Establishment of a Simplified System to Evaluate Salinity Preference and Validation of Behavioral Salinity Selection in the Japanese Medaka, Oryzias latipes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Establishment of a Simplified System to Test for Salinity Preference
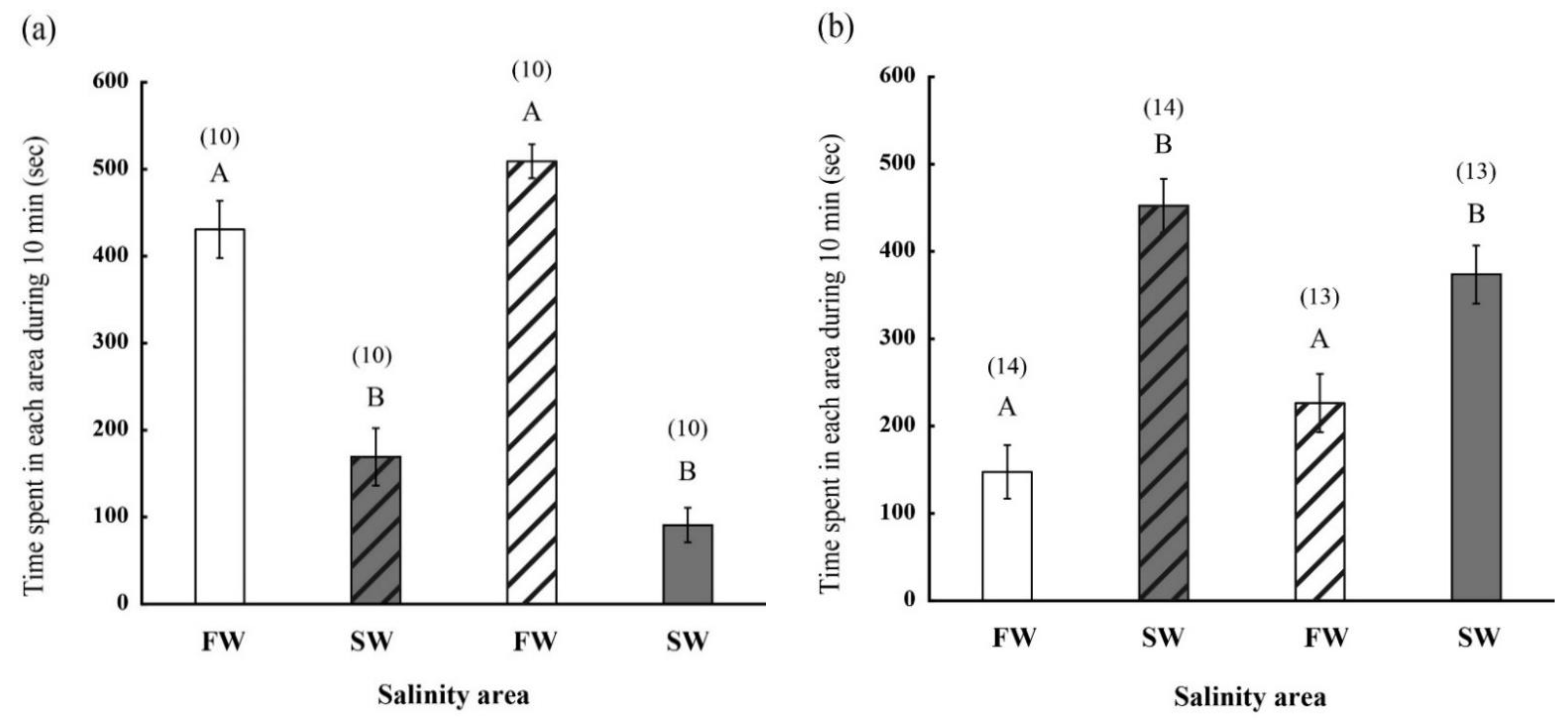
2.2. Behavior of FW- and SW-Acclimated Fish in Different Saline Environments
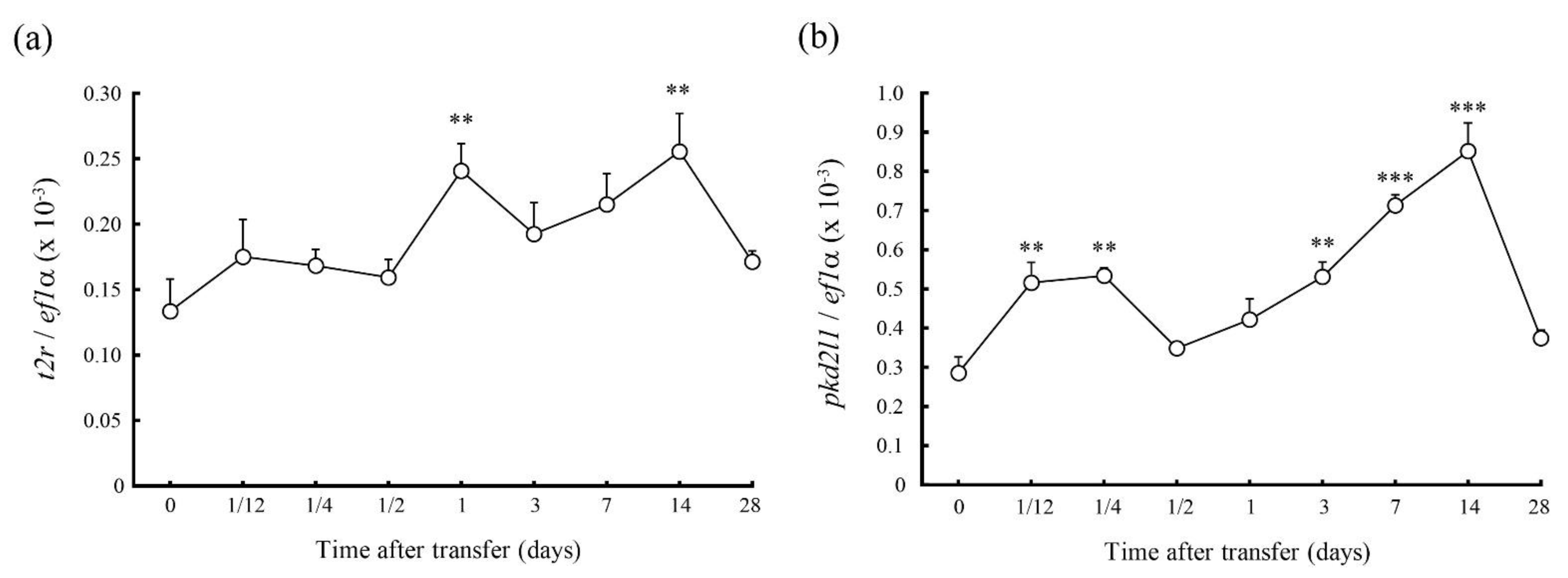
2.3. Changes in mRNA Expession of T2r and Pkd2l1 in 70% SW Challenge
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Fish
4.2. Simplified Aquarium System and Salinity Preference Experiment
4.3. Measurement of Water Osmolarity
4.4. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (Real-Time qPCR)
4.5. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evans, D.H.; Piermarini, P.M.; Choe, K.P. The Multifunctional Fish Gill: Dominant Site of Gas Exchange, Osmoregulation, Acid-Base Regulation, and Excretion of Nitrogenous Waste. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 97–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, W.S.; Grosell, M. Ion transport, osmoregulation, and acid-base balance. In The Physiology of Fishes, 3rd ed.; Evans, D.H., Claiborne, J.B., Eds.; Talylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 177–230. ISBN 13-978-0849320224. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko, T.; Watanabe, S.; Lee, K.M. Functional Morphology of Mitochondrion-Rich Cells in Euryhaline and Stenohaline Teleosts. Aqua-BioSci. Monogr. 2008, 1, 1–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, Y.; Balment, R.J. The neuroendocrine regulation of fluid intake and fluid balance. In Fish Physiology: Euryhaline Fishes; Bernier, N., van der Kraak, G., Farrell, A.P., Brauner, C.J., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009; Volume 28, pp. 365–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.-P.; Lee, T.-H.; Lin, L.-Y. Ion regulation in fish gills: Recent progress in the cellular and molecular mechanisms. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011, 301, R28–R47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varsamos, S.; Connes, R.; Diaz, J.P.; Barnabe, G.F.; Charmantier, G. Ontogeny of osmoregulation in the European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax L. Mar. Biol. 2001, 138, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Takei, Y. Diverse Adaptability in Oryzias Species to High Environmental Salinity. Zool. Sci. 2002, 19, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyanishi, H.; Inokuchi, M.; Nobata, S.; Kaneko, T. Past seawater experience enhances seawater adaptability in medaka, Oryzias latipes. Zool. Lett. 2016, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iwata, M. Downstream migratory behavior of salmonids and its relationship with cortisol and thyroid hormones: A review. Aquaculture 1995, 135, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, S.D. Smolt Physiology and Endocrinology. In Fish Physiology, Euryhaline Fishes; McCormick, S.D., Farrell, A.P., Brauner, C.J., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; Volume 32, pp. 199–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, S.D. Ontogeny and Evolution of Salinity Tolerance in Anadromous Salmonids: Hormones and Heterochrony. Estuaries 1994, 17, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, Y.; Miyanishi, H.; Nobata, S.; Wong, M.K.S.; Miyata, N.; Watanabe, T.; Ventura, A.; Shiozawa, A.; Hyodo, S.; Sato, K.; et al. Establishment and validation of aquarium system for salinity preference experiment using conscious rainbow trout. Coast. Mar. Sci. 2013, 36, 26–37. [Google Scholar]
- Kültz, D. Osmosensing. In Fish Physiology, Euryhaline Fishes; McCormick, S.D., Farrell, A.P., Brauner, C.J., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; Volume 32, pp. 45–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, Y.; Hwang, P.-P. Homeostatic Responses to Osmotic Stress. In Fish Physiology, Biology of Stress in Fish; Schreck, C.B., Tort, L., Farrell, A.P., Brauner, C.J., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; Volume 35, pp. 207–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, Y.; Okada, S.; Naito, H.; Nagai, T.; Yasuoka, A.; Matsumoto, I.; Abe, K. Two families of candidate taste receptors in fishes. Mech. Dev. 2005, 122, 1310–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Saitoh, K.; Aihara, Y.; Okada, S.; Misaka, T.; Abe, K. Transient receptor potential channel M5 and phospholipaseC-β2 colocalizing in zebrafish taste receptor cells. NeuroReport 2007, 18, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, S. The taste system of small fish species. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2015, 79, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, J.; Hoon, M.A.; Ryba, N.J.P.; Zuker, C.S. The receptors and cells for mammalian taste. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 444, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, Y.; Butnaru, M.; Von Buchholtz, L.; Ryba, N.J.P.; Zuker, C.S. High salt recruits aversive taste pathways. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 494, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanukoglu, I.; Hanukoglu, A. Epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) family: Phylogeny, structure–function, tissue distribution, and associated inherited diseases. Gene 2016, 579, 95–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christensen, E.A.F.; Grosell, M. Behavioural salinity preference of juvenile yellow perch Perca flavescens. J. Fish Biol. 2018, 92, 1620–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyer, W.R.; Farmer, D.M. Tide-Induced Variation of the Dynamics of a Salt Wedge Estuary. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1989, 19, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ralston, D.K.; Geyer, W.R.; Lerczak, J.A. Structure, variability, and salt flux in a strongly forced salt wedge estuary. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2010, 115, 06005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, W.-P.; Horng, J.-L.; Lin, L.-Y. Functional plasticity of mitochondrion-rich cells in the skin of euryhaline medaka larvae (Oryzias latipes) subjected to salinity changes. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011, 300, R858–R868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hiroi, J.; McCormick, S.D. New insights into gill ionocyte and ion transporter function in euryhaline and diadromous fish. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2012, 184, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.-H.; Lin, L.-Y.; Tseng, Y.-C.; Horng, J.-L.; Hwang, P.-P. A new model for fish ion regulation: Identification of ionocytes in freshwater- and seawater-acclimated medaka (Oryzias latipes). Cell Tissue Res. 2014, 357, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, C.J. Salt Preferences of Birds and Mammals. Physiol. Zool. 1962, 35, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmar, L.C.; Dickhoff, W.W. The parr—Smolt transformation (smoltification) and seawater adaptation in salmonids: A review of selected literature. Aquaculture 1980, 21, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoar, W. The physiology of smolting salmonids. In Fish Physiology; Hoar, W.S., Randall, D.J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1988; Volume 11B, pp. 275–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyanishi, H.; Okubo, K.; Kaneko, T.; Takei, Y. Role of cardiac natriuretic peptides in seawater adaptation of medaka embryos as revealed by loss-of-function analysis. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 304, R423–R434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oike, H.; Nagai, T.; Furuyama, A.; Okada, S.; Aihara, Y.; Ishimaru, Y.; Marui, T.; Matsumoto, I.; Misaka, T.; Abe, K. Characterization of Ligands for Fish Taste Receptors. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 5584–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamura, K.; Kobayashi, D.; Uehara, Y.; Koshida, S.; Iijima, N.; Kudo, A.; Yokoyama, T.; Takeda, H. Pkd1l1 complexes with Pkd2 on motile cilia and functions to establish the left-right axis. Development 2011, 138, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
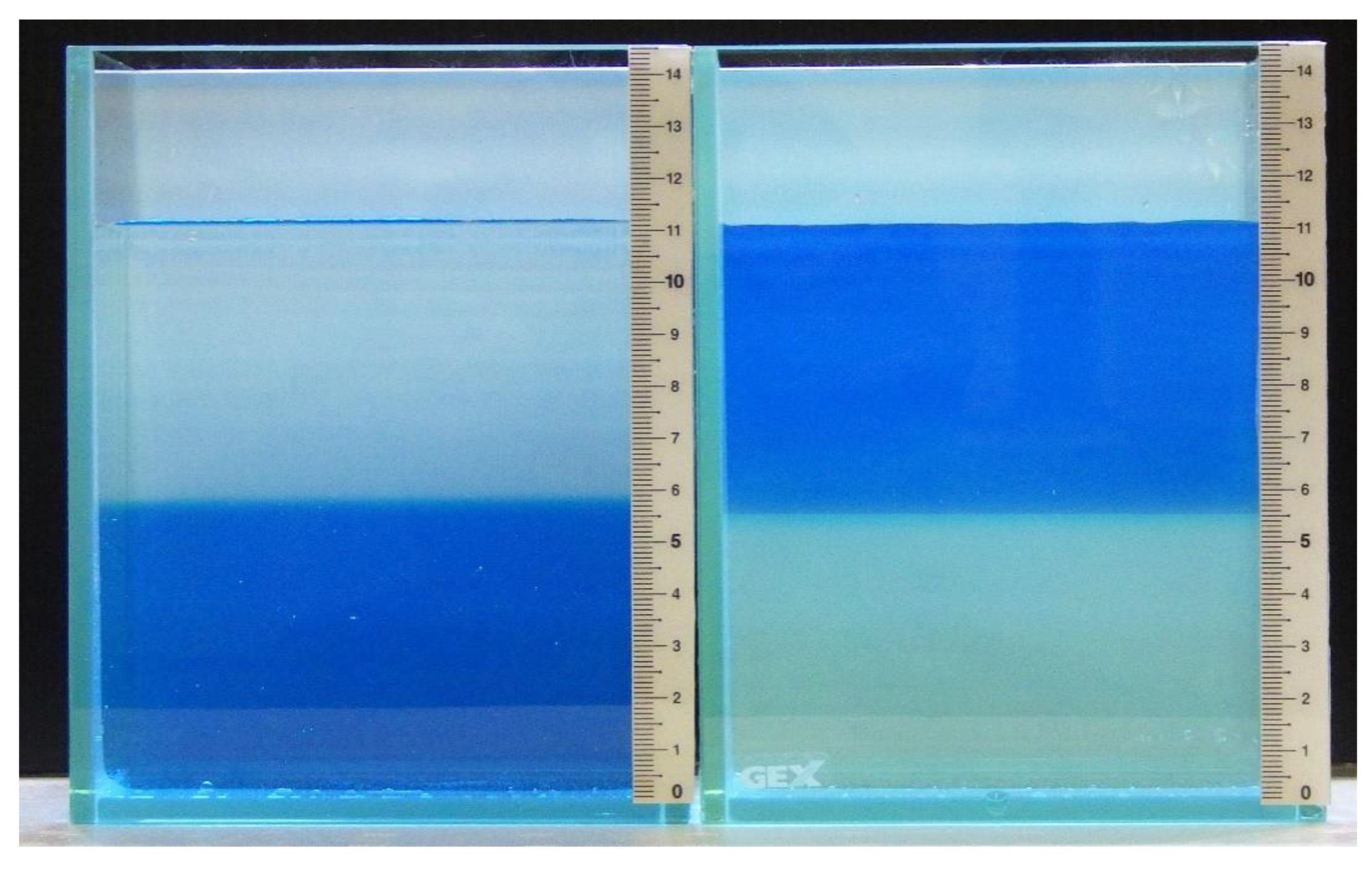

| Water Depth (cm) | Osmolality (mOsm/kg) |
|---|---|
| Freshwater | 20.5 ± 1.8 |
| 0.1 | 24.5 ± 0.4 |
| 2.2 | 30.5 ± 3.9 |
| 4.4 | 63.5 ± 16.0 |
| 6.6 | 861 ± 8.5 |
| 8.8 | 939 ± 0.5 |
| 11 | 942 ± 1.4 |
| Seawater | 943 ± 1.4 |
| Water Depth (cm) | Osmolality (mOsm/kg) | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 min after Setting | 15 min after Setting | |
| Freshwater | 33 | |
| 0.1 | 44.5 | 62 |
| 1.1 | 46 | 66 |
| 2.2 | 48.5 | 68 |
| 3.3 | 64.5 | 83.5 |
| 4.4 | 79 | 99 |
| 5.5 | 530 | 451.5 |
| 6.6 | 597.5 | 810.5 |
| 7.7 | 745.5 | 886 |
| 8.8 | 854 | 959 |
| 9.9 | 923 | 962 |
| 11 | 998 | 968.5 |
| Seawater | 1002 | |
| Gene Name | Oligo Name | Sequence (5′–3′) | Purposes |
|---|---|---|---|
| t2r | |||
| T2R-F1 | GGAGCGCATGCAGAACATTT | Standard (STD) for real-time PCR | |
| T2R-R1 | CCTCACAGGTCCAGCAAACT | STD for real-time PCR | |
| T2R-F2 | GGCTGTGCTAACCATCTTCTTC | real-time PCR | |
| T2R-R2 | TCACTTGGGCTTCTCTGCTT | real-time PCR | |
| pkd2l1 | |||
| PKD2L1-F1 | ATGAAGTCCCTGAACAATCGC | STD for real-time PCR | |
| PKD2L1-R1 | ACCGTTCGGATCTGGTAGGA | STD for real-time PCR | |
| PKD2L1-F2 | CGGATCTGGTAGGAGGGAAC | real-time PCR | |
| PKD2L1-R2 | CCGAGTGGTCTTCATCGACT | real-time PCR | |
| ef1α | |||
| EF1a-F4 | TTACCTGGTTAGGGGCAGCA | STD for real-time PCR | |
| EF1a-R1 | TATCAACAGCCTTGATGACACC | STD for real-time PCR | |
| EF1a-F6 | AGAAGGAAGCCGCTGAGATGG | real-time PCR | |
| EF1a-R6 | GCTCAGCCTTCAGTTTGTCCAA | real-time PCR |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miyanishi, H.; Uchida, K. Establishment of a Simplified System to Evaluate Salinity Preference and Validation of Behavioral Salinity Selection in the Japanese Medaka, Oryzias latipes. Fishes 2021, 6, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6020018
Miyanishi H, Uchida K. Establishment of a Simplified System to Evaluate Salinity Preference and Validation of Behavioral Salinity Selection in the Japanese Medaka, Oryzias latipes. Fishes. 2021; 6(2):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6020018
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiyanishi, Hiroshi, and Katsuhisa Uchida. 2021. "Establishment of a Simplified System to Evaluate Salinity Preference and Validation of Behavioral Salinity Selection in the Japanese Medaka, Oryzias latipes" Fishes 6, no. 2: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6020018
APA StyleMiyanishi, H., & Uchida, K. (2021). Establishment of a Simplified System to Evaluate Salinity Preference and Validation of Behavioral Salinity Selection in the Japanese Medaka, Oryzias latipes. Fishes, 6(2), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes6020018






