Past and Current Trends of Coastal Predatory Fish in the Baltic Sea with a Focus on Perch, Pike, and Pikeperch
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Monitoring and Data for Coastal Fish in the Baltic Sea
3. Past Trends of Coastal Predatory Fish
4. Current Status of Coastal Predatory Fish
5. Impacts on Coastal Predatory Fish Populations
6. Measures to Restore and Support Coastal Predatory Fish Populations
7. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pauly, D.; Christensen, V.; Dalsgaard, J.; Froese, R.; Torres, F., Jr. Fishing down marine food webs. Science 1998, 279, 860–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotze, H.K.; Lenihan, H.S.; Bourque, B.J.; Bradbury, R.H.; Cooke, R.G.; Kay, M.C.; Kidwell, S.M.; Kirby, M.X.; Peterson, C.H.; Jackson, J.B.C. Depletion, degradation, and recovery potential of estuaries and coastal seas. Science 2006, 312, 1806–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskalov, G.M. Overfishing drives atrophic cascade in the Black Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 225, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, K.T.; Petrie, B.; Choi, J.S.; Leggett, W.C. Trophic cascades in a formerly cod-dominated ecosystem. Science 2005, 308, 1621–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worm, B.; Barbier, E.B.; Beaumont, N.; Duffy, J.E.; Folke, C.; Halpern, B.S.; Jackson, J.B.C.; Lotze, H.K.; Micheli, F.; Palumbi, S.R.; et al. Impacts of biodiversity loss on ocean ecosystem services. Science 2006, 314, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casini, M.; Lövgren, J.; Hjelm, J.; Cardinale, M.; Molinero, J.C.; Kornilovs, G. Multi-level trophic cascades in a heavily exploited open marine ecosystem. Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. Ser. B 2008, 275, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, B.K.; Sieben, K.; Eklöf, J.; Ljunggren, L.; Olsson, J.; Casini, M.; Bergström, U. Effects of altered offshore food webs on coastal ecosystems emphasize the need for cross-ecosystem management. Ambio 2011, 40, 786–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daskalov, G.M.; Grishin, A.N.; Rodionov, S.; Mihneva, V. Trophic cascades triggered by overfishing reveal possible mechanisms of ecosystem regime shifts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10518–10523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieben, K.; Ljunggren, L.; Bergström, U.; Eriksson, B.K. A meso-predator release of stickleback promotes recruitment of macroalgae in the Baltic Sea. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 397, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, S.; Emanuelsson, A.; Pihl, L.; Svensson, C.-J.; Åberg, P. Shift in seagrass food web structure over decades is linked to overfishing. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 451, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Östman, Ö.; Eklöf, J.; Eriksson, B.K.; Olsson, J.; Moksnes, P.-O. Top-down control as important as nutrient enrichment for eutrophication effects in North Atlantic coastal ecosystems. J. App. Ecol. 2016, 53, 1138–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadi, S.; Austin, Å.N.; Bergström, U.; Eriksson, B.K.; Hansen, J.P.; Jacobson, P.; Sundblad, G.; van Regteren, M.; Eklöf, J.S. A cross-scale trophic cascade from large predatory fish to algae in coastal ecosystems. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B 2017, 20170045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikitch, E.K.; Santora, C.; Babcock, E.A.; Bakun, A.; Bonfil, R.; Conover, D.O.; Dayton, P.; Doukakis, P.; Fluharty, D.; Heneman, B.; et al. Ecosystem-Based Fishery Management. Science 2004, 305, 346–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, R.A.; Worm, B. Extinction, survival or recovery of large predatory fishes. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2005, 360, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, V.; Coll, M.; Piroddi, C.; Steenbeek, J.; Buszowski, J.; Pauly, D. A century of fish biomass decline in the ocean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 512, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HELCOM. Baltic Sea Action Plan. In Proceedings of the HELCOM Ministerial Meeting, Krakow, Poland, 15 November 2007; Available online: http://www.helcom.fi/Documents/Baltic%20sea%20action%20plan/BSAP_Final.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2018).
- European Commission. Directive 2008/56/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 June 2008 establishing a framework for community action in the field of marine environmental policy (Marine Strategy Framework Directive). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2008:164:0019:0040:EN:PDF (accessed on 18 December 2018).
- HELCOM. State of the Baltic Sea–Second HELCOM holistic assessment 2011-2016. Balt. Sea Env. Proc. 2018, 155. Available online: www.helcom.fi/baltic-sea-trends/holistic-assessments/state-of-the-baltic-sea-2018/reports-and-materials/ (accessed on 18 December 2018).
- Voipio, A. The Baltic Sea, 1st ed.; Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1981; Volume 30, ISBN 9780080870687. [Google Scholar]
- HELCOM. Indicator based assessment of coastal fish community status in the Baltic Sea 2005–2009. Balt. Sea Env. Proc. 2012, 131. Available online: http://www.helcom.fi/Lists/Publications/BSEP131.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2018).
- Bergström, L.; Heikinheimo, O.; Svirgsden, R.; Kruze, E.; Ložys, L.; Lappalainen, A.; Minde, A.; Dainys, J.; Jakubavičiūtė, E.; Ådjers, K.; et al. Long term changes in the status of coastal fish in the Baltic Sea. Est. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 169, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HELCOM. Status of coastal fish in the Baltic Sea during 2011–2016. Balt. Sea Env. Proc. 2018, 160. Available online: https://portal.helcom.fi/meetings/FISH%208-2018-509/Documents/Thematic%20Assessment%20Coastal%20fish.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2018).
- Olsson, J.; Mo, K.; Florin, A.-B.; Aho, T.; Ryman, N. Genetic population structure of perch, Perca fluviatilis L, along the Swedish coast of the Baltic Sea. J. Fish Biol. 2011, 79, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennerström, L.; Olsson, J.; Ryman, N.; Laikre, L. Temporally stable, weak genetic structuring in brackish water northern pike (Esox lucius) in the Baltic Sea indicates a contrasting divergence pattern relative to freshwater populations. Can, J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 74, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, L.; Bergström, U.; Olsson, J.; Carstensen, J. Coastal fish indicators response to natural and anthropogenic drivers-variability at temporal and different spatial scales Long term changes in the status of coastal fish in the Baltic Sea. Est. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 183, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Östman, Ö.; Olsson, J.; Dannewitz, J.; Palm, S.; Florin, A.-B. Inferring spatial structure from population genetics and spatial synchrony in population growth of Baltic Sea fishes: Implications for management. Fish Fish. 2017, 18, 324–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekkevold, D.; Jacobsen, L.; Hemmer-Hansen, J.; Berg, S.; Skov, C. From regionally predictable to locally complex population structure in a freshwater top predator: River systems are not always the unit of connectivity in Northern Pike Esox Lucius. Ecol. Fresh. Fish. 2015, 24, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Östman, Ö.; Lingman, A.; Bergström, L.; Olsson, J. Temporal development and spatial scale of coastal fish indicators in reference sites in coastal ecosystems: Hydroclimate and anthropogenic drivers. J. App. Ecol. 2017, 54, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, J.; Bergström, L.; Gårdmark, A. Abiotic drivers of coastal fish community change during four decades in the Baltic Sea. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2012, 69, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HELCOM. Guidelines for coastal fish monitoring sampling methods of HELCOM. 2015. Available online: http://www.helcom.fi/Documents/Action%20areas/Monitoring%20and%20assessment/Manuals%20and%20Guidelines/Guidelines%20for%20Coastal%20fish%20Monitoring%20of%20HELCOM.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2018).
- Stottrup, J.G.; Kokkalis, A.; Brown, E.J.; Olsen, J.; Anderssen, S.K.; Pedersen, E.M. Harvesting geo-spatial data on coastal fish assemblages through coordinated citizen science. Fish. Res. 2018, 208, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, P.; Tibblin, P.; Koch-Schmidt, P.; Engstedt, O.; Nilsson, J.; Nordahl, O.; Forsman, A. Ecology, evolution and management strategies of northern pike popualtions in the Baltic Sea. Ambio 2015, 44 (Suppl. 3), S451–S461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikinheimo, O.; Pekcan-Hekim, Z.; Raitaniemi, J. Spawning stock–recruitment relationship in pikeperch Sander lucioperca (L.) in the Baltic Sea, with temperature as an environmental effect. Fish. Res. 2014, 155, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HELCOM FISH PRO II. Available online: http://www.helcom.fi/helcom-at-work/projects/fish-pro (accessed on 25 December 2018).
- Ådjers, K.; Appelberg, M.; Eschbaum, R.; Lappalainen, A.; Minde, A.; Repečka, R.; Thoresson, G. Trends in coastal fish stocks of the Baltic Sea. Bor. Env. Res. 2006, 11, 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Saks, L.; Hommik, K.; Svirgsden, R. EL merestrateegia raamdirektiivi (2008/56/EÜ) kohane merekeskkonna seisundihinnang teemal kalastik ja kaubanduslikel eesmärkidel kasutatavad kalad (D1, D3, D4). 2018. Available online: https://www.envir.ee/sites/default/files/d1_d3_d4_kalad_0.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2018).
- Havs- och vattenmyndigheten. Fisk- och skaldjursbestånd i hav och sötvatten 2017. Resursöversikt. 273 s. Available online: https://www.slu.se/globalassets/ew/org/inst/aqua/externwebb/sidan-publikationer/resurs-och-miljo/fisk-och-skaldjursbestand-i-hav-och-sotvatten-2017-resursoversikt.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2018).
- Lehtonen, H.; Leskinen, E.; Selén, R. Potential reasons for the change in the abundance of pike, Esox Lucius, in the western Gulf of Finland, 1939-2007. Fish. Man. Ecol. 2009, 16, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljunggren, L.; Sandstrom, A.; Bergström, U.; Mattila, J.; Lappalainen, A.; Johansson, G.; Sundblad, G.; Casini, M.; Kaljuste, O.; Eriksson, B.K. Recruitment failure of coastal predatory fish in the Baltic Sea coincident with an offshore ecosystem regime shift. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2010, 67, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustamäki, N.; Bergström, U.; Ådjers, K.; Sevastik, A.; Mattila, J. Pikeperch (Sander lucioperca (L.)) in Decline: High Mortality of Three Populations in the Northern Baltic Sea. Ambio 2014, 43, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustamäki, N.; Tärnlund, S.; Holliland, P.B.; Blass, M.; Landfors, F.; Thunell, V.; SLU Aqua Faktablad–Resultat från övervakningen av kustfisk 2018:2. Galtfjärden (Egentliga Östersjön) 2002–2017. 2018. Available online: https://www.slu.se/globalassets/ew/org/inst/aqua/externwebb/k-lab/provfiske-vid-kusten/faktablad/2018/faktablad-galtfjarden-2018.2-002.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2018).
- Raitaniemi, J. Kalakantojen tila vuonna 2017sekä ennuste vuosille 2018 ja 2019. Luonnonvara- ja biotalouden tutkimus 36/2018. Helsinki. 99 s. 2018. Available online: http://jukuri.luke.fi/bitstream/handle/10024/542220/luke-luobio_36_2018.pdf?sequence=5&isAllowed=y (accessed on 18 December 2018).
- Bergström, L.; Karlsson, M.; Bergström, U.; Pihl, L.; Kraufvelin, P. Relative impacts of fishing and eutrophication on coastal fish assessed by comparing a no-take area with an environmental gradient. Ambio. (in press). [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.-J.; Rochet, M.-J.; Jennings, S.; Field, J.G.; Gislason, H. Using size-based indicators to evaluate the ecosystem effects of fishing. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2005, 62, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappalainen, A.; Saks, L.; Sustar, M.; Heikinheimo, O.; Jürgens, K.; Kokkonen, E.; Kurkilahti, M.; Verliin, A.; Vetemaa, M. Length at maturity as a potential indicator of fishing pressure effects on coastal pikeperch (Sander lucioperca) stocks in the northern Baltic Sea. Fish. Res. 2016, 174, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, J.; Ericsson, Y.; Östman, Ö. Storleksstruktur hos nyckelart av fisk i kustvatten–Faktablad Havsmiljödirektivets inledande bedömning. Havs- och vattenmyndigheten. 2018. Available online: https://www.havochvatten.se/download/18.1a05a1ba15fe9ddd6bcc0fd4/1512549687873/faktablad-D1C3-D4C3-kust-storleksstruktur-hos-nyckelart-fisk-i-kustvatten-samrad.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2018).
- Lindeboom, H. The Coastal Zone: An Ecosystem Under Pressure. In Oceans 2020: Science, Trends and the Challenge of Sustainability; Field, J.G., Hempel, G., Summerhayes, C.P., Eds.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; pp. 49–84. ISBN 1-55963-470-7. [Google Scholar]
- Airoldi, L.; Beck, M.W. Loss, Status and Trends for Coastal Marine Habitats of Europe. In Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review; Gibson, R.N., Atkinson, R.J.A., Gordon, J.D.M., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; Volume 45, pp. 345–405. ISBN 9781420050936. [Google Scholar]
- Möllmann, C.; Diekmann, R.; Müller-Karulis, B.; Kornilovs, G.; Plikshs, M.; Axe, P. Reorganization of a large marine ecosystem due to atmospheric and anthropogenic pressure: A discontinuous regime shift in the Central Baltic Sea. Glob. Change Biol. 2009, 15, 1377–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, N.; Persson, S.; Larsson, Å. Analyses of perch (Perca fluviatilis) bile suggest increasing exposure to PAHs and other pollutants in a reference area on the Swedish Baltic coast. Environ. Tox. Chem. 2009, 28, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetemaa, M.; Eschbaum, R.; Albert, A.; Saks, L.; Verliin, A.; Jürgens, K.; Kesler, M.; Hubel, K.; Hannesson, R.; Saat, T. Changes in fish stocks in an Estonian estuary: Overfishing by cormorants? ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2010, 67, 1972–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Östman, Ö.; Bergenius, M.; Boström, M.K.; Lunneryd, S.-G. Do cormorant colonies affect local fish communities in the Baltic Sea? Can, J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 69, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundblad, G.; Bergström, U.; Sandström, A.; Eklöv, P. Nursery habitat availability limits adult stock sizes of predatory coastal fish. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2014, 71, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyder, K.; Weltersbach, M.S.; Armstrong, M.; Ferter, K.; Townhill, B.; Ahvonen, A.; Arlinghaus, R.; Baikov, A.; Bellanger, M.; Birzaks, J.; et al. Recreational sea fishing in Europe in a global context—Participation rates, fishing effort, expenditure, and implications for monitoring and assessment. Fish Fish. 2018, 19, 224–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.P.; Sundblad, G.; Bergström, U.; Austin, Å.N.; Donadi, S.; Eriksson, B.K.; Eklöf, J.S. Recreational boating degrades vegetation important for fish recruitment. Ambio 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunde, J.; Tamario, C.; Tibblin, P.; Larsson, P.; Forsman, A. Variation in salinity tolerance between and within anadromous subpopulations of pike (Esox lucius). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibblin, P.; Koch-Schmidt, P.; Larsson, P.; Forsman, A. Effects of salinity on growth and mortality of migratory and resident forms of Eurasian perch in the Baltic Sea. Ecol. Fresh. Fish. 2012, 21, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, U.; Sundblad, G.; Downie, A.-L.; Snickars, M.; Boström, C.; Lindegarth, M. Evaluating eutrophication management scenarios in the Baltic Sea using species distribution modelling. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 50, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HELCOM. Recreational fisheries in the Baltic Sea and availability of data. 2017. Available online: https://portal.helcom.fi/meetings/FISH%206-2017-437/MeetingDocuments/3-1%20Information%20about%20Coastal%20recreational%20fisheries%20in%20the%20Baltic%20Sea%20countries.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2018).
- Edgren, J. Effects of a no-take reserve in the Baltic Sea on the top predator, northern pike. Master’s Thesis, Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden, 2005. Degree project. 23p. [Google Scholar]
- Bergström, U.; Sköld, M.; Wennhage, H.; Wikström, A. Ekologiska effekter av fiskefria områden i Sveriges kust- och havsområden. Aqua Rep. 2016, 20, 1–207. Available online: https://www.slu.se/globalassets/ew/org/inst/aqua/externwebb/sidan-publikationer/aqua-reports-xxxx_xx/aquareports-2016_20-fiskefria-omraden_20161214.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2018).
- Vetemaa, M.; Eschbaum, R.; Saat, T. The transition from Soviet system to market economy as a cause to instability in the Estonian coastal fisheries sector. Mar. Pol. 2006, 30, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraufvelin, P.; Pekcan-Hekim, Z.; Bergström, U.; Florin, A.-B.; Lehikoinen, A.; Mattila, J.; Arula, T.; Briekmane, L.; Brown, E.J.; Celmer, Z.; et al. Essential coastal habitats for fish in the Baltic Sea. Est. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 204, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engstedt, O.; Stenroth, P.; Larsson, P.; Ljunggren, L.; Elfman, M. Assessment of natal origin of pike (Esox lucius) in the Baltic Sea using Sr:Ca in otoliths. Env. Biol. Fish. 2010, 89, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohtla, M.; Vetemaa, M.; Urtson, K.; Soesoo, A. Early life migration patterns of Baltic Sea pike Esox lucius. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 80, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, J.; Engstedt, O.; Larsson, P. Wetlands for northern pike (Esox lucius L.) recruitment in the Baltic Sea. Hydrobiologia 2014, 721, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundblad, G.; Bergström, U. Shoreline development and degradation of coastal fish reproduction habitats. Ambio 2014, 43, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandström, A.; Eriksson, B.K.; Karås, P.; Isæus, M.; Schreiber, H. Boating and navigation activities influence the recruitment of fish in a Baltic Sea archipelago area. Ambio 2005, 34, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Östman, Ö.; Boström, M.K.; Bergström, U.; Andersson, J.; Lunneryd, S.-G. Estimating competition between wildlife and humans—A case of cormorants and coastal fisheries in the Baltic Sea. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, S.; Bergström, U.; Bonsdorff, E.; Härkönen, T.; Jepsen, N.; Kautsky, L.; Lundström, K.; Lunneryd, S.-G.; Ovegård, M.; Salmi, J.; et al. Competition for the fish—Fish extraction from the Baltic Sea by humans, aquatic mammals, and birds. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2018, 75, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehikoinen, A.; Heikinheimo, O.; Lappalainen, A. Temporal changes in the diet of great cormorant (Phalacrocorax carbo sinensis) on the southern coast of Finland—Comparison with available fish data. Bor. Env. Res. 2011, 16, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Heikinheimo, O.; Rusanen, P.; Korhonen, K. Estimating the mortality caused by great cormorant predation on fish stocks: Pikeperch in the Archipelago Sea, northern Baltic Sea, as an example. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 73, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, U.; Olsson, J.; Casini, M.; Eriksson, B.K.; Fredriksson, R.; Wennhage, H.; Appelberg, M. Stickleback increase in the Baltic Sea—A thorny issue for coastal predatory fish. Est. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, J. Predation of Northern Pike (Esox lucius L.) Eggs: A Possible Cause of Regionally Poor Recruitment in the Baltic Sea. Hydrobiologia 2006, 553, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byström, P.; Bergström, U.; Hjälten, A.; Ståhl, S.; Jonsson, D.; Olsson, J. Declining coastal piscivore populations in the Baltic Sea: Where and when do sticklebacks matter? Ambio 2015, 44, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heikinheimo, O.; Lehtonen, H.; Lehikoinen, A.; Hunsicker, M. Comment to Hansson, S. et al. “Competition for the fish—Fish extraction from the Baltic Sea by humans, aquatic mammals, and birds”, with special reference to cormorants, perch, and pikeperch. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2018, 75, 1832–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casini, M.; Blenckner, T.; Mollmann, C.; Gardmark, A.; Lindegren, M.; Llope, M.; Kornilovs, G.; Maris Plikshs, M.; Stenseth, N.C. Predator transitory spillover induces trophic cascades in ecological sinks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8185–8189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, N. Population level effects of reduced fecundity in the fish species perch (Perca fluviatilis) and the implications for environmental monitoring. Ecol. Mod. 2009, 220, 2051–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.A.; Casini, M.; Huss, M.; Otto, S.A.; Kadin, M.; Gårdmark, A. Food-web indicators accounting for species interactions respond to multiple pressures. Ecol. Ind. 2017, 77, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikinheimo, O.; Setälä, J.; Saarni, K.; Raitaniemi, J. Impacts of mesh-size regulation of gillnets on the pikeperch fisheries in the Archipelago Sea, Finland. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 77, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson, R.; Bergström, U.; Olsson, J. Riktlinjer för uppföljning av fiskevårdsåtgärder i kustmynnande våtmarker med fokus på gädda. Aqua Rep. 2013, 7, 1–52. [Google Scholar]
- Reusch, T.B.H.; Dierking, J.; Andersson, H.C.; Bonsdorff, E.; Carstensen, J.; Casini, M.; Czajkowski, M.; Hasler, B.; Hinsby, K.; Hyytiäinen, K.; et al. The Baltic Sea as a time machine for the future coastal ocean. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar8195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
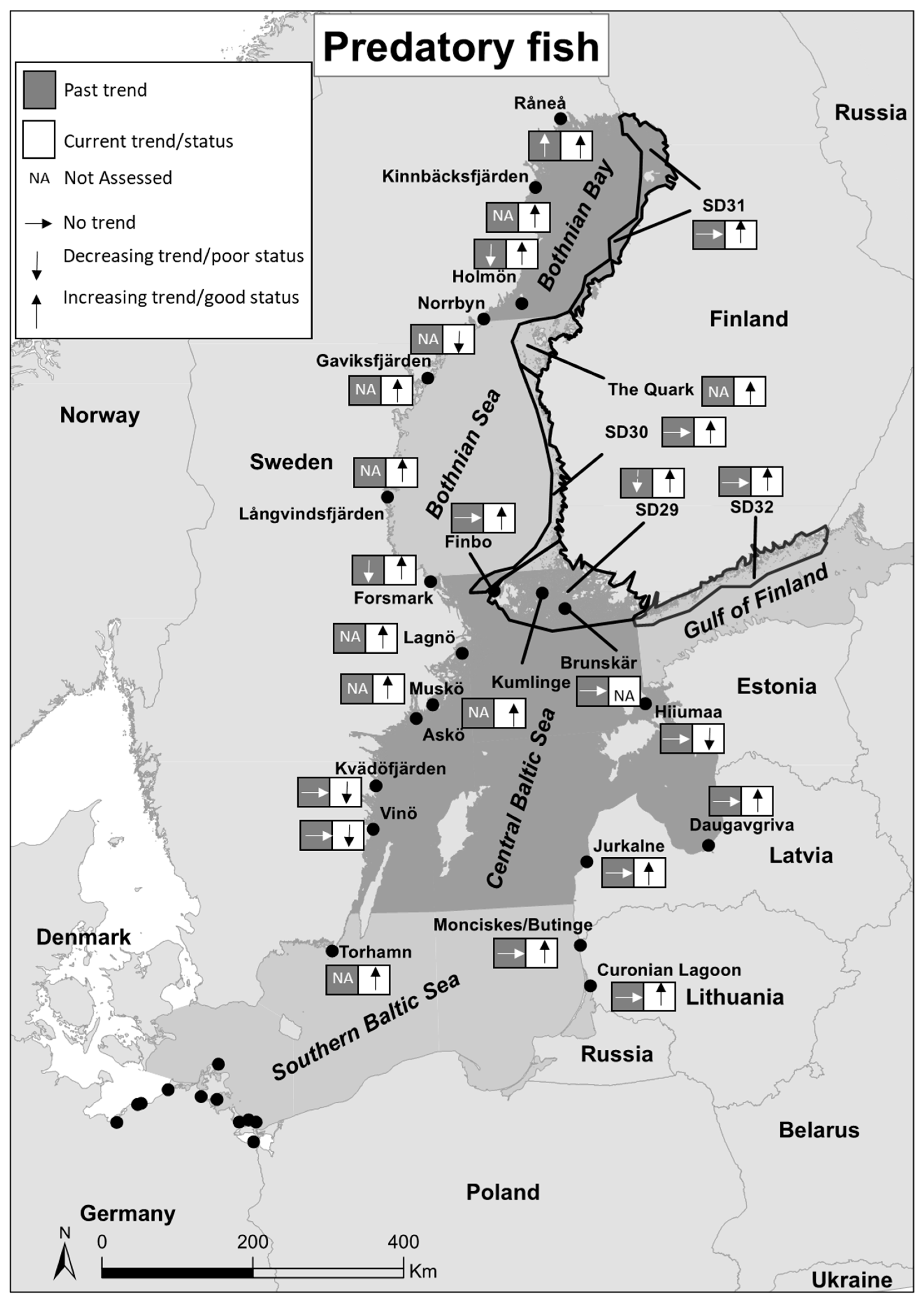





| Past Trends | Current Trends/Status | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (Time-Series) | Country | Basin | Type of Monitoring | Time for Monitoring | Species Included * | Time Period | Trend | Source | Time Period | Trend | Status | Source |
| Råneå | Sweden | Bothnian Bay | Fisheries independent | Summer | Pe, Pi, B | 1991–2009 | + | [21] | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | |
| Kinnbäcksfjärden | Sweden | Bothnian Bay | Fisheries independent | Summer | Pe, Pi, B | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | ||||
| Holmön | Sweden | Bothnian Bay | Fisheries independent | Summer | Pe, Pi, B | 1991–2009 | - | [21] | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | |
| Norrbyn | Sweden | Bothnian Bay | Fisheries independent | Summer | Pe, Pi, B | 2008–2016 | Poor | [22] | ||||
| SD 31 | Finland | Bothnian Bay | Fisheries dependent | Year around | Pe, Pi, Pp | 1991–2009 | 0 | [21] | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | |
| The Quark | Finland | Bothnian Bay | Fisheries independent | Year around | Pe, Pi, Pp | 2011–2016 | Good | [22] | ||||
| Gaviksfjärden | Sweden | Bothnian Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | Pe, Pi, B | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | ||||
| Långvindsfjärden | Sweden | Bothnian Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | Pe, Pi, B | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | ||||
| SD 30 | Finland | Bothnian Sea | Fisheries dependent | Year around | Pe, Pi, Pp | 1991–2009 | 0 | [21] | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | |
| Forsmark | Sweden | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | Pe, Pi, B, Pp | 1991–2009 | - | [21] | 2011–2016 | Good | [22] | |
| Finbo | Finland | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | Pe, Pi, B, Pp | 1991–2009 | 0 | [21] | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | |
| Kumlinge | Finland | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | Pe, Pi, B, Pp | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | ||||
| Brunskär | Finland | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | Pe, Pi, B, Pp | 1991–2004 | 0 | [21] | ||||
| SD 29 | Finland | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries dependent | Year around | Pe, Pi, Pp | 1991–2009 | - | [21] | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | |
| SD 32 | Finland | Gulf of Finland | Fisheries dependent | Year around | Pe, Pi, Pp | 1991–2009 | 0 | [21] | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | |
| Lagnö | Sweden | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | Pe, Pi, B, Pp | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | ||||
| Muskö | Sweden | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Autumn | Pe, Pi, Pp, C | 2011–2016 | Good | [22] | ||||
| Askö | Sweden | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | Pe, Pi, B, Pp | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | ||||
| Kvädöfjärden | Sweden | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer & autumn | Pe, Pi, Pp, C, T | 1991–2009 | 0 | [21] | 2011–2016 | Poor | [22] | |
| Vinö | Sweden | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | Pe, Pi, Pp, C, T | 1991–2009 | 0 | [21] | 2011–2016 | Poor | [22] | |
| Hiiumaa | Estonia | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | Pe, Pi, Pp | 1991–2009 | 0 | [21] | 2011–2016 | Poor | [22] | |
| Daugavgriva | Latvia | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | Pe, Pi, Pp | 1991–2009 | 0 | [21] | 2008–2015 | Good | [22] | |
| Jurkalne | Latvia | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | Pe, Pi, Pp, C, T | 1991–2009 | 0 | [21] | 2011–2015 | Good | [22] | |
| Monciskes/Butinge | Lithuania | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | Pe, Pi, Pp, C, T | 1991–2009 | 0 | [21] | 2008–2012 | Good | [22] | |
| Curonian Lagoon | Lithuania | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | Pe, Pi, B, Pp | 1991–2009 | 0 | [21] | 2008–2012 | Good | [22] | |
| Torhamn | Sweden | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | Pe, Pi, Pp, C, T | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | ||||
| Pomeranian Bay, Outer | Germany | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Autumn | Pe, Pi, T | 2003–2014 | 0 | NA | Unpublished | |||
| Stettin Lagoon (German part) | Germany | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | Pe | 2008-2013 | 0 | NA | Unpublished | |||
| Peene river/Achterwasser | Germany | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | Pe | 2009-2013 | 0 | NA | Unpublished | |||
| East of Usedom Peninsula | Germany | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | Pe | 2008–2013 | - | NA | Unpublished | |||
| Greifswalder Bodden | Germany | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | Pe | 2008–2013 | 0 | NA | Unpublished | |||
| Strelasund | Germany | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | Pe | 2008–2013 | 0 | NA | Unpublished | |||
| Darß-Zingst Bodden chain | Germany | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | Pe | 2008–2013 | + | NA | Unpublished | |||
| Northeast of Ruegen Island | Germany | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | Pe | 2008–2013 | 0 | NA | Unpublished | |||
| Börgerende | Germany | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | Pe | 2003–2013 | 0 | NA | Unpublished | |||
| North of Kühlungsborn city | Germany | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | Pe | 2008–2013 | 0 | NA | Unpublished | |||
| Wismar Bight and Salzhaff | Germany | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | Pe | 2008–2012 | - | NA | Unpublished | |||
| Past Trends | Current Trends/Status | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (Time-Series) | Country | Basin | Type of Monitoring | Time for Monitoring | Time Period | Trend | Source | Time Period | Trend | Status | Source |
| Råneå | Sweden | Bothnian Bay | Fisheries independent | Summer | 1994–2002 | + | [35] | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | |
| Kinnbäcksfjärden | Sweden | Bothnian Bay | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | ||||
| Holmön | Sweden | Bothnian Bay | Fisheries independent | Summer | 1989–2002 | - | [35] | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | |
| Norrbyn | Sweden | Bothnian Bay | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2008–2016 | Poor | [22] | ||||
| SD 31 | Finland | Bothnian Bay | Fisheries dependent | Year around | 2011–2016 | Good | [22] | ||||
| The Quark | Finland | Bothnian Bay | Fisheries independent | Year around | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | ||||
| Gaviksfjärden | Sweden | Bothnian Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | ||||
| Långvindsfjärden | Sweden | Bothnian Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | ||||
| SD 30 | Finland | Bothnian Sea | Fisheries dependent | Year around | 2011–2016 | Good | [22] | ||||
| Forsmark | Sweden | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 1975–2008 | + | [29] | 2011–2016 | Good | [22] | |
| Forsmark | Sweden | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 1983–2002 | + | [35] | ||||
| Finbo | Finland | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 1987–2002 | + | [35] | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | |
| Kumlinge | Finland | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | ||||
| Brunskär | Finland | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 1992–2002 | + | [35] | ||||
| Lagnö | Sweden | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | ||||
| Muskö | Sweden | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Autumn | 1991–2002 | 0 | [35] | ||||
| Askö | Sweden | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | ||||
| SD 29 | Finland | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries dependent | Year around | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | ||||
| SD 32 | Finland | Gulf of Finland | Fisheries dependent | Year around | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | ||||
| Käsmu | Estonia | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2011–2016 | Poor | [36] | ||||
| Matsalu | Estonia | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2011–2016 | Poor | [36] | ||||
| Hiiumaa | Estonia | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 1992–2002 | - | [35] | 2011–2016 | Poor | [22] | |
| Pärnu | Estonia | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2011–2016 | Poor | [36] | ||||
| Kõiguste | Estonia | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2011–2016 | Poor | [36] | ||||
| Vilsandi | Estonia | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2011–2016 | Poor | [36] | ||||
| Kihnu | Estonia | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2011–2016 | Poor | [36] | ||||
| Kvädöfjärden | Sweden | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 1971–2008 | + | [29] | 2011–2016 | Poor | [22] | |
| Kvädöfjärden | Sweden | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 1987–2002 | + | [35] | ||||
| Vinö | Sweden | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2011–2016 | Poor | [22] | ||||
| Mönsterås | Sweden | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | 1970–2003 | - | [7] | ||||
| Daugavgriva | Latvia | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 1993–2002 | 0 | [35] | 2008–2015 | Good | [22] | |
| Jurkalne | Latvia | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2011–2015 | Good | [22] | ||||
| Monciskes/Butinge | Lithuania | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2008–2012 | Good | [22] | ||||
| Curonian Lagoon | Lithuania | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 1992–2002 | - | [35] | 2008–2012 | Good | [22] | |
| Torhamn | Sweden | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2008–2016 | Good | [22] | ||||
| Pomeranian Bay, Outer | Germany | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Autumn | 2003–2014 | 0 | NA | Unpublished | |||
| Stettin Lagoon (German part) | Germany | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | 2008–2013 | 0 | NA | Unpublished | |||
| Peene river/Achterwasser | Germany | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | 2009–2013 | 0 | NA | Unpublished | |||
| East of Usedom Peninsula | Germany | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | 2008–2013 | - | NA | Unpublished | |||
| Greifswalder Bodden | Germany | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | 2008–2013 | 0 | NA | Unpublished | |||
| Strelasund | Germany | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | 2008–2013 | 0 | NA | Unpublished | |||
| Darß-Zingst Bodden chain | Germany | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | 2008–2013 | + | NA | Unpublished | |||
| Northeast of Ruegen Island | Germany | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | 2008–2013 | 0 | NA | Unpublished | |||
| Börgerende | Germany | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | 2003–2013 | 0 | NA | Unpublished | |||
| North of Kühlungsborn city | Germany | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | 2008–2013 | 0 | NA | Unpublished | |||
| Wismar Bight and Salzhaff | Germany | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | 2008–2012 | - | NA | Unpublished | |||
| Past Trends | Current Trends | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (Time-Series) | Country | Basin | Type of Monitoring | Time for Monitoring | Time Period | Trend | Source | Time Period | Trend | Status | Source |
| Råneå | Sweden | Bothnian Bay | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2002–2016 | 0 | NA | [37] | |||
| Holmön | Sweden | Bothnian Bay | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2002–2016 | 0 | NA | [37] | |||
| Western Gulf of Finland | Finland | Gulf of Finlad | Recreational fisheries | Year around | 1939–2007 | - | [38] | ||||
| Lagnö | Sweden | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2002–2016 | - | NA | [37] | |||
| Askö | Sweden | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2002–2016 | 0 | NA | [37] | |||
| Kvädöfjärden | Sweden | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2002–2016 | - | NA | [37] | |||
| Mönsterås | Sweden | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | 1970–2003 | - | [7] | ||||
| Mönsterås | Sweden | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | August | 1994–2007 | - | [39] | ||||
| Torhamn | Sweden | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2002–2016 | - | NA | [37] | |||
| Past Trends | Current Trends | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (Time-Series) | Country | Basin | Type of Monitoring | Time for Monitoring | Time Period | Trend | Source | Time Period | Trend | Status | Source |
| Forsmark | Sweden | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2002–2016 | - | NA | [37] | |||
| Galtfjärden | Sweden | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Autumn | 1995–2008 | - | [40] | 2002–2017 | - | NA | [41] |
| Ivarskärsfjärden | Finland | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2000–2009 | - | [40] | ||||
| Lumparn | Finland | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | August | 2000–2009 | - | [40] | ||||
| SD 29 | Finland | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Year around | 1981–2004 | + | [33] | 1981–2015 | NA | Poor | [42] |
| SD 32 | Finland | Gulf of Finland | Fisheries independent | Year around | 1981–2015 | NA | Good | [42] | |||
| Pärnu | Estonia | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 2011–2016 | NA | Poor | [36] | |||
| Daugavgriva | Latvia | Central Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 1992–2002 | - | [35] | ||||
| Curonian Lagoon | Lithuania | Southern Baltic Sea | Fisheries independent | Summer | 1992–2002 | 0 | [35] | ||||
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olsson, J. Past and Current Trends of Coastal Predatory Fish in the Baltic Sea with a Focus on Perch, Pike, and Pikeperch. Fishes 2019, 4, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes4010007
Olsson J. Past and Current Trends of Coastal Predatory Fish in the Baltic Sea with a Focus on Perch, Pike, and Pikeperch. Fishes. 2019; 4(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes4010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlsson, Jens. 2019. "Past and Current Trends of Coastal Predatory Fish in the Baltic Sea with a Focus on Perch, Pike, and Pikeperch" Fishes 4, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes4010007
APA StyleOlsson, J. (2019). Past and Current Trends of Coastal Predatory Fish in the Baltic Sea with a Focus on Perch, Pike, and Pikeperch. Fishes, 4(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes4010007




