Residues of 6PPD-Q in the Aquatic Environment and Toxicity to Aquatic Organisms: A Review
Abstract
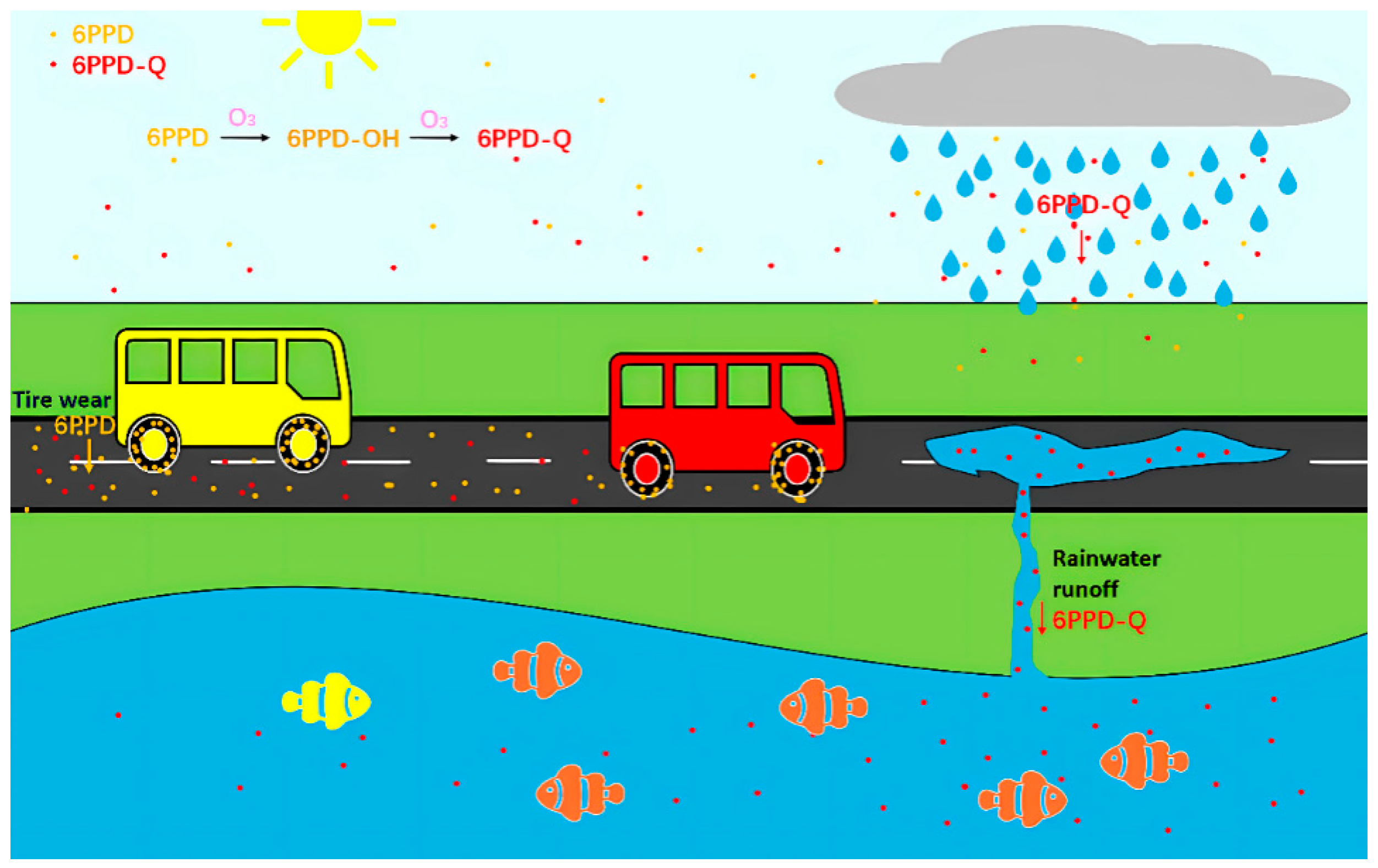
:1. Introduction
2. Distribution and Concentration of 6PPD-Q in the Environment
3. Residues of 6PPD-Q in Aquatic Environments
4. Toxicity of 6PPD-Q to Aquatic Organisms
4.1. Toxicity to Fish
4.2. Toxicity to Aquatic Crustaceans
4.3. Toxicity to Aquatic Mollusks
4.4. Toxicity to Algae and Cyanobacteria
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Xu, T.-T.; Ye, D.-M.; Lin, Z.-Z.; Wang, F.; Guo, Y. Widespread N-(1,3-dimethylbutyl)-N′-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine quinone in size-fractioned atmospheric particles and dust of different indoor environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 420–425. [Google Scholar]
- Johannessen, C.; Helm, P.; Lashuk, B.; Yargeau, V.; Metcalfe, C.D. The tire wear compounds 6PPD-quinone and 1, 3-diphenylguanidine in an urban watershed. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 82, 171–179. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Cao, G.; Zhang, J.; Wu, P.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Qi, Z.; Li, R.; Dong, C.; Cai, Z. Beyond substituted p-Phenylenediamine antioxidants: Prevalence of their quinone derivatives in PM2. 5. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 10629–10637. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Wu, P.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Z.; Hu, D.; Cai, Z. New evidence of rubber-derived quinones in water, air, and soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 4142–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, S.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, L.; Luo, X.; Chen, L.; Zheng, H.; et al. First insights into 6PPD-quinone formation from 6PPD photodegradation in water environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; He, T.; Yang, X.; Gan, Y.; Qing, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y. Analysis, environmental occurrence, fate and potential toxicity of tire wear compounds 6PPD and 6PPD-quinone. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Zhao, H.; Peter, K.T.; Gonzalez, M.; Wetzel, J.; Wu, C.; Hu, X.; Prat, J.; Mudrock, E.; Hettinger, R. A ubiquitous tire rubber–derived chemical induces acute mortality in coho salmon. Science 2021, 371, 185–189. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, X.-L.; Chen, Z.-F.; Liu, Q.-Y.; Zhou, J.-M.; Cai, W.-X.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Z. Tissue Accumulation and Biotransformation of 6PPD-Quinone in Adult Zebrafish and Its Effects on the Intestinal Microbial Community. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 10275–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Shi, R.; Zeb, A.; Li, X.; Ge, Y. Phytotoxicity of 6PPD and its uptake by Myriophyllum verticillatum: Oxidative stress and metabolic processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 955, 177248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, Q.; Lao, J.-Y.; Cao, Y.; Hong, P.; Chen, C.; Lam, E.Y.; Fang, J.K.-H.; Lee, S.; Leung, K.M.Y. Typical Tire Additives in River Water: Leaching, Transformation, and Environmental Risk Assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 18940–18949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohara, K.; Timilsina, A.; Adhikari, K.; Kafle, A.; Basyal, S.; Joshi, P.; Yadav, A.K. A mini review on 6PPD quinone: A new threat to aquaculture and fisheries. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 340, 122828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiki, K.; Yamamoto, H. Concentration and leachability of N-(1, 3-dimethylbutyl)-N′-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine (6PPD) and its quinone transformation product (6PPD-Q) in road dust collected in Tokyo, Japan. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 302, 119082. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Xiao, J.; Kiki, C.; Zhang, Y.; Manzi, H.P.; Zhao, G.; Wang, S.; Sun, Q. Unraveling the fate of 6PPD-Q in aquatic environment: Insights into formation, dissipation, and transformation under natural conditions. Environ. Int. 2024, 191, 109004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Qi, P.; Wang, Z.; Xu, H.; Jin, Y.; Wang, X. Chiral perspective evaluations: Enantioselective hydrolysis of 6PPD and 6PPD-quinone in water and enantioselective toxicity to Gobiocypris rarus and Oncorhynchus mykiss. Environ. Int. 2022, 166, 107374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiki, K.; Asahina, K.; Kato, K.; Yamagishi, T.; Omagari, R.; Iwasaki, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Yamamoto, H. Acute toxicity of a tire rubber-derived chemical, 6PPD quinone, to freshwater fish and crustacean species. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 779–784. [Google Scholar]
- Johannessen, C.; Helm, P.; Metcalfe, C.D. Detection of selected tire wear compounds in urban receiving waters. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117659. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rauert, C.; Charlton, N.; Okoffo, E.D.; Stanton, R.S.; Agua, A.R.; Pirrung, M.C.; Thomas, K.V. Concentrations of tire additive chemicals and tire road wear particles in an Australian urban tributary. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 2421–2431. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, R.F.; Smalling, K.L.; Bradley, P.M.; Greer, J.B.; Gordon, S.E.; Hansen, J.D.; Kolpin, D.W.; Spanjer, A.R.; Masoner, J.R. Tire-derived contaminants 6PPD and 6PPD-Q: Analysis, sample handling, and reconnaissance of United States stream exposures. Chemosphere 2024, 363, 142830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, L.-Y.; Shen, M.; Du, B. Widespread Occurrence and Transport of p-Phenylenediamines and Their Quinones in Sediments across Urban Rivers, Estuaries, Coasts, and Deep-Sea Regions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 2393–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, S.; Reguyal, F.; Sarmah, A.K. A bibliometric analysis of global research hotspots and progress on emerging environmental pollutants 6PPD and 6PPD-quinone from 2004 to 2024. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 362, 124969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmi, S.S.U.H.; Xu, Q.; Tayyab, M.; Pastorino, P.; Barcelò, D.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Khan, Z.H.; Li, G. Navigating the environmental dynamics, toxicity to aquatic organisms and human associated risks of an emerging tire wear contaminant 6PPD quinone. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 356, 124313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.-N.; Wu, N.-N.; Xu, R.; Liu, S.; Li, H.-X.; Lin, L.; Hou, R.; Xu, X.-R.; Zhao, J.-L.; Ying, G.-G. First Evidence of the Bioaccumulation and Trophic Transfer of Tire Additives and Their Transformation Products in an Estuarine Food Web. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 6370–6380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, D.; Ji, X.; Cantin, J.; Philibert, D.; Foster, G.; Selinger, S.; Jain, N.; Miller, J.; McIntyre, J.; de Jourdan, B. Interspecies differences in 6PPD-quinone toxicity across seven fish species: Metabolite identification and semiquantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 21071–21079. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson-Bain, K.; Roberts, C.; Kohlman, E.; Ji, X.; Alcaraz, A.J.; Miller, J.; Gangur-Powell, T.; Weber, L.; Janz, D.; Hecker, M. Apical and mechanistic effects of 6PPD-quinone on different life-stages of the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 271, 109697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosser, R.; Salole, J.; Hang, S. Toxicity of 6PPD-quinone to four freshwater invertebrate species. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 337, 122512. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, C.; Lin, J.; Kohlman, E.; Jain, N.; Amekor, M.; Alcaraz, A.J.; Hogan, N.; Hecker, M.; Brinkmann, M. Acute and Subchronic Toxicity of 6PPD-Quinone to Early Life Stage Lake Trout (Salvelinus namaycush). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, S.; Gora, A.H.; Siriyappagouder, P.; Kiron, V.; Olsvik, P.A. Toxicological effects of 6PPD and 6PPD quinone in zebrafish larvae. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Chen, C.; Guan, K.; Xu, S.; Chen, X.; Lin, Y.; Li, X.; Shan, Y. Protective role of ghrelin against 6PPD-quinone-induced neurotoxicity in zebrafish larvae (Danio rerio) via the GHSR pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 285, 117031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, C.; Kohlman, E.; Jain, N.; Amekor, M.; Alcaraz, A.J.; Brinkmann, M.; Hecker, M. Sub-chronic and acute toxicity of 6PPD-quinone to early-life stage rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). bioRxiv 2024. bioRxiv: 2024.2009. 2025.614982. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.-Y.; Gan, X.; Shen, B.; Jiang, J.; Shen, H.; Lei, Y.; Liang, Q.; Bai, C.; Huang, C.; Wu, W. 6PPD and its metabolite 6PPDQ induce different developmental toxicities and phenotypes in embryonic zebrafish. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 455, 131601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Mao, X.; Lu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Huang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Ye, C.; He, Z.; Shu, L.; Mo, D. 6PPD induces cerebrovascular defects by triggering oxidative stress and ferroptosis in zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 958, 178004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Di, S.; Wang, C.; Hu, Q.; Jin, Y. Tire rubber-derived contaminant 6PPD had the potential to induce metabolism disorder in early developmental stage of zebrafish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2025, 287, 110062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Sun, W.; Wang, B.; Shi, C.; Ran, R.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, L.; Zhang, H. Environmental concentrations of 6PPD and 6PPD-quinone induce hepatic lipid metabolism disorders in male black-spotted frogs. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Fang, L.; Di, S.; Yu, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Jin, Y. Bioaccumulation of N-(1,3-dimethylbutyl)-N′-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine (6PPD) and its potential cardiotoxicity in larval zebrafish (Danio rerio). SSRN 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasse, N.; Seiwert, B.; Massei, R.; Scholz, S.; Fu, Q.; Reemtsma, T. Uptake and Biotransformation of the Tire Rubber-derived Contaminants 6-PPD and 6-PPD Quinone in the Zebrafish Embryo (Danio rerio). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 15598–15607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Wu, F.; Zhao, Z.; Ye, T.; Luo, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H. Effects of environmental concentrations of 6PPD and its quinone metabolite on the growth and reproduction of freshwater cladoceran. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 175018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comenges, J.Z.; Fentanes, J.B.; Worth, A. Biology-based dynamic approach for the reconciliation of acute and chronic toxicity tests: Application to Daphnia magna. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 196, S125. [Google Scholar]
- Botelho, M.T.; Militão, G.G.; Brinkmann, M.; Umbuzeiro, G.d.A. Toxicity and mutagenicity studies of 6PPD-quinone in a marine invertebrate species and bacteria. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2023, 64, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Castro-Català, N.; Lizama, C.; Serra, J.; Cadena-Aizaga, M.I.; Petrovic, M.; Muñoz, I. Crawling Towards Complex Interactions: The Impact of 6ppd-Quinone and Increased Temperatures on the Freshwater Snail Radix balthica. SSRN 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallec, K.; Huvet, A.; Yeuc’h, V.; Le Goïc, N.; Paul-Pont, I. Chemical effects of different types of rubber-based products on early life stages of Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 427, 127883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Kiki, C.; Xu, Z.; Manzi, H.P.; Rashid, A.; Chen, T.; Sun, Q. Comparative growth inhibition of 6PPD and 6PPD-Q on microalgae Selenastrum capricornutum, with insights into 6PPD-induced phototoxicity and oxidative stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177627. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bourgougnon, N.; Burlot, A.-S.; Jacquin, A.-G. Chapter Five—Algae for global sustainability? In Advances in Botanical Research; Jacquot, J.-P., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Volume 100, pp. 145–212. [Google Scholar]
- You, X.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Wu, Z.; Sun, W.; Ni, J. 6PPD-quinone affects the photosynthetic carbon fixation in cyanobacteria by extracting photosynthetic electrons. Innovation 2024, 5, 100630. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yu, M.; Shi, R.; Ge, Y.; Li, J.; Zeb, A.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, W. Comparative toxic effect of tire wear particle-derived compounds 6PPD and 6PPD-quinone to Chlorella vulgaris. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihenetu, S.C.; Xu, Q.; Khan, Z.H.; Kazmi, S.S.U.H.; Ding, J.; Sun, Q.; Li, G. Environmental fate of tire-rubber related pollutants 6PPD and 6PPD-Q: A review. Environ. Res. 2024, 258, 119492. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Name | Abbreviate | Structure | Structural Formula | Molecular Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-(1,3-dimethylbutyl)-N′-phenylenediamine | 6PPD | 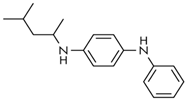 | C18H24N2 | 268.40 |
| N-(1,3-dimethylbutyl)-N′-phenylenediamine-quinone | 6PPD-Q | 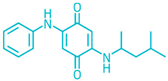 | C18H22N2O2 | 298.39 |
| Environment Type | Location | Concentration Range | Median Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Road runoff (water) | Seattle, USA | 0.8–19 μg/L | —— |
| Road runoff (water) | Los Angeles, USA | 4.1–6.1 μg/L | —— |
| urban runoff (water) | San Francisco, USA | 1.0–3.5 μg/L | —— |
| Urban streams (water) | Don River, Highland Creek, Toronto, Canada | 0.54 ± 0.04, 0.72 ± 0.26 μg/L | —— |
| River(urban affected) (water) | Southwest branch, Brisbane River, Australia | 0.4–88 ng/L | —— |
| River estuary (Sediment) | Major rivers in the Pearl River Delta, China | 1.87–18.2 ng/g | 9.03 ng/g |
| River estuary (Sediment) | Pearl River estuary, South China Sea | <MDL a–4.88 ng/g | 2.00 ng/g |
| Coastal rivers (Sediment) | Coastal areas, South China Sea | 0.431–2.98 ng/g | 1.27 ng/g |
| Coastal deep-sea (Sediment) | South China Sea deep-sea areas | <MDL–3.02 ng/g | 2.71 ng/g |
| Species of Fish | Life Cycle | Exposure Duration (h) | LC50 (μg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Danio rerio | embryo | - | 54 |
| 0ncorhynchus kisutch | juvenile fish | 24 | <0.10 |
| Oncorhynchus mykiss | juvenile fish | 72 | 1.00 |
| Salvelinus fontinalis | juvenile fish | 24 | 0.59 |
| Salvelinus namaycush | juvenile fish | 96 | 0.50 |
| Salvelinus alpinus | juvenile fish | 96 | 14.2 |
| Acipenser oxyrinchus | juvenile fish | 96 | 14.2 |
| Gobiocypris rarus | juvenile fish | 96 | 162.201 |
| Acipenser transmontanus | juvenile fish | 96 | 14.2 |
| Sciaenops ocellatus | juvenile fish | 24–72 | 500 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Huang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Hong, Y. Residues of 6PPD-Q in the Aquatic Environment and Toxicity to Aquatic Organisms: A Review. Fishes 2025, 10, 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10040146
Li C, Yang Y, Tian Z, Huang Z, Huang Y, Hong Y. Residues of 6PPD-Q in the Aquatic Environment and Toxicity to Aquatic Organisms: A Review. Fishes. 2025; 10(4):146. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10040146
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chaoju, Yuanqiang Yang, Zikun Tian, Zhiqiu Huang, Yi Huang, and Yuhang Hong. 2025. "Residues of 6PPD-Q in the Aquatic Environment and Toxicity to Aquatic Organisms: A Review" Fishes 10, no. 4: 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10040146
APA StyleLi, C., Yang, Y., Tian, Z., Huang, Z., Huang, Y., & Hong, Y. (2025). Residues of 6PPD-Q in the Aquatic Environment and Toxicity to Aquatic Organisms: A Review. Fishes, 10(4), 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10040146






