- Review
Improving Laboratory-Based Cancer Drug Discovery Study Designs for Better Research Translations
- Sivananthan Manoharan
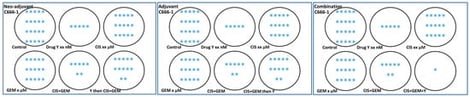
The process of developing a drug is complex and involves many steps, from basic research (bench) to patient applications (bedside), which are conducted to ensure the drug is both safe and effective. In cancer research, the failure rate is high when translating basic findings to clinical trials. One of the main factors probably contributing to high failure rates is the basic quality of in vitro and in vivo study designs. Advanced basic cancer research techniques, including various types of 3D cell culture, the use of valuable organoids, organs, or tumors on chips, traditional or automated Western blots, omics research, advanced imaging techniques, usage of cutting-edge preclinical models and others, may produce inaccurate results for translational research if the basic study design is not carefully planned, especially when drugs or compounds are involved. In this manuscript, the author discussed (i) the importance of understanding and applying pharmacokinetic data in basic research, (ii) a proper comparison of the efficacy and safety of investigational drugs with the standard of care, (iii) the importance of following the actual route of drug administration as experienced by patients, the cruciality of human-to-animal dose conversion, and dose frequencies in animal models, (iv) significance of the age, gender, and strain of mice, along with adherence to the ARRIVE guidelines for ensuring transparency in conducting and reporting preclinical research, (v) benefits of having both subcutaneous and metastasis models in preclinical studies, (vi) the impact of comorbidities and related cancer drug studies in animal models and (vii) the importance of testing drug candidate/s in model mimicking acidic tumor microenvironment.
3 March 2026