; Romdhane, L. Task-Based Design Approach: Development of a Planar Cable-Driven Parallel Robot for Upper Limb Rehabilitation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Nan, R.; Pan, Z.; Jin, C.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, P.; Li, D.; Xu, K.; Li, C.; et al. The Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) project. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Topical Meeting on Microwave Photonics (MWP), Paphos, Cyprus, 26–29 October 2015; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Z.-F.; Tang, X.; Wang, L.-P.; Chen, X. Dynamic modeling and wind vibration control of the feed support system in FAST. Nonlinear Dynam. 2012, 67, 965–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, T.; Cao, Y. Multi-Joint Bionic Mechanism Based on Non-Circular Gear Drive. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Chen, C.; Ding, Y.; Wu, K.; Zhang, G.; Yang, G. Stiffness modeling and distribution of a modular cable-driven human-like robotic arm. Mech. Mach. Theory 2023, 180, 105150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miermeister, P.; Pott, A.; Verl, A. Dynamic Modeling and Hardware-In-The-Loop Simulation for the Cable-Driven Parallel Robot IPAnema. In Proceedings of the ISR/ROBOTIK 2010, Stuttgart, Germany, 7–9 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Korayem, M.H.; Yousefzadeh, M.; Kian, S. Precise end-effector pose estimation in spatial cable-driven parallel robots with elastic cables using a data fusion method. Measurement 2018, 130, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Tian, H.; Qiao, X. Minimum Cable Tensions and Tension Sensitivity for Long-Span Cable-Driven Camera Robots with Applications to Stability Analysis. Actuators 2023, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, P.; Tian, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X. Dynamic Modeling, Workspace Analysis and Multi-Objective Structural Optimization of the Large-Span High-Speed Cable-Driven Parallel Camera Robot. Machines 2022, 10, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Max Irvine, H. CABLE Structures; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Courteille, E.; Deblaise, D. Static and dynamic stiffness analyses of cable-driven parallel robots with non-negligible cable mass and elasticity. Mech. Mach. Theory 2015, 85, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichler, J. Dynamic Analysis of an In-Flight Refueling System. J. Aircr. 1978, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniagua, K.S.; García-Fogeda, P.; Arévalo, F.; Rodriguez, J.B. Aeroelastic analysis of an air-to-air refueling hose-drogue system through an efficient novel mathematical model. J. Fluids Struct. 2020, 100, 103164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, J.M.; Schmidt, L.V.; Stuart, T.D. Dynamic modeling of a trailing wire towed by an orbiting aircraft. J. Guid. Control Dynam. 1995, 18, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etkin, B. Stability of a Towed Body. J. Aircr. 1998, 35, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribbens, W.; Saggio, F.; Wierenga, R.; Feldmann, M. Dynamic Modeling of an Aerial Refueling Hose & Drogue System. In Proceedings of the Aiaa Applied Aerodynamics Conference, Miami, FL, USA, 25–28 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Dong, X.; Liu, J.; Jian, W. Dynamics and control of the hose whipping phenomenon in aerial refueling. In Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference Proceedings, Big Sky, MT, USA, 7–14 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.; Wang, S.; Yang, M.; Dong, Y. Dynamic simulation of aerial towed decoy system based on tension recurrence algorithm. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2016, 29, 1484–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P. Periodic Optimal Control of a Towed Aerial-Cable System in Presence of Cross-Wind. In Proceedings of the Aiaa Guidance, Navigation, & Control Conference & Exhibit, Keystone, CO, USA, 21–24 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Wei, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, H. Simulation of the Reel-In Operation of Towed Target System with Constant-Length Method. In Proceedings of the AIAA Scitech 2019 Forum, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–11 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.; Beard, R.W. Towed-body trajectory tracking in aerial recovery of micro air vehicle in the presence of wind. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 29 June–1 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Wei, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, X. Simulation of the dynamic retrieval process of a towed target system under towing airplane’s wake and atmospheric turbulence. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G J. Aerosp. Eng. 2020, 234, 1518–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, B.; Duan, B.Y.; Du, J.L.; Bao, H. Dynamic modeling and active control of a cable-suspended parallel robot. Mechatronics 2008, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
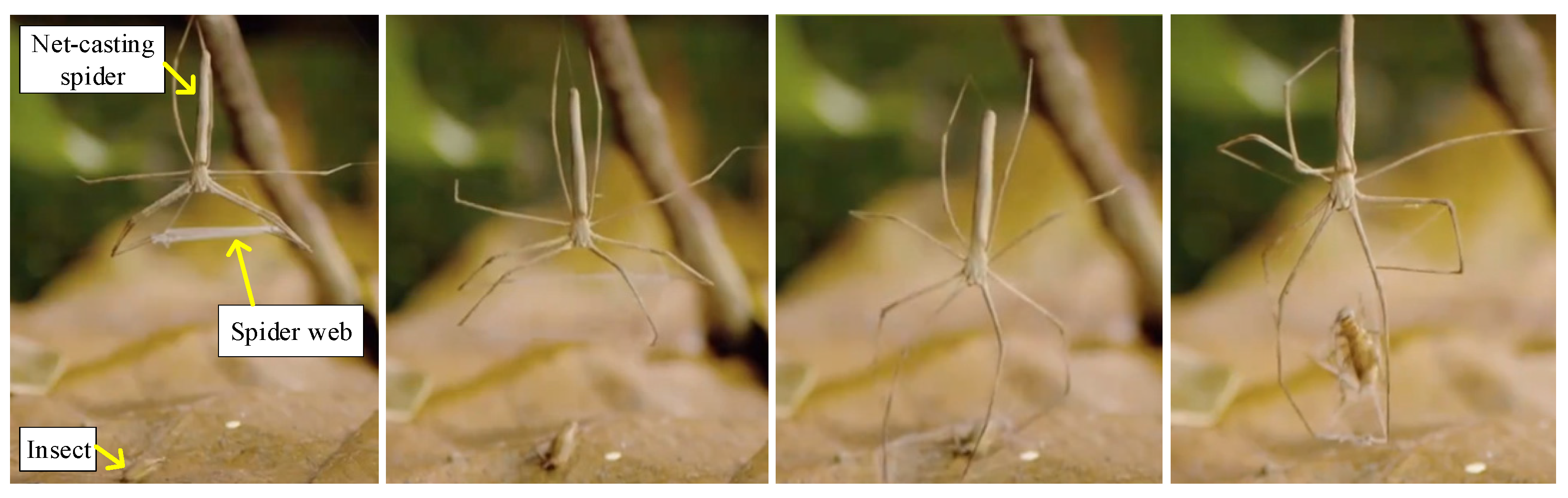
- Marx, G. On the new spider of the genus Dinopis, from the southern United States. Proc. Acad. Nat. Sci. Phila. 1889, 1889, 341–343. [Google Scholar]
- Stafstrom, J.A.; Hebets, E.A. Nocturnal foraging enhanced by enlarged secondary eyes in a net-casting spider. Biol. Lett. 2016, 12, 20160152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coddington, J.; Sobrevila, C. Web manipulation and two stereotyped attack behaviors in the ogre-faced spider Deinopis spinosus Marx (Araneae, Deinopidae). J. Arachnol. 1987, 15, 213–225. [Google Scholar]
- Arsenault, M. Workspace and stiffness analysis of a three-degree-of-freedom spatial cable-suspended parallel mechanism while considering cable mass. Mech. Mach. Theory 2013, 66, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, K. No-Preference Methods. In Nonlinear Multiobjective Optimization; Miettinen, K., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 67–76. [Google Scholar]
- Osyczka, A. An approach to multicriterion optimization problems for engineering design. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1978, 15, 309–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monarchi, D.E.; Kisiel, C.C.; Duckstein, L. Interactive multiobjective programing in water resources: A case study. Water Resour. Res. 1973, 9, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.Z.; Mirjalili, S.; Saremi, S.; Faris, H.; Aljarah, I. Grasshopper optimization algorithm for multi-objective optimization problems. Appl. Intell. 2018, 48, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.L.; Yoon, K.P. Multiple Attribute Decision Making: Methods and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, J.L.J.; Oliver, G.A.; Francisco, M.B.; Cunha, S.S.; Gomes, G.F. A Review of Multi-objective Optimization: Methods and Algorithms in Mechanical Engineering Problems. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 29, 2285–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Ying, S.; Qi, H.; Yu, L.; Li, G. Design, analysis and optimization of a hybrid fluid flow magnetorheological damper based on multiphysics coupling model. Mech. Syst. Signal. Pr. 2023, 205, 110877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.H.; Palmer, T.S.; DuPont, B. A survey of multi-objective optimization methods and their applications for nuclear scientists and engineers. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2021, 138, 103830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





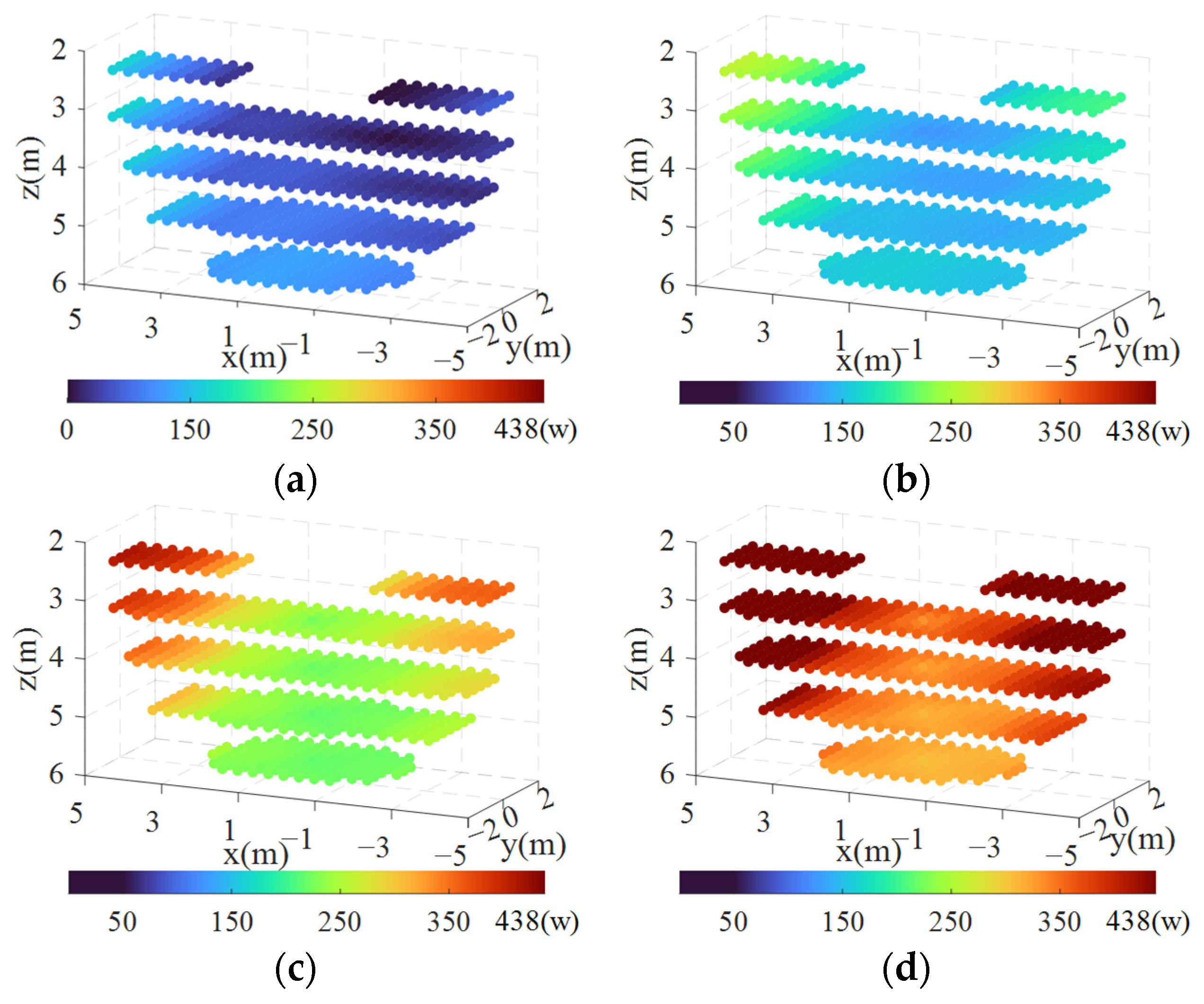
| Configuration | (m/s) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 5.6 | 4.6% | 4.6% | 4.6% | 4.6% | 4.6% | 4.6% | |
| 26.4 | 102.3% | 102.5% | 102.6% | 102.7% | 102.7% | 102.7% | |
| 50 | 341.8% | 345.8% | 348.8% | 351% | 352.2% | 352.6% | |
| 80 | 662.8% | 691.6% | 717.4% | 737.9% | 750.8% | 754.9% | |
| 100 | 801.7% | 852.4% | 902.5% | 946.9% | 977.9% | 988.4% |
| Configuration | (kN) | (m) | (m) | (m) | (m) | (m) | (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 2.87 | 5.41 | 7.53 | 9.13 | 10.12 | 10.45 | |
| 0.7 | 2.32 | 4.31 | 5.92 | 7.11 | 7.84 | 8.08 | |
| 0.9 | 1.92 | 3.54 | 4.83 | 5.77 | 6.33 | 6.52 | |
| 1.3 | 1.4 | 2.56 | 3.48 | 4.13 | 4.53 | 4.66 | |
| 2.1 | 0.89 | 1.63 | 2.2 | 2.61 | 2.85 | 2.94 | |
| 3.7 | 0.51 | 0.93 | 1.26 | 1.49 | 1.63 | 1.67 | |
| 6.9 | 0.27 | 0.5 | 0.67 | 0.8 | 0.87 | 0.9 | |
| 13.3 | 0.14 | 0.26 | 0.35 | 0.41 | 0.45 | 0.47 | |
| 26.1 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.23 | 0.24 | |
| 51.7 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.1 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.14 |
| Parameter Name | Parameter Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Cable diameter | ||
| Cable cross-sectional area | ||
| Young’s modulus | ||
| Cable density | ||
| Span 1 | ||
| Span 2 | ||
| Telescopic rod weight | ||
| Telescopic rod shortening length | ||
| Telescopic rod elongation length | ||
| Air density at 3 km altitude | ||
| Aerodynamic friction coefficient | ||
| Aerodynamic drag coefficient | ||
| Carrier aircraft flight speed | ||
| Gravity acceleration |
| CTLL (N) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Initial | 1000 | (4.6,0,3.1) |
| Optimal | 500 | (−3.4,0,4.3) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Sun, Y.; Yue, H.; Yang, J.; Yang, F.; Zhao, Y. Design and Optimization of UAV Aerial Recovery System Based on Cable-Driven Parallel Robot. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9020111
Wu J, Sun Y, Yue H, Yang J, Yang F, Zhao Y. Design and Optimization of UAV Aerial Recovery System Based on Cable-Driven Parallel Robot. Biomimetics. 2024; 9(2):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9020111
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jun, Yizhang Sun, Honghao Yue, Junyi Yang, Fei Yang, and Yong Zhao. 2024. "Design and Optimization of UAV Aerial Recovery System Based on Cable-Driven Parallel Robot" Biomimetics 9, no. 2: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9020111
APA StyleWu, J., Sun, Y., Yue, H., Yang, J., Yang, F., & Zhao, Y. (2024). Design and Optimization of UAV Aerial Recovery System Based on Cable-Driven Parallel Robot. Biomimetics, 9(2), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9020111





