The Impact of Feeding Rates on the Growth, Stress Response, Antioxidant Capacity, and Immune Defense of Koi (Cyprinus carpio var. koi)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Feed
2.2. Fish Feeding Trial
2.3. Sample Collection Methodology
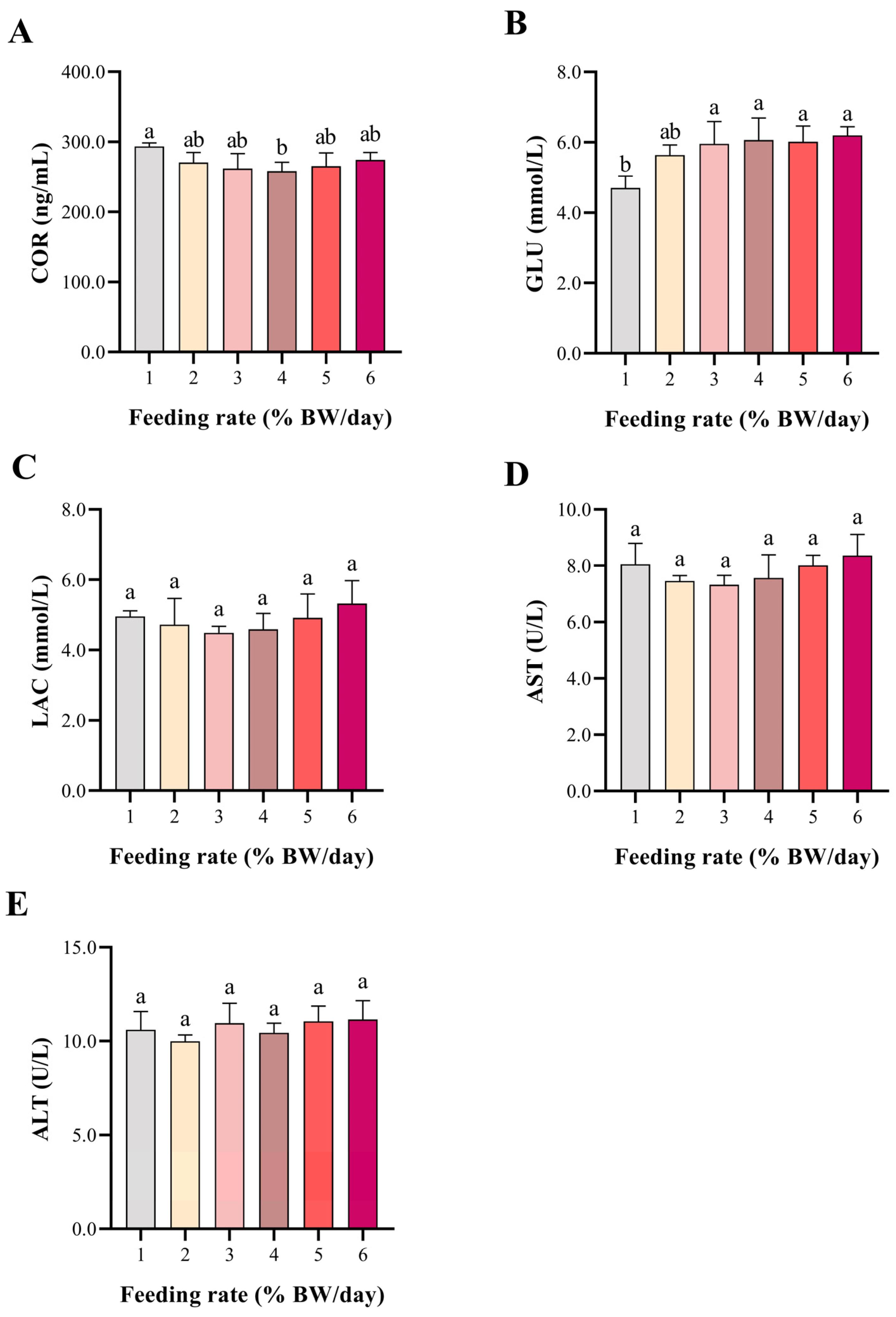
2.4. Indicators of Stress and Liver Injury
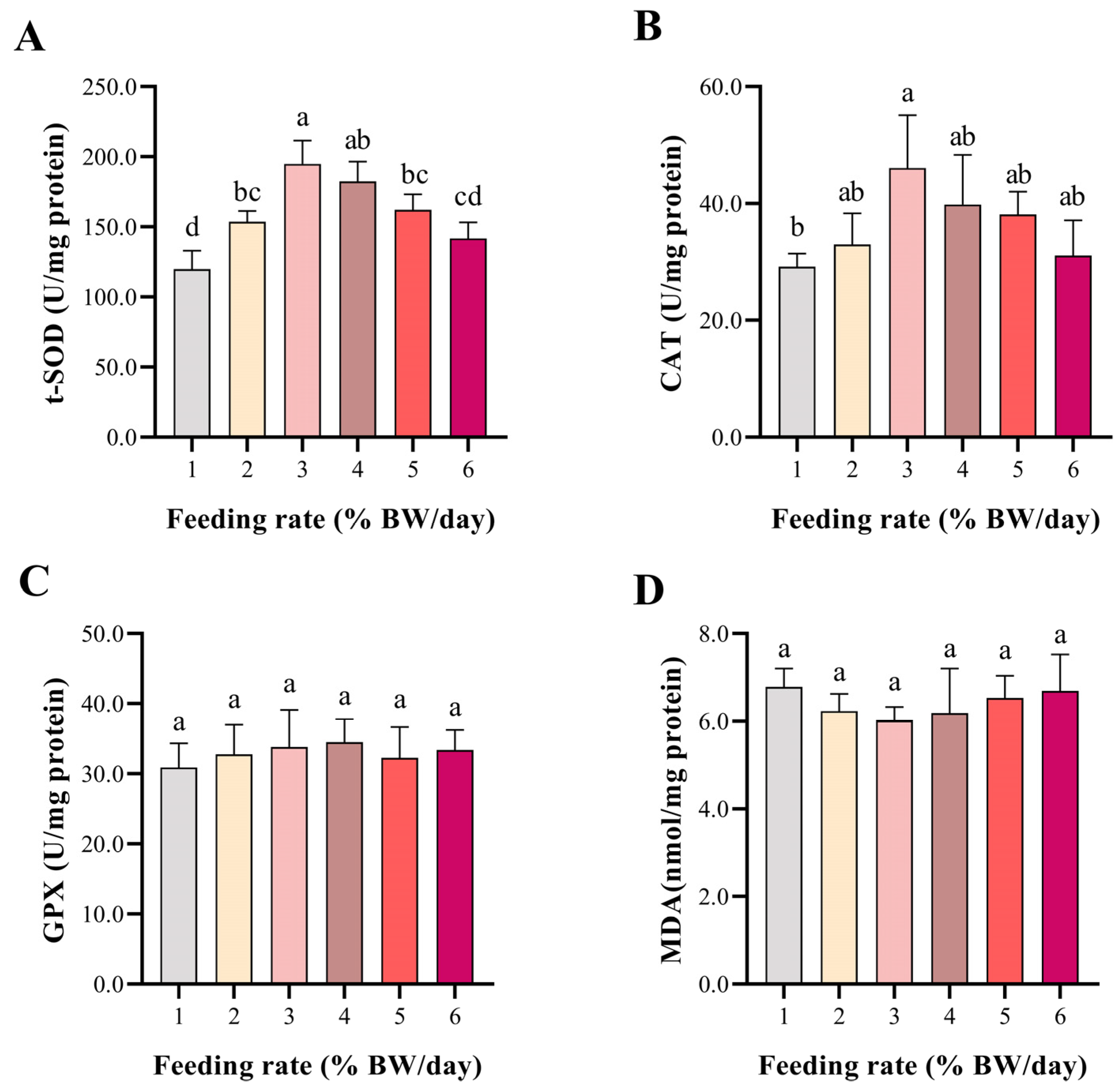
2.5. Indicators of Antioxidant Activity
2.6. Indicators of Immunity
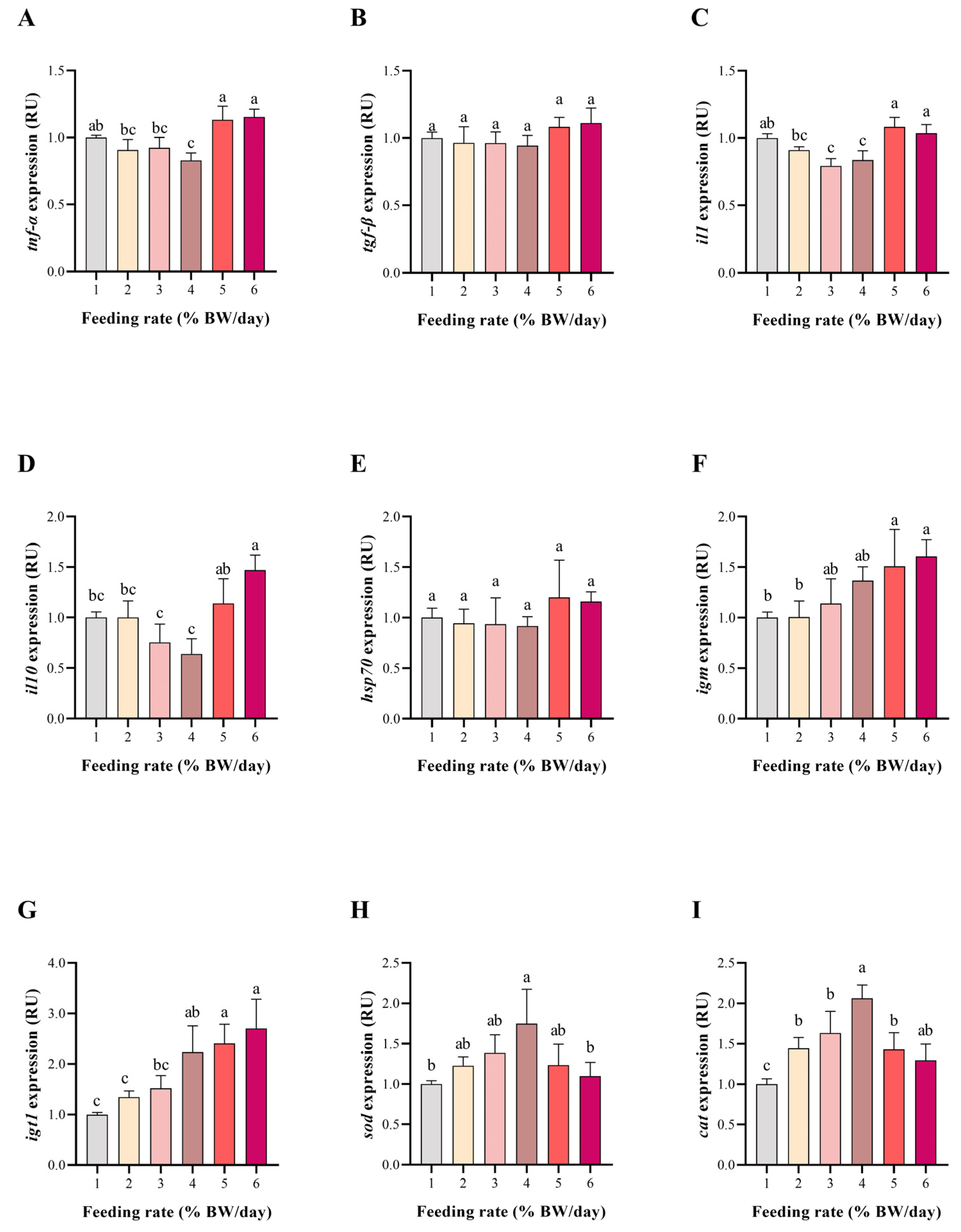
2.7. Antioxidant and Immune-Related Gene Expression
2.8. Calculation and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth
3.2. Stress and Liver Injury Indicators
3.3. Antioxidant Indicators

3.4. Immunity Indicators
3.5. Antioxidant and Immune-Related Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alam, M.S.; Liang, X.F.; Liu, L.; He, S.; Kuang, Y.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Dawar, F.U. Growth and metabolic response of chinese perch to different dietary protein-to-energy ratios in artificial diets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Hernández, M.E.; Martínez-Castellanos, G.; López-Méndez, M.C.; Reyes-Gonzalez, D.; González-Moreno, H.R. Production costs and growth performance of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in intensive production systems: A review. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriegha, O.J.; Ekokotu, P.A. Factors affecting feed intake in cultured fish species: A review. Anim. Res. Int. 2017, 14, 2697–2709. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Jain, K.K.; MunilKumar, S.; Sudhagar, S.A. Alternate feeding strategies for optimum nutrient utilization and reducing feed cost for semi-intensive practices in aquaculture system-A review. Agric. Rev. 2017, 38, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alcorn, S.W.; Pascho, R.J.; Murray, A.L.; Shearer, K.D. Effects of ration level on immune functions in chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). Aquaculture 2003, 217, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, J.; Noga, E.J. Effects of feeding rate on the expression of antimicrobial polypeptides and on susceptibility to Ichthyophthirius multifiliis in hybrid striped (sunshine) bass (Morone saxatilis♂ × M. chrysops♀). Aquaculture 2011, 318, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campelo, D.A.V.; Marques, M.H.C.; Marim, O.P.; de Moura, L.B.; Eiras, C.F.; Brabo, M.F.; Veras, G.C. Effects of feeding rates and feeding frequencies on growth performance, uniformity of the batch and survival rate of Amazon ornamental fish larvae. Int. J. Fish. Aquac. 2019, 11, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Tian, H.Y.; Zhang, D.D.; Jiang, G.Z.; Liu, W.B. Feeding frequency affects stress, innate immunity and disease resistance of juvenile blunt snout bream Megalobrama amblycephala. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 38, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardocci, G.; Navarro, C.; Cortés, P.P.; Imarai, M.; Montoya, M.; Valenzuela, B.; Jara, P.; Castillo, C.; Fernández, R. Neuroendocrine mechanisms for immune system regulation during stress in fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 40, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Li, X.F.; Tian, H.Y.; Jiang, G.Z.; Liu, W.B. Feeding rates affect growth, intestinal digestive and absorptive capabilities and endocrine functions of juvenile blunt snout bream Megalobrama amblycephala. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 42, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Xu, C.; Tian, H.Y.; Jiang, G.Z.; Zhang, D.D.; Liu, W.B. Feeding rates affect stress and non-specific immune responses of juvenile blunt snout bream Megalobrama amblycephala subjected to hypoxia. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 49, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, J. Pathophysiological effects of contemporary lifestyle on evolutionary-conserved survival mechanisms in polycystic ovary syndrome. Life 2023, 13, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.H.; Hamidoghli, A.; Hur, S.W.; Lee, B.J.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.W.; Lee, S. Growth, nutrient deposition, plasma metabolites, and innate immunity are associated with feeding rate in juvenile starry flounder (Platichthys stellatus). Animals 2024, 14, 3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichet, V.V. Nutrition and immunity: An update. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 356–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlenz, C.; Gatlin III, D.M. Interrelationships between fish nutrition and health. Aquaculture 2014, 431, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.F.; Liu, W.B.; Shi, H.J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.F. Utilization of pelleted and extruded feed by blunt snout bream Megalobrama amblycephala: Insights from growth performance, health status and feed cost. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 105, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidi, S.F.; Khan, M.A. Evaluation of feeding rate based on growth, feed conversion, protein gain and carcass quality of fingerling Indian major carp, Catla catla (Hamilton). Aquac. Res. 2014, 45, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.F.; Li, X.F.; Jiang, G.Z.; Zhang, L.; Sun, M.; Ge, Y.P.; Chen, W.L.; Liu, W.B. Feed types affect the growth, nutrient utilization, digestive capabilities, and endocrine functions of Megalobrama amblycephala: A comparative study between pelleted and extruded feed. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 48, 1025–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lygren, B.; Hamre, K.; Waagbø, R. Effects of dietary pro-and antioxidants on some protective mechanisms and health parameters in Atlantic salmon. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1999, 11, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, A.; Meseguer, J.; Esteban, M.A. Total serum immunoglobulin M levels are affected by immunomodulators in seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2004, 101, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.G.; Wu, T.X.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Pan, X.D. Effects of fish protein hydrolysate on growth performance and humoral immune response in large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea R.). J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2008, 9, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obach, A.; Quentel, C.; Laurencin, F.B. Effects of alpha-tocopherol and dietary oxidized fish-oil on the immune-response of sea bass dicentrarchus-labrax. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1993, 15, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwicki, A.K.; Anderson, D.P.; Rumsey, G.L. Dietary intake of immunostimulants by rainbow trout affects non-specific immunity and protection against furunculosis. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1994, 41, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lulijwa, R.; Alfaro, A.C.; Merien, F.; Meyer, J.; Young, T. Advances in salmonid fish immunology: A review of methods and techniques for lymphoid tissue and peripheral blood leucocyte isolation and application. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 95, 44–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linh, N.V.; Wannavijit, S.; Tayyamath, K.; Dinh-Hung, N.; Nititanarapee, T.; Sumon, M.A.A.; Srinual, O.; Permpoonpattana, P.; Doan, H.V.; Brown, C.L. Black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae meal: A sustainable alternative to fish meal proven to promote growth and immunity in koi carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Koi). Fishes 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, B.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Yin, J.; Bergmann, S.; Shi, C. Immersion immunization of koi (Cyprinus carpio) against cyprinid herpesvirus 3 (CyHV-3) with carbon nanotube-loaded DNA vaccine. Aquaculture 2021, 539, 736644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, N.; Liang, J.; Wang, Q.; Zu, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Guo, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J. Emodin resists to Cyprinid herpesvirus 3 replication via the pathways of Nrf2/Keap1-ARE and NF-κB in the ornamental koi carp (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 2021, 246, 109023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, I.; Peres, H.; Castro-Cunha, M.; Oliva-Teles, A. Effect of temperature and dietary protein/lipid ratio on growth performance and nutrient utilization of juvenile Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis). Aquac. Nutr. 2012, 18, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.U.; Ali, Q.M.; Ahmad, N.; Masood, Z.; Hossain, M.Y.; Gabol, K.; Khan, W.; Hussain, M.; Ali, A.; Attaullah, M.; et al. Assessment of growth characteristics, the survival rate and body composition of Asian Sea bass Lates calcarifer (Bloch, 1790) under different feeding rates in closed aquaculture system. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 1324–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Lu, C.; Hao, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Olsen, R.E.; Ringo, E.; Ran, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Z. Dietary succinate impacts the nutritional metabolism, protein succinylation and gut microbiota of zebrafish. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 894278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eroldoğan, O.T.; Kumlu, M.; Kiris, G.A.; Sezer, B. Compensatory growth response of Sparus aurata following different starvation and refeeding protocols. Aquac. Nutr. 2006, 12, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landgraf, K.; Schuster, S.; Meusel, A.; Garten, A.; Riemer, T.; Schleinitz, D.; Kiess, W.; Körner, A. Short-term overfeeding of zebrafish with normal or high-fat diet as a model for the development of metabolically healthy versus unhealthy obesity. BMC Physiol. 2017, 17, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Ai, Q.; Mai, K.; Xu, W.; Liufu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Cai, Y. Effects of dietary soybean saponins on feed intake, growth performance, digestibility and intestinal structure in juvenile Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Aquaculture 2011, 318, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janzen, W.J.; Duncan, C.A.; Riley, L.G. Cortisol treatment reduces ghrelin signaling and food intake in tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2012, 43, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- German, D.P.; Neuberger, D.T.; Callahan, M.N.; Lizardo, N.R.; Evans, D.H. Feast to famine: The effects of food quality and quantity on the gut structure and function of a detritivorous catfish (Teleostei: Loricariidae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 2010, 155, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellestad, L.E.; Angel, R.; Soares, J.H. Intestinal phytase II: A comparison of activity and in vivo phytate hydrolysis in three teleost species with differing digestive strategies. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2002, 26, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A. Nutritional immunity of fish intestines: Important insights for sustainable aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 642–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; He, P.; Ni, Y.; Yao, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, L. Effect of Xueniao Capsule on Escherichia coli-Induced Acute Pyelonephritis Rats by 1H NMR-Based Metabolomic Approach. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. 2019, 2019, 6723956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Wang, J.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liang, W.; Li, Z.; Yu, J.; Tang, B.; He, S. Expression of tubulin folding cofactor B in mouse hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biomed. Rep. 2017, 6, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kang, Y.J.; Lee, K.M. Effects of nitrite exposure on the hematological properties, antioxidant and stress responses of juvenile hybrid groupers, Epinephelus lanceolatus♂ × Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Xu, W.; Li, H.; Dong, B.; Geng, H.; Jin, J.; Han, D.; Liu, H.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Y.; et al. Vitamin C attenuates oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis induced by acute hypoxia through the Nrf2/Keap1 signaling pathway in gibel carp (Carassius gibelio). Antioxidants 2022, 11, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, B.A. Salmonid fishes differ in their cortisol and glucose responses to handling and transport stress. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2000, 62, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jentoft, S.; Aastveit, A.H.; Torjesen, P.A.; Andersen, Ø. Effects of stress on growth, cortisol and glucose levels in non-domesticated Eurasian perch (Perca fluviatilis) and domesticated rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 2005, 141, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Díaz, C.; Kopecka, J.; Cañavate, J.P.; Sarasquete, C.; Solé, M. Variations on development and stress defences in Solea senegalensis larvae fed on live and microencapsulated diets. Aquaculture 2006, 251, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Wang, T.; Lai, C.; Ling, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Yong, Q. The in vitro and in vivo antioxidant and immunomodulatory activity of incomplete degradation products of hemicellulosic polysaccharide (Galactomannan) from Sesbania cannabina. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 679558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddik, M.A.; Vatsos, I.N.; Rahman, M.A.; Pham, H.D. Selenium-enriched spirulina (SeE-SP) enhance antioxidant response, immunity, and disease resistance in juvenile Asian seabass, Lates calcarifer. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safwan-Zaiter, H.; Wagner, N.; Michiels, J.F.; Wagner, K.D. Dynamic Spatiotemporal Expression Pattern of the Senescence-Associated Factor p16Ink4a in Development and Aging. Cells 2022, 11, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, M.; Kubota, N.; Masuoka, N.; Hori, T.; Miyazaki, K.; Ishikawa, F. Oral administration of fermented soymilk products protects the skin of hairless mice against ultraviolet damage. Nutrients 2016, 8, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Yousefi, S.; Van Doan, H.; Ashouri, G.; Gioacchini, G.; Maradonna, F.; Carnevali, O. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense in fish: The implications of probiotic, prebiotic, and synbiotics. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 29, 198–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afifi, M.; Saddick, S.; Zinada, O.A.A. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles on the brain of Oreochromis niloticus and Tilapia zillii. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Ye, T.; Chan, Z. Analysis of natural variation in bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon) reveals physiological responses underlying drought tolerance. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e53422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beamish, F.W.H. Apparent specific dynamic action of largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1974, 31, 1763–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Olmeda, J.F.; Noble, C.; Sánchez-Vázquez, F.J. Does feeding time affect fish welfare? Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; He, K.; Luo, J.; Sun, J.; Liao, L.; Tang, X.; Liu, Q.; Yang, S. Co-modulation of liver genes and intestinal microbiome of largemouth bass larvae (Micropterus salmoides) during weaning. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Katya, K.; Hamidoghli, A.; Hong, J.; Kim, D.J.; Bai, S.C. Synergistic effects of dietary supplementation of Bacillus subtilis WB60 and mannanoligosaccharide (MOS) on growth performance, immunity and disease resistance in Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 83, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva-Teles, A. Nutrition and health of aquaculture fish. J. Fish Dis. 2012, 35, 83–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behlen, J.C.; Lau, C.H.; Pendleton, D.; Li, Y.; Hoffmann, A.R.; Golding, M.C.; Zhang, R.Y.; Johnson, N.M. NRF2-dependent placental effects vary by sex and dose following gestational exposure to ultrafine particles. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, Y.; Di Tullio, M.R.; Homma, S.; Boden-Albala, B.; Rundek, T.; Sacco, R.L.; Berry, G.; Liu, R.; Jin, Z.; Eguchi, K.; et al. Soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 level is associated with left ventricular hypertrophy: The northern Manhattan study. Am. J. Hypertens. 2009, 22, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Rish, E.Y.; Mansour, A.T.; Mansour, H.T.; Dahabiyeh, L.A.; Aleidi, S.M.; Bustanji, Y. Pregabalin inhibits in vivo and in vitro cytokine secretion and attenuates spleen inflammation in Lipopolysaccharide/Concanavalin A-induced murine models of inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Tian, R.; Zhang, H. Integrated analysis of transcriptome mRNA and miRNA profiles reveals self-protective mechanism of bovine MECs induced by LPS. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 890043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, H.Y.; Lin, K.W.; Yang, C.; Cai, P. Generation and propagation of yeast prion [URE3] are elevated under electromagnetic field. Cell Stress Chaperon. 2018, 23, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, V.L.; Worth, A.N.; Scott, R.L.; Perry, G.A.; Yan, M.; Li, Q.Z.; Swanson, P.C. IL10 restrains autoreactive B cells in transgenic mice expressing inactive RAG1. Cell Immunol. 2018, 331, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hämäläinen, S.; Solovieva, S.; Vehmas, T.; Leino-Arjas, P.; Hirvonen, A. Variations in the TNFα gene and their interactions with the IL4R and IL10 genes in relation to hand osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2014, 15, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, A.; Gali, S.; Sharma, S.; Park, J.H.; Kyung, S.Y.; Kacew, S.; Kim, I.S.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, H.S. Tenovin-1 ameliorates renal fibrosis in high-fat-diet-induced diabetic nephropathy via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory pathways. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staszek, P.; Krasuska, U.; Otulak-Kozieł, K.; Fettke, J.; Gniazdowska, A. Canavanine-induced decrease in nitric oxide synthesis alters activity of antioxidant system but does not impact S-nitrosoglutathione catabolism in tomato roots. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, A.I.; McNamara, J.M.; Barta, Z.; Klasing, K.C. The effect of energy reserves and food availability on optimal immune defence. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2007, 274, 2835–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ingredients (%) | |
|---|---|
| Fish meal | 10.00 |
| Soybean meal | 24.00 |
| Rapeseed meal | 24.00 |
| Wheat gluten | 10.30 |
| Wheat flour | 26.30 |
| Soybean oil | 3.50 |
| Ca(H2PO4)2 | 1.00 |
| Vitamin premix a | 0.15 |
| Mineral premix b | 0.15 |
| Choline chloride (50%) | 0.20 |
| Lysine (98.5%) | 0.30 |
| Methionine | 0.10 |
| Proximate composition (% dry-matter basis) | |
| Crude protein | 41.27 |
| Crude lipid | 6.57 |
| Moisture | 6.17 |
| Ash | 6.40 |
| Gross energy (MJ/kg) | 16.25 |
| Target Gene | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| tnf-α | GTGATGGTGTCGAGGAGGAAG | TCTGAGACTTGTTGAGCGTGAA | [27] |
| tgf-β | CCTGGGCTGGAAGTGGATAC | GTAAAAGATGGGCAGTGGGTC | [25] |
| il1 | GATGCAAATGCCCTCAAATACA | GGCTCTTGACGTTCCTTTTG | [25] |
| il10 | GGAGGGCTTTCCAGTGAGAC | TGTTGCACGTTTTCGTCCAG | [25] |
| hsp70 | GTGTCCATCCTGACCATTGAAGA | CTGACTGATGTCCTTCTTGTGCTTC | [25] |
| igm | CACAAGGCGGGAAATGAAGA | GGAGGCACTATATCAACAGCA | [26] |
| igt1 | AAAGTGAAGGATGAAAGTGT | TGGTAACAGTGGGCTTATT | [26] |
| sod | GATGGCAGCCTTGGAAGTGAC | TCAGAACAATCAGGAAGGAGGAA | [27] |
| cat | CTGGAAGTGGAATCCGTTTG | CGACCTCAGCGAAATAGTTG | [27] |
| β-actin | GCTATGTGGCTCTTGACTTCGA | CCGTCAGGCAGCTCATAGCT | [27] |
| Feeding Rates (% BW/Day) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LZM (U/mL) | 87.53 ± 3.23 c | 104.07 ± 3.78 bc | 112.01 ± 3.71 bc | 114.86 ± 1.77 ab | 117.44 ± 9.24 ab | 139.69 ± 9.06 a |
| C3 (mg/L) | 260.35 ± 13.45 b | 315.64 ± 27.58 ab | 339.19 ± 14.18 ab | 361.65 ± 29.87 ab | 378.43 ± 23.24 a | 377.08 ± 26.54 a |
| C4 (mg/L) | 190.36 ± 10.53 b | 226.69 ± 19.00 ab | 273.24 ± 20.10 a | 277.10 ± 20.16 a | 283.43 ± 10.68 a | 291.62 ± 15.71 a |
| IgM (g/L) | 1.89 ± 0.11 a | 1.97 ± 0.05 a | 1.99 ± 0.03 a | 1.97 ± 0.02 a | 2.01 ± 0.03 a | 2.12 ± 0.02 a |
| MPO (U/L) | 7.41 ± 0.27 b | 8.36 ± 0.30 b | 14.85 ± 0.64 a | 17.51 ± 1.04 a | 14.92 ± 1.17 a | 15.48 ± 0.54 a |
| ACP (U/L) | 194.63 ± 5.78 a | 191.35 ± 6.56 a | 212.01 ± 11.19 a | 210.31 ± 5.11 a | 187.98 ± 8.91 a | 213.68 ± 6.20 a |
| TP (g/L) | 16.32 ± 0.65 b | 31.90 ± 0.86 a | 32.75 ± 1.21 a | 34.41 ± 1.85 a | 34.51 ± 1.45 a | 32.96 ± 1.09 a |
| ALB (g/L) | 11.51 ± 0.38 b | 17.61 ± 1.37 a | 17.75 ± 1.27 a | 17.43 ± 1.10 a | 17.81 ± 1.30 a | 16.88 ± 0.79 a |
| GLO (g/L) | 4.81 ± 0.77 b | 14.30 ± 2.07 a | 14.99 ± 0.73 a | 16.98 ± 1.70 a | 16.70 ± 2.57 a | 16.09 ± 0.83 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, S.; Gao, S.; Xu, X.; Wei, Q.; Tao, Z.; Xu, G.; Liu, Q.; Wei, B.; He, C. The Impact of Feeding Rates on the Growth, Stress Response, Antioxidant Capacity, and Immune Defense of Koi (Cyprinus carpio var. koi). Fishes 2025, 10, 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10040181
Duan S, Gao S, Xu X, Wei Q, Tao Z, Xu G, Liu Q, Wei B, He C. The Impact of Feeding Rates on the Growth, Stress Response, Antioxidant Capacity, and Immune Defense of Koi (Cyprinus carpio var. koi). Fishes. 2025; 10(4):181. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10040181
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Saixing, Shengyu Gao, Xiaolong Xu, Qi Wei, Ze Tao, Gaoxiao Xu, Quanzhou Liu, Bing Wei, and Chaofan He. 2025. "The Impact of Feeding Rates on the Growth, Stress Response, Antioxidant Capacity, and Immune Defense of Koi (Cyprinus carpio var. koi)" Fishes 10, no. 4: 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10040181
APA StyleDuan, S., Gao, S., Xu, X., Wei, Q., Tao, Z., Xu, G., Liu, Q., Wei, B., & He, C. (2025). The Impact of Feeding Rates on the Growth, Stress Response, Antioxidant Capacity, and Immune Defense of Koi (Cyprinus carpio var. koi). Fishes, 10(4), 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10040181






