Simple Determination of Affinity Constants of Antibodies by Competitive Immunoassays
Abstract
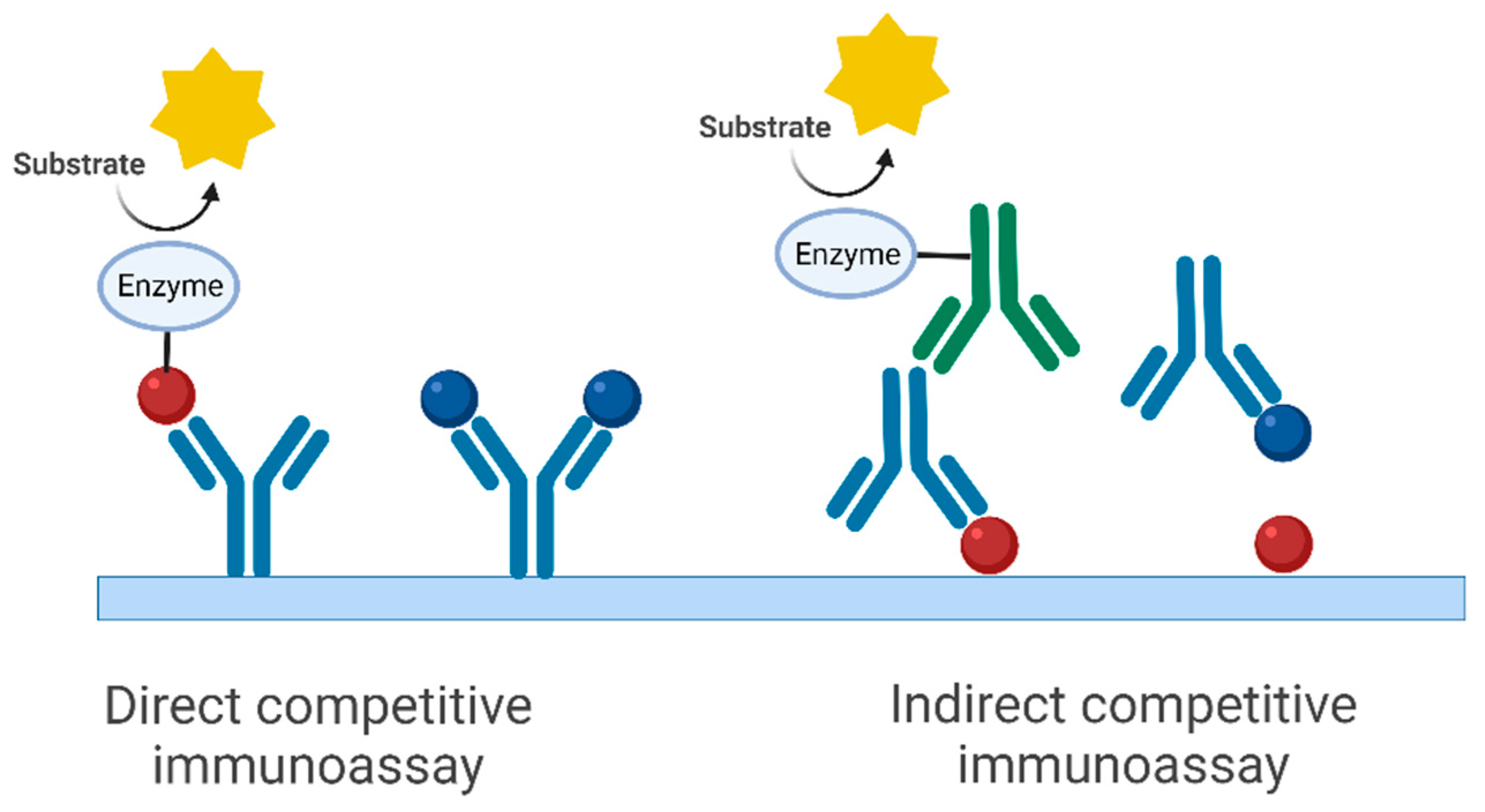
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Design
3. Results and Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Azimzadeh, A.; Van Regenmortel, M.H. Antibody affinity measurements. J. Mol. Recognit. 1990, 3, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steward, M.W.; Lew, A.M. The Importance of Antibody-Affinity in the Performance of Immunoassays for Antibody. J. Immunol. Methods 1985, 78, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, M.G. Quality Issues of Research Antibodies. Anal. Chem. Insights 2016, 11, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, M.G. Ten Basic Rules of Antibody Validation. Anal. Chem. Insights 2018, 13, 1177390118757462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, M.G. The Protocol Gap. Method Protocol. 2021, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Regenmortel, M.H.V.; Azimzadeh, A. Determination of antibody affinity. J. Immunoass. 2000, 21, 211–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.E.; Djavadiohaniance, L. Methods for Measurement of Antibody Antigen Affinity Based on ELISA and RIA. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1993, 5, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarmoskaite, I.; AlSadhan, I.; Vaidyanathan, P.P.; Herschlag, D. How to measure and evaluate binding affinities. eLife 2020, 9, e57264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbet, J.; Huclier-Markai, S. Equilibrium, affinity, dissociation constants, IC5O: Facts and fantasies. Pharm. Stat. 2019, 18, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelesarov, I.; Leder, L.; Bosshard, H.R. Probing the Energetics of Antigen-Antibody Recognition by Titration Microcalorimetry. Methods 1996, 9, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, M.M.; Raman, C.S.; Nall, B.T. Isothermal titration calorimetry of protein-protein interactions. Methods 1999, 19, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuck, P. Reliable determination of binding affinity and kinetics using surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1997, 8, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schasfoort, R.B.M.; de Lau, W.; van der Kooi, A.; Clevers, H.; Engbers, G.H.M. Method for estimating the single molecular affinity. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 421, 794–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.H.; Jiang, P.J.; Qiu, L.; Wang, C.L.; Xia, J. Resolving antibody-peptide complexes with different ligand stoichiometries reveals a marked affinity enhancement through multivalency. Talanta 2013, 115, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, A.; Ghosh, R.; Hammarstrom, S. Determination of Intrinsic Affinity Constants of Monoclonal-Antibodies against Carcinoembryonic Antigen. Mol. Immunol. 1987, 24, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornick, C.L.; Karush, F. Antibody Affinity—III The Role of Multivalence. Immunochemistry 1972, 9, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rich, R.L.; Myszka, D.G. Grading the commercial optical biosensor literature-Class of 2008: ‘The Mighty Binders’. J. Mol. Recognit. 2010, 23, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rich, R.L.; Myszka, D.G. Survey of the 2009 commercial optical biosensor literature. J. Mol. Recognit. 2011, 24, 892–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, K.M.; Arndt, K.M.; Plückthun, A. Model and simulation of multivalent binding to fixed ligands. Anal. Biochem. 1998, 261, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, V.; Rafique, A. Designing binding kinetic assay on the bio-layer interferometry (BLI) biosensor to characterize antibody-antigen interactions. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 536, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelli, D.; Scognamiglio, V.; Montanari, R. Surface plasmon resonance technology: Recent advances, applications and experimental cases. TrAC-Trend Anal. Chem. 2023, 163, 117079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, S.; Lau, E.Y.; Ovchinnikov, V. On the Rapid Calculation of Binding Affinities for Antigen and Antibody Design and Affinity Maturation Simulations. Antibodies 2022, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guest, J.D.; Vreven, T.; Zhou, J.; Moal, I.; Jeliazkov, J.R.; Gray, J.J.; Weng, Z.P.; Pierce, B.G. An expanded benchmark for antibody-antigen docking and affinity prediction reveals insights into antibody recognition determinants. Structure 2021, 29, 606–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattes, M.J. Binding parameters of antibodies reacting with multivalent antigens: Functional affinity or pseudo-affinity. J. Immunol. Methods 1997, 202, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crothers, D.M.; Metzger, H. Influence of Polyvalency on Binding Properties of Antibodies. Immunochemistry 1972, 9, 341–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitov, P.I.; Bundle, D.R. On the nature of the multivalency effect: A thermodynamic model. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 16271–16284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasting, C.; Schalley, C.A.; Weber, M.; Seitz, O.; Hecht, S.; Koksch, B.; Dernedde, J.; Graf, C.; Knapp, E.W.; Haag, R. Multivalency as a Chemical Organization and Action Principle. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10472–10498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukkur, T.K.S.; Szewczuk, M.R.; Schmidt, D.E. Determination of Total Affinity Constant for Heterogeneous Hapten-Antibody Interactions. Immunochemistry 1974, 11, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, M.A.; Panne, U.; Weller, M.G. A Novel Immunoreagent for the Specific and Sensitive Detection of the Explosive Triacetone Triperoxide (TATP). Biosensors 2011, 1, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epps, D.E.; Raub, T.J.; Caiolfa, V.; Chiari, A.; Zamai, M. Determination of the affinity of drugs toward serum albumin by measurement of the quenching of the intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence of the protein. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1999, 51, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisen, H.N.; Siskind, G.W. Variations in Affinities of Antibodies during the Immune Response. Biochemistry 1964, 3, 996–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakar, K.A.; Feroz, S.R. A critical view on the analysis of fluorescence quenching data for determining ligand-protein binding affinity. Spectrochim. Acta A 2019, 223, 117337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrack, J.; Smith, F.C. Quantitative aspects of immunity reactions: The combination of anitbodies with simple haptenes. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1932, 13, 394–402. [Google Scholar]
- Pinger, C.W.; Heller, A.A.; Spence, D.M. A Printed Equilibrium Dialysis Device with Integrated Membranes for Improved Binding Affinity Measurements. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 7302–7306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerabek-Willemsen, M.; André, T.; Wanner, R.; Roth, H.M.; Duhr, S.; Baaske, P.; Breitsprecher, D. MicroScale Thermophoresis: Interaction analysis and beyond. J. Mol. Struct. 2014, 1077, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippok, S.; Seidel, S.A.I.; Duhr, S.; Uhland, K.; Holthoff, H.P.; Jenne, D.; Braun, D. Direct Detection of Antibody Concentration and Affinity in Human Serum Using Microscale Thermophoresis. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 3523–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, T.; Arata, Y.; Shimada, I. A Multinuclear NMR-Study of the Affinity Maturation of Anti-Np Mouse Monoclonal-Antibodies—Comparison of Antibody Combining Sites of Primary Response Antibody N1g9 and Secondary Response Antibody-3b62. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 13961–13968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiskoot, W.; Hoogerhout, P.; Beuvery, E.C.; Herron, J.N.; Crommelin, D.J.A. Preparation and Application of a Fluorescein-Labeled Peptide for Determining the Affinity Constant of a Monoclonal-Antibody Hapten Complex by Fluorescence Polarization. Anal. Biochem. 1991, 196, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portmann, A.J.; Levison, S.A.; Dandliker, W.B. Anti-Fluorescein Antibody of High Affinity and Restricted Heterogeneity as Characterized by Fluorescence Polarization and Quenching Equilibrium Techniques. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1971, 43, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R. Calculation of Average Antibody-Affinity in Anti-Hapten Sera from Data Obtained by Competitive Radioimmunoassay. J. Immunol. Methods 1980, 34, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.W.; Li, Z.; Podariu, M.I.; Hage, D.S. Determination of Rate Constants and Equilibrium Constants for Solution-Phase Drug-Protein Interactions by Ultrafast Affinity Extraction. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 6454–6460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landry, J.P.; Ke, Y.H.; Yu, G.L.; Zhu, X.D. Measuring affinity constants of 1450 monoclonal antibodies to peptide targets with a microarray-based label-free assay platform. J. Immunol. Methods 2015, 417, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, F. Radioligand saturation binding for quantitative analysis of ligand-receptor interactions. Biophys. Rep. 2015, 1, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friguet, B.; Chaffotte, A.F.; Djavadiohaniance, L.; Goldberg, M.E. Measurements of the True Affinity Constant in Solution of Antigen-Antibody Complexes by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent-Assay. J. Immunol. Methods 1985, 77, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobrovnik, S.A. Determination of antibody affinity by ELISA. Theory. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2003, 57, 213–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatty, J.D.; Beatty, B.G.; Vlahos, W.G. Measurement of monoclonal antibody affinity by non-competitive enzyme immunoassay. J. Immunol. Methods 1987, 100, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, P.A. Problems and Pitfalls with Measurement of Antibody-Affinity Using Solid-Phase Binding in the Elisa. J. Immunol. Methods 1993, 164, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, M.G. Strukturelle und kinetische Untersuchungen zur Entwicklung und Optimierung von Hapten-Enzymimmunoassays (ELISAs) am Beispiel der Bestimmung von Triazinherbiziden: Dissertation-Technische Universität München, München-1992. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität München, München, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winklmair, M.; Weller, M.G.; Mangler, J.; Schlosshauer, B.; Niessner, R. Development of a highly sensitive enzyme-immunoassay for the determination of triazine herbicides. Fresenius’ J. Anal. Chem. 1997, 358, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopp, T.P.; Prickett, K.S.; Price, V.L.; Libby, R.T.; March, C.J.; Cerretti, D.P.; Urdal, D.L.; Conlon, P.J. A Short Polypeptide Marker Sequence Useful for Recombinant Protein Identification and Purification. Bio/Technology 1988, 6, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slootstra, J.W.; Kuperus, D.; Plückthun, A.; Meloen, R.H. Identification of new tag sequences with differential and selective recognition properties for the anti-FLAG monoclonal antibodies M1, M2 and M5. Mol. Divers. 1997, 2, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einhauer, A.; Jungbauer, A. Affinity of the monoclonal antibody M1 directed against the FLAG peptide. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 921, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srila, W.; Yamabhai, M. Identification of Amino Acid Residues Responsible for the Binding to Anti-FLAG™ M2 Antibody Using a Phage Display Combinatorial Peptide Library. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 171, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einhauer, A.; Jungbauer, A. The FLAG™ peptide, a versatile fusion tag for the purification of recombinant proteins. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2001, 49, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roosild, T.P.; Castronovo, S.; Choe, S. Structure of anti-FLAG M2 Fab domain and its use in the stabilization of engineered membrane proteins. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F 2006, 62, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knappik, A.; Plückthun, A. An Improved Affinity Tag Based on the Flag(R) Peptide for the Detection and Purification of Recombinant Antibody Fragments. Biotechniques 1994, 17, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hesse, A.; Weller, M.G. Protein Quantification by Derivatization-Free High-Performance Liquid Chromatography of Aromatic Amino Acids. J. Amino Acids 2016, 2016, 7374316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchipilov, T.; Meyer, K.; Weller, M.G. Quantitative (1)H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (qNMR) of Aromatic Amino Acids for Protein Quantification. Methods Protoc. 2023, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, B.N.; Paabo, S.; Stein, S. Amino-Acid-Analysis and Enzymatic Sequence Determination of Peptides by an Improved Ortho-Phthaldialdehyde Pre-Column Labeling Procedure. J. Liq. Chromatogr. 1981, 4, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountoulakis, M.; Lahm, H.W. Hydrolysis and amino acid composition analysis of proteins. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 826, 109–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinmuth-Selzle, K.; Tchipilov, T.; Backes, A.T.; Tscheuschner, G.; Tang, K.; Ziegler, K.; Lucas, K.; Pöschl, U.; Fröhlich-Nowoisky, J.; Weller, M.G. Determination of the protein content of complex samples by aromatic amino acid analysis, liquid chromatography-UV absorbance, and colorimetry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 4457–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, M.G.; Weil, L.; Niessner, R. Increased Sensitivity of an Enzyme-Immunoassay (ELISA) for the Determination of Triazine Herbicides by Variation of Tracer Incubation-Time. Mikrochim. Acta 1992, 108, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaoka, K.; Lubag, A.J.M.; Castillo-Muzquiz, A.; Kodadek, T.; Sherry, A.D. The detection limit of a Gd-based agent is substantially reduced when targeted to a protein microdomain. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2008, 26, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwaar, T.; Lettow, M.; Remmler, D.; Borner, H.G.; Weller, M.G. Efficient Screening of Combinatorial Peptide Libraries by Spatially Ordered Beads Immobilized on Conventional Glass Slides. High-Throughput 2019, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeck, A.; Weller, M.G.; Niessner, R. Characterization of a monoclonal TNT-antibody by measurement of the cross-reactivities of nitroaromatic compounds. Fresenius’ J. Anal. Chem. 1999, 364, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variation of Reagent Concentration (Either Antibody or Conjugate), Second Reagent Is Kept Constant | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (Start) | 1:3 | 1:9 | |
| Analyte concentration (mol/L) | 10-3 | 10-3 | 10-3 |
| 10-4 | 10-4 | 10-4 | |
| 10-5 | 10-5 | 10-5 | |
| 10-6 | 10-6 | 10-6 | |
| 10-7 | 10-7 | 10-7 | |
| 10-8 | 10-8 | 10-8 | |
| 10-9 | 10-9 | 10-9 | |
| 10-10 | 10-10 | 10-10 | |
| 10-11 | 10-11 | 10-11 | |
| 10-12 | 10-12 | 10-12 | |
| Direct, Competitive ELISA Competitor: FLAG Peptide | Conjugate HRP-FLAG (Tracer) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:90,000 (Start) | 1:270,000 (1:3) | 1:810,000 (1:9) | ||
| Antibody M2 | 1:90,000 (start) | 166 ± 21 nM | 139 ± 28 nM | 121 ± 30 nM |
| 1:270,000 (1:3) | 147 ± 23 nM | 133 ± 42 nM | 90 ± 13 nM | |
| 1:810,000 (1:9) | 127 ± 18 nM | 126 ± 73 nM | 90 ± 37 nM | |
| Indirect, Competitive ELISA Competitor: FLAG Peptide | Conjugate BSA-FLAG (Immobilized) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:1,500 (Start) | 1:4,500 (1:3) | 1:15,000 (1:10) | ||
| Antibody M2 | 1:30,000 (start) | 169 ± 21 nM | 146 ± 10 nM | 160 ± 16 nM |
| 1:90,000 (1:3) | 121 ± 16 nM | 104 ± 8 nM | 121 ± 16 nM | |
| 1:270,000 (1:9) | 109 ± 12 nM | 93 ± 5 nM | 93 ± 15 nM | |
| Method | Kd (nM) | FLAG Sequence | Conjugate | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| direct IA | 90 ± 37 | DYKDDDDK | HRP-CDYKDDDDK | This work |
| indirect IA | 93 ± 15 | DYKDDDDK | BSA-CDYKDDDDK | This work |
| FPIA | 150 | - | 5-FAM-SGSGDYKDDDDK | [63] |
| SPR | 50 ± 30 | DYKDDDDK | M2 (immobilized) | [64] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fischer, J.; Kaufmann, J.O.; Weller, M.G. Simple Determination of Affinity Constants of Antibodies by Competitive Immunoassays. Methods Protoc. 2024, 7, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps7030049
Fischer J, Kaufmann JO, Weller MG. Simple Determination of Affinity Constants of Antibodies by Competitive Immunoassays. Methods and Protocols. 2024; 7(3):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps7030049
Chicago/Turabian StyleFischer, Janina, Jan Ole Kaufmann, and Michael G. Weller. 2024. "Simple Determination of Affinity Constants of Antibodies by Competitive Immunoassays" Methods and Protocols 7, no. 3: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps7030049
APA StyleFischer, J., Kaufmann, J. O., & Weller, M. G. (2024). Simple Determination of Affinity Constants of Antibodies by Competitive Immunoassays. Methods and Protocols, 7(3), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps7030049







