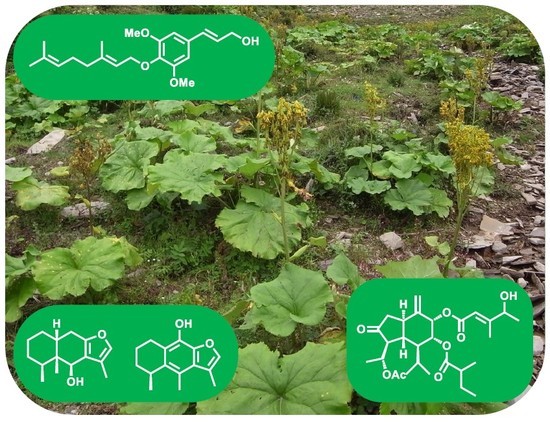
Terpenoids and Phenylpropanoids in Ligularia duciformis, L. kongkalingensis, L. nelumbifolia, and L. limprichtii
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Samples
2.2. Chemical Constituents
2.3. Genetic Study
3. Discussion
3.1. Chemotypes
3.2. Introgression and Chemical Evolution
3.3. L. limprichrii
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimantal Procedure
4.2. Plant Materials
4.3. Extraction and Purification
4.4. (2E)-3-(4-Hydroxy-3-Methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-yl 3-Methylpentanoate (2)
4.5. (2Z)- and (2E)- 3-[3,5-Dimethoxy-4-((2E)-3,7-Dimethylocta-2,6-Dien-1-yl)Oxyphenyl]prop-2-Enal (8a and 8b)
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, S.W.; Deng, D.S.; Liu, J.Q. The origin, evolution and distribution of Ligularia Cass. (Compositae). Acta Phytotaxon. Sin. 1994, 32, 514–524. [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda, C.; Hanai, R.; Nagano, H.; Tori, M.; Gong, X. Diversity of furanoeremophilanes in major Ligularia species in the Hengduan Mountains. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2012, 7, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, C.; Hanai, R.; Tori, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Saito, Y.; Nagano, H.; Ohsaki, A.; Hirota, H.; Kawahara, T.; Gong, X. Diversity in furanoeremophilane composition produced by Ligularia species (Asteraceae) in the Hengduan Mountains area of China. J. Synth. Org. Chem. Jpn. 2014, 72, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, N.G.; Madyastha, K.M. Biosynthesis of β-substituted furan skeleton in the lower furanosesquiterpenoids: a model study. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 290, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S. Flora Republicae Popularis Sinicae, Vol. 77, Part 2; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Illarionova, I.D. Ligularia. In Flora of China; Wu, Z.Y., Raven, P.H., Hong, D.Y., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China; Missouri Botanical Garden Press: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2011; Volume 20–21, pp. 376–415. [Google Scholar]
- Nagano, H.; Hanai, R.; Yamada, H.; Matsushima, M.; Miura, Y.; Hoya, T.; Ozawa, M.; Fujiwara, M.; Kodama, H.; Torihata, A.; et al. Chemical and genetic study of Ligularia duciformis and related species in Sichuan and Yunnan provinces of China. Chem. Biodivers. 2012, 9, 789–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, H.; Horiguchi, Y.; Kawaii, S.; Hanai, R.; Gong, X.; Kuroda, C. The first isolation of furanoeremophilane from Ligularia nelumbifolia. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2014, 9, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, C.; Ueshino, T.; Nagano, H. Ehrlich’s reaction of furanoeremophilanes. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2004, 77, 1737–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, C.; Nishio, E. Substituent effect in color of Ehrlich’s test of tetrahydrobenzofuran. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2007, 2, 581–585. [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya, H.; Takeda, Y.; Zhang, R.S.; Tong, R.X.; Kitagawa, I. Indonesian medicinal plants. III. On the constituents of the bark of Fagara rhetza (Rutaceae). (1): Alkaloids, phenylpropenoids, and acid amide. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1992, 40, 2325–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohlmann, F.; Zdero, C.; Natu, A.A. Weitere bisabolen-derivate und andere inhaltsstoffe aus Südafrikanischen Senecis-arten. Phytochemistry 1978, 17, 1757–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlmann, F.; Grenz, M.; Gupta, R.K.; Dhar, A.K.; Ahmed, M.; King, R.M.; Robinson, H. Eudesmane derivatives from Verbesina species. Phytochemistry 1980, 19, 2391–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Jia, Z.; Yang, L. Sinapyl alcohol derivatives and other constituents from Ligularia nelumbifolia. Phytochemistry 1994, 37, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, D.; Reynolds, W.F.; Buchanan, G.; Reese, P.B.; Enriquez, R.G. Assignment of 1H and 13C spectra and investigation of hindered side-chain rotation in lupeol derivatives. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2000, 38, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tori, M.; Fujiwara, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Gong, X.; Shen, Y.; Hanai, R.; Kuroda, C. New oplopane-type sesquiterpenoids from Ligularia duciformis. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2007, 2, 357–360. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.-R.; Ma, Q.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-X.; Yi, T.-M.; Li, C.-S.; Zhou, J. Palaeophytochemical components from the miocene-fossil wood of Pinus griffithii. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2009, 56, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terabe, M.; Tada, M.; Takahashi, T. Absolute stereochemistry of cacalol. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1978, 51, 661–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romo, J.; Joseph-Nathan, P. The constituents of Cacalia decomposita A. Gray. Structures of cacalol and cacalone. Tetrahedron 1964, 20, 2331–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omura, K.; Nakanishi, M.; Takai, K.; Naya, K. The sesquiterpenes of Cacalia species: 8-Oxocacalol and the stereochemistry of cacalone epimers. Chem. Lett. 1978, 1257–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, H.; Tozyo, T.; Minato, H. Studies on sesquiterpenoids—IX. Structure of ligularol and ligularone from Ligularia sibirica Cass. Tetrahedron 1965, 21, 2605–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tori, M.; Watanabe, A.; Matsuo, S.; Okamoto, Y.; Tachikawa, K.; Takaoka, S.; Gong, X.; Kuroda, C.; Hanai, R. Diversity of Ligularia kanaitzensis in sesquiterpenoid composition and neutral DNA sequences. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 4486–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, Y.; Takashima, Y.; Kamada, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Suenaga, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Matsunaga, Y.; Hanai, R.; Kawahara, T.; Gong, X.; et al. Chemical and genetic diversity of Ligularia virgaurea collected in northern Sichuan and adjacent areas of China. Isolation of 13 new compound. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 10011–10029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, H.; Torihata, A.; Matsushima, M.; Hanai, R.; Saito, Y.; Baba, M.; Tanio, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; Takashima, Y.; Ichihara, M.; et al. Chemical and genetic study of Ligularia cyathiceps in Yunnan Province of China. Helv. Chim. Acta 2009, 92, 2071–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, R.; Tanabe, S.; Aoyama, N.; Okamoto, Y.; Tori, M.; Zhang, N.; Gong, X.; Kuroda, C. Chemical and genetic study of two Ligularia hybrids in Shangrila County, Yunnan Province, China. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 1057–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Hanai, R.; Yamada, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Nagano, H.; Kawahara, T.; Yu, J.-J.; Gong, X.; Kuroda, C. Chemical constituents of Ligularia nelumbifolia and L. subspicata hybrid collected in Shangrila County, Yunnan Province of China. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2012, 7, 1565–1568. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-M.; Zhao, J.-Q.; Yang, J.-L.; Tao, Y.-D.; Mei, L.-J. Chemical constituents from Ligularia purdomii (Turrill) Chittenden. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2017, 72, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, H.; Matsushima, M.; Yamada, H.; Hanai, R.; Gong, X.; Kuroda, C. Two new furanoeremophilane sesquiterpenoids from Ligularia oligonema. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Isolated compounds are not available from the authors. |




| Sample No. 1 | Species | Locality 2 | Isolated Compounds | Chemotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (2011-12) | L. duciformis | Jiajinshan (Baoxing) | 1, 5 | 3 |
| 2 (2011-29) | L. nelumbifolia | Bamei (Daofu) | 3, 7, 9 | 3 |
| 3 (2011-82) | L. kongkalingensis | Yinduo (Xinlong) | 3, 4 | 3 |
| 4 (2012-10) | L. kongkalingensis | Zheduoshan (Kangding) | 9 | 4 |
| 5 (2012-28) | L. duciformis | Yulin (Kangding) | 2, 6, 9, 10, 11 | 2 |
| 6 (2015-33) | L. nelumbifolia | Zhongfengshan (Heishui) | 3, 4, 8, 9, 14, 15 | 1 |
| 7 (2015-37) | L. duciformis | Zhongfengshan (Heishui) | 12, 13 | 1 |
| 8 (2015-40) | unidentified 3 | Zhongfengshan (Heishui) | 3, 4, 8 | 3 |
| 9 (2010-32) | L. limprichtii | Gemo (Aba) | 3 | 3 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuroda, C.; Kobayashi, R.; Nagata, A.; Nakadozono, Y.; Itoh, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Tori, M.; Hanai, R.; Gong, X. Terpenoids and Phenylpropanoids in Ligularia duciformis, L. kongkalingensis, L. nelumbifolia, and L. limprichtii. Molecules 2017, 22, 2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122062
Kuroda C, Kobayashi R, Nagata A, Nakadozono Y, Itoh T, Okamoto Y, Tori M, Hanai R, Gong X. Terpenoids and Phenylpropanoids in Ligularia duciformis, L. kongkalingensis, L. nelumbifolia, and L. limprichtii. Molecules. 2017; 22(12):2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122062
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuroda, Chiaki, Ryohei Kobayashi, Ayumi Nagata, Yumi Nakadozono, Taketo Itoh, Yasuko Okamoto, Motoo Tori, Ryo Hanai, and Xun Gong. 2017. "Terpenoids and Phenylpropanoids in Ligularia duciformis, L. kongkalingensis, L. nelumbifolia, and L. limprichtii" Molecules 22, no. 12: 2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122062
APA StyleKuroda, C., Kobayashi, R., Nagata, A., Nakadozono, Y., Itoh, T., Okamoto, Y., Tori, M., Hanai, R., & Gong, X. (2017). Terpenoids and Phenylpropanoids in Ligularia duciformis, L. kongkalingensis, L. nelumbifolia, and L. limprichtii. Molecules, 22(12), 2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122062