Textural Features of Mouse Glioma Models Measured by Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MR Images with 3D Isotropic Resolution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Model
2.2. Data Acquisition
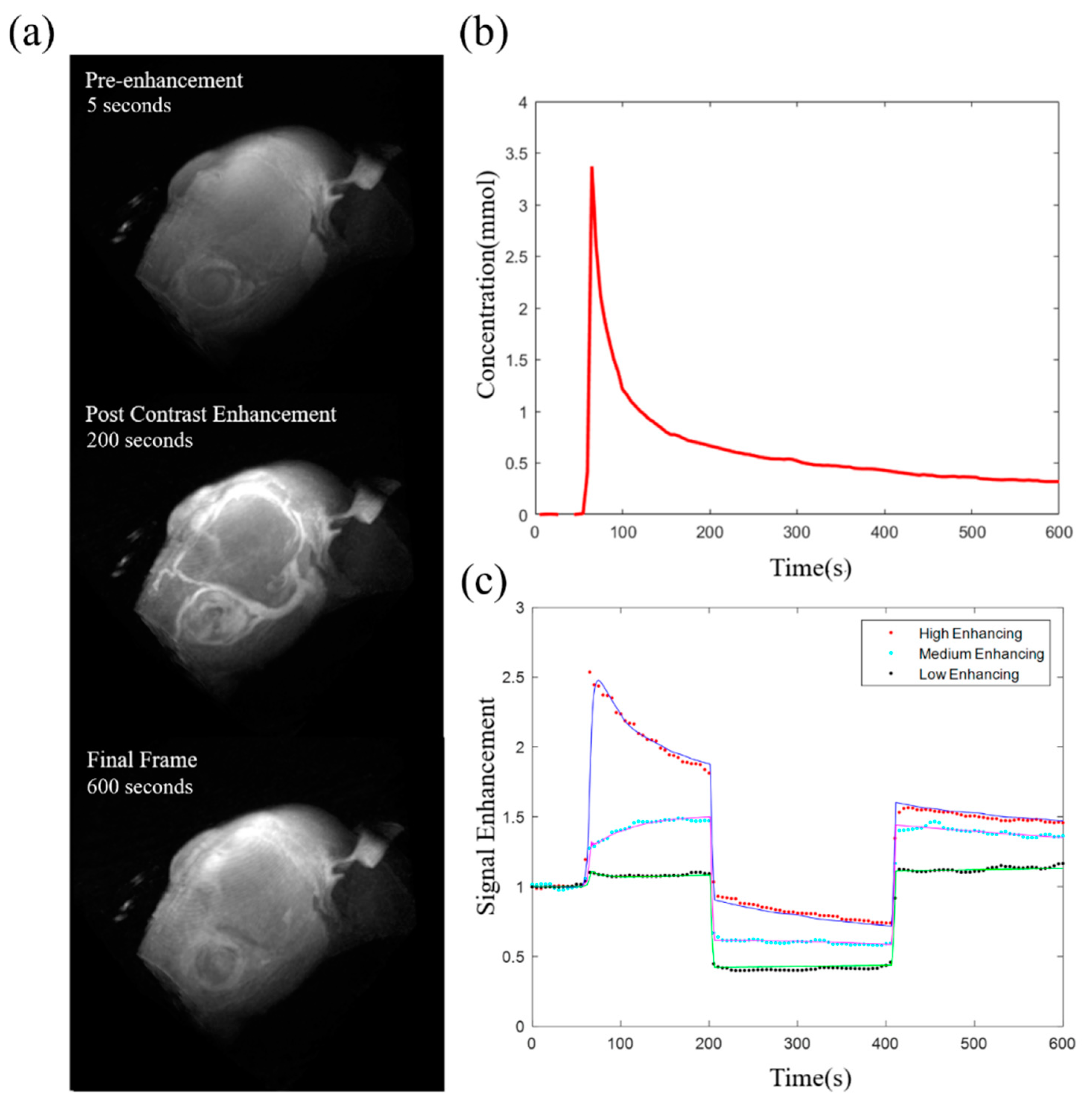
2.3. Image Reconstruction and PK Parameter Maps
2.4. Assessment of Isotropic versus Anisotropic Resolution Images
3. Results
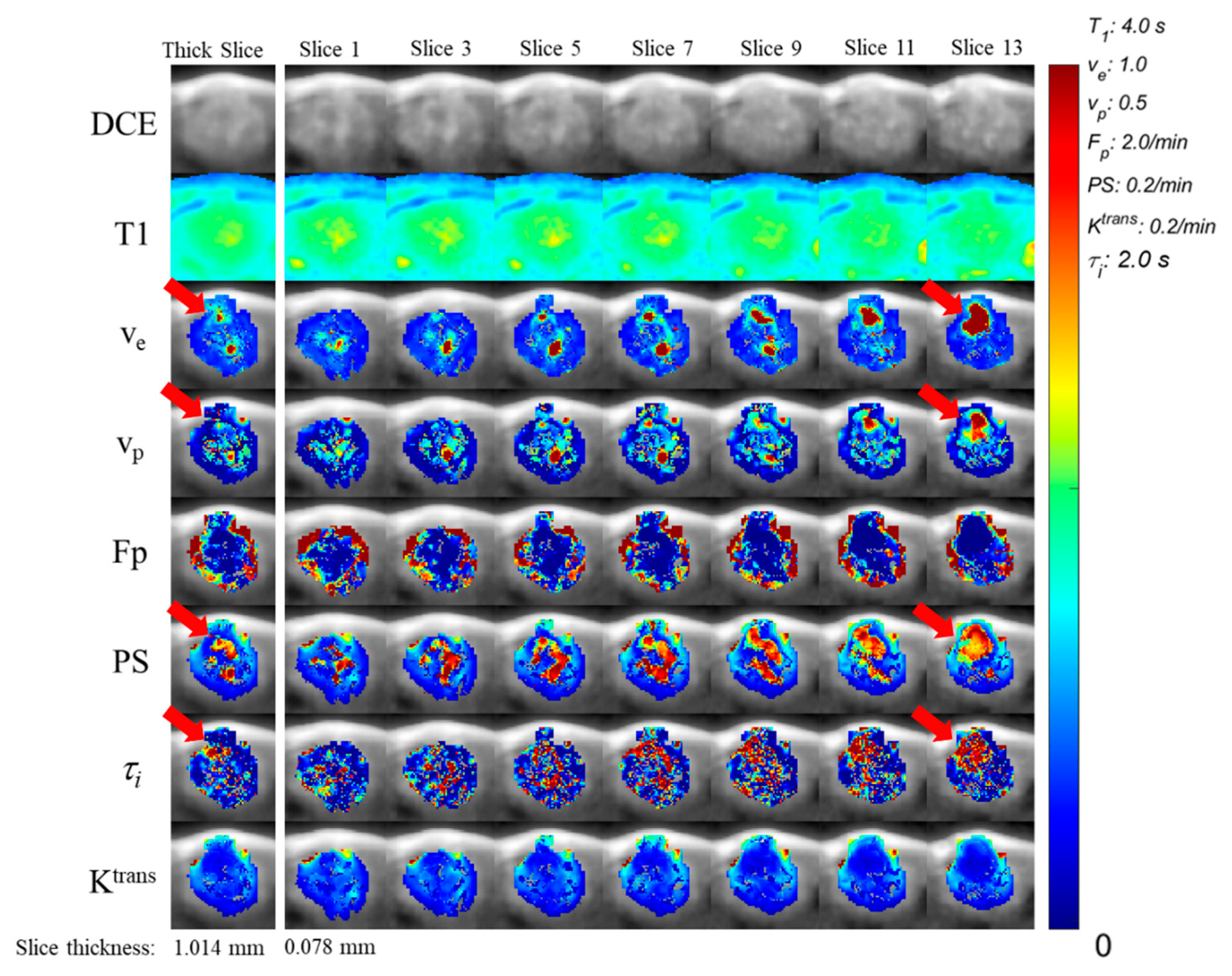
3.1. Isotropic vs. Anisotropic Resolution Images
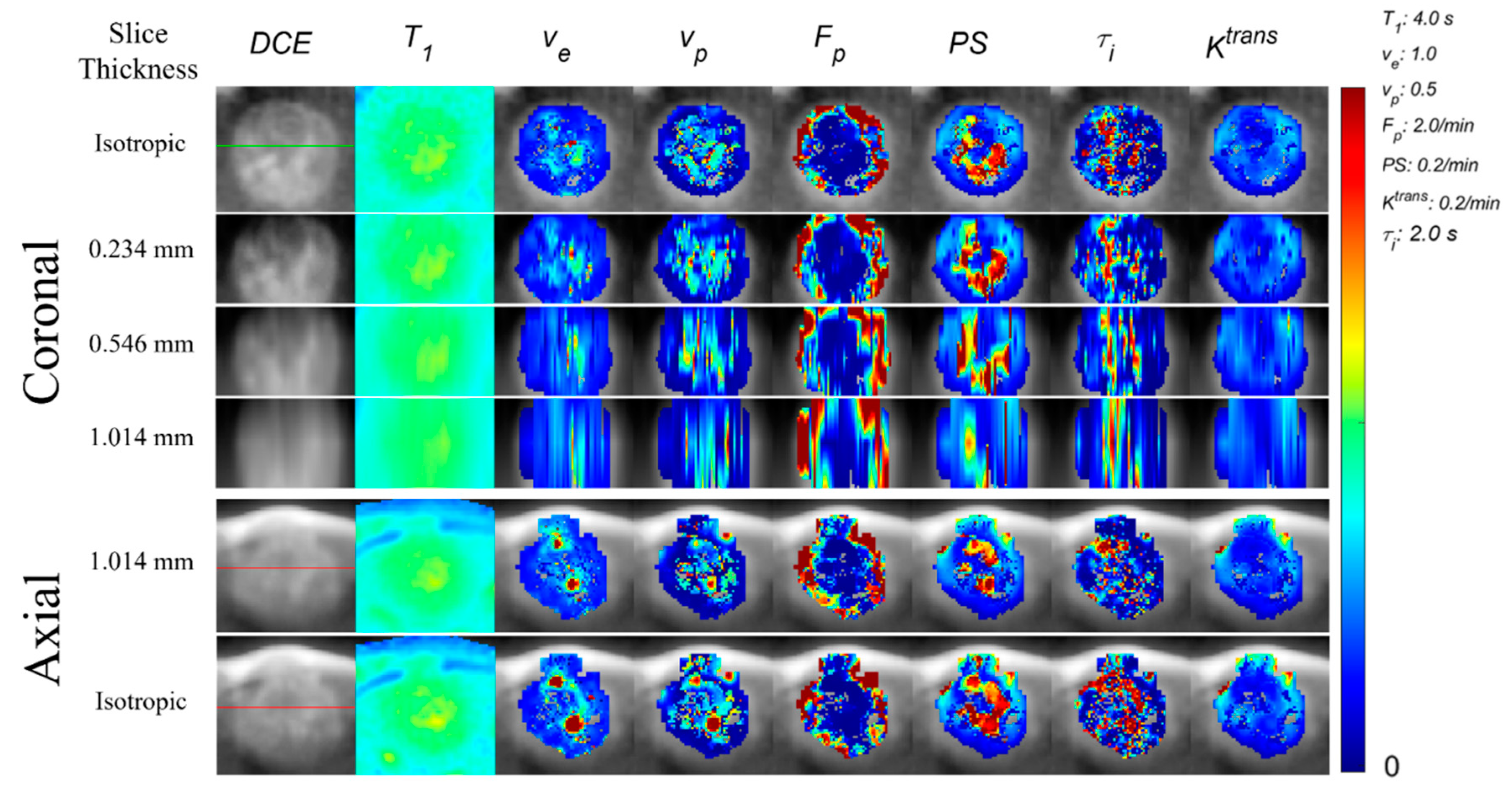
3.2. Anisotropic Resolution Images in Different Orientations
3.3. Texture Features Reported in DCE-MRI Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.A.; Dinstein, I. Textural Features for Image Classification. IEEE Syst. Man Cybern. Soc. 1973, SMC-3, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Shaw, A.T. Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowski, M.R.M.; Bressem, K.K.; Franz, L.; Kader, A.M.; Niehues, S.M.; Keller, S.; Rueckert, D.; Adams, L.C. De Novo Radiomics Approach Using Image Augmentation and Features from T1 Mapping to Predict Gleason Scores in Prostate Cancer. Investig. Radiol. 2021, 56, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duron, L.M.; Heraud, A.; Charbonneau, F.; Zmuda, M.; Savatovsky, J.; Fournier, L.M.; Lecler, A.M. A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Radiomics Signature to Distinguish Benign from Malignant Orbital Lesions. Investig. Radiol. 2021, 56, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Rios-Velazquez, E.; Leijenaar, R.; Carvalho, S.; van Stiphout, R.G.P.M.; Granton, P.; Zegers, C.M.L.; Gillies, R.; Boellard, R.; Dekker, A.; et al. Radiomics: Extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Gu, Y.; Basu, S.; Berglund, A.; Eschrich, S.A.; Schabath, M.B.; Forster, K.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Dekker, A.; Fenstermacher, D.; et al. Radiomics: The process and the challenges. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1234–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Liang, C.; Liang, C.; Liu, Z. Effects of contrast-enhancement, reconstruction slice thickness and convolution kernel on the diagnostic performance of radiomics signature in solitary pulmonary nodule. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampin, G. Radiomics Digital Phantom. Cancer Data 2016, 41, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRue, R.T.H.M.; Van Timmeren, J.E.; De Jong, E.E.C.; Feliciani, G.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Schreurs, W.M.J.; Sosef, M.N.; Raat, F.H.P.J.; Van Der Zande, F.H.R.; Das, M.; et al. Influence of gray level discretization on radiomic feature stability for different CT scanners, tube currents and slice thicknesses: A comprehensive phantom study. Acta Oncol. 2017, 56, 1544–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq-Ul-Hassan, M.; Zhang, G.G.; Latifi, K.; Ullah, G.; Hunt, D.C.; Balagurunathan, Y.; Abdalah, M.A.; Schabath, M.B.; Goldgof, D.G.; Mackin, D.; et al. Intrinsic dependencies of CT radiomic features on voxel size and number of gray levels. Med. Phys. 2017, 44, 1050–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ger, R.B.; Zhou, S.; Chi, P.-C.M.; Lee, H.J.; Layman, R.R.; Jones, A.K.; Goff, D.L.; Fuller, C.D.; Howell, R.M.; Li, H.; et al. Comprehensive Investigation on Controlling for CT Imaging Variabilities in Radiomics Studies. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackin, D.; Fave, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Jones, A.K.; Ng, C.S.; Court, L. Harmonizing the pixel size in retrospective computed tomography radiomics studies. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornacon-Wood, I.; Faivre-Finn, C.; O’Connor, J.P.; Price, G. Radiomics as a personalized medicine tool in lung cancer: Separating the hope from the hype. Lung Cancer 2020, 146, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, B.; Zhong, F.; Guo, Q.; Li, K.; Hou, Y.; Lin, N. MRI-based texture analysis of the primary tumor for pre-treatment prediction of bone metastases in prostate cancer. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 60, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, M.; Yu, J.; Peng, G.; Jun, L.; Feng, S.; Fang, L. Correlation between DCE-MRI radiomics features and Ki-67 expression in invasive breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 5084–5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, G.; Tudorica, A.; Afzal, A.; Chui, S.Y.-C.; Naik, A.; Troxell, M.L.; Kemmer, K.A.; Oh, K.Y.; Roy, N.; Jafarian, N.; et al. DCE-MRI Texture Features for Early Prediction of Breast Cancer Therapy Response. Tomography 2017, 3, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Feng, L.; Otazo, R.; Kim, S.G. Rapid dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for small animals at 7T using 3D ultra-short echo time and golden-angle radial sparse parallel MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 81, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kim, G. Estimation of cellular-interstitial water exchange in dynamic contrast enhanced MRI using two flip angles. NMR Biomed. 2019, 32, e4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, G.; Kiessling, F.; Lucht, R.; Darai, S.; Wasser, K.; Delorme, S. Microcirculation and microvasculature in breast tumors: Pharmacokinetic analysis of dynamic MR image series. Magn. Reson. Med. 2004, 52, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, H.M. Reaction Rates by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. J. Chem. Phys. 1958, 28, 430–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, R.G.; Fishbein, K. Measurement of Spin–Lattice Relaxation Times and Concentrations in Systems with Chemical Exchange Using the One-Pulse Sequence: Breakdown of the Ernst Model for Partial Saturation in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. 2000, 142, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Rooney, W.D.; Springer, C.S. A unified magnetic resonance imaging pharmacokinetic theory: Intravascular and extracellular contrast reagents. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005, 54, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Griethuysen, J.J.M.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, D.; Diaconis, P. On the histogram as a density estimator:L 2 theory. Probab. Theory Relat. Fields 1981, 57, 453–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Ji, Y.; Qi, L.; Guo, X.; Jian, X.; Liu, P. Breast cancer Ki67 expression prediction by DCE-MRI radiomics features. Clin. Radiol. 2018, 73, 909.e1–909.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Chen, X.; Fang, J.; Kang, H.; Xue, W.; Tong, H.; Cao, P.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W. Textural features of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI derived model-free and model-based parameter maps in glioma grading. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 47, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Gao, B.B.; Dong, B.; Cheriyath, S.S.P.; Song, Q.W.; Xu, B.; Wei, Q.; Xie, L.Z.; Guo, Y.; Miao, Y.W. Preoperative vascular heterogeneity and aggressiveness assessment of pituitary macroadenoma based on dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI texture analysis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 129, 109125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Gao, F.; Duan, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Bai, G.; Tao, W. Radiomic features of Pk-DCE MRI parameters based on the extensive Tofts model in application of breast cancer. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2020, 43, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayerhoefer, M.E.; Szomolanyi, P.; Jirak, D.; Berg, A.; Materka, A.; Dirisamer, A.; Trattnig, S. Effects of Magnetic Resonance Image Interpolation on the Results of Texture-Based Pattern Classification a phantom study. Investig. Radiol. 2009, 44, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baessler, B.; Weiss, K.; dos Santos, D.P. Robustness and Reproducibility of Radiomics in Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Phantom Study. Investig. Radiol. 2019, 54, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santarosa, C.; Castellano, A.; Conte, G.M.; Cadioli, M.; Iadanza, A.; Terreni, M.R.; Franzin, A.; Bello, L.; Caulo, M.; Falini, A.; et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced and dynamic susceptibility contrast perfusion MR imaging for glioma grading: Preliminary comparison of vessel compartment and permeability parameters using hotspot and histogram analysis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2016, 85, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebulla, J.; Kim, E.; Rhie, K.; Zhang, J.; Pathak, A.P. Multiscale and multi-modality visualization of angiogenesis in a human breast cancer model. Angiogenesis 2014, 17, 695–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sala, E.; Mema, E.; Himoto, Y.; Veeraraghavan, H.; Brenton, J.; Snyder, A.; Weigelt, B.; Vargas, H. Unravelling tumour heterogeneity using next-generation imaging: Radiomics, radiogenomics, and habitat imaging. Clin. Radiol. 2017, 72, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brynolfsson, P.; Nilsson, D.; Torheim, T.; Asklund, T.; Karlsson, C.T.; Trygg, J.; Nyholm, T.; Garpebring, A. Haralick texture features from apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) MRI images depend on imaging and pre-processing parameters. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carré, A.; Klausner, G.; Edjlali, M.; Lerousseau, M.; Briend-Diop, J.; Sun, R.; Ammari, S.; Reuzé, S.; Andres, E.A.; Estienne, T.; et al. Standardization of brain MR images across machines and protocols: Bridging the gap for MRI-based radiomics. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-H.; Park, H.; Ko, E.S. Radiomics in Breast Imaging from Techniques to Clinical Applications: A Review. Korean J. Radiol. 2020, 21, 779–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, M.L.; McIntosh, C.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Milosevic, M.; Wee, L.; Dekker, A.; Huang, S.H.; Purdie, T.; O’Sullivan, B.; Aerts, H.J.; et al. Vulnerabilities of radiomic signature development: The need for safeguards. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 130, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duron, L.; Balvay, D.; Perre, S.V.; Bouchouicha, A.; Savatovsky, J.; Sadik, J.-C.; Thomassin-Naggara, I.; Fournier, L.; Lecler, A. Gray-level discretization impacts reproducible MRI radiomics texture features. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwier, M.; van Griethuysen, J.; Vangel, M.G.; Pieper, S.; Peled, S.; Tempany, C.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Kikinis, R.; Fennessy, F.M.; Fedorov, A. Repeatability of Multiparametric Prostate MRI Radiomics Features. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornacon-Wood, I.; Mistry, H.; Ackermann, C.J.; Blackhall, F.; McPartlin, A.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Price, G.; O’Connor, J.P.B. Reliability and prognostic value of radiomic features are highly dependent on choice of feature extraction platform. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 6241–6250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuter, M.; Gerstner, E.R.; Rapalino, O.; Batchelor, T.T.; Rosen, B.; Fischl, B. Impact of MRI head placement on glioma response assessment. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2014, 118, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Study | Acquisition Resolution | Cancer Type | Predicting | Parameter | Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W. Ma et al. (2018) [26] | 0.98 × 0.49 × 1.8 mm | Breast Cancer | Ki-67 expression | Post-Contrast T1-w DCE | First-Order: Mean, SD, Skewness, and Kurtosis GLCM: Energy (Joint energy), Entropy (Joint entropy), Contrast, Correlation, Homogeneity (Inverse difference), and IDM |
| Y. Wang et al. (2019) [15] | 0.89 × 0.89 × 3 mm | Prostate Cancer | Bone Metastases | Post-Contrast T1-w DCE | First-Order: 0.025 quartile GLCM: Auto correlation, Cluster prominence, Difference entropy, Dissimilarity, Homogeneity, IDM, and IDMNGLRLM: Short run low grey level emphasis and Short run high grey level emphasis |
| Thibault et al. (2016) [17] | 1 × 1 × 1.4 mm | Breast Cancer | Response to Treatment | Ktrans τi | GLCM: Entropy difference, Contrast, Variance differences, and Inertia GLRLM: Gray-level nonuniformity and Long-run emphasis GLCM: Mean |
| ve | GLCM: Contrast and Inertia | ||||
| Xie T et al. (2017) [27] | 0.74 × 0.53 × 6.0 mm | Glioma | Grading Ki-67 expression | Ktrans ve, vp, Ktrans, vp | GLCM: Energy (Joint Energy), Entropy (Joint Entropy), Inertia (Contrast), and Correlation IDM GLCM: Energy, Entropy, and IDM GLCM: Energy (Joint Energy) and IDM |
| Liu YYG et al. (2020) [28] | 0.6 × 0.8 × 3 mm | Pituitary macroadenoma | Tumor ‘Aggressiveness’ via Heterogeneity in Vasculature | Ktrans ve Ktrans, ve Kep | First-Order: Skewness First-Order: Mean GLRLM: Long-run emphasis, Gray-level non-uniformity, High gray-level run emphasis, and Short run emphasis GLCM: Difference entropy GLRLM: Gray level non-uniformity and Run length non-uniformity |
| Zhou X et al. (2020) [29] | 1.4 × 1.3 × 4 mm | Breast Cancer | Benign/malignancy | Ktrans, ve Kep, ve ve | GLCM: Entropy (Joint entropy) GLRLM: Short run low grey level emphasis GLCM: Cluster shade |
| vp | GLCM: IDM | ||||
| Molecular Subtype | Ktrans, ve Ktrans ve vp | GLCM: Entropy (Joint entropy) GLRLM: Grey level non uniformity and Long run emphasis GLRLM: Short run emphasis First-Order: Entropy GLSZM: Zone percentage GLRLM: Short run high grey level emphasis and Short run low grey level emphasis GLSZM: High grey level emphasis |
| Percent of Features Demonstrating Significant Difference from Isotropic Resolution | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Texture Features (n = 75) | Histogram Features (n = 18) | |||||
| 1.014 mm | 0.546 mm | 0.234 mm | 1.014 mm | 0.546 mm | 0.234 mm | |
| ve | 29.3 | 22.7 | 1.3 | 16.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| vp | 24.0 | 13.3 | 5.3 | 33.3 | 22.2 | 16.7 |
| FP | 53.3 | 52.0 | 42.7 | 44.4 | 33.3 | 16.7 |
| PS | 13.3 | 17.3 | 2.7 | 38.9 | 44.4 | 33.3 |
| τi | 33.3 | 34.7 | 30.7 | 55.6 | 61.1 | 44.4 |
| Ktrans | 16.0 | 17.3 | 0.0 | 33.3 | 27.8 | 27.8 |
| T1-w | 48.0 | 66.7 | 46.7 | 55.6 | 72.2 | 38.9 |
| Total | 31.0 | 32.0 | 18.5 | 39.7 | 37.3 | 25.4 |
| Ax | Cor | Sag | Ax | Cor | Sag | |
| ve | 29.3 | 28.0 | 28.0 | 16.7 | 33.3 | 11.1 |
| vp | 24.0 | 18.7 | 24.0 | 33.3 | 38.9 | 38.9 |
| FP | 53.3 | 60.0 | 57.3 | 44.4 | 50.0 | 38.9 |
| PS | 13.3 | 18.7 | 26.7 | 38.9 | 38.9 | 50.0 |
| τi | 33.3 | 32.0 | 33.3 | 55.6 | 72.2 | 66.7 |
| Ktrans | 16.0 | 62.7 | 62.7 | 33.3 | 44.4 | 44.4 |
| T1-w | 48.0 | 10.7 | 58.7 | 55.6 | 38.9 | 61.1 |
| Total | 31.0 | 33.0 | 41.5 | 39.7 | 45.2 | 44.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiser, K.; Zhang, J.; Kim, S.G. Textural Features of Mouse Glioma Models Measured by Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MR Images with 3D Isotropic Resolution. Tomography 2023, 9, 721-735. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9020058
Kiser K, Zhang J, Kim SG. Textural Features of Mouse Glioma Models Measured by Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MR Images with 3D Isotropic Resolution. Tomography. 2023; 9(2):721-735. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9020058
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiser, Karl, Jin Zhang, and Sungheon Gene Kim. 2023. "Textural Features of Mouse Glioma Models Measured by Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MR Images with 3D Isotropic Resolution" Tomography 9, no. 2: 721-735. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9020058
APA StyleKiser, K., Zhang, J., & Kim, S. G. (2023). Textural Features of Mouse Glioma Models Measured by Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MR Images with 3D Isotropic Resolution. Tomography, 9(2), 721-735. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9020058




