- Feature Paper
- Article
Lower Bound on the Overlattice-Based Sieve Algorithm
- Tongchen Shen,
- Xiangxue Li and
- Licheng Wang
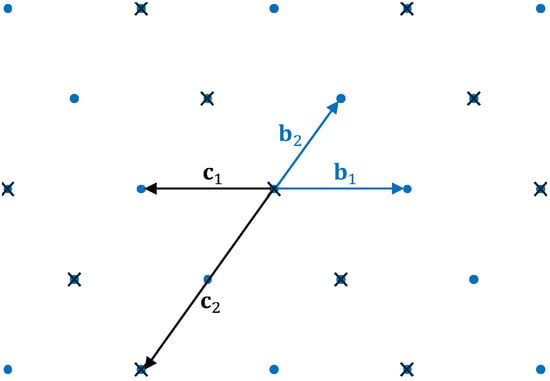
Lattice-based cryptography stands as one of the most pivotal candidates in post-quantum cryptography. To configure the parameters of lattice-based cryptographic schemes, a thorough comprehension of their concrete security is indispensable. Lattice sieving algorithms represent among the most critical tools for conducting concrete security analysis. Currently, the state-of-the-art BDGL-sieve (SODA 2016) achieves a time complexity of
1 January 2026