Dynamic Contrast Enhanced-MR CEST Urography: An Emerging Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Upper Urinary Tract Obstruction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Imaging Modalities
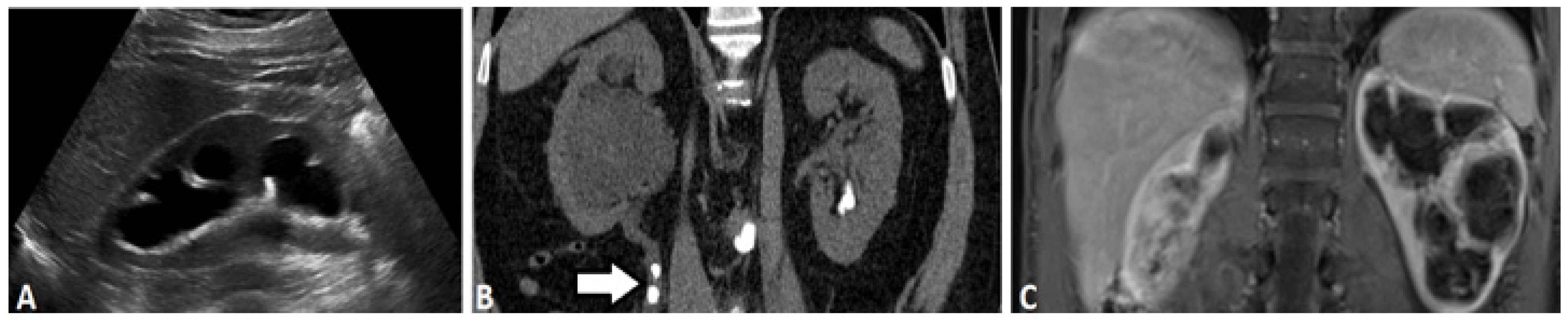
2.1. Ultrasound-Based Urography
2.2. X-ray Based Urography
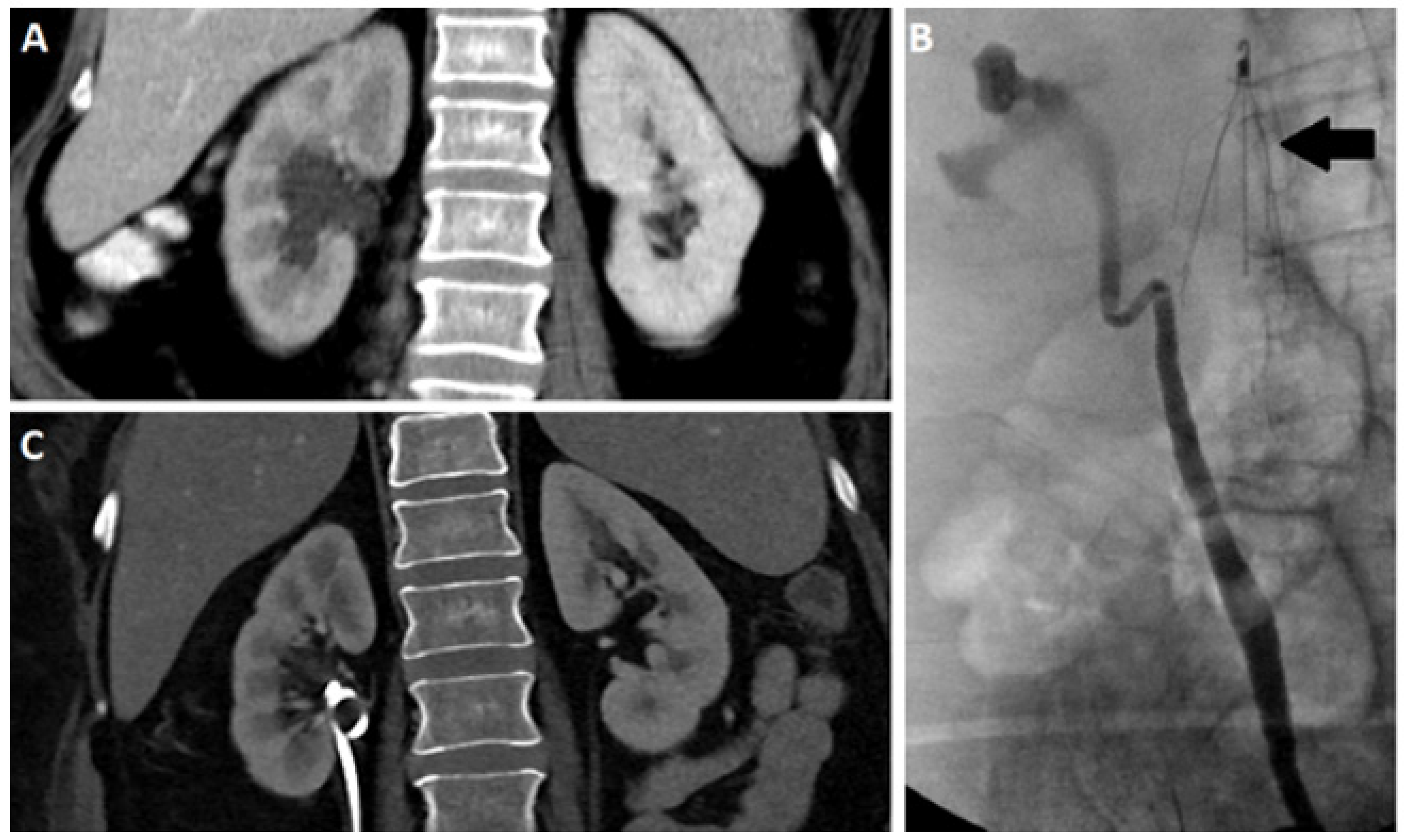
2.3. Computed Tomography
2.4. Nuclear Scintigraphy
2.5. Magnetic Resonance (MR) Based Urography
3. The Emergence of New DCE-MRU Technologies
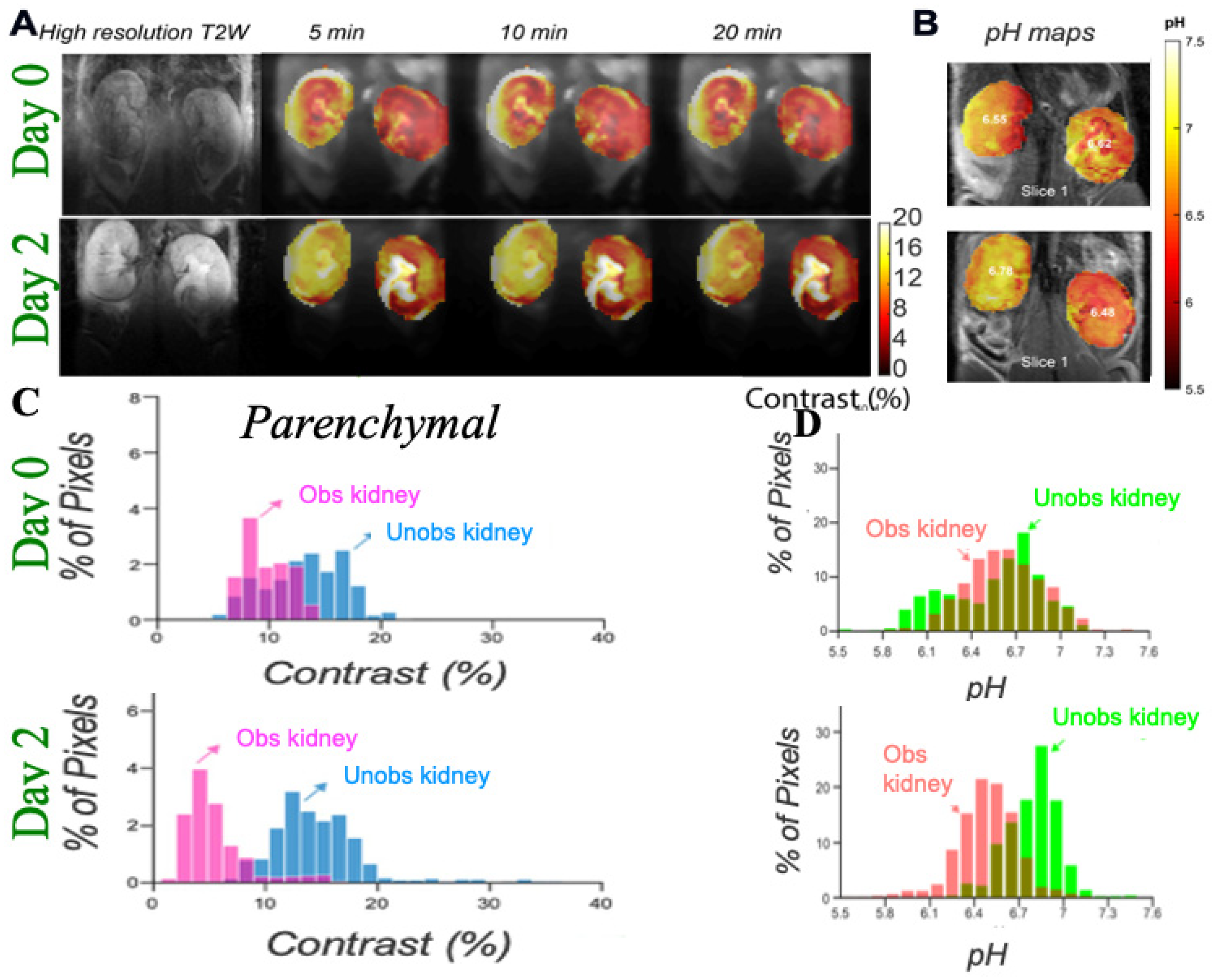
3.1. DCE-MR CEST Urography
3.2. CEST MRI at 3T Using Iopamidol
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarhan, O.; Helmy, T.; Abou-El Ghar, M.; Baky, M.A.; El-Assmy, A.; Dawaba, M. Long-term functional and morphological outcome after pyeloplasty for huge renal pelvis. BJU Int. 2011, 107, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, C.P.; Tolley, E.; Tourville, E.; Sharadin, C.; Giel, D.W.; Gleason, J.M. Hydronephrosis after pyeloplasty: Will it go away? Urology 2018, 121, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, D.A.; Eisenstein, L.G.; Jones, D.S. Hidden in Plain Sight—Reconsidering the Use of Race Correction in Clinical Algorithms. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, J.; Dent, C.; Tarabishi, R.; Mitsnefes, M.M.; Ma, Q.; Kelly, C.; Ruff, S.M.; Zahedi, K.; Shao, M.; Bean, J.; et al. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. Lancet 2005, 365, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helenon, O.; Correas, J.M.; Balleyguier, C.; Ghouadni, M.; Cornud, F. Ultrasound of renal tumors. Eur. Radiol. 2001, 11, 1890–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auer, T.; Heidegger, I.; De Zordo, T.; Junker, D.; Jaschke, W.; Steinkohl, F.; Aigner, F. Fusion Imaging of Contrast-enhanced Ultrasound with CT or MRI for Kidney Lesions. In Vivo 2019, 33, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lewington, A.; Kanagasundaram, S. Renal Association Clinical Practice Guidelines on Acute Kidney Injury. Clin. Pract. 2011, 118, C349–C390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrepetis, K.; Siafakas, I.; Lykourinas, M. Evolution of retrograde pyelography and excretory urography in the early 20th century. J. Endourol. 2001, 15, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Westphalen, A.C.; Zagoria, R.J. CT and MRI of small renal masses. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodger, F.; Roditi, G.; Aboumarzouk, O.M. Diagnostic Accuracy of Low and Ultra-Low Dose CT for Identification of Urinary Tract Stones: A Systematic Review. Urol. Int. 2018, 100, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herschorn, S.; Radomski, S.B.; Shoskes, D.A.; Mahoney, J.; Hirshberg, E.; Klotz, L. Evaluation and Treatment of Blunt Renal Trauma. J. Urol. 1991, 146, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, A.; Sandler, C.M.; Ernst, R.D.; Goldman, S.M.; Raval, B.; Fishman, E.K. Renal inflammatory disease: The current role of CT. Crit. Rev. Diagn. Imaging 1997, 38, 369–415. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gorin, M.A.; Rowe, S.P. Urinary Tract Imaging: Basic Principles of Nuclear Medicine in Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology Twelfth Edition Review; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, P.V. Functional MRI of the kidney: Tools for translational studies of pathophysiology of renal disease. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2006, 290, F958–F974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bokacheva, L.; Rusinek, H.; Zhang, J.L.; Lee, V.S. Assessment of Renal Function with Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MR Imaging. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2008, 16, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, R.A.; Votaw, J.R.; Salman, K.; Sharma, P.; Lurie, C.; Kalb, B.; Martin, D.R. Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of renal structure and function related to disease: Technical review of image acquisition, postprocessing, and mathematical modeling steps. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 33, 1270–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taton, B.; De La Faille, R.; Asselineau, J.; Perez, P.; Merville, P.; Colin, T.; Combe, C.; Sourbron, S.; Grenier, N. A prospective comparison of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI and 51Cr-EDTA clearance for glomerular filtration rate measurement in 42 kidney transplant recipients. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 117, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Rusinek, H.; Bokacheva, L.; Chen, Q.; Storey, P.; Lee, V.S. Use of cardiac output to improve measurement of input function in quantitative dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 30, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buckley, D.L.; Shurrab, A.E.; Cheung, C.M.; Jones, A.P.; Mamtora, H.; Kalra, P.A. Measurement of single kidney function using dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI: Comparison of two models in human subjects. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2006, 24, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.L.; Rusinek, H.; Chandarana, H.; Lee, V.S. Functional MRI of the kidneys. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 37, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.L.; Morrell, G.; Rusinek, H.; Sigmund, E.E.; Chandarana, H.; Lerman, L.O.; Prasad, P.V.; Niles, D.; Artz, N.; Fain, S.; et al. New magnetic resonance imaging methods in nephrology. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Annet, L.; Hermoye, L.; Peeters, F.; Jamar, F.; Dehoux, J.P.; Van Beers, B.E. Glomerular filtration rate: Assessment with dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI and a cortical-compartment model in the rabbit kidney. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2004, 20, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourbron, S.P.; Michaely, H.J.; Reiser, M.F.; Schoenberg, S.O. MRI-Measurement of Perfusion and Glomerular Filtration in the Human Kidney with a Separable Compartment Model. Investig. Radiol. 2008, 43, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivier, P.H.; Storey, P.; Rusinek, H.; Zhang, J.L.; Yamamoto, A.; Tantillo, K.; Khan, U.; Lim, R.P.; Babb, J.S.; John, D.; et al. Kidney Function: Glomerular Filtration Rate Measurement with MR Renography in Patients with Cirrhosis. Radiology 2011, 259, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choyke, P.L.; Austin, H.A.; Frank, J.A.; Girton, M.E.; Diggs, R.L.; Dwyer, A.J.; Miller, L.; Nussenblatt, R.; McFarland, H.; Simon, T. Hydrated clearance of gadolinium-DTPA as a measurement of glomerular filtration rate. Kidney Int. 1992, 41, 1595–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, K.; Tang, H.; Mishra, P.K.; Macura, S.I.; Lerman, L.O. Measurement of murine kidney functional biomarkers using DCE-MRI: A multi-slice TRICKS technique and semi-automated image processing algorithm. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 63, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.; Summers, P.E.; Keevil, S.F.; Saks, A.M.; Diskin, J.; Hilton, P.J.; Ayers, A.B. Magnetic resonance renography: Optimisation of pulse sequence parameters and Gd-DTPA dose, and comparison with radionuclide renography. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1997, 15, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoruk, U.; Saranathan, M.; Loening, A.M.; Hargreaves, B.A.; Vasanawala, S.S. High temporal resolution dynamic MRI and arterial input function for assessment of GFR in pediatric subjects. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 75, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krepkin, K.; Won, E.; Ramaswamy, K.; Triolo, M.; Stiffelma, M.; Rusinek, H.; Chandarana, H. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MR renography for renal function evaluation in ureteropelvic junction obstruction: Feasibility study. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 202, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Regan, F.; Bohlman, M.E.; Khazan, R.; Rodriguez, R.; SchultzeHaakh, H. MR urography using HASTE imaging in the assessment of ureteric obstruction. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1996, 167, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuther, G.; Kiefer, B.; Wandl, E. Visualization of urinary tract dilatation: Value of single-shot MR urography. Eur. Radiol. 1997, 7, 1276–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudon, M.; Durand, E.; Grenier, N.; Prigent, A.; Balvay, D.; Chaumet-Riffaud, P.; Chaumoitre, K.; Cuenod, C.A.; Filipovic, M.; Galloy, M.A.; et al. Chronic Urinary Obstruction: Evaluation of Dynamic Contrast-enhanced MR Urography for Measurement of Split Renal Function. Radiology 2014, 273, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basak, S.; Buckley, D.L.; Chrysochou, C.; Banerji, A.; Vassallo, D.; Odudu, A.; Kalra, P.A.; Sourbron, S.P. Analytical validation of single-kidney glomerular filtration rate and split renal function as measured with magnetic resonance renography. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 59, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, L.Z.; Chen, J.J.; Yang, X.X.; Senpan, A.; Allen, J.S.; Yanaba, N.; Caruthers, S.D.; Lanza, G.M.; Hammerman, M.R.; Wickline, S.A. Assessing intrarenal nonperfusion and vascular leakage in acute kidney injury with multinuclear 1H/19F MRI and perfluorocarbon nanoparticles. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 71, 2186–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chacon-Caldera, J.; Maunder, A.; Rao, M.; Norquay, G.; Rodgers, O.I.; Clemence, M.; Puddu, C.; Schad, L.R.; Wild, J.M. Dissolved hyperpolarized xenon-129 MRI in human kidneys. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 83, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niles, D.J.; Gordon, J.W.; Huang, G.W.; Reese, S.; Adamson, E.B.; Djamali, A.; Fain, S.B. Evaluation of renal metabolic response to partial ureteral obstruction with hyperpolarized C-13 MRI. NMR Biomed. 2018, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.H.; Longo, D.L.; Aime, S.; Sun, P.Z. Quantitative description of radiofrequency (RF) power-based ratiometric chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) pH imaging. NMR Biomed. 2015, 28, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, M.T.; Gilad, A.A.; Bulte, J.W.M.; van Zijl, P.C.M. Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer Imaging: Advances and Applications; Pan Stanford Publishing: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- García-Martín, M.-L.; Hérigault, G.; Rémy, C.; Farion, R.; Ballesteros, P.; Coles, J.A.; Cerdán, S.; Ziegler, A. Mapping Extracellular pH in Rat Brain Gliomas in Vivo by H Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Imaging: Comparison with Maps of Metabolites. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 6524–6531. [Google Scholar]
- Van Sluis, R.; Bhujwalla, Z.M.; Raghunand, N.; Ballesteros, P.; Alvarez, J.; Cerdan, S.; Galons, J.P.; Gillies, R.J. In vivo imaging of extracellular pH using 1H MRSI. Magn. Reson. Med. 1999, 41, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R.J.; Raghunand, N.; Garcia-Martin, M.L.; Gatenby, R.A. pH imaging. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2004, 23, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, A.I.; Zhang, X.M.; Wojtkowiak, J.W.; Martinez, G.V.; Gillies, R.J. Imaging pH and metastasis. NMR Biomed. 2011, 24, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, G.V.; Zhang, X.; García-Martín, M.L.; Morse, D.L.; Woods, M.; Sherry, A.D.; Gillies, R.J. Imaging the extracellular pH of tumors by MRI after injection of a single cocktail of T1 and T2 contrast agents. NMR Biomed. 2011, 24, 1380–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raghunand, N.; Howison, C.; Sherry, A.D.; Zhang, S.; Gillies, R.J. Renal and systemic pH imaging by contrast-enhanced MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2003, 49, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhujwalla, Z.M.; Artemov, D.; Ballesteros, P.; Cerdan, S.; Gillies, R.J.; Solaiyappan, M. Combined vascular and extracellular pH imaging of solid tumors. NMR Biomed. 2002, 15, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penet, M.F.; Artemov, D.; Farahani, K.; Bhujwalla, Z.M. MR—Eyes for cancer: Looking within an impenetrable disease. NMR Biomed. 2013, 26, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreev, O.A.; Dupuy, A.D.; Segala, M.; Sandugu, S.; Serra, D.A.; Chichester, C.O.; Engelman, D.M.; Reshetnyak, Y.K. Mechanism and uses of a membrane peptide that targets tumors and other acidic tissues in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crawford, T.; Moshnikova, A.; Roles, S.; Carter, L.M.; Lewis, J.S.; Engelman, D.M.; Andreev, O.A.; Reshetnyak, Y.K. ICG pHLIP: A novel agent for fluorescence-guided surgery. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Demoin, D.W.; Wyatt, L.C.; Edwards, K.J.; Abdel-Atti, D.; Sarparanta, M.; Pourat, J.; Longo, V.A.; Carlin, S.D.; Engelman, D.M.; Andreev, O.A.; et al. PET Imaging of Extracellular pH in Tumors with 64Cu- and 18F-Labeled pHLIP Peptides: A Structure–Activity Optimization Study. Bioconjug. Chem. 2016, 27, 2014–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Huang, G.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Ramezani, S.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Zeng, Z.; Luo, M.; et al. A transistor-like pH nanoprobe for tumour detection and image-guided surgery. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, T.; Wang, C.; Lin, Z.; Huang, G.; Sumer, B.D.; Gao, J. Molecular basis of cooperativity in pH-triggered supramolecular self-assembly. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aime, S.; Delli Castelli, D.; Fedeli, F.; Terreno, E. A Paramagnetic MRI-CEST Agent Responsive to Lactate Concentration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 9364–9365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aime, S.; Barge, A.; Delli Castelli, D.; Fedeli, F.; Mortillaro, A.; Nielsen, F.U.; Terreno, E. Paramagnetic Lanthanide(III) complexes as pH-sensitive chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) contrast agents for MRI applications. Magn. Reson. Med. 2002, 47, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.K.; Soesbe, T.C.; Kiefer, G.E.; Zhao, P.Y.; Sherry, A.D. A Responsive Europium(III) Chelate That Provides a Direct Readout of pH by MRI. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 14002–14003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delli Castelli, D.; Terreno, E.; Aime, S. YbIII-HPDO3A: A Dual pH- and Temperature-Responsive CEST Agent. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 1798–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, V.R.; Li, Y.G.; Chen, L.Q.; Howison, C.M.; Flask, C.A.; Pagel, M.D. Measuring in vivo tumor pHe with CEST-FISP MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 67, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McVicar, N.; Li, A.X.; Suchy, M.; Hudson, R.H.E.; Menon, R.S.; Bartha, R. Simultaneous in vivo pH and temperature mapping using a PARACEST-MRI contrast agent. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 70, 1016–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, D.D.; Ferrauto, G.; Cutrin, J.C.; Terreno, E.; Aime, S. In vivo maps of extracellular pH in murine melanoma by CEST–MRI. Magn. Reson. Med 2014, 71, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, K.M.; Balaban, R.S. Determination of pH using water protons and chemical exchange dependent saturation transfer (CEST). Magn. Reson. Med. 2000, 44, 799–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Payen, J.F.; Wilson, D.A.; Traystman, R.J.; van Zijl, P.C.M. Using the amide proton signals of intracellular proteins and peptides to detect pH effects in MRI. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aime, S.; Calabi, L.; Biondi, L.; De Miranda, M.; Ghelli, S.; Paleari, L.; Rebaudengo, C.; Terreno, E. Iopamidol: Exploring the potential use of a well-established x-ray contrast agent for MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005, 53, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, M.T.; Gilad, A.A.; Zhou, J.Y.; Sun, P.Z.; Bulte, J.W.M.; van Zijl, P.C.M. Quantifying exchange rates in chemical exchange saturation transfer agents using the saturation time and saturation power dependencies of the magnetization transfer effect on the magnetic resonance imaging signal (QUEST and QUESP): Ph calibration for poly-L-lysine and a starburst dendrimer. Magn. Reson. Med. 2006, 55, 836–847. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, K.W.Y.; Liu, G.S.; Song, X.L.; Kim, H.; Yu, T.; Arifin, D.R.; Gilad, A.A.; Hanes, J.; Walczak, P.; van Zijl, P.C.M.; et al. MRI-detectable pH nanosensors incorporated into hydrogels for in vivo sensing of transplanted-cell viability. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.Z.; Benner, T.; Kumar, A.; Sorensen, A.G. Investigation of optimizing and translating pH-sensitive pulsed-chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) imaging to a 3T clinical scanner. Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 60, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.L.; Deng, P.C.; Chen, J.; Zhou, B.; Hu, J.; Zou, J.; Lu, W.J.; Xiang, P.; et al. H-1 NMR-based metabolic profiling of human rectal cancer tissue. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.Q.; Howison, C.M.; Jeffery, J.J.; Robey, I.F.; Kuo, P.H.; Pagel, M.D. Evaluations of extracellular pH within in vivo tumors using acidoCEST MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 72, 1408–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Longo, D.L.; Sun, P.Z.; Consolino, L.; Michelotti, F.C.; Uggeri, F.; Aime, S. A General MRI-CEST Ratiometric Approach for pH Imaging: Demonstration of in Vivo pH Mapping with Iobitridol. J. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 14333–14336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Longo, D.L.; Busato, A.; Lanzardo, S.; Antico, F.; Aime, S. Imaging the pH evolution of an acute kidney injury model by means of iopamidol, a MRI-CEST pH-responsive contrast agent. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 70, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, D.L.; Cutrin, J.C.; Michelotti, F.; Irrera, P.; Aime, S. Noninvasive evaluation of renal pH homeostasis after ischemia reperfusion injury by CEST-MRI. NMR Biomed. 2017, 30, e3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavuluri, K.; Manoli, I.; Pass, A.; Li, Y.G.; Vernon, H.J.; Venditti, C.P.; McMahon, M.T. Noninvasive monitoring of chronic kidney disease using pH and perfusion imaging. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindeman, L.R.; Randtke, E.A.; High, R.A.; Jones, K.M.; Howison, C.M.; Pagel, M.D. A comparison of exogenous and endogenous CESTMRI methods for evaluating in vivo pH. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 2766–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, I.Y.; Igarashi, T.; Longo, D.L.; Aime, S.; Sun, P.Z. A generalized ratiometric chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI approach for mapping renal pH using iopamidol. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 1553–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.K.; Zhang, S.R.; Soesbe, T.C.; Yu, J.; Vinogradov, E.; Lenkinski, R.E.; Sherry, A.D. pH imaging of mouse kidneys in vivo using a frequency-dependent paraCEST agent. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 75, 2432–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, S.H.; Wendland, M.F.; Zhang, B.; Tran, A.; Tang, A.; Vandsburger, M.H. Noninvasive imaging of renal urea handling by CEST-MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 83, 1034–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavuluri, K.; Rosenberg, J.T.; Helsper, S.; Bo, S.W.; McMahon, M.T. Amplified detection of phosphocreatine and creatine after supplementation using CEST MRI at high and ultrahigh magnetic fields. J. Magn. Reson. 2020, 313, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Song, X.; Ray Banerjee, S.; Li, Y.; Byun, Y.; Liu, G.; Bhujwalla, Z.M.; Pomper, M.G.; McMahon, M.T. Developing imidazoles as CEST MRI pH sensors. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2016, 11, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaba, M.; Mohan, C. Development of drugs based on imidazole and benzimidazole bioactive heterocycles: Recent advances and future directions. Med. Chem. Res. 2016, 25, 173–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penning, T.D.; Zhu, G.D.; Gandhi, V.B.; Gong, J.C.; Liu, X.S.; Shi, Y.; Klinghofer, V.; Johnson, E.F.; Donawho, C.K.; Frost, D.J.; et al. Discovery of the Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase (PARP) Inhibitor 2-[(R)-2-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]-1H-benzimidazole-4-carboxamide (ABT-888) for the Treatment of Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.M.; Munson, K.; Vagin, O.; Sachs, G. The gastric HK-ATPase: Structure, function, and inhibition. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2009, 457, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sachs, G.; Shin, J.M.; Vagin, O.; Lambrecht, N.; Yakubov, I.; Munson, K. The Gastric H,K ATPase as a Drug Target. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 41, S226–S242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naik, P.; Murumkar, P.; Giridhar, R.; Yadav, M.R. Angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AT1) selective nonpeptidic antagonists—A perspective. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 8418–8456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcóstegui, R.; Labeaga, L.; Innerárity, A.; Berisa, A.; Orjales, A. Preclinical Pharmacology of Bilastine, a New Selective Histamine H1 Receptor Antagonist. Drugs R D 2005, 6, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.K.; Schlosser, M.J.; van Zijl, P.C.M.; Pomper, M.G.; Golay, X.; Zhou, J.Y. Amide proton transfer imaging of human brain tumors at 3T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2006, 56, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.M.; Pollard, A.C.; Pagel, M.D. Clinical applications of chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 47, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, K.M.; Randtke, E.A.; Yoshimaru, E.S.; Howison, C.M.; Chalasani, P.; Klein, R.R.; Chambers, S.K.; Kuo, P.H.; Pagel, M.D. Clinical Translation of Tumor Acidosis Measurements with AcidoCEST MRI. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2017, 19, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Yadav, N.N.; Knutsson, L.; Hua, J.; Kalyani, R.; Hall, E.; Laterra, J.; Blakeley, J.; Strowd, R.; Pomper, M.; et al. Dynamic glucose-enhanced (DGE) MRI: Translation to human scanning and first results in glioma patients. Tomography 2015, 1, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Zhu, H.; Lim, M.; Blair, L.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A.; Messina, S.A.; Eberhart, C.G.; Pomper, M.G.; Laterra, J.; Barker, P.B.; et al. Three-dimensional amide proton transfer MR imaging of gliomas: Initial experience and comparison with gadolinium enhancement. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 38, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bo, S.; Sedaghat, F.; Pavuluri, K.; Rowe, S.P.; Cohen, A.; Kates, M.; McMahon, M.T. Dynamic Contrast Enhanced-MR CEST Urography: An Emerging Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Upper Urinary Tract Obstruction. Tomography 2021, 7, 80-94. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7010008
Bo S, Sedaghat F, Pavuluri K, Rowe SP, Cohen A, Kates M, McMahon MT. Dynamic Contrast Enhanced-MR CEST Urography: An Emerging Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Upper Urinary Tract Obstruction. Tomography. 2021; 7(1):80-94. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleBo, Shaowei, Farzad Sedaghat, KowsalyaDevi Pavuluri, Steven P. Rowe, Andrew Cohen, Max Kates, and Michael T. McMahon. 2021. "Dynamic Contrast Enhanced-MR CEST Urography: An Emerging Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Upper Urinary Tract Obstruction" Tomography 7, no. 1: 80-94. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7010008
APA StyleBo, S., Sedaghat, F., Pavuluri, K., Rowe, S. P., Cohen, A., Kates, M., & McMahon, M. T. (2021). Dynamic Contrast Enhanced-MR CEST Urography: An Emerging Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Upper Urinary Tract Obstruction. Tomography, 7(1), 80-94. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7010008







