Sub-Lethal Effects of Predators in Aquaculture: Assessment of Chronic Exposure to Conspecific Alarm Substance on Feeding and Growth Performances of Nile Tilapia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Fish and Holding Conditions
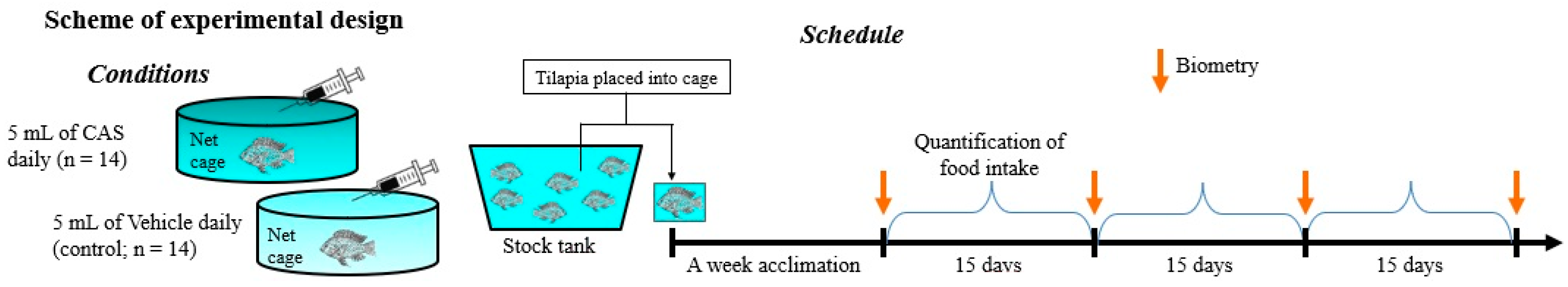
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Technical Procedures
2.4.1. Experimental Apparatus
2.4.2. Conspecific Alarm Substance (CAS) Preparation
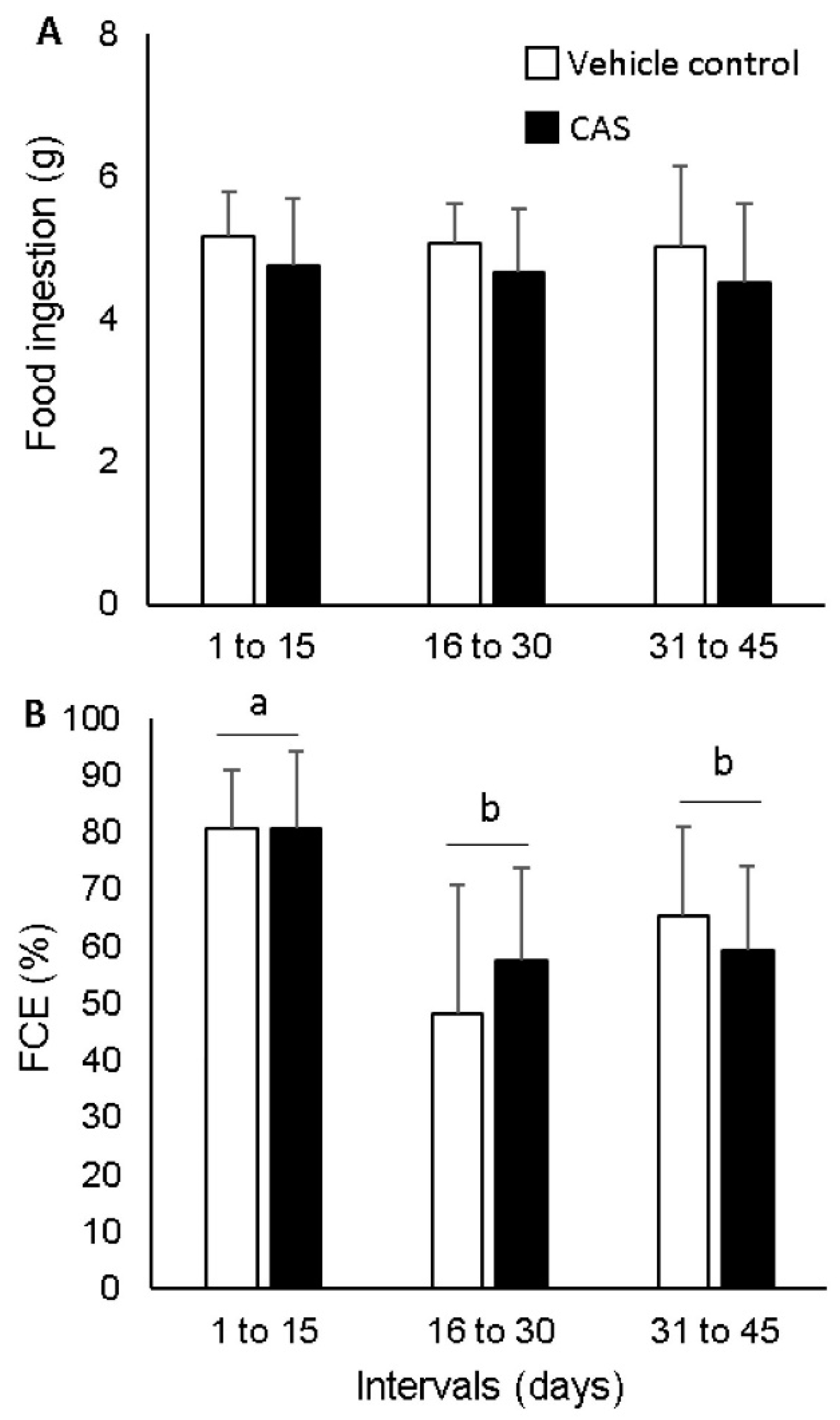
2.4.3. Growth and Feeding Performance Calculations
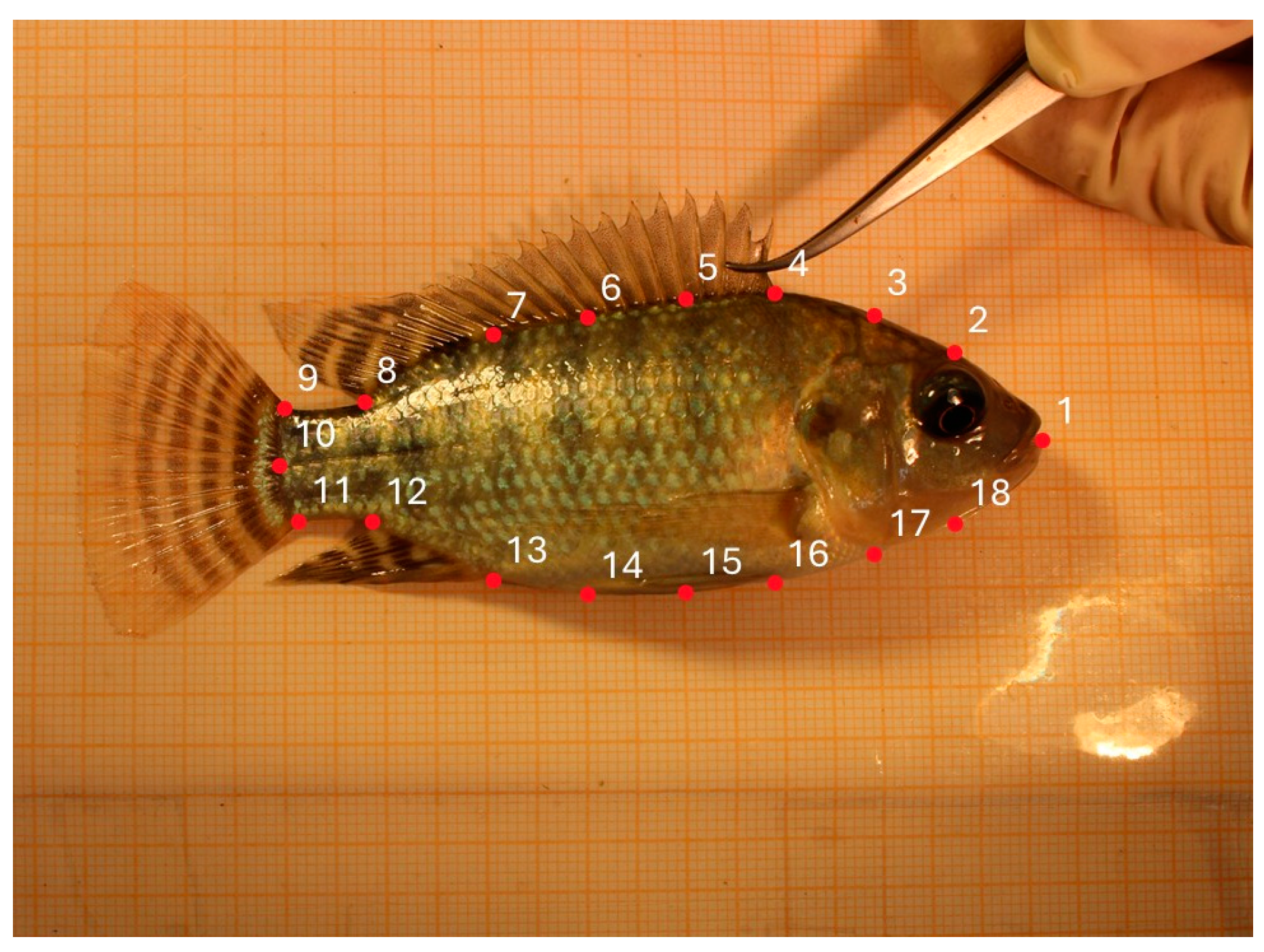
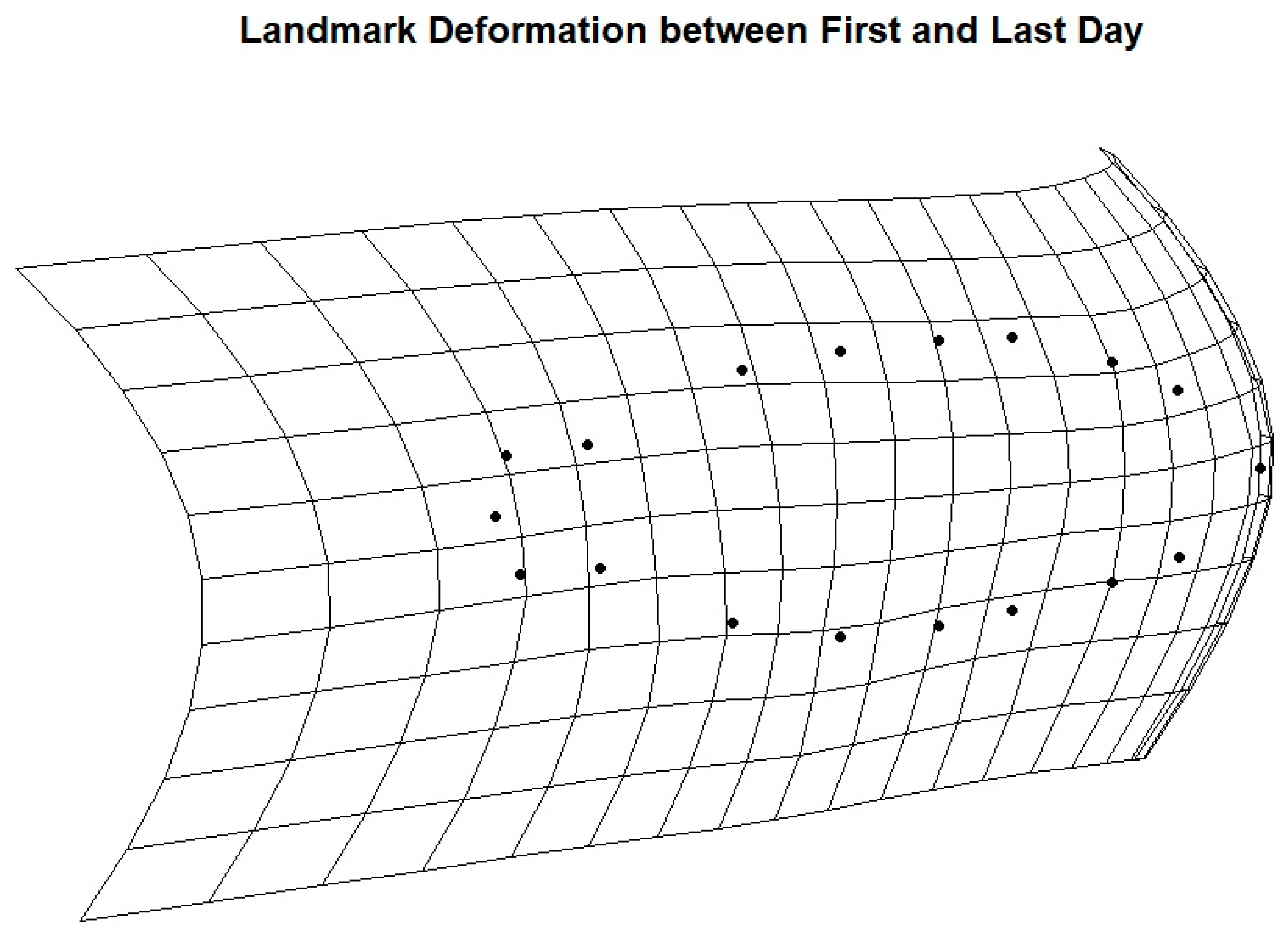
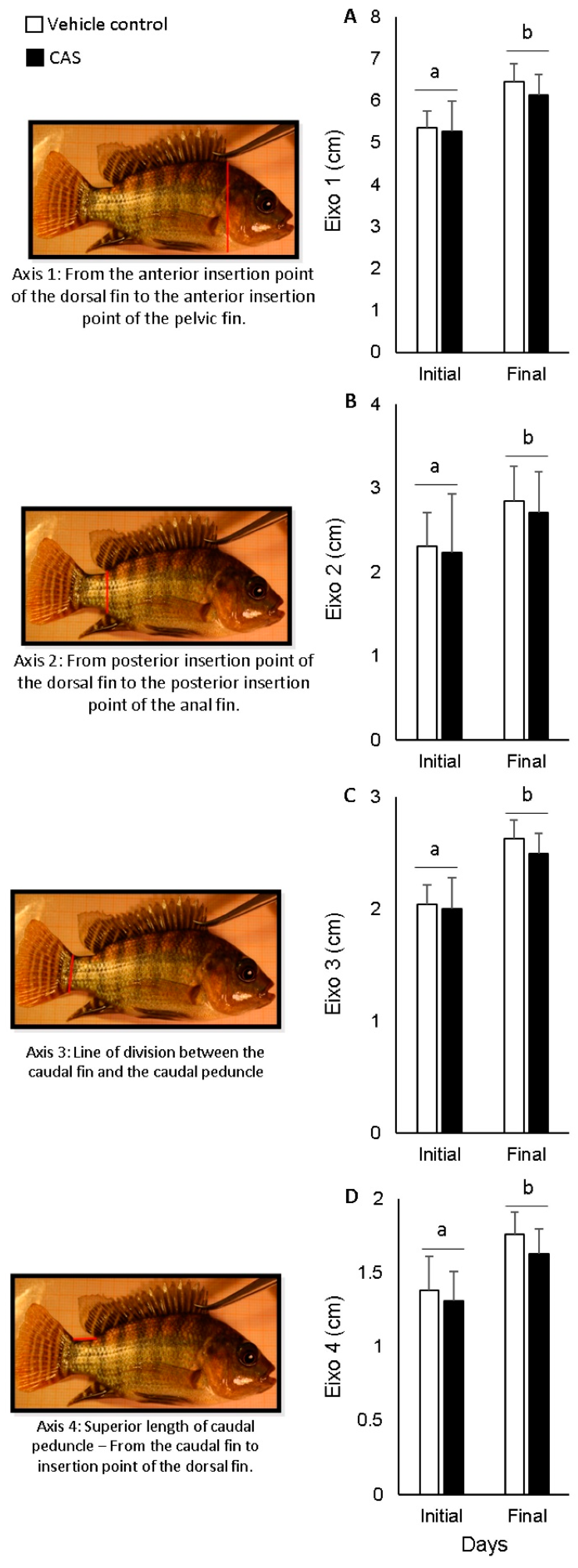
2.4.4. Body Axes
2.5. Statistical Analyses
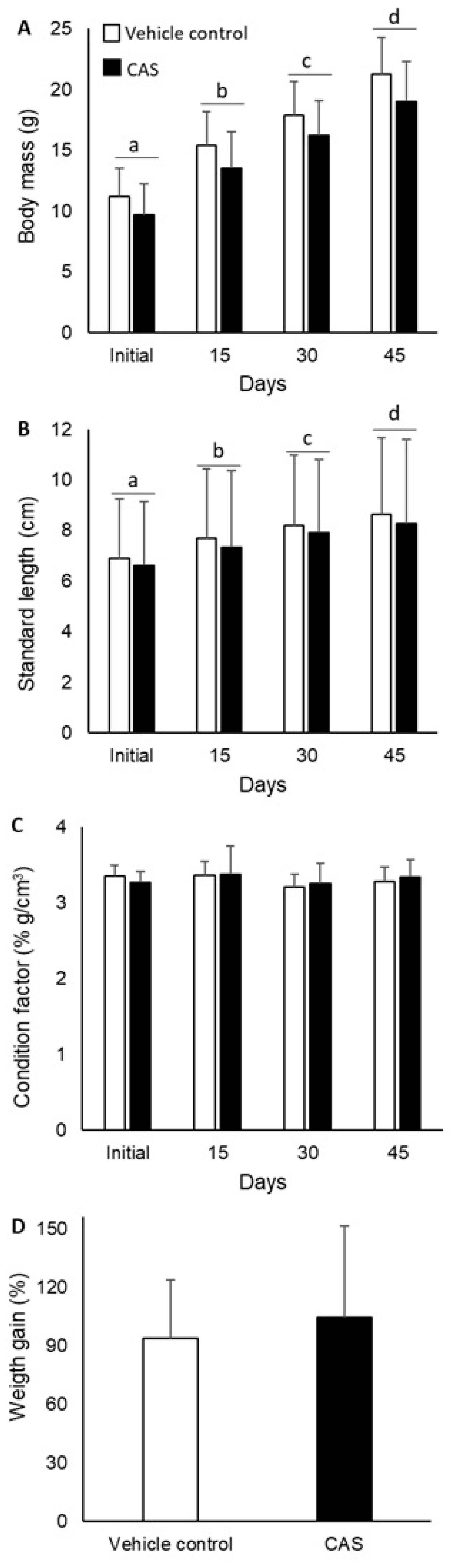
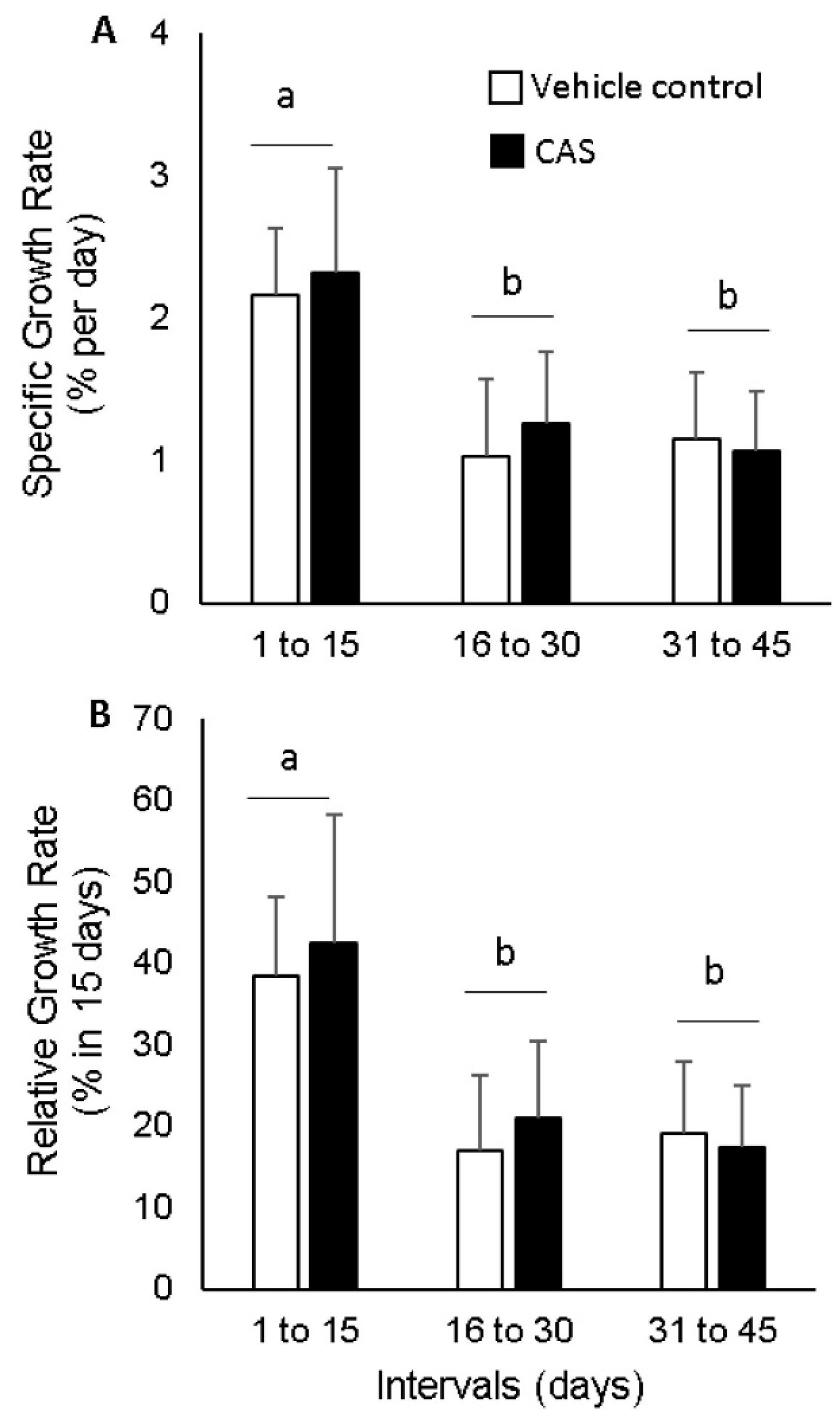
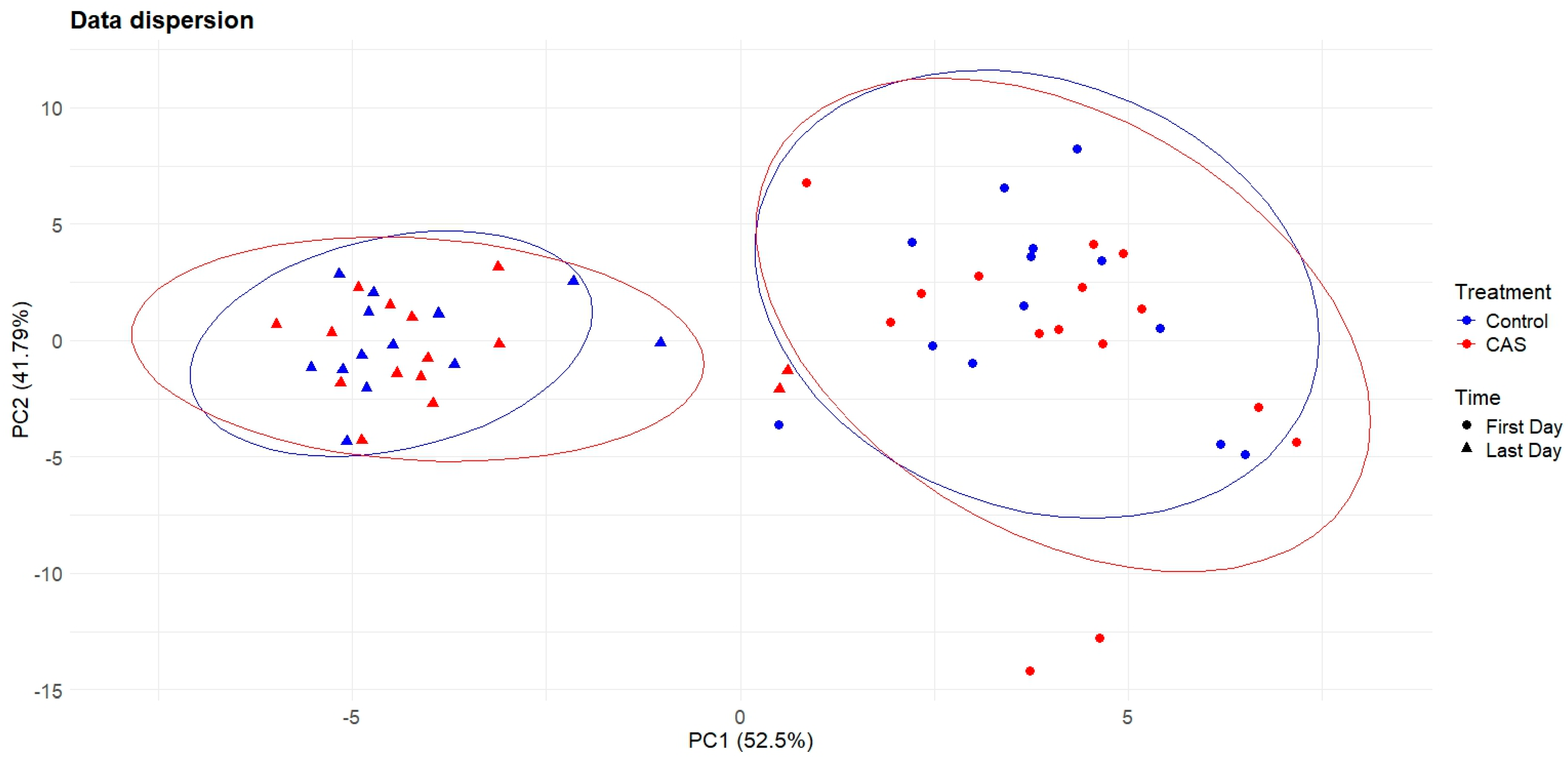
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quick, N.J.; Middlemas, S.J.; Armstrong, J.D. A survey of antipredator controls at marine salmon farms in Scotland. Aquaculture 2004, 230, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Jerez, P.; Fernandez-Jover, D.; Bayle-Sempere, J.; Valle, C.; Dempster, T.; Tuya, F.; Juanes, F. Interactions between bluefish Pomatomus saltatrix (L.) and coastal sea-cage farms in the Mediterranean Sea. Aquaculture 2008, 282, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fregadolli, C.H. Laboratory analysis of predation by cyclopoid copepods on first-feeding larvae of cultured Brazilian fishes. Aquaculture 2003, 228, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, R.K.; Portella, M.C. Effect of prey concentrations and feed training on production of Hoplias lacerdae juvenile. An. Acad. Bras. Ciências 2015, 87, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenici, P.; Blake, R. The kinematics and performance of fish fast-start swimming. J. Exp. Biol. 1997, 200, 1165–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, W. Distribution of fright reaction and alarm substance cells in fishes. Copeia 1977, 4, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endler, J.A. Defense against predators. In Predator–Prey Relationships: Perspectives and Approaches From the Study of Lower Vertebrates; Feder, M.E., Lauder, G.V., Eds.; University of Chicago: Chicago, IL, USA, 1986; pp. 109–134. [Google Scholar]
- Chivers, D.P.; Smith, R.J.F. Chemical alarm signalling in aquatic predator-prey systems: A review and prospectus. Ecoscience 1998, 5, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaquinto, P.C.; Volpato, G.L. Hunger suppresses the onset and the freezing component of the antipredator response to conspecific skin extract in pintado catfish. Behaviour 2001, 138, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, L.M.; Urbinati, E.C.; Hoffmann, A. The role of olfaction in the behavioural and physiological responses to conspecific skin extract in Brycon cephalus. J. Fish Biol. 2003, 63, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, R.E.; Barbosa, A.; Giassi, A.C.C.; Hoffmann, A. The ‘Club’ Cell and Behavioural and Physiological Responses to Chemical Alarm Cues in the Nile Tilapia. Mar. Freshwater Behav. Physiol. 2010, 43, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisenden, B.D. Olfactory assessment of predation risk in the aquatic environment. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London B Biol. Sci. 2000, 355, 1205–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathis, A. Alarm responses as a defense: Chemical alarm cues in nonostariophysan fishes. In Fish Defenses Vol. 2: Pathogens, Parasites and Predators; Zaccone, G., Perriére, C., Mathis, A., Kapoor, B.G., Eds.; Science Publishers: Enfield, NH, USA, 2009; pp. 323–386. [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen, E.A.; Closs, G.P. Anti-predator response of naïve and experienced common bully to chemical alarm cues. J. Fish Biol. 2004, 64, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yan, Z.; Lin, A.; Li, X.; Li, K. Non-Dose-Dependent Relationship between Antipredator Behavior and Conspecific Alarm Substance in Zebrafish. Fishes 2023, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.D.; Cowman, P.F.; McCormick, M.I. Chemical alarm cues are conserved within the coral reef fish family pomacentridae. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, F.H.C.; Miyai, C.A.; Pinho-Neto, C.F.; Barreto, R.E. Stress responses to chemical alarm cues in the Nile tilapia. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 149, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, S.L.; Dill, L.M. Behavioral decisions made under the risk of predation: A review and prospectus. Can. J. Zool. 1990, 68, 619–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartosiewicz, M.; Gliwicz, Z.M. Temporary Intermissions in Capturing Prey (Daphnia) by Planktivorous Fish (Rutilus rutilus): Are They Due to Scramble Competition or the Need for Antipredation Vigilance? Hydrobiologia 2011, 668, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Schwarzkopf, L. Foraging behaviour of the Peaceful Dove (Geopelia striata) in relation to predation risk: Group size and predator cues in a natural environment. Emu 2013, 113, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, J.; Senar, J.C. Antipredator behavioural compensation of proactive personality trait in male Eurasian siskins. Anim. Behav. 2014, 90, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, G. Antipredator Vigilance Decreases with Food Density in Staging Flocks of Semipalmated Sandpipers (Calidris pusilla). Can. J. Zool. 2014, 92, 785–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams, M.V.; Sutterlin, A. The Foraging and Antipredator Behaviour of Growth-Enhanced Transgenic Atlantic Salmon. Anim. Behav. 1999, 58, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.K.; Ramnarine, I.; Brown, G.E. Compensatory foraging in Trinidadian guppies: Effects of acute and chronic predation threats. Curr. Zool. 2014, 60, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, C.M.; Flecker, A.S. Metabolic stoichiometry and the ecology of fear in Trinidadian guppies: Consequences for life histories and stream ecosystems. Oecologia 2014, 176, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lönnstedt, O.M.; McCormick, M.I.; Chivers, D.P. Predator-induced changes in the growth of eyes and false eyespots. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chivers, D.P.; Zhao, X.; Brown, G.E.; Marchant, T.A.; Ferrari, C.O.M. Predator-induced changes in morphology of a prey fish: The effects of food level and temporal frequency of predation risk. Evol. Ecol. 2008, 22, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brönmark, C.; Miner, J.G. Predator-induced phenotypical change in body morphology in crucian carp. Science 1992, 258, 1348–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklöv, P.; Svanbäck, R. Predation risk influences adaptive morphological variation in fish populations. Am. Nat. 2006, 167, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, R.L.; Hardy, R.W.; Buschmann, A.H.; Bush, S.R.; Cao, L.; Klinger, D.H.; Little, D.C.; Lubchenco, J.; Shumway, S.E. A 20-year retrospective review of global aquaculture. Nature 2021, 591, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, W.C.; Barros, H.P.; Moraes-Valenti, P.; Bueno, G.W.; Cavalli, R.O. Aquaculture in Brazil: Past, present and future. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 19, 100611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpato, G.L.; Bovi, T.S.; de Freitas, R.H.A.; da Silva, D.F.; Delicio, H.C.; Giaquinto, P.C.; Barreto, R.E. Red Light Stimulates Feeding Motivation in Fish but Does Not Improve Growth. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.D.O.; Volpato, G.L. Heterogeneous growth in the Nile tilapia: Social stress and carbohydrate metabolism. Physiol. Behav. 1993, 54, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpato, G.L.; Fernandes, M.O. Social control of growth in fish. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 1994, 27, 797–810. [Google Scholar]
- Corrêa, S.A.; Fernandes, M.O.; Iseki, K.K.; Negrão, J.A. Effect of the establishment of dominance relationships on cortisol and other metabolic parameters in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2003, 36, 1725–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lugert, V.; Thaller, G.; Tetens, J.; Schulz, C.; Krieter, J. A review on fish growth calculation: Multiple functions in fish production and their specific application. Rev. Aquac. 2016, 8, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootton, R.J. Ecology of Teleost Fishes; Fish Fish. Series 1; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1990; p. 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, R. Cube law, condition factor and weight-length relationships: History, meta-analysis and recommendations. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2006, 22, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohlf, F.J. tpsUtil. Version 1.26; Department of Ecology and Evolution, State University of New York at Stony Brook, Stony Brook: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Rohlf, F.J. TpsDig. Version 2.04; Department of Ecology and Evolution, State University of New York at Stony Brook, Stony Brook: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mojekwu, T.O.; Anumudu, C.I. Advanced techniques for morphometric analysis in fish. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2015, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Ashraf, I.; François, B.; Kolomenskiy, D.; Lechenault, F.; Thiria, B. Burst-and-coast swimmers optimize gait by adapting unique intrinsic cycle. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekár, S.; Brabec, M. Generalized estimating equations: A pragmatic and flexible approach to the marginal GLM modelling of correlated data in the behavioural sciences. Ethology 2018, 124, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Khatun, M. Production performances of monosex Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus in brackishwater ponds. Bangladesh J. Zool. 2014, 42, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Silva, T.S.; Santos, L.D.; Silva, L.C.R.; Michelato, M.; Furuya, V.R.B.; Furuya, W.M. Length-weight relationship and prediction equations of body composition for growing-finishing cage-farmed Nile tilapia. Rev. Bras. Zootecnia 2015, 44, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, V.B.; Silva, V.V.; Almeida, M.V.; Mareco, E.A.; Salomão, R.A.S. Performance of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus strains in Brazil: A comparison with Philippine strain. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2019, 47, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, A.C.C.; Soares, S.M.; Fortuna, M.; Costa, V.C.; Barletto, I.P.; Mozatto, M.T.; Siqueira, L.; Barcellos, H.H.A.; Barreto, R.E.; Barcellos, L.J.G. A single exposure to sub-lethal concentrations of a glyphosate-based herbicide or fluoxetine-based agent on growth performance in Nile tilapia. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2023, 86, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, A. Growth and stress in fish production. Aquaculture 1993, 111, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Weerd, J.; Komen, J. The effects of chronic stress on growth in fish: A critical appraisal. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 1998, 120, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, R.E.; Gontijo, A.M.M.C.; Delicio, H.C. Correlations Between Pre- and Post-Fasting Growth in Nile Tilapia. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2008, 34, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, S.; Ebeneezar, S.; Ramudu, R.; Pal, M. Compensatory Growth and Production Economics of Silver Pompano, Trachinotus blochii (Lacepede, 1801), Fingerlings Stunted by Feed and Space Deprivation. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1234667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.O.; Ali, M.E.; Aziz, A.A. Length-Weight Relationships and Condition Factors of Six Fish Species in Atbara River and Khashm el-Girba Reservoir, Sudan. Int. J. Agric. Sci. 2011, 3, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde-Sieira, M.; Chivite, M.; Míguez, J.M.; Soengas, J.L. Stress effects on the mechanisms regulating appetite in teleost fish. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, J.P.G.A.; Isaac, A.B.J.; Silva, R.B.; Toledo, L.C.S.; Barcellos, L.J.G.; Delicio, H.C. Acute Effects of Fluoxetine on Stress Responses and Feeding Motivation in Nile Tilapia. Fishes 2023, 8, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvigo, A.L.; Miyai, C.A.; Sanches, F.H.; Barreto, R.E.; Costa, T.M. Combined Effects of Predator Odor and Alarm Substance on Behavioral and Physiological Responses of the Pearl Cichlid. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 206, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, B.A.; Iwama, G.K. Physiological Changes in Fish from Stress in Aquaculture with Emphasis on the Response and Effects of Corticosteroids. Ann. Rev. Fish Dis. 1991, 1, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, B.A. Stress in Fishes: A Diversity of Responses with Particular Reference to Changes in Circulating Corticosteroids. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2002, 42, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, B.A.; Schreck, C.; Barton, L. Effects of Chronic Cortisol Administration and Daily Acute Stress on Growth, Physiological Conditions, and Stress Responses in Juvenile Rainbow Trout. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1987, 2, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pereira, R.T.; Arvigo, A.L.; Miyai, C.A.; Silveira, A.R.; Giaquinto, P.C.; Delicio, H.C.; Barcellos, L.J.G.; Barreto, R.E. Sub-Lethal Effects of Predators in Aquaculture: Assessment of Chronic Exposure to Conspecific Alarm Substance on Feeding and Growth Performances of Nile Tilapia. Fishes 2025, 10, 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10040174
Pereira RT, Arvigo AL, Miyai CA, Silveira AR, Giaquinto PC, Delicio HC, Barcellos LJG, Barreto RE. Sub-Lethal Effects of Predators in Aquaculture: Assessment of Chronic Exposure to Conspecific Alarm Substance on Feeding and Growth Performances of Nile Tilapia. Fishes. 2025; 10(4):174. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10040174
Chicago/Turabian StylePereira, Rafaela Torres, Alexandre Luiz Arvigo, Caio Akira Miyai, Augusto Rysevas Silveira, Percília Cardoso Giaquinto, Helton Carlos Delicio, Leonardo José Gil Barcellos, and Rodrigo Egydio Barreto. 2025. "Sub-Lethal Effects of Predators in Aquaculture: Assessment of Chronic Exposure to Conspecific Alarm Substance on Feeding and Growth Performances of Nile Tilapia" Fishes 10, no. 4: 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10040174
APA StylePereira, R. T., Arvigo, A. L., Miyai, C. A., Silveira, A. R., Giaquinto, P. C., Delicio, H. C., Barcellos, L. J. G., & Barreto, R. E. (2025). Sub-Lethal Effects of Predators in Aquaculture: Assessment of Chronic Exposure to Conspecific Alarm Substance on Feeding and Growth Performances of Nile Tilapia. Fishes, 10(4), 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10040174






