-
 Development of Cardiac Computed Tomography for Evaluation of Aortic Valve Stenosis
Development of Cardiac Computed Tomography for Evaluation of Aortic Valve Stenosis -
 Fat Fraction MRI for Longitudinal Assessment of Bone Marrow Heterogeneity in a Mouse Model of Myelofibrosis
Fat Fraction MRI for Longitudinal Assessment of Bone Marrow Heterogeneity in a Mouse Model of Myelofibrosis -
 Feasibility of Sodium and Amide Proton Transfer-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Methods in Mild Steatotic Liver Disease
Feasibility of Sodium and Amide Proton Transfer-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Methods in Mild Steatotic Liver Disease
Journal Description
Tomography
Tomography
is an international, peer-reviewed open access journal on imaging technologies published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, MEDLINE, PMC, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Radiology, Nuclear Medicine and Medical Imaging)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 26.7 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Impact Factor:
2.2 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.2 (2024)
Latest Articles
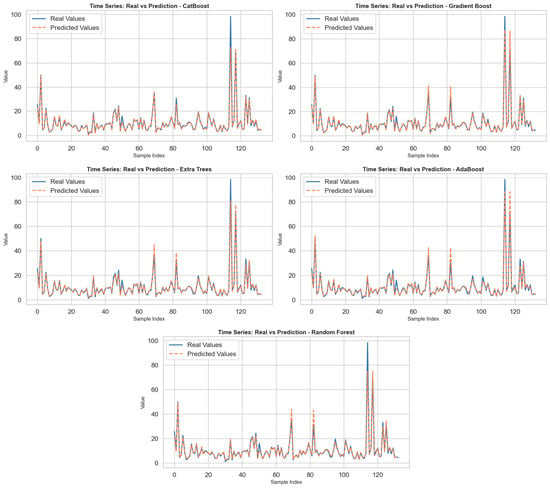
Prediction of Breast Radiation Absorbed Dose Chest CT Examinations Using Machine Learning Techniques
Tomography 2025, 11(12), 142; https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11120142 (registering DOI) - 16 Dec 2025
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: The breast is a highly radiosensitive organ that is directly exposed to ionizing radiation during chest computed tomography (CT) examinations. Excessive radiation exposure increases the risk of radiation-induced malignancies, highlighting the importance of accurate and patient-specific dose estimation. This study aims
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The breast is a highly radiosensitive organ that is directly exposed to ionizing radiation during chest computed tomography (CT) examinations. Excessive radiation exposure increases the risk of radiation-induced malignancies, highlighting the importance of accurate and patient-specific dose estimation. This study aims to estimate the effective radiation dose absorbed by the breast during chest CT examinations using a machine learning (ML)-based personalized prediction approach. Methods: In this retrospective study, a total of 653 female patients who underwent both mammography and chest CT between 2020 and 2024 were included. A structured database was created incorporating demographic and anatomical parameters, including body weight, height, body mass index (BMI), and breast thickness (mm) obtained from mammography, along with dose length product (DLP) values from chest CT scans. Five regression-based ML algorithms—CatBoost, Gradient Boosting, Extra Trees, AdaBoost, and Random Forest—were implemented to predict breast radiation dose. Model performance was evaluated using Mean Squared Error (MSE), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE), and the Coefficient of Determination (R2). Results: Among the evaluated models, the CatBoost algorithm optimized with Particle Swarm Optimization (CatBoostPSO) achieved the best overall predictive performance, yielding the lowest MSE (0.3795), MAE (0.3846), and MAPE (4.37%), along with the highest R2 value (0.9875). CatBoost and Gradient Boosting models demonstrated predictions most closely aligned with ground truth values, indicating that ensemble-based and dynamically optimized models are particularly effective for breast dose estimation. Conclusions: The proposed machine learning framework enables rapid, accurate, and clinically applicable estimation of breast radiation dose during chest CT examinations. This patient-specific approach has strong potential to support personalized radiation dose monitoring and optimization strategies, contributing to improved radiation safety in clinical practice.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Volume and Attenuation Characteristics of Chronic Subdural Hematoma: An Annotated Patient Cohort of 257 Patients with Interrater Reliability Assessments
by
Mattias Drake, Emma Hall, Birgitta Ramgren, Björn M. Hansen and Johan Wassélius
Tomography 2025, 11(12), 141; https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11120141 - 16 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Accurate volumetry and imaging characterization of chronic subdural hematoma (cSDH) are essential for prognostication and treatment planning, but manual assessment is time-consuming and therefore underutilized. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed preoperative non-contrast CT (NCCT) scans of 257 patients undergoing first-time surgery for uni-
[...] Read more.
Background: Accurate volumetry and imaging characterization of chronic subdural hematoma (cSDH) are essential for prognostication and treatment planning, but manual assessment is time-consuming and therefore underutilized. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed preoperative non-contrast CT (NCCT) scans of 257 patients undergoing first-time surgery for uni- or bilateral cSDH. Hematoma volumes were measured manually using a semi-automated area-outlining tool on every second axial slice and compared with the volumes estimated through the ABC/2 formula. Hematoma attenuation patterns and components were categorized, and interrater reliability was assessed for volume, maximum diameter, and imaging features using intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) and Cohen’s κ. Results: A total of 339 hematomas were evaluated. Manual and ABC/2 volume measurements correlated strongly (R2 = 0.83, ICC [3, 1] = 0.90). The interrater agreement for manual volumetry was excellent (ICC [2, 1] = 0.96). Agreement was also excellent for maximum diameter (ICC [2, 1] > 0.9) and good for midline shift assessment (κ = 0.81). Agreement was moderate for the identification of fresh clots, trabeculations, and laminations (κ = 0.62–0.72) but poor for general attenuation patterns (κ = 0.44). Conclusions: The manual volumetry of cSDH is feasible and highly reproducible between raters of different experience levels. These results provide a robust reference standard for the validation of automated volumetry tools and support the implementation of quantitative hematoma assessment in future clinical trials and routine care.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Neuroimaging)
►▼
Show Figures
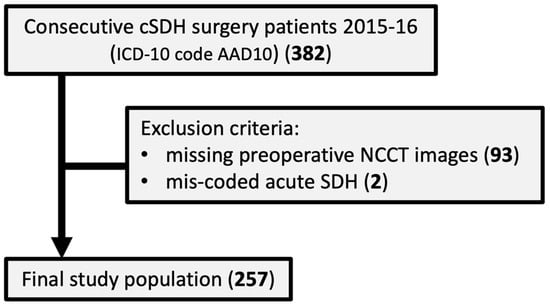
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Pilot Evaluation of a Deep Learning Model for Nasogastric Tube Verification on Chest Radiographs: A Single-Center Retrospective Study
by
Sang Won Park, Doohee Lee, Jae Eun Song, Yoon Kim, Hyun-Soo Choi, Seung-Joon Lee, Woo Jin Kim, Kyoung Min Moon and Oh Beom Kwon
Tomography 2025, 11(12), 140; https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11120140 - 15 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Accurate confirmation of nasogastric (NG) tubes is essential for patient safety, but delays and variability in interpretation remain common in clinical practice. Deep learning (DL) models have shown potential for assisting in this task, but real-world performance, particularly in detecting malpositioned tubes,
[...] Read more.
Background: Accurate confirmation of nasogastric (NG) tubes is essential for patient safety, but delays and variability in interpretation remain common in clinical practice. Deep learning (DL) models have shown potential for assisting in this task, but real-world performance, particularly in detecting malpositioned tubes, remains insufficiently characterized. Methods: We conducted a pilot evaluation of a previously developed DL model using 135 chest radiographs from Kangwon National University Hospital. Expert physicians established the reference standard. Model performance was assessed and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and precision recall curve (PRC) analyses were performed. Differences between correctly classified and misclassified cases were examined using Wilcoxon rank-sum and Fisher’s exact tests to explore potential clinical or radiographic contributors to model failure. Results: The model correctly classified 129 of 135 cases. The sensitivity was 96.1% (95% confidence interval (CI): 92.2–98.9%), specificity was 85.7% (95% CI: 42.2–97.7%), positive predictive value (PPV) was 99.2% (95% CI: 96.1–99.9%), negative predictive value (NPV) was 54.5% (95% CI: 25.4–80.8%), balanced accuracy was 90.8%, and F1-score was 0.976. The area under the ROC curve was 0.970 (95% CI: 0.929–1.000) and that under the PRC was 0.727 (95% CI: 0.289–1.000), reflecting substantial uncertainty related to the very small number of incomplete cases (n = 6). No statistically significant differences in clinical or radiographic characteristics were observed between correctly classified and misclassified cases. Conclusions: The DL model performed well in identifying correctly positioned NG tubes but demonstrated limited and unstable performance for detecting incomplete placements. Given the safety implications of misclassification, the model should be used only as an assistive tool with mandatory physician oversight. Larger, multi-center studies with greater representation of incomplete cases are required to obtain more reliable estimates and support safe clinical implementation.
Full article
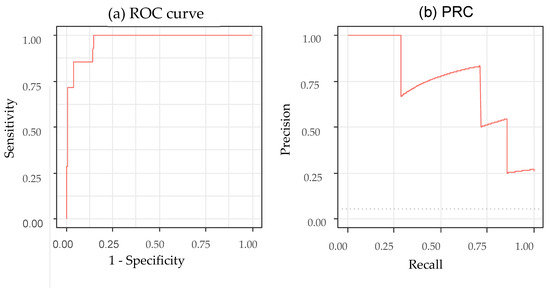
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Aortic Valve Calcium Scoring Using True and Virtual Non-Contrast Reconstructions on Photon-Counting CT with Differing Slice Increments: Impact on Calcium Severity Classifications
by
Mandeep Singh, Amirhossein Moaddab, Doosup Shin, Jonathan Weber, Karen Chau, Ali H. Dakroub, Roosha Parikh, Karli Pipitone, Ziad A. Ali and Omar K. Khalique
Tomography 2025, 11(12), 139; https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11120139 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Aortic valve calcification is commonly evaluated using 3.0 mm true non-contrast (TNC) computed tomography (CT) images. This study evaluates the reproducibility of virtual non-contrast (VNC) reconstructions at different slice intervals using photon-counting detector CT (PCD-CT). Methods: In this retrospective study,
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Aortic valve calcification is commonly evaluated using 3.0 mm true non-contrast (TNC) computed tomography (CT) images. This study evaluates the reproducibility of virtual non-contrast (VNC) reconstructions at different slice intervals using photon-counting detector CT (PCD-CT). Methods: In this retrospective study, we included 279 consecutive patients, who underwent PCD-CT for evaluation of native aortic valve between February 2023 and December 2023 with both TNC and VNC images at 3.0 and 1.5 mm slice intervals. Aortic valve calcium score (AVCS) and aortic valve calcium volume (AVCV) were compared between the two methods using paired t-tests. Agreement for continuous variables was assessed using inter-class coefficients (ICCs). Cohen’s Kappa (κ) was calculated to evaluate the agreement between different modalities in diagnosing severe AV calcification. Results: Compared to the standard, TNC images at 1.5 mm intervals showed higher AVCS (mean difference: −290 ± 418, p < 0.001), with high reproducibility between techniques (CS: ICC 0.969, [IQR 0.962, 0.975]). Compared with reference, VNC showed no significant differences in AVCS at either slice intervals, with excellent reproducibility (3.0 mm, ICC 0.970 [0.963, 0.976]; 1.5 mm, ICC 0.971 [0.964, 0.977]). Compared to TNC 3.0 mm, strong concordance was observed using other reconstruction techniques in assessing severe AV calcification (κ = 0.81 [95% CI: 0.74–0.88], 0.83 [95% CI: 0.76–0.90], and 0.83 [95% CI: 0.76–0.90] for TNC at 1.5 mm, VNC at 3.0 mm, and 1.5 mm, respectively), with low misclassification rates. Conclusions: Our study highlights high reproducibility in the evaluation of AVCS by VNC reconstruction at 3.0 and 1.5 mm intervals compared with reference offering a reliable alternative with an excellent diagnostic accuracy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cardiovascular Imaging)
►▼
Show Figures
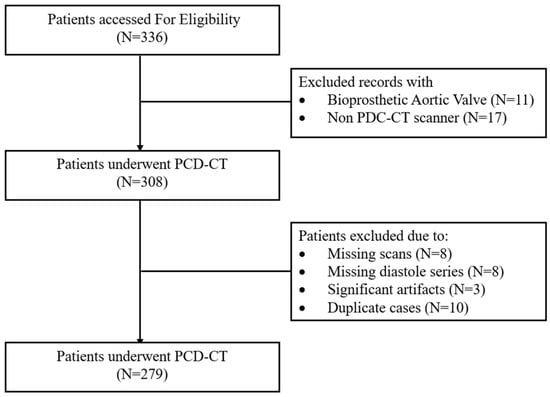
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Clinically Focused Computer-Aided Diagnosis for Breast Cancer Using SE and CBAM with Multi-Head Attention
by
Zeki Ogut, Mucahit Karaduman and Muhammed Yildirim
Tomography 2025, 11(12), 138; https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11120138 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Breast cancer is one of the most common malignancies in women worldwide. Early diagnosis and accurate classification in breast cancer detection are among the most critical factors determining treatment success and patient survival. In this study, a deep learning-based model was developed
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Breast cancer is one of the most common malignancies in women worldwide. Early diagnosis and accurate classification in breast cancer detection are among the most critical factors determining treatment success and patient survival. In this study, a deep learning-based model was developed that can classify benign, malignant, and normal breast tissues from ultrasound images with high accuracy and achieve better results than the methods commonly used in the literature. Methods: The proposed model was trained on a dataset of breast ultrasound images, and its classification performance was evaluated. The model is designed to effectively learn both local textural features and global contextual relationships by combining Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) blocks, which emphasize channel-level feature importance, and Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) attention mechanisms, which focus on spatial information, with the MHA structure. The model’s performance is compared with three commonly used convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and three Vision Transformer (ViT) architectures. Results: The developed model achieved an accuracy rate of 96.03% in experimental analyses, outperforming both the six compared models and similar studies in the literature. Additionally, the proposed model was tested on a second dataset consisting of histopathological images and achieved an average accuracy of 99.55%. The results demonstrate that the model can effectively learn meaningful spatial and contextual information from ultrasound data and distinguish different tissue types with high accuracy. Conclusions: This study demonstrates the potential of deep learning-based approaches in breast ultrasound-based computer-aided diagnostic systems, providing a reliable, fast, and accurate decision support tool for early diagnosis. The results obtained with the proposed model suggest that it can significantly contribute to patient management by improving diagnostic accuracy in clinical applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Imaging in Cancer Diagnosis)
►▼
Show Figures
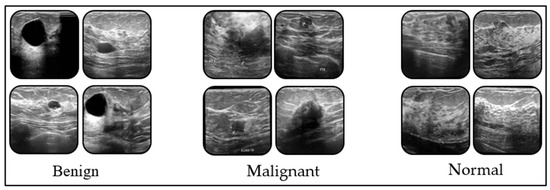
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Angiovolume and Peak Enhancement on Preoperative CAD-Derived MRI as Prognostic Factors in Primary Operable Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
by
Bo La Yun, Sun Mi Kim, Sung Ui Shin, Su Min Cho, Yoon Yeong Choi and Mijung Jang
Tomography 2025, 11(12), 137; https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11120137 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: To identify preoperative MRI features using computer-assisted diagnosis (CAD) that are associated with invasive disease-free survival (IDFS) and distant metastasis-free survival (DDFS) in patients with primarily operable triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Methods: This retrospective study was approved by the institutional review board
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: To identify preoperative MRI features using computer-assisted diagnosis (CAD) that are associated with invasive disease-free survival (IDFS) and distant metastasis-free survival (DDFS) in patients with primarily operable triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Methods: This retrospective study was approved by the institutional review board with informed consent was waived. Between January 2012 and December 2014, 74 consecutive women with primary TNBC (mean age, 51 years; range, 29–77 years) who underwent preoperative MRI were included and followed until August 2021. Dynamic contrast-enhanced and T2-weighted images were obtained using 3T scanners. Peritumoral edema and central necrosis were evaluated retrospectively. CAD was used to extract 3D diameters, angiovolume, and kinetic parameters, and kinetic heterogeneity was calculated. Cox proportional hazards models were used to assess associations between MRI features and IDFS and DDFS, adjusting for clinicopathologic factors. Results: During a median follow-up of 80.9 months, 12 patients developed invasive disease, and 8 developed distant metastasis. In multivariable analysis, peak enhancement (hazard ratio [HR], 1.40; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.06–1.84; p = 0.019) and angiovolume (HR, 2.86; 95% CI, 1.26–6.47; p = 0.012) were independently associated with IDFS, whereas angiovolume (HR, 2.47; 95% CI: 1.28–4.78; p = 0.007) was independently associated with DDFS. Conclusions: Preoperative CAD-derived MRI features, particularly peak enhancement and angiovolume, were associated with IDFS in TNBC patients whereas angiovolume alone was associated with DDFS.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cancer Imaging)
►▼
Show Figures
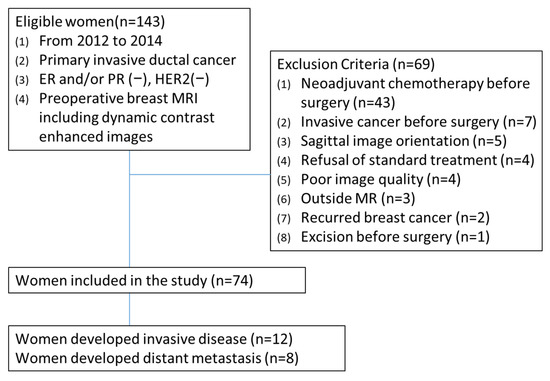
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Quantitative Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Forearm in Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1
by
Sydney Eierle, Tanja Taivassalo, Hyunjun Park, Korey D. Cooke, Zahra Moslemi, Sean C. Forbes, Glenn A. Walter, Krista Vandenborne, S. H. Subramony and Donovan J. Lott
Tomography 2025, 11(12), 136; https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11120136 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Introduction: Myotonic dystrophy type 1 is the most prevalent muscular dystrophy in adults, characterized by weakness, impaired functional abilities, and myotonia. However, little is known about the relationship between quantitative MRI measures (fat fraction and T2 relaxation time) and clinical findings of
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Myotonic dystrophy type 1 is the most prevalent muscular dystrophy in adults, characterized by weakness, impaired functional abilities, and myotonia. However, little is known about the relationship between quantitative MRI measures (fat fraction and T2 relaxation time) and clinical findings of the upper extremity. This study assessed forearm muscle structure in patients with myotonic dystrophy using quantitative MRI and correlated these measures with strength, function, and handgrip myotonia. Materials and Methods: Eighteen adults with myotonic dystrophy type 1 underwent MRI using three-point Dixon and T2 spin echo imaging of the forearm. Results: The average fat fraction and T2 relaxation time were greatest in the flexor digitorum profundus (26.7% and 55.6 ms, respectively). Correlations were found between quantitative MRI values and clinical tests of strength (r = −0.61 to −0.92, p < 0.01), function (r = −0.64 to −0.83, p < 0.01), and handgrip myotonia (r = 0.48, p < 0.05). Overall, the anterior forearm fat fraction values showed higher correlations with strength and function compared to those of the posterior forearm. Discussion: Our results support the use of quantitative MRI measures to assess forearm disease pathology and show potential to monitor the effectiveness of therapeutic treatments in patients with myotonic dystrophy type 1.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Projection Images for Visual Quality Control of Automated Left and Right Lung Segmentations on T1-Weighted MRI in Large-Scale Clinical Cohort Studies
by
Tobias Norajitra, Christopher L. Schlett, Ricarda von Krüchten, Prerana Agarwal, Ashis Ravindran, Thuy Duong Do, Lisa Kausch, Stefan Karrasch, Hans-Ulrich Kauczor, Klaus Maier-Hein and Claudius Melzig
Tomography 2025, 11(12), 135; https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11120135 - 29 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: To assess diagnostic accuracy of two-dimensional (2D) projection methods for rapid visual quality control of automated volumetric (3D) lung segmentations compared with slice-based 3D review of segmentation results for application in large-scale studies. Methods: Segmentation of right and left lungs
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: To assess diagnostic accuracy of two-dimensional (2D) projection methods for rapid visual quality control of automated volumetric (3D) lung segmentations compared with slice-based 3D review of segmentation results for application in large-scale studies. Methods: Segmentation of right and left lungs on T1-weighted MRI of 300 participants of the German National Cohort (NAKO) study was performed using the nnU-NET framework. Three variants of 2D projection images of segmentation masks were created: maximum intensity projection (MIP) using pseudo-chromadepth encoding with different color spectra for right and left lung (Colored_MIP) and standard deviation projection of segmentation mask outlines, encoded in black-and-white (Gray_outline) or using color-encoding (Colored_outline). The worst of two ratings by two independent raters conducting slice-based review for segmentation errors on underlying imaging data and review for mislabeling errors served as the standard of reference. All variants were evaluated by five raters each for identification of segmentation errors and the majority rating was used as index test. The time required for review was recorded and diagnostic accuracies were calculated. Results: Sensitivities of Colored_MIP, Colored_outline and Gray_outline were 88.2% [95%-CI 78.7%; 94.4%], 89.5% [80.3%; 95.3%] and 78.9% [68.1%; 87.5%]; specificities were 98.7% [96.1%; 99.7%], 96.4% [93.1%; 98.5%] and 98.7% [96.1%; 99.7%]; and F1-scores were 0.918, 0.895 and 0.863, respectively. Mean time per case and rater required for evaluation was 2.8 ± 0.9 s for Colored_outline, 1.7 ± 0.1 s for Colored_MIP, and 2.0 ± 0.4 s for Gray_outline. Conclusions: The 2D segmentation mask projection images enabled the detection of segmentation errors of automated 3D segmentations of left and right lungs based on MRI with high diagnostic accuracy, especially when using color-encoding. The method enabled evaluation within a matter of seconds per case. Segmentation mask projection images may assist in visual quality control of automated segmentations in large-scale studies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Cutting-Edge Applications: Artificial Intelligence and Deep Learning Revolutionizing CT and MRI)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Question of Dose? Ultra-Low Dose Chest CT on Photon-Counting CT in People with Cystic Fibrosis
by
Marcel Opitz, Matthias Welsner, Halil I. Tazeoglu, Florian Stehling, Sivagurunathan Sutharsan, Dirk Westhölter, Erik Büscher, Christian Taube, Nika Guberina, Denise Bos, Marcel Drews, Daniel Rosok, Sebastian Zensen, Johannes Haubold, Lale Umutlu, Michael Forsting and Marko Frings
Tomography 2025, 11(12), 134; https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11120134 - 27 Nov 2025
Abstract
Objective: Chest computed tomography (CT) is a key component of the diagnostic assessment of people with cystic fibrosis (PwCF) and is increasingly replacing chest radiography. Due to improvements in life expectancy, radiation exposure has become a growing concern in PwCF. Photon-counting CT (PCCT)
[...] Read more.
Objective: Chest computed tomography (CT) is a key component of the diagnostic assessment of people with cystic fibrosis (PwCF) and is increasingly replacing chest radiography. Due to improvements in life expectancy, radiation exposure has become a growing concern in PwCF. Photon-counting CT (PCCT) has the potential to reduce the risk of radiation-induced malignancies while maintaining diagnostic accuracy. This study aimed to compare the radiation dose and image quality of low-dose high-resolution (LD-HR) and ultra-low-dose high-resolution (ULD-HR) CT protocols using PCCT in PwCF. Methods: This retrospective study included 72 PwCF, with 36 undergoing a LD-HR chest CT protocol and 36 receiving an ULD-HR protocol on a PCCT. The radiation dose and image quality were assessed by comparing the effective dose and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Three blinded radiologists evaluated the overall image quality, sharpness, noise, and assessability of the bronchi, bronchial wall thickening, and bronchiolitis using a five-point Likert scale. Results: The ULD-HR PCCT protocol reduced radiation exposure by approximately 65% compared with the LD-HR PCCT protocol (median effective dose: 0.19 vs. 0.55 mSv, p < 0.001). While LD-HR images were consistently rated higher than ULD-HR images (p < 0.001), both protocols maintained diagnostic significance (median image quality rating of “4-good”). The average SNR of the lung parenchyma was significantly lower with ULD-HR PCCT compared to LD-HR PCCT (p < 0.001). Conclusions: ULD-HR PCCT significantly reduced radiation exposure while maintaining good diagnostic image quality in PwCF. The effective dose of ULD-HR PCCT is only twice that of a two-plane chest X-ray, making it a viable low-radiation alternative for routine imaging in PwCF.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Medical Image Analysis in CT Imaging)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Quantitative Ultrasound Grayscale Analysis and Size of Benign and Malignant Solid Thyroid Nodules
by
Salahaden R. Sultan, Faisal Albin Hajji, Abdulrahman Alhazmi, Shahad Alamri, Abrar Alsulami, Ahmed Albukhari, Asseel Filimban, Bander Almutairi, Ahmad Albngali, Reham Kaifi, Mohammad Khayat, Mohammed Alkharaiji, Mohammad Khalil and Abrar Alfatni
Tomography 2025, 11(12), 133; https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11120133 - 27 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Ultrasound is the primary imaging modality for evaluating thyroid nodules, with echogenicity and nodule size serving as parameters for malignancy risk stratification. Though the TI-RADS classification system is standardized, interpretation varies among observers due to subjectivity, and can affect diagnostic consistency. This
[...] Read more.
Background: Ultrasound is the primary imaging modality for evaluating thyroid nodules, with echogenicity and nodule size serving as parameters for malignancy risk stratification. Though the TI-RADS classification system is standardized, interpretation varies among observers due to subjectivity, and can affect diagnostic consistency. This study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic and interobserver agreement of quantitative ultrasound gray-scale analysis and nodule area in differentiating benign from malignant solid thyroid nodules. Methods: This retrospective study reviewed 600 patients who underwent thyroid ultrasound at King Abdulaziz University Hospital, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, in 2023 and 2024. Of these 600, 107 adult patients with 116 solid thyroid nodules (96 benign and 20 malignant) who subsequently underwent ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration were included in the final analysis. From B-mode ultrasound images, the grayscale median (GSM) values of each nodule and adjacent normal thyroid tissue were measured using Adobe Photoshop. The GSM ratio (GSMr) was calculated by dividing nodule GSM by normal tissue GSM. Nodule size, taken as cross-sectional area, was assessed using ImageJ software version 1.53. The Mann–Whitney U test was used to compare GSMr and the area between benign and malignant nodules. Inter-observer agreement was evaluated using the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). Results: Malignant nodules had significantly lower GSMr compared to benign nodules (malignant: median 0.76, IQR 0.27; benign: median 0.88, IQR 0.55, p = 0.02). Malignant nodules were also significantly larger than benign nodules (malignant: median 2.77 cm2, IQR: 5.08; benign: median 1.78 cm2, IQR 1.65, p = 0.02). Inter-observer reproducibility was excellent for both GSMr (ICC = 0.998) and area (ICC = 0.997). Conclusions: Quantitative ultrasound assessment of grayscale echogenicity and nodule area provides valuable diagnostic information for differentiating benign from malignant solid thyroid nodules. These objective measures may enhance diagnostic confidence and support more precise clinical decision-making in thyroid nodule evaluation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Imaging in Cancer Diagnosis)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Accuracy of Ultra-Fast Low-Field MRI (0.55 T) for Lung Nodule Detection with Ultra-Short Echo Time Sequences
by
Maximilian Hinsen, Armin Michael Nagel, Nadine Bayerl, Hans-Peter Fautz, Thomas Benkert, Matthias Stefan May, Michael Uder and Rafael Heiss
Tomography 2025, 11(12), 132; https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11120132 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Lung nodules are a common radiological finding that can be caused by a variety of reasons, ranging from benign granulomas and scarring to the early stages of primary lung malignancies and metastases [...]
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
3D Imaging of Proton FLASH Radiation Using a Multi-Detector Small Animal PET System
by
Wen Li, Yuncheng Zhong, Youfang Lai, Lingshu Yin, Daniel Sforza, Devin Miles, Heng Li and Xun Jia
Tomography 2025, 11(12), 131; https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11120131 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Objectives: Ultra-high dose-rate FLASH radiotherapy has demonstrated strong potential in reducing normal tissue toxicity while maintaining effective tumor control. However, its underlying radiobiological mechanisms remain unclear, highlighting the need for novel approaches to probe the effects of radiation during and immediately after delivery.
[...] Read more.
Objectives: Ultra-high dose-rate FLASH radiotherapy has demonstrated strong potential in reducing normal tissue toxicity while maintaining effective tumor control. However, its underlying radiobiological mechanisms remain unclear, highlighting the need for novel approaches to probe the effects of radiation during and immediately after delivery. This study presents the first exploration of 3D PET imaging of positron-emitting nuclei (PENs) generated by a FLASH proton beam. Methods: A home-built 12-panel preclinical small-animal PET system was employed for recording coincidence events. A 142.4 MeV FLASH proton beam with a 100 ms delivery time was directed into a solid water phantom. PET coincidence signals were recorded during the first 1 s and up to 11 min. The system’s capability for 3D localization was also assessed, and Monte Carlo simulations were performed for validation. Results: The PET system successfully recorded coincidence data within the first second, including the 100 ms beam delivery interval. Detector dead-time effects under the high beam flux were observed, leading to underestimated event counts. Following irradiation, the measured activity and decay behavior were consistent with simulations. The PET system accurately reconstructed the spatial distribution of PEN activities, with discrepancies in measured versus calculated line profiles ranging from 3.35–6.85%. Reconstructed PET images enabled reliable 3D localization with sub-millimeter accuracy in both lateral and depth dimensions. Conclusions: Our findings demonstrate that a multi-detector PET system is a promising tool for investigating the radiation effects of FLASH beams.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Multimodal CT and MRI Radiomics Integrated with Clinical Models Predict Pathological Complete Response in ESCC Following Neoadjuvant Immunochemotherapy
by
Longgao Liu, Chufeng Zeng, Lizhi Liu, Shumin Zhou, Weihua Wu, Peng Lin, Jianhua Fu, Tiehua Rong, Xu Zhang and Xiaodong Su
Tomography 2025, 11(11), 130; https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11110130 - 19 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: This research focused on evaluating the utility of multimodal radiomics integrated with machine learning to predict pathological complete response (pCR) in a prospective cohort of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) patients undergoing neoadjuvant immunochemotherapy (nICT). Methods: We retrospectively analyzed prospectively collected trial
[...] Read more.
Background: This research focused on evaluating the utility of multimodal radiomics integrated with machine learning to predict pathological complete response (pCR) in a prospective cohort of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) patients undergoing neoadjuvant immunochemotherapy (nICT). Methods: We retrospectively analyzed prospectively collected trial data from 66 ESCC patients. Radiomic features were extracted from computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images. Four machine learning algorithms—Random Forest (RF), logistic regression, Support Vector Machine, and Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost)—were applied with leave-one-out cross-validation to predict pCR after nICT. The predictive performance of the models was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic curve analysis. Results: In total, 851 features were identified. Among the four machine learning algorithms, the XGBoost machine learning method demonstrated the best model performance across CT, MRI, and clinical feature-based models. Furthermore, the integrated model demonstrated superior performance compared to individual models based solely on CT, MRI, or clinical features across all machine learning algorithms. Among these, the XGboost-based integrated model achieved the highest performance on the test set, with an AUC of 0.961, a TPR of 84.2%, a TNR of 95.7%, a PPV 88.9% of and a NPV of 93.8%. Decision curve analysis validated the model’s robust clinical utility, with calibration curves demonstrating strong concordance between predicted and observed therapeutic responses. Conclusions: The study demonstrates the potential for predicting pCR in patients with ESCC treated with standardized neoadjuvant chemotherapy and PD-1 inhibitors using machine learning methods that integrate multimodal CT and MRI images with clinical features.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Clinical Value of Routine Preoperative Ultrasonography in Bariatric Surgery Candidates: A Retrospective Analysis of 1119 Cases
by
Sangar Abdullah, Güney Özkaya, Adnan Gündoğdu and Murat Şendur
Tomography 2025, 11(11), 129; https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11110129 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Preoperative evaluation in bariatric surgery aims to minimize perioperative risks and identify comorbid abdominal pathologies that may influence surgical planning. The role of routine abdominal ultrasonography (USG) remains debatable. Methods: This retrospective study included 1119 consecutive candidates for bariatric surgery who underwent
[...] Read more.
Background: Preoperative evaluation in bariatric surgery aims to minimize perioperative risks and identify comorbid abdominal pathologies that may influence surgical planning. The role of routine abdominal ultrasonography (USG) remains debatable. Methods: This retrospective study included 1119 consecutive candidates for bariatric surgery who underwent routine preoperative ultrasonography (USG) between January 2022 and October 2024. Patients were stratified by BMI and categorized according to USG findings as normal, incidental, requiring follow-up/concomitant procedures, or necessitating cancellation. Baseline characteristics, USG findings, surgical outcomes, and predictors of cancellation were analyzed using univariate, multivariate, and Firth’s penalized logistic regression analyses. Ultrasonographic findings were further stratified as clinically significant (requiring intervention) or non-clinically significant (not requiring intervention) to standardize interpretation. Results: Abnormal USG findings were present in 77.5% of patients, with hepatic steatosis (60.8% [n = 680]), hepatomegaly (21.5%), and gallstones (13.9%) being the most frequent. Higher BMI was significantly associated with hepatomegaly, steatosis, and gallstones (all p < 0.05), but not with surgical cancellation. Bariatric surgery was cancelled in 11 patients (1.0%) due to critical findings exclusively identified on USG, including large ovarian/uterine masses, choledochal cysts, and suspected malignancies. In multivariate and Firth-adjusted regression, large ovarian/uterine masses (adjusted OR 12.9, 95% CI 3.0–55.2, p = 0.001; Firth OR 11.4, 95% CI 2.5–51.4, p = 0.002) and choledochal cysts (Firth OR 29.7, 95% CI 1.8–489.5, p = 0.048) emerged as independent predictors of cancellation. Conclusions: Although the overall cancellation rate was low, the detection of critical USG findings in 1.0% of patients had major clinical implications, preventing inappropriate or unsafe surgery and enabling timely referral for specialist management. Routine preoperative ultrasonography thus offers a clinically meaningful safeguard in bariatric surgery, supporting its inclusion in preoperative assessment algorithms.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Comparison of Virtual Dose Simulator and K-Factor Methods for Effective Dose Assessment in Thoracic CT
by
Roch Listz Maurice
Tomography 2025, 11(11), 128; https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11110128 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Rationale and Objective: Medical imaging, particularly computed tomography (CT), is the largest man-made contributor to collective radiation exposure. This study compares methods for assessing CT radiation dose, focusing on thoracic examinations. Population investigated: We retrospectively analyzed 3956 non-contrast thoracic CT exams from 1553
[...] Read more.
Rationale and Objective: Medical imaging, particularly computed tomography (CT), is the largest man-made contributor to collective radiation exposure. This study compares methods for assessing CT radiation dose, focusing on thoracic examinations. Population investigated: We retrospectively analyzed 3956 non-contrast thoracic CT exams from 1553 females (mean age 70 ± 12 years) and 2403 males (mean age 69 ± 12 years). Methods: Data were acquired using a Siemens Somatom Force CT-Scanner (installed in 2015). Exposure parameters and patient somatic data were recorded and used as inputs for the Virtual Dose Simulator (VDS), which served as the gold standard for effective dose (EDref) measurement. Additionally, ED was calculated using two ICRP-103 K-factor methods: Shrimpton et al. (EDshr) and Romanyukha et al. (EDrom). Results: Regression analysis demonstrated strong linear relationships between EDref and both weight and BMI (R2 ≥ 0.84), with EDref values ranging from 1.55 to 4.59 mSv. Even stronger linear relationships were observed between EDref and CT scanner tube current, particularly for women (R2 = 0.93) and men (R2 = 0.90). Similar trends emerged for dose-length product (DLP), which showed high correlations for both women (R2 = 0.95) and men (R2 = 0.94). Compared to VDS, EDrom underestimated women’s doses by 10% and slightly overestimated men’s doses by 1%, while EDshr underestimated the effective dose by 18% for women and 9% for men. Conclusion: This study demonstrates that K-factor methods provide a simple, efficient, and clinically practical approach for both individual cumulative dose monitoring (critical for patients requiring repeated imaging) and population-level dose assessment (essential for epidemiological risk evaluation). The high reliability of K-factor-based estimates, as demonstrated in this work, underscores their potential for integration into clinical practice to enhance dose optimization and patient safety.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Photon-Counting Micro-CT for Bone Morphometry in Murine Models
by
Rohan Nadkarni, Zay Yar Han, Alex J. Allphin, Darin P. Clark, Alexandra Badea and Cristian T. Badea
Tomography 2025, 11(11), 127; https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11110127 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: This study evaluates photon-counting CT (PCCT) for the imaging of mouse femurs and investigates how APOE genotype, sex, and humanized nitric oxide synthase (HN) expression influence bone morphology during aging. Methods: A custom-built micro-CT system with a photon-counting detector (PCD) was used
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: This study evaluates photon-counting CT (PCCT) for the imaging of mouse femurs and investigates how APOE genotype, sex, and humanized nitric oxide synthase (HN) expression influence bone morphology during aging. Methods: A custom-built micro-CT system with a photon-counting detector (PCD) was used to acquire dual-energy scans of mouse femur samples. PCCT projections were corrected for tile gain differences, iteratively reconstructed with 20 µm isotropic resolution, and decomposed into calcium and water maps. PCD spatial resolution was benchmarked against an energy-integrating detector (EID) using line profiles through trabecular bone. The contrast-to-noise ratio quantified the effects of iterative reconstruction and material decomposition. Femur features such as mean cortical thickness, mean trabecular spacing (TbSp_mean), and trabecular bone volume fraction (BV/TV) were extracted from calcium maps using BoneJ. The statistical analysis used 57 aged mice representing the APOE22, APOE33, and APOE44 genotypes, including 27 expressing HN. We used generalized linear models (GLMs) to evaluate the main interaction effects of age, sex, genotype, and HN status on femur features and Mann–Whitney U tests for stratified analyses. Results: PCCT outperformed EID-CT in spatial resolution and enabled the effective separation of calcium and water. Female HN mice exhibited reduced BV/TV compared to both male HN and female non-HN mice. While genotype effects were modest, a genotype-by-sex stratified analysis found significant effects of HN status in female APOE22 and APOE44 mice only. Linear regression showed that age significantly decreased cortical thickness and increased TbSp_mean in male mice only. Conclusions: These results demonstrate PCCT’s utility for femur analysis and reveal strong effects of sex/HN interaction on trabecular bone health in mice.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Prediction of Microsatellite Instability in Colorectal Cancer Using Two Internally Validated Radiomic Models
by
Antonio Galluzzo, Ginevra Danti, Linda Calistri, Diletta Cozzi, Daniele Lavacchi, Daniele Rossini, Lorenzo Antonuzzo, Sebastiano Paolucci, Francesca Castiglione, Luca Messerini, Fabio Cianchi and Vittorio Miele
Tomography 2025, 11(11), 126; https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11110126 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
Objectives: To develop two different radiomic models based on preoperative contrast-enhanced computed tomography (PP CT) to predict microsatellite instability (MSI) in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC) before surgery. Methods: PP CT scans of 115 CC patients were segmented using 3DSlicer (v5.6.1). Model I
[...] Read more.
Objectives: To develop two different radiomic models based on preoperative contrast-enhanced computed tomography (PP CT) to predict microsatellite instability (MSI) in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC) before surgery. Methods: PP CT scans of 115 CC patients were segmented using 3DSlicer (v5.6.1). Model I included images from three different scanners (GE, Siemens, Philips), while Model II used only one scanner (GE). For Model I, 80 patients were used for training and 35 for internal validation; for Model II, 46 and 24 patients were used, respectively. Data on sex, age, tumour location, and MSI genomic status were collected. A total of 107 radiomic features (RFs) were extracted, and 30 and 35 RFs were identified as relevant for Models I and II, respectively, using the t-test or Mann–Whitney test (p < 0.05). The most robust RFs were selected using the LASSO regression method. Both models were internally validated. Results: Model I, based on 2 RFs and 1 clinical feature (LOCATION) achieved an AUC of 0.76 (95% CI: 0.65–0.87) in the training cohort and 0.74 (95% CI: 0.56–0.92) in the validation cohort. Model II, based on 3 RFs, achieved an AUC of 0.85 (95% CI: 0.73–0.96) in the training cohort and 0.72 (95% CI: 0.50–0.94) in the validation cohort. Conclusions: Both radiomic models showed good performance in distinguishing between MSI and non-MSI tumours, potentially reducing the need for invasive histological testing and improving treatment timing. Despite achieving a higher AUC, Model II showed signs of overfitting when compared to Model I, which incorporated two RFs and one clinical feature (LOCATION). Radiomics may function as a non-invasive preoperative screening tool to inform decisions regarding MSI testing and treatment. Building radiomic models on larger, more diverse datasets is preferable to enhance generalizability and reduce overfitting.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Abdominal Imaging)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Spontaneous Pneumothorax: A Review of Underlying Etiologies and Diagnostic Imaging Modalities
by
Rupali Jain, Vinay Kandula, Drew A. Torigian and Achala Donuru
Tomography 2025, 11(11), 125; https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11110125 - 7 Nov 2025
Abstract
This review focuses on the diverse etiologies of secondary spontaneous pneumothorax (SSP) and the crucial role of imaging in their diagnosis. Unlike primary spontaneous pneumothorax (PSP), which is typically due to ruptured blebs, SSP results from a wide array of underlying pulmonary conditions
[...] Read more.
This review focuses on the diverse etiologies of secondary spontaneous pneumothorax (SSP) and the crucial role of imaging in their diagnosis. Unlike primary spontaneous pneumothorax (PSP), which is typically due to ruptured blebs, SSP results from a wide array of underlying pulmonary conditions that can pose significant diagnostic challenges. These include infections like tuberculosis, airway diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, malignancies (primary and metastatic), interstitial lung diseases like sarcoidosis, cystic lung diseases such as lymphangioleiomyomatosis, and connective tissue disorders. In women, catamenial pneumothorax secondary to endometriosis should be considered. The role of radiologists is crucial in uncovering these underlying conditions. While chest radiography is the initial imaging modality, computed tomography (CT) provides superior sensitivity for detecting subtle parenchymal abnormalities. Advanced techniques like photon-counting detector CT offer further benefits, including enhanced spatial resolution, reduced noise, and lower radiation dose, potentially revealing underlying causes that might be missed with conventional CT. This enhanced visualization of subtle parenchymal changes, small airways, and vascular structures can be the key to diagnosing the underlying cause of pneumothorax. Recognizing the diverse etiologies of SSP and utilizing advanced imaging techniques is paramount for accurate diagnosis, appropriate management, and improved patient outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cardiovascular Imaging)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparison of Retinal Thickness Measurements Using Optos Monaco and Heidelberg Spectralis OCT Across ETDRS Sectors in Normal Eyes
by
Kakarla V. Chalam, Lourdes Ceja, Rene Obispo, Minali Prasad and Anny M. S. Cheng
Tomography 2025, 11(11), 124; https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11110124 - 5 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Purpose: To compare retinal thickness measurements obtained with the Optos Monaco and Heidelberg Spectralis optical coherence tomography (OCT) systems across 9 Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS) sectors in a cohort comprising normal eyes. Methods: Paired OCT scans from 64 eyes of 32
[...] Read more.
Purpose: To compare retinal thickness measurements obtained with the Optos Monaco and Heidelberg Spectralis optical coherence tomography (OCT) systems across 9 Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS) sectors in a cohort comprising normal eyes. Methods: Paired OCT scans from 64 eyes of 32 participants with normal retinal findings were acquired on both devices. Thickness measurements were obtained for the central subfield and the inner and outer sectors of the superior, nasal, inferior, and temporal quadrants. Outcomes included mean thickness, mean interdevice difference (Heidelberg minus Monaco), Pearson correlation coefficients, and Bland–Altman analyses. Scatterplots and Bland–Altman plots were constructed to evaluate agreement and assess potential interchangeability. Results: The Heidelberg Spectralis yielded significantly greater retinal thickness values than the Optos Monaco in all ETDRS sectors (p < 0.001), with mean differences ranging from +16.9 µm (outer superior) to +26.8 µm (inner superior). Pearson correlation coefficients indicated strong positive agreement (r ≥ 0.8) for the central subfield and most inner sectors, and moderate to strong positive agreement (r ≥ 0.5) in a single outer sector. Bland–Altman analyses demonstrated a statistically significant systematic bias favoring greater measurements with Heidelberg in most quadrants, with limits of agreement indicating clinically relevant variability. Although the relative agreement was high, absolute differences limit direct interchangeability. Conclusions: Optos Monaco and Heidelberg Spectralis exhibit strong linear correlation in retinal thickness measurements but show significant systematic differences. Interchangeable use requires the application of correction factors where segmentation variability may be greater.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
AI-Written Scientific Manuscripts
by
Emilio Quaia
Tomography 2025, 11(11), 123; https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11110123 - 30 Oct 2025
Abstract
This editorial provides insights on AI-written scientific manuscripts which represent an increasingly frequent phenomenon that must be managed by authors, reviewers and journal editors [...]
Full article

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Tomography Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
- 10th Anniversary
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Anatomia, Biomedicines, IJMS, Medicina, Tomography
Human Anatomy and Pathophysiology, 3rd Edition
Topic Editors: Francesco Cappello, Mugurel Constantin RusuDeadline: 31 May 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Tomography
Emergent Perspectives in Oncology Imaging
Guest Editors: Mariano Scaglione, Leandra PiscopoDeadline: 30 December 2025
Special Issue in
Tomography
Orthopaedic Radiology: Clinical Diagnosis and Application
Guest Editor: Olumide A. DanisaDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Tomography
Cutting-Edge Applications: Artificial Intelligence and Deep Learning Revolutionizing CT and MRI
Guest Editor: Giovanni FotiDeadline: 25 March 2026
Special Issue in
Tomography
Oncogenic Risk Related to Ionizing Radiation and Environmental Impact in Radiology
Guest Editor: Emilio QuaiaDeadline: 31 March 2026