Sand Goby—An Ecologically Relevant Species for Behavioural Ecotoxicology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
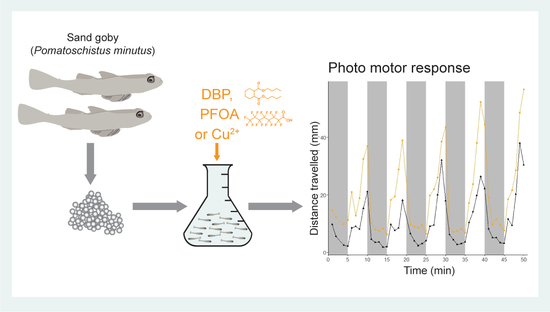
2.1. Photo-Motor Response of Sand Goby Larvae
2.2. Locomotion-Based Behavioural Endpoints
2.2.1. Number of Movements
2.2.2. Duration of Movements
2.2.3. Total Distance Travelled
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sand Goby Husbandry
4.2. Breeding for Exposures
4.3. Chemicals and Exposure Design
4.4. Behavioural Toxicity Assay
4.5. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brockmeier, E.K.; Hodges, G.; Hutchinson, T.H.; Butler, E.; Hecker, M.; Tollefsen, K.E.; Garcia-Reyero, N.; Kille, P.; Becker, D.; Chipman, K.; et al. The role of omics in the application of adverse outcome pathways for chemical risk assessment. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 158, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beliaeff, B.; Burgeot, T. Integrated biomarker response: A useful tool for ecological risk assessment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2002, 21, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingston, D.R.; Förlin, L.; George, S.G. Molecular biomarkers and toxic consequences of impact by organic pollution in aquatic organisms. In Water Quality & Stress Indicators in Marine and Freshwater Systems: Linking Levels of Organisation; Sutcliffe, D.W., Ed.; FBA Special Publications; Freshwater Biological Association: Ambleside, UK, 1994; pp. 154–171. ISBN 9780900386534. [Google Scholar]
- Wernersson, A.-S.; Carere, M.; Maggi, C.; Tusil, P.; Soldan, P.; James, A.; Sanchez, W.; Dulio, V.; Broeg, K.; Reifferscheid, G.; et al. The European technical report on aquatic effect-based monitoring tools under the water framework directive. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2015, 27, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandstrom, O.; Larsson, A.; Andersson, J. Three decades of Swedish experience demonstrates the need for integrated long-term monitoring of fish in marine coastal areas. Water Qual. Res. J. Can. 2005, 40, 233–250. [Google Scholar]
- Benninghoff, A.D. Toxicoproteomics—The next step in the evolution of environmental biomarkers? Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 95, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brausch, J.M.; Connors, K.A.; Brooks, B.W.; Rand, G.M. Human pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment: A review of recent toxicological studies and considerations for toxicity testing. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 218, 1–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miracle, A.L.; Ankley, G.T. Ecotoxicogenomics: Linkages between exposure and effects in assessing risks of aquatic contaminants to fish. Reprod. Toxicol. 2005, 19, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahamonde, P.A.; Feswick, A.; Isaacs, M.A.; Munkittrick, K.R.; Martyniuk, C.J. Defining the role of omics in assessing ecosystem health: Perspectives from the Canadian environmental monitoring program. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhardt, A.; Schmidt, S.; Höss, S. Measurement of movement patterns of Caenorhabditis elegans (Nematoda) with the Multispecies Freshwater Biomonitor®(MFB)—A potential new method to study a behavioral toxicity parameter of nematodes in sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 120, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellou, J. Behavioural ecotoxicology, an “early warning” signal to assess environmental quality. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, P.D. Behavioural toxicity of organic chemical contaminants in fish: Application to ecological risk assessments (ERAs). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2009, 66, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Champagne, D.L.; Richardson, M.K. Behavioral profiling of zebrafish embryos exposed to a panel of 60 water-soluble compounds. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 228, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, F.; Ye, Y.; Peng, T.; Fu, Z. Embryonic exposure to cadmium (II) and chromium (VI) induce behavioral alterations, oxidative stress and immunotoxicity in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2015, 48, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokel, D.; Peterson, R.T. Using the zebrafish photomotor response for psychotropic drug screening. Methods Cell Biol. 2011, 105, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokel, D.; Bryan, J.; Laggner, C.; White, R.; Cheung, C.Y.J.; Mateus, R.; Healey, D.; Kim, S.; Werdich, A.A.; Haggarty, S.J.; et al. Rapid behavior-based identification of neuroactive small molecules in the zebrafish. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2010, 6, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rihel, J.; Prober, D.A.; Arvanites, A.; Lam, K.; Zimmerman, S.; Jang, S.; Haggarty, S.J.; Kokel, D.; Rubin, L.L.; Peterson, R.T.; et al. Zebrafish behavioral profiling links drugs to biological targets and rest/wake regulation. Science 2010, 327, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ašmonaite, G.; Boyer, S.; de Souza, K.B.; Wassmur, B.; Sturve, J. Behavioural toxicity assessment of silver ions and nanoparticles on zebrafish using a locomotion profiling approach. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 173, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thit, A.; Skjolding, L.M.; Selck, H.; Sturve, J. Effects of copper oxide nanoparticles and copper ions to zebrafish (Danio rerio) cells, embryos and fry. Toxicol. In Vitro 2017, 45, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khezri, A.; Fraser, T.; Nourizadeh-Lillabadi, R. A mixture of persistent organic pollutants and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid induces similar behavioural responses, but different gene expression profiles in zebrafish larvae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michiels, E.D.G.; Vergauwen, L.; Hagenaars, A.; Fransen, E.; Dongen, S.V.; Van Cruchten, S.J.; Bervoets, L.; Knapen, D. Evaluating complex mixtures in the zebrafish embryo by reconstituting field water samples: A metal pollution case study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, C.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, D.; Zuo, Z. Maternal and embryonic exposure to the water soluble fraction of crude oil or lead induces behavioral abnormalities in zebrafish (Danio rerio), and the mechanisms involved. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogl, C.; Grillitsch, B.; Wytek, R. Qualification of spontaneous undirected locomotor behavior of fish for sublethal toxicity testing. Part I. Variability of measurement parameters under general test conditions. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1999, 18, 2736–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, A.S.; Salierno, J.D.; Gipson, G.T.; Molteno, T.C.A.; Hunter, C. A video-based movement analysis system to quantify behavioral stress responses of fish. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3993–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fini, J.-B.; Mughal, B.B.; Le Mével, S.; Leemans, M.; Lettmann, M.; Spirhanzlova, P.; Affaticati, P.; Jenett, A.; Demeneix, B.A. Human amniotic fluid contaminants alter thyroid hormone signalling and early brain development in Xenopus embryos. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denoël, M.; Libon, S.; Kestemont, P.; Brasseur, C.; Focant, J.-F.; De Pauw, E. Effects of a sublethal pesticide exposure on locomotor behavior: A video-tracking analysis in larval amphibians. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuklina, I.; Kouba, A.; Kozák, P. Real-time monitoring of water quality using fish and crayfish as bio-indicators: A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 5043–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Campana, O.; Wlodkowic, D. A Millifluidic System for Analysis of Daphnia magna Locomotory Responses to Water-born Toxicants. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tooming, E. The Sublethal Effects of Neurotoxic Insecticides on the Basic Behaviours of Agriculturally Important Carabid Beetles. Ph.D. Thesis, Eesti Maaülikool, Tartu, Estonia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Faimali, M.; Garaventa, F.; Piazza, V.; Greco, G.; Corrà, C.; Magillo, F.; Pittore, M.; Giacco, E.; Gallus, L.; Falugi, C.; et al. Swimming speed alteration of larvae of Balanus Amphitrite as a behavioural end-point for laboratory toxicological bioassays. Mar. Biol. 2006, 149, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, P.C. Offshore entrainment of anchovy spawning habitat, eggs, and larvae by a displaced eddy in 1985. Calif. Coop. Ocean. Fish. Investig. Rep. 1986, 27, 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Genner, M.J.; Halliday, N.C.; Simpson, S.D.; Southward, A.J.; Hawkins, S.J.; Sims, D.W. Temperature-driven phenological changes within a marine larval fish assemblage. J. Plankton Res. 2010, 32, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somarakis, S.; Drakopoulos, P.; Filippou, V. Distribution and abundance of larval fish in the northern Aegean Sea—Eastern Mediterranean—In relation to early summer oceanographic conditions. J. Plankton Res. 2002, 24, 339–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, J.S.; Weis, P. Tolerance and Stress in a Polluted Environment. Bioscience 1989, 39, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, C.J. Ecotoxicological aspects of dithiocarbamates. In Rijkswaterstaat Communications No. 44; Rijkswaterstaat: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals/Section 2: Effects on Biotic Systems Test No. 210: Fish, Early-Life Stage Toxicity Test; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 1992; ISBN 9789264070103. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2 Test No. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2013; ISBN 9789264203709. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, J.R.; Panter, G.H.; Weltje, L.; Thorpe, K.L.; Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development; United States Environmental Protection Agency. Test concentration setting for fish in vivo endocrine screening assays. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKim, J.M. Evaluation of Tests with Early Life Stages of Fish for Predicting Long-Term Toxicity. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1977, 34, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maya, N.; Crispo, C.; McFarland, V. Toxicity of extracts from municipal wastewater to early life stages of Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) to evaluate removals of micropollutants by wastewater treatment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 37, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raine, J.C.; Turcotte, D.; Tumber, V.; Peru, K.M.; Wang, Z.; Yang, C.; Headley, J.V.; Parrott, J.L. The effect of oil sands tailings pond sediments on embryo-larval walleye (Sander vitreus). Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, B.; Fischer, J.; Schiwy, S.; Hollert, H.; Schulz, R. Towards more ecological relevance in sediment toxicity testing with fish: Evaluation of multiple bioassays with embryos of the benthic weatherfish (Misgurnus fossilis). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 619–620, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Nie, F.; Hay, A.; Lin, H.; Ma, Y.; Ju, X.; Gong, D.; Chen, J.; Gooneratne, R. Histopathological changes in zebrafish embryos exposed to DLPCBs extract from Zhanjiang coastal sediment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, P.J.P. Fishes of the North-Eastern Atlantic and the Mediterranean; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Healey, M.C. The distribution and abundance of sand gobies, Gobius minutus, in the Ythan estuary. J. Zool. 1971, 163, 177–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonds, M.; Van Buurt, G. The influence of temperature and salinity on development and survival of goby eggs (Pisces, Gobiidae). Hydrobiol. Bull. 1974, 8, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesthagen, I.H. Migrations, breeding, and growth in Pomatoschistus minutus (Pallas) (Pisces, Gobiidae) in Oslofjorden, Norway. Sarsia 1977, 63, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breder, C.M.; Rosen, D.E. Modes of Reproduction in Fishes; Natural History Press: Garden City, NY, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren, E. Sexual selection and sex roles in the sand goby. Behav. Conserv. Littoral Fishes 1999, 249–274. [Google Scholar]
- Hesthagen, I.H. Gobies of the genus Pomatoschistus as nest-builders. Fauna 1979, 32, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Lissåker, M.; Kvarnemo, C. Ventilation or nest defense—Parental care trade-offs in a fish with male care. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2006, 60, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, E.L.; Mück, I.; Heubel, K.; Svensson, O. Acoustic and visual courtship traits in two sympatric marine Gobiidae species—Pomatoschistus microps and Pomatoschistus minutus. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2016, 99, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindström, K.; Hellström, M. Male size and parental care in the sand goby, Pomatoschistus minutus. Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 1993, 5, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.G.; Walker, D.; Lindström, K.; Kvarnemo, C.; Avise, J.C. Surprising similarity of sneaking rates and genetic mating patterns in two populations of sand goby experiencing disparate sexual selection regimes. Mol. Ecol. 2001, 10, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.G.; Walker, D.; Kvarnemo, C.; Lindström, K.; Avise, J.C. How cuckoldry can decrease the opportunity for sexual selection: Data and theory from a genetic parentage analysis of the sand goby, Pomatoschistus minutus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9151–9156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, A.; Kvarnemo, C.; Lindström, K.; Svensson, O. Genetic mating patterns studied in pools with manipulated nest site availability in two populations of Pomatoschistus minutus. J. Evol. Biol. 2006, 19, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saaristo, M.; Craft, J.A.; Lehtonen, K.K.; Lindström, K. Sand goby (Pomatoschistus minutus) males exposed to an endocrine disrupting chemical fail in nest and mate competition. Horm. Behav. 2009, 56, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saaristo, M.; Craft, J.A.; Lehtonen, K.K.; Björk, H.; Lindström, K. Disruption of sexual selection in sand gobies (Pomatoschistus minutus) by 17α-ethinyl estradiol, an endocrine disruptor. Horm. Behav. 2009, 55, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, C.D.; Brown, E.; Craft, J.A.; Davies, I.M.; Moffat, C.F.; Pirie, D.; Robertson, F.; Stagg, R.M.; Struthers, S. Effects of sewage effluent and ethynyl oestradiol upon molecular markers of oestrogenic exposure, maturation and reproductive success in the sand goby (Pomatoschistus minutus, Pallas). Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 62, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.D.; Brown, E.; Craft, J.A.; Davies, I.M.; Megginson, C.; Miller, C.; Moffat, C.F. Bioindicators and reproductive effects of prolonged 17β-oestradiol exposure in a marine fish, the sand goby (Pomatoschistus minutus). Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 81, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waring, C.P.; Stagg, R.M.; Fretwell, K.; McLay, H.A.; Costello, M.J. The impact of sewage sludge exposure on the reproduction of the sand goby, Pomatoschistus minutus. Environ. Pollut. 1996, 93, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaristo, M.; Craft, J.A.; Lehtonen, K.K.; Lindström, K. An endocrine disrupting chemical changes courtship and parental care in the sand goby. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 97, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthiessen, P.; Allen, Y.; Bamber, S.; Craft, J.; Hurst, M.; Hutchinson, T.; Feist, S.; Katsiadaki, I.; Kirby, M.; Robinson, C.; et al. The impact of oestrogenic and androgenic contamination on marine organisms in the United Kingdom—Summary of the EDMAR programme. Mar. Environ. Res. 2002, 54, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.D.; Craft, J.A.; Moffat, C.F.; Davies, I.M.; Brown, E.S.; Megginson, C. Oestrogenic markers and reduced population fertile egg production in a sand goby partial life-cycle test. Mar. Environ. Res. 2004, 58, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solé, M.; Kopecka, J.; Parra, L.M.G. de la Seasonal variations of selected biomarkers in sand gobies Pomatoschistus minutus from the Guadalquivir Estuary, Southwest Spain. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2006, 50, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humble, J.L.; Saaristo, M.; Lindström, K. Effects of 17α-ethinyl estradiol exposure on estrogen receptors α and β and vitellogenins A, B and C mRNA expression in the liver of sand goby (Pomatoschistus minutus). Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 96, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvarnemo, C. Temperature differentially affects male and female reproductive rates in the sand goby: Consequences for operational sex ratio. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 1994, 256, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Omo, G. Behavioural Ecotoxicology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; ISBN 9780471968528. [Google Scholar]
- Vignet, C.; Bégout, M.-L.; Péan, S.; Lyphout, L.; Leguay, D.; Cousin, X. Systematic screening of behavioral responses in two zebrafish strains. Zebrafish 2013, 10, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rihel, J.; Schier, A.F. Behavioral screening for neuroactive drugs in zebrafish. Dev. Neurobiol. 2012, 72, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staples, C.A.; Adams, W.J.; Parkerton, T.F.; Gorsuch, J.W.; Biddinger, G.R.; Reinert, K.H. Aquatic toxicity of eighteen phthalate esters. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1997, 16, 875–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosell, M.; Blanchard, J.; Brix, K.V.; Gerdes, R. Physiology is pivotal for interactions between salinity and acute copper toxicity to fish and invertebrates. Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 84, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jantzen, C.E.; Annunziato, K.A.; Bugel, S.M.; Cooper, K.R. PFOS, PFNA, and PFOA sub-lethal exposure to embryonic zebrafish have different toxicity profiles in terms of morphometrics, behavior and gene expression. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 175, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agus, H.H.; Sümer, S.; Erkoç, F. Toxicity and molecular effects of di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP) on CYP1A, SOD, and GPx in Cyprinus carpio (common carp). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaparro-Ortega, A.; Betancourt, M.; Rosas, P.; Vázquez-Cuevas, F.G.; Chavira, R.; Bonilla, E.; Casas, E.; Ducolomb, Y. Endocrine disruptor effect of perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) on porcine ovarian cell steroidogenesis. Toxicol. In Vitro 2018, 46, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boas, M.; Frederiksen, H.; Feldt-Rasmussen, U.; Skakkebæk, N.E.; Hegedüs, L.; Hilsted, L.; Juul, A.; Main, K.M. Childhood exposure to phthalates: Associations with thyroid function, insulin-like growth factor I, and growth. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1458–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, M.T.; Brennan, R.J.; Hu, W.; Ayanoglu, E.; Lau, C.; Ren, H.; Wood, C.R.; Corton, J.C.; Kavlock, R.J.; Dix, D.J. Toxicogenomic study of triazole fungicides and perfluoroalkyl acids in rat livers predicts toxicity and categorizes chemicals based on mechanisms of toxicity. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 97, 595–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieu-Denoncourt, J.; Wallace, S.J.; de Solla, S.R.; Langlois, V.S. Plasticizer endocrine disruption: Highlighting developmental and reproductive effects in mammals and non-mammalian aquatic species. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2015, 219, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Colborn, T.; Hayes, T.B.; Heindel, J.J.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Lee, D.-H.; Shioda, T.; Soto, A.M.; vom Saal, F.S.; Welshons, W.V.; et al. Hormones and endocrine-disrupting chemicals: Low-dose effects and nonmonotonic dose responses. Endocr. Rev. 2012, 33, 378–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, G.R.; Sloman, K.A. The effects of environmental pollutants on complex fish behaviour: Integrating behavioural and physiological indicators of toxicity. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 68, 369–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhardt, A. Aquatic behavioral ecotoxicology—Prospects and limitations. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2007, 13, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhardt, A.; Janssens de Bisthoven, L.; Soares, A.M.V. Evidence for the Stepwise Stress Model: Gambusia holbrooki and Daphnia magna under acid mine drainage and acidified reference water stress. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4150–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaetke, L.M.; Chow, C.K. Copper toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidant nutrients. Toxicology 2003, 189, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, H.A.; Hassan, M.H.; El-Beshbishy, H.A.; Alahdal, A.M.; Osman, A.-M.M. Dibutyl phthalate induces oxidative stress and impairs spermatogenesis in adult rats. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2016, 32, 1467–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, L.D.; Seibert, J.; Soanes, K.H. Distinct models of induced hyperactivity in zebrafish larvae. Brain Res. 2012, 1449, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saili, K.S.; Corvi, M.M.; Weber, D.N.; Patel, A.U.; Das, S.R.; Przybyla, J.; Anderson, K.A.; Tanguay, R.L. Neurodevelopmental low-dose bisphenol A exposure leads to early life-stage hyperactivity and learning deficits in adult zebrafish. Toxicology 2012, 291, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Cartlidge, R.; Walpitagama, M.; Kaslin, J.; Campana, O.; Wlodkowic, D. Unsuitable use of DMSO for assessing behavioral endpoints in aquatic model species. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvarnemo, C. Food affects the potential reproductive rates of sand goby females but not of males. Behav. Ecol. 1997, 8, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullander, S.O.; Nyman, L.; Jilg, K.; Delling, B. Nationalnyckeln Till Sveriges Flora och Fauna; Strålfeniga Fiskar. Actinopterygii; ArtDatabanken SLU: Uppsala, Sweden, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Huyse, T.; Houdt, J.V.; Volckaert, F.A.M. Paleoclimatic history and vicariant speciation in the “sand goby” group (Gobiidae, Teleostei). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2004, 32, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, O.; Gräns, J.; Celander, M.C.; Havenhand, J.; Leder, E.H.; Lindström, K.; Schöld, S.; van Oosterhout, C.; Kvarnemo, C. Immigrant reproductive dysfunction facilitates ecological speciation. Evolution 2017, 71, 2510–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonds, M. Remarks on the rearing of gobies (Pomatoschistus minutus and P. lozanoi) for experimental purposes. Helgol. Wiss. Meeresunters 1970, 20, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, L.M. Nest defense by deceit in the fathead minnow, Pimephales promelas. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1983, 13, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamatsu, T. Stages of normal development in the medaka Oryzias latipes. Mech. Dev. 2004, 121, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrenberg, S.Z.; Ejdung, G. Daily activity pattern of the sand goby, Pomatoschistus minutus (Pisces), at low light intensity. Hydrobiologia 2008, 603, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustavsson, M.B.; Magnér, J.; Almroth, B.C.; Eriksson, M.K.; Sturve, J.; Backhaus, T. Chemical monitoring of Swedish coastal waters indicates common exceedances of environmental thresholds, both for individual substances as well as their mixtures. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals/OECD Series on Testing and Assessment Guidance Document on Aquatic Toxicity Testing of Difficult Substances and Mixtures; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2002; ISBN 9789264078406. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team (2013). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria. Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 15 July 2017).





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asnicar, D.; Ašmonaitė, G.; Birgersson, L.; Kvarnemo, C.; Svensson, O.; Sturve, J. Sand Goby—An Ecologically Relevant Species for Behavioural Ecotoxicology. Fishes 2018, 3, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes3010013
Asnicar D, Ašmonaitė G, Birgersson L, Kvarnemo C, Svensson O, Sturve J. Sand Goby—An Ecologically Relevant Species for Behavioural Ecotoxicology. Fishes. 2018; 3(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes3010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsnicar, Davide, Giedrė Ašmonaitė, Lina Birgersson, Charlotta Kvarnemo, Ola Svensson, and Joachim Sturve. 2018. "Sand Goby—An Ecologically Relevant Species for Behavioural Ecotoxicology" Fishes 3, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes3010013
APA StyleAsnicar, D., Ašmonaitė, G., Birgersson, L., Kvarnemo, C., Svensson, O., & Sturve, J. (2018). Sand Goby—An Ecologically Relevant Species for Behavioural Ecotoxicology. Fishes, 3(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes3010013